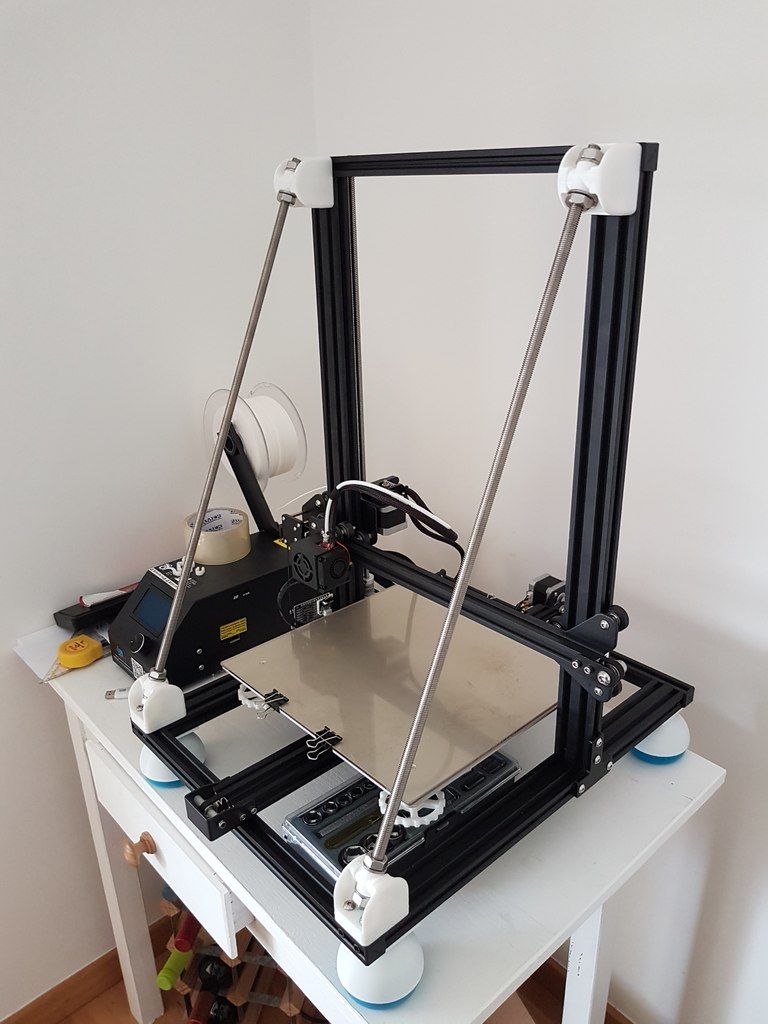
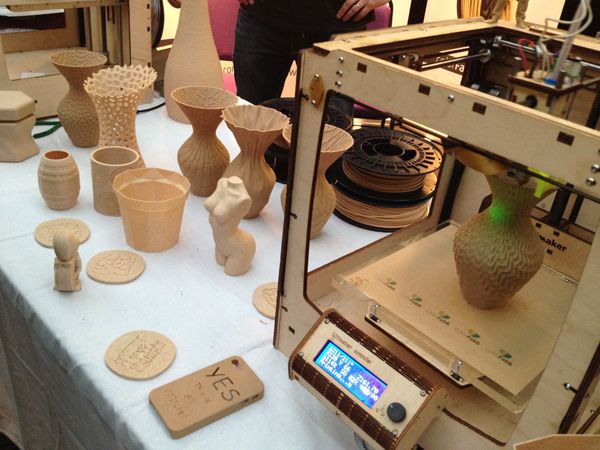
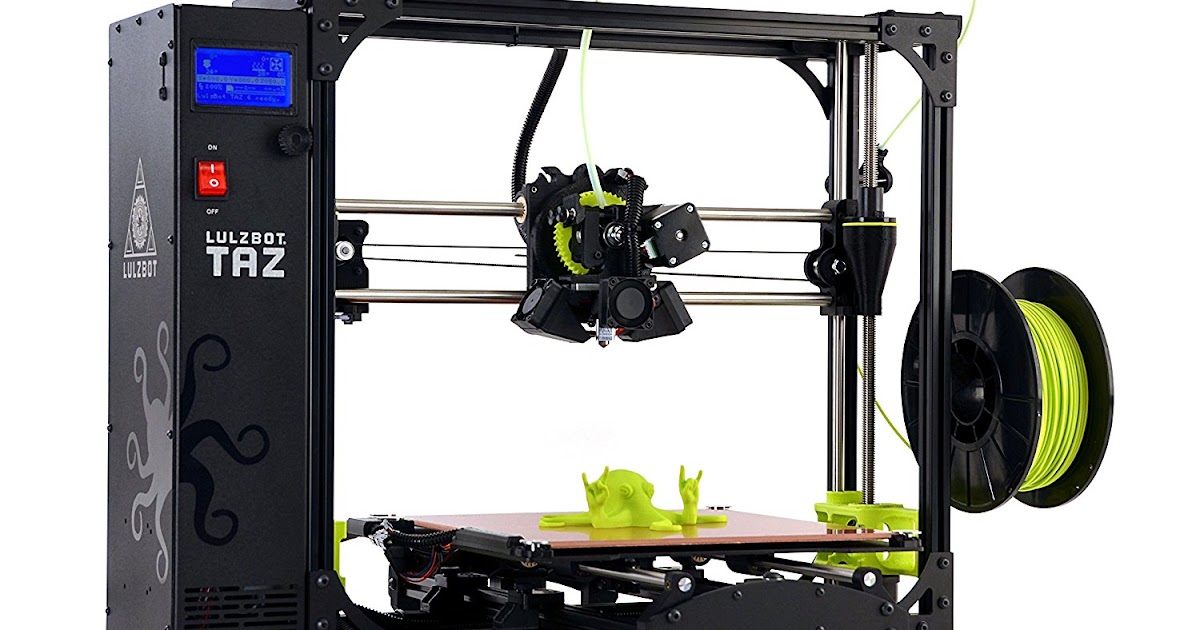
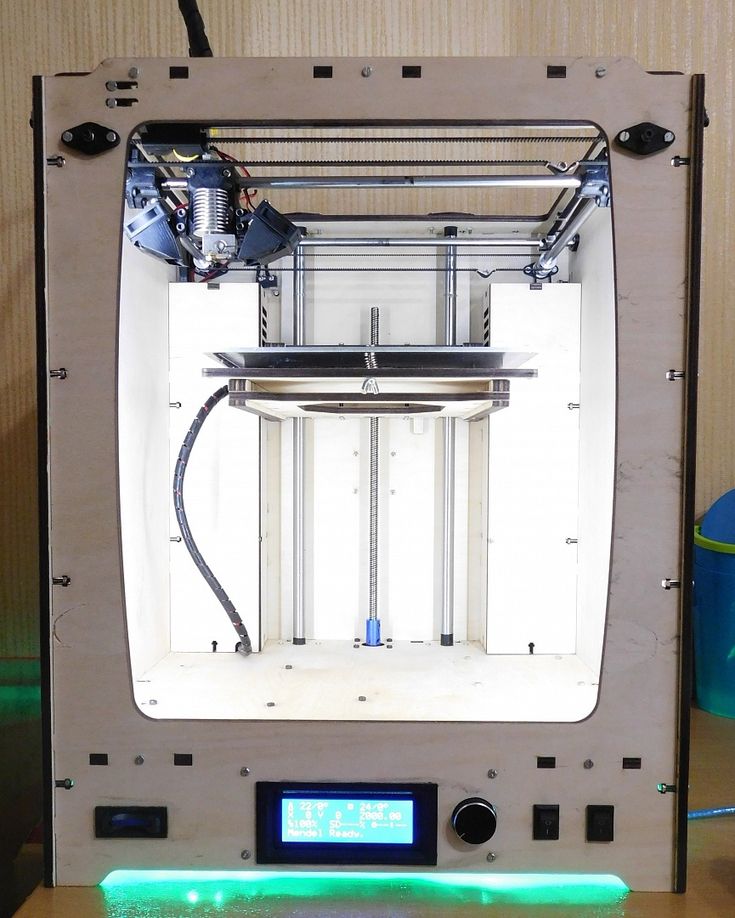
Must have 3d printing tools
Essential tools for every 3D printing professional
Lana Lozova15 December 2020
News
To get the best from your 3D printer, you need to be armed with the right tools for the job. From removing support material to improving build plate adhesion, here’s a list of must-have tools, all designed to make your life easier.
The essential 3D printer owner’s toolkit
There are certain tools that most 3D printer users possess. These vital pieces of equipment ensure that your prints run smoothly, and that you get the best results possible. You don’t necessarily need to invest in them all at once – but over time, it’s likely you’ll end up adding them all to your tool collection.
Glue stick
Build plate adhesion is an important part of creating great 3D prints. Glue sticks come in particularly handy when you’re trying to get your print to stick – simply cover your print bed with soluble glue, and the adhesion will improve immediately. Some people favor hair spray, but we’d personally recommend glue, as you can be more precise with the application, plus there’s less risk of accidentally spraying the gantry or moving parts. For material-specific adhesion guidelines, check out this support article.
Spatula or palette knife
On occasion, you might find that your 3D print has stuck a bit too well to your build plate. When this happens, a spatula or palette knife normally solves the problem. All you’ll need to do is ease it gently under the print and carefully lift it up.
Over time, you’ll probably get a collection of different palette knives. To start with, we’d recommend getting a palette knife that’s stiff, and one that’s flexible. Titan’s stainless steel scrapers have a tapered tip, which we find works particularly well.
Deburring tool / knife and cutting mat
A deburring tool is great for cleaning up modeled holes, and for removing small pieces of plastic from your printed parts, especially brim. You’ll also need knives to tidy up your prints, as they seldom turn out completely perfect. A deft flick of the knife can remove unsightly plastic blobs or filament strings, making the end result look smoother and cleaner.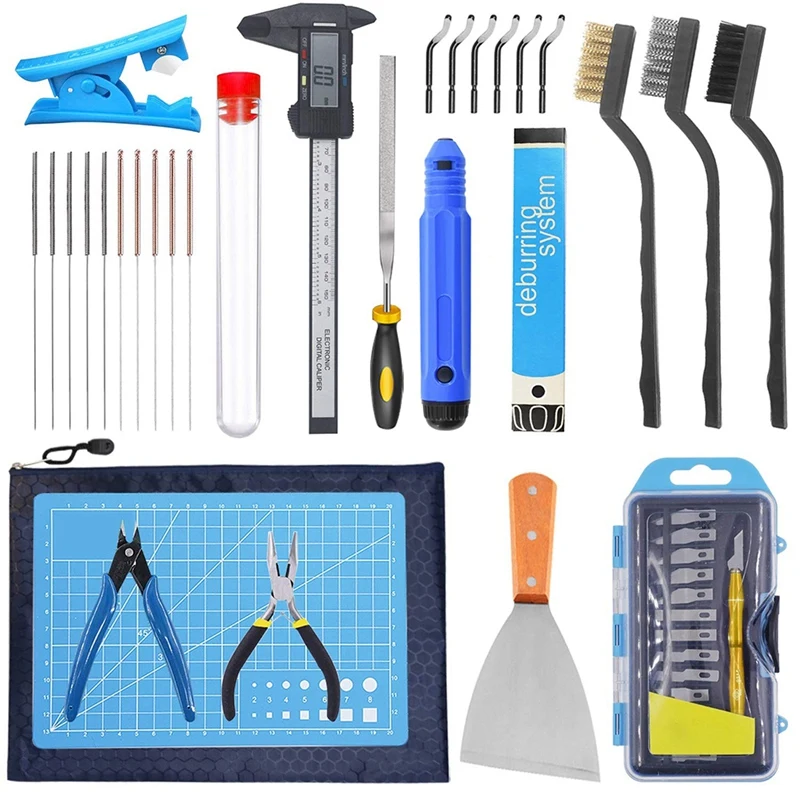 We recommend investing in a knife with exchangeable blades (such as an X-Acto knife), and a cutting mat too.
We recommend investing in a knife with exchangeable blades (such as an X-Acto knife), and a cutting mat too.
Pliers
Pliers have a variety of uses, from print core maintenance to fixing your 3D printer. Look for a good quality pair of pliers with a rubberized, slip-resistant grip. You’re likely to need more than one type – we’d recommend needle nose and wire-cutting pliers (which are particularly useful for snipping away support material or trimming filament).
Blue tape
Masking tape is one of the most basic tools you’re likely to own, and also one of the most widely used. Adding masking tape to the print bed is a simple, effective way to help your 3D printed object adhere to the print bed. It also makes removing the finished print far easier, and it protects your print bed from scratches.
Make sure you choose masking tape with a width of at least 50mm (2 inches). When the tape’s wide, it means you’ll need fewer strips to cover your print bed – something you’ll be grateful for if you need to resurface your print bed on a regular basis!
Magnalube and Unilube
Sometimes, you’ll need to lubricate the X and Y axles, just to ensure they keep running smoothly. The best lubricant to use is Unilube, and all it takes is a single drop to resolve any issues with dryness. For the Z trapezoidal leadscrew, use Magnalube.
The best lubricant to use is Unilube, and all it takes is a single drop to resolve any issues with dryness. For the Z trapezoidal leadscrew, use Magnalube.
It’s important not to use WD40, as this affects the axle coating and can cause damage to your printer. Read more about it here.
Digital caliper
A digital caliper has many applications in 3D printing. It’s useful for checking the precision of your prints, and you can also use it to dimension parts to replicate in CAD software. Calipers are also handy for checking filament measurements – as filaments aren’t often manufactured to exact measurements. Simply measure it at a few different positions, average the readings, then adjust the filament diameter in your slicing software if necessary.
Analogue calipers work too, but don’t offer the same precision.
Tweezers
Tweezers are useful to have to hand whenever you’re printing. They’re great for plucking oozing filament from the extruder nozzle before it starts printing (which means no more burnt fingers). They’re also handy for cleaning up your print afterwards. We’d recommend purchasing a set of tweezers in various shapes and sizes, to ensure you’re covered for every eventuality.
They’re also handy for cleaning up your print afterwards. We’d recommend purchasing a set of tweezers in various shapes and sizes, to ensure you’re covered for every eventuality.
Sandpaper
It’s a good idea to have a selection of sandpaper in a variety of different grits. These will all prove useful when you’re post-processing your 3D prints. Our recommendation? Have a selection from coarse (220 grit) to fine (1000 grit), and invest in well-known brands such as 3M, as they’re likely to last you longer than cheaper, inferior types.
Screwdrivers / hex key screwdrivers
Most people already own a good selection of screwdrivers and hex keys. If you don’t, it’s worthwhile getting some, as you’ll periodically need to re-tighten the gantry screws and the stepper motors of your 3D printer. Hex nuts and bolts are widely used in 3D printer assembly, so it’s also a wise idea to have a set of hex key screwdrivers and wrenches.
Adhesion sheets
Adhesion sheets are compatible with most materials, and boost adhesion to the build plate. They’re a good replacement for a glue stick, as they’re easy to remove and can be used multiple times. Another advantage is that they’ve been specially developed to cope with high temperatures, unlike masking tape. However, it’s important to check that the sheet is applied correctly, as air bubbles mean you won’t have a flat printing surface. You can find out how to apply the sheet here.
They’re a good replacement for a glue stick, as they’re easy to remove and can be used multiple times. Another advantage is that they’ve been specially developed to cope with high temperatures, unlike masking tape. However, it’s important to check that the sheet is applied correctly, as air bubbles mean you won’t have a flat printing surface. You can find out how to apply the sheet here.
Desiccant and re-sealable bags
3D printer filament absorbs water over time. This causes degradation, that eventually leads to complications during printing. To avoid water absorption, simply store your filament in a sealed container or plastic bag, and add some desiccant to ensure all moisture is removed from the environment. Silica gel works perfectly. Here are some more storage recommendations to help you. For a more automated solution, the Ultimaker S5 Material Station was developed to store and deliver material in optimal conditions for 3D printing.
Permanent marker
Permanent markers (such as Sharpies) are useful for marking 3D prints, especially when you’re running multiple prints of the same model, but with different slicer settings. Simply note down the sequence and settings for each print on the finished objects, and you’ll be able to tell them apart later on. Even leading architects do this: The team at Killa Design draw on their models to note where their design can be improved.
Simply note down the sequence and settings for each print on the finished objects, and you’ll be able to tell them apart later on. Even leading architects do this: The team at Killa Design draw on their models to note where their design can be improved.
Advanced 3D Printing Kit
The Advanced 3D Printing Kit for Ultimaker 2+ contains two 0.4mm nozzles, two TFM couplers, 25 adhesion sheets and a door. These keep your 3D printer running smoothly for longer. The nozzles and TFM couplers are convenient replacements, the adhesion sheets are great for keeping your models in position, and the door keeps warmth inside the printer, which prevents certain materials from warping and delaminating. Find out more here.
Other useful tools
The following tools might not be as essential as the list above, but they’re certainly useful to have around. Obviously, it depends on what you’ll be using your 3D printer for, as some are more suited to particular jobs than others.
Flashlight.
 If your 3D printer already has integrated lighting, you won’t need this. Otherwise, it’s a useful tool to have, even in well-lit areas. The inside of an enclosed 3D printer can be dark, which makes it different to judge print quality on detailed models. A compact LED light works perfectly.
If your 3D printer already has integrated lighting, you won’t need this. Otherwise, it’s a useful tool to have, even in well-lit areas. The inside of an enclosed 3D printer can be dark, which makes it different to judge print quality on detailed models. A compact LED light works perfectly.Paper towels. Paper towels are always useful for cleaning and drying your build plate, and best of all, they’re cheap too!
Pencils and paper. You’ll inevitably need to jot down dimensions and make sketches while printing, so it’s a good idea to have paper and pencils to hand at all times.
Wire cutter. Wire cutters are excellent for removing support and creating a cleaner, neater finish.
Dremel. A Dremel is a handheld, high-speed rotary tool, which features a range of accessories. These accessories let you undertake a variety of applications, including cutting, sanding, carving and grinding. When you’re 3D printing, it can be used to remove support material, sand down rough edges, or polish 3D prints made from metal-containing filaments.

Extra filament. It’s always useful to have an additional filament spool to hand. A spool lasts a while, but won’t keep you printing forever! Also, it’s nice to have a variety to choose from, depending on your requirements.
Extra glass plate. If you are printing 24/7, having a spare glass plate could really speed up your workflow. It allows you to quickly swap glass plates when starting a new print, instead of having to wait until the build plate has cooled down to remove the print.
Dissolving kit (bucket of water and pump). You’ll need to be able to remove your water-soluble PVA after printing – and a bucket of water does the job nicely! A pump ensures PVA supports dissolve faster.
With the right tools, the chances of producing a flawless 3D print are greatly increased. A 3D printer and a computer do most of the hard work, but it’s the tools that polish and perfect the models afterwards!
Show off just how powerful 3D printing is at work with this expert guide. Insights include:
Insights include:
• How to get buy-in from everyone in the office
• Important and practical setup considerations
• 3 workflow options that will save development time
• And lots more handy tips and tricks!
Top 15 Must-Have 3D Printer Accessories and Tools
3D printing industry has seen an accelerated growth in development over the years. From the massive and quite expensive 3D printers in the past, the models available today are more compact, affordable and easy to use. However, successful 3D printing does not only depend on the 3D printer itself. There are a variety of 3D printer accessories that play an important role when it comes to the quality of the final product.
With the right accessories, you can turn your average 3D printer into an incredible machine and you can be more assured that your prints will come out exactly as desired.
From removing support material to improving bed plate adhesion, here is a list of the top 15 3D printer accessories that will help you get the most of your 3D printer.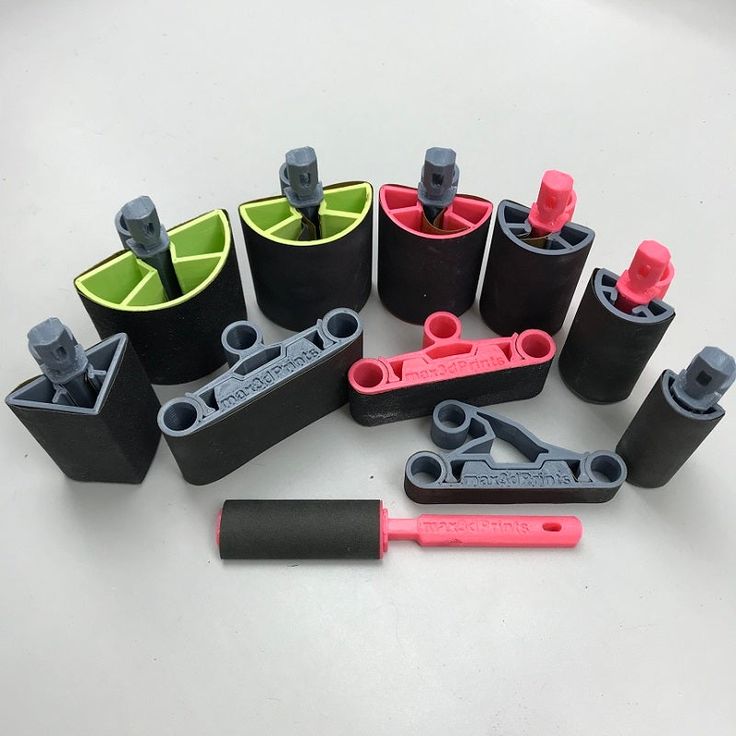
Disclosure: There are affiliate links in this article. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Filament Storage Container
Get it on Amazon / AliExpress / Banggood
One of the most important accessories a 3D printer owner must possess is an appropriate filament storage container.
Most of the 3D printer owners don’t pay attention to that, which can lead to so many problems like clogging, bad layer adhesion, breakage, etc. That’s why it is very important to safely store your filaments in a moisture free environment.
The first option is a filament box, which keeps your filament dry, dust-free, and also dispenses filament. It has temperature and humidity sensor, and you can also print directly from the box.
Vacuum Sealed Storage Containers
Get it on Amazon
Another great option are vacuum sealed storage containers. They come in a pack of 5, which is pretty awesome.
Masking Tape
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Masking tape is one of the most widely used 3D printing accessories. It is used to help each print adhere better to the print bed and is highly recommended. Furthermore, the finished print is much easier to remove from the bed as well as protect it from scratches.
Make sure you choose masking tape with a width of at least 5 cm (2 inches). Having a wider tape means you’ll need fewer strips to cover your print bed, which will lead to better results.
Alternative: Kapton Tape
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Although masking tape has been widely used for covering print beds and is cheaper option, Kapton tape is much better in the long term since it handles high temperatures better. This tape also prevents severe warping resulting in a much better 3D print. Kapton tape can be combined with other products, such as hairspray for best results.
PVA Glue Stick
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
When 3D printing, it’s vital to ensure good adhesion of your print to the build plate. So, another way to increase plate adhesion is covering your print bed with washable glue stick. You can apply glue directly to your build plate and wipe it off easily with water.
So, another way to increase plate adhesion is covering your print bed with washable glue stick. You can apply glue directly to your build plate and wipe it off easily with water.
This is one of the best bed adhesion solutions and works well with most materials, except for those prone to very high warpage like ABS and polycarbonate.
It works pretty well and it can easily be found at a wide variety of stores and at a very reasonable price.
Alternative: Hair Spray
Get it on Amazon
Many people also recommend spraying the bed with hair spray. Using hairspray to add an extra layer of ‘stickiness’ to your print bed is a quick and easy process.
But you must be careful with this method because using hairspray regularly and without proper care can damage your printer.
3D Print Removal Tool
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Sometimes you might find that your 3D print has stuck to your build plate. A 3D print removal tool, or spatula, can easily solve this problem. All you need to do is to put it gently underneath the print and carefully lift it up. You can also use this tool for scraping off little bits of filament.
A 3D print removal tool, or spatula, can easily solve this problem. All you need to do is to put it gently underneath the print and carefully lift it up. You can also use this tool for scraping off little bits of filament.
You probably got a one with your 3D printer, but that’s just a generic spatula which sometimes doesn’t do the job.
This set of different spatulas ensures you always have the right tool for removing any object you print. These spatulas are as thin as a knife blade, but without the sharp edge. They’re also usually angled in such a way that you can hold the handle parallel to the bed. It will prevent you from scratching the tray or damaging the part. I consider this set as an essential 3D printer accessory.
Carving Tools
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
When printing parts with a lot of little details and supporting material, you need to do some extra work to get a good finished look. For finishing the 3D prints where a little work is required, this set of carving tools is perfect for smoothing out your final product by removing excess filament and bringing to perfection all the little details.
This set contains 12 different carving tools of varying shapes and sizes that will meet most of your needs.
Alternative: Diamond Needle File Set
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Another tool perfect for working on small, delicate projects is a diamond needle file. This set includes 6 pieces with different shape and size, and each one serves a different purpose.
Pliers
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Needle-nose pliers can allow you to get into the fiddly areas of your 3D printer and your prints while providing a good, strong grip. Always look for a good quality pair of pliers with a rubberized, slip-resistant grip.
They can be used to remove jams in your 3D printer, to cut filaments, or to install new filaments. Sometimes, the prints get stuck to the print beds, so they can also be used to remove those prints.
Tweezers
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
A full set of tweezers with various shapes and sizes is a must when it comes to the more complicated tasks with 3D printing. They offer a very good and cheap solution for very fine and high precision adjustments in your 3D printer or printed parts.
They offer a very good and cheap solution for very fine and high precision adjustments in your 3D printer or printed parts.
They’re great for plucking oozing filament from the extruder nozzle without burning your fingers. Also, they can be used for post-processing finishing of your prints.
Sandpaper
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Having a set of sandpapers in a variety of different grits can be very useful in the post-processing step of your printing. A good sandpaper will help you define the details on your print and smooth out any rough edges and surfaces.
We recommend buying a set of good quality sandpaper from a well-known brand, from coarse (120 grit) to fine (1000 grit or more). Good quality sandpaper does not wear out easily, making it last longer and saving you money in the long run.
Alternative: Rotary Tool
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
As an alternative, you can use a rotary tool with different accessories, which will make things much easier and accurate as well.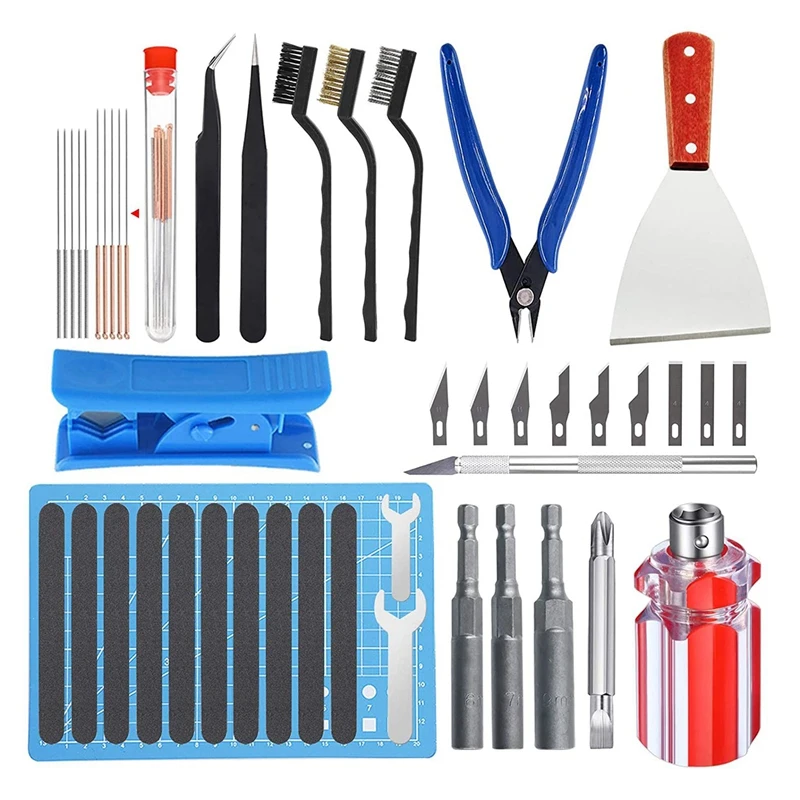
Digital Caliper
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
A digital caliper is a must-have tool for detail-oriented 3D print maker. When 3D printing, there can be a lot of measurements involved, so this tool will help you increase efficiency and accuracy, which is very important.
It enables you to make very precise measurements of a part you want to replicate in 3D, to verify the dimensions of a calibration print, or to check the precision of the measurements of your prints versus the dimensions in the source CAD model.
Calipers are also handy for checking the accuracy of your 3D printing filaments, since the actual filament diameters often differ from what is advertised. This will help you make the necessary adjustment.
The key to successful 3D print lies in getting a good first layer. And to get a good first layer, you need to have the right print bed surface which needs to have a smooth finish and to be rigid and durable as well.
Some people like to swap out their default print beds for glass plated ones, because they handle heat better and won’t warp the printed parts as easily.
Borosilicate Glass Bed
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Borosilicate glass can withstand extremely high temperatures, since it’s tempered. Also, it helps giving the print a smooth finish. When buying glass print bed make sure its dimensions match your model of 3D printer.
Alternative: Heat Bed Platform Sticker
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
This printing surface is compatible with almost every printing material. You can print directly onto the surface without any additional adhesives. Once you’re done printing, it is very easy to remove your printed part without damaging it.
You can use it for multiple prints and all you need to do is to wipe down with isopropyl alcohol between prints. Also, it can be easily cut to the desired size with a utility knife.
Nozzle Set
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Nozzles come in many different shapes and sizes, but they all have the same function. Why would you want to have more than one size nozzle?
Why would you want to have more than one size nozzle?
There are a few reasons why: for example, you want to print a larger model quickly, so you need to use a larger nozzle; you want fine details on your print, or you have an intricate print, so you need to use smaller nozzle; or your current nozzle gets clogged, so you need to replace it.
Nozzle Cleaning Kit
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
The extruder nozzle can easily get clogged with melted plastic after frequent use. It is one of the most significant parts of your 3D printer, so it is very important to keep it maintained, ensuring the quality of your 3D prints.
Cleaning the nozzles is not as easy as it seems, so you want to make sure you have the right tool for this purpose. There are special nozzle cleaning kits, designed for cleaning different sizes of nozzles, so as long as you have this accessory, you’ll always be able to keep your 3D printer clean and ready for the next print.
Solutions for Better Finish
After a part comes out of the printer, it needs to undergo a surface finishing process before it’s ready for use because you can often see its laminated appearance and roughness. So, there are so many reasons to finish a 3D printed part, for example, you might want to enhance its appearance, to smooth out uneven surfaces, or to improve its durability.
So, there are so many reasons to finish a 3D printed part, for example, you might want to enhance its appearance, to smooth out uneven surfaces, or to improve its durability.
Depending on the 3D printing material, you can choose acetone, or XTC-3D high performance 3D print coating.
Acetone
Get it on Amazon
By using acetone, you can easily achieve a smooth and polished surface to your ABS 3D prints. A thin layer of this product is just enough to get a better finish. Be very careful when deciding to use acetone, since it is not compatible with all materials.
XTC-3D High Performance 3D Print Coating
Get it on Amazon
We know that ABS can be smoothed with acetone, but when it comes to PLA, that’s not the case. This epoxy is a protective coating for smoothing and finishing 3D printed parts.
You just need to mix the two liquids together and apply the mixture onto any 3D print. It dries uniformly without leaving brush strokes. Working time is about 10 minutes, and it takes about 4 hours to cure.
Working time is about 10 minutes, and it takes about 4 hours to cure.
Super Glue
Thicker: Get it on Amazon
Thinner: Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Super glue has endless supply of uses for 3D printing jobs, and is incredibly effective. It can be used to fill in gaps, to repair broken parts, and to combine two or more smaller 3D printed parts together.
Different types of glue are used for different jobs. For example, for filling gaps a thicker type of glue is required whilst for delicate procedures, like combining two components together, a thinner type of glue is more appropriate.
Alternative: Acetone
Get it on Amazon
Acetone can be used for bonding 3D printed parts made of PLA, ABS or HIPS. In fact, it can be used for any material soluble in acetone. It gives very strong bond, and, if done properly it creates invisible seam.
Additional 3D Printer Accessories – 3D Scanner
Get it on Amazon / Banggood
Having a 3D scanner will take your 3D printing experience to the next level, as it enables you to create accurate 3D models from actual real objects.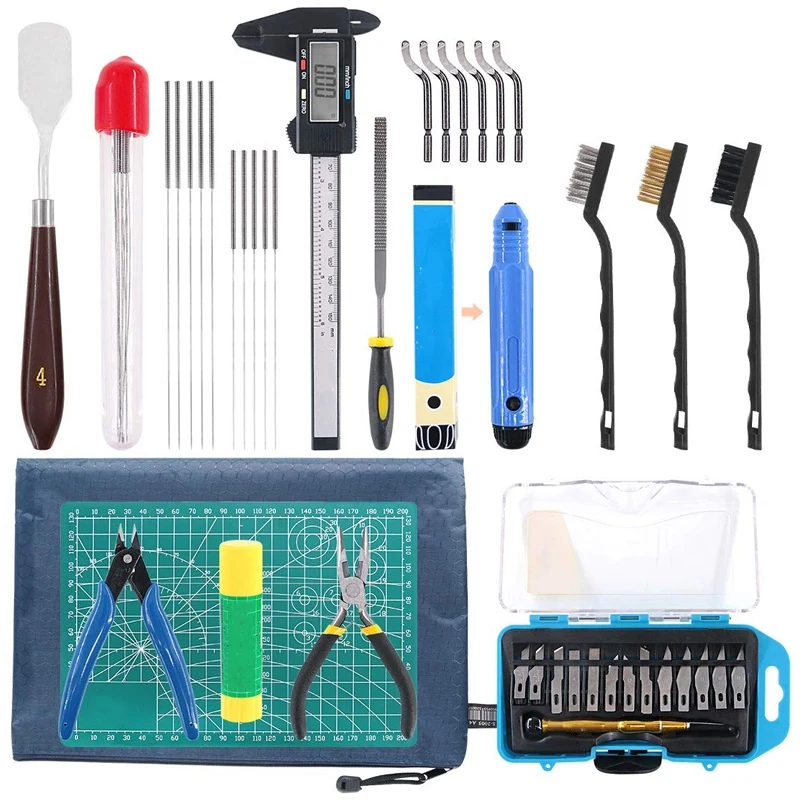
There are so many portable, relatively cheap and easy to use scanners on the market. It’s an ideal choice for anyone who wants a compact device that’s easy to carry around and is one of the most beginner-friendly machines around.
Read more: Creality CR-10 V3 Review – Is It the Best Mid-Range 3D Printer?
Conclusion
Choosing the right 3D printer accessories greatly increases the chances of creating a flawless 3D print. These decent investments can make the 3D printing process much easier and enjoyable.
Which of these 3D printer accessories do you already use? Do you have some other useful 3D printer accessories that are not on the list and should be? I’d love to hear about it in the comments section below.
If you want to buy a 3D printer check out our list of the best budget friendly 3D printers that are ideal for hobbyists and beginners who are just getting started.
3D printing tools. What you need to have on hand.
If you have a 3D printer, then you will have to master the intricacies of 3D printing. And to facilitate this process, you need to acquire some tools (Tools for 3D printing).
Today we will talk about what kits and tools you may need.
Spatula, scraper…
You may need a spatula and scraper to get started. These can be painting or artistic devices that help to remove the finished model from the working platform. They are especially indispensable in cases where you print with difficult-to-separate plastic. nine0003
To remove the model with the blunt end of the spatula, try to pry the model from one side. Once you succeed, try to delete the model manually. If this does not work, then try to squeeze the spatula between the table and the model and slightly raise it.
It is important to be very careful not to scratch the surface of the table and injure yourself.
Deburring tool
This tool is the most indispensable tool of all. It really makes it easy to remove supports, clean up the model. At the same time, the tool is safe, and it is much more convenient to use it than to wield a knife. This tool will be especially useful when cleaning round holes. nine0015
This tool will be especially useful when cleaning round holes. nine0015
Utility knife
This is a knife used for cutting appliqués, sometimes called a hobby knife. This tool is ideal for precise cutting of ABS, PLA and other popular plastics. It is important that this knife is very sharp. But it is also important to follow safety measures when working with the tool.
Pliers, round nose pliers
These tools are extremely useful when removing supports. At the same time, pliers are also useful for the 3D printer itself and for post-processing. Supports can be cut a little with a sharp knife and then with pliers it will be easy to remove them not one by one, but in blocks. nine0015
Wood carving set
This set is very useful for fine cleaning of models. The tips in this set have a variety of shapes, which allows for high-quality cleaning of models of any geometry and even in hard-to-reach places: corners, roundness, etc.
Super Glue
In fact, the choice of adhesives is now simply huge, and their possibilities are almost endless. Be sure to get superglue, as it is suitable not only for repairing or filling gaps, but also for gluing individual printed nodes. Be sure to focus on the viscosity of the composition, and also select the right tool. If you need to fill gaps, then we recommend choosing denser compositions than for assembling small parts. An important note - superglue works great with plastics such as ABS and PLA. nine0015
Files
A set of mini files will come in handy. Various forms of tools will allow grinding and smoothing of various surfaces.
Sanding (sanding) paper
With the help of grinding, surfaces can be significantly smoothed, achieving the ideal condition of the models. Especially grinding will be relevant if in the future the model will be stained. Sandpaper with a grit size of 120-200 will be the ideal solution for all types of plastics. Models made of ABS are particularly suitable for sanding. nine0015
Models made of ABS are particularly suitable for sanding. nine0015
Instead of a conclusion
All the 3D printing tools that we reviewed above will not gather dust on the shelf, waiting in the wings. If you are into 3D printing, then all of them will be in your favor. This is, in fact, the base that any 3D printer should have. Many manufacturers equip their 3D printers with a set of tools that can help with their work. If your equipment comes with a tool kit, take a close look at it so you don't waste money on what you already have. nine0003
3D printing for dummies or "what is a 3D printer?"
- 1 3D printing term
- 2 3D printing methods
- 2.1 Extrusion printing
- 2.2 Melting, sintering or gluing
- 2.3 Stereolithography
- 2.4 Lamination
- 3 Fused Deposition Printing (FDM)
- 3.1 Consumables nine0067 3.
- 3.3 Working platform
- 3.4 Positioners
- 3.5 Control
- 3.6 Varieties of FDM printers
- 4 Laser Stereolithography (SLA)
- 4.1 Lasers and projectors
- 4.2 Cuvette and resin
- 4.3 Varieties of Stereolithography Printers
 2 Extruder
2 Extruder 3D printing term
The term 3D printing has several synonyms, one of which quite briefly and accurately characterizes the essence of the process - "additive manufacturing", that is, production by adding material. The term was not coined by chance, because this is the main difference between multiple 3D printing technologies and the usual methods of industrial production, which in turn received the name "subtractive technologies", that is, "subtractive". If during milling, grinding, cutting and other similar procedures, excess material is removed from the workpiece, then in the case of additive manufacturing, material is gradually added until a solid model is obtained. nine0003
nine0003
Soon 3D printing will even be tested on the International Space Station
Strictly speaking, many traditional methods could be classified as "additive" in the broad sense of the word - for example, casting or riveting. However, it should be borne in mind that in these cases, either the consumption of materials is required for the manufacture of specific tools used in the production of specific parts (as in the case of casting), or the whole process is reduced to joining ready-made parts (welding, riveting, etc.). In order for the technology to be classified as “3D printing”, the final product must be built from raw materials, not blanks, and the formation of objects must be arbitrary - that is, without the use of forms. The latter means that additive manufacturing requires a software component. Roughly speaking, additive manufacturing requires computer control so that the shape of final products can be determined by building digital models. It was this factor that delayed the widespread adoption of 3D printing until the moment when numerical control and 3D design became widely available and highly productive. nine0003
nine0003
3D printing techniques
There are a lot of 3D printing technologies, and even more names for them due to patent restrictions. However, you can try to divide technologies into main areas:
Extrusion printing
This includes methods such as deposition fusion (FDM) and multi-jet printing (MJM). This method is based on the extrusion (extrusion) of consumables with the sequential formation of the finished product. As a rule, consumables consist of thermoplastics or composite materials based on them. nine0003
Melting, sintering or bonding
This approach is based on bonding powdered material together. Formation is done in different ways. The simplest is gluing, as is the case with 3D inkjet printing (3DP). Such printers deposit thin layers of powder onto the build platform, which are then selectively bonded with a binder. Powders can be made up of virtually any material that can be ground to a powder—plastic, wood, metal. nine0003
nine0003
This model of James Bond's Aston Martin was successfully printed on Voxeljet's SLS printer and blown up just as successfully during the filming of Skyfall instead of the expensive original
sintering (SLS and DMLS) and smelting (SLM), which allow you to create all-metal parts. As with 3D inkjet printing, these devices apply thin layers of powder, but the material is not glued together, but sintered or melted using a laser. Laser sintering (SLS) is used to work with both plastic and metal powders, although metal pellets usually have a more fusible shell, and after printing they are additionally sintered in special ovens. DMLS is a variant of SLS installations with more powerful lasers that allow sintering metal powders directly without additives. SLM printers provide not just sintering of particles, but their complete melting, which allows you to create monolithic models that do not suffer from the relative fragility caused by the porosity of the structure. As a rule, printers for working with metal powders are equipped with vacuum working chambers, or they replace air with inert gases. Such a complication of the design is caused by the need to work with metals and alloys subject to oxidation - for example, with titanium. nine0003
As a rule, printers for working with metal powders are equipped with vacuum working chambers, or they replace air with inert gases. Such a complication of the design is caused by the need to work with metals and alloys subject to oxidation - for example, with titanium. nine0003
Stereolithography
How an SLA printer works
Stereolithography printers use special liquid materials called "photopolymer resins". The term "photopolymerization" refers to the ability of a material to harden when exposed to light. As a rule, such materials react to ultraviolet irradiation.
Resin is poured into a special container with a movable platform, which is installed in a position near the surface of the liquid. The layer of resin covering the platform corresponds to one layer of the digital model. Then a thin layer of resin is processed by a laser beam, hardening at the points of contact. At the end of illumination, the platform together with the finished layer is immersed to the thickness of the next layer, and illumination is performed again.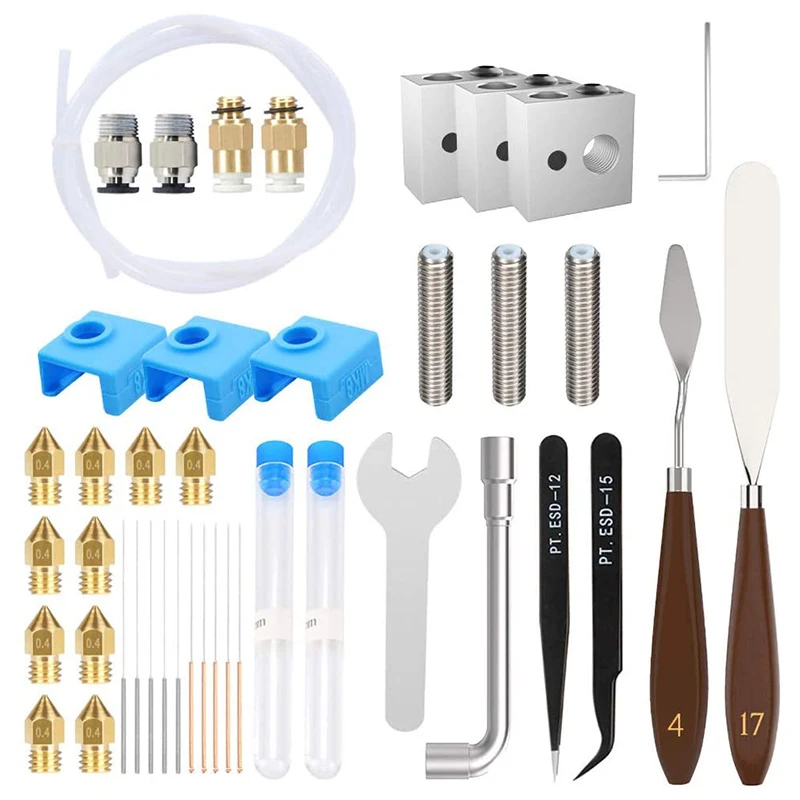 nine0003
nine0003
Lamination
Laminating (LOM) 3D printers workflow
Some 3D printers build models using sheet materials - paper, foil, plastic film.
Layers of material are glued on top of each other and cut along the contours of the digital model using a laser or a blade.
These machines are well suited for prototyping and can use very cheap consumables, including regular office paper. However, the complexity and noise of these printers, coupled with the limitations of the models they produce, limit their popularity. nine0003
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) and laser stereolithography (SLA) have become the most popular 3D printing methods used in the home and office.
Let's take a closer look at these technologies.
Fused Deposition Printing (FDM)
FDM is perhaps the simplest and most affordable 3D construction method, which is the reason for its high popularity.
High demand for FDM printers is driving device and consumable prices down rapidly, along with technology advances towards ease of use and improved reliability. nine0003
Consumables
ABS filament spool and finished model
FDM printers are designed to print with thermoplastics, which are usually supplied as thin filaments wound on spools. The range of "clean" plastics is very wide. One of the most popular materials is polylactide or "PLA plastic". This material is made from corn or sugar cane, which makes it non-toxic and environmentally friendly, but makes it relatively short-lived. ABS plastic, on the other hand, is very durable and wear-resistant, although it is susceptible to direct sunlight and can release small amounts of harmful fumes when heated. Many plastic items that we use on a daily basis are made from this material: housings for household appliances, plumbing fixtures, plastic cards, toys, etc. nine0003
In addition to PLA and ABS, printing is possible with nylon, polycarbonate, polyethylene and many other thermoplastics that are widely used in modern industry. More exotic materials are also possible, such as polyvinyl alcohol, known as "PVA plastic". This material dissolves in water, which makes it very useful for printing complex geometric patterns. But more on that below.
More exotic materials are also possible, such as polyvinyl alcohol, known as "PVA plastic". This material dissolves in water, which makes it very useful for printing complex geometric patterns. But more on that below.
Model made from Laywoo-D3. Changing the extrusion temperature allows you to achieve different shades and simulate annual rings
It is not necessary to print with homogeneous plastics. It is also possible to use composite materials imitating wood, metals, stone. Such materials use all the same thermoplastics, but with impurities of non-plastic materials.
So, Laywoo-D3 consists partly of natural wood dust, which allows you to print "wooden" products, including furniture.
The material called BronzeFill is filled with real bronze, and models made from it can be ground and polished, achieving a high similarity to products made from pure bronze. nine0003
One has only to remember that thermoplastics serve as a binding element in composite materials - they determine the thresholds of strength, thermal stability and other physical and chemical properties of finished models.
Extruder
Extruder - FDM print head. Strictly speaking, this is not entirely true, because the head consists of several parts, of which only the feed mechanism is directly "extruder". However, by tradition, the term "extruder" is commonly used as a synonym for the entire print assembly. nine0003
FDM extruder general design
The extruder is designed for melting and applying thermoplastic thread. The first component is the thread feed mechanism, which consists of rollers and gears driven by an electric motor. The mechanism feeds the thread into a special heated metal tube with a small diameter nozzle, called a "hot end" or simply a "nozzle". The same mechanism is used to remove the thread if a change of material is needed. nine0003
The hot end is used to heat and melt the thread fed by the puller. As a rule, nozzles are made from brass or aluminum, although more heat-resistant, but also more expensive materials can be used. For printing with the most popular plastics, a brass nozzle is quite enough. The “nozzle” itself is attached to the end of the tube with a threaded connection and can be replaced with a new one in case of wear or if a change in diameter is necessary. The nozzle diameter determines the thickness of the molten filament and, as a result, affects the print resolution. The heating of the hot end is controlled by a thermistor. Temperature control is very important, because when the material is overheated, pyrolysis can occur, that is, the decomposition of plastic, which contributes both to the loss of the properties of the material itself and to clogging of the nozzle. nine0003
For printing with the most popular plastics, a brass nozzle is quite enough. The “nozzle” itself is attached to the end of the tube with a threaded connection and can be replaced with a new one in case of wear or if a change in diameter is necessary. The nozzle diameter determines the thickness of the molten filament and, as a result, affects the print resolution. The heating of the hot end is controlled by a thermistor. Temperature control is very important, because when the material is overheated, pyrolysis can occur, that is, the decomposition of plastic, which contributes both to the loss of the properties of the material itself and to clogging of the nozzle. nine0003
PrintBox3D One FDM Extruder
To prevent the filament from melting too early, the top of the hot end is cooled by heatsinks and fans. This point is of great importance, since thermoplastics that pass the glass transition temperature significantly expand in volume and increase the friction of the material with the walls of the hot end. If the length of such a section is too long, the pulling mechanism may not have enough strength to push the thread. nine0003
If the length of such a section is too long, the pulling mechanism may not have enough strength to push the thread. nine0003
The number of extruders may vary depending on the purpose of the 3D printer. The simplest options use a single printhead. The dual extruder greatly expands the capabilities of the device, allowing you to print one model in two different colors, as well as using different materials. The last point is important when building complex models with overhanging structural elements: FDM printers cannot print “over the air”, since the applied layers require support. In the case of hinged elements, temporary support structures have to be printed, which are removed after printing is completed. The removal process is fraught with damage to the model itself and requires accuracy. In addition, if the model has a complex structure with internal cavities that are difficult to access, building conventional supports may not be practical due to the difficulty in removing excess material. nine0003
nine0003
Finished model with PVA supports (white) before and after washing
In such cases, the same water-soluble polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) comes in handy. Using a dual extruder, you can build a model from waterproof thermoplastic using PVA to create supports.
After printing, PVA can simply be dissolved in water and a complex product of perfect quality can be obtained.
Some FDM printers can use three or even four extruders. nine0003
Work platform
Heated platform covered with removable glass work table
Models are built on a special platform, often equipped with heating elements. Preheating is required for a wide range of plastics, including the popular ABS, which are subject to a high degree of shrinkage when cooled. The rapid loss of volume by cold coats compared to freshly applied material can lead to model distortion or delamination. The heating of the platform makes it possible to significantly equalize the temperature gradient between the upper and lower layers.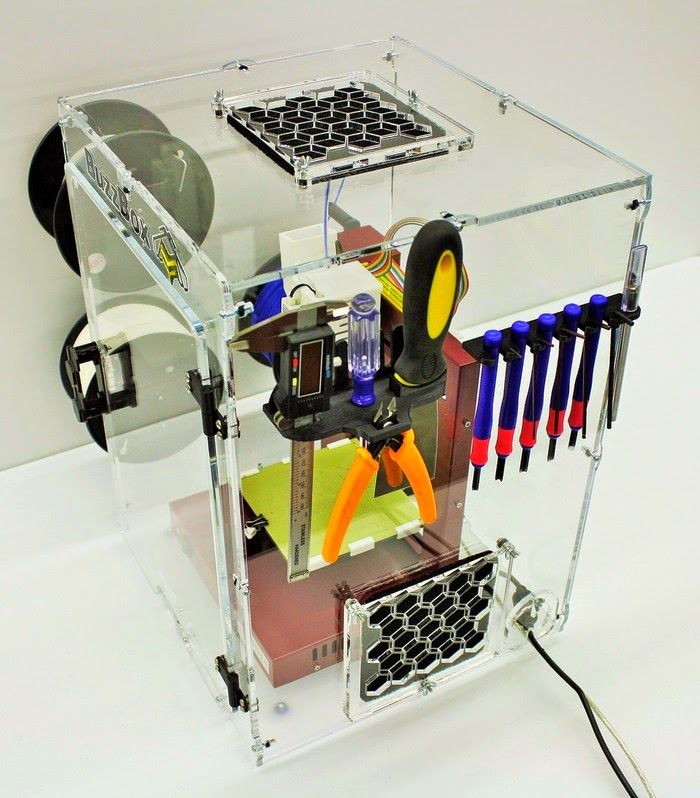 nine0003
nine0003
Heating is not recommended for some materials. A typical example is PLA plastic, which requires a fairly long time to harden. Heating PLA can lead to deformation of the lower layers under the weight of the upper ones. When working with PLA, measures are usually taken not to heat up, but to cool the model. Such printers have characteristic open cases and additional fans blowing fresh layers of the model.
Calibration screw for work platform covered with blue masking tape
The platform needs to be calibrated before printing to ensure that the nozzle does not hit the applied layers or extend too far causing air-to-air printing resulting in plastic vermicelli. The calibration process can be either manual or automatic. In manual mode, calibration is performed by positioning the nozzle at different points on the platform and adjusting the platform inclination using the support screws to achieve the optimal distance between the surface and the nozzle.
As a rule, platforms are equipped with an additional element - a removable table. This design simplifies the cleaning of the working surface and facilitates the removal of the finished model. Stages are made from various materials, including aluminum, acrylic, glass, etc. The choice of material for the manufacture of the stage depends on the presence of heating and consumables for which the printer is optimized.
For a better adhesion of the first layer of the model to the surface of the table, additional tools are often used, including polyimide film, glue and even hairspray! But the most popular tool is inexpensive, but effective masking tape. Some manufacturers make perforated tables that hold the model well but are difficult to clean. In general, the expediency of applying additional funds to the table depends on the consumable material and the material of the table itself. nine0003
Positioning mechanisms
Scheme of operation of positioning mechanisms
Of course, the print head must move relative to the working platform, and unlike conventional office printers, positioning must be carried out not in two, but in three planes, including height adjustment.
Positioning pattern may vary. The simplest and most common option involves mounting the print head on perpendicular guides driven by stepper motors and providing positioning along the X and Y axes. nine0003
Vertical positioning is carried out by moving the working platform.
On the other hand, it is possible to move the extruder in one plane and the platforms in two.
SeemeCNC ORION Delta Printer
One option that is gaining popularity is the delta coordinate system.
Such devices are called "delta robots" in the industry.
In delta printers, the print head is suspended on three manipulators, each of which moves along a vertical rail.
The synchronous symmetrical movement of the manipulators allows you to change the height of the extruder above the platform, and the asymmetric movement causes the head to move in the horizontal plane.
A variant of this system is the reverse delta design, where the extruder is fixed to the ceiling of the working chamber, and the platform moves on three support arms. nine0003
nine0003
Delta printers have a cylindrical build area, and their design makes it easy to increase the height of the working area with minimal design changes by lengthening the rails.
In the end, everything depends on the decision of the designers, but the fundamental principle does not change.
Control
Typical Arduino-based controller with add-on modules
FDM printer operation, including nozzle and platform temperature, filament feed rate, and stepper motors to position the extruder, is controlled by relatively simple electronic controllers. Most controllers are based on the Arduino platform, which has an open architecture. nine0003
The programming language used by printers is called G-code (G-Code) and consists of a list of commands executed in turn by the 3D printer systems. G-code is compiled by programs called "slicers" - standard 3D printer software that combines some of the features of graphics editors with the ability to set print options through a graphical interface. The choice of slicer depends on the printer model. RepRap printers use open source slicers such as Skeinforge, Replicator G and Repetier-Host. Some companies make printers that require proprietary software. nine0003
The choice of slicer depends on the printer model. RepRap printers use open source slicers such as Skeinforge, Replicator G and Repetier-Host. Some companies make printers that require proprietary software. nine0003
The code for printing is generated using slicers
As an example, we can mention the Cube printers from 3D Systems. There are companies that offer proprietary software but allow third-party software, as is the case with the latest generation of MakerBot 3D printers.
Slicers are not designed for 3D design per se. This task is done with CAD editors and requires some 3D design skills. Although beginners should not despair: digital models of a wide variety of designs are offered on many sites, often even for free. Finally, some companies and individuals offer 3D design services for custom printing. nine0003
Finally, 3D printers can be used in conjunction with 3D scanners to automate the process of digitizing objects. Many of these devices are designed specifically to work with 3D printers. Notable examples include the 3D Systems Sense handheld scanner and the MakerBot Digitizer handheld desktop scanner.
Notable examples include the 3D Systems Sense handheld scanner and the MakerBot Digitizer handheld desktop scanner.
MakerBot Replicator 5th Generation FDM Printer with built-in control module on the top of the frame
The user interface of a 3D printer can consist of a simple USB port for connecting to a personal computer. In such cases, the device is actually controlled by the slicer. nine0003
The disadvantage of this simplification is a rather high probability of printing failure when the computer freezes or slows down.
A more advanced option includes an internal memory or memory card interface to make the process standalone.
These models are equipped with control modules that allow you to adjust many print parameters (such as print speed or extrusion temperature). The module may include a small LCD display or even a mini-tablet. nine0003
Varieties of FDM printers
Professional Stratasys Fortus 360mc FDM printer that allows printing with nylon
FDM printers are very, very diverse, ranging from the simplest homemade RepRap printers to industrial installations capable of printing large-sized objects.
Stratasys, founded by FDM inventor Scott Crump, is a leader in industrial plant manufacturing. nine0003
You can build the simplest FDM printers yourself. Such devices are called RepRap, where "Rep" indicates the possibility of "replication", that is, self-reproduction.
RepRap printers can be used to print custom built plastic parts.
Controller, rails, belts, motors and other components can be easily purchased separately.
Of course, assembling such a device on your own requires serious technical and even engineering skills. nine0003
Some manufacturers make it easy by selling DIY kits, but these kits still require a good understanding of the technology.
A variant of the popular late 3rd generation Prusa RepRap printer
If you like to make things with your own hands, then RepRap printers will pleasantly please you with the price: the average cost of the popular early generation Prusa Mendel design is about $500 in a complete set. nine0003
nine0003
And, despite their "homemade nature", RepRap printers are quite capable of producing models with quality at the level of expensive branded counterparts.
Ordinary users who do not want to delve into the intricacies of the process, but require only a convenient device for household use, can purchase a ready-made FDM printer.
Many companies are focusing on the development of the consumer market segment, offering 3D printers for sale that are ready to print “straight out of the box” and do not require serious computer skills. nine0003
3D Systems Cube consumer 3D printer
The most famous example of a consumer 3D printer is the 3D Systems Cube.
While it doesn't boast a huge build area, ultra-fast print speed, or superb model build quality, it's easy to use, affordable, and safe: This printer has received the necessary certification to be used even by children.
Mankati FDM printer demonstration: http://youtu. be/51rypJIK4y0 nine0003
be/51rypJIK4y0 nine0003
Laser Stereolithography (SLA)
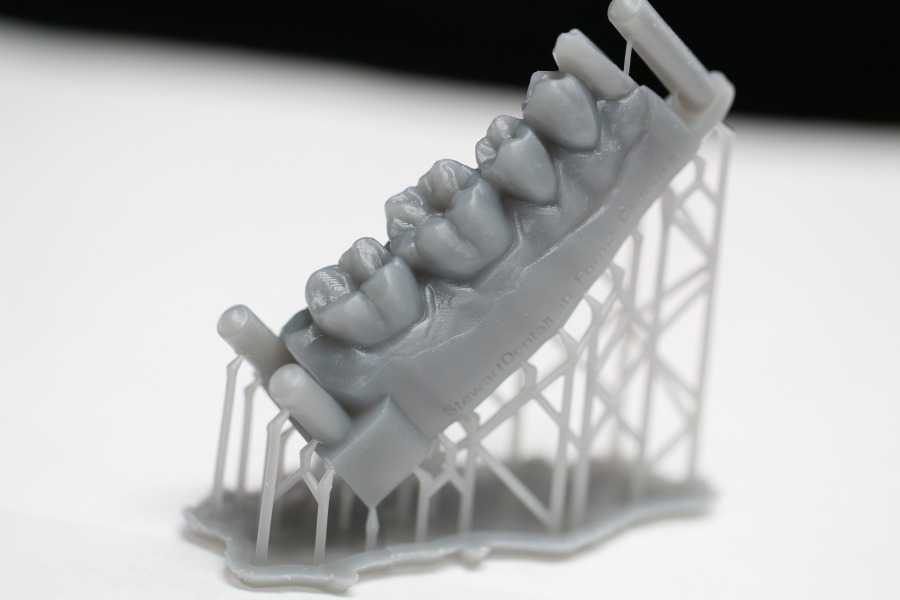
Stereolithographic 3D printers are widely used in dental prosthetics
Stereolithographic printers are the second most popular and widespread after FDM printers.
These units deliver exceptional print quality.
The resolution of some SLA printers is measured in a matter of microns - it is not surprising that these devices quickly won the love of jewelers and dentists. nine0003
The software side of laser stereolithography is almost identical to FDM printing, so we will not repeat ourselves and will only touch on the distinctive features of the technology.
Lasers and projectors
Projector illumination of a photopolymer model using Kudo3D Titan DLP printer as an example
The cost of stereolithographic printers is rapidly declining due to growing competition due to high demand and the use of new technologies that reduce the cost of construction. nine0003
nine0003
Although the technology is collectively referred to as "laser" stereolithography, most recent developments use UV LED projectors for the most part.
Projectors are cheaper and more reliable than lasers, do not require the use of delicate mirrors to deflect the laser beam, and have higher performance. The latter is explained by the fact that the contour of the whole layer is illuminated as a whole, and not sequentially, point by point, as is the case with laser options. This variant of the technology is called projection stereolithography, "DLP-SLA" or simply "DLP". However, both options are currently common - both laser and projector versions. nine0003
Cuvette and resin
Photopolymer resin is poured into a cuvette
A photopolymer resin that looks like epoxy is used as consumables for stereolithographic printers. Resins can have a variety of characteristics, but they all share one key feature for 3D printing applications: these materials harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. Hence, in fact, the name "photopolymer".
Hence, in fact, the name "photopolymer".
When polymerized, resins can have a wide variety of physical characteristics. Some resins are like rubber, others are hard plastics like ABS. You can choose different colors and degrees of transparency. The main disadvantage of resins and SLA printing in general is the cost of consumables, which significantly exceeds the cost of thermoplastics. nine0003
On the other hand, stereolithographic printers are mainly used by jewelers and dentists who do not need to build large parts but appreciate the savings from fast and accurate prototyping. Thus, SLA printers and consumables pay for themselves very quickly.
An example of a model printed on a laser stereolithographic 3D printer. In this case, the printer uses a leveling device to flatten the thin layer of resin covering the platform just prior to irradiation. As the model is being made, the platform, together with the finished layers, is “embedded” in the resin. Upon completion of printing, the model is removed from the cuvette, treated with a special solution to remove liquid resin residues and placed in an ultraviolet oven, where the final illumination of the model is performed. nine0003
Upon completion of printing, the model is removed from the cuvette, treated with a special solution to remove liquid resin residues and placed in an ultraviolet oven, where the final illumination of the model is performed. nine0003
Some SLA and DLP printers work in an "inverted" scheme: the model is not immersed in the consumable, but "pulled" out of it, while the laser or projector is placed under the cuvette, and not above it. This approach eliminates the need to level the surface after each exposure, but requires the use of a cuvette made of a material transparent to ultraviolet light, such as quartz glass.
The accuracy of stereolithographic printers is extremely high. For comparison, the standard for vertical resolution for FDM printers is considered to be 100 microns, and some variants of SLA printers allow you to apply layers as thin as 15 microns. But this is not the limit. The problem, rather, is not so much in the accuracy of lasers, but in the speed of the process: the higher the resolution, the lower the print speed.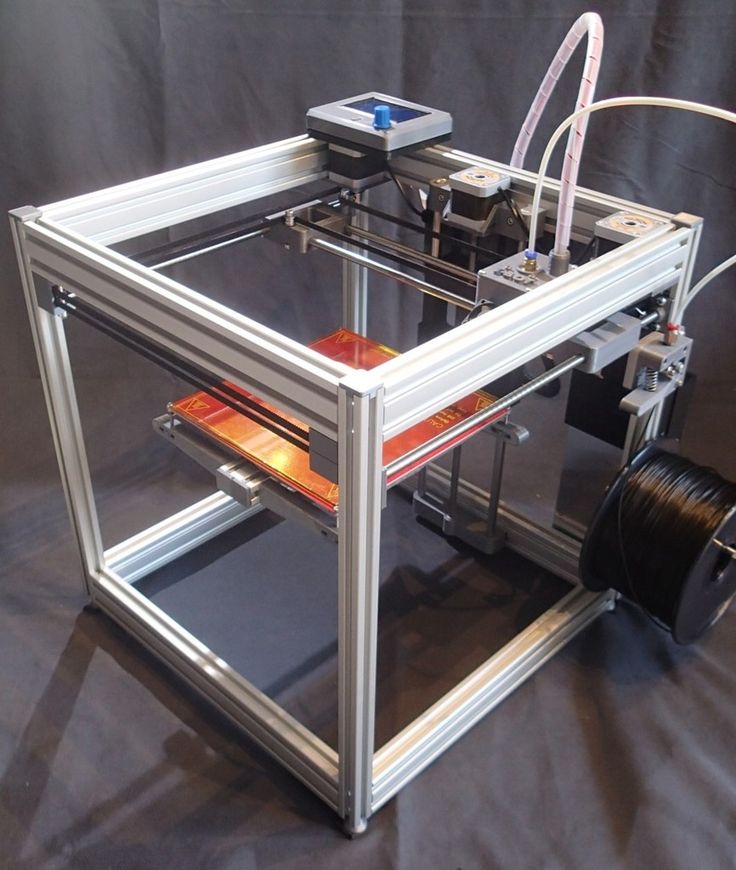 The use of digital projectors allows you to significantly speed up the process, because each layer is illuminated entirely. As a result, some DLP printer manufacturers claim to be able to print with a vertical resolution of one micron! nine0003
The use of digital projectors allows you to significantly speed up the process, because each layer is illuminated entirely. As a result, some DLP printer manufacturers claim to be able to print with a vertical resolution of one micron! nine0003
Video from CES 2013 showing Formlabs Form1 stereolithography 3D printer in action: http://youtu.be/IjaUasw64VE
Stereolithography Printer Options
Formlabs Form1 Desktop Stereolithography Printer
As with FDM printers, SLA printers come in a wide range in terms of size, features and cost. Professional installations can cost tens if not hundreds of thousands of dollars and weigh a couple of tons, but the rapid development of desktop SLA and DLP printers is gradually reducing the cost of equipment without compromising print quality. nine0003
Models such as the Titan 1 promise to make stereolithographic 3D printing affordable for small businesses and even home use at around $1,000.












