3D printing and laser cutting
What laser cutting contributes to 3D printing
3D printing is already in the mouth of everyone and the vast majority of people are generally aware of the advantages it brings, both in the daily life of a particular user and a professional user, but what is not so well known is that there are machines that can complement this technology. In this case we will talk about laser cutters.
3D printers and laser cutters are totally different machines and perform opposite jobs, but at construction level they are similar. A 3D printer uses the raw material with a different shape to the final piece (filament, pellet, resin, etc.), to obtain an object in three dimensions. In contrast, a laser cutter needs the raw material with the same shape and larger size (wood sheet, steel, etc.) than the final piece, and can only operate in two dimensions. The advantage of laser cutters (professionals), is that they can work with an infinity of materials, especially metals, at high speeds.
Image 1: Metal laser cutting machine. Source: Lasercutting
The laser cutter is a machine that uses a system of rails to move a head, where it locates the laser, which can cut metal materials and other types of materials, such as wood or leather, all with thicknesses of up to 6 mm. At an industrial level, the use of laser cutters is very widespread, since they offer easily reproducible results with really narrow slot widths, and small radius holes and curves. In general, it provides value in complex flat pieces, which, in general, would be much more expensive with another type of manufacturing process. In addition, these machines can work at very high speeds without losing accuracy and even with a perfect surface finish, free of burrs.
Within the laser cutters there are two types, depending on the laser they use: CO2 laser and laser diode (Mr Beam II). The CO2 laser works by Carbon Dioxide and other concentrated chemical elements inside a glass tube where two diode bars generate the laser beam.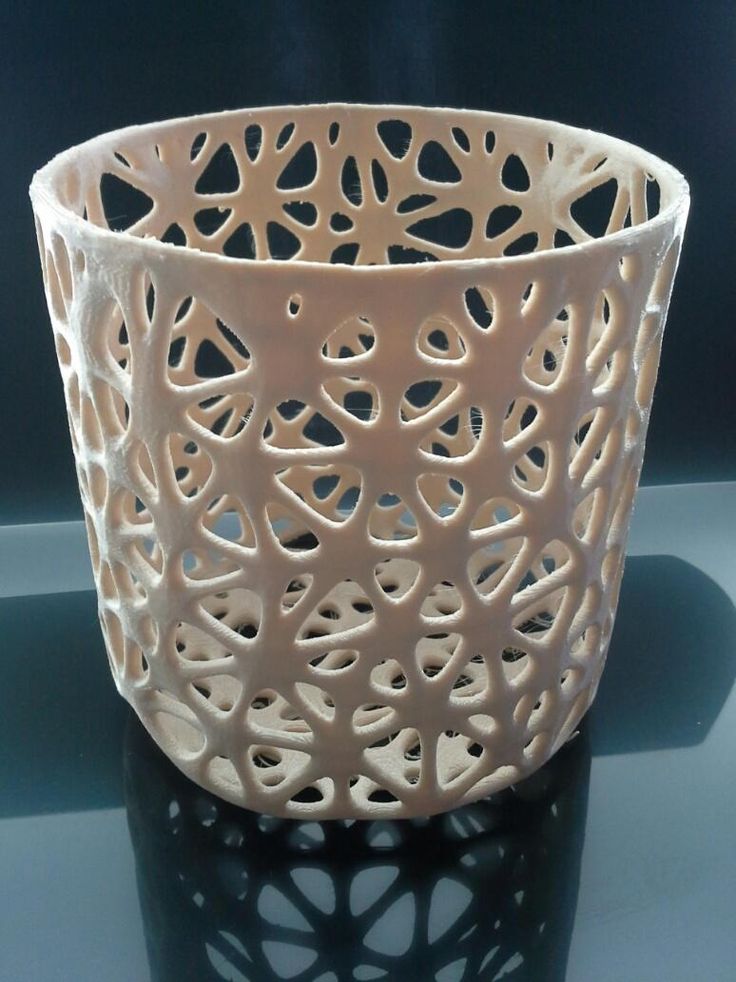 The disadvantage of this type of laser is the width of the laser and its short operating life (1000-15000 hours). The laser diode has an operation similar to an LED but very high power and where all the light is concentrated in one point. They are much more accurate than CO2 lasers and their life is very high.
The disadvantage of this type of laser is the width of the laser and its short operating life (1000-15000 hours). The laser diode has an operation similar to an LED but very high power and where all the light is concentrated in one point. They are much more accurate than CO2 lasers and their life is very high.
At the professional level, but in non-industrial sectors, there are laser cutters such as Mr Beam II, which offer the possibility of cutting and engraving a large quantity of materials. In this specific case, this cutter has a 5W class 1 laser head, inside a metal casing with a safety cover and with a fume extraction and filtering system. All this, we must add the lid camera to facilitate the placement of the design you want to cut or burn, and its connectivity through WLAN.
Image 2: Mr Beam II laser cutter. Source: Mr Beam
Currently, there are also 3D printers on the market that can perform engraving work on certain materials such as plastic, wood, leather, cardboard or paper. This is the case of the 3D FDM XYZ Da Vinci Pro Series and Da Vinci Color Series. To make both printed pieces and to record certain materials, these printers have two interchangeable heads, thus concentrating two manufacturing processes increasingly demanded.
This is the case of the 3D FDM XYZ Da Vinci Pro Series and Da Vinci Color Series. To make both printed pieces and to record certain materials, these printers have two interchangeable heads, thus concentrating two manufacturing processes increasingly demanded.
Image 3: XYZ Da Vinci 1.0 Pro. Source: XYZ Printing
A laser cutter increases the production power and expands the work field of a 3D printer user, thanks to being able to complement printed pieces with pieces cut or laser engraved, such as making the structural part of a model with a printer 3D and then join the parts of much detail cut by laser. This saves time and manufacturing cost, achieving a great final finish.
Image 4: Modified piece with a laser cutter. Source: Mr Beam
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter and you will receive every month in your email the latest news and tips on 3D printing.
* By registering you accept our privacy policy.
3D printing and laser cutting: How to choose?
Posted By Lucie Gaget on May 2, 2018 |
At Sculpteo, we are offering two different services: a 3D printing service and a laser cutting service. Both of these two manufacturing techniques are offering the possibility to use different materials,. We are going to see in this blogpost what the specificities of each of these manufacturing techniques and what their benefits are. Which one would be more appropriate for your project? And why? Follow the guide, and choose between 3D printing and laser cutting!
Rethinking your manufacturing process
Choosing the right manufacturing technique
When starting your business or rethinking your manufacturing process, it can be really hard to find the best manufacturing technique for your company. You might be looking for a manufacturer for your business, both for production or prototyping, and you obviously want to find a reliable partner offering the best quality for a lower price. In this case, digital manufacturing might be the solution.
In this case, digital manufacturing might be the solution.
A lot of industries are making the most of digital manufacturing. These manufacturing techniques could perfectly fit your company and help you to reach all of your professional goals. But how do they work?
The benefits of digital manufacturing
In order to use digital manufacturing, you have to create your 3D or 2D projects on your computer. You can create any design such as mechanical designs, architectural design, artistic designs, even the most complicated ones!
Sculpteo’s services are helping companies to develop their products everyday, using 3D printing or laser cutting. These manufacturing techniques have their own advantages, their differences but also their similarities. Indeed, both of these techniques will speed up your manufacturing process and will help you to create accurate 3D objects. They are also great tools for mass customization, it becomes really easy to get custom-made items at a lower price thanks to digital manufacturing, as only the 3D or 2D model needs to be modified to make a new object.
You want to make the most of digital manufacturing but you don’t know which of these manufacturing methods will be the most adapted to your project? Don’t worry, we are going to help you choose between additive manufacturing and laser cutting.
What is 3D printing?
How does it work?
3D printing is a manufacturing process in which a part is built by adding material layer by layer, by opposition to subtractive methods where material is being removed to create an object. First, you need to create a 3D file using a 3D modeling software and choose the material that you want There are actually different manufacturing methods, it depends on the materials and techniques that you choose and need for your project.
There are powder-based methods, creating parts additively by sintering fine polymer powder particles, to fuse them together locally with a laser. You can get 3D printed plastic parts using this method. There are also processes to create 3D printed resin parts, using a liquid that is solidified by UV light layer by layer to create rigid and highly detailed parts.
Learn more about 3D printing technologies right here.
You can 3D print:
- Plastics with technologies such as Selective Laser Sintering or Multi Jet Fusion.
- Resins with technologies such as the CLIP technology or Polyjet
- Metals with technologies such as Selective Laser Melting, Direct Metal Laser Sintering, or Binder Jetting.
All these technologies also offer the possibility to print with different 3D printing materials. The opportunities are really numerous, that is why 3D printing can be a really convenient manufacturing technique for diverse projects. If you want to use 3D printing you will also have to choose the 3D printing materials really adapted to the parts that you want to create.
What kind of projects is it possible to create with 3D printing?
3D printing actually allows to use a wide range of different 3D printing materials and techniques, leading to really impressive projects: 3D printed homes, 3D printed jaws, 3D printed prostheses or 3D printed fashion accessories.
This technology is now useful and essential for diverse industries, from healthcare to fashion and architecture! It is even possible to create electronics projects, such as 3D printed robots.
https://www.poppy-project.org/fr/robots/poppy-humanoid
What is laser cutting?
How does it work?
You actually have the choice between two different techniques: laser cutting or laser engraving. Laser cutting is a technology using a high-powered laser beam to actually cut the material, while laser engraving will simply engrave your part. This manufacturing technique will turn your 2D design into a real object.
What kind of projects is it possible to create with laser cutting?
If you choose to use this manufacturing method for your project, you will access a wide range of materials, from acrylic to wood. What is it possible to laser cut or engrave?
Thanks to our laser cutting service, you can laser cut or engrave acrylic, plywood, MDF, cardboard, POM. This will offer a lot of possibilities to create your projects, especially to create large parts at a lower cost, but still with interesting details. Laser cutting will be the perfect solution to make original custom items, such as custom visit cards or decorations.
This will offer a lot of possibilities to create your projects, especially to create large parts at a lower cost, but still with interesting details. Laser cutting will be the perfect solution to make original custom items, such as custom visit cards or decorations.
3D printing or laser cutting: What is the best for you?
Both of these manufacturing techniques are efficient and quick to make good prototypes or even great end-use products. Some of your products might be doable with both! But one of these techniques is always more adapted than the other, it always depends on the nature of the project, the material, the size and the final use of your parts.
You will have to ask yourself several questions. Is your project doable by assembly of different laser cutting parts? Will your part be adapted to the 3D printing process or will they take too much space in the build chamber?
The benefits of 3D printing
Prototyping and production: Everything is possible with additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing will really allow you to produce high quality prototypes. Using a 3D modeling software, you will be able to create simple or complex designs, and make as many iterations as you need at a lower price.
Using a 3D modeling software, you will be able to create simple or complex designs, and make as many iterations as you need at a lower price.
Additive manufacturing will really help you to create high quality prototypes but also finished products, at a lower cost than with techniques such as injection molding. By using 3D printing, you will definitely save time, money and improve your product development process.
Create complex designs
3D printing could really be a great asset for your company. Indeed, everything is now 3D printable from fashion accessories to mechanical devices. Professional 3D printers are now able to create any items, even with complex design, impossible to make in just one part with any other manufacturing technique.
Make the most of the various 3D printing materials
It is an interesting methods if you need to manufacture complex and resistant objects made in one part. Among the variety of materials available, you will certainly find one with properties meeting your expectations. Does your part need to be heat resistant? Flexible? Do you need special finishings? Find the perfect materials and all the options available for your project on our material pages!
Does your part need to be heat resistant? Flexible? Do you need special finishings? Find the perfect materials and all the options available for your project on our material pages!
If you are working in the medical field and need a biocompatible material, 3D printing is certainly the best choice. For instance, you can use our biocompatible resins to create prosthesis or other kinds of medical devices. That wouldn’t be possible with laser cutting, that is why, for these kind of project, additive manufacturing will be the perfect solution!
If you need to create a metal 3D object, 3D printing is the perfect method for you. For instance, you can 3D print stainless steel, or aluminium.
The benefits of laser cutting
Work on bigger parts and flat surfaces
The main difference between laser cutting and 3D printing is that laser cutting only allows to work on flat surfaces. If you need a 3D objects, you will have to assembly laser cut parts. It can still be a solution to give life to your projects, it will be cheaper, especially if your are planning to make big sized project. Indeed, laser cutting is great to work on bigger surface than additive manufacturing.
Indeed, laser cutting is great to work on bigger surface than additive manufacturing.
As this manufacturing technique is convenient to create large parts, at Sculpteo we used it to create tables for an exhibition.
You can choose your dimensions, and it will create your object with a really high precision. Keep in mind that some projects will be cheaper to produce using laser cutting, as they might be a little bit too big to be 3D printed and thus, they would be quite expensive. The price is really one of the biggest advantages of laser cutting. It is really becoming a convenient and efficient manufacturing techniques if you need to create products such as furnitures.
Many materials available for your laser cutting projects
Thanks to the various materials offered by this manufacturing technique, laser cutting will be perfect to create diverse custom items, such as custom visit cards, boxes, decorations, furnitures. For instance, to created our tables, we used MDF material (Medium-Density Fibreboard). You could even make circuit boards. Watch this video to see how it is possible to make laser cut circuit boards:
You could even make circuit boards. Watch this video to see how it is possible to make laser cut circuit boards:
Like 3D printing, it can be great to produce amazing jewelry, but it will allow you to use different materials like wood. Check out our last blog post about the most impressive projects made using laser cut wood, it could be a great inspiration for you!
If you need to work on wooden parts, you will have to choose laser cutting instead of additive manufacturing. Indeed, it is not possible to work on wooden projects with professional 3D printers yet, laser cutting is way more adapted. You will get laser cut objects with a high quality.
But wood is not the only material that you can laser cut. Acrylic is also a great material, offering a lot of possibilities in terms of transparency and colors.
Make the most of the design possibilities
You can laser cut a lot of different designs, it is possible to make complex creation with this technique, that is why it is particularly useful if you need to create custom-made parts. You can also combine it with the use of laser engraving to add even more details and personalization on your products! You will see, laser cutting will be the perfect solution to make really accurate parts.
You can also combine it with the use of laser engraving to add even more details and personalization on your products! You will see, laser cutting will be the perfect solution to make really accurate parts.
If you are planning to create your projects with laser cutting, be sure to choose the best software to create your 2D design. And if you need a little help, we have laser cutting tutorials available on our site. It will allow you to get designs prepared for laser cutting.
Can’t make a decision? Use both!
You definitely can’t choose because you find that these two manufacturing techniques are both amazing? Don’t choose and use both. You can totally build an entire project using these two techniques. That is actually what two of our designers did here at Sculpteo: they created a bike with 70% of parts made using additive manufacturing and laser cutting. Check out how our designers created this project.
You can see that both 3D printing and laser cutting have big advantages and could improve your manufacturing process. If you still have questions about these two manufacturing techniques, don’t hesitate to contact our sales team. They will help you to make the best choice to manufacture your parts! Once that you have your 2D and 3D designs ready, you can upload them on our 3D printing service or our laser cutting service, we will send you your parts in a few days!
If you still have questions about these two manufacturing techniques, don’t hesitate to contact our sales team. They will help you to make the best choice to manufacture your parts! Once that you have your 2D and 3D designs ready, you can upload them on our 3D printing service or our laser cutting service, we will send you your parts in a few days!
If you are interested in 3D printing and laser cutting, subscribe to our weekly newsletter to get all the latest news about digital manufacturing.
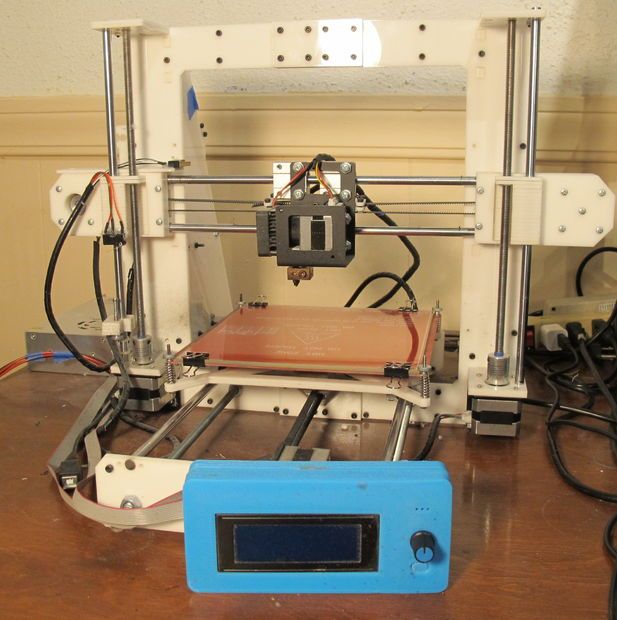
How to turn your 3D printer into a laser engraver/cutter
3DPrintStory Reviews How to turn your 3D printer into a laser engraver/cutter
If you want to create something more than just 3D printed parts, or simply expand the range of materials you work with, laser cutting and engraving is a great choice.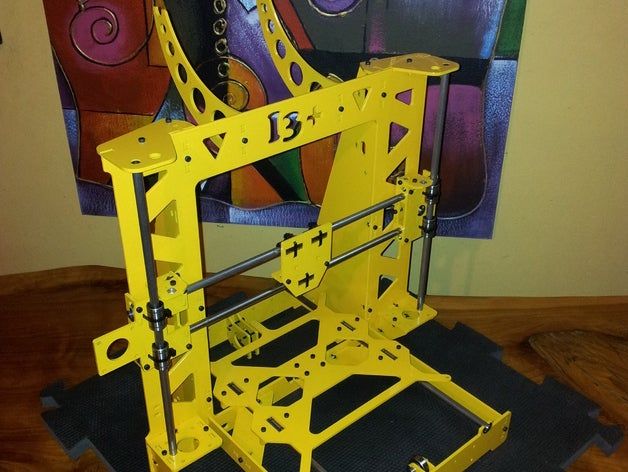 It allows you to work with other materials and does not require special experience. nine0005
It allows you to work with other materials and does not require special experience. nine0005
But perhaps the best part is that this technology can be easily used by upgrading your 3D printer. The motion system of 3D printers far exceeds the requirements for laser cutting, and laser diode modules can be as small as hot end nodes.
Converting a 3D printer into a laser cutter and engraver is a pretty big deal. In this article, we'll talk about laser technology in general, and then we'll discuss the main steps involved in converting your 3D printer. nine0005
What is laser cutting and engraving?
Laser cutting is a process in which a laser beam selectively removes material along a specific path by vaporizing it. Engraving is basically the same, but instead of removing material, it marks the surface, changing its appearance through oxidation.
Two laser technologies are mainly used for the manufacture of tabletop machines: CO2 and diode. CO2 lasers are powerful enough to cut most materials, including some metals, and are widely used in industry. nine0005
nine0005
However, CO2 laser machines are bulky and require rather expensive and fragile equipment such as CO2 tubes, mirrors and lenses. On the other hand, diode lasers are lightweight and relatively cheap, since they consist mainly of one small module.
Diode lasers are much less powerful than CO2 and are best suited for engraving and cutting thin sheets of balsa and plywood. In comparison, a CO2 laser can deliver up to 400W, while diode lasers can only deliver 10W maximum. nine0005
Do you need to convert your 3D printer to a laser engraver?
Converting a 3D printer to a CO2 laser machine can be quite a challenge given the size of the tubes and the complex system of mirrors. For this reason, it is much better to use diode lasers.
However, please note that these lasers can only cut certain materials such as paper, cardboard, balsa and plywood with a thickness of 3 to 5 mm. Due to the wavelength of the laser, it cannot cut or engrave transparent materials such as acrylic. nine0005
nine0005
Also be aware of the safety requirements when using lasers. Class 4 lasers are dangerous to the eyes, so the use of safety goggles is mandatory. In addition, the products of combustion emitted during the operation of the laser can be harmful to our health, so enclosure and proper ventilation are required.
Take all of this into account before deciding to convert your 3D printer to a laser machine. Given the risks involved, it is especially important to take precautions. nine0005
How to turn a 3D printer into a laser cutter/engraver?
The process of converting a 3D printer to a laser machine varies but usually involves the same steps.
First of all, we need to choose the laser module that best suits our requirements (eg functionality and price). Next, we need to figure out how to adapt it to the electronics and physical interface of the 3D printer.
Laser module
Powerful solid state lasers are a relatively recent development, but the market has quickly caught up with demand for diode laser modules. nine0005
nine0005
The laser power is always between 1 and 10 W. Some white label lasers you see online are listed as 30W or even 40W, but that is definitely not optical power output.
Power will determine which materials can be engraved and whether materials such as wood (and how thick) can be cut. Laser manufacturers usually provide a list of materials that can be engraved and cut, so be sure to check it out.
Variable focal length, which you sometimes see as an advertised feature, is not really important here, as the 3D printer's Z-axis can raise or lower the module to fit a fixed distance. nine0005
The air blower is an interesting feature as it blows air directly onto the surface to disperse particles that interfere with the laser, resulting in cleaner cuts. Some lasers have this feature built in.
Compatibility and connection
Most laser modules can be connected directly to the 3D printer control board. The partial cooling fan on a 3D printer requires an adjustable power output to control its speed, and it is this port that can power and drive the laser. nine0005
nine0005
Some lasers require a special 12V power input. This is usually via a separate driver board, which can be powered by either the printer's power supply or an external power supply. This setup also requires a connection to the printer through the fan port.
Refer to the laser manufacturer's documentation for correct connection instructions.
Installation
Installation and mounting of the laser module is perhaps the only major equipment change in the entire conversion process. Although some lasers come with non-standard brackets, some adaptation will always be required. nine0005
Fortunately, you already have a 3D printer, so anything is possible. You may be able to find suitable designs on sites like Thingiverse. Otherwise, it might be time to try some 3D modeling software like Tinkercad or similar. The model doesn't have to be fancy, just a joint between holes and screws that will be used to hold the hot end.
Once you've attached the laser module to your 3D printer, you're done! However, in order to start engraving or cutting, you may need a new firmware. nine0005
nine0005
Next steps
The laser cutter and engraver is one of the coolest machines we can have at home because it allows us to make things from a wider range of materials than extruded plastic filament. Converting a 3D printer to a laser printer is an inexpensive option, and you can always go back to 3D printing in the end.
By the way, for Ender and CR-10 users, Creality offers special laser kits to add (not replace) laser modules to these printers. nine0005
Be sure to check out some step-by-step guides online. For example, Instructables user Goss Adema has documented converting the Anet A8 to a laser cutter and engraver, and the TeachingTech YouTube channel has great step-by-step instructions on how to do it on any 3D printer.
How do 3D printing lasers differ from cutting lasers?
EOS uses lasers to fuse polymer powders (SLS) and metals (DMLS). nine0085
Over the past four decades, laser cutting machines have become a must-have tool for the vast majority of sheet metal fabricators.
From CO2 lasers to their newer and more capable solid-state counterparts, what began as a laboratory experiment in the 1960s is today the method of choice for quickly and accurately cutting virtually any metal less than 2.54 cm thick.
However, soon after lasers began to appear in workshops everywhere, another use was found for collimated light, which seems destined to play an equally important role in production. nine0005
In 1987, 3D Systems co-founder Chuck Hull sold the first SLA-1 machine using an ultraviolet laser to cure thin layers of photoreactive resin. Additive manufacturing (AM), better known as 3D printing, was born.
Since then, 3D printing has evolved from a photopolymer-only prototyping process to a viable method for producing final parts. With a variety of materials available, including engineering plastics, superalloys such as titanium and INCONEL, maraging steels, tool steels, and stainless steels, there is nothing that 3D printers cannot produce. And while laser light is not the only technology used to solidify, sinter, melt, or otherwise combine these various materials, it is definitely the leader in additive manufacturing. nine0005
And while laser light is not the only technology used to solidify, sinter, melt, or otherwise combine these various materials, it is definitely the leader in additive manufacturing. nine0005
Note: This article is a translation.
Long live the difference?
How is a laser capable of cutting through 18mm thick steel different from a laser used to print tooling for press brakes, assembly fixtures and robotic end effectors?
"Metal 3D printing in industry mainly uses fiber lasers with a wavelength of 1070 nanometers, that is, in the infrared range, while for cutting, a continuous solid-state fiber or disk laser with a wavelength in the range from 1030 to 1080 nm is usually used" , explains Dave Locke, Additive Manufacturing Sales Specialist at TRUMPF Inc. nine0005
Obviously the wavelengths are similar, but this is not the case for power. The power of lasers installed in TRUMPF printers for metal processing by powder coating (PBF) does not exceed 500 W. Lasers used for cutting, on the contrary, produce up to 6 kilowatts - 12 times more. If you put that much laser power into a 3D printer, it will burn a hole in the bottom of the machine.
Lasers used for cutting, on the contrary, produce up to 6 kilowatts - 12 times more. If you put that much laser power into a 3D printer, it will burn a hole in the bottom of the machine.
However, it is important to understand that laser power is only one operating parameter of many, whether the metal is being fused or cut into pieces. In addition to power, manufacturers are also looking to provide versatility. For example, they go to great lengths to make their products "customizable" (adjustable to work with different materials) depending on the grade and thickness of the material being cut. nine0005
Fiber lasers are now able to effectively cut thicker materials that were previously reserved for CO2 lasers.
"bell-shaped Gaussian waveform, similar to that generated by fiber lasers provide very high spot densities, which is what gives them the ability to cut through thin materials,” explains Dustin Deal, product manager for Amada America's laser division. “However, this small spot size becomes less effective when you move up to 1.3 mm cm and above, and this is the reason why CO2 lasers have long offered better speeds and better edge quality on thicker materials."
“However, this small spot size becomes less effective when you move up to 1.3 mm cm and above, and this is the reason why CO2 lasers have long offered better speeds and better edge quality on thicker materials."
"But as technology evolved, Amada (and other companies) found ways to adjust the laser beam diameter and waveform to create a larger spot - shaped like a hat. This is why, and for other reasons, Amada has completely switched to fiber in its standard line of laser cutting machines,” says Deal.
Does this mean that CO2 lasers are going down in history? Unlikely. "Polymers are basically transparent to shorter fiber laser wavelengths, so using them in 3D printing is like shining a flashlight through the snow," says Damien Gray, Principal Laser Optics Engineer at EOS North America Inc, Pflugerville, Texas. It goes right through. "The light from a CO2 laser, on the other hand, is strongly absorbed by most polymers." nine0005
This is good news for selective laser sintering (SLS), the plastic alter ego of PBF metal printing. But there is a caveat: CO2 lasers provide lower print resolution and cannot do the fine details that fiber lasers can.
But there is a caveat: CO2 lasers provide lower print resolution and cannot do the fine details that fiber lasers can.
David Cullen, Director of Application Engineering, 3D Systems Inc. in Rock Hill, South Carolina, explained that the CO2 laser used in his company's SLS printers has a wavelength of about 10,600 nm, which is 10 times longer than a conventional fiber laser. As the wavelength increases, so does the spot size. nine0005
"You get a print resolution of 475 microns, or about half a millimeter, which is much better than a powder coated machine," he says. "On a positive note, the SLS print speed is one of the fastest in the industry."
Two spots beat one
Like laser cutting equipment manufacturers, 3D printer manufacturers use advanced optics and electronics to change laser parameters on the fly - at least in some cases. nine0005
The detail layer is printed on an SLA 3D printer from 3D Systems, the inventor of the stereolithography system.
The SLS setup just reviewed has a fixed beam size, but Cullen said stereolithography (SLA), the technology his company was founded on, now offers two spot sizes.
"By adjusting the crystal orientation in the YAG laser, we can generate a large spot to quickly scan large areas on the inside of a part, and then dynamically switch to a small spot for fine detail and contour tracking," he said. "The result is better part quality and faster assembly." nine0005
Ankit Saharan, application development and R&D manager at EOS, agreed on the importance of spot size control, but added that in the case of additive laser manufacturing, there are many more characteristics than spot size and the wavelength or type of laser used for it. creation.
"A small spot size is better than a large spot because the smaller the spot, the smaller the melt pool, which means less stress in the workpiece," Saharan said. "We start at around 45 µm on small platforms and go up to 100 µm on large platforms.