Filament voor 3d printer
3D Printer Filament | MatterHackers
- Home
- Store
- 3D Printer Filament
At MatterHackers, we take pride in offering the largest selection of 3D printing filament available. From our affordable MH Build Series filament, to our professional-grade PRO Series filament, you can find any material, like PLA, ABS, NylonX, PETG, TPU, TPE, Flexibles, Polycarbonate, and more! Along with our industry-proven brand of filament, we also carry other top-notch materials from ColorFabb, Taulman3D, NinjaTek, Ultimaker, 3DFuel, and more.
3D Printer Filament Collections
All 3D Printer Filament
Getting Started
3D Printer Filament Comparison Guide
3D Printer Filament
PLA Filament
The most common filament, PLA is a great go-to material for its ease of use.
Metal 3D Printing Filament
Print with real metal on your desktop 3D printer.
ABS Filament
ABS is a durable material perfect for projects that need strength.
PETG Filament
PETG is a strong, reliable material that is great for end-use parts.
Nylon Filament
Nylon and Nylon Composites for strong, functional 3D printed parts.
Quantum Dual-Color PLA
Mind-bending, dichromatic PLA that works on every printer
Support Filament
Dissolvable and breakaway support materials for dual extrusion 3D printing.
MH Build Series Filament
MH Build Series filament is designed and priced for every maker
MH Build Series PLA
An affordable, low-cost PLA filament intended for producing quality, 3D printed parts.
MH Build Series ABS
An affordable 3D printing filament meant for every maker with projects that require durable and temperature resistant parts.
MH Build Series PETG
An affordable, low-cost PETG filament intended for producing tough and sturdy 3D printed parts.
MH PVA Support Filament
MH PVA Support Filament is a dissolvable support material for dual extrusion parts.
PRO Series Filament
When reliability and consistency counts, be a PRO.
PRO Series PLA
PRO Series PLA is intended for producing professional, high quality, 3D printed parts.
PRO Series ABS
A formulation intended to help your prints stand out with a beautiful, glossy, opaque finish.
PRO Series PETG
Temperature resistance and fantastic visual performance with translucent colors
PRO Series Tough PLA
Strong like ABS and much easier to use - it's the best material for reliably printing functional prototypes.
PRO Series Flex
All the benefits of flexible filament together with improved strength over other flexible filaments
PRO Series Nylon
The strength and durability of Nylon now in vibrant colors.
PRO Series Ryno
Excellent at bridging and retraction to keep your parts clean with minimal post-processing.
NylonX
The durability of Nylon combined with the stiffness of carbon fiber
NylonG
Glass infused nylon for strong, functional prints
Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA
Carbon Fiber reinforced PLA adds more strength and rigidity compared to regular PLA.
ColorFabb
With several varieties available, ColorFabb filament is consistent and reliable.
ColorFabb Fill Series
PLA filaments infused with wood, metal and glow-in-the-dark particles for eye-popping prints.
ColorFabb PLA/PHA Series
A unique 3D printing filament tougher and less brittle than just PLA.
MadeSolid
Affordable materials from MadeSolid - limited time only.
NinjaTek
High quality and industry-leading flexible materials.
PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol)
Polyvinyl Alcohol, a water-soluble support material that dissolves away in a water bath to leave only your perfectly printed part.
Polymaker Filament
Browse all filament collections from Polymaker!
Polypropylene Filament
Polypropylene (PP) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic filament used to produce durable and lightweight prototypes through Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF).
Proto-Pasta PLA Blends
PLA filaments blended with metal, wood and glow-in-the-dark materials for cool print effects.
Soft PLA
Soft PLA is a flexible material great for parts that need to bend to fit their environment.
PRO Series TPU
Strong yet bendable filament that has excellent layer to layer bonding.
Taulman 3D
High-strength nylons and engineering-grade materials for functional 3D printing.
Ultimaker ABS Filament
Get beautiful, glossy prints with Ultimaker ABS filament
Ultimaker CPE Filament
Get high impact strength and chemical resistance with Ultimaker CPE
Ultimaker Materials
High-grade filament for any 3D printer from Ultimaker
Ultimaker Nylon Filament
Get impact and abrasion resistance with Ultimaker Nylon filament
Ultimaker PLA Filament
Highly versatile, easy to print and available in a variety of colors.
Ultimaker Polycarbonate Filament
3D Print molds, tools, and functional Prototypes with Ultimaker PC
Ultimaker TPU Filament
Get qualities of rubber and plastic and resistance with Ultimaker TPU
Fillamentum
From ASA to exotic colors, Fillamentum provides a quality 3D printing experience.
3DXTech Filament
Explore advanced manufacturing filament from PEEK to ESD-safe materials.
Proto-Pasta
Metallic filament and unique composites make Proto-Pasta 3D filament stand out.
SpoolWorks
3D printing materials from the creators of the industry-leading All-metal v6 HotEnd.
PRO Series Breakaway Support Material
Provides fast, easy, and clean mechanical breakaway for 3D printed parts.
AprintaPro Filament
3D printing filament with great layer adhesion that produces excellent parts.
Kodak 3D Printing Filament
A wide range of 3D printing materials with a focus on color and quality.
eSUN
Consistent and reliable 3D printing filament for entry-level 3D printing.
BASF Ultrafuse 316L Metal 3D Printing Filament
Reliable metal manufacturing for industrial applications - right from your desktop 3D printer.
FiberForce Pantone (R) Certified PLA
Browse a selection of Pantone® certified colors.
Ultimaker Tough PLA Filament
The ease of PLA printing with the impact resistance and stiffness of ABS.
Kai Parthy Lay Series
Browse unique and experimental 3D printing materials.
DSM 3D Printing Filament
Engineering-grade, advanced 3D printing materials for industrial production.
Engineering Grade Filament
High-temperature and advanced materials used in several industrial applications.
MakerBot 3D Printing Filament
Rigorously tested for quality, and optimized for Method Printers.
Fillamentum ExtraFill Series
An excellent baseline PLA that prints amazingly well.
Fillamentum Extrafill ABS Filament
Premium ABS Filament with a wide variety of vibrant colors.
Fillamentum Crystal Clear Series
An incredible line of semi-transparent, colored materials.
Fillamentum FlexFill Series
Flexfill is rubbery and elastic, making it impact, oil and abrasion-resistant.
Fillamentum Vertigo Series
Vertigo PLA series reflect light and create awesome, eye-catching prints with flecks of gold, silver and blue.
Fillamentum PVC Vinyl Filament
Fillamentum PVC Vinyl Filament
Fillamentum ASA Series
A rugged weather-resistant material that is much more resistant to UV light.
Fillamentum TimberFill Series
Made from a PLA base with wood particulate, Timberfill gives you 3D prints that look like they were carved from wood.
Fillamentum CPE
Fillamentum CPE
Dow OBC 3D Printer Filament
Strength and Flexibility in One Easy-to-Print Material
Raise3D Filaments
Browse Raise 3D selection of 3D printing filaments
Kodak Nylon 3D Printing Filament
Kodak Nylon 3D Printing Filament
Kodak PLA+ 3D Printer Filament
Kodak PLA+ 3D Printer Filament
Kodak Flex 98 3D Printing Filament
Kodak Flex 98 3D Printing Filament
Kodak PLA Tough 3D Printer Filament
Kodak PLA Tough 3D Printer Filament
Kodak PETG 3D Printer Filament
Kodak PETG 3D Printer Filament
Kodak ABS 3D Printing Filament
Kodak ABS 3D Printing Filament
BASF Ultrafuse 3D Printer Filament
Industrial grade filament for technical and engineering level 3D printing.
BASF Advanced Specialty Materials
Sophisticated, advanced materials created by the world's leading chemical company.
Clearance Items - Materials
Filament and resins at reduced prices for great savings.
Metallic 3D Printing Filament
Browse real stainless steel metal filament and metal composites
Guides & Articles
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With PLA Filament
Discover the best practices for 3D printing with PLA filament - from finding the right temperature, to which surfaces to 3D print on, this step-by-step guide will help you succeed with 3D printing PLA.
How To Succeed When Printing With ABS
ABS filament is a versatile material that's a great option for when you need your 3D-printed parts to be strong and heat-resistant. Learn how to print this material like a Pro in this in-depth guide.
How to Succeed when 3D Printing with PETG Filament
This in-depth guide provides everything you need to succeed when printing with PETG filament. Embrace the fantastic properties of durable and easy to print, PETG filament!
How to Succeed with 3D Printing Metal on a Desktop 3D Printer
The time is here to explore easy and affordable metal 3D printing. 3D printing with real metal on a desktop 3D printer is now possible using Ultrafuse Metal 3D printing filament from BASF Forward AM.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With Nylon
Learn how to 3D print Nylon like a pro. Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
How To Succeed When Printing With Flexible Filament
Let’s take a look at what makes flexible filaments easier to print and how you can add flexible filament to your 3D printing material toolbox.
How to Succeed with NylonX
NylonX has quickly become one of our favorite filaments for strong, durable, and ready-to-use parts. Here's an in-depth look at Nylon X, and some printing tips to get the most out of this great new material.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing with MH Build Resin
Make SLA resin 3D printing easier with this helpful detailed article on how to successfully fine-tune photopolymer resin to your 3D printer.
How To Succeed: 3D Printing with Nylon and Nylon Composites
Nylon and nylon composites perform exceptionally well in a variety of uses, it just takes a gentler touch to print it successfully.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With ASA Filament
Follow this step-by-step guide to learn how to print with ASA, the perfect material for any outdoor projects.
What is 3D printing filament?
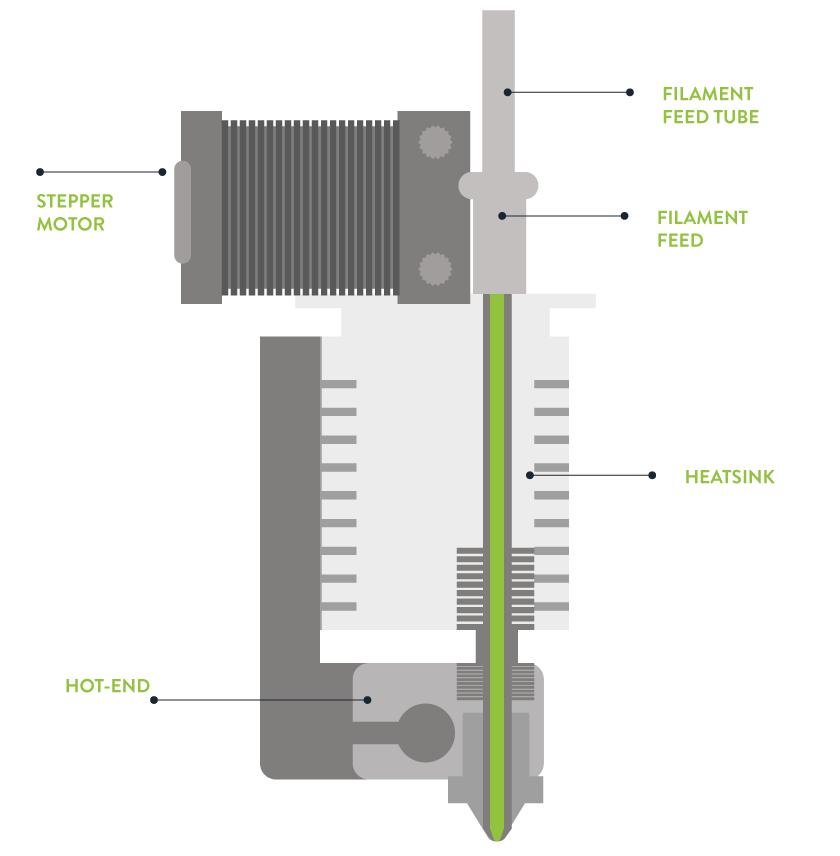
3D printing filament is a thermoplastic, or polymer, that melts when heated and is extruded through a nozzle layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object. After the filament is extruded, it cools and becomes the surface the next layer is deposited on top of.
After the filament is extruded, it cools and becomes the surface the next layer is deposited on top of.
3D printing filament is sold in spools ranging in weight from 0.5 kg to 10 kg. It comes in two diameters; 1.75mm and 2.85mm.
The most commonly used filaments are PLA and ABS. Both have advantages for different applications.
What types of filament are there?
Below is a chart showing the more common types of filament, along with their transition temperatures, bed temperatures, and ideal printing surfaces.
| Filament | Common Transition Temps | Common Bed Temps | Printing Surface |
| PLA | 205±15 °C | 40±15 °C | Glass |
| ABS | 230±10 °C | 90±10 °C | Glass with ABS slurry or kapton tape |
| PETG | 245±10 °C | 60±10 °C | Blue painters tape or bed adhesive |
| Nylon | 255±15 °C | 70±10 °C | Garolite |
| ASA | 250±10 °C | 90±10 °C | Hairspray, bed adhesive |
| Polypropylene | 250±15 °C | 110±10 °C | Packing tape or polypropylene |
| TPU/TPE | 230±10 °C | 50±15 °C | Glass, painters tape |
| PCTPE | 235±10 °C | 70±10 °C | Glass with kapton tape or hairspray |
| Polycarbonate | 290±20 °C | 130±15 °C | Gluestick/hairspray |
| PVA Support | 180±20 °C | 45±10 °C | LayerLock PEI |
| Breakaway Support | 210±10 °C | 50±5 °C | LayerLock PEI |
| HIPS Support | 230±10 °C | 50±10 °C | Glass with kapton tape or hairspray |
Dow OBC 3D Printer Filament
OBC 3D printing filament is a breakthrough 3D printing material from the chemists at Dow Chemical. Designed for high-performance 3D printing, OBC is made from a unique polyethylene-based blend that brings polyolefin material properties to 3D printing. By blending these two together, not only does it have excellent dimensional stability and superior chemical resistance, it is incredibly easy to print and is also lightweight. Step into a new world of expanded capabilities for 3D printing materials with OBC.
Designed for high-performance 3D printing, OBC is made from a unique polyethylene-based blend that brings polyolefin material properties to 3D printing. By blending these two together, not only does it have excellent dimensional stability and superior chemical resistance, it is incredibly easy to print and is also lightweight. Step into a new world of expanded capabilities for 3D printing materials with OBC.
Guides & Articles
How to Succeed with Quantum Dichromatic PLA Filament
Follow this guide for tips and tricks on how to get the best results when 3D printing with Quantum Dichromatic PLA filament.
How To Succeed with LayerLock SLA Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for Laser, DLP, and SLA resin prints using LayerLock SLA Resin 3D Printing Build Surfaces.
How To Build A Successful Makerspace
Find out the necessary components to create an effective space for your maker community.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing with Polypropylene
Successfully produce 3D printed parts out of polypropylene filament with these tips on achieving stronger bed adhesion and minimizing shrinkage.
Tech Breakdown and How to Succeed: Ionic Hybrid Support Material
Supporting engineering-grade filament has been difficult without a support material dedicated to higher temperature 3D printing. Ionic aims to solve that.
How To Succeed with OBC 3D Printing Filament
From Dow Chemical, OBC combines flexible and rigid into one unique material with properties of both.
How To Succeed with LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for NylonX, NylonG, and standard filaments using LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces.
How to Succeed with LayerLock Powder Coated PEI Build Plates
Powder coated PEI steel sheets are a great alternative build surface for strong bed adhesion. Here's how you can succeed using this durable build plate.
Here's how you can succeed using this durable build plate.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With Nylon
Learn how to 3D print Nylon like a pro. Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With ASA Filament
Follow this step-by-step guide to learn how to print with ASA, the perfect material for any outdoor projects.
How to Succeed when 3D Printing with Polycarbonate Filament
Follow these helpful steps to start successfully printing with this extremely tough, professional grade material.
How to Succeed with NylonX
NylonX has quickly become one of our favorite filaments for strong, durable, and ready-to-use parts. Here's an in-depth look at Nylon X, and some printing tips to get the most out of this great new material.
filament from plastic bottles, how to make
filament production By making filaments for printing on a 3D printer on their own, the user can save a lot of money spent on consumables.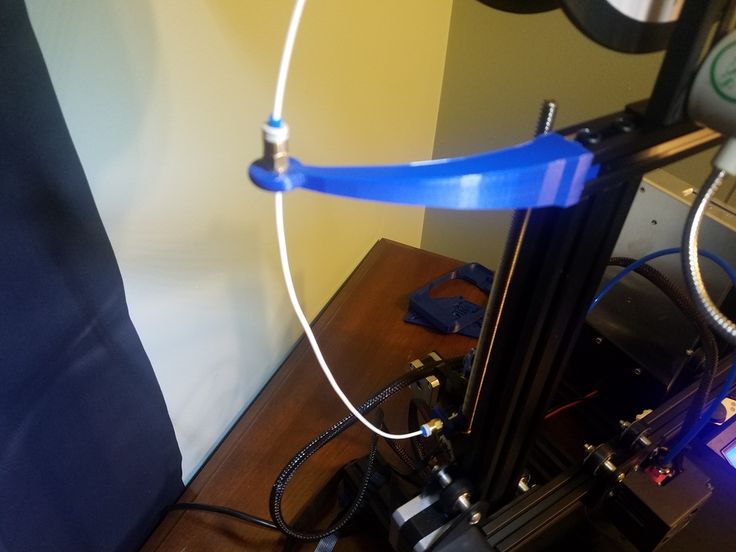 Plastic filament for printing can be made from PET bottles. Consider which bottles are suitable for this, the procedure for manufacturing a filament, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of this method.
Plastic filament for printing can be made from PET bottles. Consider which bottles are suitable for this, the procedure for manufacturing a filament, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of this method.
Is it possible to make plastic for a 3D printer from PET bottles?
When making plastic filament for 3D printing, it is recommended to use the following types of PET bottles:
- Blue. Such bottles have the hardest plastic, but when melted, it will be the most fluid of all.
- White and green. The plastic of these bottles is softer than that of the blue ones. In molten form, the material is thicker.
- Brown. These bottles have the softest plastic. When molten, it is highly viscous (similar to ABS filament). nine0010
How to make DIY thread and print with plastic bottles?
Preparatory work
Bottles must be unraveled into ribbons before production starts.
Soft bottles have a thinner plastic, so it is better to break them into strips of 10 mm.
Containers with medium hard or harder plastic material can be cut into thin strips, about 7 mm thick.
PET bottle 3D printer filament tools
To create a filament from PET bottles, you will need the following tools:
- utility knife or bottle cutter;
Important! When choosing a bottle cutter, you need to pay attention to the accuracy of cutting plastic. The width of different cut strips should not differ by more than 0.1 mm.
- oven;
- plastic crusher;
- homemade vertical extruder - it has a metal pipe with a drill screw that rotates with a stepper motor, and a nozzle with two heaters from a 3D printer; nine0010
- rotary table;
- large basin;
- cold water.
Step-by-step instructions
The production of PET bottle filament for 3D printing is carried out in the following order:
- Cut plastic bottles must be melted in an oven at 180 °C.
 The melting time depends on the number of bottles.
The melting time depends on the number of bottles. Help. It takes approximately 40 minutes to melt 10 plastic bottles.
- After melting, the plastic must be completely cool. All excess moisture will evaporate from the material, and it will crystallize. In appearance, the polymer resembles glass.
- The cooled material must be ground in a crusher into a finer fraction.
- The crushed plastic is then fed into the vertical extruder. The rotating screw moves the ground polymer to the bottom of the device to the nozzle with heaters. The plastic starts to melt.
- The molten PET plastic leaves the nozzle and enters a basin of cold water, which is located on a rotating table. The rotation of the table will prevent sticking of the material. The thread must be cooled as quickly as possible so that it becomes flexible and transparent. In this case, it can be used for 3D printing.
- Let the homemade filament dry well before printing.
 Since in the presence of a large amount of moisture, a thread of molten plastic will exit the extruder in the form of foam. It is recommended to dry the skeins of thread in a closed container with silica gel at a temperature of 50–60 °C. To do this, you can use the oven or simply place the container on the radiator. nine0010
Since in the presence of a large amount of moisture, a thread of molten plastic will exit the extruder in the form of foam. It is recommended to dry the skeins of thread in a closed container with silica gel at a temperature of 50–60 °C. To do this, you can use the oven or simply place the container on the radiator. nine0010
When using ready-made filament for 3D printing on a printer, several nuances should be taken into account:
- Print the product on a cold table, the temperature of which does not exceed 35 ° C. This limitation of the temperature regime is due to the fact that the plastic must quickly cool down to a temperature below 70 ° C. Otherwise, the material may almost completely lose its strength properties.
- Extruder temperature should be around 265°C. But it may differ depending on the printing speed and the type of plastic from which the filament is made. nine0010
- If the feed mechanism of the 3D printer is made of brass, then it is better to put a thin-walled rubber hose on the roller.
 It will not allow the PET thread to slide.
It will not allow the PET thread to slide.
The pros and cons of using bottles to create plastic
The main advantage of recycling PET bottles for plastic 3D printing filaments is that you can save on the purchase of industrial filaments and recycle unnecessary packaging, which, when taken to landfills, greatly pollutes the environment .
Disadvantages of using homemade filament:
- you can print products only at a low speed, as the thread breaks when it is increased;
- requires a crusher to grind the material and a separate extruder to transport the plastic;
- It is not possible to print large items because the thread length is limited.
Making your own 3D printing filament is a great way to save on consumables and recycle unwanted PET bottles. Homemade filaments are close in properties to purchased ones. Therefore, they can be used to print small products of excellent quality. nine0003
- March 14, 2021
- 13309
Get expert advice
What is 3D printer filament and how to choose it?
December 3, 2021
To print objects on a 3D printer, he needs the appropriate material. 3D printers typically use special plastics that have different properties depending on their composition. These plastics are called filaments. And because of their shape, in the form of a thin thread, everyone is used to calling them that way. And you yourself choose which filament for a 3D printer to buy in order to get the desired result. nine0003
It is important to understand that during the printing process, the filament is heated, melted and extruded through the 3D printer's extruder nozzle. There are many 3D printing filaments used in printing today, from standard plastic filaments to metallic imitations or wood or flexible filaments.
It's important to choose the right filament for your 3D printer. Using filament with the wrong diameter or settings will inevitably result in printing failure or damage to the printer. This can be avoided if you understand which filament is best for your printer and your part. All 3D printers have a unique set of temperatures, speeds, and features that you must also consider in order to buy the right filament. nine0003
Using filament with the wrong diameter or settings will inevitably result in printing failure or damage to the printer. This can be avoided if you understand which filament is best for your printer and your part. All 3D printers have a unique set of temperatures, speeds, and features that you must also consider in order to buy the right filament. nine0003
Each filament has its own set of characteristics both in terms of appearance and physical properties. Each offers its own set of features that you need to know to optimize your printing. You also need to consider what properties are needed for the object you are printing. Will the material be used indoors or outdoors? Should the part move and flex, or should it be absolutely rigid? What forces will be applied to the object? What post-processing methods will be applied to the finished 3D print? It depends on what thread you need to buy. nine0003
Of the many threads available, some are more popular than others. These are such filaments as ABS, PLA and PET/PETG.