Sciaky 3d printing
Sciaky, Inc. | Metal Additive Manufacturing
Sciaky, Inc. | Metal Additive Manufacturing | EB Welding
Sciaky &
AM FORWARD
We are preparing to meet the needs of SME suppliers participating in the AM Forward program.
Learn more
EB Welding
Excellence
Sciaky’s electron beam (EB) welding systems outperform & outlast the competition.
Learn more
EBAM
® =Fast Parts
EBAM
® is the fastest metal deposition process in the 3D printing market.Learn more
EBAM
® =Cost Effective
EBAM
® is the most cost effective metal 3D printing process on the market.Learn more
EB Job Shop
No other EB welding job shop in the world can match Sciaky’s wide range of capabilities.
Learn more
Sciaky began developing its groundbreaking Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing (EBAM®) technology in 1996 to help manufacturers save significant time and money on the production of large, high-value metal parts like Titanium. Our innovative Electron Beam (EB) Welding systems and job shop services have been the gold standard in the EB fabrication market since the 1950s.
Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing reduces the time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing (i.e. forging and casting). And, compared to other metal additive manufacturing processes, EBAM® has a faster deposition rate by up to a factor of ten and provides true scalability for part size and quality. Simply put: EBAM® technology is the most cost-effective industrial metal 3D printing process in the world.
In addition, EBAM® can be utilized anywhere in the product life cycle: from rapid prototypes and production parts to repair and remanufacturing applications. Plus, Sciaky’s patented Closed-Loop Control technology ensures that part production can be replicated according to the same established parameters (i.e. geometry, material properties, and material composition), from the first part to the last.
Sciaky’s EB Welding technology provides exceptional weld quality with a high depth-to-width ratio and maximum penetration with minimal distortion. We have been at the forefront of EB Welding advancement for over six decades. Our state-of-the-art internal moving EB Welding gun is the most innovative gun on the market. Whether you have a traditional welding requirement that calls for joining common metals, or a more exotic application with refractory alloys, Sciaky’s EB Welding technology delivers remarkable results. Plus, our EB Welding technology is an excellent choice for joining dissimilar metals.
Welding Solutions
Sciaky provides its world-class EB Welding Systems, Advanced Arc Welding Systems, and EB Welding Job Shop Services to a wide range of industries like aerospace, defense, automotive, energy, healthcare, semiconductor, oil & gas.
ELECTRON BEAM
WELDERS
ADVANCED
ARC WELDERS
WELDING
JOB SHOP
Latest News:
- Sciaky’s Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing (EBAM®) Surpasses 40 lbs. of Titanium/Hour, Making it the Highest Deposition Rate in the World for Industrial Metal 3D Printing
Affiliations:
- AmericaMakes
- Association of the US Army
- The American Welding Institute
- Center for Innovative Materials
- Additive Manufacturing Users Group
- The Alliance for the Development of Additive Processing Technologies
- National Defense Industrial Assoc.
- The Welding Institute Ltd.
- Michigan Aerospace Manufacturers Association
- International Titanium Association
Made in America.
Deployed Globally.
Sciaky is based in Chicago, IL, USA. Its welding systems and EBAM® industrial 3d printing machines are
distributed internationally and found in manufacturing plants and advanced research and
development facilities around the world. Contact a sales rep in your area by clicking here.
Contact a sales rep in your area by clicking here.
N. America
- United States
- Mexico
- Canada
S. America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Columbia
- Chile
- Peru
- & More
Europe
- Germany
- France
- United Kingdom
- Italy
- Spain
- Switzerland
- Russia
- & More
Asia
- China
- Israel
- India
- South Korea
- Japan
- Vietnam
- Singapore
- & More
TAI to 3D print 6 meter-long aerostructures with the "world's largest" electron beam machine from Sciaky
0Shares
Insiders and analysts predict the 3D printing trends to watch out for in our latest series of articles focused on the future of 3D printing.
Metal 3D printing specialist Sciaky has revealed that it plans to ship the “world’s largest” electron beam (EB) directed energy deposition (DED) system to aircraft manufacturer Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI).
As part of a new partnership between the firms, TAI is set to install a custom Sciaky 300″ x 108″ x 132″ build volume 300 Series Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing (EBAM) 3D printer. Once fitted, the large-format system will be used to create titanium aerostructures up to 6 meters in length, in the course of several pilot projects that are expected to help TAI master its deployment of the technology.
“Sciaky’s EBAM systems are the most widely sold, large-scale DED metal 3D printers in the world, having approved parts on land, sea, air, and space applications,” said Scott Phillips, President of Sciaky. “We applaud TAI’s vision for innovation and their ambitious plans to 3D print some of the largest titanium aerostructures in the world.”
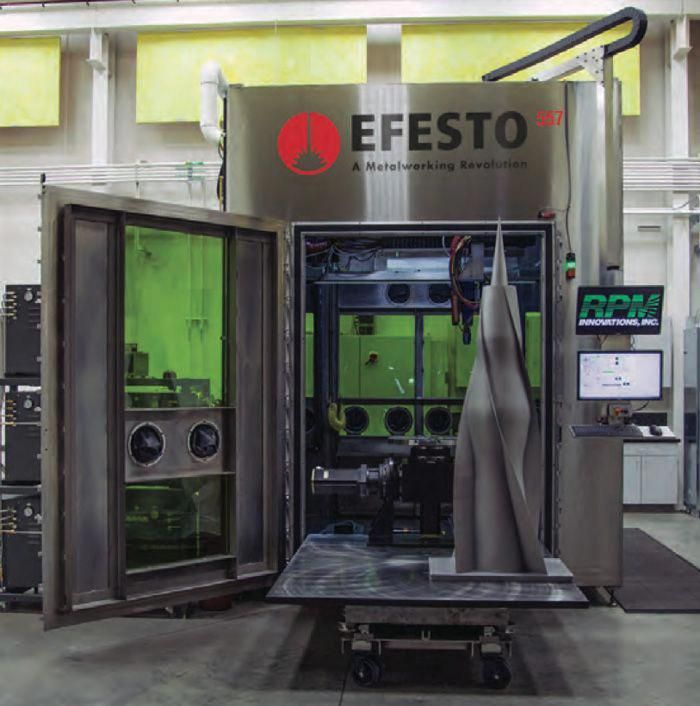
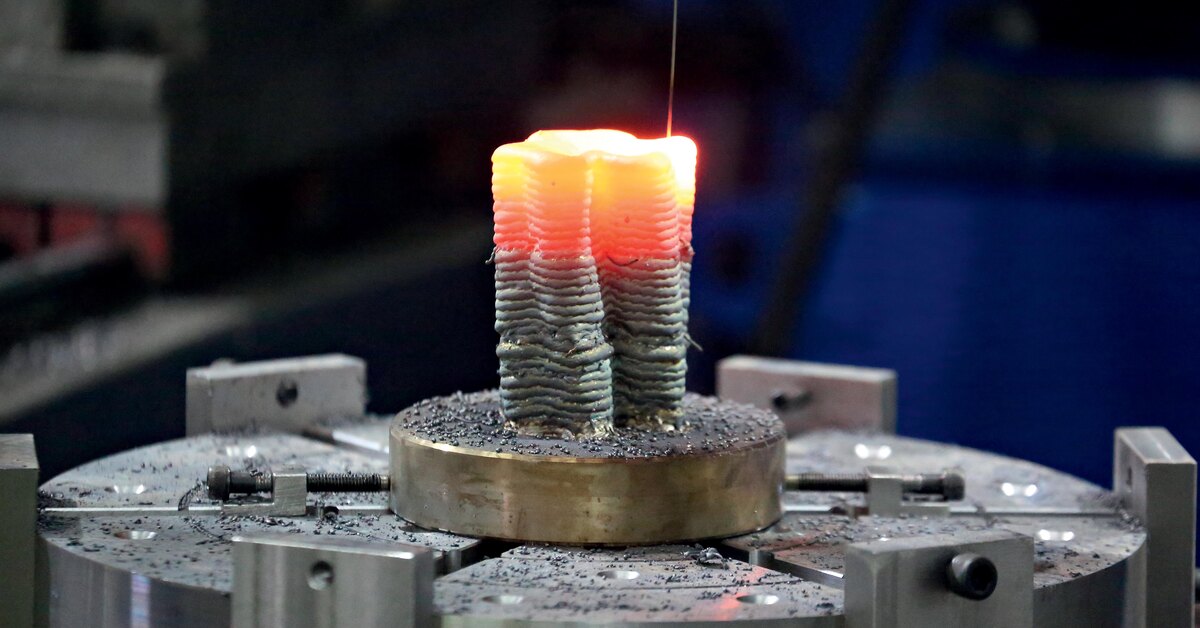
Sciaky’s 300 Series EBAM 3D printer. Photo via Sciaky.
Photo via Sciaky. High-throughput metal 3D printing
Offered initially as a service, before being incorporated into a turnkey system after a surge in client demand, Sciaky EBAM is essentially a process in which an EB gun is used to deposit wire feedstock layer-by-layer. With a deposition rate of up to 25 lbs per hour, and a dual wire feed system that allows two metals to be combined into a single melt pool, the approach enables the rapid fabrication of custom alloy parts.
At present, the company markets its EBAM technology both as a service at its 3D Printing Facility, and in the shape of its five large-format machines. The largest system in Sciaky’s offering is its 300 Series, which, thanks to its High Efficiency Pumping–Chamber and 280” x 48” x 48” part envelope, is capable of churning out colossal components at pace.
The 3D printer also comes fitted with the firm’s proprietary Interlayer Real-time Imaging and Sensing System or ‘IRSS.’ Designed to reduce variability during part production, IRSS is effectively a suite of closed-loop sensors, software logic and CNC controls which monitor key deposition parameters, and makes adjustments in real-time to ensure that throughput doesn’t come at the cost of product quality.
In the past, Sciaky has deployed its technology alongside the likes of Airbus to 3D print structural wing parts for its airplanes, and continually hailed the process’ aircraft frame, jet engine and missile production potential, thus its partnership with TAI is very much in keeping with its wider strategy of targeting heavy duty aerospace applications.
Sciaky’s EBAM systems feature a dual wire feed configuration. Photo via Sciaky.Sciaky’s Turkish Aerospace deal
While Turkish Aerospace was launched under Turkey’s Ministry of Industry and Technology to reduce the country’s reliance on defense imports in 1973, TAI itself wasn’t founded until 1984, when it was established as a joint Turkish-US firm, tasked with not only building F-16 aircraft, but handling their onboard system integration and flight testing.
Since then, Turkish Aerospace has undergone a wider restructuring that has seen it broaden its activities, with the aim of becoming a hub for the development of innovative aviation and aerospace technologies. This 2005 revamp effectively saw the firm reorganize into six groups focused on the production of structural, aircraft, helicopter, UAV, space system and national combat aircraft components.
This 2005 revamp effectively saw the firm reorganize into six groups focused on the production of structural, aircraft, helicopter, UAV, space system and national combat aircraft components.
Having previously dipped its toe into 3D printing, by working with the FIT Additive Manufacturing Group to produce satellite-steering device holders called ‘star tracker brackets,’ TAI has now penned a contract with Sciaky, in a deal that is set to take its adoption of advanced technologies a step further, by seeing it install a custom 300 Series EBAM 3D printer at its plant in Turkey’s capital, Ankara.
According to Sciaky, following fitting and configuration, the machine will be used to “3D print some of the largest titanium aerostructures in the industry.” Although TAI has yet to confirm the exact parts it intends to produce, the term ‘aerostructure’ can describe anything from an aircraft’s fuselage to its wing surfaces, thus it has left plenty of scope for the technology to be deployed across its business.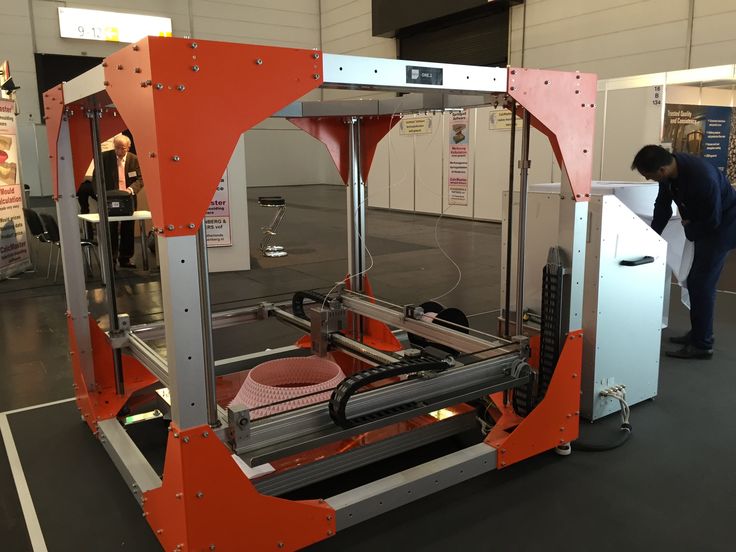
What has been confirmed, is that the 3D printer will be utilized to manufacture titanium parts up to six meters-long, with TAI also set to benefit from its combined EB welding and 3D printing functionalities for applications that require both. Moving forwards, Sciaky says it has committed to conducting a “series of projects” with its new partner, but the delivery schedule for its machine is “still being finalized.”
FIT AG’s 3D printed star tracker bracket on display at Formnext in 2019. Photo via FIT AG.Deploying wire-fed DED
While Sciaky’s machines continue to deposit alloys at a record-breaking pace, it’s far from the only developer of wire-fed DED technology. Reliance Precision and the University of Huddersfield, for example, are working on a fresh approach to EBAM as part of an Innovate UK-backed project that’s designed to broaden the process’ industry adoption.
Elsewhere, in another Innovate-UK program, Hybrid Manufacturing Technologies (HMT) is leading the development of a new compact wire-feed system called ‘FastWireAM. ’ As part of the project, which has been set up to fast-track the technology’s R&D, consultancy firm TWI and wire feedstock producer Epoch Wires have committed to optimizing its performance and accelerating its uptake as well.
’ As part of the project, which has been set up to fast-track the technology’s R&D, consultancy firm TWI and wire feedstock producer Epoch Wires have committed to optimizing its performance and accelerating its uptake as well.
In defense-related applications, researchers at Penn State’s College of Engineering have also been awarded $434,000 by the US Army to develop an improved means of 3D printing high-strength alloys. Using a computer modeling-based approach, the team aims to identify a Laser Directed Energy Deposition (L-DED) setup that’s capable of producing more robust metals with enhanced material efficiency.
To stay up to date with the latest 3D printing news, don’t forget to subscribe to the 3D Printing Industry newsletter or follow us on Twitter or liking our page on Facebook.
For a deeper dive into additive manufacturing, you can now subscribe to our Youtube channel, featuring discussion, debriefs, and shots of 3D printing in-action
. Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Are you looking for a job in the additive manufacturing industry? Visit 3D Printing Jobs for a selection of roles in the industry.
Featured image shows an engineer using Sciaky’s 300 Series EBAM 3D printer. Photo via Sciaky.
Tags 300 Series EBAM airbus Epoch Wires FIT Additive Manufacturing Group Hybrid Manufacturing Technologies Innovate UK Penn State University Reliance Precision Sciaky Scott Phillips Turkish Aerospace Industries TWI University of Huddersfield US Army
Paul Hanaphy
Paul is a history and journalism graduate with a passion for finding the latest scoop in technology news.
What is 3D printing and how it can be used! Interesting!
What is 3D printing
3D printing technology was patented in the 80s of the last century, but gained popularity relatively recently. New, promising techniques have been developed and the possibilities of 3D technologies have reached a completely new level.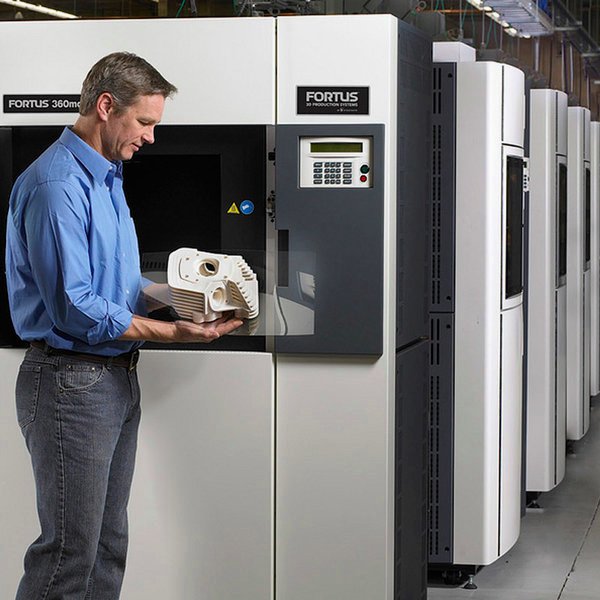 However, to this day, the technique is not known in all circles, and not everyone is aware of what 3D printing is. In today's article, we will try to explain in detail and in an accessible way what 3D printing is and where it is used.
However, to this day, the technique is not known in all circles, and not everyone is aware of what 3D printing is. In today's article, we will try to explain in detail and in an accessible way what 3D printing is and where it is used.
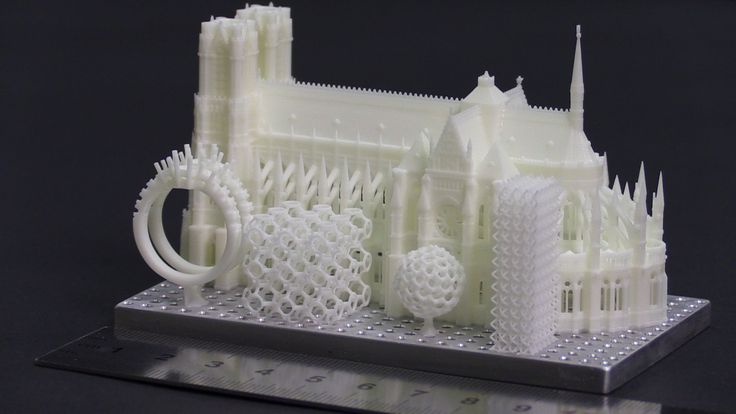
In short, 3D printing is a technique for manufacturing three-dimensional products based on digital models. Regardless of the specific technology, the essence of the process is the gradual layer-by-layer reproduction of objects.
This process uses a special device - a 3D printer, which prints certain types of materials. More details about it are written here. Other names for the technology are rapid prototyping or additive manufacturing. Often the phrase "additive technologies" is used in the meaning of "3D technologies".
3D printing steps
To make it clearer what 3D printing is, let's take a look at the playback process step by step. Below are the specific stages of 3D printing. How it works:
- 3D modeling of the required object is performed according to certain rules;
- The file with the digital model is loaded into the slicer program, which generates the control code for the 3D printer;
- Sets required 3D printing options;
- The code is written to a removable memory that connects to the 3D printer;
- 3D model reproduced.
Objects are reproduced gradually. According to the required shape, the selected material is applied layer by layer, forming the finished product. It is worth noting that the possibilities of 3D printing are almost limitless, that is, anything can be made. In some technologies, very thin overhanging elements are provided with supports, thanks to which they can be avoided from sagging.
Naturally, this is a very simplified description of the stages of 3D printing, but they give a very clear idea of the essence of the technique.
Other questions and answers about 3D printers and 3D printing:
- Basics What is 3D scanning?
- Basics What is a 3D model?
3D Printing Technologies
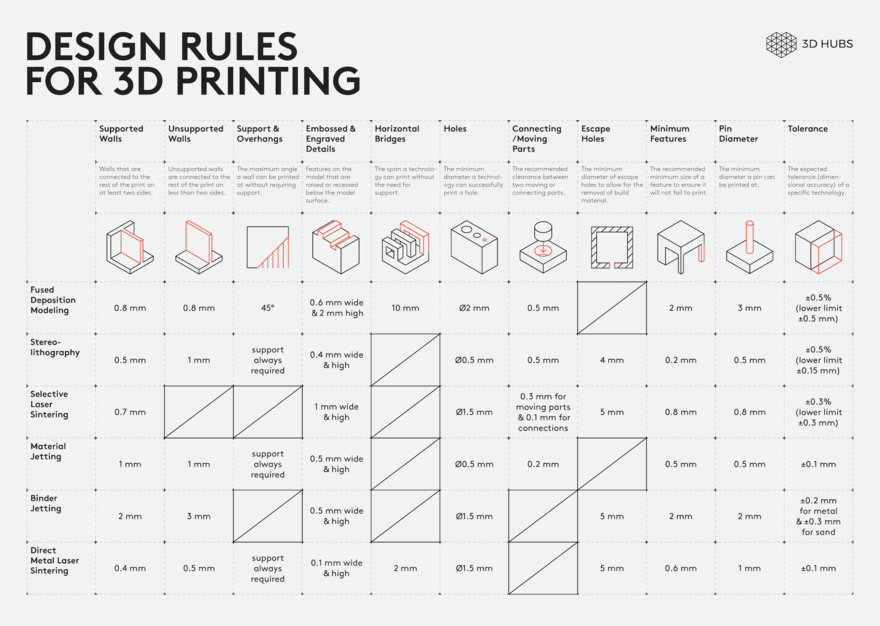
Different 3D printing technologies are used to reproduce different objects. They differ both in the consumables used, and in the speed and accuracy of printing. Here are the main 3D printing technologies:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) .
 One of the most common 3D printing technologies, used in most desktop 3D printers, and represents an ideal price / quality ratio. Printing occurs by layer-by-layer supply of a thread of molten plastic;
One of the most common 3D printing technologies, used in most desktop 3D printers, and represents an ideal price / quality ratio. Printing occurs by layer-by-layer supply of a thread of molten plastic; - Laser stereolithography (SLA) . The formation of the object occurs due to the layer-by-layer illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin by a laser, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage;
- Selective laser sintering (SLS) . Reproduction is performed by layer-by-layer melting of a special powder under the action of laser radiation. This 3D printing method is widely used in the industry for the manufacture of durable metal elements
3D Printing Applications
As you may have guessed by now, 3D printing is extremely versatile. The second name of the technology - rapid prototyping - speaks for itself. In the manufacture of prototypes and models of models, 3D printing can be simply indispensable. It is also a very cost-effective solution for small-scale production. In the aerospace and automotive industries, 3D technologies are already being used with might and main due to the high profitability and speed of manufacturing components. Culinary professionals are working on the development of 3D food printers, and in medicine, 3D printing has become something of a technology of the future. With the help of 3D bioprinting, it is planned to produce bones, organs and living tissues, but for now, implants and full-fledged medicines are printed on 3D printers. Desktop 3D printers can be used for domestic purposes: for repairs, making various household items, and so on. And designers, fashion designers, sculptors and artists appreciate the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling as an unusual way to realize their talent.
The second name of the technology - rapid prototyping - speaks for itself. In the manufacture of prototypes and models of models, 3D printing can be simply indispensable. It is also a very cost-effective solution for small-scale production. In the aerospace and automotive industries, 3D technologies are already being used with might and main due to the high profitability and speed of manufacturing components. Culinary professionals are working on the development of 3D food printers, and in medicine, 3D printing has become something of a technology of the future. With the help of 3D bioprinting, it is planned to produce bones, organs and living tissues, but for now, implants and full-fledged medicines are printed on 3D printers. Desktop 3D printers can be used for domestic purposes: for repairs, making various household items, and so on. And designers, fashion designers, sculptors and artists appreciate the possibilities of 3D printing and 3D modeling as an unusual way to realize their talent.
Well, that was a brief description of what 3D printing is. We hope we were able to provide the necessary information in an accessible way. If you have additional questions that we have not covered, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add your questions! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
We also want to remind you about the possibility to order 3D printing, 3D scanning, 3D modeling services or purchase of related equipment and consumables with delivery throughout Ukraine in 3DDevice. If you have any questions, please contact us at one of the phone numbers listed here. We look forward to collaborating!
Return to the main page
3D printing on order in Nizhny Novgorod, cost of services
The cost of printing on a 3d printer allows you to use the service not only for commercial and state enterprises, but also for individuals - innovative production technologies have become widely available. Prototyping of 3d models is the reading of information from a computer program by special equipment and translation into a real object by successive building up layer by layer until the formation of a finished product. ProPlast-NN LLC carries out 3d printing to order - the price of is calculated individually depending on the size of the object, the number of ordered samples, the material from which they will be made and the method of prototyping.
ProPlast-NN LLC carries out 3d printing to order - the price of is calculated individually depending on the size of the object, the number of ordered samples, the material from which they will be made and the method of prototyping.
3d printing and prototyping - the latest technologies in practice
The combination of computer technology with production allows you to multiply the speed of production, reduce the cost of creating the necessary items. Volumetric printing is developing at a rapid pace, from the realm of fantasy, it has become a familiar production process, which can be carried out using various methods. Order 3d printing in Nizhny Novgorod for one model or batch of products, just call Pro Plast-NN LLC at the numbers listed on the site. The customer will receive a three-dimensional plastic part, made with a high degree of accuracy according to the drawings or based on a real analogue. Small-scale production of products by 3D printing and prototyping is possible.
Where created 3d models and prototypes are used
Prototyping on 3d printers allows you to quickly and at low cost get a sample of the desired part from a polymer material, made with a high degree of accuracy, without roughness or distortion. Depending on the technology used and the material from which the sample is made, the product acquires high-tech properties: ideal shape, strength, plasticity, temperature stability. Models have found application in many areas, so they make custom 3d printing companies of different specializations:
- medicine;
- automotive;
- serial industrial production: mechanical engineering, instrumentation, metallurgy;
- architecture - when creating models of buildings and complexes;
- designs;
- souvenir production.
How 3d prototyping is carried out
The basis for prototyping is a 3d image of an object, compiled by a computer program with three-dimensional modeling functions. 3d custom prototyping is performed with high accuracy of transferring an image into a physical object using one of several possible methods:
3d custom prototyping is performed with high accuracy of transferring an image into a physical object using one of several possible methods:
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling). A moving molten polymer thread forms an object of complex geometric shape in layers, which can subsequently withstand high mechanical and thermal loads.
- SLS (Eng. Selective Laser Sintering). This is the sintering of a powder in a container under the targeted action of a laser beam.
- MJM (from the English. Multi Jet Modeling - modeling with many nozzles). Multi-nozzle 3d printer prototyping , applying molten material with multiple inkjet heads, based on the principle of a laser printer.
- LOM (from the English Laminated Object Manufacturing - the production of an object by lamination). Bonding layer by layer of thin films, as is done with lamination. After reaching the desired volume with a laser tool, an object of the desired shape is cut out of the mass.

- SLM (from English Selective Laser Melting - selective laser melting). Selective fusion of metal with a targeted laser beam, resulting in a solid object.
- EBM (from the English Electron Beam Melting - electron beam melting). Creation of a product from a powder that is melted by a directed electron beam.
- STL (from English stereolithography - stereolithography). Purposeful formation of a solid object by a laser beam directed into a container with liquid polymer rubber.
Benefits of 3d printing and prototyping
What are the advantages and benefits for a customer who decides to order a 3D printing with a printer?
Before launching a new product into mass production, an enterprise can purchase a prototype, test it, make changes to avoid errors in the design development of the product, and reduce the cost of production.
If a private or public enterprise needs to produce a small batch of products, it is more profitable for him to apply for a small-scale prototyping service than to carry out design and engineering development and testing of prototypes, reconfigure production, use labor resources and equipment. Printing on a 3D printer at affordable prices will save businesses a significant amount, reduce production costs.
Printing on a 3D printer at affordable prices will save businesses a significant amount, reduce production costs.
The desired samples can be obtained in a short period, regardless of the degree of complexity of the object being created. Typically, the prototyping process lasts from one to ten days, depending on the specifics of the chosen manufacturing method. You can place an order for 3D printing at Pro Plast-NN LLC - we will answer your questions, calculate the cost, conclude an agreement and print products in a short time.
The cost of 3d printing with the printer is low, which allows customers to reduce their own costs for design development, testing and sample production. LLC "Pro Plast-NN" makes high-quality 3D printing - the price is calculated by managers individually, depending on the volume, complexity of the work, the chosen manufacturing method and the material from which the sample is printed.
The cost of prototyping and creating 3d models
Answer to question how much it costs to print on a 3d printer depends primarily on the number of ordered products, the material from which the product is made, the size of the object, and the technology of its manufacture.