Expensive 3d printer
The Five Most Expensive 3D Printers on the Market Today
Electronics
ByGarrett Parker Posted on Updated on
What began as a novelty in the technology world has rapidly advanced to a new way of manufacturing a variety of goods. 3D printing is taking the world by storm and it’s now used to create parts for jets, automobiles, shoes, and even homes that people can live in. The first 3D printer prototypes were smaller and we were amazed watching them slowly create objects through a computer program, but when we viewed one at the local fair some years back, we didn’t imagine what they would be capable of. Some of the 3D printers used privately and commercially range from small in size to very large. This technology is fascinating, and in researching them, we were curious about how much they cost. We thought you’d enjoy what we found out so we’re sharing the five most expensive 3D printers in 2018.
5. The Box – $310,000
Th Box is a 3D printer that is available for purchase if you have the $310,000 it retails for. The Box was created by two Swedish students who were working on a hobbyist project. Jacob Lundin and Cim Bergdahl were the pair responsible for the concept of the Box and deserve the credit for its development. They joined with others who had an interest in furthering the development of their project and formed BLB industries which manufactures this unique 3D printer that is among thee fastest and largest in the entire world, and it works through a Fused Granular Fabrication process. This 3D printer is fifth on our list because although it’s quite expensive, there are four more that are even higher in price.
4. 3D Platform Excel – $450,000-1,200,000
The 3D Platform Excel is the fourth most expensive printer in the world. You may notice that there is a broad price range and this is because this machine is customizable and although the base size is 13 x 328 x 13 feet, we learned that there is an infinite range of length dimensions possible. This 3D printer is unique, and although the base model is not the largest, there is a full potential for manufacturing it in a size that would place it in the lead. There are other customizable features available for the tech savvy who have specific projects in mind. This printer uses the Fused Deposition Modeling process. The company that manufactures this printer is 3D Platform and they offer several large 3D printers.
This 3D printer is unique, and although the base model is not the largest, there is a full potential for manufacturing it in a size that would place it in the lead. There are other customizable features available for the tech savvy who have specific projects in mind. This printer uses the Fused Deposition Modeling process. The company that manufactures this printer is 3D Platform and they offer several large 3D printers.
3. Optomec LENS 850-R – $1,200,000
The Optomec company manufactures and sells the LENS 850-R 3D system. It’s the third most expensive printer in the world. It operates through the Laser Engineered Net Shaping process, also referred to as LENS, hence the name of the printer model. It’s available for sale for $1.2 million. The unique LENS process builds a print layer by layer and it melts metal powder through a high power laser. This printer has the capacity to build objects from scratch as well as making repairs to existing items that are damaged.
2.
 SonicLayer 7200 – $2,500,00
SonicLayer 7200 – $2,500,00Fabrisonic is the company that manufactures and sells the SonicLayer 7200. It’s tied for the most expensive position with a price tag of $2.5 million. This printer has been described as a CNC mill. It’s a complicated machine that has tremendous potential and capacities. It uses the Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing process, also known as UAM. Ultrasonic waves are used to bond metal layers together, so it doesn’t require high temperatures to operate.
1. Imprimere’s Model 2156 – $2,500,000
The most expensive 3D printer in the world is in a tying position with the SonicLayer 7200. It’s the Imprimere’s Model 2156. The Im company manufactures and sells it commercially. This 3D printer uses the Concrete Deposition process and is used in the construction business and holds promise for revolutionizing the industry through a more consistent fully automated building process that reduces costs. This amazing technology is used to or printing with concrete as well as for grinding, milling and 3D scanning. It also has the capability of traveling on tracks for up to 70 meters. It’s an exciting and innovative development in 3D technology that holds promise for changing the way that buildings are constructed.
It also has the capability of traveling on tracks for up to 70 meters. It’s an exciting and innovative development in 3D technology that holds promise for changing the way that buildings are constructed.
Final thoughts
It’s truly amazing how far 3D technology has come. The things that were once believed to be speculative and based on futuristic fantasy are now becoming realities that are useful in real life applications. Having accomplished this level of advancement, it makes one wonder what we’re going to see next?
Garrett Parker
Garrett by trade is a personal finance freelance writer and journalist. With over 10 years experience he's covered businesses, CEOs, and investments. However he does like to take on other topics involving some of his personal interests like automobiles, future technologies, and anything else that could change the world.
Similar Posts
The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
While we'd hesitate to call 3D printing a mature technology, you might say it has reached its teenage years. Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
PC Labs has been reviewing 3D printers since 2013. Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
Filament feeders had to be coaxed into delivering filament from the spool to the extruder. Print beds had to be manually aligned. The extruder or hot end had to be positioned just right to minimize the gap between the nozzle and the build plate (the flat surface on which the object is printed). Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Not so much anymore. While they can still be rebellious at times, 3D printers have grown up a lot, and achieving the 3D printer basics has gotten a lot less likely to end in a shouting match over small things. And they've gotten a lot more affordable, too, for curious DIY-ers and hobbyists to try.
If you're in the market for a beginner or low-cost 3D printer, it's important to know how lower-end models differ. Read on for mini-reviews of the top budget 3D printers we've tested. After that, we go into more detail on understanding the 3D printer specs and tech relevant to beginning buyers. Ready to take the plunge? Read on.
Original Prusa Mini
Best Overall Budget 3D Printer
4.5 Outstanding
Bottom Line:
It requires assembly and calibration care (plus shipping from the Czech Republic), but the Original Prusa Mini is a compact, open-frame 3D printer that consistently produces superb-quality output for a great price.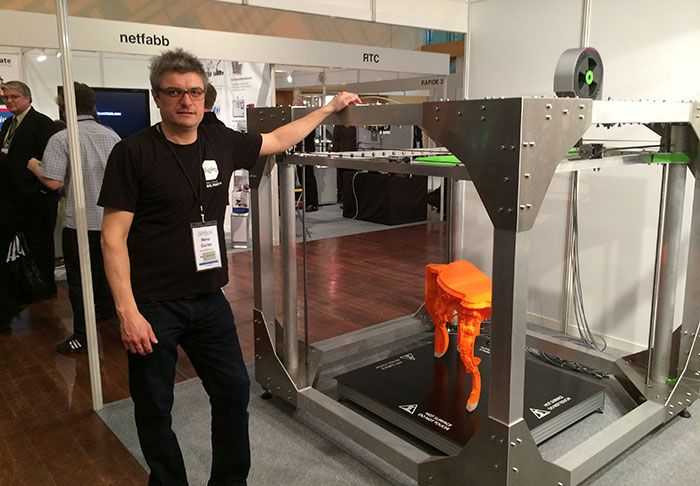
PROS
- Top-notch object quality
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Useful, professionally printed user guide
- Great support resources
- Versatile, user-friendly software
CONS
- First-layer calibration can be tricky
- Only includes starter packets of filament
- Requires monitoring if young children or pets are around
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | $399.00 | $399.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Original Prusa Mini Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Mini
Best Budget 3D Printer for Schools, Community Centers
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Mini is a consumer-oriented 3D printer that provides a winning combination of low price, ease of setup and use, solid print quality, and smooth, misprint-free operation.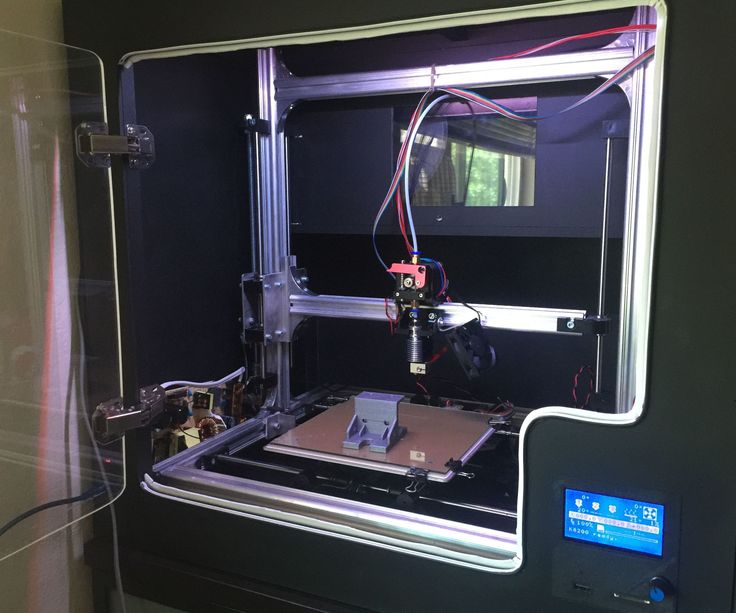
PROS
- Very low price.
- Reasonably priced filament.
- Good print quality.
- No misprints in testing.
- Easy setup and operation.
- Quiet.
- Prints over a USB or Wi-Fi connection.
CONS
- Occasional problems in trying to launch prints.
- Removing printed objects from the print bed is sometimes tricky.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | $199.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Amazon | $199.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Mini Review
Toybox 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Children
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The Toybox 3D Printer works well as a model designed for children, offering reliable printing from a browser or mobile device and a few thousand toys to print, plus creative options to output drawings or photos. Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
PROS
- Reliable, misprint-free printing
- Easy setup
- One-touch operation
- Well-composed help resources
- Access to more than 2,000 printable toys and projects
- Lets you create your own printable designs
CONS
- Tiny build area
- Not ideal for importing 3D files created elsewhere
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Toybox Labs | $379.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Toybox 3D Printer Review
Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Beginners, Non-Techies
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
3D printing gurus will be intrigued by the Monoprice Mini Delta V2's use of the delta rather than Cartesian coordinate system, but beginners will just enjoy its low price, ease of use, and speedy printing.
PROS
- Sub-$200 price
- Quick, nearly misprint-free printing
- Easy setup and operation
- Sturdy steel-and-aluminum frame
- Supports multiple filament types
CONS
- Tiny build area
- So-so print quality
- Mere one-year warranty
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $179.99 | $179.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer Review
Anycubic i3 Mega S
Best Budget 3D Printer With an Open Design, Big Build Area
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Anycubic i3 Mega S, an inexpensive open-frame 3D printer, produced decent-quality prints in our testing. To get the most out of it, though, may require precise calibration.
PROS
- Modestly priced
- Large build area for an inexpensive printer
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Generally solid print quality
- Uses well-known Cura software
CONS
- Finicky print-platform alignment
- Supported coils of filament are small
- Poorly placed spool holder
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $229. 98 98 | $229.98 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $279.00 | $279.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic i3 Mega S Review
Anycubic Vyper
Best Budget 3D Printer for the Biggest Build Area Possible
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Anycubic's modestly priced Vyper whips up large 3D prints on its open-frame design, and provides automatic print-bed leveling. Just know that some minor assembly is required—and printed objects may require a bit of cleanup.
PROS
- Relatively large build area
- Automatic bed leveling
- Simple assembly
CONS
- Short (one-year) warranty
- Includes only a small starter filament coil
- Using Cura software with the Vyper requires tweaking a couple of settings
- Test prints showed some "hairy" filament residue
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $429. 99 99 | $429.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $369.00 | $319.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic Vyper Review
Creality Ender-3 V2
Best Budget 3D Printer for Tinkerers and DIY Types
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Hands-on tweaking defines Creality's budget-price Ender-3 V2, an open-frame 3D printer that you build from a kit. It produces generally above-par prints, but its print bed can be tricky to keep leveled.
PROS
- Inexpensive
- Slightly above-average print quality
- Good-size build area for its price
- Supports several filament types
CONS
- Manual print-bed leveling can be tricky
- Setup instructions could be deeper, more legible
- Questionable quality control on some parts
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299. 00 00 | $246.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Creality Ender-3 V2 Review
Flashforge Finder 3D Printer
Best 3D Printer for the Very Tightest Budgets
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Flashforge Finder 3D Printer is moderately priced and offers good print quality, but it proved tricky to get up and running in our tests.
PROS
- Quiet.
- Good print quality.
- Connects via USB 2.0 cable, USB thumb drive, or Wi-Fi.
- Reasonably priced.
CONS
- Some objects pulled off the platform during testing.
- Poor documentation.
- Modest build volume.
- Limited to printing with polylactic acid filament (PLA).
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $729.00 | $729.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Flashforge Finder 3D Printer Review
Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Dabbling in Small Objects
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer is a compact, stylish 3D printer with above-par overall print quality, but, alas, a tiny build area for the money.
PROS
- Small, lightweight for a desktop 3D printer.
- Easy to set up and use.
- Supports PLA, PETG, and wood composite filaments.
- Multiple-color support.
- Wi-Fi camera monitors print jobs.
- Prints from USB drives, SD cards, or mobile devices.
CONS
- High price for its capabilities.
- Small build area.
- Too-brief warranty.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $699.00 | $699.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro
Best Budget 3D Printer With Closed Design, Roomy Build Area
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro is a moderately priced closed-frame 3D printer with a large build volume and overall good performance, but a potentially balky filament-feeding system.
PROS
- Spacious build area
- Works with third-party filaments
- Self-leveling print bed
CONS
- Build plate is not heated
- Limited to PLA- and PETG-based filaments
- Guide tube is prone to detaching
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Best Buy | $449.95 | $449.95 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro Review
Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Cheap Filament
3. 0 Average
0 Average
Bottom Line:
The Monoprice Voxel is an under-$400 3D printer that's easy to set up and use. It exhibits generally good print quality, but it was unable to print two of our test objects.
PROS
- Easy to set up and use.
- Budget price for printer and filament spools.
- Supports PLA, ABS, and several composite filament types.
- Versatile software.
- Prints over Ethernet or Wi-Fi, or from a USB thumb drive.
CONS
- Frequent misprints on certain test objects.
- Slightly balky touch screen.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $449.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Walmart | $429.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer Review
Buying Guide: The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
How to Buy a Cheap 3D Printer
The biggest changes to 3D printers over the last few years have come to the cheaper models. Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
What separates more expensive 3D printers from cheap ones ("cheap" defined as $500 or less, for the purposes of this article) is often a select group of features. These include the build volume, the type of frame, the varieties of supported filament, the software, and the connectivity mix. Let's run through those in turn.
What's the Right Build Volume for a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer’s build volume is the maximum dimensions (HWD) of a part that it can print. (We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(Credit: Molly Flores)
As a general rule, inexpensive 3D printers have small build volumes, while more expensive ones have larger build volumes. This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.
Should I Get an Open-Frame or Closed-Frame 3D Printer?
Which brings us to the frame "form factor" question: open-frame versus closed-frame. Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
Low-cost 3D printers include both open-frame and closed-frame models, as well as a few stereolithography printers. If a relatively large build volume is a priority, you’re likely to get more bang for the buck with an open-frame model. Open-frames do have some clear downsides by definition: They tend to be noisy, emit odors when certain plastics are melted, and provide little protection for someone who might touch the hot extruder.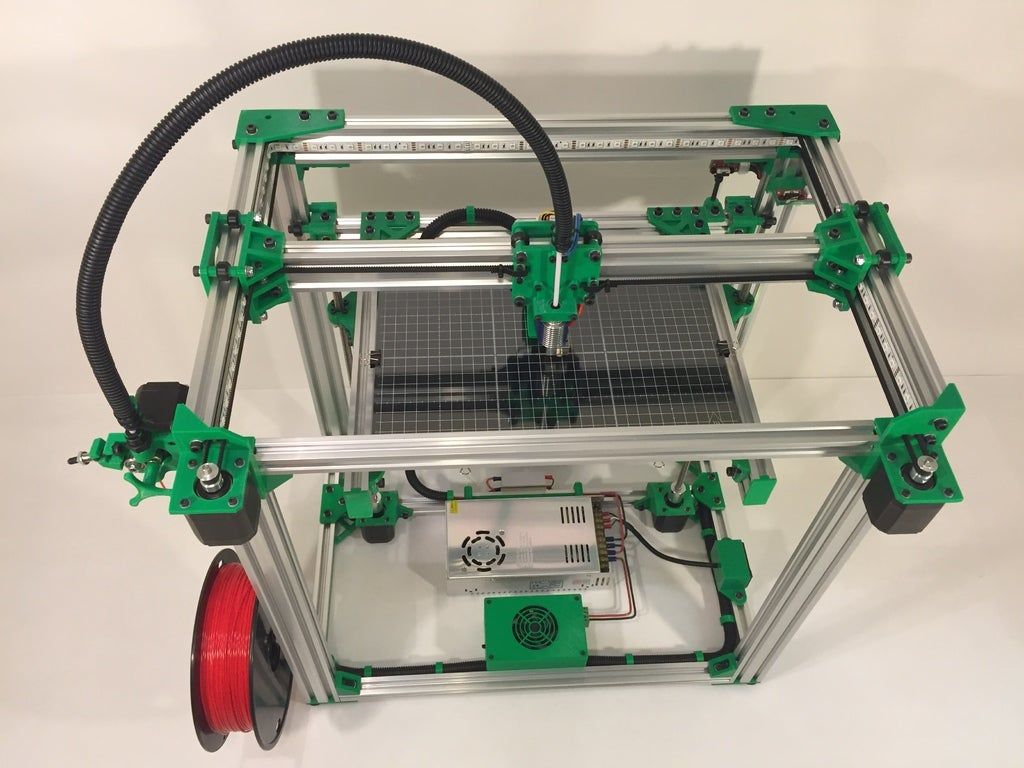
(Credit: Molly Flores)
Also, recognize some potential negatives of open frames, depending on the model. Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
What Should I Look for in 3D Printer Software and Connectivity?
Gone are the days when tinkerers had to cobble together several different programs to get a 3D printer to run. Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
3D printing software performs three main functions: processing an object file (resizing, moving, rotating, and in some cases duplicating it), slicing it (into virtual layers, based on your chosen resolution), and printing it. These are almost universally combined into a seamless process. Some high-end printers have software that supports a wider range of settings you can tweak, but even the basic suites work at least reasonably well.
More likely to vary among the cheaper set is the array of connection options from model to model. Nearly all have a USB Type-A port to fit a thumb drive for printing from document files. Most also have a USB Type-B port for connecting directly to a computer, and some offer Wi-Fi, too (or as an alternative), while a handful let you connect via Ethernet to share the printer across a local network.
Some printers support storing 3D files on an SD or microSD card (which may also contain the printer’s system files). Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
While high-end 3D printers tend to have an abundance of connection choices, discount models vary widely in their choices. Some are generous and some are basic, so it pays to assess what a given model offers.
What Should I Look for in Filament Support?
Filament support tends to be a key area that separates the cheaper models from the higher-end ones. (See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
(See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
Recommended by Our Editors
3D Printing: What You Need to Know
3D Printer Filaments Explained
(Credit: Molly Flores)
PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable, plant-based polymer, while ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the same tough plastic that Legos are made from. Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Many entry-level and low-price 3D printers stick exclusively to PLA. If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
Should I Consider a 3D Printing Pen Instead?
Although they aren’t printers per se, inexpensive 3D pens are close kin to 3D printers—using the same filament types and a similar extrusion system—and we include them in the 3D printing category. Rather than tracing out a programmed pattern, you use the 3D pen much like a normal pen, except that you draw with molten plastic. You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
(Credit: 3Doodler)
Most 3D pens cost less than $100, and some cost $50 or less. At a glance, 3D pens may appear to be toys, but some artists and craftspeople have taken to them, as it is possible to make quite complicated and beautiful objects with them. If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
So, What Is the Best Cheap 3D Printer to Buy?
Buying a budget 3D printer needn’t mean a world of sacrifice. Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Many casual 3D-printing experimenters will be fine with printing over a USB cable or from a thumb drive, and sticking to PLA may be the best choice for a starter 3D printer. If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Below, check out a spec breakdown of the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed, paralleling our picks above. Also, for a look at the broader market, see our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
The most expensive 3D printers in the world
- home
- News AT
- World
- The most expensive 3D printers in the world
Various technologies do not stand still, they are constantly evolving. This article proposes to consider the evolution of industrial 3D printers today, which are the most expensive in the world and why. nine0014
This article proposes to consider the evolution of industrial 3D printers today, which are the most expensive in the world and why. nine0014
3D printers are unique in terms of the variety of different 3D printing methods, materials used and their applications. You can spend as little as $100 to get a reliable 3D printer to make a huge variety of parts from affordable plastic material. On the other hand, you can spend over a million dollars to buy a 3D printer to 3D print parts with large and complex construction geometries. They can be used in the aerospace industry, the production of space satellites or miniature biocompatible devices for medical purposes. The most expensive 3D printers on the market today use 1 to 12 powerful lasers to fuse metal powder, sinter polymer materials, or polymerize resin, and 3D printing from a given 3D model occurs by applying the powder layer by layer, which is a process additive manufacturing. nine0014
It can be noted that the size of the 3D printer does not determine how expensive the 3D printer will be. Today, the price often depends on advanced patented technologies and features that allow a 3D printer to produce fast and high-quality 3D-printed parts without requiring special technical knowledge from the operator.
Today, the price often depends on advanced patented technologies and features that allow a 3D printer to produce fast and high-quality 3D-printed parts without requiring special technical knowledge from the operator.
Some of the most expensive printers are not even for sale. Carbon 3D's 3D printers are available for rent only, which allows them to be used by many users. Others use their 3D printers on a project-by-project basis, such as the Vulcan construction printer from homebuilder Icon 3. nine0014
Stargate, the world's largest metal 3D printer built by Relativity Space to 3D print rockets, it's not for sale, but if it was, it would definitely be on our list. Many of the most exciting technologies in 3D printing can only be used for custom 3D printing, not for purchase. (Source: Relativity Space)
Let's look at the criteria that affect the cost of a modern industrial 3D printer.
Features 3 D -printers affecting their price:
- The uniqueness of technology when creating
- How automated the processes in 3D printer
- The size of the working chamber
- Functions allowing quality control
- Self -software software
- Numerous controls and adjustments
- Controlled environment inside the working chamber (use of inert gas, possibility of heating/cooling the working platform)
Let's break down these features:
Features that drive up the price of 3D printers include printer technology-specific software, real-time 3D printing control systems, and anything that automates processes that sometimes are performed manually in cheaper systems (layer leveling, subsequent post-processing or powder sieving) or processes that require knowledge of metallurgy or polymers.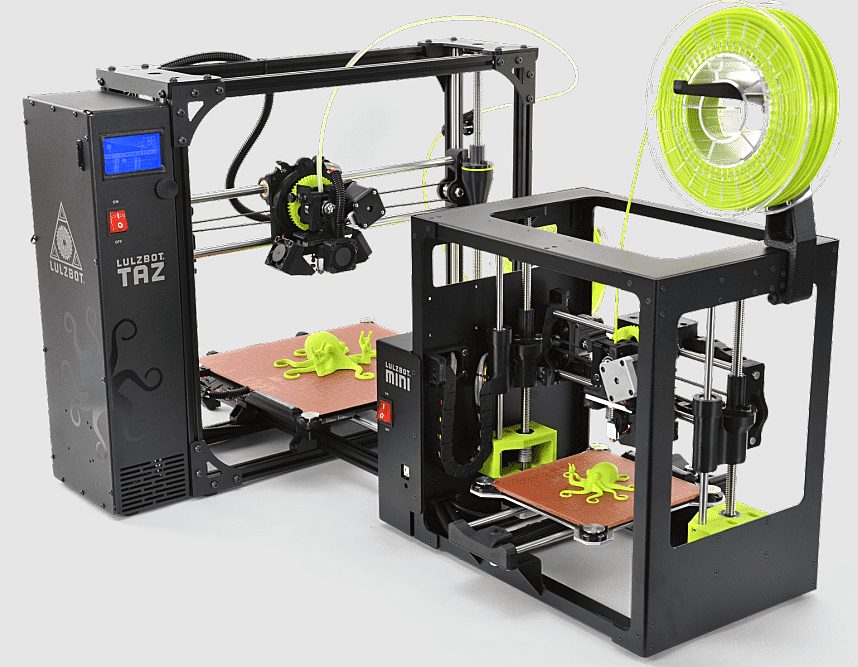
Production technology that requires a vacuum chamber in a 3D printer, filling the working chamber with an inert gas, or printers that are certified for use in clean rooms and have these characteristics are significantly reflected in the final price of this equipment.
The materials used in the 3D printing process also have a significant impact on the final cost of a 3D printer. Many 3D printers only work with proprietary materials that have been developed by the manufacturer for that 3D printer. They can be metal powder, special resins filled with carbon fiber particles, and unique polymer powders. At this point in time, it is possible to 3D print anything from pure gold to advanced engineering plastics on 3D printers, even in the harsh environment of space. nine0014
There are 3D printers that can 3D print multiple materials in one job, and there are multicolor 3D printers that are also in the higher price segment.
THE MOST EXPENSIVE 3 D -PRINTERS
The 3D printer manufacturers discussed below are reluctant to publish exact prices for their products. This is due not only to competition, but also to the fact that 3D printers have a basic package, as well as a package with additional options according to customer requirements. That said, with that in mind, below is a look at some of the most expensive 3D printers available today - all costing over half a million US dollars - and what they provide. nine0014
This is due not only to competition, but also to the fact that 3D printers have a basic package, as well as a package with additional options according to customer requirements. That said, with that in mind, below is a look at some of the most expensive 3D printers available today - all costing over half a million US dollars - and what they provide. nine0014
E-Plus3D EP-M450H
3D printer EP-M450H LPBF (Source: E-Plus 3D)
E-PLUS3D produces industrial metal 3D printers with a large camer of the building for additive manufacturing for various industries in the country. These 3D printers are used in the aerospace, automotive, electronics, and engineering industries to produce not only large-sized parts such as heavy-duty molds, but also mass-produced parts. nine0014
The EP-M450H Metal 3D Printer is the company's largest 3D printer with a build chamber of 456 x 456 x 1080 mm, producing 99.9% density metal parts from a wide range of materials at a speed of 55 cm³ per hour.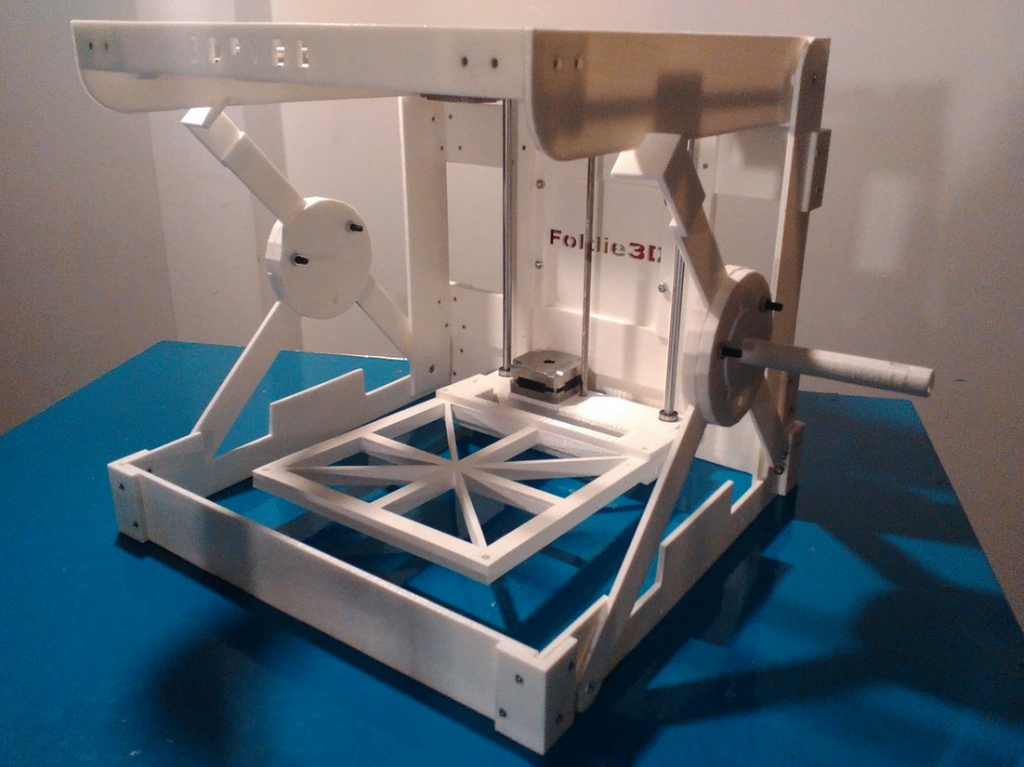
XJet Carmel 1400C
Israeli company XJet has developed a unique ceramic 3D printing technology. NanoParticle Jetting (NPJ) technology allows the production of metal and ceramic parts with a high level of detail, smooth surface roughness and geometric accuracy. The high cost of this 3D printer is not only due to the technology itself, patented materials that make this printer a serious investment, but also to the advanced automation of the 3D printer itself, which makes it easy to use. nine0014
Carmel 1400C, equipped with one of the largest 1400 cm² work platform in the industry, which allows you to simultaneously produce several ceramic parts.
SLM Solutions NXG Xll 600
Large Metal 3D Printer NXG XII 600 (Source: SLM Solutions) range of printers, but its NXG Xll 600 is what the company says is a revolution in industrial additive manufacturing. The NXG XII 600 was designed for high-volume additive manufacturing and features the industry's first 12 1,000W lasers with a 600x600x600 build chamber.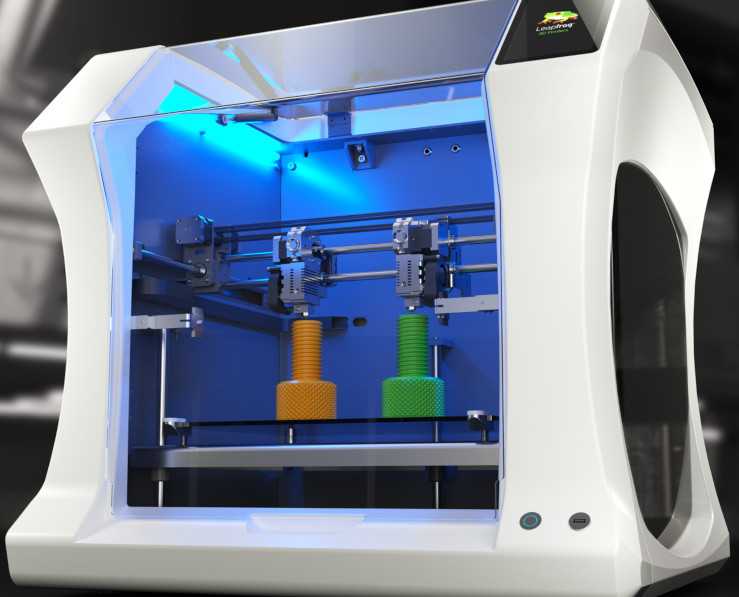 Lasers provide high build speed up to 1000 cm 3 /h and capacity not available for other machines.
Lasers provide high build speed up to 1000 cm 3 /h and capacity not available for other machines.
In addition to lasers, the NXG Xll 600 has all the benefits that SLM Solutions customers have been asking for over the years, including automatic start-up, laser focusing, closed powder feed and material screening, and other latest developments.
UpNano NanoOne Bio
The Austrian company UpNano has developed a two-photon 3D printer using hydrogel-based bio-ink, which allows direct printing of 3D structures containing living cells, both at the meso- and microscale. The NanoOne Bio printer is based on the NanoOne line of laser printers capable of creating structures of 12 orders. The new hydrogel is the only commercially available resin that allows live cells to be embedded directly from culture plates into 3D printed structures for biological applications. nine0014
UpNano claims that the combination of X Hydrobio INX U200 and NanoOne Bio opens up new possibilities in biomedical research and development, both in industry and academia, allowing pharmaceutical companies and research institutes to create cell models that mimic natural growth conditions in the body person.
Black Buffalo 3D
Black Buffalo's new 1G construction printer (Source: Black Buffalo)
Black Buffalo 3D, an American company based in South Korea, officially unveiled its Nexcon 1G earlier this year, which is a 3D printer for building houses and other large concrete objects. The printer can create a 92.9 square meter structure in less than 20 hours. It uses Black Buffalo's patented cementitious material, the company calls it ink, that can be dyed to a chosen color and is also customizable to 3D print locally according to the temperature, humidity and altitude conditions of the area. nine0014
The Nexcon 1G is a modular 3D construction printer that can be extended along the X, Y and Z axes to scale up (or down) a project up to three stories high. The 1G printer is unique in that users can reposition the base rails and move the printer to a new printable area without having to remove the X or Z axis.
Optomec LENS 860
Energy Deposition (DED), which allows the recovery of large titanium components, such as those used in aircraft engines. Optomec offers several models of 3D printers that have large build chambers like 860x600x610 and laser power of 3 kW. nine0014
Optomec offers several models of 3D printers that have large build chambers like 860x600x610 and laser power of 3 kW. nine0014
The LENS 860 machining systems are ideal for the fabrication, repair or coating of medium to large metal parts.
ExOne S-Max Pro
While many ExOne printers (now owned by Desktop Metal), they are still very affordable given that high volume 3D printers can cost quite a few zeros.
3D printers are used to 3D print complex and detailed sand molds and cores for foundries producing large metal parts for industrial use. The S-Max Pro features a 1,260 liter build chamber for fast 3D printing of sand molds and cores. A new automated print head enables fast 3D printing, while improved sand compaction ensures the density and strength of complex sand mold designs. As the most advanced system in the ExOne family of sand 3D printers, the S-Max Pro is focused on continuous 24/7 production and offers Industry 4.0 integration with cloud connectivity and real-time machine monitoring. nine0014
nine0014
In conclusion, I would like to know the opinion of Russian industrialists and users of industrial 3D printers: Is it possible to integrate these 3D printers into the Russian industry? Do Russian developers of this equipment need to produce the same expensive 3D printers in Russia?
Share article:
8 nuances worth paying attention to
Sooner or later, everyone will learn about 3D printing. And only a few lucky people, imbued with the opportunities that 3D printing opens up, catch themselves thinking that they want to purchase a 3D printer. The desire gradually develops into a serious decision and the search for the right option begins. And here the potential buyer is faced with the fact that he does not fully understand what to choose among the whole variety of 3D printers. We will try to answer this question in as much detail as possible. What to look for, and how to make a choice? We want to offer a small checklist of the nuances that you need to pay attention to when choosing a 3D printer. You need to decide for yourself for what tasks you will use this technique? What features should a 3D printer have to solve your problems? nine0014
You need to decide for yourself for what tasks you will use this technique? What features should a 3D printer have to solve your problems? nine0014
Tip 1 : Decide on 3D printing technology
The first step is to decide on the technology of 3D printing. There are two main paths here. If you are faced with the task of manufacturing high-precision and miniature products, such as jewelry, then 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology are suitable for you. Such printers are specially designed for the manufacture of high-precision models. 3D printing in these printers occurs using a laser beam that illuminates the photopolymer resin. Hence the accuracy of the models. Prominent representatives of this segment: Form 2 3D printer or B9 3D printercreator If you are faced with a wider range of tasks, and functionality, part size, and low manufacturing cost are more important, then an FDM printer will suit you. 3D printing on this equipment involves layer-by-layer melting of plastic. If according to SLA printers everything is clear. The scope of their application is jewelry, dentistry, high-precision prototypes of small parts. Then we will dwell on FDM printers in more detail. There is a lot more variety of different options for implementing printers. nine0014
If according to SLA printers everything is clear. The scope of their application is jewelry, dentistry, high-precision prototypes of small parts. Then we will dwell on FDM printers in more detail. There is a lot more variety of different options for implementing printers. nine0014
Nuance 2: Evaluate your needs
Of course, you always want to get all the best and with maximum opportunities. Do you need all this to solve your current problems? What can be cited as an example? For example, the size of the working area of the FDM 3D printer. There are printers on the market with a large print area (1m x 1m x 1m), and with a very small one (100mm x 100mm x100mm). But for most tasks, a certain standard has already developed. This is the printable area within 200 x 200 x 200 mm. With slight fluctuations in size in one direction or another. Most 3D printers have exactly this size of the working area. This volume is enough to solve 95% of any tasks. But options are possible ... If you plan to manufacture small parts, then a smaller size will probably be enough for you. But if your work will be related to manufacturing, for example, a master model for casting, or large prototypes, then only then it makes sense to pay attention to a printer with a large print area. In other cases, the size of the print area larger than the standard is nothing more than a nice bonus. But as they say, you have to pay for everything. Therefore, most often it makes sense to focus on the “standard” print area. And even if the part you need to print is larger than the working area of your 3D printer, you can always cut it in a special editor, and then print 2 parts of the model and glue them together. nine0014
But options are possible ... If you plan to manufacture small parts, then a smaller size will probably be enough for you. But if your work will be related to manufacturing, for example, a master model for casting, or large prototypes, then only then it makes sense to pay attention to a printer with a large print area. In other cases, the size of the print area larger than the standard is nothing more than a nice bonus. But as they say, you have to pay for everything. Therefore, most often it makes sense to focus on the “standard” print area. And even if the part you need to print is larger than the working area of your 3D printer, you can always cut it in a special editor, and then print 2 parts of the model and glue them together. nine0014
Nuance 3 : Decide on the complexity of the products
You should decide for yourself how complex models you will print on a 3D printer. If you plan to manufacture complex prototypes, or complex art models, then you need a 3D printer that can print with two materials.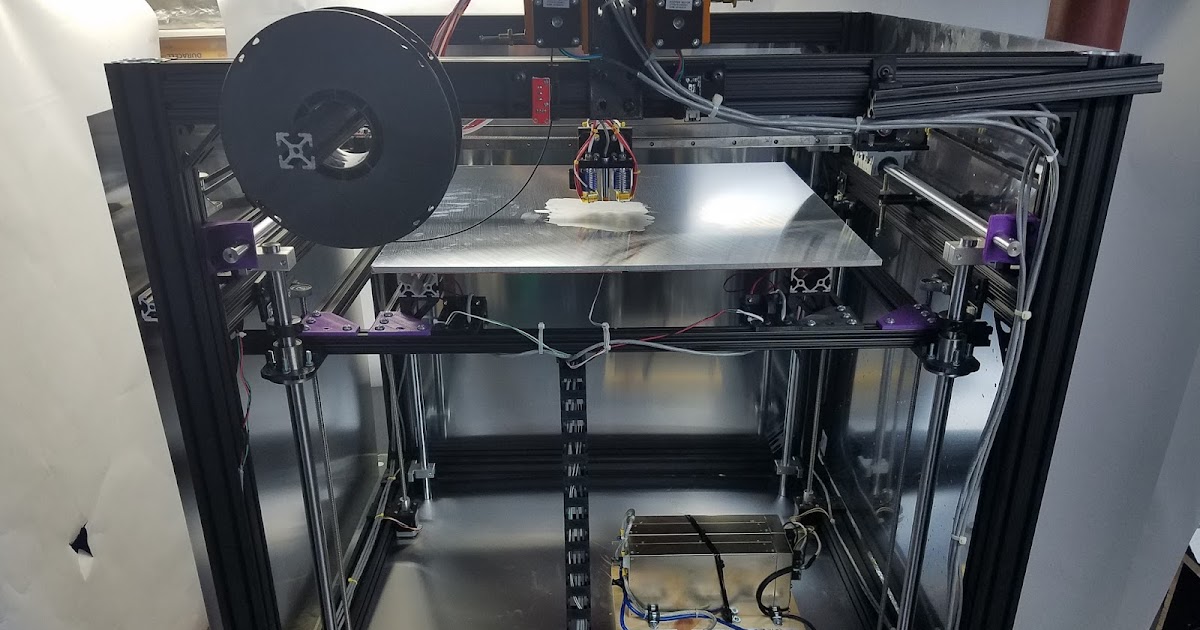 This is necessary so that your printer can print supports from soluble material. If the models are not the most complex, then you can get by with one extruder and save the budget. A complex model is a model with a large number of elements suspended in the air, or a model whose elements have angles of more than 30 degrees. nine0014
This is necessary so that your printer can print supports from soluble material. If the models are not the most complex, then you can get by with one extruder and save the budget. A complex model is a model with a large number of elements suspended in the air, or a model whose elements have angles of more than 30 degrees. nine0014
Point 4: Decide on the list of materials to be used.
Another important point. You must immediately determine for yourself a list of possible materials with which you are going to print. This primarily applies to materials with a high degree of shrinkage, such as ABS and Nylon. In order to print with such materials, a heated table is clearly required in a 3D printer. And it is very desirable to have a closed case to provide a thermal circuit around the model. If you plan to print only with PLA plastic. You don't need a heated table. But still it is better that the printer has a heated table. Now the difference in the cost of printers with a heated table is practically the same as the cost without it. But you get a universal solution with which you can perform the full range of tasks facing a 3D printer. One more moment. Ability to print with flexible materials Quite a number of 3D printers face the problem of printing with flexible materials. Of course, printing with various Flexes and Rubbers is very interesting at first glance. But the use of these materials in life is not very common. Usually, for most people, this happens like this: A couple of models are printed, and the understanding comes that this is not a fast and rather complicated process. And this is where the acquaintance with flexible materials ends. Therefore, it makes sense to demand such an opportunity from the printer if printing with such materials is very necessary. nine0014
Now the difference in the cost of printers with a heated table is practically the same as the cost without it. But you get a universal solution with which you can perform the full range of tasks facing a 3D printer. One more moment. Ability to print with flexible materials Quite a number of 3D printers face the problem of printing with flexible materials. Of course, printing with various Flexes and Rubbers is very interesting at first glance. But the use of these materials in life is not very common. Usually, for most people, this happens like this: A couple of models are printed, and the understanding comes that this is not a fast and rather complicated process. And this is where the acquaintance with flexible materials ends. Therefore, it makes sense to demand such an opportunity from the printer if printing with such materials is very necessary. nine0014
Nuance 5: Construction and kinematics
Next, you need to pay attention to the design of the 3D printer.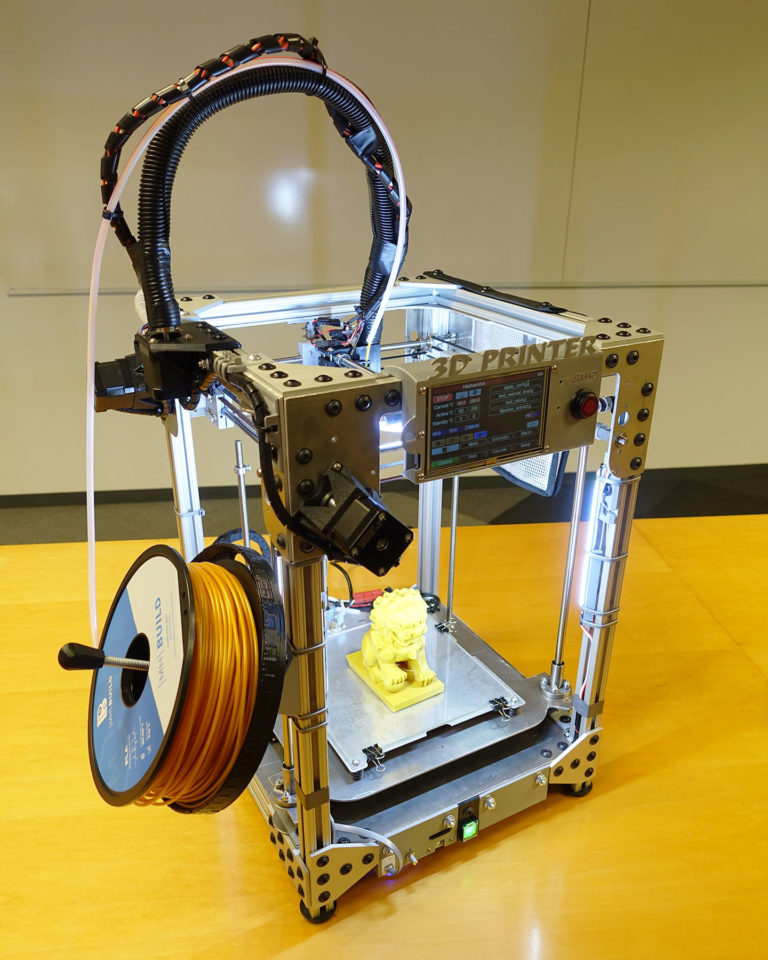 Even if you are not a great specialist in technology, you can immediately see that some printers have an open design. And others are closed. As they like to be called in the Russian-speaking community "cubes". What does the appearance say? Printers with an open design, usually have kinematics with a horizontally moving table (based on Prusa 3D printers). This kinematics has some inherent flaws. Such as, not the highest print speed and possible print quality problems associated with the complexity of the settings. First of all, this is the so-called wobble. Also, the lack of a closed case can cause print quality problems with high shrinkage plastics (ABS, Nylon). The main advantage of printers of this design is their price. It is usually lower. But as you know, you have to pay for everything. In this case, the worst performance. The so-called "cubes" today, is the main design, which is represented by leading manufacturers on the market. Such printers are built according to the lifting table scheme.
Even if you are not a great specialist in technology, you can immediately see that some printers have an open design. And others are closed. As they like to be called in the Russian-speaking community "cubes". What does the appearance say? Printers with an open design, usually have kinematics with a horizontally moving table (based on Prusa 3D printers). This kinematics has some inherent flaws. Such as, not the highest print speed and possible print quality problems associated with the complexity of the settings. First of all, this is the so-called wobble. Also, the lack of a closed case can cause print quality problems with high shrinkage plastics (ABS, Nylon). The main advantage of printers of this design is their price. It is usually lower. But as you know, you have to pay for everything. In this case, the worst performance. The so-called "cubes" today, is the main design, which is represented by leading manufacturers on the market. Such printers are built according to the lifting table scheme.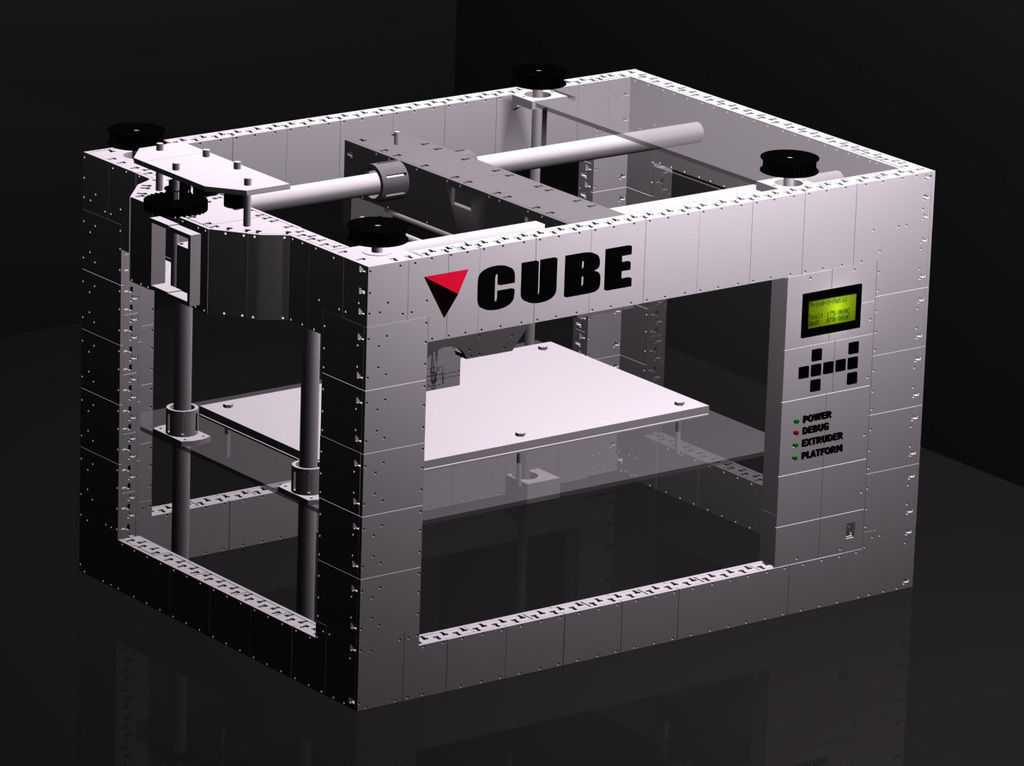 And they lack most of the shortcomings that are inherent in printers from the previous group. “Cubes” usually have a closed body, which allows the highest quality printing with plastics with a high degree of shrinkage. Closed case printers are more rigid. This results in better quality printing. The kinematics of moving the print head is represented by various designs. They have their pros and cons. But most of them have advantages over moving table printer circuits. nine0014
And they lack most of the shortcomings that are inherent in printers from the previous group. “Cubes” usually have a closed body, which allows the highest quality printing with plastics with a high degree of shrinkage. Closed case printers are more rigid. This results in better quality printing. The kinematics of moving the print head is represented by various designs. They have their pros and cons. But most of them have advantages over moving table printer circuits. nine0014
Nuance 6: Diameter and interchangeable nozzle
Most 3D printers on the market come with 0.3-0.4mm nozzles. This is enough to solve the vast majority of tasks facing a 3D printer. Some of the printers have the ability to install a nozzle of a different diameter, others do not. As we wrote above, the need to print with nozzles with a diameter other than 0.3-0.4 mm arises very infrequently. This mainly concerns, or personal experiments, or some very specific tasks. If you do not plan to do this, then this opportunity is not so necessary. What do we mean by specific tasks? This is especially true for printing large items, where it is very important to reduce the printing time. This can be achieved by using large diameter nozzles. For example, with a diameter of 0.6-0.8 mm, or even a diameter of 1 mm. For printers with a large printable area, the ability to change nozzles is already a vital necessity. Therefore, here, as in the case of a heated table, the ability to change nozzles is a good bonus. It is not mandatory, but very useful if you do not have to pay extra for it. nine0014
If you do not plan to do this, then this opportunity is not so necessary. What do we mean by specific tasks? This is especially true for printing large items, where it is very important to reduce the printing time. This can be achieved by using large diameter nozzles. For example, with a diameter of 0.6-0.8 mm, or even a diameter of 1 mm. For printers with a large printable area, the ability to change nozzles is already a vital necessity. Therefore, here, as in the case of a heated table, the ability to change nozzles is a good bonus. It is not mandatory, but very useful if you do not have to pay extra for it. nine0014
Nuance 7: Print thickness
It is important to understand that most models on a 3D printer are printed with a layer of 0.1-0.2 mm. These are the optimal values that allow you to achieve quality and acceptable print speed. There are a certain number of printers that allow you to print with a layer of less than 0. 05 mm, and get very high quality prints. But then there is the problem of a sharp increase in print time. And if such print quality is important to you, then it probably makes sense to turn your attention to 3D printers, which we talked about at the very beginning of the article. These are 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology. nine0014
05 mm, and get very high quality prints. But then there is the problem of a sharp increase in print time. And if such print quality is important to you, then it probably makes sense to turn your attention to 3D printers, which we talked about at the very beginning of the article. These are 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology. nine0014
Nuance 8: Extruder type
Today there are two main types of extruder. This is a direct extruder in which the bar feed motor is located in the printhead itself. And the so-called Bowden extruder, where the plastic feed motor is located on the body. And the plastic itself is fed to the extruder through a fluoroplastic tube. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of extruder? Bowden extruder, due to the lack of a motor on the print head, has less weight. And therefore, it has greater positioning accuracy, which affects the print quality. And a higher speed of movement, which, accordingly, has a positive effect on the speed of printing. But it has one drawback. It is usually difficult to print with flexible plastics on a Bowden extruder. Such as Rubber or Flex. All its positive features, this extruder reveals when using plastic with a diameter of 2.85-3.00 mm. But this type of plastic is less common than the now standard plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. And therefore, users of printers with such plastic are often deprived of the opportunity to use new types of materials. Which are primarily produced in the most common form factor of 1.75mm. The direct extruder usually doesn't have such big problems with flexible plastics. Easier to set up, but due to the greater mass of the print head, it is inferior to the Bowden extruder in terms of speed and positioning accuracy. What to prefer? This is the user's choice. We just wanted to talk about the pros and cons of these extruder types. Of course, there are many more nuances when choosing a 3D printer. But we think that even our small list will force you to look and study some points that you may not have thought about more closely.
But it has one drawback. It is usually difficult to print with flexible plastics on a Bowden extruder. Such as Rubber or Flex. All its positive features, this extruder reveals when using plastic with a diameter of 2.85-3.00 mm. But this type of plastic is less common than the now standard plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. And therefore, users of printers with such plastic are often deprived of the opportunity to use new types of materials. Which are primarily produced in the most common form factor of 1.75mm. The direct extruder usually doesn't have such big problems with flexible plastics. Easier to set up, but due to the greater mass of the print head, it is inferior to the Bowden extruder in terms of speed and positioning accuracy. What to prefer? This is the user's choice. We just wanted to talk about the pros and cons of these extruder types. Of course, there are many more nuances when choosing a 3D printer. But we think that even our small list will force you to look and study some points that you may not have thought about more closely.