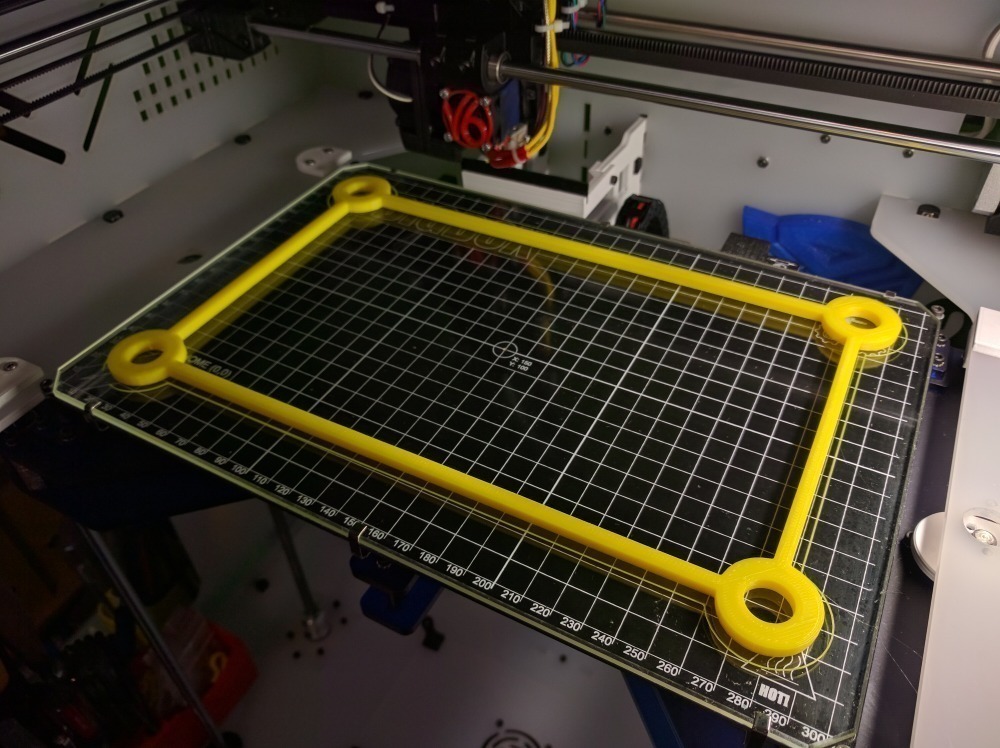
Test prints 3d printer
Top Ten Calibration Prints for Your 3D Printer
Get the most out of your 3D printer with these calibration tests which are designed to reveal small adjustments you can make to get your 3D prints to really shine.
Updated on November 9, 2022
by
MatterHackers
With this set of 3D models, you can fine-tune your 3D printer to optimize your it's capabilities and get the best 3D printed parts possible. Let's dive in!
Jump To:
- Vertical Surface Test
- Horizontal Finish Test
- Dimensional Accuracy Test
- Overhang Test
- Bridging Test
- Negative Space Test
- Retraction Performance Test
- Support Material Test
- Full Bed Dimensional Accuracy Test
- Z Wobble Test
- Squareness Test
- Download Calibration Models
Vertical Surface Test
This test is designed to look for "ghosting" or “ringing,” where features echo and ring out along vertical surfaces.
As the print head makes a quick movement, it can oscillate, which creates a ring effect.The oscillations diminish on longer lines and the vertical surfaces clear up until a sharp turn is made again. Ghosting can come from a lack of rigidity like a loosely mounted hotend or a wobbly frame, springy belts, printing at high speeds with a heavy direct-drive print head, a bed that isn't rigidly mounted, or firmware settings for acceleration or jerk that are too high for what the printer can achieve.
Some printers can handle high jerk and acceleration, where others will falter and show significant error because of it.
Vertical Surface Test
Horizontal Finish Test
With three different sections - flat, slope, and domed - you are able to see any sort of artifact or ridges from where the perimeters start and end. The more noticeable these points, the lower the score.
Cleaning this up depends on slice settings about perimeters, like start and end overlap, overlap percentage, and where the seam (start/end point of each outer perimeter) is located.
Horizontal Surface Test
Dimensional Accuracy Test
When you're printing coasters and keychains, it doesn't really matter if a part is 0.2mm too wide, but for multi-part prints that need to fit together, the accuracy of each part is very important to keep things fitting properly. Slots for connector pieces can be just fine off of Printer A but too tight to use from Printer B, or holes for nuts and bolts are supposed to allow for easy installation, but require unnecessary force to assemble.
The second level of this pyramid is supposed to be 20mm wide and deep, and loses points based on the average deviation from 20mm; if the average deviation is between 0 and 0.1mm, a full 5 points is earned. If the deviation is between 0.1mm and 0.2mm, 4 points are earned, and so on.
If you get a bad score, you should run through a calibration sequence for your extruder, making sure that your e-steps are accurate. You can find a helpful guide on how to do that here.
Dimensional Accuracy Test
Overhang Test
This test is designed to see how well the printer can cool down the hot plastic as it is extruded; the better the cooling, the cleaner the bottom surface is. Printing speed does affect cooling, so the lower the print speed, the more time for freshly laid down filament to cool before the next layer is ready.
A small print with high print speeds is going to need much more cooling than a large print at slow speeds since material will have only a very brief amount of time to cool enough to solidify.
It is important to consider that the type of fan used for layer cooling (axial vs radial) and the direction your fan outlet is facing will impact how well an overhang is printed, so it would be wise to print this test rotated every 90 degrees to see if some faces fair better than others. You might even consider a new ducting for the cooling fan to try and direct the airflow toward the part.
Drooping, curling, and hanging filament all lower the score, especially when the lower angles have difficulty.
Overhang Test
Bridging Test
Most slicers have the ability to detect bridging, which is where filament needs to cross an unsupported span. Usually the slicer will turn up the layer cooling fan, slow down the print speed, and change how the this section is printed so the span is efficiently crossed with long strands rather than small zigzags.
This bridging test piece tests a bridging condition, but most models won’t have bridges this obvious or long. You can expect to see some minor bridging over holes in the side of a model, over grooves, or over slots for inset nuts.
You get 1 point for each clean bridge.
Bridging Test
Negative Space Test
Much like the dimensional accuracy test, it's important that negative space is accurately replicated. When you're trying to insert screws cleanly without drilling it out or threading the plastic, it's important to know how much extra space you need to model into your part to accommodate. In general, when I need to insert an M3 bolt, I'll model a 3.2mm hole to make sure it slides in easily.
In general, when I need to insert an M3 bolt, I'll model a 3.2mm hole to make sure it slides in easily.
In general, if you precisely calibrate the steps/mm for the extruder, start and end overlap, and seam alignment, you can push out all 5 pins without much force. If there's difficulty removing any of the pins, there’s still something that needs to be calibrated out to achieve tighter tolerances. One point is earned for every pin that can be pushed out.
Negative Space Test
Retraction Performance Test
This test is hard to quantify the difference between a 4 and a 5, but the main thing this is looking for is retraction optimization. This is one of the toughest slice settings to calibrate due to just how many factors affect retraction, like the number of retraction settings, and even things like layer cooling, print speed, extruder style, or even your extruder's ability to extrude and retract without chewing the filament.
Retraction Test
Support Material Test
Whether you're using a dedicated support material like PVA or HIPS or you're using a single extruder printer and using the same material as your support material, it's important to have your support settings calibrated. Same material supports are printed with what's called an "air gap" where the print head rises above the print to create a slight gap between the roof of the support and the bottom of the printed part, giving the filament extra time to cool and droop onto the supports, preventing them from permanently adhering to each other. That air gap is something that needs to be optimized; too small and the supports adhere to the finished print, too large and the bottom surface will be really stringy and droopy until it can recover.
Same material supports are printed with what's called an "air gap" where the print head rises above the print to create a slight gap between the roof of the support and the bottom of the printed part, giving the filament extra time to cool and droop onto the supports, preventing them from permanently adhering to each other. That air gap is something that needs to be optimized; too small and the supports adhere to the finished print, too large and the bottom surface will be really stringy and droopy until it can recover.
Dedicated support materials produce a bottom surface finish almost as clean as the top surface, because they are printed without an air gap since they can be dissolved away. The test model has separate sections for intricate supporting and a flat bottom surface, because an air gap optimized for one may not be enough for the other.
Support Test
Full Bed Dimensional Accuracy Test
While the dimensional accuracy test checks the accuracy of a fairly small part, this test checks accuracy across the entire bed. A small error in the dimensional accuracy test will compound into a larger discrepancy across the bed, which is 10 times longer than the first test. The smallest difference in expected vs actual measurement just means that any multi-part prints are going to skew depending on the orientation the part was printed in.
A small error in the dimensional accuracy test will compound into a larger discrepancy across the bed, which is 10 times longer than the first test. The smallest difference in expected vs actual measurement just means that any multi-part prints are going to skew depending on the orientation the part was printed in.
Full Bed Dimensional Accuracy Test
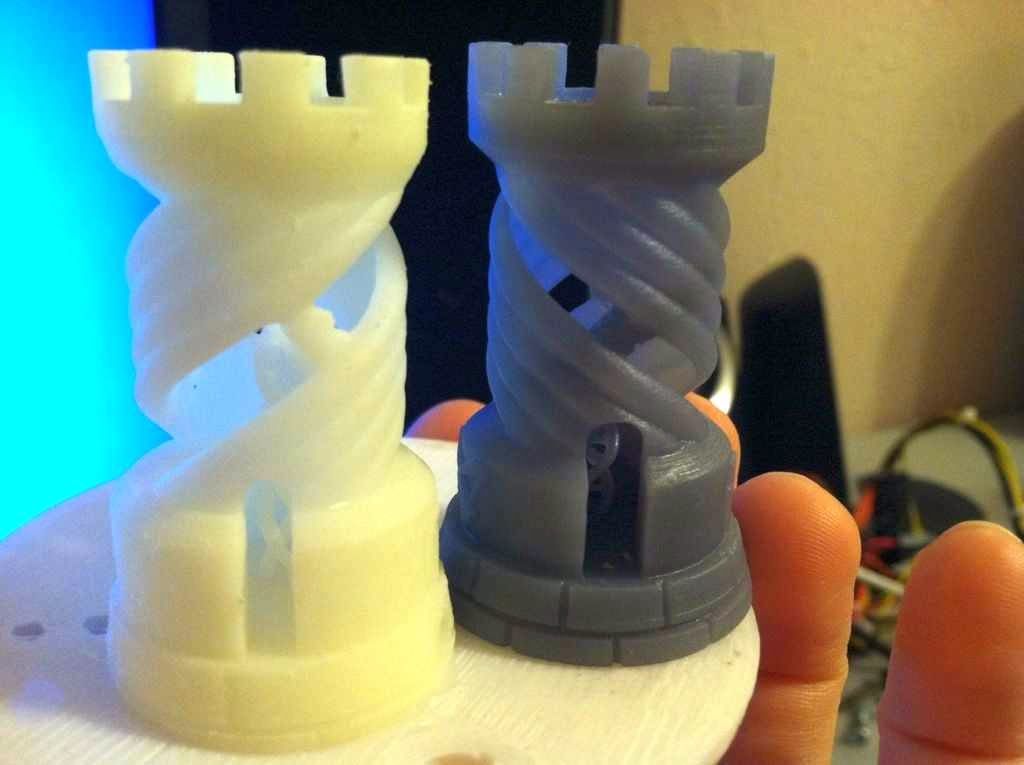
Z Wobble Test
Unlike every other test, which uses a scale to grade the proficiency of the 3D printer, this test is simply a pass or fail. The tower has a wide brim to make sure it is well adhered to the bed, and to ensure that any sort of issue in the walls of the tower comes from the printer's structure, and not because it tipped off of the bed. If there is any wobble, it should be cyclical and repeat with a period identical to the pitch of the lead screw attached to the Z axis. If the lead screw had an 8mm pitch, then you should see the pattern repeat every 8mm.
A key thing to watch out for is to make sure that your Z axis is properly constrained and not over constrained. Properly constrained means you have smooth rods, linear rails, or extrusions with V-slot wheels making sure that the Z axis only moves on Z and doesn't shift around. Rods, rails, and wheels should be tensioned or secured so that they don't wiggle or move when the Z axis is raising or lowering. Over-constrained is something like installing bearings at the top of the leadscrews in a support bracket. This is actually counter intuitive, because no lead screw is perfectly straight and adding that bearing causes a deflection in the lead screw. There should in general only be two part interacting with the lead screw: a coupler that attaches it to a motor (or be part of the motor) and a lead screw nut, anything else is overconstraining it and can hurt print quality more than help.
Properly constrained means you have smooth rods, linear rails, or extrusions with V-slot wheels making sure that the Z axis only moves on Z and doesn't shift around. Rods, rails, and wheels should be tensioned or secured so that they don't wiggle or move when the Z axis is raising or lowering. Over-constrained is something like installing bearings at the top of the leadscrews in a support bracket. This is actually counter intuitive, because no lead screw is perfectly straight and adding that bearing causes a deflection in the lead screw. There should in general only be two part interacting with the lead screw: a coupler that attaches it to a motor (or be part of the motor) and a lead screw nut, anything else is overconstraining it and can hurt print quality more than help.
Z Wobble Test
Squareness Test
This test was developed to make sure that the printer's X and Y axis are assembled square with each other; this test will determine if the printhead moves on X, does it move a marginal amount on Y as well, or vice versa. Using an angle gauge, you will measure each of the five squares and determine how far off each corner is from 90 degrees. The further off from 90, the lower the printer's score.
Using an angle gauge, you will measure each of the five squares and determine how far off each corner is from 90 degrees. The further off from 90, the lower the printer's score.
Squareness Test
These are the top ten ...really 11 prints because there's just no way to cut out any one of these, they all serve a very specific purpose that without them you're missing some element of troubleshooting and calibrating your 3d printer to perform at its absolute best. And these are the tests that we run to make sure that the printers that we work with are running at their best as well, so I hope that with these calibration prints you’re better equipped to help calibrate your own 3D printer and getting it to perform at the best that it absolutely can.
All of these calibration prints, collected by Make, can be found in one place on Thingiverse here:
https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2755063
Happy calibrating!
Article Tags
- 3D Printing
- Firmware
- 3D Design
- MatterControl
- Press Releases
- Small Business
- Automotive
- E3D
- Jewelry Making
- Engineering
- Entertainment Industry
- MatterControl Touch
- ESD Materials
- NylonX
- BCN3D
- Open Source
- Crafty Pen
- Digital Fabrication Anatomy
- How To
- Hardware and Upgrades
- Tips and Tricks
- Weekend Builds
- Top Ten
- Education
- Tech Breakdown
- Women in 3D Printing
- Project Ideas
- Advanced Materials
- Reference
- Pulse Dual Extrusion
- Product Spotlight
- Aerospace
- Jobs
- Military & Government
- Multi-Tool Machines
- Getting Started
- Healthcare
- How To Succeed With Any 3D Printing Material
- Creality3D
- Architecture
- 3D Printer Reviews
- Hacker of the Month
Related Products
View all related productsBest Test Models for 3D Printing
You can end up in one of three situations that require using test models for 3D printing. First, when using a new printer. Second, when checking out a new type of material. Third, when testing the properties of a familiar type of material to find the limits of its strength. In this review, we will talk about the seven test models we find most useful or interesting.
First, when using a new printer. Second, when checking out a new type of material. Third, when testing the properties of a familiar type of material to find the limits of its strength. In this review, we will talk about the seven test models we find most useful or interesting.
Read the article below to learn more.
Source: help.prusa3d.com
1. 3D Benchy
3D Benchy is the most popular 3D printing test model. This tugboat figurine perfectly shows the abilities of FDM 3D printers of any price range. 3D Benchy will help you find the parameters that need to be set to get perfect prints.
Source: thingiverse.com
Using 3D Benchy for test printing allows you to see how good a printer will be at creating curved surfaces, inclined elements, arcs, and holes. The model is available in different versions, including a multi-color one. Printing standard-sized 3D Benchy will take approximately an hour — knowing this will help to determine the level of efficiency of a printer.
Printing standard-sized 3D Benchy will take approximately an hour — knowing this will help to determine the level of efficiency of a printer.
Download the model from Thingiverse.
2. “All in One” 3D Printing Test
A complex 3D printing test model will allow checking the quality of resulting overhangs, bridges, as well as extrusion stability and changes of stringing (spaghettification) and it depends on temperature.
An important advantage of this model is an inclusion of an instruction that describes the ways to solve potential problems.
Source: thingiverse.com
The pros of this project include the ability to check how thin walls, hollow cylinders or overhangs will look, as well as how their quality will depend on speed, temperature and cooling settings.
Download the model from Thingiverse.
3.
 XYZ 20 mm Calibration Cube
XYZ 20 mm Calibration CubeThe main purpose of the XYZ 20 mm calibration cube is to find out how the extruder’s movement depends on the steps of a stepper motor. This 3d printing test model helps ensure that the distance of 20 mm on a drawing translates to 20 mm in a printed model. The calibration cube will also allow us to find out how extrusion and print quality depend on the nozzle temperature.
Source: thingiverse.com
Download the model from Thingiverse
4. Compact Temperature Calibration Tower
This temperature calibration tower showcases a 3D printer’s abilities to utilize the same with different temperatures. The model demonstrates the quality of overhangs and tunnels, as well as how good the printer is at producing curved elements.
Source: thingiverse.com
This simple tool makes it easier to find the abilities of the materials that weren’t used before or were only printed at a certain temperature. It’s important to keep in mind that the printing temperature for each element must be set in slicing software or manually using G-code.
Download the model from Thingiverse
5. Open-Source Assessment Model
Source: github.com
3D printing test model by Kickstarter and Autodesk was developed with the consideration of the experience of using other testing models. This one can be considered multi-purpose. It includes bridges, overhangs, small details, and the elements to access the dimensional accuracy of 3D printing. Before printing one should keep in mind the size of an overhang at the upper level. This means that a user should know the temperature at which the model will not deform.
Download the model from Github
6. Quick Stringing Test
When printing complex models without knowing about the properties of a filament and a printer, one can encounter an issue called stringing or spaghettification: it’s when extruder motion stretches the filament, creating thin threads in the air.
Source: thingiverse.com
It is caused by a filament leakage when the extruder is inactive. Filament retraction function is used to avoid it. The correct retraction level should be based on extruder head movement speed, nozzle temperature, and filament properties.
This test model is used to quickly check if the printer is set up correctly. If there are no strings between vertical pyramids, then the parameters are set correctly. If the horizontal filament lines are present, then some parameters are set incorrectly and should be changed.
Download the model from Thingiverse
7. PolyPearl Tower
Another way to test printing parameters is the PolyPearl Tower. The features of this complex model allow one to check the quality of bridges, curves, overhangs, to see if there’s some stringing and find out how rigid the model is. The model can be used for stress-testing to find out the physical limits of a filament with a certain temperature and printing speed.
Source: thingiverse.com
Download the model from Thingiverse
Conclusion
3D printing test models can save the time and resources of a user. They don’t take longer than an hour to print, their quality shows whether the printing parameters were set correctly or need to be changed. Users can easily change the settings of a 3D printer if needed.
Buy a 3D printer and 3D printing materials at Top 3D Shop — and get officially distributed products with a warranty, service, and technical support.
8 test print models
3D printer test models are required for:
- When you bought a new printer and need to test it on your favorite media
- When you have purchased new media and need to check the print specifications
- When you have been using a material for a long time but do not know its tensile strengths
We will talk about the 8 models most used for testing in 3D printing.
1 3D Benchy
3D Benchy is one of the most popular 3D printer test models. The boat figurine perfectly demonstrates the capabilities of FDM printers in any price category. Such a model will help you determine exactly the settings you need to set in order to get the perfect 3D print.
Printing 3D Benchy - will allow you to see how the printer copes with the "rendering" of curved surfaces, inclined planes, arcs, holes. The model is available in several versions, including multi-color. It takes approximately one hour to print a standard size 3D Benchy.
Download model on Thingiverse
2. All-in-one 3D printer test
A comprehensive test model for a 3D printer will allow you to check the quality of printed overhangs, bridges, extrusion stability, the possibility of “snot” and the dependence of the result on temperature. An important advantage of this model is the instructions for it, which indicate potential solutions to various problems.
Quite a complex model in terms of setting all the parameters, but it's worth it, try it.
Download Thingiverse model
3. XYZ 20mm Calibration Cube
The main purpose of the XYZ 20 mm calibration cube is to establish the dependence of the movement of the extruder on the step of the motor. A test model for a 3D printer helps to make sure that 20 mm in the drawing corresponds to 20 mm of the printed product. At the same time, the calibration cube helps to establish the dependence of the degree of extrusion and print quality on the temperature of the extruder.
A test model for a 3D printer helps to make sure that 20 mm in the drawing corresponds to 20 mm of the printed product. At the same time, the calibration cube helps to establish the dependence of the degree of extrusion and print quality on the temperature of the extruder.
Download Thingiverse Model
4. Matter Hackers' Mascot Phil A. Ment
This is a small astronaut figurine that has elements designed to test 3D printing.
These are small inserts, small relief details, overhangs, vertical and horizontal cylinders, fillets, chamfers, lintels and a perfectly domed helmet.
A feature of the model is the ability to obtain accurate data for different dimensions of the printed product.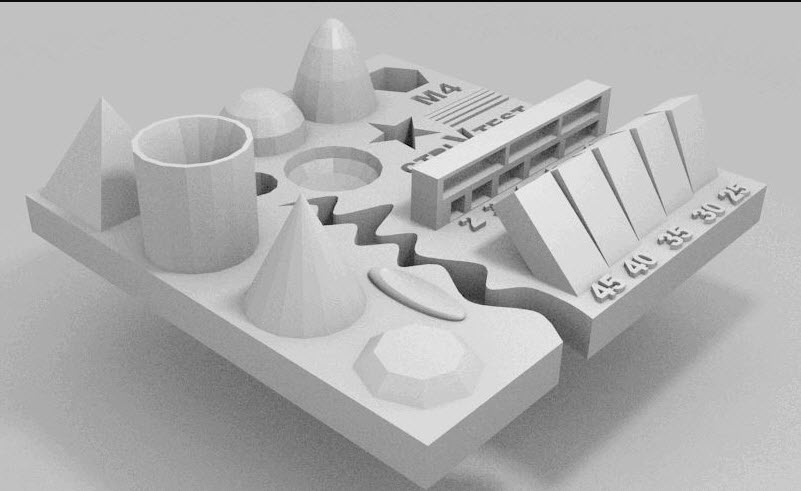
Download model on Thingiverse
5. Smart compact temperature calibration tower
The calibration scale demonstrates the capabilities of the 3D printer when printing at different temperatures with one filament. The test model clearly shows the quality of overhangs, lintels, tensions, and the product can also be used to judge the ability of a 3D printer to print curved surfaces with a certain plastic.
A simple and intuitive tool allows you to find out the possibilities of materials that have not previously been used in work or printed with only one temperature.
It is important to consider that the print temperature setting for each signed element (floor) must be set in the slicer or manually in Gcode.
Download model on Thingiverse
6. Open-Source Printer Evaluation
This is a universal print model from Kickstarter and Autodesk. It was created taking into account the experience of using other models for testing. It contains bridges, overhangs, fine detailing and elements for assessing the spatial accuracy of 3D printing.
Download model on Github
7. Economical Stringing Test
When printing complex-shaped objects, without knowing the capabilities of the filament and the printer, the user may encounter stringing (from string - string), and in Russian simply “snot” - when plastic reaches for the extruder, forming thin plastic fibers in the air. Such “snot” appears when the extruder is idle. To avoid this, the retract function is used - the retraction of the filament during idle movement. Correct setting of the retract level requires consideration of extruder speed, extruder temperature and filament properties.
Such “snot” appears when the extruder is idle. To avoid this, the retract function is used - the retraction of the filament during idle movement. Correct setting of the retract level requires consideration of extruder speed, extruder temperature and filament properties.
This test model is used to quickly check the correct setting of the 3D printer. If the strings between the vertical pyramids do not form, then the settings are correct. If horizontal plastic filaments appear, then some of the 3D printing parameters should be changed.
Download model on Thingiverse
8. PolyPearl Tower (Pearl Tower)
The design features of the model allow you to check the quality of jumpers, bends, protrusions, fix the appearance of “snot” and establish the strength of the model as a whole. This model can also be used as a stress test that determines the physical limits of a filament at a given temperature and print speed.
This model can also be used as a stress test that determines the physical limits of a filament at a given temperature and print speed.
Download model on Thingiverse
Conclusion
To improve your filament printing skills on your printer, we highly recommend doing a couple of test prints from this article. Thus, you will save more on plastic, because you will use the desired print settings.
Buy plastic for 3D printing at REC - get officially delivered products with warranty, service and technical support.
Test file for 3D printing from photopolymer. Calibration
All 3D printers require calibration from time to time, and photopolymer devices are no exception. We have collected here the most popular test 3D models, with which you can carry out diagnostics and calibration.
3D printing technology
Among 3D printing technologies, photopolymer stands apart. This is the second most popular printing method after FDM, the essence of which is squeezing molten plastic through a nozzle. A relatively inexpensive plastic thread is used as a material in FDM technology.
A relatively inexpensive plastic thread is used as a material in FDM technology.
Photopolymer printing uses resins that cure with light. There are several variations of technology: SLA, LCD and DLP . They differ in light source and printing speed. But in any case, this is always the exposure of the photopolymer resin layers. The finished model, due to the peculiarities of the printing technology and the material itself, needs to be washed and additionally cured.
Resin printing technologies are different, but they all rely on a number of common settings and factors. Among them:
- authorization;
- intercoat adhesion;
- exposure time;
- smoothing index;
- resin characteristics.
How do I check the print settings and determine if they need to be adjusted? For this, calibration or test models were created. Such models allow you to test the settings. There are many options, but there are several popular ones that have proven their effectiveness in practice:
- AmeraLabs Town
- HARZ Labs Test
- Siraya Tech
- Validation Matrix
Let's dwell on each in more detail . .. /www.thingiverse.com/thing:2810666
.. /www.thingiverse.com/thing:2810666
Lithuanian photopolymer resin manufacturer AmeraLabs has developed a versatile Town calibration model for testing purposes. It is called a universal part because it allows you to check not only the printer settings, but also the quality of the resin. A total of ten tests are included in the model. Each is enclosed in "buildings" of different heights and located at different angles. The model is very effective and therefore can often be seen in tutorials and simple resin printing videos.
There are ten tests in total, as mentioned earlier, we note three to understand the possibilities:
- gaps of different widths (0.1-1mm) - checking the quality of the light source and exposure time;
- holes of different heights - checking exposure time, adhesion of layers;
- cross bridge - checking layer height and resin quality.
Analysis of deformations, inconsistencies allows you to identify problems and make appropriate adjustments.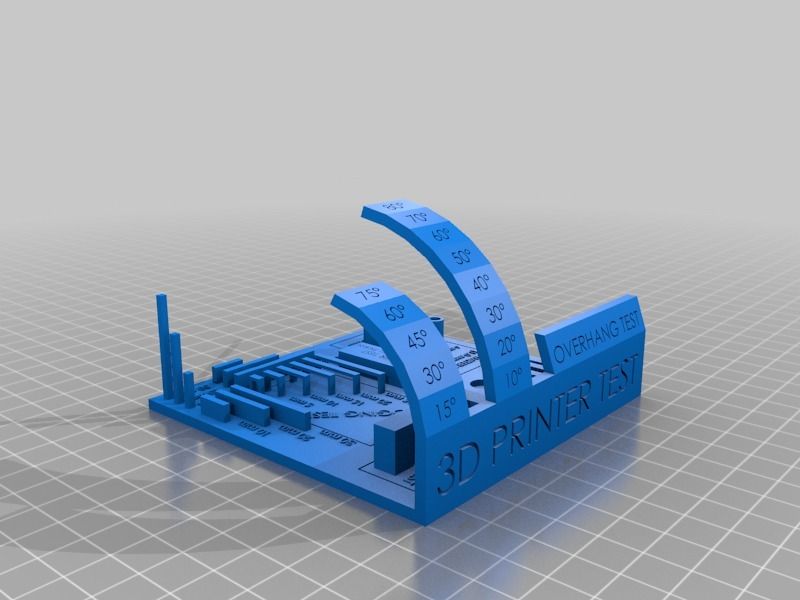
3D model for calibration HARZ Labs Test
Download link (copy the link and paste in the address bar): https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:2776522
HARZ Labs is a leading company in the production of photopolymer resin. But it produces resins for photopolymer printing. For the purpose of testing, a calibration model was developed.
Siraya Tech
calibration 3D model Download link (copy the link and paste it into the address bar): https://www.thingiverse.com/thing:5438127
Test model from a Hong Kong resin manufacturer. There are five testing sections in the model. Three are for checking exposure. The model allows you to quickly find and fix the problem. The fact is that resolution and exposure are checked right during printing, problems will be visible even before the model is printed to the end. With a print height of 3.5 mm, holes, recessed text, objects of a round and triangular shape should be clearly visible.