Pvc filament 3d printer
Fillamentum PVC Vinyl 3D Printing Filament
Fillamentum PVC Vinyl Filament
Fillamentum
Fillamentum ASA Series
A rugged weather-resistant material that is much more resistant to UV light.
Fillamentum ExtraFill Series
An excellent baseline PLA that prints amazingly well.
Fillamentum FlexFill Series
Flexfill is rubbery and elastic, making it impact, oil and abrasion-resistant.
Fillamentum Crystal Clear Series
An incredible line of semi-transparent, colored materials.
Fillamentum TimberFill Series
Made from a PLA base with wood particulate, Timberfill gives you 3D prints that look like they were carved from wood.
Fillamentum Vertigo Series
Vertigo PLA series reflect light and create awesome, eye-catching prints with flecks of gold, silver and blue.
Fillamentum Extrafill ABS Filament
Premium ABS Filament with a wide variety of vibrant colors.
Fillamentum PVC Vinyl Filament
Fillamentum PVC Vinyl Filament
Guides & Articles
How to Succeed with Quantum Dichromatic PLA Filament
Follow this guide for tips and tricks on how to get the best results when 3D printing with Quantum Dichromatic PLA filament.
How To Succeed with LayerLock SLA Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for Laser, DLP, and SLA resin prints using LayerLock SLA Resin 3D Printing Build Surfaces.
How To Build A Successful Makerspace
Find out the necessary components to create an effective space for your maker community.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing with Polypropylene
Successfully produce 3D printed parts out of polypropylene filament with these tips on achieving stronger bed adhesion and minimizing shrinkage.
Tech Breakdown and How to Succeed: Ionic Hybrid Support Material
Supporting engineering-grade filament has been difficult without a support material dedicated to higher temperature 3D printing. Ionic aims to solve that.
Ionic aims to solve that.
How To Succeed with OBC 3D Printing Filament
From Dow Chemical, OBC combines flexible and rigid into one unique material with properties of both.
How To Succeed with LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for NylonX, NylonG, and standard filaments using LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces.
How to Succeed with LayerLock Powder Coated PEI Build Plates
Powder coated PEI steel sheets are a great alternative build surface for strong bed adhesion. Here's how you can succeed using this durable build plate.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With Nylon
Learn how to 3D print Nylon like a pro. Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With ASA Filament
Follow this step-by-step guide to learn how to print with ASA, the perfect material for any outdoor projects.
How to Succeed when 3D Printing with Polycarbonate Filament
Follow these helpful steps to start successfully printing with this extremely tough, professional grade material.
How to Succeed with NylonX
NylonX has quickly become one of our favorite filaments for strong, durable, and ready-to-use parts. Here's an in-depth look at Nylon X, and some printing tips to get the most out of this great new material.
Fillamentum Black Vinyl 303 PVC Filament - 1.75mm (0.75kg)
- Home
- Store
- 3D Printer Filament
- Fillamentum
- Fillamentum PVC Vinyl Filament
This PVC (Polyvinylchloride) filament provides chemical and flame resistance along with high impact resistance and great hardness and mechanical properties. Ideal for producing engineering products like industrial piping or fluid containers.
Note: Printing with PVC can release small amounts of chlorine gas and should be done in a well-ventilated environment and with care.
Remove from wishlist Add to wishlist loading...
Tagged: 0.75kg Filament Spools, 1.75mm Filament and Fillamentum
Product No. loading...
Notify me when this item becomes available Success You will be notified when ... becomes available.Safety Note: Printing with PVC can release chlorine gas and should be done in a well-ventilated environment and with care. We recommend printing with a BOFA PrintPro 2 Fume Extractor. Make sure to review the PVC Safety Recommendations from Fillamentum.
Chemical ResistancePVC is a favorite production material around the world thanks to its chemical resistance, making this filament great for parts that will be in contact with oils or salts. Vinyl 303 also has a flame retardant feature that means it may be the right choice in environments where open flames are a possibility. These chemical resistances are further enhanced by the mechanical properties of this material, with low moisture absorption, high impact strength, and also exceptional rigidity in load bearing applications. If your next project calls for flame and/or chemical resistance, Fillamentum Vinyl 303 might be the ideal material for you.
These chemical resistances are further enhanced by the mechanical properties of this material, with low moisture absorption, high impact strength, and also exceptional rigidity in load bearing applications. If your next project calls for flame and/or chemical resistance, Fillamentum Vinyl 303 might be the ideal material for you.
Fillamentum is a trusted producer of high quality, beautiful materials 3D printing filaments. From their diverse Vertigo series to the ever-expanding Flexfill line, there is likely a Fillamentum product that suits your needs. The newest addition to their catalog are these industrial-focused materials to bring a new, exciting element to their lineup. These materials are intended for use in demanding situations where other materials would not succeed, but there are safety considerations when using this material. Be sure to review and follow the safety considerations provided by the manufacturer.
Technical Specifications- Filament Diameter: 1.
 75mm or 2.85mm ± 0.05mm
75mm or 2.85mm ± 0.05mm - Filament Weight: 750g
- Safety Warning: This material has specific safety considerations, and it's important to review and follow the safety recommendations provided by the manufacturer.
- Download Safety Data Sheet
- Download Technical Data Sheet
- Nozzle Temp: 215 - 230°C
- Bed Temp: 80°C
- Nozzle Compatibility: This material can only be printed with a brass nozzle, because the Chlorine content will corrode steel used for hardened nozzles. This material is not abrasive.
- Print in a well-ventilated area, preferably using a fume extractor.
What you need to know about 3D printing
China's dominance of the world's manufacturing industries dates back to the late 1980s when Western companies found that any import or shipping costs were offset by startlingly lower labor costs and government regulations, but it wasn't until the turn of the century that they really came into their own. . For decades, China has dominated industries as diverse as textiles, personal electronics, toys, iron and metal manufacturing, and even aircraft and automobiles. They finally displaced the United States from the lead in manufacturing a few years ago and have continued to be at the top ever since.
. For decades, China has dominated industries as diverse as textiles, personal electronics, toys, iron and metal manufacturing, and even aircraft and automobiles. They finally displaced the United States from the lead in manufacturing a few years ago and have continued to be at the top ever since.
While Asia as a whole has been slow to embrace 3D printing technology, it didn't take long for China to catch up as it is the world's top seller of 3D printers this year. Since 2011, the Chinese 3D printing market has doubled every year and is expected to reach $1.5 billion in 2016. Their growth rate is outpacing the rest of the world and is likely to surpass the United States as the world's largest 3D printing market by 2018 if this growth continues. A 3D printer can produce one part at a time with an accuracy of 0.1mm or less. Desktop printers are already available on the market and allow you to produce small products in almost any shape. The Chinese 3D market is developing at a breakneck pace, which means that the production of PVC toys is also being created faster, more beautiful, better quality, and the price is able to satisfy any customer.
In this article, we want to highlight for you in detail what 3D toy printing is, what are its main advantages and types, and how to use them.
The 3D Printer is a manufacturing tool used to create 3D objects (artifacts) and in our case computer generated toys. 3D printers come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and types, but at their core, they are all computer-controlled additive manufacturing machines. Just as paper printers apply ink in a single layer to create an image, 3D printers apply material layer by layer to create a 3D object.
Key benefits
3D printers can produce custom parts relatively quickly and cheaply, making 3D printers one of the best tools for rapid prototyping.
3D printing allows designers of toy manufacturers to immediately move from idea to reality, with the help of 3D printing they can quickly change designs and can easily create complex geometric shapes of a toy. In short, at the push of a button, manufacturers can create whatever the customer likes.
In short, at the push of a button, manufacturers can create whatever the customer likes.
With a 3D printer, a part can be designed and manufactured at low cost, and then the design can be modified, printed, and tested multiple times in rapid succession before the part goes into mass production.
Just by pressing a button, whatever you create will be created. Other production methods such as drilling machine, lathe or milling machine should take longer, and the shapes may be slightly different from your desires. Because of the way the parts are created, 3D printers can produce many complex geometries, including natural shapes such as prosthetic limbs or animal models, or more complex shapes such as polyhedra or replicas of scale buildings. 3D printers open up a lot of opportunities for manufacturers simply because they allow people to create things they couldn't before.
A 3D design can be easily modified on a computer and then reprinted. This means that files can be customized for specific people or things and easily printed without changing device settings. The ability to create personalized content is appreciated by both small businesses and large manufacturers as it allows them to create designs. The design can be printed and modified according to the needs of the recipient.
The ability to create personalized content is appreciated by both small businesses and large manufacturers as it allows them to create designs. The design can be printed and modified according to the needs of the recipient.
How to work with a 3D printer?
To more specifically understand how 3D printers work and how to design them, you need to understand the different types of 3D printers on the market. Although materials and methods for creating parts vary greatly, all 3D printers create parts by adding material layer by layer, fusing each layer together to create a solid object.
There are several different types of 3D printing processes: some are more suitable for large scale production, others allow multiple materials or colors to be used during printing, and some types of printers can even be built fairly easily due to the way they work.
1 Type: Fused Deposition Modeling ( FDM ).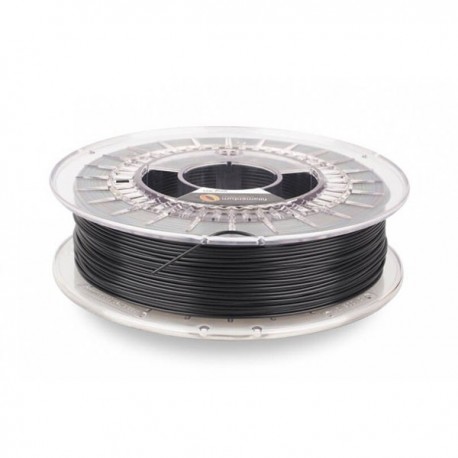 Probably one of the most common types of 3D printing and the easiest to understand. In this type of 3D printing, a material, usually ABS or PLA plastic, is melted by the printer head and extruded onto the base of the printer, similar to how ink is applied to a page on a paper printer. The printer's extruder head lays down material layer by layer to build a 3D model, and each layer fuses with the previous one as it cools.
Probably one of the most common types of 3D printing and the easiest to understand. In this type of 3D printing, a material, usually ABS or PLA plastic, is melted by the printer head and extruded onto the base of the printer, similar to how ink is applied to a page on a paper printer. The printer's extruder head lays down material layer by layer to build a 3D model, and each layer fuses with the previous one as it cools.
FDM printers are very common desktop printers because they are inexpensive and easy to build. Their accuracy depends on the quality of the motors that control the position of the extruder head relative to the assembly platform, as well as the thinness of the extruder head when extruding the material. As the material is built up layer by layer, the printed parts tend to be weak along their horizontal cross sections. In addition, any protrusions of 3D printed parts on FDM printers require a support material to hold the protrusion. Multi-head FDM printers can print on soluble media that dissolves when immersed in certain chemicals, while single-extruder printers print on less dense material that can break off after printing is complete. Multiple extruder heads also allow FDM printers to print in different colors or materials, expanding their capabilities.
Multiple extruder heads also allow FDM printers to print in different colors or materials, expanding their capabilities.
Type 2: Stereolithography( SLA ) is the oldest 3D printing method that uses a laser to cure a liquid resin with UV light. While FDM printers draw out layers of filament to form a 3D model, an SLA printer's laser beam draws out a section of the part to solidify liquid resin layer by layer, creating a 3D part. While most other 3D printers print from the bottom of the part and work their way up, SLA printers can print from top to bottom. The laser and resin bath is at the base of the printer, and the part is attached to the lower build platform and rises up as it prints.
SLA printers can be very fast and accurate due to their nature. However, the resin itself is expensive, and because it is photocurable, it must be stored in special containers. Most resins are usually very brittle after curing and won't withstand much force, so SLA printing is usually useful when it comes to prototyping but not manufacturing. Like FDM printers, SLA printers require support structures for printed parts, but their materials are limited because they can only print on cured resin and cannot print on multiple media types at once. However, the accuracy of SLA printers allows them to print very complex and fine structures.
Like FDM printers, SLA printers require support structures for printed parts, but their materials are limited because they can only print on cured resin and cannot print on multiple media types at once. However, the accuracy of SLA printers allows them to print very complex and fine structures.
Type 3: Selective ( SLS ) Laser sintering is very similar to stereolithography in that a laser is used to solidify the material and form a solid shape. The biggest difference between the two technologies is that SLA printing uses liquid resin, while laser sintering cures the powder material. Layers of powder are laid down on a print bed and the particles of each layer are laser cured. Selective laser sintering has the advantage that it can work on a wide range of materials, including plastics, glass, and some metals.
No support material is required to print parts on an SLS machine because the parts are under tension so they can be used to create more complex and precise parts than most other printers.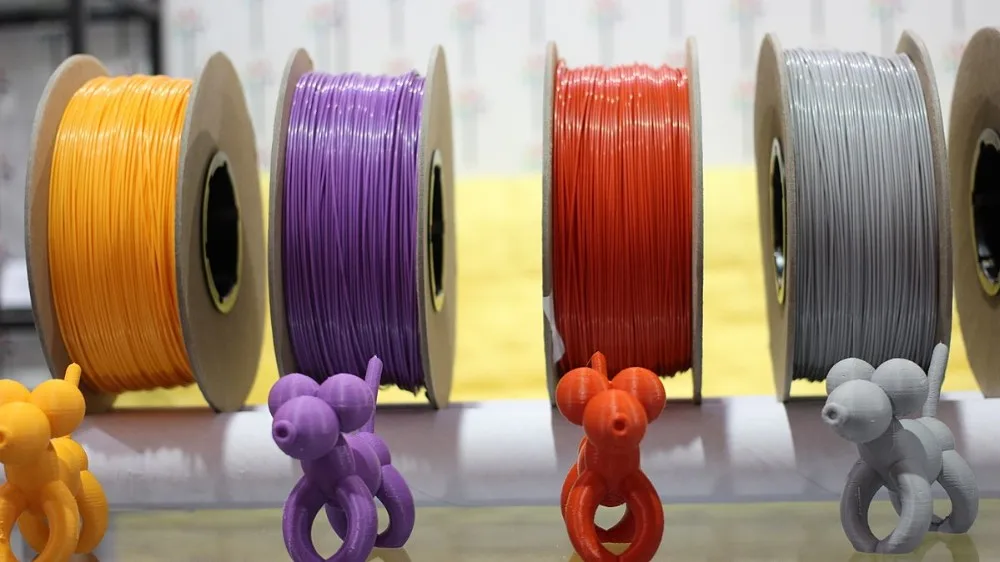 However, they are usually only found in industry, as they require high power lasers and can be very expensive.
However, they are usually only found in industry, as they require high power lasers and can be very expensive.
3 D -Design
3D printers allow designers to jump straight from conceptual ideas and designs to physical models. To do this, the toy must be designed on a computer using some kind of 3D design software. Once a part is designed, it can be imported into the software specific to the 3D printer being used, which will cut the part and send the printer a list of the paths and directions used to create the part.
You may be interested in our other articles
- Plastic Toys: Manufacturing Process in China
- Equipment for the production of plastic products
- Drawing a logo on goods from China
- Is it worth creating your own trend?
- Ordering souvenirs from China
- Attractions Ningbo
- Sewing equipment from China
3D printers can radically change the window market
One of the brightest innovative expositions at Interplastica 2017 was 3D printing technology. The WINDOWS MEDIA portal tells about the features of an innovation that can radically change the entire structure and technology for the production of plastic windows.
The WINDOWS MEDIA portal tells about the features of an innovation that can radically change the entire structure and technology for the production of plastic windows.
photo: 3D printing will make it possible to produce plastic windows almost at home
3D printing: the new world of the new century
photo: Fused Filament 3D printer
The 3D printing method is able to amaze the imagination of the most sophisticated customer in technology. Within half an hour, the computer is able to process the digital model created according to the wishes of the client, send it for printing to a special 3D printer with one press of the Start button, and start manufacturing the order by layer-by-layer deposition of a plastic thread according to the algorithm prescribed by the program. What seemed like science fiction for several years and still looks like a description of the reality of the distant future, in fact, is already happening in the present. Today's world of 3D printing is familiar with a list of more than ten technologies for digital 3D reproduction, produced from a given model using a wide variety of materials.
Today's world of 3D printing is familiar with a list of more than ten technologies for digital 3D reproduction, produced from a given model using a wide variety of materials.
3D reproduction: limitless possibilities
photo: spools of multi-colored plastic filament for 3D printing
In addition to spools of multi-colored plastic filaments, 3D printers work with metals, plaster, photopolymer resins, thermoplastics, rubber, sand and wax, actively using ultraviolet and laser radiation, LED projections and lamination in the manufacture of finished products.
photo: an example of high-precision prototyping on a 3D printer using MJM 9 technology0098
At the same time, the dimensions of the finished "printed" objects range from high-precision millimeter to large-scale meters, and their number can be both single and serial.
3D printer: from uniqueness to popularity
Most 3D technologies appeared in the US, Europe or Israel in the 80s and 90s of the 20th century.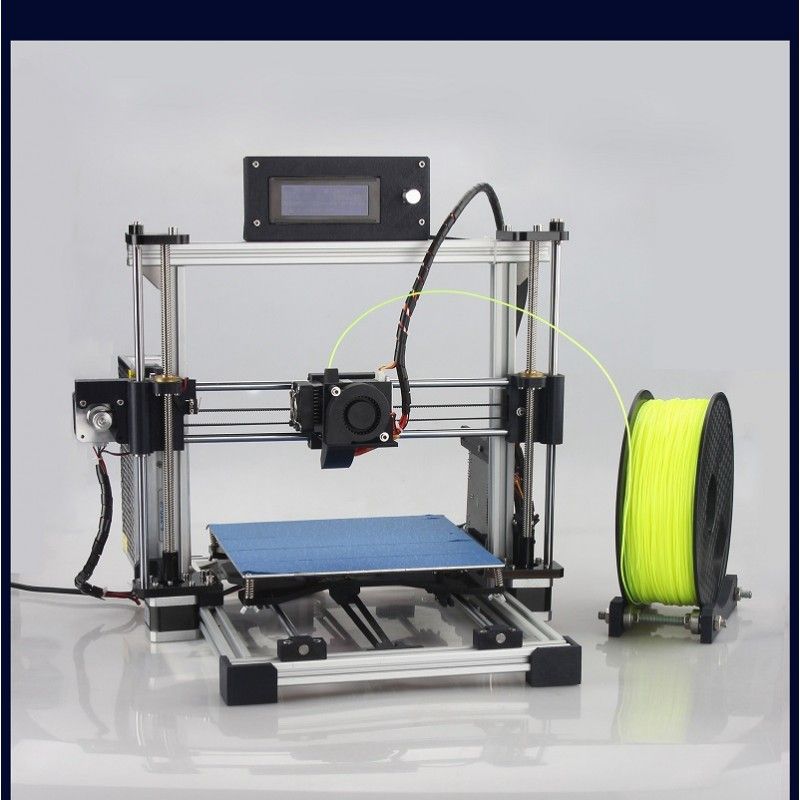 Despite almost thirty years of history, the speed of distribution and breadth of use of this innovation is only gaining momentum. Until now, such low rates of innovation have been associated primarily with the high cost of the equipment required for 3D production and its maintenance. However, in recent years, the technology has become more accessible and popular for a wide range of users.
Despite almost thirty years of history, the speed of distribution and breadth of use of this innovation is only gaining momentum. Until now, such low rates of innovation have been associated primarily with the high cost of the equipment required for 3D production and its maintenance. However, in recent years, the technology has become more accessible and popular for a wide range of users.
photo: testing a prototyping device, working with metal
The opportunities that it provides in terms of speed, high precision and uniqueness of the manufactured products are complemented by a clear reduction in labor costs and energy costs, which increases the profitability of 3D printing in the eyes of manufacturers, and it makes it more and more attractive and promising.
Plastic filaments in 3D space
photo: One of the most advanced 3D printers for printing with MJM technology
Of the full range of 3D printing possibilities, the technology of layer-by-layer deposition of a plastic thread FDM (sometimes you can also find its other name - FFF) and the MJM multi-jet modeling technology, which works with thermoplastics and photopolymer resins, and allows you to create unique high-precision objects, are directly related to the window market with micro detail.
photo: latest multicolor FDM printer
FDM printers use polyetherimide, polycarbonate, ABS, polyphenylsulfone as materials. Therefore, sometimes among 3D printing services you can find the name ABS printing. In cases where such abbreviations are used, spools with rods or threads of plastic of different colors are used as raw materials for the manufacture of products.
Different types of reproduction by fusing threads in layers according to a digital model are also called additive. The concept of a layer has entered the production lexicon due to the fact that the printing of a 3D object begins with the processing of a digital computer model: it is divided into layers that are oriented in a certain way in the printing program.
photo : 3D printer, PolyJet printing technology
The program provides for the presence of hanging elements in the object, which may require temporary supports. They are easily removed after the completion of the object manufacturing process. The program also provides for the use of different colors of the same material (plastic) in the production of one unit of production.
The program also provides for the use of different colors of the same material (plastic) in the production of one unit of production.
photo: FDM printer extruder
Fusing is the process of extruding particles of molten plastic filament from the extruder onto a support. The product is formed in layers, from the bottom up.
photo: 3D printed statuettes of the Golden Window Award
An example of objects created in such a printer are the shimmering statuettes of the Golden Window 2016 Award, which can be seen and even picked up on March 29, 2017.
3D printing could revolutionize the window market
The spread of 3D printing could fundamentally change many markets, and the window market in particular. Prototyping technology is still relatively new and imperfect, however, given the speed of technology development in the world as a whole, it can be assumed that in about a quarter of a century, 3D printing may move from the production of piece models to mass production. In the segment of the production of PVC window profiles and plastic windows, including, and then the industry will face big changes.
In the segment of the production of PVC window profiles and plastic windows, including, and then the industry will face big changes.
The production of window profiles and, in part, windows can move into the realm of 3D execution. The benefits of such a prospect are obvious: it will make it possible to exclude from the window production cycle the stage of window profile extrusion, the manufacture of a sealant and its pulling; eliminates some of the main, familiar stages of window production: cutting window frames, reinforcing, welding. On a 3D printer, it will be possible to print finished window frames (already cut, with a sealant, reinforced and welded), to the size of the customer and in the shortest possible time.
photo: it is possible that windows will soon be printed on printers
3D printing technology does not require the manufacture of expensive extrusion tools, only an electronic 3D model is needed. This results in significant savings compared to conventional extrusion.
Thus, 3D printing technology, if properly developed, can radically change the entire process of plastic window production. Instead of a complex multi-stage process, window production can become a simple technological process.
What is needed for progress
photo: this is how windows are produced now
For the forecast to come true, there must be changes in the recipe of the window profile, which at the moment cannot do without reinforcement. The ability to print a ready-to-use frame resistant to static loads would enable a new technological breakthrough in the window industry. If the market got rid of it, it would move to the innovative chain “window manufacturer – buyer”. The new technology is the exact opposite of the classic window manufacturing process. Also, window sills would be printed directly in the company.
photo: colored windows - first in line for printing
The role of the window company in production would become predominant, and its client would have the opportunity to unlimited individual choice of window frame - any size and color available in the software that could be produced the window company itself almost in the presence of the buyer.
Extrusion tool manufacturers would be replaced by 3D printer software providers, which would provide the windowmaker with an important database of profile printing systems.
Such reflections may seem fantastic only at first glance, a closer acquaintance with 3D technology and the current situation in the window market, allow us to talk about the forecast for the widespread use of 3D printing as a very realistic prospect for the development of the window market in the next 20- 25 years.
While 3D printing continues to be a rather expensive manufacturing technology, its scope of use extends mainly to the production of piece, experimental prototypes for testing complex, micro-detailed mass-produced products. However, observing the pace of development and introduction of the most complex technologies into mass production only over the past ten years, using the example of mobile devices, wireless Internet networks, LED technologies, the so-called. generation 4.0 machines and many other high-tech innovations, we can say with great confidence that the 3D printing method will move from the category of elite and narrow-profile to the area of widespread use in a quarter of a century or even less.