Radial 3d printer
Cartesian, Delta, and Polar: The Most Common 3D Printers
3D Printing & Imaging
3
If you’re a regular reader here at Make, then you have seen many 3D printers. We talk about them all the time, and have even done comprehensive comparisons between many of the commercially available desktop printers in our Special 3D Printer Shootout Issue. One common question we get though, is “why does that one look different than the one over there?”. To hopefully answer that question a bit, we’d like to take you through the 3 most common filament based printer configurations. We’ll toss in some quirky and interesting oddballs at the end too.
Cartesian
Let’s start with the Cartesian. These printers are named after the most widely used coordinate system which helps robots to decide where and how to move. They will typically have a square print bed which will run along the Y-axis. The X-axis will carry the print head and for the Z-axis (up and down) movement, the print bed may descend as it does on this Ultimaker 2 or the X-axis will rise up as the printer builds objects like it does on the Printrbot Simple.
Delta
Another popular printer style is called the Delta. Delta printers also work within the Cartesian plane however as you can see when you look at the DeltaMaker, they can’t be mistaken for Cartesians. Deltas will usually feature a circular print bed. The extruder will be suspended above that by three arms in a triangular configuration (thus the name “Delta”). These nifty robots were designed for speed and they also have the advantage of a print bed that does not move which could be advantageous for certain prints.
Polar
If Cartesian and Delta printers are too straightforward for you, how about a Polar 3D printer? Photos simply don’t do these bad boys justice so check out a video instead.
These machines use polar coordinates. This system is similar to the Cartesian except that the coordinate sets describe points on a circular grid rather than a square. Yes, with a little rocket science, we can have a printer with a spinning bed and a print head that moves up, down, left and right. No need for forward and backward movement! On a side note, did you know that you can make a rocket engine with any of these printers?
Others
Lastly, let’s not overlook those oddball printers that we find in the robust RepRap community. There’s a fellow by the name of Nicholas Seward who is creating some beautiful bots. Check out his SCARA (Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm) style printer.
He also designed a Delta variation called the GUS Simpson that is, well, poetry. I mean just look!
So whether you want to make rocket engines, Yoda figures or robots with positronic brains, there is a 3D printer out there for you. Have fun in the new age!
Tagged 3D Printing cartesian deltaOur websites use cookies to improve your browsing experience. Some of these are essential for the basic functionalities of our websites. In addition, we use third-party cookies to help us analyze and understand usage. These will be stored in your browser only with your consent and you have the option to opt-out. Your choice here will be recorded for all Make.co Websites.
Some of these are essential for the basic functionalities of our websites. In addition, we use third-party cookies to help us analyze and understand usage. These will be stored in your browser only with your consent and you have the option to opt-out. Your choice here will be recorded for all Make.co Websites.
Allow Non-Necessary Cookies Allow Non-Necessary Cookies
Radial best STL files for 3D printing・Cults
Alfawise U30 Pro - 5015 Radial Fan Duct
Free
New Ventilation for: Alfawise U30 Pro - Fan Duct with BLTouch
Free
Alfawise U30 Pro - Fan Duct with BLTouch
Free
Fan Duct for Alunar M505/M506 3D Printer
Free
Gee Bee R2 with radial 7 cylinders engine
Free
9-cylinder engine
€4
7 cylinder engine
€4
K40 Laser Air Assist, radial fan, no screws, just clip on
€0. 50
50
Radial flow impeller, Ventilation Fan 8mm Bore
€2
RADIAL TRAY FOR SMD ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
€1
Alcoa Wheels with Chevy Caps Reversable Dually Wheels
€4.71
Boost Intake Elbow N Throttle Body for Single Plane intake
€3.76
SBC Single Turbo Higgins Race Motor Small Block Chev
€12.25
20inch Concave Trident Soft Edge Wheels 3x Offsets
€4.71
20inch Concave Trident Hard Edge Wheels 3x Offsets
€4.71
20inch Billet Drilled Steel Wheels with Spinner 2x Offsets
€4.71
20inch Billet 1967 Chev Hubcap Wheels with Spinner 2x Offsets
€4.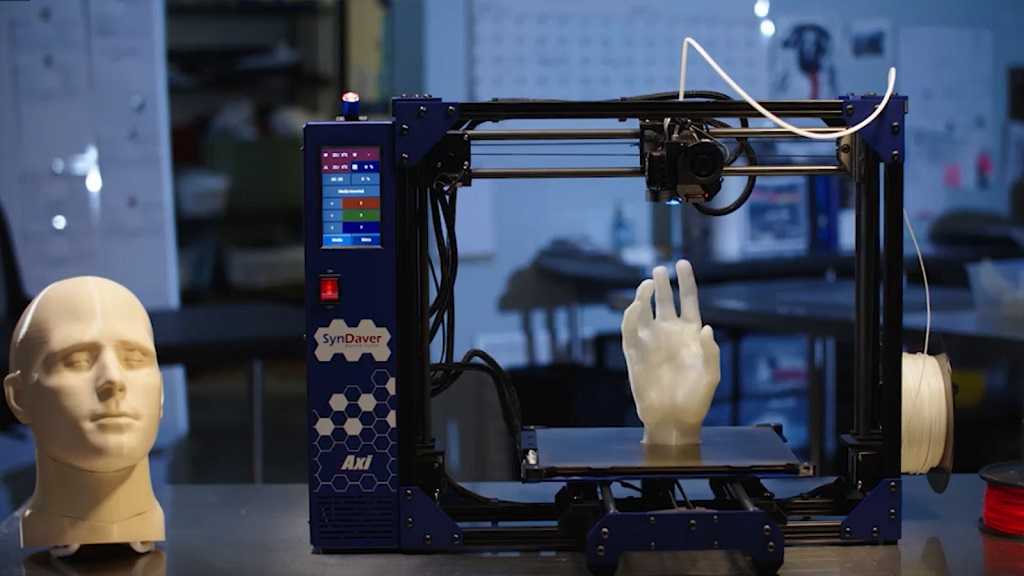 71
71
20inch Billet Steel Wheels with Spinner 2x Offsets
€4.71
Brembo RCS Lever
€20
Working Radial Engine Fidget- Planetary Gears
€2.10
Weld Pro Star
€7.07
flow conveyor tevo little monster
Free
Radial Engine, 14-Cylinders, Cutaway
€56.58
Radial Engine, 7-Cylinder, Optional Parts Kit (3) to 14-Cylinder
€23.58
Rear fanduct radial fan 50mm "SCORPIO" / Smartrapcore V1.2.4
Free
20inch Concave M1 style Wheels deep offset w Tires
€4.99
V8 engine
€1. 50
50
Jet engine
€2.50
radial section cut-off airplane engine
€1.50
Legacy Aviation Muscle Coupe Dummy Radial
Free
20inch Speedline Concave Wheels 2 styles 3 offsets w Tires
€4.71
20inch Concave Testarossa Wheels 3 offsets w Tires
€4.71
SBC Small Block Chev Drag Street 3 versions NA NOS Injected
€12.25
Robo 3d R1 blower fan mount for e3d v6
Free
Radial Blower Fan for C/D-bot
Free
Wheel Centre Lock Nut x4 styles
€3.76
20inch HEX FANs Concave Wheel w Tires
€4.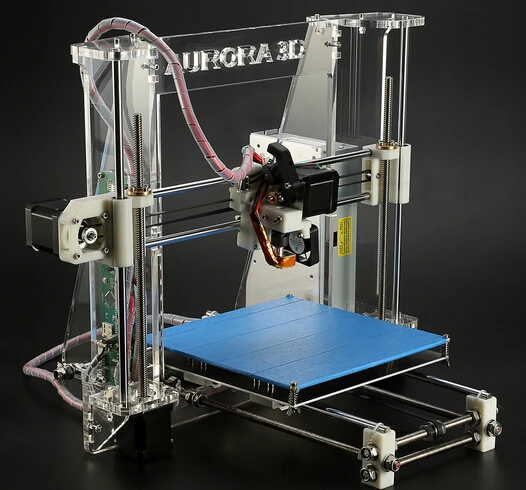 71
71
20inch CYBER FAN Concave Wheel w Tires
€4.71
20inch LIGHTNING Concave Wheels 3 offsets w Tires
€4.71
20inch Concave THUNDER Wheels w Tires
€4.71
20inch INTERLINK Concave Wheels 3 offsets w Tires
€4.71
20inch TRINITY Concave Wheels 3 offsets w Tires
€4.71
20inch HURACAN Concave Wheels 3 offsets w Tires
€4.71
Ender 5 Plus complete mount + fanduct system for E3D Volcano and more
Free
Rally Fans Wheel N Tire set 3 offsets with Centrelock Hub
€4.71
20" Low Profile Stretch Tire Tyre Directional
€3. 76
76
PRO MOD Chassis Rear Diff Brakes Suspension Combo
€5.65
Radial Engine, 'Spirit of St. Louis', 1927, First Transatlantic
€42.44
model of the best circular airflow of the nozzle
How to upgrade the blower unit of a 3D printer and maximize print quality?
One of the parameters of the 3D printer that affects the quality of the model is the cooling of the filament. Airflow is responsible for lowering the temperature of the plastic. It is proposed to increase the capabilities of the cooling unit by installing powerful fans and upgrading the air duct.
Why do I need airflow for a 3D printer?
The principle of FDM printing is to heat the plastic to a softening temperature and extrude it through a nozzle onto the worktable. Further, the polymer solidifies, the layers at the same time are connected, forming a homogeneous three-dimensional object. But the heated plastic has fluidity, and if the previous layer does not have time to cool down to the curing temperature, the model begins to lose its desired shape. The heat of the heated nozzle also has its effect: the already cooled layer softens again when the extruder moves directly above it. nine0003
But the heated plastic has fluidity, and if the previous layer does not have time to cool down to the curing temperature, the model begins to lose its desired shape. The heat of the heated nozzle also has its effect: the already cooled layer softens again when the extruder moves directly above it. nine0003
Temperature deformation is especially noticeable on miniature and thin-walled objects. This is due to the following points:
- small parts are constantly exposed to heat coming from the nozzle;
- thin model elements heat up faster.
To prevent the temperature rise of already finished layers and to cool the last of the printed ones faster, 3D printers are equipped with airflow.
What is a cooling unit? nine0023
The blower unit consists of the following components:
- fan;
- air duct.
Fan speed and start times are set in the slicer. The duct creates a directional flow, providing cooling to the desired area.
Important! Slicer airflow settings are set by default. But for each type of plastic and the shape of the 3D part, it is recommended to set special parameters, which makes it possible to maximize the quality of the model. nine0003
There are no universal values, each user of a printing device selects them empirically.
How can I improve print quality with airflow?
To set the cooling of the model as correctly as possible, consider the following:
- Type of plastic. ABS and PETG have a high melting point and require less airflow. Large objects sometimes print with the fan turned off. Parts made of PLA, especially small ones, may require 100% airflow; when printing several figures at the same time, the fan speed can be reduced to 60-70%. nine0016
- Model value. When printing large-sized objects, the plastic has time to cool down so much that when the next portion of plastic comes from the extruder, the previous layer does not heat up to the critical fluidity temperature.
 Accordingly, the formation of a part with a small surface area should occur with blowing, the intensity of which will be the higher, the smaller the size of the print area.
Accordingly, the formation of a part with a small surface area should occur with blowing, the intensity of which will be the higher, the smaller the size of the print area. - The shape of the feature. Here, the wall thickness, the presence of supports and the density of filling are taken into account. Models with small, thin, openwork elements are printed, be sure to turn on the fan. The same requirement applies to parts with less than 30% infill. The higher the percentage of filling, the less airflow is allowed. nine0016
Important! When setting the fan operation mode in the slicer, all the above conditions are taken into account. Experienced users recommend keeping statistics on settings and print results. So by trial and error, over time, the maximum quality of the final result is achieved.
It is not always possible to achieve the desired result by changing the software settings of standard equipment. The maximum effect is achieved by installing high-power fans and other designs and replacing air ducts. nine0003
nine0003
The best models of blowing nozzle for 3D printer
To modify the plastic cooling system, three blowing options are most often used:
- Direct (one-way) with an improved air duct and a more powerful fan.
- Double-sided.
- Circular.
Any of these is suitable for improving the print quality of a 3D model.
Straight
The simplest option is to replace the stock fan with a "snail" or the same, but more powerful, and leave the standard air duct. But another solution is also proposed: the installation of an improved duct. It has a reshaped spout, which allows for a more directed air flow, and a seat for a fan. nine0003
By redirecting the air jet, more precise cooling of the target area is achieved with minimal impact on nozzle temperature. And due to the installation of a productive fan, a wide adjustment of the blowing speed is provided.
Double ended
Dual outlet ducting is another way to improve your airflow system. But separating the air stream into two significantly reduces the power of each. This means that a stronger air blower is needed (the standard one will definitely not cope). Most often, seats for two fans are formed in the duct box - one for each outlet. Double-sided blowing does not have a noticeable disadvantage of one-sided blowing, when, depending on the direction of movement of the extruder, there is a different cooling intensity of the plastic. nine0003
But separating the air stream into two significantly reduces the power of each. This means that a stronger air blower is needed (the standard one will definitely not cope). Most often, seats for two fans are formed in the duct box - one for each outlet. Double-sided blowing does not have a noticeable disadvantage of one-sided blowing, when, depending on the direction of movement of the extruder, there is a different cooling intensity of the plastic. nine0003
Circular
Circular, or annular, cooling is a uniform blowing of the zone from all sides. The air flow is directed in such a way that it does not affect the nozzle. The standard fan also needs to be replaced here. Instead, they put one or two more powerful ones, for the installation of which a seat is provided on a modified duct box.
Users of 3D printers who have applied this solution note the following drawback: the circular air duct strongly blocks the view, making it difficult to control the quality of the print. nine0003
nine0003
Important! Any increase in fan power results in increased noise during fan operation. The same can be said about installing two coolers at once. Experienced users recommend paying attention to expensive models of well-known brands, whose developers have made every effort to reduce the noise of their devices.
***
Changing the airflow settings has a significant effect on the quality of 3D printing. When software settings are not enough, you should pay attention to the modernization of the cooling unit. Users offer different solutions, tested on their own experience. It remains to choose the appropriate one for the tasks assigned to the printer. nine0003
- May 17, 2021
- 7198
Get expert advice
"THE IDEA OF [PRINTING WITH POLYSTYRENE CONCRETE] APPEARED THREE YEARS AGO AND WENT TO IT 30 YEARS."
INTEREST IN CONSTRUCTION 3D PRINTING IS GROWING AROUND THE WORLD, WITH MOST DEVELOPED 3D PRINTERS WORKING WITH CEMENT AND SAND MIXTURES.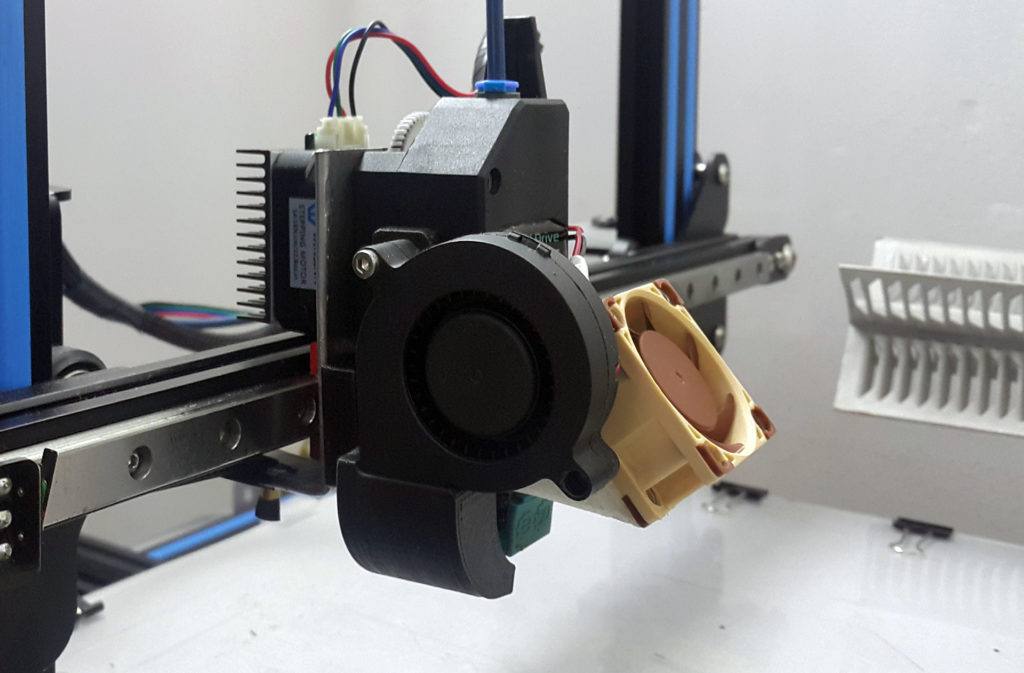 HOWEVER, THE NOVOSIBIRSK STATE UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND CONSTRUCTION (SIBSTRIN) DEVELOPED A PRINT HEAD CAPABLE OF PRINTING SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH STRUCTURAL AND HEAT-INSULATING MATERIAL - POLYSTYRENE CONCRETE. nine0003
HOWEVER, THE NOVOSIBIRSK STATE UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND CONSTRUCTION (SIBSTRIN) DEVELOPED A PRINT HEAD CAPABLE OF PRINTING SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH STRUCTURAL AND HEAT-INSULATING MATERIAL - POLYSTYRENE CONCRETE. nine0003
About the technical features of the development, the principles of its operation and the potential for application in construction, we decided to talk with the head of the Department of Technology and Organization of Construction of NGASU (Sibstrin), Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor, Vladimir Viktorovich Molodin.
3DPulse.ru: Vladimir Viktorovich, good afternoon. When did you get interested in building 3D printing? How did the idea to create your own additive technology for construction come about and how long did you work on its development? nine0003
Vladimir Molodin: I worked in the real sector of the economy for a long time - I was the director of a construction company. I noticed that in Russia labor productivity is low (about 30% of developed countries), especially in construction, where the level of mechanization is low, and robotization is generally in its infancy. With the level of technology that we have today: our destiny is to drag ourselves in the tail of the world economy.
I noticed that in Russia labor productivity is low (about 30% of developed countries), especially in construction, where the level of mechanization is low, and robotization is generally in its infancy. With the level of technology that we have today: our destiny is to drag ourselves in the tail of the world economy.
When I first saw a 3D printer, I thought - why not use this toy to print houses? Began to purposefully get acquainted with the novelty. The 3D printer itself has been developed in sufficient detail and is being successfully implemented in various sectors of the economy. For the needs of construction 3D printing, this is enough for now. Again, we are not in the lead here. nine0003
Print head issue. Today, in building 3D printing, almost all printers use cement-sand mixtures and use single-nozzle print heads in different variations for this purpose. However, the enclosing structures to be printed must have thermal insulation properties, which cement-sand mixtures cannot provide. But, heads capable of printing simultaneously with structural and heat-insulating material are practically inoperable. Therefore, building 3D printing is developing in the direction of printing with a heavy cement-sand mixture of fixed formwork, followed by filling manually formed cavities with structural reinforced concrete and thermal insulation. nine0003
But, heads capable of printing simultaneously with structural and heat-insulating material are practically inoperable. Therefore, building 3D printing is developing in the direction of printing with a heavy cement-sand mixture of fixed formwork, followed by filling manually formed cavities with structural reinforced concrete and thermal insulation. nine0003
Robotization of the process is realized only 30÷40%. The problem is solved only partially.
30 years ago, our department proposed, widely and successfully introduced a technology for manufacturing building products from one-stage polystyrene concrete.
Its essence is that in order to overcome the flotation of foamed polystyrene granules when mixed with a cement-sand mortar, non-foamed beaded polystyrene granules were introduced into the composition of the cement-sand mixture during its manufacture and due to a fairly close density, distributed evenly over it. In the mold, the mixture was forced to heat up, and the polystyrene granules foamed directly in the cement-sand mass. Due to the high heat treatment temperature, the products quickly set and hardened. nine0003
In the mold, the mixture was forced to heat up, and the polystyrene granules foamed directly in the cement-sand mass. Due to the high heat treatment temperature, the products quickly set and hardened. nine0003
Thinking about the improvement of 3D construction printing, the idea arose to use this forgotten technology here. Only now there is no form. The mixture with non-foamed polystyrene granules is fed directly onto the previously molded layer of the printed wall, between two moving electrodes, to which an electric current is applied.
Passing current through itself, the mixture heats up and reaches a temperature of 80÷90°C beaded polystyrene granules foam. At these temperatures, the mixture quickly loses its mobility and after a few minutes a new layer can be laid on the molded layer without fear of the lower one spreading.
So, the idea appeared three years ago, and it took 30 years to get there.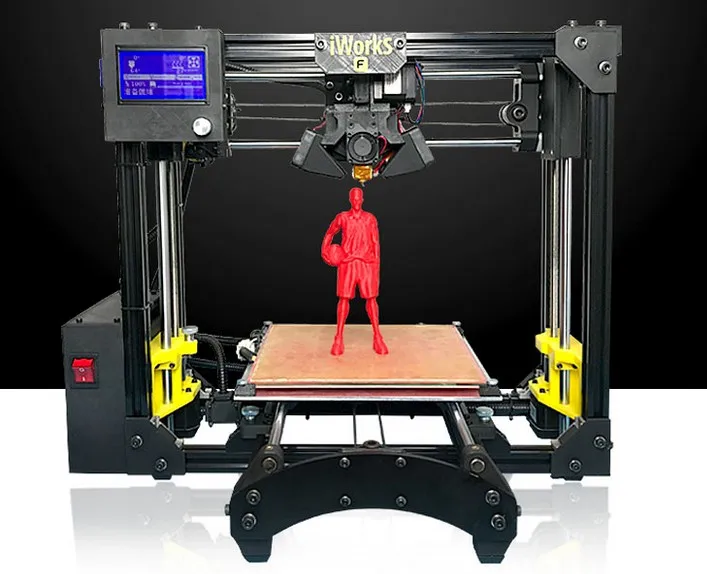
Vladimir Molodin: The print head proposed by us at the output provides a layer of heat-insulating structural material 70 mm thick and 150÷500 mm wide with easily adjustable strength and thermal conductivity. The mixture is supplied by a peristaltic pump. She successfully passed the test.
What characteristics should it have?
Vladimir Molodin: As already mentioned, the composition of the mixture: cement, sand, beaded polystyrene granules, water and standard additives. An increase in the content of polystyrene leads to an increase in the resistance to heat transfer of the wall and a decrease in strength characteristics. And vice versa. High heat treatment temperatures drastically reduce the time until the material loses its mobility and gains strength. Including at low positive temperatures, without the installation of a greenhouse. nine0003
3DPulse. ru: What objects have you already printed, have you tested them, what did they show?
ru: What objects have you already printed, have you tested them, what did they show?
Vladimir Molodin: So far, only fragments of enclosing structures that have been comprehensively studied in terms of basic parameters.
3DPulse.ru: Have you measured the characteristics of the printed samples in terms of strength, resistance to heat transfer, their water absorption, etc.? nine0003
Vladimir Molodin: Absolutely. We started doing this as soon as the first samples were molded. There is no point in developing technology if you are not sure of the quality of its results. The strength, frost resistance, water absorption, thermal conductivity and uniformity of distribution of polystyrene over the mass of the material were studied.
How environmentally friendly is this material? Can it be recycled and reused? nine0003 Vladimir Molodin: The resulting material is environmentally friendly in the operation of buildings built with its use. 3DPulse.ru: In a recent interview with Novosibirsk News, you said that the laboratory sample of the printer is now disassembled and will be assembled in the fall. What improvements will be added to the updated model? Tell us about your plans for using the plant. nine0003 Vladimir Molodin: I must say that the pandemic has made serious adjustments to our work. The university was closed for almost the entire last year, and experimental work, alas, cannot be performed remotely. Now my assistants Ivan Gasenko, Pavel Timin, Oleg Platoshechkin and Nikita Kalashnikov are hastily working on launching the upgraded printer. We hope that everything will work out, and from September we will start working on it in a new 3D printing laboratory. The main task is to work out the heat treatment modes to enter the real production. Let's talk about 3D construction printing in general. How promising do you think this construction method is? What are its advantages over traditional technologies? Vladimir Molodin: It has already been said that the growth of GDP, so necessary for Russia for its sustainable development, is largely ensured by the growth of labor productivity, which, according to various estimates, does not exceed 30–40% of labor productivity in America today. The total digitalization of all spheres of our life inevitably raises, in connection with the need for productivity growth, the issue of deep and intensive automation and robotization of production processes. 3D printing is the most realistic technology that can solve this problem today. The search here goes in different directions. The proposed technology has a number of advantages over existing ones. nine0003 First, there is no need to form the formwork first and then manually fill it. Secondly, a cement-sand mortar with non-foamed polystyrene granules is used as a printing material, which, due to forced electrical heating of the mixture, foam directly in the working head, leaving a uniformly insulated layer of polystyrene concrete at the exit. nine0003 Thirdly, at the outlet, the polystyrene concrete layer has a temperature of 80÷90°C, and while still between the electrodes, it loses its mobility. With a new pass of the printer, he is not threatened by the spreading under pressure of the layers laid above. Fourthly, by dosing the amount of polystyrene into the initial mixture, it is possible to give the finished product greater strength or better thermal performance. Fifthly, due to the filling of the finished product with heat-insulating granules, its specific heat capacity increases and, consequently, the duration of cooling and acquiring strength. I am sure that the best solution will be found in the coming years. Maybe it will be our technology. We will see! 3DPulse.ru: Vladimir Viktorovich, what, in your opinion, is currently limiting the promotion and development of 3D construction printing? Vladimir Molodin: The development of a new technology is quite costly and apart from the confidence of the authors, there is no guarantee that it will "shoot". Interested companies and corporations do not want to invest in a risky business. They need a finished product that will give competitive advantages tomorrow and start making a profit. So, for now, only the university and the fund for supporting young scientists partially support the purchase of components and provide a free roof over their heads with their meager funds. 3DPulse.ru: Will your method be successful in the near future (a year or two) or is it not worth waiting for mass application of construction printers? Vladimir Molodin: If we succeed in everything we expect, with the funding we have today, and we don’t have to wait another year for the pandemic at home, just a year or two. If there is financial support and there is no need to reinvent the wheel, but it will be possible to invite the necessary specialists and purchase the necessary materials and components, things can move much faster. nine0003 3DPulse.ru: In what industries does 3D printing have the best prospects - in individual housing construction, in industrial construction? Vladimir Molodin: Of course, the first stage will be the construction of one-two-story family houses, the need for which is huge. 3DPulse.ru: We, as an information resource, often receive inquiries about where to buy a printer for 3D printing houses. Do you plan to commercialize your plant or blends in the future? nine0003 Vladimir Molodin: Absolutely. The technology and equipment are patented (RF patent 2 739 244 "Device and method for the manufacture of heat-insulating walls from polystyrene concrete using a 3D printer"). At the same time, the tasks of the third generation university are: the transfer of knowledge, the extraction of new knowledge and the commercialization of knowledge. 3DPulse.ru: A few years ago in our country, several well-known projects for the construction of houses using construction 3D printing ApisKor, Spetsavia were carried out. How do you rate them for your time? Why do you think they were not followed by a boom in this technology? nine0003 Vladimir Molodin: These were, without exaggeration, breakthrough solutions with a vision of fantastic commercialization. "Spetsavia" started serial production of large 3D printers for construction. Nikita Chen-yun-tai, of course, a talented engineer and entrepreneur, managed to "unwind" his radial printer. But they did not solve the problem - they printed the same fixed formwork and further - according to the text. Therefore, the explosive introduction did not work. I hope we can resolve this issue. nine0003 Do you plan to implement such a project and would you live in such a house yourself or would you prefer more traditional materials? Vladimir Molodin: So far, we are solving the problem of building strong and heat-efficient walls 100% robotically. These will be full-fledged walls in terms of comprehensive reliability for the inhabitants. nine0003 As far as I know, there are no floor printing solutions in our understanding of flat slabs yet.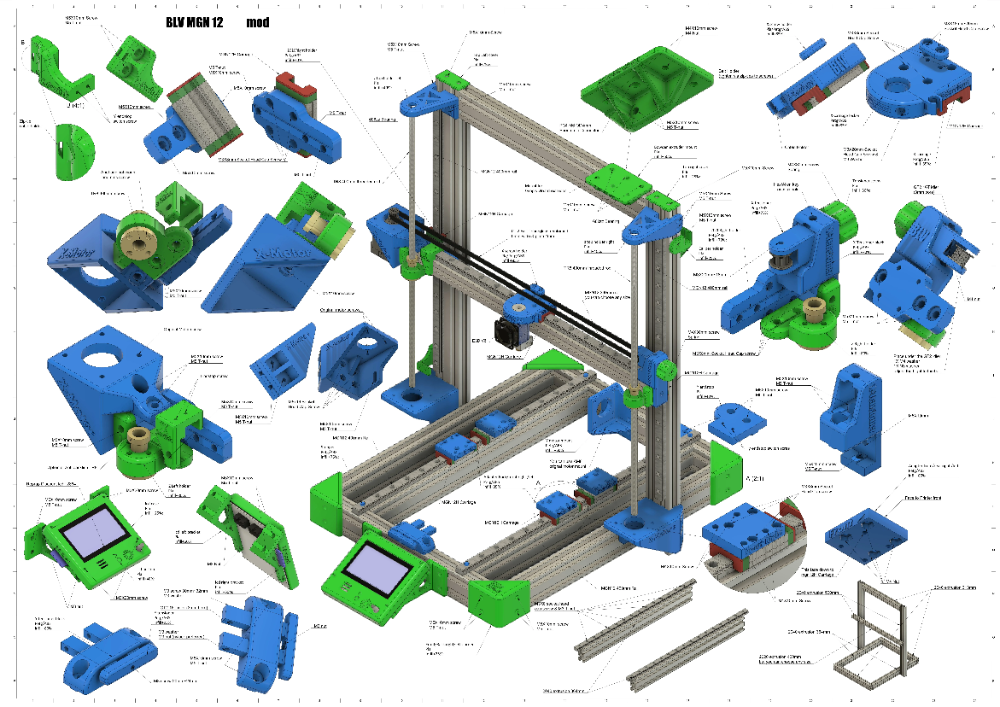 Recycling of the material is quite real, as it is a conventional cement-based artificial conglomerate.
Recycling of the material is quite real, as it is a conventional cement-based artificial conglomerate.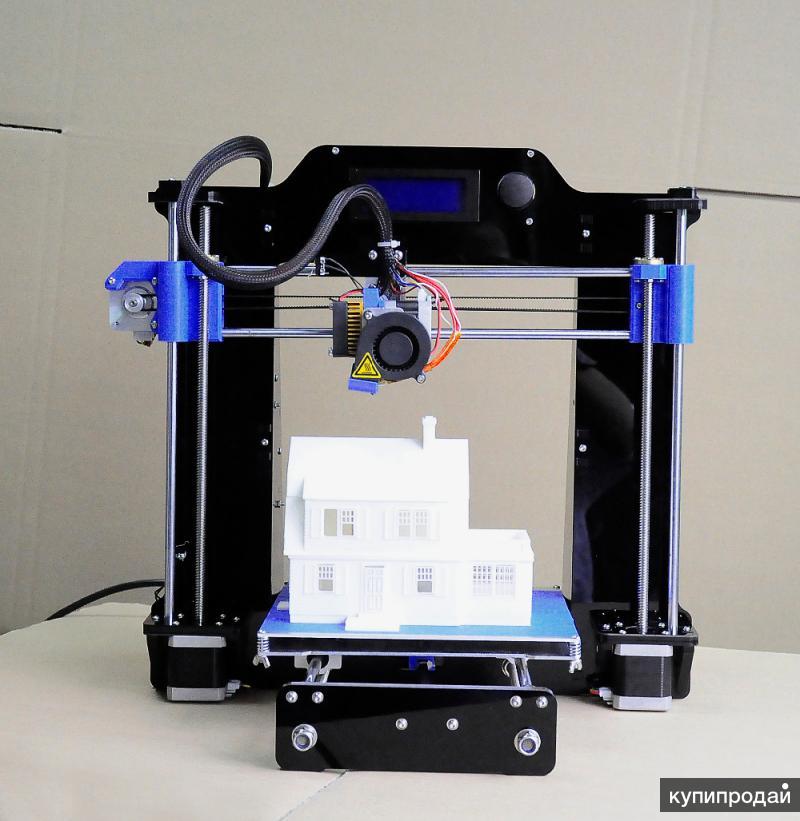  nine0003
nine0003 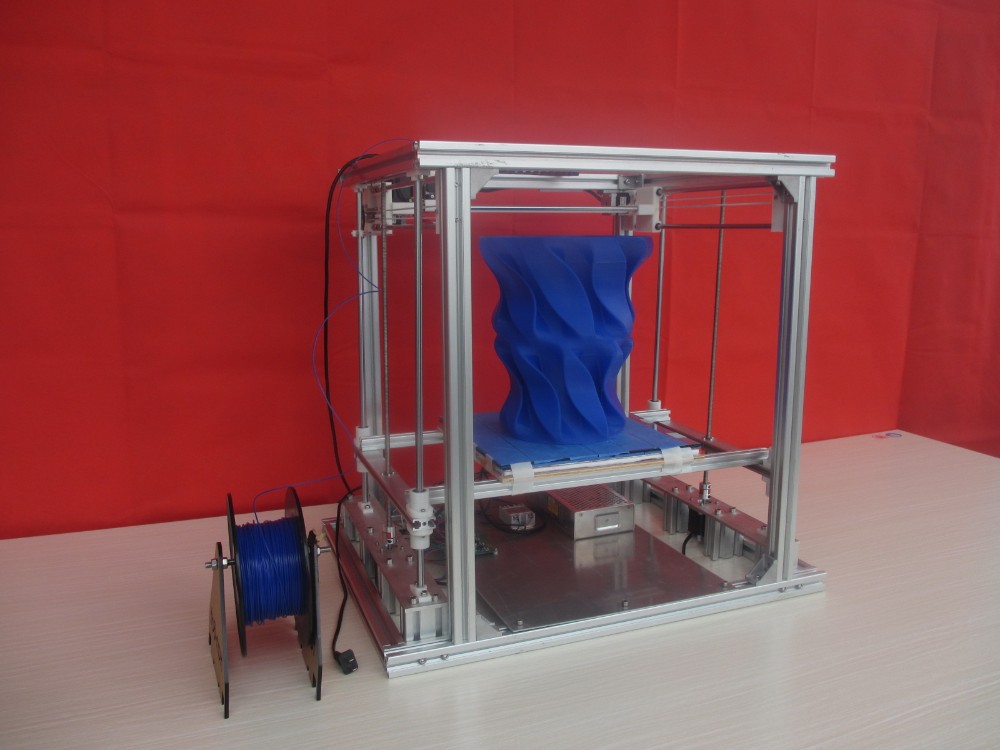 The printing material is laid immediately on the entire width of the wall. The process of building a building envelope is 100% robotic.
The printing material is laid immediately on the entire width of the wall. The process of building a building envelope is 100% robotic.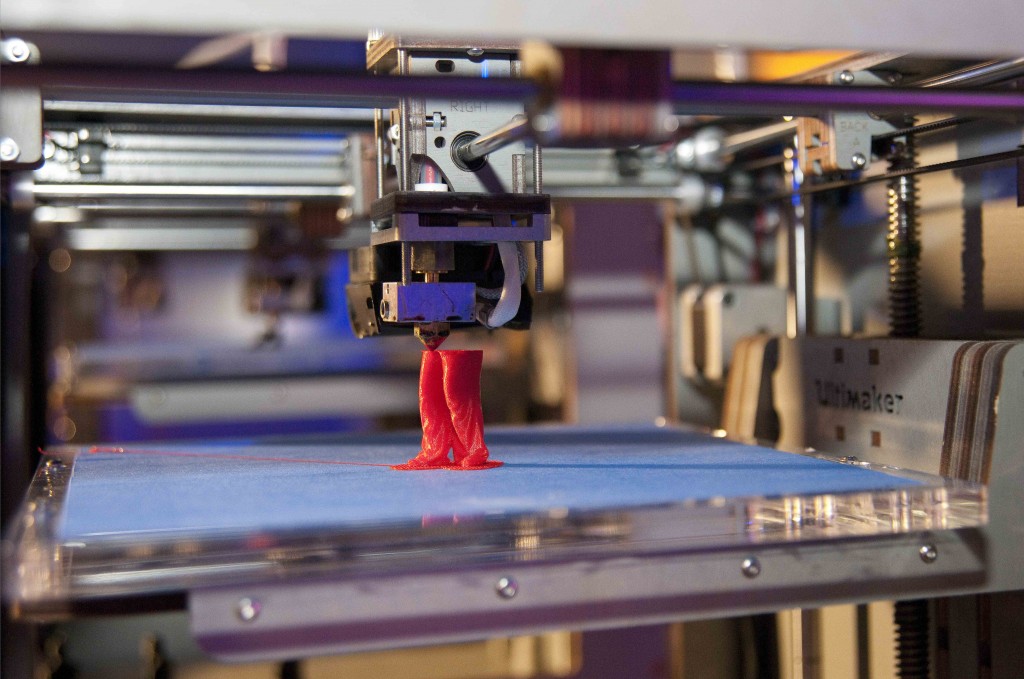  This means that in areas with a temperate cold climate, it is possible to do without an expensive greenhouse all year round, without which construction 3D printers do not work in the northern latitudes. nine0003
This means that in areas with a temperate cold climate, it is possible to do without an expensive greenhouse all year round, without which construction 3D printers do not work in the northern latitudes. nine0003  The rest is from my own pocket and from a junkyard ...
The rest is from my own pocket and from a junkyard ...  And then it will be "tied" wherever it is appropriate.
And then it will be "tied" wherever it is appropriate.  However, they solved private issues and did not solve the issue of 100% robotization.
However, they solved private issues and did not solve the issue of 100% robotization. 
Learn more