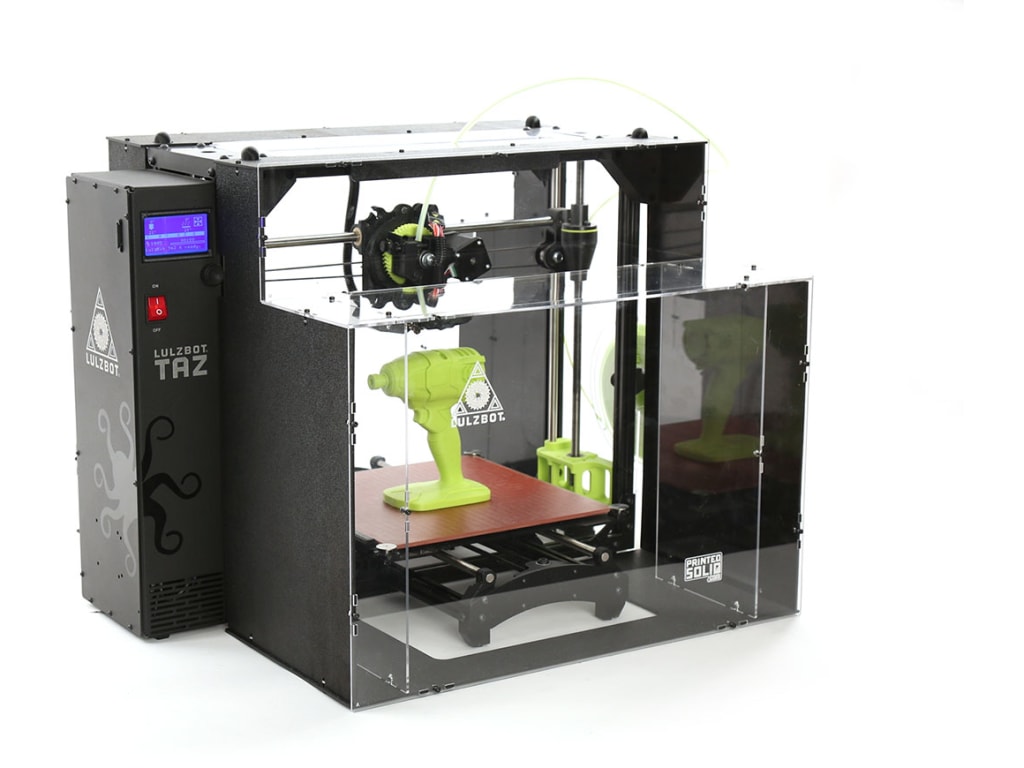
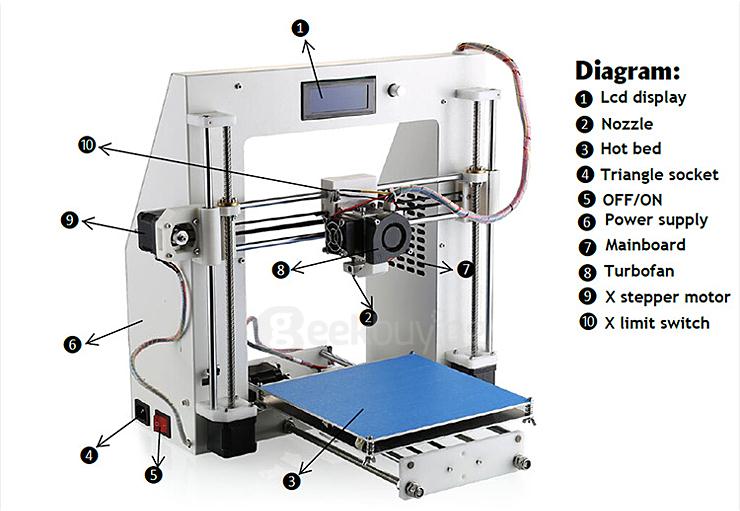
How to have something 3d printed
3D Printing in 3 Steps (Yes, Only 3!)
3D Printing in 3 Steps (Yes, Only 3!) | Staples.comby Kevin Ackerman, Staples® Contributing Writer
Since it gives computer users the ability to produce tangible objects in a variety of materials and colors right from their desktop, 3D printing seems as if it would be technically complicated (or just magical). But in reality, it’s not all that different from printing in two dimensions on paper.
To produce a printed page, all computer users need is a document, a computer and access to a printer — and, of course, ink and paper. Likewise, printing in 3D only requires three similar things. Sure, the technologies differ, but that’s the basic gist, as these three steps explain.
Step 1: Develop a Concept
If you were to open a document file on your computer, hit some random keys on your keyboard and press Print, you’d have a paper printout — though it wouldn’t make much sense. With 3D printing, you can’t make a shape that easily, not even a poor one, so it’s worth beginning the process by putting some thought into your object.
Start by knowing what you’d like to print in three dimensions. If you don’t have an idea or concept, there are plenty of free suggestions online to get you started. Web sites like Thingiverse.com offer a library of pre-designed objects that you can print with any 3D printer to gain experience. Or you can be inspired by people who are already using 3D printing technology.
Phoenix-based sculptor Kevin Caron uses 3D printing to refine his artwork before making full-sized versions. "Mostly what I'm doing is proof of concept designs. You know, will it stand up, does it look right and are the proportions correct on it?” he says.
And Chris Considine, CEO and founder of Los Angeles–based CXC Simulations, uses 3D printing to prototype custom-designed parts for racing simulators that are so realistic, they are used by professional race car drivers. "We need 3D orienting to see if the part feels exactly how we want it to feel,” he says.” We went through about 30 versions before we found the one that was perfect for us. Other than 3D printing, there’s truly no way you could have done that without building it over and over again."
"We need 3D orienting to see if the part feels exactly how we want it to feel,” he says.” We went through about 30 versions before we found the one that was perfect for us. Other than 3D printing, there’s truly no way you could have done that without building it over and over again."
Step 2: Hop on a Computer
Once you know what you want to produce, it’s time to sit down at a computer and make it happen. 3D prints are most commonly generated from an STL or .stl file. Standing for “stereolithography” (what 3D printing was named when it was first invented), this file format is to 3D printing what the .doc file is to document output.
To open and manipulate an STL file, you’ll need computer-aided design (CAD) software. For decades, these programs have been used by everyone from architects to product designers, so there are many kinds of CAD software available.
SketchUp is a free modeling program designed to be straightforward and allow anyone to create three-dimensional renderings, whether simple or complicated. Likewise, Tinkercad keeps the design process easy by providing just three simple tools. It also runs in a Web browser and offers step-by-step design lessons to demonstrate how easy 3D printing can be.
Likewise, Tinkercad keeps the design process easy by providing just three simple tools. It also runs in a Web browser and offers step-by-step design lessons to demonstrate how easy 3D printing can be.
Meanwhile, programs like AutoCAD are favored by many experienced professionals, having been used in the design and prototyping of millions of products throughout the years.
To run these programs, you don’t need a particularly powerful computer. Caron uses an HP desktop machine to create his digital sculptures. "It's not a big screaming gaming computer by any means,” he says. "It's just a small office computer and it handles the CAD program just fine.”
Step 3: Get Access to a 3D Printer
Most people assume they need to own a 3D printer to produce digitally rendered objects, but that isn’t true. Sure, owning a desktop 3D printer can put your designs within arm’s reach. But driving across town to pick up your objects at a Staples 3D printing service location or having them delivered by mail can be just as convenient for some businesses.
For example, Caron owns a CubeX™ commercial 3D printer. With the ability to print objects up to the size of a basketball, this device produces designs in plastic and in more than 4,000 different colors. He’s also used print-on-demand services to produce sculptures that he couldn’t make on his office’s machine.
"They’re breathtaking when you see them,” he says of the two acrylic sculptures. "The detail that I could view on the computer came out in the print — it just blew me away.” Caron is planning to scale his designs down and turn them into jewelry to sell. "I've gotten one back in a polished glass and it's stunning. You can’t tell it from gold other than by the weight."
If you are interested in using 3D printing but need help with these steps, visit one of our stores that offers 3D printing services (currently in Los Angeles and New York City). There, we can help you with all the steps, from getting in touch with designers to actual 3D printing. You can even get in our 3D printing photo booth and have your face put on a figurine.
You can even get in our 3D printing photo booth and have your face put on a figurine.
Go from Concept to Reality
Some businesses would argue that 3D printing, whether it’s done in the office or at an outside service, is worth its weight in gold. "I can go from concept in my head to holding the part in sometimes as quickly as an hour,” says Considine. "It’s a very powerful thing for an engineer to have. It's liberating."
Related Articles
7 Things You Didn't Know About 3D Printing
In the ever-expanding universe of 3D printing, no one knows it all. Though the technology has been around since the 1980s, it’s only recently... Read more
8 Tips from MakerBot for Making Better 3D-Printed Objects for Your Small Business
Both an art and a science, 3D printing is actually easy to do, but difficult to master. The experts at MakerBot have seen... Read more
The experts at MakerBot have seen... Read more
Carrie Mae Rose
Does mankind’s destiny lie in the stars? Artist Carrie Mae Rose thinks so. Her show... Read more
Custom 3D Printing Service from Print a Thing
Do-it-yourselfers
Hard to find, custom designed 3D parts.
We manufacture them quickly and affordably. Just for you.
Order TodayEntrepreneurs
It didn’t exist before you imagined it.
Print a Thing is your one stop shop to turn your dreams into reality.
We offer custom 3D printing services that will fit your needs.
Scroll Down to
Learn More
So here’s how it works...
Step 1:
Make or find a 3D model
of the item you want.
Step 2:
Build your order by picking
quality, priority, material, and color.
Step 3:
We match you up
with the best printer based on your needs.
Step 4:
Your print is delivered
to your doorstep hassle free.
Top 3D Printing Markets
New York, New York
Los Angeles, California
Chicago, Illinois
Miami, Florida
Dallas, Texas
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Houston, Texas
Atlanta, Georgia
Toronto, Ontario
Washington, District of Columbia
Have a 3D Printer?
Maximize it & make some money!
You probably bought a 3D printer because you are creative and you love new technology, but you are finding that your printer is unused most of the time. You can change that, share your passion with a vibrant community of entrepreneurs and creators and make money along the way.
You can change that, share your passion with a vibrant community of entrepreneurs and creators and make money along the way.
At Print a Thing we are on a mission to democratize 3D printing and make it available to everyone. Join us and turn your printer and your passion into a money making business. We do all the calculations for you. All you have to do is select the job you want from a list of jobs and follow our instructions on how to print and mail the items.
Become a Supplier!
Our Philosophy.
We want to change the world for the better through technology, and we see democratized 3d printing as a way to do it. When anyone can make completely unique physical objects at a reasonable price, without having the money or technical skills to own and operate a 3d printer of their own, a whole new creative energy will be released throughout the world. We built Print a Thing in the hopes that it would be a positive force for startups, do-it-yourselfers and creative spirits everywhere.
We built Print a Thing in the hopes that it would be a positive force for startups, do-it-yourselfers and creative spirits everywhere.
3D printing for "dummies" or "what is a 3D printer?"
- 1 3D printing term
- 2 3D printing methods
- 2.1 Extrusion printing
- 2.2 Melting, sintering or gluing
- 2.3 Stereolithography
- 2.4 Lamination
- 3 Fused Deposition Printing (FDM)
- 3.1 Consumables
- 3.2 Extruder
- 3.3 Working platform
- 3.4 Positioners
- 3.5 Control
- 3.6 Varieties of FDM printers
- 4 Laser stereolithography (SLA)
- 4.1 Lasers and projectors
- 4.2 Cuvette and resin
- 4.
 3 Types of stereolithographic printers
3 Types of stereolithographic printers
3D printing term
The term 3D printing has several synonyms, one of which quite briefly and accurately characterizes the essence of the process - "additive manufacturing", that is, production by adding material. The term was not coined by chance, because this is the main difference between multiple 3D printing technologies and the usual methods of industrial production, which in turn received the name "subtractive technologies", that is, "subtractive". If during milling, grinding, cutting and other similar procedures, excess material is removed from the workpiece, then in the case of additive manufacturing, material is gradually added until a solid model is obtained.
Soon 3D printing will even be tested on the International Space Station
Strictly speaking, many traditional methods could be classified as "additive" in the broad sense of the word - for example, casting or riveting. However, it should be borne in mind that in these cases, either the consumption of materials is required for the manufacture of specific tools used in the production of specific parts (as in the case of casting), or the whole process is reduced to joining ready-made parts (welding, riveting, etc.). In order for the technology to be classified as “3D printing”, the final product must be built from raw materials, not blanks, and the formation of objects must be arbitrary - that is, without the use of forms. The latter means that additive manufacturing requires a software component. Roughly speaking, additive manufacturing requires computer control so that the shape of final products can be determined by building digital models. It was this factor that delayed the widespread adoption of 3D printing until the moment when numerical control and 3D design became widely available and highly productive.
However, it should be borne in mind that in these cases, either the consumption of materials is required for the manufacture of specific tools used in the production of specific parts (as in the case of casting), or the whole process is reduced to joining ready-made parts (welding, riveting, etc.). In order for the technology to be classified as “3D printing”, the final product must be built from raw materials, not blanks, and the formation of objects must be arbitrary - that is, without the use of forms. The latter means that additive manufacturing requires a software component. Roughly speaking, additive manufacturing requires computer control so that the shape of final products can be determined by building digital models. It was this factor that delayed the widespread adoption of 3D printing until the moment when numerical control and 3D design became widely available and highly productive.
3D printing techniques
3D printing technologies are numerous, and there are even more names for them due to patent restrictions. However, you can try to divide technologies into main areas:
However, you can try to divide technologies into main areas:
Extrusion printing
This includes methods such as deposition deposition (FDM) and multi-jet printing (MJM). This method is based on the extrusion (extrusion) of consumables with the sequential formation of the finished product. As a rule, consumables consist of thermoplastics or composite materials based on them.
Melting, sintering or bonding
This approach is based on bonding powdered material together. Formation is done in different ways. The simplest is gluing, as is the case with 3D inkjet printing (3DP). Such printers deposit thin layers of powder onto the build platform, which are then selectively bonded with a binder. Powders can be made up of virtually any material that can be ground to a powder—plastic, wood, metal.
This model of James Bond's Aston Martin was successfully printed on Voxeljet's SLS printer and blown up just as successfully during the filming of Skyfall instead of the expensive original
sintering (SLS and DMLS) and smelting (SLM), which allow you to create all-metal parts. As with 3D inkjet printing, these devices apply thin layers of powder, but the material is not glued together, but sintered or melted using a laser. Laser sintering (SLS) is used to work with both plastic and metal powders, although metal pellets usually have a more fusible shell, and after printing they are additionally sintered in special ovens. DMLS is a variant of SLS installations with more powerful lasers that allow sintering metal powders directly without additives. SLM printers provide not just sintering of particles, but their complete melting, which allows you to create monolithic models that do not suffer from the relative fragility caused by the porosity of the structure. As a rule, printers for working with metal powders are equipped with vacuum working chambers, or they replace air with inert gases. Such a complication of the design is caused by the need to work with metals and alloys subject to oxidation - for example, with titanium.
As with 3D inkjet printing, these devices apply thin layers of powder, but the material is not glued together, but sintered or melted using a laser. Laser sintering (SLS) is used to work with both plastic and metal powders, although metal pellets usually have a more fusible shell, and after printing they are additionally sintered in special ovens. DMLS is a variant of SLS installations with more powerful lasers that allow sintering metal powders directly without additives. SLM printers provide not just sintering of particles, but their complete melting, which allows you to create monolithic models that do not suffer from the relative fragility caused by the porosity of the structure. As a rule, printers for working with metal powders are equipped with vacuum working chambers, or they replace air with inert gases. Such a complication of the design is caused by the need to work with metals and alloys subject to oxidation - for example, with titanium.
Stereolithography
How an SLA printer works
Stereolithography printers use special liquid materials called "photopolymer resins". The term "photopolymerization" refers to the ability of a material to harden when exposed to light. As a rule, such materials react to ultraviolet irradiation.
The term "photopolymerization" refers to the ability of a material to harden when exposed to light. As a rule, such materials react to ultraviolet irradiation.
Resin is poured into a special container with a movable platform, which is installed in a position near the surface of the liquid. The layer of resin covering the platform corresponds to one layer of the digital model. Then a thin layer of resin is processed by a laser beam, hardening at the points of contact. At the end of illumination, the platform together with the finished layer is immersed to the thickness of the next layer, and illumination is performed again.
Lamination
Laminating (LOM) 3D printers workflow
Some 3D printers build models using sheet materials - paper, foil, plastic film.
Layers of material are glued on top of each other and cut to the contours of the digital model using a laser or a blade.
These machines are well suited for prototyping and can use very cheap consumables, including regular office paper. However, the complexity and noise of these printers, coupled with the limitations of the models they produce, limit their popularity.
However, the complexity and noise of these printers, coupled with the limitations of the models they produce, limit their popularity.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Laser Stereolithography (SLA) are the most popular 3D printing methods used in the home and office.
Let's take a closer look at these technologies.
Fused Deposition Printing (FDM)
FDM is perhaps the simplest and most affordable 3D construction method, which makes it very popular.
High demand for FDM printers is driving device and consumable prices down rapidly, along with technology advances towards ease of use and improved reliability.
Consumables
ABS filament spool and finished model
FDM printers are designed to print with thermoplastics, which are usually supplied as thin filaments wound on spools. The range of "clean" plastics is very wide. One of the most popular materials is polylactide or "PLA plastic". This material is made from corn or sugar cane, which makes it non-toxic and environmentally friendly, but makes it relatively short-lived. ABS plastic, on the other hand, is very durable and wear-resistant, although it is susceptible to direct sunlight and can release small amounts of harmful fumes when heated. Many plastic items that we use on a daily basis are made from this material: housings for household appliances, plumbing fixtures, plastic cards, toys, etc.
This material is made from corn or sugar cane, which makes it non-toxic and environmentally friendly, but makes it relatively short-lived. ABS plastic, on the other hand, is very durable and wear-resistant, although it is susceptible to direct sunlight and can release small amounts of harmful fumes when heated. Many plastic items that we use on a daily basis are made from this material: housings for household appliances, plumbing fixtures, plastic cards, toys, etc.
In addition to PLA and ABS, printing is possible with nylon, polycarbonate, polyethylene and many other thermoplastics that are widely used in modern industry. More exotic materials are also possible, such as polyvinyl alcohol, known as "PVA plastic". This material dissolves in water, which makes it very useful for printing complex geometric patterns. But more on that below.
Model made from Laywoo-D3. Changing the extrusion temperature allows you to achieve different shades and simulate annual rings
It is not necessary to print with homogeneous plastics. It is also possible to use composite materials imitating wood, metals, stone. Such materials use all the same thermoplastics, but with impurities of non-plastic materials.
It is also possible to use composite materials imitating wood, metals, stone. Such materials use all the same thermoplastics, but with impurities of non-plastic materials.
So, Laywoo-D3 consists partly of natural wood dust, which allows you to print "wooden" products, including furniture.
The material called BronzeFill is filled with real bronze, and models made from it can be ground and polished, achieving a high similarity to products made from pure bronze.
One has only to remember that thermoplastics serve as a binding element in composite materials - they determine the thresholds of strength, thermal stability and other physical and chemical properties of finished models.
Extruder
Extruder - FDM print head. Strictly speaking, this is not entirely true, because the head consists of several parts, of which only the feed mechanism is directly "extruder". However, by tradition, the term "extruder" is commonly used as a synonym for the entire print assembly.
FDM extruder general design
The extruder is designed for melting and applying thermoplastic thread. The first component is the thread feed mechanism, which consists of rollers and gears driven by an electric motor. The mechanism feeds the thread into a special heated metal tube with a small diameter nozzle, called a "hot end" or simply a "nozzle". The same mechanism is used to remove the thread if a change of material is needed.
The hot end is used to heat and melt the thread fed by the puller. As a rule, nozzles are made from brass or aluminum, although more heat-resistant, but also more expensive materials can be used. For printing with the most popular plastics, a brass nozzle is quite enough. The “nozzle” itself is attached to the end of the tube with a threaded connection and can be replaced with a new one in case of wear or if a change in diameter is necessary. The nozzle diameter determines the thickness of the molten filament and, as a result, affects the print resolution. The heating of the hot end is controlled by a thermistor. Temperature control is very important, because when the material is overheated, pyrolysis can occur, that is, the decomposition of plastic, which contributes both to the loss of the properties of the material itself and to clogging of the nozzle.
The heating of the hot end is controlled by a thermistor. Temperature control is very important, because when the material is overheated, pyrolysis can occur, that is, the decomposition of plastic, which contributes both to the loss of the properties of the material itself and to clogging of the nozzle.
PrintBox3D One FDM Printer Extruder
To prevent the filament from melting too early, the top of the hot end is cooled by heatsinks and fans. This point is of great importance, since thermoplastics that pass the glass transition temperature significantly expand in volume and increase the friction of the material with the walls of the hot end. If the length of such a section is too long, the pulling mechanism may not have enough strength to push the thread.
The number of extruders may vary depending on the purpose of the 3D printer. The simplest options use a single printhead. The dual extruder greatly expands the capabilities of the device, allowing you to print one model in two different colors, as well as using different materials. The last point is important when building complex models with overhanging structural elements: FDM printers cannot print “over the air”, since the applied layers require support. In the case of hinged elements, temporary support structures have to be printed, which are removed after printing is completed. The removal process is fraught with damage to the model itself and requires accuracy. In addition, if the model has a complex structure with internal cavities that are difficult to access, building conventional supports may not be practical due to the difficulty in removing excess material.
The last point is important when building complex models with overhanging structural elements: FDM printers cannot print “over the air”, since the applied layers require support. In the case of hinged elements, temporary support structures have to be printed, which are removed after printing is completed. The removal process is fraught with damage to the model itself and requires accuracy. In addition, if the model has a complex structure with internal cavities that are difficult to access, building conventional supports may not be practical due to the difficulty in removing excess material.
Finished model with PVA supports (white) before and after washing
In such cases, the same water-soluble polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) comes in handy. Using a dual extruder, you can build a model from waterproof thermoplastic using PVA to create supports.
After printing, PVA can be simply dissolved in water and a complex product of perfect quality can be obtained.
Some FDM printers can use three or even four extruders.
Working platform
Heated platform covered with removable glass work table
Models are built on a special platform, often equipped with heating elements. Preheating is required for a wide range of plastics, including the popular ABS, which are subject to a high degree of shrinkage when cooled. The rapid loss of volume by cold coats compared to freshly applied material can lead to model distortion or delamination. The heating of the platform makes it possible to significantly equalize the temperature gradient between the upper and lower layers.
Heating is not recommended for some materials. A typical example is PLA plastic, which requires a fairly long time to harden. Heating PLA can lead to deformation of the lower layers under the weight of the upper ones. When working with PLA, measures are usually taken not to heat up, but to cool the model. Such printers have characteristic open cases and additional fans blowing fresh layers of the model.
Such printers have characteristic open cases and additional fans blowing fresh layers of the model.
Calibration screw for work platform covered with blue masking tape
The platform needs to be calibrated before printing to ensure that the nozzle does not hit the applied layers and move too far causing air-to-air printing resulting in plastic vermicelli. The calibration process can be either manual or automatic. In manual mode, calibration is performed by positioning the nozzle at different points on the platform and adjusting the platform inclination using the support screws to achieve the optimal distance between the surface and the nozzle.
As a rule, platforms are equipped with an additional element - a removable table. This design simplifies the cleaning of the working surface and facilitates the removal of the finished model. Stages are made from various materials, including aluminum, acrylic, glass, etc. The choice of material for the manufacture of the stage depends on the presence of heating and consumables for which the printer is optimized.
For a better adhesion of the first layer of the model to the surface of the table, additional tools are often used, including polyimide film, glue and even hairspray! But the most popular tool is inexpensive, but effective masking tape. Some manufacturers make perforated tables that hold the model well but are difficult to clean. In general, the expediency of applying additional funds to the table depends on the consumable material and the material of the table itself.
Positioning mechanisms
Scheme of operation of positioning mechanisms
Of course, the print head must move relative to the working platform, and unlike conventional office printers, positioning must be carried out not in two, but in three planes, including height adjustment.
Positioning pattern may vary. The simplest and most common option involves mounting the print head on perpendicular guides driven by stepper motors and providing positioning along the X and Y axes.
Vertical positioning is carried out by moving the working platform.
On the other hand, it is possible to move the extruder in one plane and the platforms in two.
SeemeCNC ORION Delta Printer
One option that is gaining popularity is the delta coordinate system.
Such devices are called "delta robots" in the industry.
In delta printers, the print head is suspended on three manipulators, each of which moves along a vertical rail.
The synchronous symmetrical movement of the manipulators allows you to change the height of the extruder above the platform, and the asymmetric movement causes the head to move in the horizontal plane.
A variant of this system is the reverse delta design, where the extruder is fixed to the ceiling of the working chamber, and the platform moves on three support arms.
Delta printers have a cylindrical build area, and their design makes it easy to increase the height of the working area with minimal design changes by extending the rails.
In the end, everything depends on the decision of the designers, but the fundamental principle does not change.
Control
Typical Arduino-based controller with add-on modules
The operation of the FDM printer, including nozzle and platform temperature, filament feed rate, and stepper motors for positioning the extruder, is controlled by fairly simple electronic controllers. Most controllers are based on the Arduino platform, which has an open architecture.
The programming language used by the printers is called G-code (G-Code) and consists of a list of commands executed in turn by the 3D printer systems. G-code is compiled by programs called "slicers" - standard 3D printer software that combines some of the features of graphics editors with the ability to set print options through a graphical interface. The choice of slicer depends on the printer model. RepRap printers use open source slicers such as Skeinforge, Replicator G and Repetier-Host. Some companies make printers that require proprietary software.
Some companies make printers that require proprietary software.
Program code for printing is generated using slicers
As an example, we can mention Cube printers from 3D Systems. There are companies that offer proprietary software but allow third-party software, as is the case with the latest generation of MakerBot 3D printers.
Slicers are not intended for 3D design per se. This task is done with CAD editors and requires some 3D design skills. Although beginners should not despair: digital models of a wide variety of designs are offered on many sites, often even for free. Finally, some companies and individuals offer 3D design services for custom printing.
Finally, 3D printers can be used in conjunction with 3D scanners to automate the process of digitizing objects. Many of these devices are designed specifically to work with 3D printers. Notable examples include the 3D Systems Sense handheld scanner and the MakerBot Digitizer handheld desktop scanner.
MakerBot Replicator 5th Generation FDM Printer with built-in control module on the top of the frame
The user interface of a 3D printer can consist of a simple USB port for connecting to a personal computer. In such cases, the device is actually controlled by the slicer.
The disadvantage of this simplification is a rather high probability of printing failure when the computer freezes or slows down.
A more advanced option includes an internal memory or memory card interface to make the process standalone.
These models are equipped with control modules that allow you to adjust many print parameters (such as print speed or extrusion temperature). The module may include a small LCD display or even a mini-tablet.
Varieties of FDM printers
Professional Stratasys Fortus 360mc FDM printer that allows printing with nylon
FDM printers are very, very diverse, ranging from the simplest homemade RepRap printers to industrial installations capable of printing large-sized objects.
Stratasys, founded by Scott Crump, the inventor of FDM technology, is a leader in the production of industrial installations.
You can build the simplest FDM printers yourself. Such devices are called RepRap, where "Rep" indicates the possibility of "replication", that is, self-reproduction.
RepRap printers can be used to print custom built plastic parts.
Controller, rails, belts, motors and other components can be easily purchased separately.
Of course, assembling such a device on your own requires serious technical and even engineering skills.
Some manufacturers make it easy by selling DIY kits, but these kits still require a good understanding of the technology. RepRap Printers
And, despite their "homemade nature", RepRap printers are quite capable of producing models with quality at the level of expensive branded counterparts.
Ordinary users who do not want to delve into the intricacies of the process, but require only a convenient device for household use, can purchase a ready-made FDM printer.
Many companies are focusing on the development of the consumer market segment, offering 3D printers for sale that are ready to print “right out of the box” and do not require serious computer skills.
3D Systems Cube consumer 3D printer
The most famous example of a consumer 3D printer is the 3D Systems Cube.
While it doesn't boast a huge build area, ultra-fast print speeds, or superb build quality, it's easy to use, affordable, and safe: This printer has received the necessary certification to be used even by children.
Mankati FDM printer demonstration: http://youtu.be/51rypJIK4y0
Laser Stereolithography (SLA)
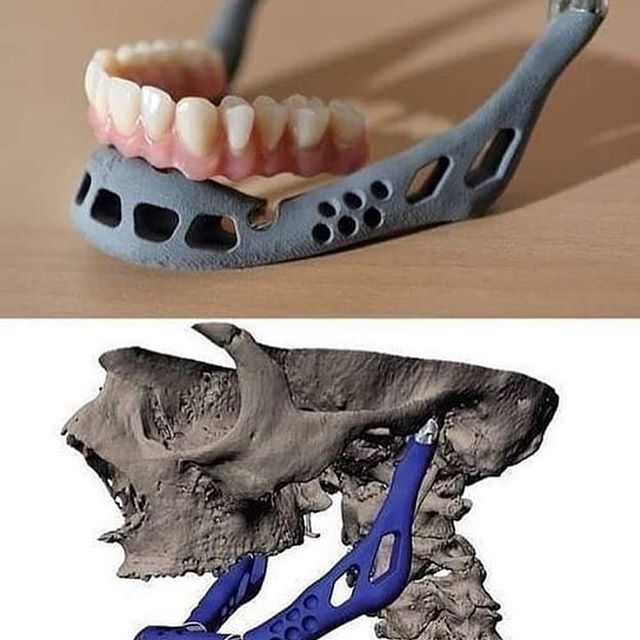
Stereolithographic 3D printers are widely used in dental prosthetics
Stereolithographic printers are the second most popular and widespread after FDM printers.
These units deliver exceptional print quality.
The resolution of some SLA printers is measured in a matter of microns - it is not surprising that these devices quickly won the love of jewelers and dentists.
The software side of laser stereolithography is almost identical to FDM printing, so we will not repeat ourselves and will only touch on the distinctive features of the technology.
Lasers and projectors
Projector illumination of a photopolymer model using Kudo3D Titan DLP printer as an example
The cost of stereolithography printers is rapidly declining due to growing competition due to high demand and the use of new technologies that reduce the cost of construction.
Although the technology is generically referred to as "laser" stereolithography, most recent developments use UV LED projectors for the most part.
Projectors are cheaper and more reliable than lasers, do not require the use of delicate mirrors to deflect the laser beam, and have higher performance. The latter is explained by the fact that the contour of the whole layer is illuminated as a whole, and not sequentially, point by point, as is the case with laser options. This variant of the technology is called projection stereolithography, "DLP-SLA" or simply "DLP". However, both options are currently common - both laser and projector versions.
This variant of the technology is called projection stereolithography, "DLP-SLA" or simply "DLP". However, both options are currently common - both laser and projector versions.
Cuvette and resin
Photopolymer resin is poured into a cuvette
A photopolymer resin that looks like epoxy is used as consumables for stereolithographic printers. Resins can have a variety of characteristics, but they all share one key feature for 3D printing applications: these materials harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. Hence, in fact, the name "photopolymer".
When polymerized, resins can have a wide variety of physical characteristics. Some resins are like rubber, others are hard plastics like ABS. You can choose different colors and degrees of transparency. The main disadvantage of resins and SLA printing in general is the cost of consumables, which significantly exceeds the cost of thermoplastics.
On the other hand, stereolithography printers are mainly used by jewelers and dentists who do not need to build large parts but appreciate the savings from fast and accurate prototyping. Thus, SLA printers and consumables pay for themselves very quickly.
Thus, SLA printers and consumables pay for themselves very quickly.
Example of a model printed on a laser stereolithographic 3D printer
Resin is poured into a cuvette, which can be equipped with a lowering platform. In this case, the printer uses a leveling device to flatten the thin layer of resin covering the platform just prior to irradiation. As the model is being made, the platform, together with the finished layers, is “embedded” in the resin. Upon completion of printing, the model is removed from the cuvette, treated with a special solution to remove liquid resin residues and placed in an ultraviolet oven, where the final illumination of the model is performed.
Some SLA and DLP printers work in an "inverted" scheme: the model is not immersed in the consumable, but "pulled" out of it, while the laser or projector is placed under the cuvette, and not above it. This approach eliminates the need to level the surface after each exposure, but requires the use of a cuvette made of a material transparent to ultraviolet light, such as quartz glass.
The accuracy of stereolithographic printers is extremely high. For comparison, the standard for vertical resolution for FDM printers is considered to be 100 microns, and some variants of SLA printers allow you to apply layers as thin as 15 microns. But this is not the limit. The problem, rather, is not so much in the accuracy of lasers, but in the speed of the process: the higher the resolution, the lower the print speed. The use of digital projectors allows you to significantly speed up the process, because each layer is illuminated entirely. As a result, some DLP printer manufacturers claim to be able to print with a vertical resolution of one micron!
Video from CES 2013 showing Formlabs Form1 stereolithography 3D printer in action: http://youtu.be/IjaUasw64VE
Stereolithography Printer Options
Formlabs Form1 Desktop Stereolithography Printer
As with FDM printers, SLA printers come in a wide range in terms of size, features and cost. Professional installations can cost tens if not hundreds of thousands of dollars and weigh a couple of tons, but the rapid development of desktop SLA and DLP printers is gradually reducing the cost of equipment without compromising print quality.
Professional installations can cost tens if not hundreds of thousands of dollars and weigh a couple of tons, but the rapid development of desktop SLA and DLP printers is gradually reducing the cost of equipment without compromising print quality.
Models such as the Titan 1 promise to make stereolithographic 3D printing affordable for small businesses and even home use at around $1,000. Formlabs' Form 1 is available now for a factory selling price of $3,299.
The developer of the DLP printer Peachy generally intends to overcome the lower price barrier of $100.
At the same time, the cost of photopolymer resins remains quite high, although the average price has fallen from $150 to $50 per liter over the past couple of years.
Of course, the growing demand for stereolithographic printers will stimulate the growth in the production of consumables, which will lead to further price reductions.
Go to the main page of the Encyclopedia of 3D printing
How to 3D Print | ichip.
 ru
ru Preparation
Using the Holes and Columns test pattern as an example, we will show how to properly prepare an object and print it on the Ultimaker printer. First of all, install the SketchUp 3D editor. Then you need to “teach” him to understand the STL format common in 3D printing. This is done using a plugin that can be downloaded from extensions.sketchup.com. After you have copied its file to disk, open SketchUp, go to the menu "Window | Preferences | Extensions", click on the "Install Extension" button and specify the location of the plugin file.
Creating our own object
In the Start SketchUp window, select the "Product design and Woodworking - Millimeters" template. The program will create a spatial coordinate system that can be enlarged or reduced by rotating the mouse wheel, and clicking on it can be rotated. The red axis shows the width of the item, the blue one shows the height, and the green one shows the depth. To create the rectangular shape of our test object, first draw out the main shape. To do this, select "Restangle" from the toolbar.
To do this, select "Restangle" from the toolbar.
A feature of the SketchUp program is that at the starting point of the object (in our case, in the center of the coordinate system), you need to click the mouse button and, without releasing it, drag. Place the cursor in the area between the green and red coordinates.
To precisely set the dimensions of the figure, simply enter "110;40" on the keyboard and press "Enter" - you will get a rectangle with a width and height of 110 and 40 mm, respectively. The 2D rectangle can then be formed into a 3D rectangle using the Push/Pull tool. Click on the rectangle and drag it up. To set the exact height to 10mm, simply key in the value "10" and then press "Enter".
Refine the shape
Now add columns and holes where the printer will show the accuracy of its work. To do this, use the "Circle" tool to draw circles on the surface of a rectangular shape. To achieve their exact location, create temporary guide lines and use a ruler. The exact size of the radius of the circle is entered using the keyboard.
The exact size of the radius of the circle is entered using the keyboard.
Circle rows can be rotated 180° with the Rotate tool and copied by pressing the Ctrl key. Now with the Pull/Push Tool, on one side of the rectangle, push the circles to get the holes, and on the other side, pull them up to get the columns.
From SketchUp to printer software
Your model is ready. Click "File | Export to DXF or STL. If there is no such menu item, it means that some error occurred during the installation of the STL plugin (see step 1). Confirm the prompts "Export entire model?" and "Export unit: Millimeters". Under "Export to DXF options" select "stl" format. Save the file with ".stl" extension. In the printer program (in our example, this is the Cura application for the Ultimaker device), load the model through the File | Load Model file…". After that, set basic settings such as print quality and media. Going to "File | Save GCode", save the model as a print job.
If something goes wrong while printing, go back to your computer and click on "Expert | Switch to full settings …” - here you can fine-tune settings for the printed object such as layer thickness, the degree of filling of the base, hanging elements and voids, as well as the speed and temperature of printing. Then copy the ".gcode" file to the SD memory card.
Then copy the ".gcode" file to the SD memory card.
Taping the Print Bed
Check your printer manual to see if you need to tape the print bed with self-adhesive film. In the case of the Ultimaker, this is necessary because the hot print head can melt the Plexiglas platform and prevent the finished item from being removed from it. A spool of adhesive tape is included with the device.
If you run out of it, use regular crepe tape instead. Take out the printing plate and make sure that the strips lie on it without wrinkles or overlaps. This works best if you align the next strip with the long side of the previous one and then press it firmly.
Getting Ready and Starting
Before each printing process, check the position of the print platform and correct it if necessary. The detailed manual for the printer (see wiki.ultimaker.com/Calibrate) spans many pages. In principle, it is important for you to adjust the four screws at the corners of the platform (see photo on the right) so that the distance between the print head and the surface of the platform is equal to the thickness of a regular sheet of paper everywhere.
Insert an SD card with the ".gcode" file stored on it into the printer controller and select "Card Menu". The display will list all ".gcode" files that the device finds on the card. After selecting the desired file, start printing.
Troubleshooting errors
When you first attempt printing, it is highly recommended that you regularly check the progress of the process and stop it if problems occur. The unfinished item becomes unusable. So, during our tests on the Ultimaker printer, there were sometimes delays in loading material. To temporarily stop the material feed, the printer pulled the plastic filament back a little.
The already heated plastic was held up in front of the extruder when re-feeding and caused a blockage. In this case, you must first pull out all the material from the top of the extruder. The hot nozzle should be cleaned carefully using two twisted strands of copper cable. After clearing the jam, try to find the cause of the printing error on the manufacturer's website.