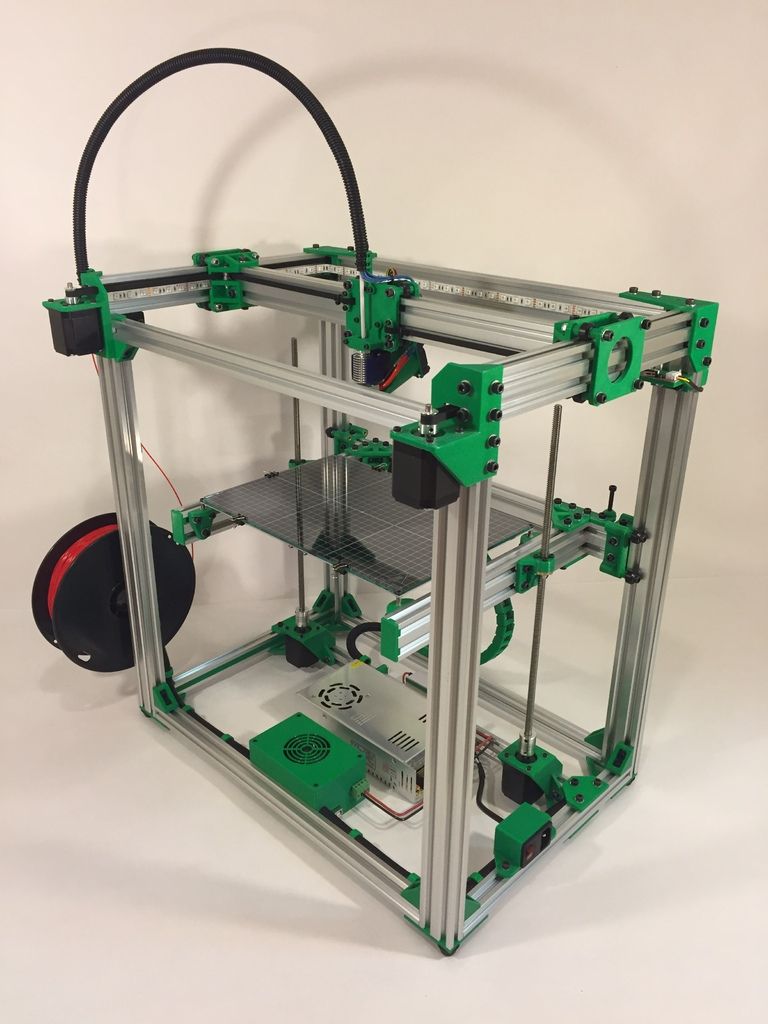
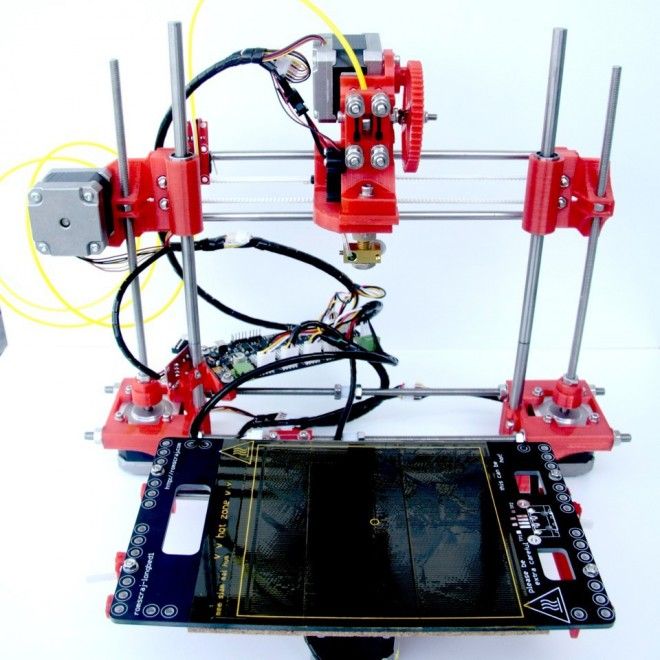
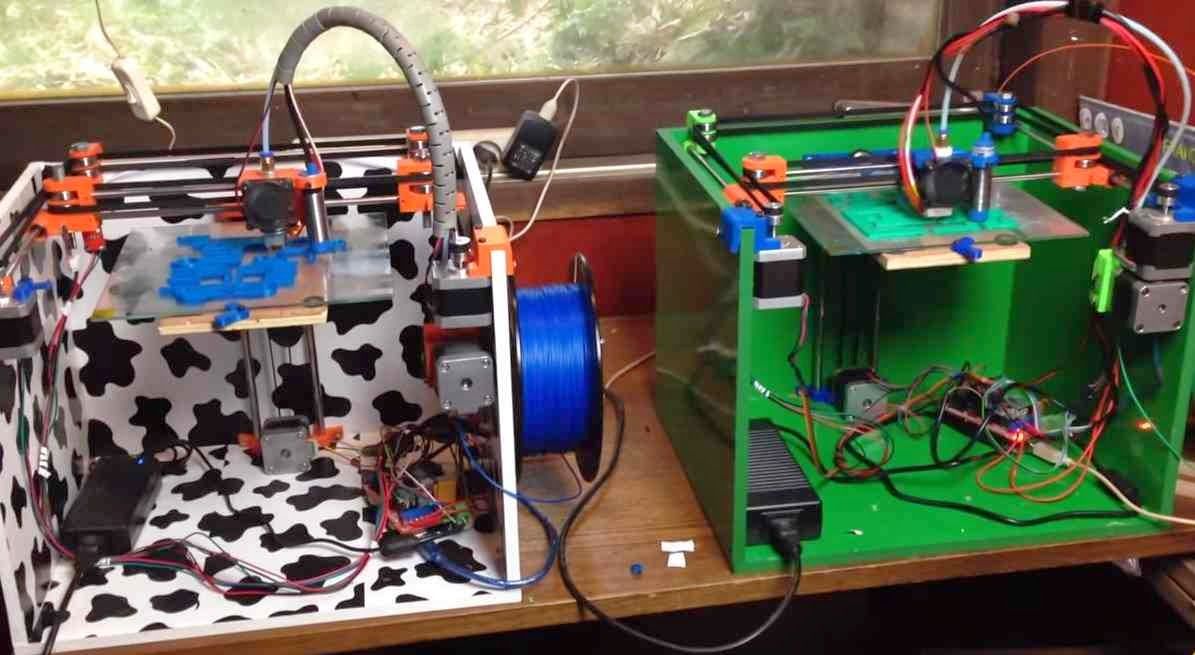
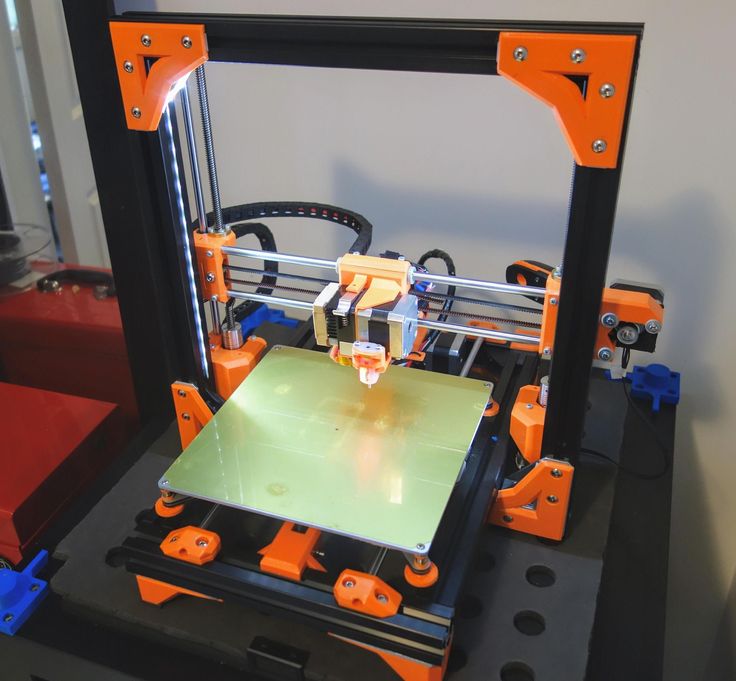
Food grade 3d printers
The Essential Guide to Food Safe 3D Printing
3D printing offers unparalleled design freedom to produce custom parts and complex or organic shapes that would be costly or impossible to manufacture with traditional manufacturing methods.
These benefits can be compelling for a range of food-related applications. However, if 3D printed parts are intended for food contact items, you‘ll have to consider safety practices and regulations to avoid contact with toxic substances and prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria.
Food safe 3D printing is possible and the variety of materials approved as food safe is increasing, but there is a high degree of ambiguity around the workflows and finding the appropriate applicable regulations can be a challenge.
Read on for an introduction to food safety, food safety considerations for 3D printing, and a variety of methods to produce food safe products with common 3D printing processes, including stereolithography (SLA), fused deposition modeling (FDM), and selective laser sintering (SLS).
Please note
No Formlabs resins are food safe unless users take additional steps.
Video Guide
Having trouble finding the best 3D printing technology for your needs? In this video guide, we compare FDM, SLA, and SLS technologies across popular buying considerations.
Watch the Videos
To begin, it’s important to clarify a few key terms:
- Food grade means that the material is either safe for human consumption or permitted to come in contact with food.
- Food safe means that a food grade material meets the requirements determined by the intended use and will not create a food-safety hazard.
- Food contact surfaces include any surface that may come into direct contact with food. These surfaces must be made of nontoxic materials and designed to withstand the environment of their intended use, including exposure to cleaning compounds, sanitizing agents, and cleaning procedures.

Food grading and food safety concern a specific way to ingest parts, called migration. Particles as small as a few nanometers and up to several hundred nanometers may get transferred each time various materials encounter with each other, for example from components of the 3D printer to the 3D printed object, and from the object to the food.
Because migration levels are very low on occasional contact, food grading typically concerns items that are in prolonged contact with food such as containers, straws, utensils, plates, and food molds. Different testing institutions will adhere to different government-imposed risk tolerances and approved substances, which for the US is described by the FDA CFR 21 and for the EU in guidelines 10/2011.
Look for these labels indicating FDA and EU approval. Beware that a material being ‘compliant with’ doesn’t mean that it is explicitly approved by the institutions, so always check the technical datasheets for a certificate.
To be considered food safe according to the FDA Food Code, a material has to meet the following requirements:
- No migration of deleterious substances
- Does not impart colors, odors, or tastes
- Safe under normal use conditions
- Durable, corrosion-resistant, and nonabsorbent
- Sufficient in weight to withstand repeated washing
- Finished to have a smooth, easily cleanable surface without breaks and sharp internal angles
- Resistant to pitting, chipping, crazing, scratching, scoring, distortion, and decomposition
- Accessible to inspection
Any FDA or EU approved material includes not only the raw polymer but also the additives or masterbatch.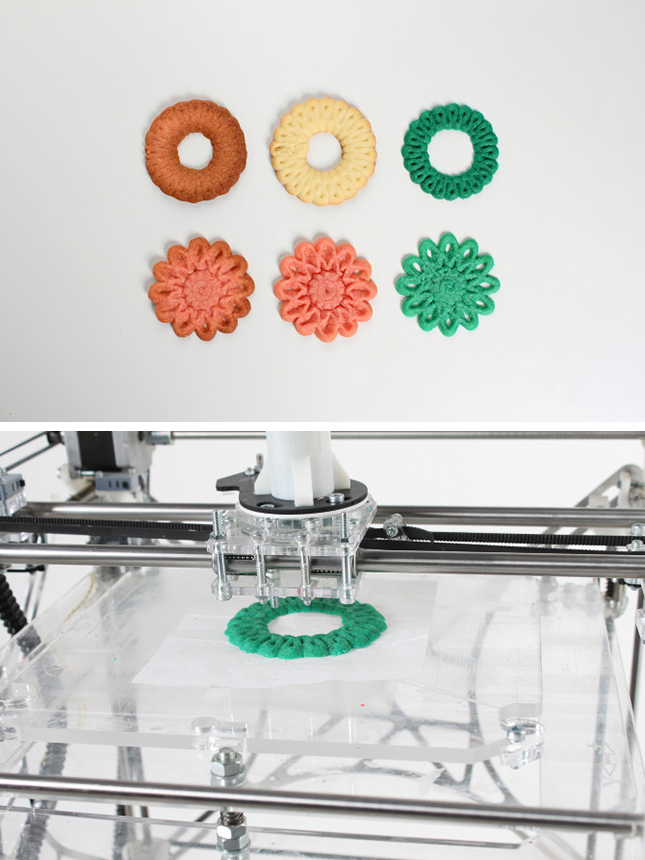 These might contain components such as plasticizers, impact and heat distortion modifiers, UV-stabilizers, flame retardants, anti-fouling, anti-static, anti-slip, foaming and clarifying agents, anti-oxidants, aromatic nucleators, carbon alloys, phosphorescents, fillers, thickeners, chain extenders, metal deactivators, dyes, and a carrier resin.
These might contain components such as plasticizers, impact and heat distortion modifiers, UV-stabilizers, flame retardants, anti-fouling, anti-static, anti-slip, foaming and clarifying agents, anti-oxidants, aromatic nucleators, carbon alloys, phosphorescents, fillers, thickeners, chain extenders, metal deactivators, dyes, and a carrier resin.
A 3D printed part can turn into a petri dish squirming with bacteria within weeks. Even though some materials will survive the dishwasher, so will dangerous bacteria such as E. coli and salmonella that live in the little nooks and crannies. Some toxic molds find favorable growth conditions on several types of plastic and are hard to remove. Neither cleaning with bleach nor microwaving your polymers is an option for eliminating germs.
While bacteria buildup might not be an issue for disposable items, if you’re planning to create a part for long-term use, using a food safe coating is highly recommended.
The best option to reduce the risk of particle migration and bacteria buildup is by dip coating the 3D printed parts with a food grade epoxy or polyurethane resin, such as Masterbond’s EP42HT-2FG or ArtResin or an FDA approved PTFE (known as Teflon®) to seal their surface.
However, note that coating also doesn’t guarantee food safety for prolonged use as not all of these coatings are dishwasher safe, and they may degrade over time, exposing the original, potentially non-safe surface.
Most 3D printing materials have a low heat deflection temperature (HDT), which means that the 3D printed parts might become brittle and crack, or deform and warp at elevated temperatures. If you’re planning to clean a 3D printed part in a dishwasher, make sure to double check that the material is dishwasher safe and if there are any specific recommendations for washing temperature.
As particles might migrate from components of a 3D printer to 3D printed parts, it is crucial that any components that might come in contact with the 3D printing material or the part are food grade and do not contain or leach harmful chemicals.
This includes taking precautions when using multiple materials, as some materials previously used in the 3D printer might have contained toxic particles and made contact with some components.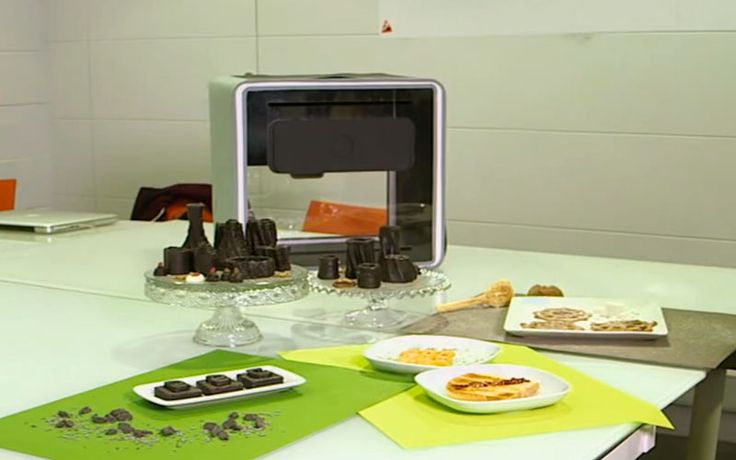
Many 3D printing materials are not food safe and might contain toxic chemicals. Only use materials to 3D print parts intended for food contact that are certified for food safety.
As may be expected, the risk of migration is higher if the food is exposed to the 3D printed part for an extended time period. In general, try to limit food contact time and take further precautions for parts that will be in contact with food for longer periods of time.
Think about the reason why you’d like to use 3D printing for a food contact item. If it’s to create custom shapes and forms, in most cases, there are indirect ways to use 3D printing to create these custom parts, for example with molding. See an example in the next section.
SLA 3D printing uses a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization, resulting in parts that have the highest resolution and accuracy, the clearest details, and the smoothest surface finish of all plastic 3D printing technologies.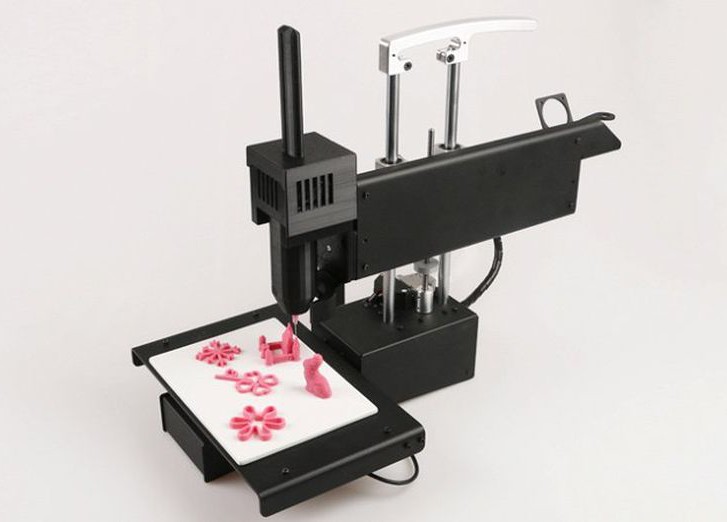
Is resin food safe? The answer is no. Substances may migrate from SLA parts which makes none of the resins and printed parts food safe by default. While some resins for dental and medical applications are certified biocompatible, that doesn’t mean that they’re food safe. These materials are certified for specific applications and should not be used for food contact products.
SLA parts have a smooth surface finish that makes it easier to use coatings to seal their surface and prevent the buildup of bacteria. The factors which affect the ultimate smoothness of a part include resin type, layer thickness, build orientation, mesh triangulation resolution of the 3D model, and the curing profile of the SLA resin. Printed parts require washing and post-curing according to the manufacturer's instructions before the coating is applied. However, note that coatings don’t guarantee food safety, as the coating may interact with the resin or degrade over time, exposing the original, potentially non-safe surface.
White Paper
Looking for a 3D printer to realize your 3D models in high resolution? Download our white paper to learn how SLA printing works and why it's the most popular 3D printing process for creating models with incredible details.
Download the White Paper
Creating custom molds is a common way to leverage the benefits of SLA 3D printing to produce highly detailed custom parts without having the 3D printing parts come into direct contact with food. While SLA 3D prints aren’t suitable for directly molding foods, SLA 3D printers are perfect tools to create mold negatives, which can be vacuum formed using food safe plastic.
The tools and techniques for creating 3D printed food molds are easy to master, and the results are often stunning.
3D printed molds for thermoforming and silicone enabled the creation of unique shapes and designs.
Learn more about creating molds for vacuum forming in our in-depth tutorial.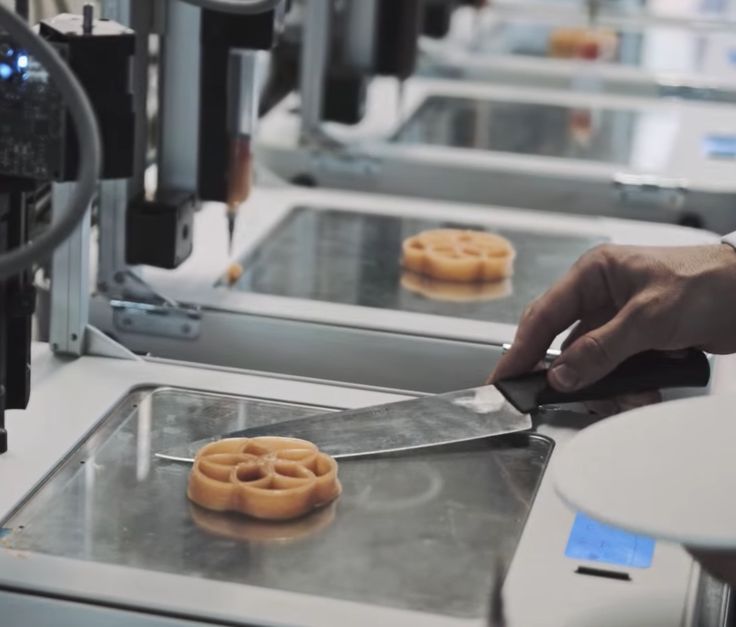
Electroplating is the process of coating parts with metal using an electric current. The process is most commonly used for decorative purposes or to prevent corrosion by creating a durable surface.
SLA parts are ideal for electroplating due to their smooth surface finish. However, as plastics are nonconductive surfaces, SLA 3D prints have to be rendered conductive by coating with graphite, conductive lacquer, electroless plate, or a vaporized coating.
Food safe metal coatings are available, but as the process involves various chemicals, making sure that the workflow is approved for food contact is the developer’s own liability.
SLA 3D printing offers the unique possibility to produce ceramic parts. After 3D printing, parts can be fired in a kiln to burn out the resin and form a true ceramic part that is strong and heat-resistant. With subsequent food safe glazing, the parts will become more hygienic and resistant to most chemicals.
A variety of food safe glazes are available on the market, but make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions in accordance with food safety guidelines.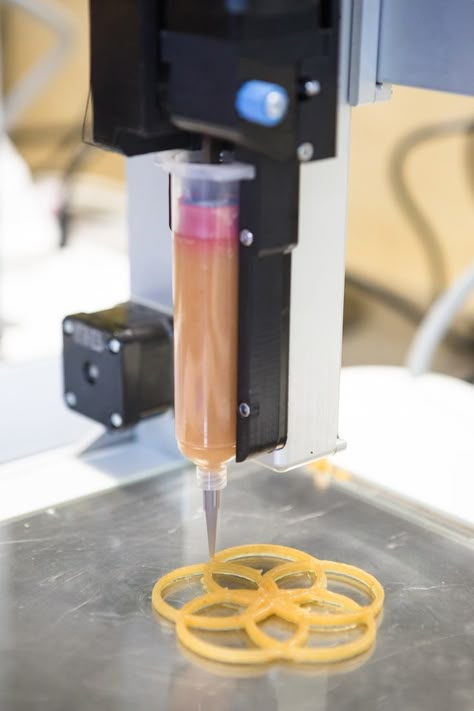
3D printing in ceramics is ideal for fabricating complex geometries that wouldn’t be possible by hand.
Learn More About Ceramics
Sample part
See and feel Formlabs quality firsthand. We’ll ship a free sample part to your office.
Request a Free Sample Part
FDM is a 3D printing process that builds parts by melting and extruding thermoplastic filament, which a print nozzle deposits layer by layer in the build area.
The extruded material is circular in cross-section, which leaves very narrow crevices in between layers with a depth directly proportional to layer height. It is recommended in any case to print at the lowest feasible layer height for food safe parts.
Consequently, the main challenge with FDM parts is avoiding the buildup of bacteria. To be truly food safe in the long term, an FDM 3D print needs to have a smooth surface. Chemical smoothing with solvents like acetone, d-Limonene, or ethyl acetate removes many of the irregularities of the print resulting in a smooth, glossy appearance.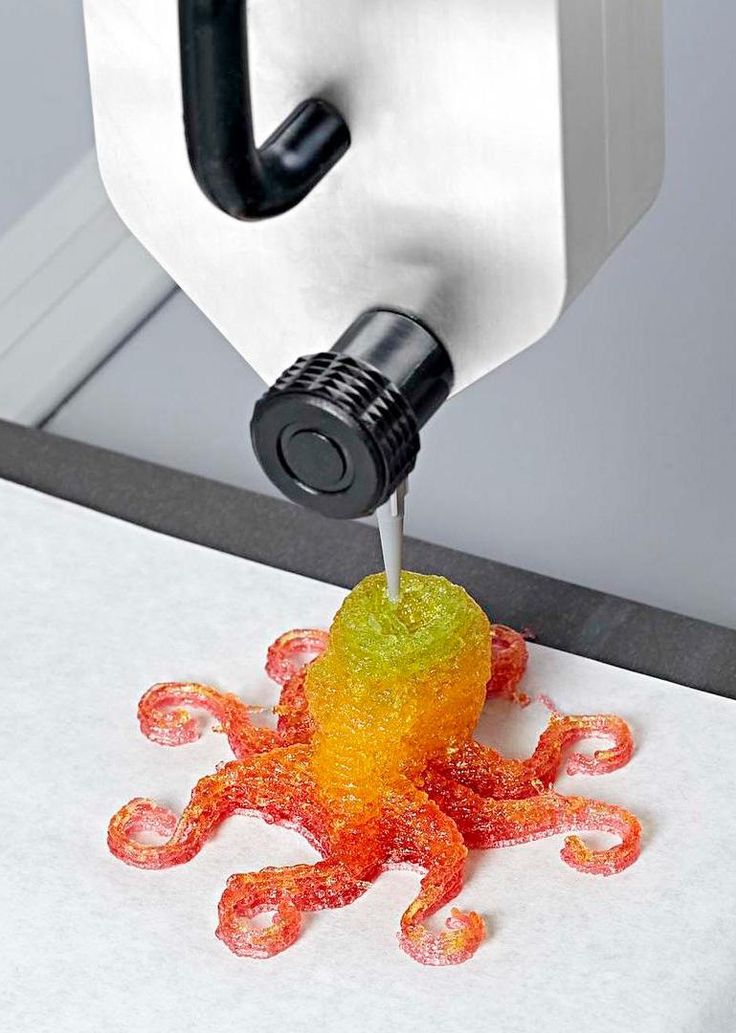 However, applying a subsequent food safe coating is still highly recommended.
However, applying a subsequent food safe coating is still highly recommended.
Layers showing on FDM (left) and SLA (right) 3D prints.
Food grade filaments do not contain any composite particles so will not wear down the nozzle into the print. Nevertheless, avoid brass nozzles that contain lead and use a dedicated stainless steel nozzle instead for all food contact items.
Always check the compatibility of your 3D printer’s components with the filament. For example, PEI is a material that is FDA compliant and offers great mechanical benefits but needs to be processed at over 300 °C, which requires a specific printer solution.
The most common questions around FDM food safety concern two popular materials. Is PLA food safe? Is ABS food safe? The answer is, it depends.
Food safe 3D printing filaments include PLA, PP, co-polyester, PET, PET-G, HIPS, and nylon-6, as well as some brands of ABS, ASA, and PEI. Having to run parts through the dishwasher rules out PET, nylon, and PLA because these plastics soften and distort around 60–70 °C. For applications involving hot liquids, co-polyester, High Temperature PLA or PEI are most suited.
For applications involving hot liquids, co-polyester, High Temperature PLA or PEI are most suited.
While not reflected in the regulations, some studies suspect that polystyrene may leach styrenes, co-polyesters might cause health concerns and that food grade FDM filaments might lose their safe status due to oxidation and thermal degradation from the printing process.
| Filament | Brand | FDA | EU | Smoothable | Dishwasher safe | Hot liquids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Adwire PRO | Approved | NA | Yes, acetone | Yes | Yes |
| Innofil3D | Approved except red, orange, and pink | Approved except red, orange, and pink | Yes, acetone | Yes | Yes | |
| ASA | Innofil3D | NA | Compliant | Yes | No | |
| Bendlay | Orbi-Tech | NA | Compliant | Yes, brake cleaner | No | No |
| Biocompound | Extrudr GreenTEC | NA | Compliant | |||
| Co-Polyester | Colorfabb XT | Approved | Compliant | No | Yes | Yes |
| HIPS | Easyfil | Compliant | Compliant | Yes, d-limonene | Yes | No |
| Fillamentum | NA | Compliant | Yes, d-limonene | Yes | No | |
| InnoFil3D | Approved | Approved | Yes, d-limonene | Yes | No | |
| Nylon | Taulman Nylon 680 | Compliant | NA | No | No | |
| PEI | ULTEM® 1000 | Compliant | NA | Yes | Yes | |
| PET | InnoPet EPR | Approved except red and orange | Approved except red and orange | Yes, ethyl acetate | No | No |
| Refil | Approved | NA | Yes, ethyl acetate | No | No | |
| Taulman T-Glase | Approved | NA | Yes, ethyl acetate | No | No | |
| Verbatim | Compliant | NA | Yes, ethyl acetate | No | No | |
| PET-G | Extrudr MF | NA | Approved | Yes, ethyl acetate | No | No |
| HDGlass | Approved | Approved | Yes, ethyl acetate | No | No | |
| PLA | Filaments. | Approved | NA | No | No | No |
| Fillamentum | NA | Compliant | No | No | No | |
| Innofil3D | Approved except red, orange, pink, apricot skin, grey, and magenta | Approved except red, orange, pink, apricot skin, grey, and magenta | No | No | No | |
| Copper3D PLActive Antibacterial | Approved | Compliant | No | No | No | |
| Makergeeks | Approved | NA | No | No | No | |
| Purement Antibacterial | Approved | Approved | No | No | No | |
| PLA-HT | Makergeeks Raptor | Approved | NA | No | Yes | Yes |
| Makergeeks Raptor | Approved | NA | No | Yes | Yes | |
| PP | Centaur | Compliant | Compliant | No | Yes | Yes |
| InnoFil3D | Approved | Approved | No | Yes | Yes | |
| Nunus | Compliant | Compliant | No | Yes | Yes | |
| Verbatim | Compliant | NA | No | Yes | Yes | |
| SBS | Filamentarno | NA | Approved only in Russia | Yes, d-limonene | Yes | Yes |
Selective Laser Sintering is a 3D printing process that use a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of polymer powder. The most common material for laser sintering is nylon, a popular engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties.
While some SLS powders are graded food safe, the particles on the surface of printed parts might not fuse completely, resulting in parts that are inherently porous and do not deal well with moisture and mold growth. Even though the nylon 12 powder can be steam cleaned in an autoclave, it is best to coat SLS parts with food safe coatings to seal their surface.
A common post-processing step for SLS parts is dying. But note that after an SLS part has been dyed, the dye may leach into the printed part which renders the item not food safe.
White Paper
Looking for a 3D printer to create strong, functional parts? Download our white paper to learn how SLS printing works and why it's a popular 3D printing process for functional prototyping and end-use production.
Download the White Paper
Food safety with 3D printing is not a simple matter that will boil down to a clear yes or no answer. Producing 3D printed parts for food contact items requires careful consideration of the risks depending on their intended use.
For further information on food safety and 3D printing, we recommend reading the following:
- FDA Regulations CFR 21
- EU Guidelines 10/2011
- Risk Assessment of 3D Printers and 3D Printed Products
- The Tricky Business of Choosing Plastic for Food Contact Applications
How to make food-grade 3D printed models
You’ve probably noticed that we mention the food-safe properties of some filaments. And it’s true, there are several materials that can be considered food-safe, or food-grade to be specific (only certain manufacturers have proper certification), but it’s still necessary to coat the surface to make it truly safe for direct food contact. Let’s see why the surface coating is so important, how to add it properly, and what to avoid during the whole process.
Important regulations
First, let’s talk about regulations: In Europe, there is regulation no. 10/2011 that summarizes safe and unsafe materials. In the USA this issue is covered by the FDA CFR 21 document. While there are many materials that are classified as food-grade, there are only a handful of manufacturers who have completed the rigorous and costly certification process. In general, certified materials are more expensive. If you need to make food-grade parts for your business, you will be interested mostly in materials with a valid certification.
Food-safe filaments
Let’s take a look at materials that are (not) suitable for direct contact with food. As we mentioned above, you can buy materials with food-grade certification (PLA by Filaments. ca for example). But some filaments should be safe even without any certification, for example, PLA, PETG, or PP. On the other hand, some materials are rather unsafe and shouldn’t be used for direct food contact – for example, most ABS or ASA filaments. Unfortunately, it gets more complicated, because we need to take into account the pigments that are used to produce various materials. Even potentially safe filaments might contain unsafe pigments that might be dangerous when in direct contact with food. Therefore it’s good to ask a manufacturer about additives used, or use natural filament with no added coloring. Most of our PLA and PETG Prusaments (excluding PLA Army Green)* contain inorganic non-migratory pigments that should be safe, but keep in mind that we didn’t acquire any certification. If you print food-grade objects with our filaments, you should do it only for personal use, not for sale.
*Our coloring manufacturer confirmed that these colors should be safe for food contact: PLA Galaxy Black, PLA Galaxy Silver, PLA Azure Blue, PLA Lipstick Red, PLA Galaxy Purple, PLA Jet Black, PLA Prusa Orange, PLA Pineapple yellow, PLA Royal Blue, PLA Ms. Pink, PLA Opal Green, PLA Pearl mouse, PETG Jet Black, PETG Prusa Orange, PETG Signal White, PETG Carmine Red, PETG Yellow Gold, PETG Urban Grey, PETG Ultramarine Blue, PETG Galaxy Black, PETG Pistachio Green, and PETG Terracotta Light.
3D printer preparation
Once you select the right filament job, it’s time to prepare the printer. First, you need to keep it as clean as possible (outside and inside). You should try cold pull if you aren’t sure whether the extruder is clean enough. Then you should consider changing the brass nozzle for a stainless steel one: Brass nozzles (and even our hardened steel nozzles) might cause a health risk due to lead present in the alloy. Few sources also claim that it’s not wise to print with an extruder containing PTFE tube, due to Teflon toxicity at high temperatures. However, it releases only a small amount of toxic particles with temperatures exceeding 240°C and significant amounts with temperatures over 260°C. PTFE, therefore, poses no real danger if you print with PLA or PETG. If you are still not sure, try to use a special extruder without a PTFE tube.
No print is food-safe without surface coating
Choosing the right filament and using a well-maintained printer is just the beginning. The print itself will never be food-grade for one simple reason – FFF 3D printing produces objects containing gaps between the layers. These gaps can become the breeding ground for the growth of bacteria and fungi, which can cause an illness. Of course, you can reduce the number of gaps by decreasing the layer height and adding a 100% infill, but the results will never be good enough. You should make the surface as smooth as possible. Unfortunately, this cannot be done properly with chemical smoothing: ASA and ABS are mostly unsafe materials and PLA/PETG can be smoothed only with dangerous chemicals. Plus, the result is never perfect – there are lots of tiny bubbles that can contain bacteria. We have prepared a simple test to show you the real danger of untreated models: We printed three PLA cups where the first remained untreated, the second was smoothed with chloroform and the third was coated with epoxy resin. Then we simulated regular usage by pouring milk inside every two days and washing it with warm water after several minutes or hours. After 14 days of testing, we performed a smear test of the surface and cultivated present bacteria on LB agar plates for 7 days. As you can see, untreated print got the worst results (largest colonies) and epoxy resin the best results (no colonies).
This method was inspired by a test made by University Novi Sad, mentioned in My Tech Fun video.
Negative control was made by cultivating smear test from freshly printed PLA cup (no milk was involved), positive control was a smear test of sink surface. Bacterial colony present in negative control may have grown due to contamination from air or other sources.
Safety first
It’s obvious that the surface must be coated to become consistent, smooth, and easily washable. This can be achieved with clear and food-grade epoxy resins. But be aware that there are more rules to follow! Failure to follow these rules might lead to contaminating or even poisoning the food.
Resins are usually toxic materials that are not appropriate for food contact and all epoxy resins are toxic when in liquid form! Similar to filaments, many epoxy resins should be food-safe after curing. But most of them aren’t certified and suitable for commercial use. It’s recommended to use the one with proper certification, even though it might cost you more. For example, we have used Efkoresin Art UV which is certified according to EU regulations 10/2011.
Once again we would caution you regarding the use of uncertified resins! Especially if you do 3D printing for a living and sell food-grade products to your customers!
The last thing to keep in mind is the toxicity of uncured resins (this even applies to those with certification). If the resin is not cured enough, it might become toxic! You should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations because an incorrect ratio of resin and hardener might be toxic. And once again, we must emphasize the fact that liquid resins are toxic. Please, use gloves and a respirator (spray paint half-mask) to prevent allergies and other health issues.
If you follow the rules mentioned above, you can be sure that your 3D printed kitchenware will be truly food-grade. But be aware that resin-coated 3D prints will have some limitations compared to regular dishes. We’re talking about wear and heat resistance: This process is not suitable for producing chopping boards (prone to scratching) or for products which will be exposed to heat – such as hot soups, microwave ovens, or dishwashing machines (read more about material deformation in our annealing article).
Is SLA technology food-safe?
Some of you might come up with questions about using SLA resins either for printing the dishes or food-grade coating. In short: It is not a good idea. Most SLA resins are toxic both in cured and liquid forms. Resins are also very prone to wear (forming a fine powder on the surface). There are various dental or low odor resins but these are made for special purposes and they are very expensive. If you wish to make 3D printed dishes, it’s better to stick to FFF printers and certified epoxy resins.
We hope that our article proved that printing food-grade dishes is not as simple as printing normal models. You need to follow many detailed rules as mentioned above to ensure that your model does not become toxic or full of pathogens. This is especially important if you run a 3D printing business for a living. Either way, surface food-grade coating surely brings new horizons to 3D printing.
Note that the same methods can be used to make 3D prints for completely different applications, but with similar requirements. For instance, you can imagine some aquarium accessories, where you need to coat the surface to prevent the buildup of algae.
Try to make nice food-grade print yourselves and show us the results. But don’t forget: Safety first! And as always – happy printing!
90,000 characteristics, pros and cons of each model07.04.2021
Content
-
- What is a food 3D printer
- Field of use
- used raw materials
- 9000 9000 9000 9000
- Top 10 Best Food Printers: A List of the Most Current Models
- 1. PancakeBot 2.0
- 2. Wiiboox Sweetin
- 3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
- 4. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus Food 3D Printer with Cooling Chamber
- 5. byFlow Focus
- 6. Chefjet Pro
- 7. Foodini
- 8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer Commercial ArtcakesOT7 .90BOT Printer F5
- 10. ZMorph VX
- What is a food 3D printer
- Selection guide
- Output
A food printer is a high-tech device that is used to create culinary masterpieces. The decorative design of food products has reached a new level thanks to the use of modern technologies: high-quality and large-format printing is carried out on cakes, waffles, pancakes and even coffee. Here are the top best 3D food printers in different price categories for people who are fond of cooking. nine0003
What is a 3D food printer
The main feature of a food 3D printer is the raw materials used: instead of printing ink, the device is filled with edible ingredients. The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer. nine0003
Application
Futuristic 3D Printed Sugar Candy
Cookies printed with icing
Chocolate logos of famous companies
Cream Photo Print
Buying a food 3D printer is worth the owners of coffee houses, author's bakeries and private workshops. The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products. nine0003
Raw materials used
The following ingredients are used as raw materials:
-
Chocolate without additives and impurities;
-
Mastic;
-
Sugar;
-
Whipped cottage cheese;
-
Vegetable and fruit pastes; nine0003
-
Fish and meat pates;
-
Flour;
-
Cheese, etc.
Confectionery drawing is applied to sugar, wafer or shock transfer paper. The first type has a sweetish aftertaste and aroma of vanilla. Due to the snow-white surface, no additional coating is required: the drawings look bright and clear. Wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a particular taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used. nine0003
Interesting! Food printers are involved in waste reduction. Unattractive fruit and confectionery leftovers are used in the preparation of printing mixes. This makes it possible to use the means of production more efficiently.
Types of 3D food printers
Cooking enthusiasts can take advantage of the following food printing devices:
-
Food 3D printers are devices that print dishes whose recipes are listed in a database. The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges; nine0003
-
Confectionery printers are used to transfer images onto specialty paper or to design small confectionery products such as candies.
Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer;
-
Food plotters transfer the image not to paper, but directly to the finished product. For example, a plotter is used to transfer an image directly onto a cake. nine0003
There are several types of food 3D printers:
-
Extrusion - paint is applied to the surface before the dish is created. The process is controlled by the computer with the loaded image. The system has an extruder that heats the food mixture, and the distribution of raw materials depends on the print head. The raw material is loaded into a syringe placed in the head. This means that in order to combine different shades, you have to periodically stop printing and change the syringe; nine0003
-
A carousel-type food 3D printer also has an extruder, but its main feature is the method of feeding raw materials: the containers rotate around the working surface, the supply and dosage of the material used depends on the recipe specified in the program.
The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
Popular brands
Eminent manufacturers offer the best value for money food 3D printer. High-quality devices provide accurate printing, high speed, durability, simplicity and ease of use.
Wiibox
This company manufactures 3D printers with high build quality and high productivity. These are universal mechanisms that fill both chocolate paste and mashed potatoes. Numerous positive reviews confirm the high quality of Wiibox products. nine0003
byFlow
The Dutch company byFlow specializes in food printing technology. The pursuit of excellence helps the company open up new horizons: the technique prints products from spinach, meat emulsion and other materials. High build quality, ease of use and durability - all these characteristics are applicable to the products of this company.
Choc Edge
Choc Edge is committed to revolutionizing the world of chocolate making. Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Attention! Printing dishes helps save time on cooking: instead of culinary worries, the user can simply activate the printing process and get on with other things.
nine0134Free shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Available on credit. To checkout, add the product to the cart and follow the instructions Go nine0003
Manufacturer Wiiboox Free Shipping
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Top 10 Best Food Printers: Most Current Model List
Before you buy a food 3D printer, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular devices on the world market.
The top is based on ratings and customer reviews. nine0003
1. PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 is easy to use, which means it's suitable for inexperienced users too. Users can choose from suggested designs in the software, or create their own. Used to print pancakes.
Pros:
Ease of operation;
A wide range of proposed projects; nine0003
High speed.
Cons:
2. Wiiboox Sweetin
Buying a food printer from Wiiboox is worth not only for confectionery lovers, but also for ordinary chefs: the device prints cakes, cookies and even mashed potatoes. The main raw materials can be meat, cheese, chocolate, jam, mashed potatoes, dough and much more. A convenient touch panel helps to set the desired mode of operation, and a stylish appearance complements the interior of any establishment. nine0003
Pros:
Versatility: the ability to print not only sweet dishes, but also side dishes;
Attractive appearance;
High build quality;
Convenient control by touch panel.
![]()
nine0173 Cons:
High price.
3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
When talking about which chocolate 3D printer to buy, it is worth mentioning the numerous advantages of Choc Creator V2.0 Plus. The new model has become more perfect: the developers have worked hard to eliminate the shortcomings of the previous version. The modern model has small dimensions, so it can be used in any kitchen, and the uniform heating of the syringe ensures high-quality and uninterrupted operation. In practice, the chocolate printer has shown tremendous potential: it prints complex figures from chocolate. nine0003
Pros of :
Attractive appearance;
Uninterrupted work;
Durability;
The ability to create durable and beautiful chocolate figures.
Cons :
4.
Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
The new version of the Choc Creator V2.0 Plus printer is equipped with cooling chambers by popular demand. Users say that maintaining the optimal temperature in the room to preserve the integrity of chocolate figures is too problematic: therefore, the new device cools the raw materials. The price of a food 3D printer with a cooling system is slightly higher than a classic one, but the high performance of the final product justifies any costs. nine0003
Pros of :
Availability of a cooling system for finished products;
High printing precision;
Long service life;
Ease of use: you can turn the fans on and off with the side buttons.
Cons :
High price.
Attention! Confectionery food 3D printers are often used by artists to create edible masterpieces.
This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef.
5. byFlow Focus
Food printer from the Dutch company byFlow, which specializes in 3D printing of food. The compact high-tech device is used for the bakery industry, and the cartridges are suitable for the application of any pasty ingredients. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
6. Chefjet Pro
Buying a ChefJet Pro food printer is a must for people who dream of making bright and stylish sweets. The device is created on the principle of inkjet printing: sugar-containing powder materials are used instead of paints. The final product is made by powder layering. The printer is suitable for combining different shades and creating gradients. nine0003
Pros:
The ability to create unique flavors;
Neat and bright printing;
Aesthetic appearance of the device.
![]()
Cons:
- nine0015
High price.
7. Foodini
The 3D food printer from Foodini works on the principle of a stationary printer, but instead of printing inks, layer-by-layer imposition of edible raw materials is used: dough, cream, chocolate, cream, etc. The device is versatile: the user himself can choose the material, or use ready-made cartridges with products.
Pros:
Practicality; nine0003
High build quality;
Attractive appearance;
Availability of an online platform with unique recipes.
Cons:
8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer
The closed MMuse 3D printer is suitable for chocolate printing. Chocolate beans are used as raw materials: they are heated in an extruder and fed to the work surface through the print head.
nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
9. ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5
ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5 3D Printer
A food printer from Chinese manufacturers is used in the process of making pancakes of various shapes. Ease of operation allows the device to be used by children under adult supervision. nine0003
Pros:
Ease of operation;
High build quality;
Affordable cost.
Cons:
10. ZMorph VX
A multifunctional 3D printer capable of printing not only food, but also rubber, ABS plastic, polylactide, PVA, nylon, elastic and metal materials. The product is able to print with chocolate, butter, cookies, icing and other ingredients. In addition, there is a function of engraving and CNC milling. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
High price.
![]()
Selection guide
The modern market offers a wide range of food printers. Before making a purchase, you need to carefully study the characteristics of each model and build on your own preferences. Experts have created several recommendations for choosing: nine0003
In case you want to create realistic images for confectionery 3D printing, pay attention to the diameter of the nozzle: the narrower it is, the more accurate the image will be;
- nine0007
It is better for people living in regions with a warm climate to purchase chocolate 3D printers with a cooling system: such devices ensure that the figurines are kept at the optimum temperature;
The possibility of self-refilling the cartridge is the most practical and economical way to operate the printer;
Print speed is an important consideration for restaurant owners. Large batches of dishes must be produced quickly, and for home use this is not a very strict selection criterion.
![]()
Output
In the catalog of our online store, you can choose the best food printers from famous brands to create culinary masterpieces. Explore our range, learn about the characteristics of each printer and make great purchases. nine0003
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
how it works, a review of culinary (confectionery) models and examples of work for cakes and chocolate printing products. Interest in 3D food printing is understandable - every year manufacturers release new models that open up more and more prospects for owners of 3D printers. In the article we will talk about the device of a 3D food printer and what can be done with it. We'll also talk about 3D printing with sugar and chocolate, edible prints on drinks, and even 3D pancakes. Get ready to be amazed - the scale of food printing on 3D printers will amaze even the most sophisticated user.
nine0003
How it works and types of devices
The principle of operation of a 3D food printer is similar to a conventional inkjet printer. The only difference is that instead of simple ink cartridges in a food 3D printer, food coloring cartridges are used. The memory of the device allows you to store many recipes. To print the desired dish, you just need to select the saved recipe and press the button. After the dish is sent to print, the printer will begin to lay out the ingredients in layers on the work surface or directly on the plate. The printed dish can be sent to cool in the refrigerator or baked in the oven. nine0003
Views
Despite the fact that 3D food printing technology is the youngest in the field of 3D modeling, it is dynamically developing and improving in several directions at once. Food 3D printers have significant differences and are divided into several types:
- Food extrusion type 3D printer - this type of device extrudes the edible mass layer by layer onto the work surface until the dish is completely formed.
The operation of the printer is controlled by a computer, on which the three-dimensional model of the object and the recipe are located. The printer itself, like its inkjet counterparts, is very simple - it consists of a table and a print head. The head moves along three coordinate axes, and an extruder is placed inside it to heat the mixture. The extruder is the main element of extrusion type printers. The printing ingredients are filled into a special syringe, which is placed in the print head. A significant disadvantage of this type of device is that the more complex the model in terms of composition and color scheme, the more often you will have to stop printing and replace the syringe. Extrusion-type printers include Chokola 3D - the device allows you to work with chocolate and pasty ingredients. nine0012
Please note! The smaller the diameter of the nozzle through which the raw material is squeezed out, the neater, more accurate and more realistic the printed dish will be.
![]()
- 3D food carousel printer - despite the fact that the main working element of this type of printer is an extruder, such devices are called carousels because of the feed mechanism. The carousel 3D printer rotates over the working surface of the container with raw materials, selecting the desired ingredient and squeezing out the dosage of the product indicated in the recipe. Outwardly, the printer really resembles a kind of carousel - containers with products rotate at a slow pace over the table. An almost unlimited number of recipes can be stored in the base of a carousel-type food 3D printer, and special skills are not needed to use it. All that is required from the user is to simply press a button and start printing. The carousel printer independently dispenses raw materials, alternately squeezing out the food mixture from the desired container. Depending on the model of the device, the containers can be from 4 to 16 pieces. Author's product from Martha Stewarts Crafts - the Cricut Cake carousel printer will help you create an original cookie or decoration for a festive cake.
The owner of the printer just needs to press the start button - everything else will be done by Cricut Cake. Included with the device is a large cookbook with ideas for creating real edible works of art. nine0012
What can be done with a 3D food printer?
A wide range of 3D compatible ingredients allows you to create virtually any 3D model - the scale is limited only by the user's imagination. With the help of a food 3D printer, you can create figures of any complexity that will give even a simple cake a designer look.
Three-dimensional models of the bride and groom or any hero of the occasion; mask-cast of chocolate; planes, cars and cartoon characters on cakes for children; voluminous bouquets; edible figurines; original inscriptions and company logos - all this can be printed on a food 3D printer. nine0003
That is why such devices are gaining more and more popularity in hand made confectioneries - exclusive products attract customers and emphasize the professionalism of the creator.
![]()
Printing pancakes
If you are not impressed by unusual cake decorations and original edible models, and you think that 3D food printing is just pampering, then especially for you and other connoisseurs of a rational approach, manufacturers have released 3D printers that bake pancakes. The device is a dream of housewives and pancake lovers, it costs more than a pancake maker or an ordinary frying pan, but can even the most modern pancake maker bake pancakes in the shape of a dinosaur, your favorite character or even your own head for breakfast? nine0003
As an example, consider the PancakeBot model, which not only bakes pancakes and pancakes, but also knows how to create shadows and halftones. Thanks to these unique features, 3D images printed on the PancakeBot are as realistic and voluminous as possible. During the printing process, the printer immediately fries the products.
The PancakeBot uses a heated non-stick surface as its working base and computer controlled heat and extruder action.
The model is equipped with one print head, connects to a computer via an SD card or USB cable. The productivity of the printer is 100mm/s. nine0003
Like any device, PancakeBot and other 3D food printers have their advantages and disadvantages.
The main drawback of the design of printers that print pancakes, users consider the inadmissibility of even the slightest lumps in the dough. The fact is that even the smallest lump can clog the nozzles of the device and stall the printing process. The problem is solved simply - just monitor the viscosity of the dough.
The advantages of PancakeBot are highly appreciated by artists and creative personalities - the user can draw absolutely everything that his talent and imagination allow him to draw. nine0003
Indisputable plus - simple ingredients. PancakeBot does not require expensive raw materials - the printer works with a simple pancake dough, the taste of which depends only on the user.
Please note! The manufacturer's website notes that any image can be downloaded to the PancakeBot's SD card, be it pictures downloaded from the Internet or your own photos.
![]()
Another benefit of PancakeBot is its availability. The device is relatively inexpensive. nine0003
PancakeBot will suit both private mini-confectioneries and catering chains, as well as simple pancake lovers — unusual pancakes and pancakes will delight children, decorate any holiday and surprise customers.
Sugar printing
Back in 2013, architects Kyle and Liz von Hasseln founded The Sugar Lab and, to the delight of sweet lovers, found a new application for 3D inkjet printing. Using the ChefJet confectionery food 3D printer as an example, we will talk about the production of three-dimensional models from sugar. nine0003
ChefJet applies a thin layer of granulated candy to the work surface and then selectively glues it with water, which is fed through the nozzle of the print head. The ChefJet head follows the contours of a digital model, moving in two dimensions. The printer then applies a new layer of ingredients, repeating the process to form the next layer of the shape.
![]()
Food additives and dyes make it possible to create models of various flavors and colors. nine0003
The ChefJet is a little too big for a typical kitchen, but the size of the working area inspires respect and allows you to decorate the average birthday cake.
Even the most inexpensive version of ChefJet has a significant plus - the printer can print mint, vanilla, chocolate, cherry and apple candies and icing. The disadvantage of the basic configuration is the inability to print multi-color sweets.
A more advanced version of the ChefJet allows you to print different colors of candy and mix flavors. The professional model is overshadowed by only one comparative drawback - the dimensions of the device have increased somewhat. nine0003
Perhaps the main advantage of ChefJet is the ability of the printer to work not only on powdered sugar, but also on caramel and even on chocolate chips.
The use of additive manufacturing allows ChefJet to create highly geometrically accurate sugar models.
![]()
Please note! ChefJet can even print hollow sugar products with free-flowing fillings in any flavor. For example, it is quite possible to print an edible rattle - ChefJet accurately prints edges, avoiding sharp corners and unsafe chips. nine0003
The ChefJet 3D Food Printer is designed for professional chefs and confectioners who will operate printers in bakeries, pastry shops and restaurants. Especially for users, the manufacturer plans to complete the devices with software and a digital cookbook. As an example, the manufacturer cites the possibility of printing figurines for wedding cakes.
Perhaps the high cost of ChefJet is the main disadvantage of this printer. However, there is always an opportunity to save money - on the market you can find used devices in good condition at a lower price. nine0003
Chocolate printing
Choc Creator 2.0 Plus is the best example of a chocolate printing 3D food printer.
In our opinion, this is one of the most stable working models, affordable and creating real miracles from chocolate.
Choc Creator 2.0 Plus is the perfect assistant for chocolatiers, professional confectioners and just lovers of real Belgian chocolate.
Choc Creator 2.0 Plus was developed taking into account all the disadvantages of the previous version - the creators improved the convenience and technology of work, but did not forget about the design of the device - the new Choc Creator conquers with its compact dimensions, high performance, intuitive interface and unlimited possibilities for working with chocolate . nine0003
A few words about the design - the printer is equipped with a 5-inch touch screen. The start and settings buttons are conveniently located on the screen.
Choc Creator 2.0 Plus will fit both in a professional pastry chef's kitchen and in an apartment - the printer can easily be placed on a bar counter, window sill and any other flat surface.
![]()
Another indisputable plus for visuals is the opportunity to observe the process of printing chocolate figures.
Choc Creator 2.0 Plus is a master of chocolate, from miniature cake decorating figures to large chocolate models. nine0003
The manufacturer's concern for its customers deserves special attention, which is felt from the moment you open the box with the printer. First, Choc Creator 2.0 Plus is in assembled condition. Secondly, a small transparent suitcase, complete with the necessary accessories, emphasizes the premium model. Inside the case are:
- stainless steel syringe;
- two nozzles of different diameters;
- special needle for cleaning clogged nozzles; nine0012
- magnets for easy paper fixing;
- 5 loading heads;
- Stylish USB flash drive in gold casing;
- height calibration disc;
- hex.
The manufacturer has not forgotten about the brush for cleaning the syringe, the stylus for the touchscreen and other useful little things that express concern for the buyer.
It would seem that Choc Creator 2.0 Plus is one solid plus, but there is also a relatively small drawback - the printer only works on high-quality raw materials without additives. nine0003
The creators of the printer strongly recommend using only Belgian chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 54.5%.
Choc Creator 2.0 Plus will suit both professional chocolatiers and confectioners, as well as simple connoisseurs of quality chocolate.
3D printing on drinks
Just a few years ago, only a few baristas could draw a simple pattern on coffee. The process took time, and the result did not always meet the client's expectations. Serious competition for the creative workers of coffee houses and their flowers on the foam was 3D printers. These devices can print anything on any drink, including milkshakes and beer. nine0003
CafeMaker is a 3D inkjet printer that can print images on various types of drinks, and can do it with three food colors at the same time.
CafeMaker's print speed is 10 seconds/cup, allowing you to design your drinks in seconds.
Important! The CafeMaker doesn't just print on drinks, it can also print on small cream cakes.
An indisputable plus of CafeMaker is its own CupShow application, in which you can select pictures for printing from those saved in the device's memory, as well as create inscriptions, logos, or even print personal photos.
CafeMaker can print in one color or in a set of cyan, red and yellow.
The process of refilling the CafeMaker is similar to working with a conventional inkjet printer - dye is slowly poured into the cartridge, and then the finished cartridges are placed inside the device. nine0003
A small drawback of the device lies in its requirements for a cup or glass - containers should not be transparent, their height should not exceed 18 cm, and their diameter should not exceed 11 cm.
restaurant - any client will be happy to receive a cup of coffee, a glass of beer or a cupcake with an original image.
![]()
Printing with paste ingredients
Printing with sugar and chocolate is no longer just a fantasy. Now you will not surprise anyone with three-dimensional models from familiar products, so 3D printer manufacturers decided to take a step towards lovers of everything unusual and create devices that print almost any product from various ingredients. nine0003
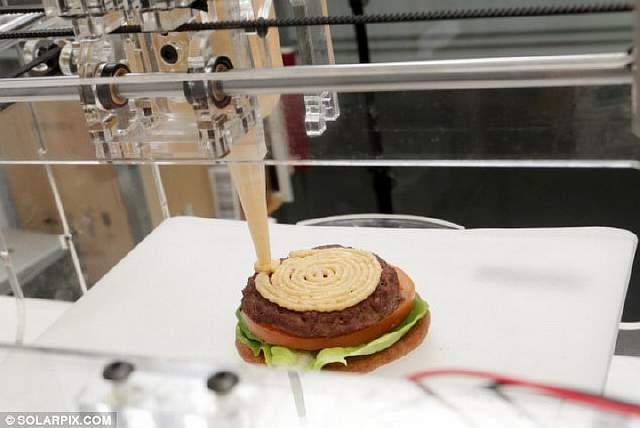
The Foodini 3D printer will give a confident rebuff to multicookers and other kitchen gadgets - the device can independently print dumplings, prepares the finest Italian pasta, cookies, donuts covered with icing, and even hamburgers.
Up to five different textures can be loaded into the Foodini printer at the same time. Thanks to the nozzles of different diameters, which are supplied with the printer, a wide variety of dishes are suitable for printing.
Unlike its counterparts, Foodini has firmly taken its place in the restaurant business. Of course, not all establishments can afford an expensive unit.
For example, the Foodini printer is used in one of the most popular restaurants in Barcelona, La Enoteca. One of the institution's most unusual dishes is seafood puree, which is almost impossible to decorate by hand so gracefully. nine0003
The print speed of the Foodini printer is 100 mm/s, which is another advantage of the device.
Perhaps the only relative disadvantage of Foodini is its high price, but it is compensated by the increased interest of customers in the dishes produced and, as a result, an increase in the institution's profit. The Foodini printer is ideal for restaurants and other catering establishments that want to emphasize the creative approach of the management and the chef, as well as the high class of the company. nine0003
What kind of raw material is used for printing?
The following ingredients can be used as raw materials for 3D edible printing:
- plain chocolate and chocolate chips;
- food mastic;
- sugar;
- curd mass;
- fish, meat and liver pates;
- cheese;
- vegetable and fruit pastes;
- flour;
- food colors and flavors.
![]()
Learn more