How do you 3d print food
Food 3D printing Guide - how does it work and what can be done today
How does a food 3D printer work?The concept is the same as traditional 3D printing: a food 3D printer heats up edible ingredients before 3D printing them on the build plate, layer by layer. Another option, similar to SLS 3D printing, is to use ingredients in the form of a dry powder that is then solidified by the food 3D printer.
Discover our selection of the best food 3D printers to 3D print food or chocolate at home.
3D printing of sweet desserts
3D printing chocolateBecause of its natural physical properties, chocolate suits 3D printing perfectly. It melts at the temperature of the human body and solidifies as soon as it cools down. It is therefore easy to create customized chocolate desserts without changing the chocolate’s original taste.
Choc Edge has already released two versions of its 3D printer to make all types of chocolate designs. The 3Drag printer uses FDM technology. It is possible to 3D print almost any chocolate design that the user creates.
3D printing with sugarSugar is a malleable material that can take many forms and colors, and it is also compatible with 3D printing. Some research groups such as The CandyFab Project or the Sugar Lab from 3D Systems have developed 3D printers specialized in the printing of sugar and candies with creative 3D shapes, as shown in photos on their websites.
Sugar candy 3D printed with a Chefjet 3D printer from 3D Systems.Food 3D printing: a marketing tool
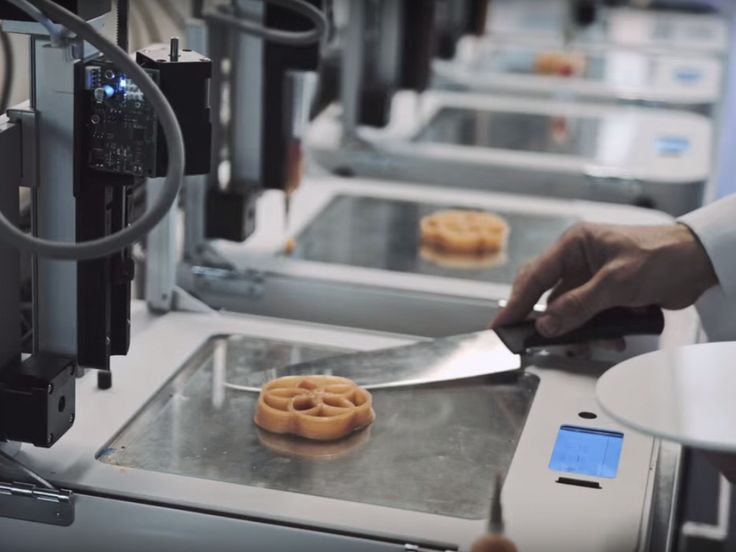
Custom 3D printed biscuitsFood 3D printing provides the opportunity to satisfy customers to see their own customized cookies created before their eyes.
This is how Oreo chose to exhibit 3D printers during the SXSW 2014 festival, allowing customers to choose the color of their Oreos’ cream.
Oreo at the SXSW festival with 3D printed cream.3D print edibles that look like you
With the best 3D scanners it is possible to create a 3D model of your own head, and to 3D print it with edible food. Some manufacturers provide the opportunity to eat pancakes or waffles with the shape of your face.
A 3D printed “face pancake” by the design company Kinneir Dufort.For one of their marketing campaigns, mayonnaise manufacturer Hellmann’s even offered customers the possibility to 3D print their face on burger buns.
Create your own product line3D printing enables the consumer to participate in the creation of a new range of products. Barilla, for example, organized a contest in 2014 to reward the best 3D model design for a new Barilla pasta.
In two months, designers sent out 216 pasta proposals from 20 different countries, and the winning design was sold by Barilla as a new product!
Barilla new pasta design by Loris Tupin, French designer at the Barilla contest.
3D printing for the food industry
100% 3D printed mealsFoodini 3D printers sold by Natural Machines and Bocusini, which successfully ran a Kickstarter crowdfunding campaign, are among the most successful 3D food printers.
These two 3D printers allowed for the very first fully 3D printed meals. These are made of successive layers, in the same way that pizzas are prepared.
The dough is cooked during 3D printing, while the tomato sauce (made of powder), water, and oil are added, followed by a layer of protein.
3D printing meatFurther pushing the boundaries of 3D printing, some scientists want to use biomaterials and animal stem cells to create 3D printed meat.
Scientists behind this approach point out the huge amount of resources needed for meat production through livestock and highlight food 3D printing as a solution to the growing needs of the world’s growing population.
Steak chips by Modern Meadow.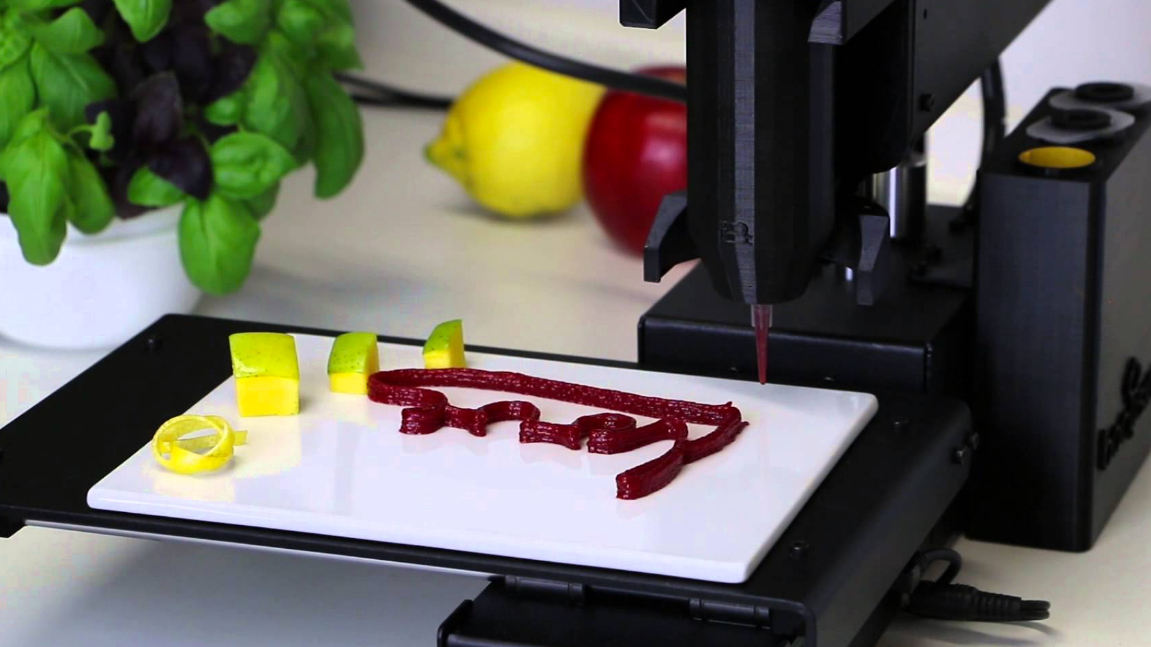
Brooklyn-based Modern Meadow has already successfully 3D printed steak chips made from synthetic animal protein. The company has attracted the attention of New York’s wealthiest investors, including the Rockefellers. They are now even 3D printing vegan leather.
3
D printing organic foodChloé Rutzerveld, a Dutch culinary designer, managed to 3D print a structure made of a succession of layers of dough, made of edible soil.
Organic 3D printed food by Dutch designer Chloé Rutzerveld.Mushrooms seeds, spores, and yeast are then added after a few days to offer an innovative and eco-friendly snack.
Food 3D printing in space
The strength of 3D printing is that they enable the production of a wide variety of products with reduced amounts of raw material.
Based on this simple principle, engineers see 3D printing as the ideal technology to feed astronauts on long space missions. Edibles can even last for 30 years in special plastic bags.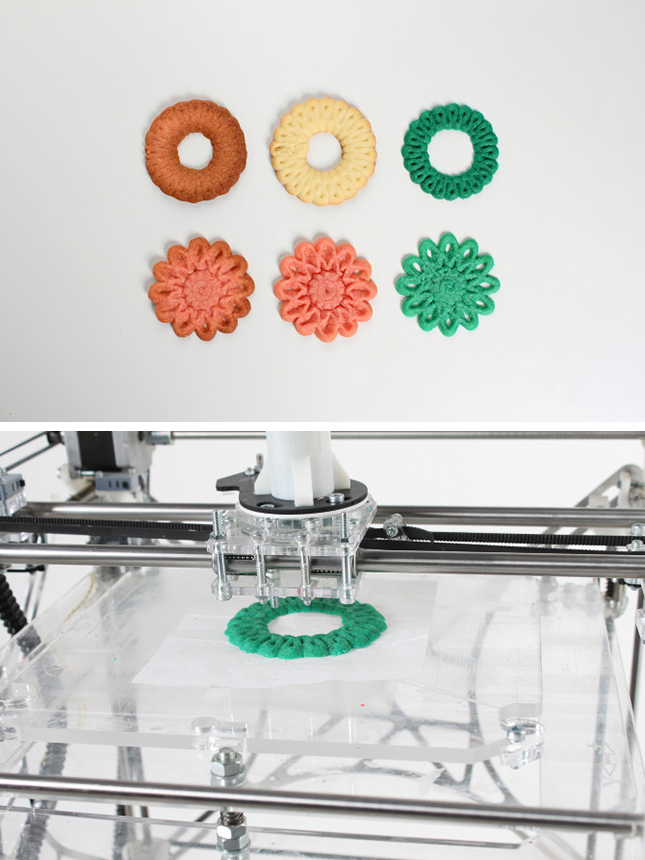
3D printed food for seniors:
The ‘Performance’ projectThis initiative plans to make food for the elderly with a 3D printer. Some companies such as Gel Manche already offer products with a different texture, called “smooth food”. This technology restores the product to its original form, but its texture is soft and can be swallowed very easily by people with chewing or swallowing difficulties.
Gel Manche’s 3D printed food menu.How 3D Printing Food Works
How 3D-printed food could change the way we cook and eat
Since the 1980s, steady progress has been made in 3D printing materials, from thermoplastics to metals and now even food. Complicated cake decorations and intricate chocolates take advantage of the complex geometries possible with additive manufacturing (AM) processes. Thanks to multi-nozzle printers, it is possible to print everything from beet, spinach and carrot salad towers to pizzas. How much more appealing might children find soup laced with 3D-printed dumplings shaped like cat paws?
How much more appealing might children find soup laced with 3D-printed dumplings shaped like cat paws?
How to 3D print food
In the world of additive manufacturing, 3D printers extrude thermoplastic and even titanium filaments. When 3D-printed food is extruded, it is deposited by a nozzle guided by an STL file derived from CAD data. The digital information directs the nozzle to deposit “build material” one layer at a time. The extrusion process in a 3D-binding printer requires food of even consistency and proper viscosity for two key reasons: First, it must emerge smoothly from the nozzle. Second, it must maintain its shape upon deposition.
At first thought, the idea of sitting down to a meal of blended, extruded food is uninspiring until one realizes that extruded food is already both commonplace and tasty. pasta, sausages, breadsticks and certain breakfast cereals are all produced via extrusion. The path to tasty extruded food of consistent quality is already well established.
Direct 3D printing of food via extrusion
So exactly how does 3D-printed extruded food make a contribution to gastronomy and the culinary arts?
Chocolate is one of the tastiest of edibles that can be extruded through a heated nozzle to create intricate and creative designs direct from CAD data. The design freedom and customization that 3D printing offers in the food industry is unprecedented.
Traditionally, chocolate creations are produced by pouring liquid chocolate into molds. However, there are two inherent limitations to this process. First, molds are cost-effective for quantity production rather than limited runs. Second, design intricacy is limited by what can be successfully pulled from the mold.
Since no mold is required, it is far easier to maintain the geometry of 3D-printed chocolates from production to consumption. It is also possible to calibrate chocolate’s viscosity so it will maintain geometry as it is laid down on the print bed, layer after layer. AM processes allow for the creation of truly intricate, one-of-a-kind chocolate products. It is even possible for consumers to customize an edible item at a computer and then see their design materialize.
AM processes allow for the creation of truly intricate, one-of-a-kind chocolate products. It is even possible for consumers to customize an edible item at a computer and then see their design materialize.
Belgian chocolate is world-renowned for its quality. Now, a factory in Belgium called Miam (“yum” in French) is using four specialty 3D printers to create ready-to-eat delectable edibles from milk chocolate, dark chocolate or white chocolate. A nearby brewery commissioned The Miam Factory to 3D print chocolate beer bottles that served as memorable awards following an Easter egg hunt.
It is also easy to see how smooth, fluid products like cream cheese and mashed potatoes are amenable to the 3D-printing process. Extrusion systems with multiple nozzles allow for more complex entrees. For example, a multi-nozzle print head can automate pizza-making by depositing dough, sauce and cheese. The same process is possible for extruding different cake batters to create elaborate baked goods.
Mold Printing Food
Some foods that begin as liquids cannot be extruded. Flavored gelatin is one example of a food that benefits from using another approach to 3D-printed food. For example, stereolithography (SLA) may take data directly from CAD software to create molds that are then used in food production.
3D-printed molds made of food-safe silicone are also used with chocolate and cake batter. For example, a Ukrainian pastry chef uses 3D printing to fabricate unique spherical cake molds.
Is 3D-Printed Food Safe?
However it is produced, food for human consumption must meet stringent federal requirements designed to ensure safety. When the Food Safety and Modernization Act became law in 2011, those regulations became more stringent than ever. The FSMA, the most sweeping food safety legislation in seven decades, meshes well with the potential for safe 3D-printed food. Eventually, FSMA regulations regarding food safety may amplify the demand for 3D-printed food. What's more, a custom nutrition process may help those with serious food allergies since it is possible to replicate 3D-printed food with such precision.
What's more, a custom nutrition process may help those with serious food allergies since it is possible to replicate 3D-printed food with such precision.
Is Anyone Eating 3D-Printed Food?
Is anyone eating 3D-printed food? The answer is a resounding yes! Novelty items earlier produced by consumer printers have paved the way for professional printers to produce food in restaurants and commercial kitchens.
At one gourmet restaurant in the United Kingdom, everyone is eating 3D-printed food because that is all that is served. The enterprising entrepreneurs at London’s Food Ink decided to push additive manufacturing to its logical extreme. Everything is 3D printed, including the utensils, plates, tables and chairs. At Miramar, a gourmet restaurant in Spain, food printers take on more mundane tasks, freeing chefs to better focus on their creative cuisine.
There is also a practical side to 3D-printed food. “SmoothFood” is already being served at more than 1,000 German nursing homes.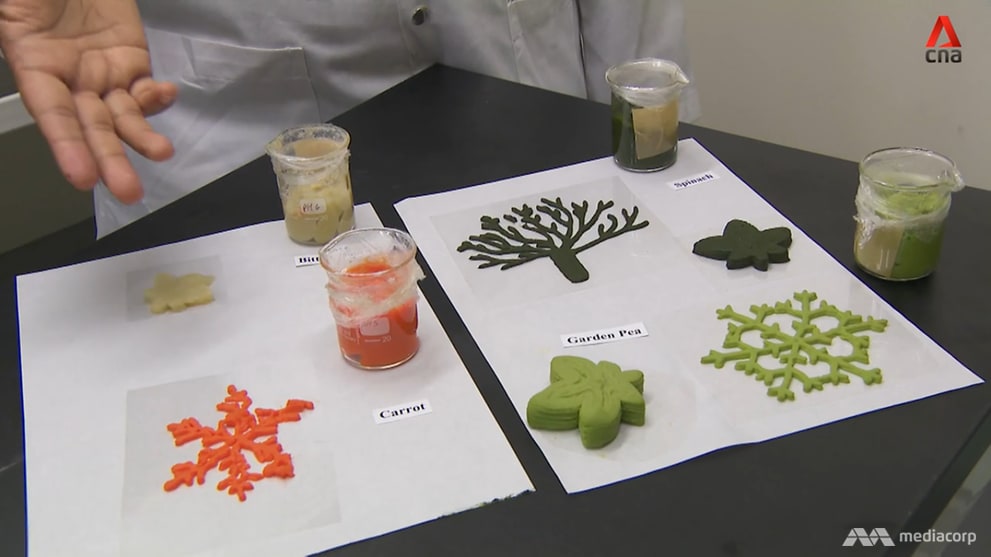 Extruded food meets the needs of older residents who have difficulty chewing and swallowing. Various foods, including pork, chicken, potatoes, pasta and peas, are first cooked and then pureed before they are extruded and printed into recognizable shapes. 3D printing allows for food presentations that are visually appealing and therefore appetizing. With the infusion of $4 million from the European Union (EU), 14 companies in five countries are collaborating to expand the reach of SmoothFood.
Extruded food meets the needs of older residents who have difficulty chewing and swallowing. Various foods, including pork, chicken, potatoes, pasta and peas, are first cooked and then pureed before they are extruded and printed into recognizable shapes. 3D printing allows for food presentations that are visually appealing and therefore appetizing. With the infusion of $4 million from the European Union (EU), 14 companies in five countries are collaborating to expand the reach of SmoothFood.
3D-printed food offers both terrestrial and extraterrestrial appeal. If you think the idea of 3D-printed food is “out of this world,” so does NASA. In 2013, it awarded a Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) Phase I contract to a Texas company so it could explore the potential for printing food on deep space missions. Astronauts would use a modest-sized 3D printer to transform space-saving bulk foods into tasty entrees.
The future of 3D-printed food
In the future, 3D-printed food may help feed the world’s population in a simultaneously sustainable and nutritious manner.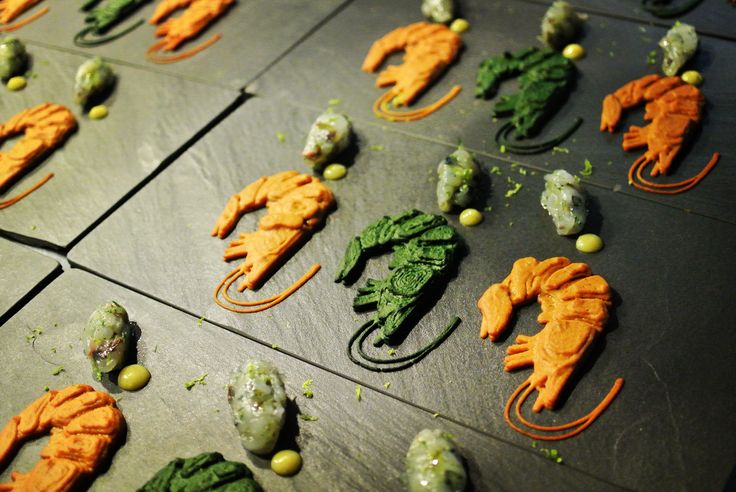 For example, researchers at the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research in Germany print food using a type of algae rich in protein and antioxidants. Expanding protein sources for a growing global population helps ensure ingredient availability.
For example, researchers at the Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research in Germany print food using a type of algae rich in protein and antioxidants. Expanding protein sources for a growing global population helps ensure ingredient availability.
Can a 3D printer be used to print food?
3856 views Posted on: 06/24/2019
Author: 3D4U.COM.UA
Three-dimensional printing is in demand today in many areas of human activity, including the creation of ready-made food with its help. If a printer with a plastic extruder can only create replicas of food, despite the fact that the price of 3D prototyping is quite low, some modern models can also print full-fledged meals. So, the ZMorph company has developed a device that allows you to change the print head with a plastic string to a cartridge for dough, pasta or chocolate. nine0003
The Choc Edge 3D printer is for chocolate printing only. As a rule, the extruder draws a contour with a thick mass, which is heated so that it does not freeze in the nozzle.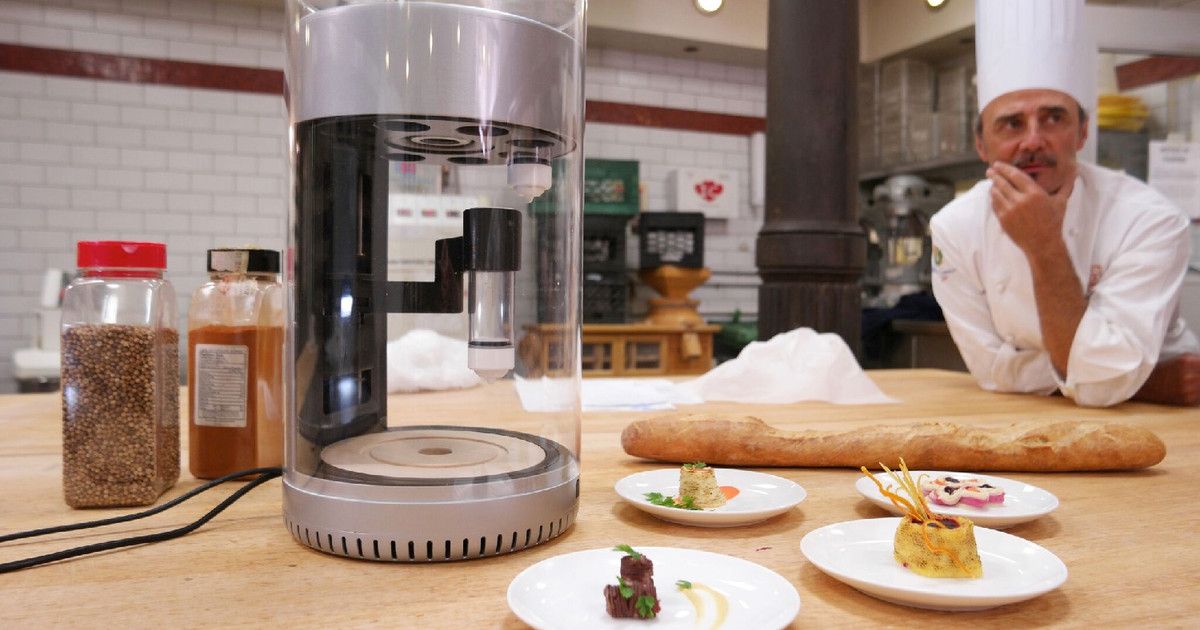 However, by setting a low speed to allow the already formed pattern to harden, you can apply new layers and print the product up to a certain height. Another printer, Chocola3D, can create not only chocolate products, but also beautiful cream desserts or pasta dishes.
However, by setting a low speed to allow the already formed pattern to harden, you can apply new layers and print the product up to a certain height. Another printer, Chocola3D, can create not only chocolate products, but also beautiful cream desserts or pasta dishes.
Cakes can only be called food conditionally, a diet made entirely of them will not be good for health, since a person also needs hot food. The Pancakebot 3D printer only prepares pancakes and pancakes, depending on the dough in the cartridge, and immediately fries them on a metal baking sheet. At the same time, he can draw any contours, thanks to which snacks are very interesting in shape. Soon it will be possible to supply an ordinary household device with the Discov3ry extruder developed by Structur3d for chocolate and icing, especially since the price of a 3D printer in Ukraine is quite affordable. nine0003
However, 3D printing technology researchers have gone further, and today good results have already been achieved in obtaining special nanocellulose, which is well absorbed by the body.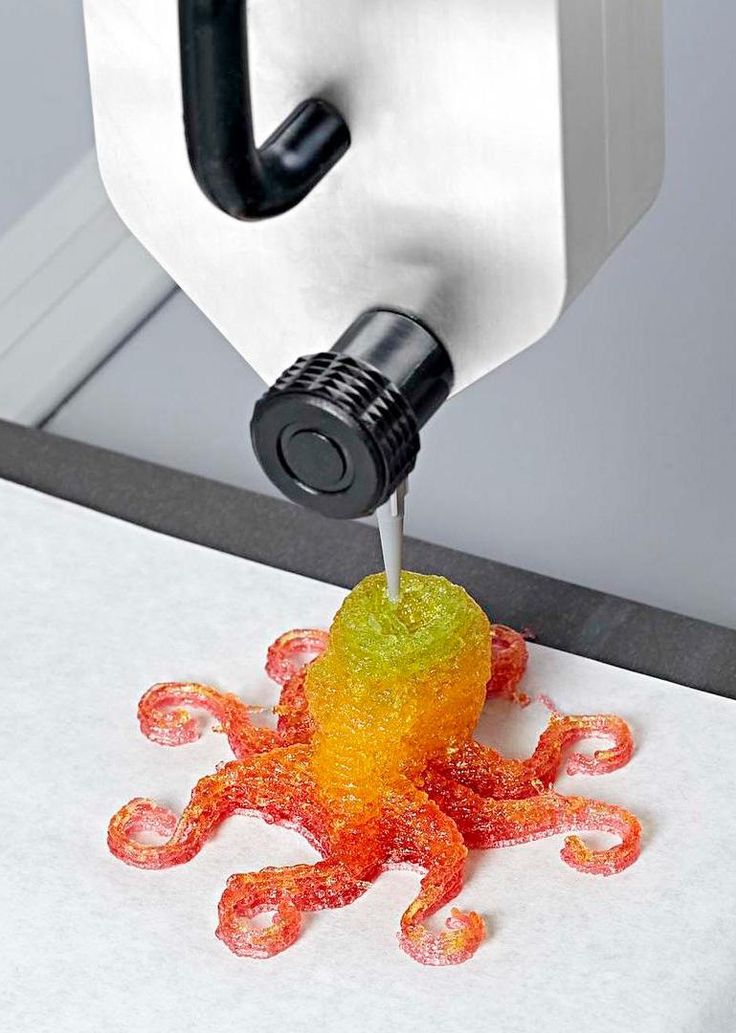 Any plant organic matter can be processed into it. This product, as a binder and filler, is mixed with precisely measured portions of proteins, fats and carbohydrates to create a particular dish. Today, such a printer is capable of printing only dough-like mass, but in the future it is planned to use laser processing to shape the appearance of any dish right in the process of creation. nine0003
Any plant organic matter can be processed into it. This product, as a binder and filler, is mixed with precisely measured portions of proteins, fats and carbohydrates to create a particular dish. Today, such a printer is capable of printing only dough-like mass, but in the future it is planned to use laser processing to shape the appearance of any dish right in the process of creation. nine0003
Related items
- Top 20 interesting toys for children on a 3D printer.
Category: 3D printing
02/15/2022
11398 views
What kind of toys can be created with a 3d printer? What are the advantages of 3d printing toys at home? In this article you will find...
Read more - 12 common 3D printing mistakes to avoid.
4879 views
As an industry, 3D printing is evolving every day, so it's important to know all aspects of this technology today. In this...
Read more - 9 romantic 3D printed gifts for Valentine's Day.

Category: 3D printing
02/09/2022
1905 views
3D printing can help you create unique and personalized gifts for your significant other. Compilation 9...
Read more - What can be printed on a 3D printer?
Category: 3D printing
03.02.2022
2577 views
When hearing about a 3D printer for the first time, most people are interested in the question of what can be printed on a 3D printer. In this article...
Read more - Why Succeeding With a 3D Printer Is Easier Than You Think.
Category: 3D printing business ideas
02/01/2022
1956 views
Arguments in favor of a business with a 3D printer. Why the first steps in such a business are much easier to take than in any other.
Read more
Printing food on a 3D printer - New technologies
More recently, the very idea of inventing artificial food could only be heard in science fiction films and works, it was there that we could see how edible dishes suddenly appeared on a tray from some incomprehensible machines, made from nothing at all.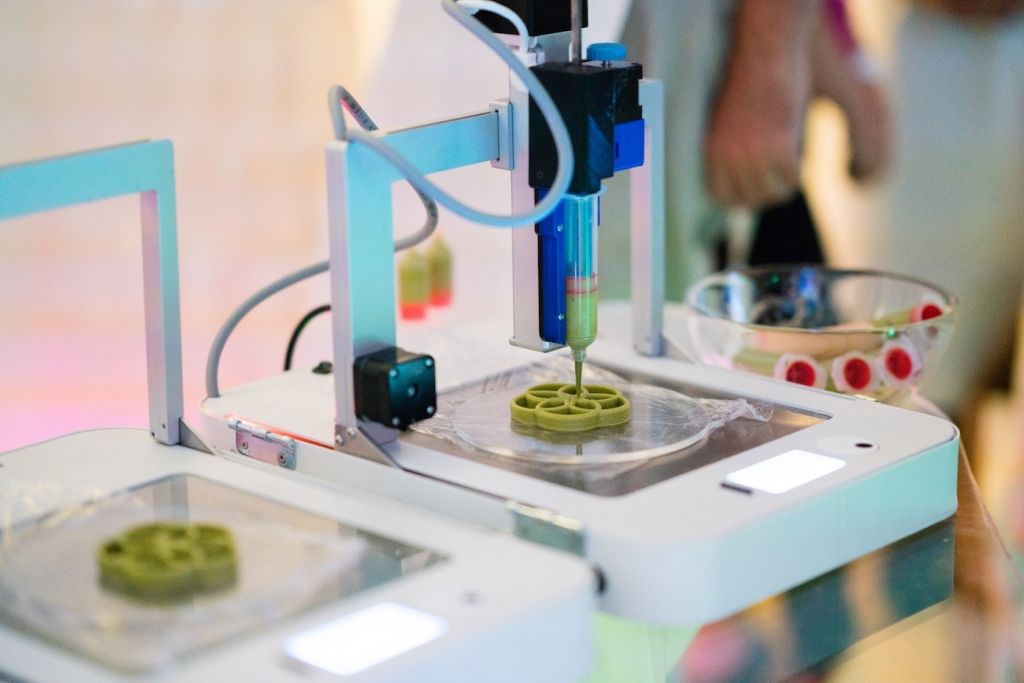 nine0003
nine0003
The cheeseburgers and hamburgers presented in these pictures are not real, they were not made in the McDonald chain, if you look closely at their structure, you will notice that they seem to stick together and do not have clear boundaries and fillings, and all because that they were ... printed on a 3D printer.
Well, it's time to take a closer look at this new miracle invention from Texas-based Systems and Materials Research Corporation, which, with the support of NASA, promises to print pizza on its new 3D printer by the end of this year. nine0003
The device, developed by Systems and Materials Research Corporation, is capable of delivering tasty and balanced meals based on several powders and pastes. First, the printer mixes all the ingredients in certain proportions, after which the resulting substance falls in layers on a heated plate at the bottom of the device.
Technically, pastes consist of the main ingredients: proteins, carbohydrates and fats, the combination of which achieves the desired consistency, color and taste.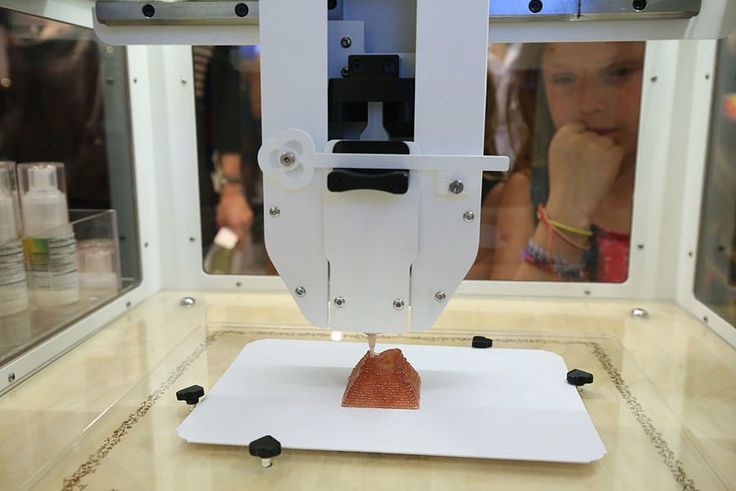 So far, it is impossible to print organic food, such as an orange or an apple, their "internal device" consisting of living cells is too complicated, but this, according to the developers, is just a matter of time. nine0003
So far, it is impossible to print organic food, such as an orange or an apple, their "internal device" consisting of living cells is too complicated, but this, according to the developers, is just a matter of time. nine0003
But meat lovers can now sleep, or rather, eat in peace, the meat has already been printed, and for this it was not necessary to kill a single animal, which is very welcome to wildlife advocates. I personally have a lot of doubts about the taste qualities of the resulting edible print, but company representatives assure that the taste is exactly what it should be.
They have been trying to fake the taste of products for a long time with the help of various flavors, but as we all know, the difference between natural juice and flavors that are identical to natural is huge, it can only be missed by a person who has never in his life did not taste the taste of this real product. nine0003
The lead developer of the device, Anjan Contractor, believes that soon such printers will appear in every kitchen, and in stores, instead of the usual food, special cartridges will be sold.