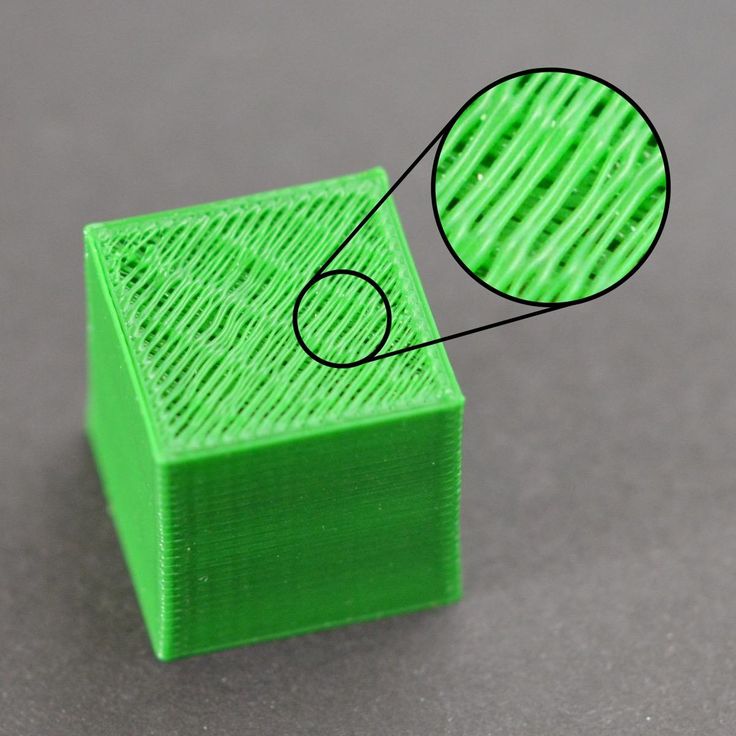
Common 3d print issues
Lines on the Side of Print
Lines on the Side of Print
The sides of your 3D printed part are composed of hundreds of individual layers. If things are working properly, these layers will appear to be a single, smooth surface. However, if something goes wrong with just one of these layers, it is usually clearly visible from the outside of the print. These improper layers may appear to look like lines or ridges on the sides of your part. Many times the defects will appear to be cyclical, meaning that the lines appear in a repeating pattern (i.e. once every 15 layers). The section below will look at several common causes for these issues.
Common Solutions
Inconsistent extrusion
The most common cause for this issue is poor filament quality. If the filament does not have very tight tolerances, then you will notice this variation on the side walls of your print. For example, if your filament diameter varied by just 5% over the length of the spool, the width of the plastic extruded from the nozzle could change by as much as 0. 05mm. This extra extrusion will create a layer that is wider than all the others, which will end up looking like a line on the side of the print. To create a perfectly smooth side wall, your printer needs to be able to produce a very consistent extrusion which requires high-quality plastic. For other possible causes of variation, please read the Inconsistent Extrusion section.
Temperature variation
Most 3D printers use a PID controller to regulate the temperature of the extruder. If this PID controller is not tuned properly, the temperature of the extruder may fluctuate over time. Due to the nature of how PID controllers work, this fluctuation is frequently cyclical, meaning that the temperature will vary with a sine wave pattern. As the temperature gets hotter, the plastic may flow differently than when it is cooler. This will cause the layers of the print to extrude differently, creating visible ridges on the sides of your print. A properly tuned printer should be able to maintain the extruder temperature within +/-2 degrees. During your print, you can use Simplify3D’s machine control panel to monitor the temperature of your extruder. If it is varying by more than 2 degrees, you may need to recalibrate your PID controller. Please consult your printer manufacturer for exact instructions on how to do this.
During your print, you can use Simplify3D’s machine control panel to monitor the temperature of your extruder. If it is varying by more than 2 degrees, you may need to recalibrate your PID controller. Please consult your printer manufacturer for exact instructions on how to do this.
Mechanical issues
If you know that inconsistent extrusion and temperature variation are not to blame, then there may be a mechanical issue that is causing lines and ridges on the sides of your print. For example, if the print bed wobbles or vibrates while printing, this can cause the nozzle position to vary. This means that some layers may be slightly thicker than others. These thicker layers will produce ridges on the sides of your print. Another common issue is a Z-axis threaded rod that is not being positioned properly. For example, due to backlash issues or poor motor controller micro-stepping settings. Even a small change in the bed position can have a major impact on the quality of each layer that is printed.
Related Topics
Not Extruding at Start of Print
Not Extruding at Start of Print
This issue is a very common one for new 3D printer owners, but thankfully, it is also very easy to resolve! If your extruder is not extruding plastic at the beginning of your print, there are four possible causes. We will walk through each one below and explain what settings can be used to solve the problem.
Common Solutions
Extruder was not primed before beginning the print
Most extruders have a bad habit of leaking plastic when they are sitting idle at a high temperature. The hot plastic inside the nozzle tends to ooze out of the tip, which creates a void inside the nozzle where the plastic has drained out. This idle oozing can occur at the beginning of a print when you are first preheating your extruder, and also at the end of the print while the extruder is slowly cooling. If your extruder has lost some plastic due to oozing, the next time you try to extrude, it is likely that it will take a few seconds before plastic starts to come out of the nozzle again. If you are trying to start a print after you nozzle has been oozing, you may notice the same delayed extrusion. To solve this issue, make sure that you prime your extruder right before beginning a print so that the nozzle is full of plastic and ready to extrude. A common way to do this in Simplify3D is by including something called a skirt. The skirt will draw a circle around your part, and in the process, it will prime the extruder with plastic. If you need extra priming, you can increase the number of skirt outlines on the Additions tab in Simplify3D. Some users may also prefer to manually extrude filament from their printer using the Jog Controls in Simplify3D’s Machine Control Panel prior to beginning the print.
If you are trying to start a print after you nozzle has been oozing, you may notice the same delayed extrusion. To solve this issue, make sure that you prime your extruder right before beginning a print so that the nozzle is full of plastic and ready to extrude. A common way to do this in Simplify3D is by including something called a skirt. The skirt will draw a circle around your part, and in the process, it will prime the extruder with plastic. If you need extra priming, you can increase the number of skirt outlines on the Additions tab in Simplify3D. Some users may also prefer to manually extrude filament from their printer using the Jog Controls in Simplify3D’s Machine Control Panel prior to beginning the print.
Nozzle starts too close to the bed
If the nozzle is too close to the build table surface, there will not be enough room for plastic to come out of the extruder. The hole in the top of the nozzle is essentially blocked so that no plastic can escape. An easy way to recognize this issue is if the print does not extrude plastic for the first layer or two, but begins to extrude normally around the 3rd or 4th layers as the bed continues to lower along the Z-axis. To solve this problem, you can use the very handy G-Code offsets which can be found on the G-Code tab of Simplify3D’s process settings. This allows you to make very fine adjustments to the Z-axis position without needing to change the hardware. For example, if you enter a value of 0.05mm for the Z-axis G-Code offset, this will move the nozzle 0.05mm further away from the print bed. Keep increasing this value by small increments until there is enough room between the nozzle and the build platform for the plastic to escape.
To solve this problem, you can use the very handy G-Code offsets which can be found on the G-Code tab of Simplify3D’s process settings. This allows you to make very fine adjustments to the Z-axis position without needing to change the hardware. For example, if you enter a value of 0.05mm for the Z-axis G-Code offset, this will move the nozzle 0.05mm further away from the print bed. Keep increasing this value by small increments until there is enough room between the nozzle and the build platform for the plastic to escape.
The filament has stripped against the drive gear
Most 3D printers use a small gear to push the filament back and forth. The teeth on this gear bite into the filament and allow it to accurately control the position of the filament. However, if you notice lots of plastic shavings or it looks like there is a section missing from your filament, then it’s possible that the drive gear has removed too much plastic. Once this happens, the drive gear won’t have anything left to grab onto when it tries to move the filament back and forth. Please see the Grinding Filament section for instructions on how to fix this issue.
Please see the Grinding Filament section for instructions on how to fix this issue.
The extruder is clogged
If none of the above suggestions are able to resolve the issue, then it is likely that your extruder is clogged. This can happen if foreign debris is trapped inside the nozzle, when hot plastic sits inside the extruder too long, or if the thermal cooling for the extruder is not sufficient and the filament begins to soften outside of the desired melt zone. Fixing a clogged extruder may require disassembling the extruder, so please contact your printer manufacturer before you proceed. We have had great success using the “E” string on a guitar to unclog extruders by feeding it into the nozzle tip, however, your manufacturer should also be able to provide recommendations.
Related Topics
Problems, defects, 3D printing errors and solutions
Often during the operation of a 3D printer, problems may arise due to which defects appear on the finished model. Or instead of a neat product, plastic noodles suddenly appear on the table.
Or instead of a neat product, plastic noodles suddenly appear on the table.
In fact, the causes of defects can be conditionally divided into 2 types - these are physical and software.
Physical ones are those that arise due to problems with the mechanics or any other causes that can be eliminated physically. These include problems with printer mechanisms (belt tension, backlash), clogged or deformed nozzle, incorrect table geometry, etc.
Software - these are defects that occur due to incorrect slicer settings or, less often, errors in the printer firmware. For example, incorrectly selected print speed, retract settings, incorrectly selected temperature for plastic, etc.
Very rarely, the problem may lie in the wrong or “flying” printer firmware (although usually the printer simply will not start then), overheating of some boards during printing, etc. These are rather special cases, so we will not consider them.
Model peels off or does not stick to the build plate
This is the most common 3D printing problem. Every 3D printer has had a case when the first layer treacherously rolls, clinging to the extruder, or the most offensive - when it tears off a partially printed model from the table. The first layer must stick tightly otherwise nothing will be printed.
Every 3D printer has had a case when the first layer treacherously rolls, clinging to the extruder, or the most offensive - when it tears off a partially printed model from the table. The first layer must stick tightly otherwise nothing will be printed.
Gap between table and nozzle 9 too large0023
This is the most common reason. You just need to set the correct gap between the table and the nozzle.
Modern printers often use an auto-calibration (auto-leveling) table system or an auxiliary table leveling program. To calibrate such printers, use the instructions. If there is no manual, it can be downloaded from the manufacturer's website.
If you have a simple printer without auto-calibration, a self-assembly or KIT kit, use a probe or a piece of paper folded in half to calibrate. The probe should be slightly pressed against the table by the nozzle. Before calibration, the table and extruder must be heated. Align the table surface over each adjustment screw (there may be 3 or 4) in turn, and only then check the center point.
If you're having trouble getting your table surface perfectly level, try raft printing. Raft is a thick substrate in several layers that is printed under the model. It will help smooth out the slight curvature of the table.
A small cheat sheet to determine the correct gap on the first layer
Plastic with poor adhesion
Some types of plastic, due to various reasons, such as large shrinkage, do not adhere well to the surface of the printing platform. In this case, try using stickers or special 3D adhesives to improve adhesion between the table and the first layer of plastic.
In the early days of 3D printing, there were experiments with different homemade 3D adhesive recipes. ABS diluted in acetone, BF glue, sugar syrup and even beer. Some experiments have been successful. Until now, some enthusiasts use some types of hairspray or glue sticks as 3D glue. But still they are inferior in their properties to industrial 3D adhesives.
Some types of high temperature plastics with a high percentage of shrinkage (ABS, Nylon, etc.) may peel off the table during printing. This is due to uneven cooling and “compression” of the model (the lower layers have already cooled down, but the upper ones have not yet). For such plastics, it is imperative to use a 3D printer with a heated table and a closed case.
Plastic temperature too low
The hotter the plastic is when it exits the nozzle, the better it will adhere to the print bed. It is better to print the first 5-10 layers at a higher temperature (+ 5-10 degrees) and turn off the blower fan.
Wrong first layer settings (speed and thickness)
A thicker layer sticks easier, so the standard first layer is 0.3mm thick. With an increase in print speed, the heating block may simply not have time to heat the plastic to the desired temperature and it will stick to the table worse. Before printing, check the speed and thickness settings of the first layer in the slicer.
A lot depends on how the 3D printer prints the first layer. Try to control the printing of the first layer and only then leave the printer to work alone.
Plastic does not choke from nozzle
The printer has already begun to print, but the print table remains empty. Or part of the model did not print.
Clogged nozzle
In 3D printing, a nozzle is a consumable. The nozzles are clogged or worn out (frequency depends on the type of plastic). The simplest thing is to replace the nozzle. But if there was no spare at hand, you can try to clean the old one. To do this, there is a whole set of thin needles. Or you can heat a clogged nozzle above the melting point of the plastic and “burn out” the blockage. But later it is still better to replace the nozzle.
Low temperature nozzle
You need to increase the temperature of the extruder in the slicer settings or check the thermistor and heating block. Sometimes the thermistor may not read the temperature correctly due to a malfunction or incorrect 3D printer firmware settings.
Sometimes the thermistor may not read the temperature correctly due to a malfunction or incorrect 3D printer firmware settings.
If the problem occurs after replacing the thermistor - contact the manufacturer or read articles about PID tuning.
Empty extruder
As the extruder heats up, plastic begins to ooze out of the nozzle. Because of this, the extruder may start printing half empty. Because of this, part of the first layer is not printed. You can push the plastic manually by simply pushing the bar into the nozzle. Or solve this problem programmatically - in the slicer, add a contour print around the model (one line).
Some manufacturers and 3D enthusiasts add a line print on the edge of the table at the beginning of each GCode. This is done so that there is plastic in the nozzle by the time the model is printed.
Feed mechanism does not push through plastic
The plastic pushes the feed mechanism to the extruder - a motor with a special pulley put on the shaft. If for some reason the plastic is not pushed through (nozzle clogged, extruder temperature low, etc.), then the pulley “gnaws” through the bar. You need to push the plastic bar with your hands or cut off the damaged piece.
If for some reason the plastic is not pushed through (nozzle clogged, extruder temperature low, etc.), then the pulley “gnaws” through the bar. You need to push the plastic bar with your hands or cut off the damaged piece.
Elephant foot
The first layers of the model are wider and protrude beyond the boundaries of the model. This is due to the fact that the upper layers put pressure on the first ones that have not yet cooled down and flatten them.
High table temperature
Due to the too high temperature of the table, the lower layers remain soft for a long time. Try lowering the table temperature. It is better to reduce gradually (in increments of 5 degrees). You can try to turn on the blower when printing the first layers.
Small gap between nozzle and platen
If, when printing the first layer, the nozzle is too close to the table, then excess plastic will be forced out. After a few coats, this will not be as noticeable, but can lead to the effect of an “elephant's foot”.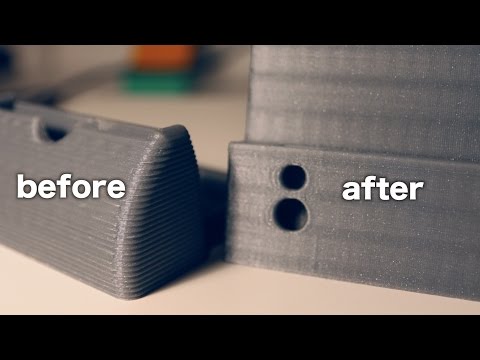
Plastic re-extrusion
When too much material is squeezed out of the nozzle, the walls of the model are not smooth, but bumpy, with sagging.
The solution is software - in the settings of the slicer, you need to set the material feed rate (fluidity) to a lower value. The average value is 95-98%.
It is worth checking the diameter of the rod. If its size is greater than 1.75, then the plastic will be squeezed out more than necessary.
Plastic underextrusion
The plastic is squeezed out too little, because of this, gaps may appear between the layer. The finished model will be fragile and fragile.
Wrong thread diameter
Check the filament diameter in the slicer settings. Sometimes, instead of the popular 1.75, the default is 2.85.
Incorrect feed rate settings
Check the fluidity settings in the slicer. The average should be 95-98%.
Clogged nozzle
Something could get into the nozzle and partially block the exit of the plastic. Visually, the plastic will choke from the nozzle, but in a smaller amount than necessary for printing.
Hairiness or cobwebs on finished model
Thin threads of plastic protrude from the outer wall of the model (most often on one side). The defect appears due to the flow of plastic from the nozzle during idle movement.
Insufficient retract
A retract is a slight pull of a plastic filament from an extruder. Due to the retract when the extruder is idle (from layer to layer or from model to model), heated plastic does not drip from the nozzle. For some flowable plastics (eg PETG) the speed and amount of retraction must be increased.
"Hairiness" can be easily removed by grinding or cutting off the threads with a sharp scalpel.
High temperature extruder
The higher the extruder temperature, the more liquid the plastic becomes. It is important to find a balance so that the plastic is not too liquid and sticks well in layers.
It is important to find a balance so that the plastic is not too liquid and sticks well in layers.
In the selection of the optimal extruder temperature, a test model - a tower - helps a lot. It clearly shows how plastic behaves when printed at different temperatures.
.
Temperature test
Top "perforated" or uneven
The top of the model is bumpy or with holes. The problem may arise if the top of the model is flat. For example, like a cube.
Insufficient airflow
When printing the top plane (cover), the plastic does not have time to cool down and remains too liquid. Because of this, the threads are torn and holes are formed. Increase the fan speed on the last layers.
Few top layers
The top of the print may be too thin and deform as a result. Check slicer settings. The number of upper layers is not recommended to be set less than 6.
Low percentage of filling
If the infill percentage is too low, then the top layer will simply have nothing to rely on. Increase the fill percentage in the slicer settings.
Increase the fill percentage in the slicer settings.
Model deformation
Some parts of the model seem to have melted in some places or on one side. The problem most often occurs when printing with PLA plastic. The defect appears due to the fact that the plastic does not have time to cool and deforms.
Insufficient airflow model
Turn the fans on to maximum. If their power is not enough (in some printers, the fan is located only on one side), you can put a regular desktop fan and direct it to the 3D printer table.
Small model
Small models are difficult to blow well. Try to print small pieces alongside larger ones, or place several identical models in different corners of the table. So the plastic will have more time to cool.
Layer offset
Layers shift along the x or y axis during printing.
Print head jam
Turn off the printer and try to move the extruder along the x and y axes with your hands. The extruder must move freely. If there are jams, check the mechanics of the printer. Bearing wear or the curvature of the shafts may be to blame.
The extruder must move freely. If there are jams, check the mechanics of the printer. Bearing wear or the curvature of the shafts may be to blame.
Electronics overheating
Sometimes electronics problems can be to blame for misaligned layers. The most common cause is overheating of the drivers or too low current exposed to them.
Table top is loose
This is most often seen in 3D printers with glass. During printing, the nozzle may hit the model and move the glass slightly. Before printing, check if the glass or other printing surface is well fixed on the heating table.
Skip layers
Small holes are visible on the print, or the shell of the model is not continuous.
Teflon tube deformed
There are 2 types of thermal barriers - all-metal and with a Teflon tube. If overheated, the Teflon tube may deform. Plastic will pass through it, but in a smaller amount.
Low extruder temperature or high print speed
If the extruder is not heated enough, then the plastic will not be liquid enough and simply will not have time to be forced through the nozzle. The higher the print speed, the higher the extruder temperature should be.
Sometimes the outer walls print well, but the infill is “torn”. In this case, slow down the infill print speed in the slicer.
Model bundle
Cracks form on the surface of the printout during or after printing. Cracks can be large or very small. Most often, this problem occurs with plastics with a high percentage of shrinkage - ABS or Nylon.
Sudden temperature difference (if model delaminates during printing)
With a sharp temperature difference (for example, a draft), part of the model cools down faster. This leads to uneven shrinkage and incorrect distribution of internal stress. For plastics with low shrinkage, this is not critical. But if the shrinkage percentage is more than a few percent, the model may burst in layers.
But if the shrinkage percentage is more than a few percent, the model may burst in layers.
For printing with such plastics, it is recommended to use a printer with a closed housing. If this is not possible, try to avoid drafts and sudden temperature changes in the room where the 3D printer prints as much as possible.
Print temperature
Due to too low printing temperatures, the layers may not “stick” well to each other. Raise the print temperature in the slicer settings.
Hardening (if the model cracks after printing)
Sometimes cracks appear on the model a few days after printing. This is due to uneven distribution of internal stress after cooling. You can try to “harden” the finished product.
For hardening, the model is placed, for example, in an oven, and heated to the softening temperature of the plastic. After that, the heating is turned off and the oven is left to cool slowly with the model inside. Due to this, the stress inside the print is distributed more evenly. But accuracy is very important in this method - if you make a little mistake with the temperature, the finished product can “float”.
Due to this, the stress inside the print is distributed more evenly. But accuracy is very important in this method - if you make a little mistake with the temperature, the finished product can “float”.
Ringing
In places where the extruder changed direction, ripples are visible. Most often it looks like a shadow around the “sharp” protruding elements of the model.
Mechanical problems
Sometimes the problem occurs due to extruder play. Check if the extruder mount to the rails is loose. Be sure to check the tension of all belts.
High print speed or high accelerations
Moving the extruder too fast can cause vibrations that cause ripples on the wall of the model. The lighter the weight of the extruder, the less noticeable the ripples will be. To get rid of ringing, simply reduce the print speed in the slicer settings.
Slits for thin-walled models (not solid shell)
The thin wall of the model is not solid, but consists of two thin walls with a narrow gap between them. This problem is often faced by fans of printing "cutting" for baking.
This problem is often faced by fans of printing "cutting" for baking.
Left model with wall defect, right without
Wall thickness and nozzle diameter mismatch
If the wall thickness is 1 mm, and the nozzle diameter is 0.4, it turns out that for a solid wall, 2 nozzle passes are few, and 3 are already many. The result will depend on the slicer algorithm, but most often you will get 2 walls with a thin slot in the middle (the slicer cannot change the wall thickness). The solution to the problem may be a slight refinement of the 3D model or the use of a different slicer.
Algorithms for calculating 3D models are constantly being improved and refined, and now this problem is less common.
When modeling, take into account not only the thickness of the nozzle, but also the percentage of “overlapping” of lines on each other. If you have a nozzle with a diameter of 0.4 - make the wall in your model not 0.
8, but 0.7 - 0.75.
Wrong model geometry
When instead of a circle you get an oval, and instead of a square you get a semblance of a rhombus.
The main reason is malfunctions in the mechanics of the printer. Be sure to check:
Belts
Check belt tension in x and y. Belts stretch over time and may need to be tightened or replaced. Each 3D printer has its own way of tightening the belt. If the belts are slightly stretched, you can tighten them with the help of a "spring".
Loose pulleys, etc.
Check if all bolts and nuts are tight. Are there backlashes. Pay special attention to tightening the pulleys located on the motors along the x and y axes.
Sagging of some parts of the model
Some parts are not printed, broken, or instead of a neat surface, a swollen plastic snot is obtained.
No support for overhangs
A 3D printer cannot print in the air, so if there are overhanging elements in the model, you need to set supports - supports. The slicer can set the necessary support itself, you need to check the appropriate box in the settings.
The slicer can set the necessary support itself, you need to check the appropriate box in the settings.
When printing with soluble support, you can set the gap between the model and support - 0. This will make the surface smoother. If the support material and the model are the same, you need to add a small gap. Otherwise, it will be difficult to separate the support from the model.
Split model
Sometimes the supports can take more plastic than the model. In this case, to save material and time, it will be more convenient to cut the model. If you have more than one 3D printer, then the model will print several times faster.
When cutting the model, you can leave grooves or mortgages so that the pieces of the model are connected without displacement.
Totals
In this article, we talked about the most popular 3D printing defects and how to solve them. Don't be intimidated by such a long list. Some problems are rare and you are unlikely to encounter them.
Some problems are rare and you are unlikely to encounter them.
There is a list of problems that arise due to the design features of a 3D printer, so try to choose a printer that suits your needs. To do this, you need to understand what products and what material you need.
Problems associated with printing algorithms are quickly eliminated by software developers.
Do not be afraid of possible difficulties and each print will be successful.
20 Most Common 3D Printing Problems (Part 1)
Good afternoon dear 3D Today community! I would like to present you a translation of the article Troubleshooting Guide to 20 Common 3D Printing Problems, which will be divided into 2 parts.
Everyone has problems with printing. We had enough of them to analyze and find solutions for the 20 most common 3D printing problems. In this article, we share our experience and hope that now you do not have to spend extra time diagnosing and solving problems that have arisen.
If you cannot determine what the problem is, compare it with the description.
3D Printing Issue #1: Warp - First Layer Peeling
Description of Issue
At the base of the model, the print rises and does not stick to the platform. This problem can also cause horizontal cracks in the top sections of the printout.
Why did the problem occur?
Deformation of the print base is due to the nature of the plastic. ABS and PLA plastic cools very quickly and this is what can cause the first layer to come off.
Solve 3D printing problem: Printout warped
1. Use heated bed. The easiest solution to this problem is to use a heatbed and set the temperature just below the melting temperature of the plastic. If you set the temperature correctly, the first layer will not come off the platform. The printer bed temperature is often set automatically by the slicer. The recommended temperature for your plastic is listed on the side of the package or reel.
The recommended temperature for your plastic is listed on the side of the package or reel.
2. Use adhesive . If your printout is lifting around the edges, apply a thin layer of glue (or hairspray) to the platform to increase adhesion.
3. Try another platform. Change the platform to a platform with more adhesion. Manufacturers like Lulzbot use a PEI (Polyetherimide) coating that provides a good grip even without the use of glue. XYZPrinting Some printers include a few pieces of thermal tape for the liner. This is a good solution for cool platforms. Zortrax 3D choose a different solution - a perforated backing to which the printout adheres, thereby relieving the user of the problem of deformation at the base.
4. Calibrate the platform. Improper platform calibration can also affect the print quality of the first layer. Check the level of the platform and correct the height if necessary.
5. Increase contact between printout and platform.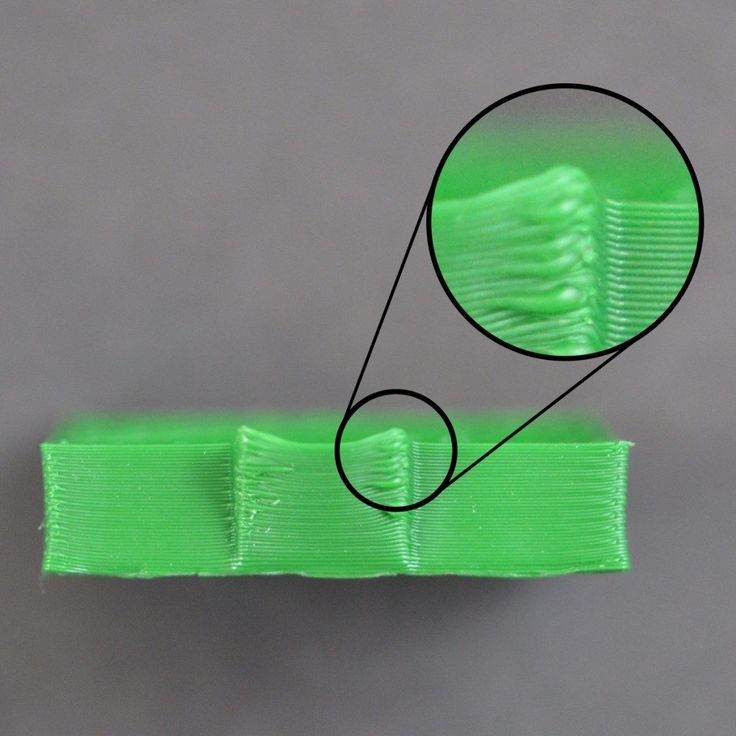 Often this problem also occurs due to insufficient contact between the model and the substrate. It can be easily corrected using the printer software by adding a skirt or backing.
Often this problem also occurs due to insufficient contact between the model and the substrate. It can be easily corrected using the printer software by adding a skirt or backing.
6. Optimize temperature settings. If none of the methods worked, check the advanced settings of the printer software and the printer itself. Try increasing the platform temperature by 5 degrees.
7. Pay attention to the fan settings. As a general rule, the fans should switch to full power as soon as the print reaches a height of 0.5 millimeters, but you can increase the height to 0.75 millimeters to allow the layers to cool naturally.
8. Even if your printer has a heated bed, it is recommended that you use glue (or varnish) and constantly adjust the bed level.
3D Print Warp: Checklist to Avoid Problems
- Use Heated Platform
- Use Glue (Varnish) for More Adhesion
- Instead of Glass Platform, Use Kapton/Heat Tape/Glue/Varnish
- Recalibrate Platform or substrate
- Adjust temperature and fan settings
3D printing issue #2: First layer misalignment (Elephant's foot)
Problem description
The base of the model is slightly off.
Why did the problem occur?
Typically, the base of the model is shifted due to the weight of the print, which presses on the first layer when the lower layers have not yet had time to cool. Often happens with heated bed printers.
3D Printing Solution: First Layer Offset
1. Correct balance. In order to get rid of the problem of first layer displacement, printed models must be sufficiently cooled to support the weight of the entire structure. Here you should be careful: excessive hypothermia can lead to deformation of the first layer. Finding a balance is hard enough. Start by lowering the platform temperature 5 degrees (but no more than 20 degrees below the recommended temperature). If Bottom / Top Thickness is set to 0.6 millimeters, turn on the fan immediately at a height slightly lower.
2. Platform level. Most 3D printing problems are related to the wrong platform level. For each printer, there is a specific approach for platform level calibration. Check the manufacturer's recommendations to determine what you need. Print out a calibration cube and look at the quality of the plastic feed. The calibration cube will help you determine if the plastic has been laid flat, and if the nozzle is too close to the platform and scrapes the melted plastic, or too high causing the plastic to bubble.
Check the manufacturer's recommendations to determine what you need. Print out a calibration cube and look at the quality of the plastic feed. The calibration cube will help you determine if the plastic has been laid flat, and if the nozzle is too close to the platform and scrapes the melted plastic, or too high causing the plastic to bubble.
3. Raise the nozzle. Raising the nozzle a little can often help. The main thing is not to raise it too high.
4. Smoothen the corners of the model. If all else fails, try chamfering the corners of the model base. Of course, this is only possible if you created the model yourself or if you have access to the source file. Start with 5mm and 45º bevel and experiment to get the best result.
First Layer Offset in 3D Printing: Checklist to Avoid Problems
- Balance Platform Temperature and Fan Speed
- Raise Printer Platform
- Check Floor Height
- Make model corners smoother
Description of the problem
The first layer does not look right, some fragments are missing. There are unnecessary lines at the bottom.
There are unnecessary lines at the bottom.
Why did the problem occur?
Such 3D printing problems usually indicate that the platform level has not been set correctly. If the nozzle is too far from the platform, unnecessary lines often appear at the bottom of the printout or the first layer does not stick. If the nozzle is too close to the platform, this can cause formation bubbling.
Also note that the platform must be clean. Fingerprints on the platform may cause the first layer to not adhere to the platform.
3D printing problem solution: Other first layer problems
1. Set the platform level. Each printer has its own platform level configuration process. For example, the latest Lulzbots use auto-calibration, while Ultimaker offers step-by-step manual calibration. But to set up the Prusa i3 platform level, you will need to spend a lot of time studying the issue.
2. Set nozzle height. If the nozzle is too high, the plastic will not stick to the platform, if it is too low, the nozzle will scrape the printout.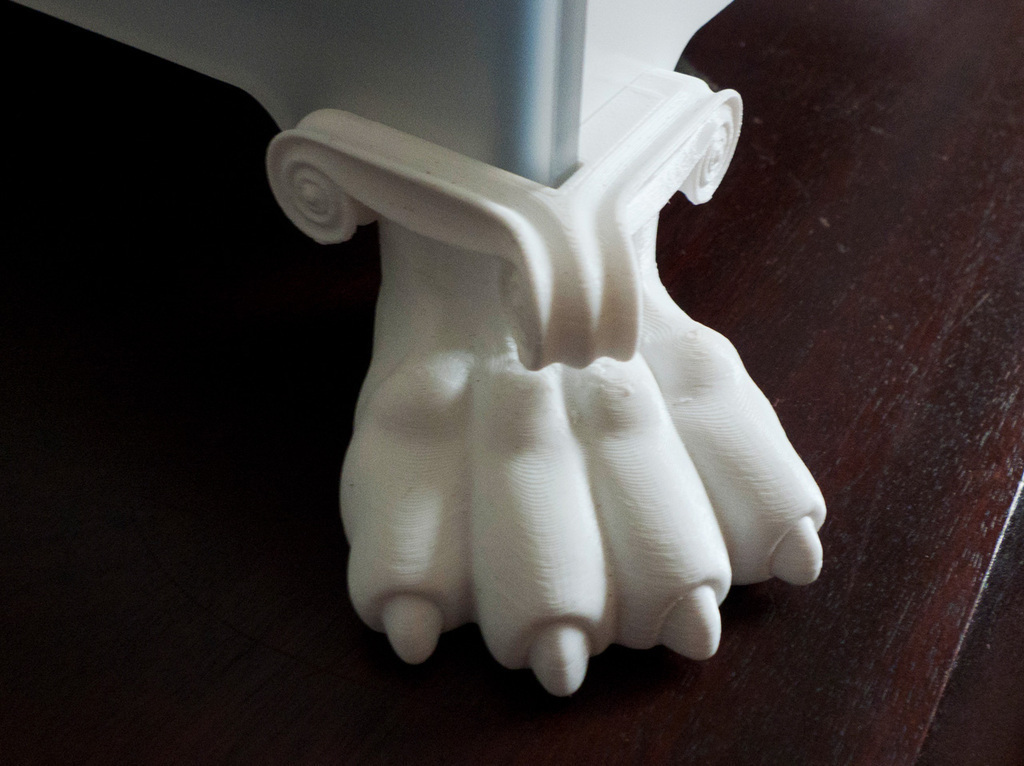
3. Clean the platform. Be sure to clean the printer platform regularly, especially if you are using adhesive. Fingerprints, dust and adhesive residue affect how well the model sticks to the platform.
4. Use glue (varnish). Apply a thin layer of adhesive to the platform to increase the adhesion of the model to the platform. Remember to clean the platform regularly as excess glue can cause the opposite effect.
Layers shift in the middle of the printout.
The printer straps are not tight enough. The top plate is not attached and moves independently of the bottom plate. One of the rods in the Z-axis is not perfectly aligned
Solution to 3D printing problem: Misaligned layers in the model
1. Check the belts. First of all, check how tight the straps are: they shouldn't hang loose, but they shouldn't be too tight either. If you pull on the straps, you should feel a slight resistance. If you feel that the top strap is tighter than the bottom strap, this is a sure sign that they are not tight enough.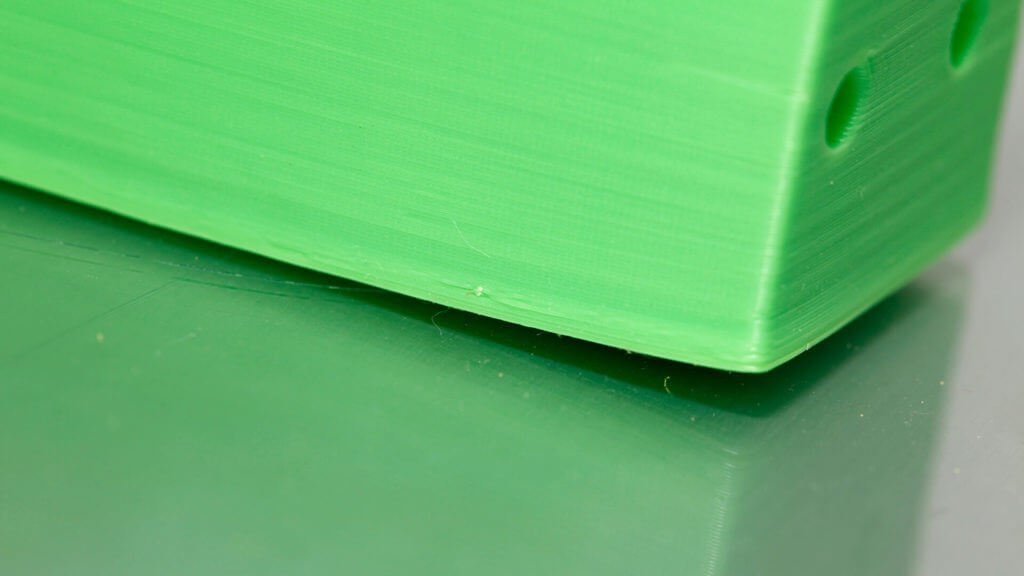
2. Check the cover. Check the cover, rods and other parts on top of the printer (if you have coreXY). Make sure all parts are properly fastened.
3. Check the z-axis screws. Many printer manufacturers use threaded studs more often than trapezoid screws, and while both do the job, the studs tend to bend over time. No need to disassemble the printer to check if the rods are straight. Simply use software such as Printrun to move the print head up and down. If one of the Z axis bars is bent, you will definitely notice it. Unfortunately, it is almost impossible to straighten a bent stud, but on the other hand, this is a great reason to replace old threaded rods with trapezoidal screws.
Supreme displacement: Checklist
- Check belts tension
- Check if the upper lid is
- Make sure that the hairpins along the zis are even
The description of 3D 9,000 9: the absent layers of 9000 9000: the absent layers of 9000 9000: the absent layers 9000: problems
Gaps in the model appear due to the fact that some layers are missing (partially or completely).
The printer was unable to produce the required amount of plastic to print the missing layers. In 3D printing, this problem is also known as under-extruding. The essence of the problem may lie in the plastic itself (for example, a different diameter of the material), in the coil, in the feed mechanism (extruder) or in a clogged nozzle.
Friction can cause plastic to get stuck. It could also be that the z-axis screws (studs) are not properly aligned with the linear bearings.
There may also be a problem with screws (studs) in the Z axis and with the bearings themselves.
3D Printing Solution: Missing Layers
1. Mechanical Check . If suddenly you find missing layers in the print - it's time to take a little care of your printer. Start by checking the screws (studs) and make sure they are firmly attached to the bearings or clamps.
2. Check rod alignment. Check that all screws (studs) are aligned and not misaligned. Turn off the power and gently move the print head along the X and Y axes. If there is any resistance, then there is some problem. It is easy enough to understand what exactly the problem lies in - a slightly bent rod or bearings.
Turn off the power and gently move the print head along the X and Y axes. If there is any resistance, then there is some problem. It is easy enough to understand what exactly the problem lies in - a slightly bent rod or bearings.
3. Worn bearings. Worn bearings make noise. You may also feel the rattle of the print head, while the printer vibrates slightly. In this case, turn off the power and move the print head along the X and Y axes to find out where the worn bearing is.
4. Check the oil. Remember to regularly lubricate the moving parts of the printer. Sewing machine oil is ideal for lubrication - you can buy it at any hardware store at an affordable price. Before applying oil, make sure the studs (screws) are clean. If the studs(screws) have dirt or print material residue, clean them.
Then connect to the printer via a program (eg Pronterface) to move the print head in the X and Y axes and check that the studs are evenly lubricated. If you apply a little more oil, just wipe off the excess.
5. Underextruded . The last cause of the problem may be insufficient extrusion. There can be many solutions to this problem, and all of them are described in Section 9.
Checklist
- Check the printer mechanism to make sure the moving parts are tight.
- Recheck printer design and alignment
- Check for worn bearings and bent pins
- Use some oil to lubricate parts
3D printing issue #6: Cracks in tall objects
Problem description
Cracks on the sides of the model, most commonly in tall models.
The problem can occur unexpectedly, and most often occurs in large printers, especially if you do not monitor their work.
On the upper layers, the material cools faster because the heat from the platform does not reach the required height. Because of this, the adhesion of the upper layers is lower.
3D Printing Solution: Cracks in Tall Objects
1. Extruder Temperature . Start by increasing the extruder temperature - 5-10ºC is best. On the side of the plastic box you will find the highest temperature for plastic, try not to raise the temperature to this value.
Extruder Temperature . Start by increasing the extruder temperature - 5-10ºC is best. On the side of the plastic box you will find the highest temperature for plastic, try not to raise the temperature to this value.
2. Fan direction and speed . Double check your fans and make sure they are pointed at the model. If the direction is correct, reduce their speed.
Checklist
- Check the maximum possible temperature of the extruder and increase the current temperature by 10ºC in one attempt.
- Check the direction and speed of the cooling fans.
3D Printing Issue #7: Holes in the top layer
Description of the issue
Holes and gaps in the top surface of the printout.
The two most common causes of this problem are improper top coat cooling and top coat not thick enough.
Solution to 3D printing problem: Holes on the top layer
1. Filament diameter . Often the problem happens with plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. Holes in the top layer are a problem with all 3D printers, but they happen more often with printers that use 1.75mm filament than with printers that print with filament larger than 2.85mm.
Filament diameter . Often the problem happens with plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. Holes in the top layer are a problem with all 3D printers, but they happen more often with printers that use 1.75mm filament than with printers that print with filament larger than 2.85mm.
2. Check the location of the fan . Cooling can cause this problem, so check the fans first. When the printer starts printing, the fans are at their lowest speed or off. After printing the first layer, the fans start to work. Check if they start working and also check if they continue working when printing is finished. If all is well, double-check if the direction of the fan is set correctly - they should blow over the model.
3. Set fan speed in G-Code. Another cooling issue is related to excessive plastic in the top layer. It must cool quickly so as not to fall between the already printed supporting elements. The fan speed can be adjusted with G-Code ( is usually G-Code for Fan On is M106 and M107 Fan Off ). Also set the fan speed to maximum for the upper layers.
Also set the fan speed to maximum for the upper layers.
For example, for a 1cm x 1cm cube, the height of the top layer would be 0.1mm. In this case, when generating a G-code through CURA for Prusa i3, the G-code indicates that the number of layers for the cube is 100. Considering that we specified heights of 0.6 mm for the top and bottom layers, it is worth editing the value to LAYER: 94
4. Increase the thickness of the top layer . One of the simplest solutions to the problem is to increase the thickness of the top layer. In most applications, you will be able to adjust the thickness using the ‘Bottom / Top Thickness setting’ advanced settings. You need to increase the thickness of the top and bottom layers up to 6 times the other layers and up to 8 times for smaller nozzles and plastics. If the layer height is 0.1mm, then the height of the top and bottom layers should be 0.6mm. If there are still holes and bald spots in the top layer, increase the thickness to 0. 8mm.
8mm.
Cheklist:
- Use a larger diameter
- Make sure that the direction and speed of the fans are correct
- Manually set the fan speed
- Enlarge the thickness of the upper layer
- Check the diameter of the Philiment
- Use the caliper diameter
- Check whether
- EXTRITITION PSTOMENTS PROBLEM OF
problem.
Description of the problem
Cobwebs or hairs appear between model elements when printing.
When the printer head moves over an open surface (without extrusion), i.e. from one object to another, the plastic flows out of the nozzle.
3D printing solution: Hairs, webs
1. Turn on retract . Retraction is an important factor for the quality of the finished model and can be enabled in the slicer. It functions quite simply and works by pulling the filament back into the nozzle before the head starts to move. The bottom line is that it prevents plastic from flowing out of the nozzle, which creates a "spider web" between objects.
2. Retraction activation in settings . Most apps like Cura offer pull activation in settings and this is set by default. However, if you want more options, you can customize them further. For example, you can set the minimum head path before activating retraction.
3. Minimum distance (mm) . If retraction is not working correctly, the easiest way to fix this is to reduce the minimum distance. Reduce it by 0.5mm until hairiness disappears. Activate retraction (retract) to increase the speed of printing.
This problem has several causes. First of all, the thread diameter may not match the diameter set in the slicer. Also, the amount of extruded material may be lower due to incorrectly configured firmware. Another problem is that the nozzle can become clogged and this will cause under extrusion.
3D Printing Solution: Underextruding
1. Check filament diameter . Start with the simplest solution - check the filament diameter settings in your slicer. If you are not sure about the filament diameter and the recommended temperature, check the information on the packaging.
If you are not sure about the filament diameter and the recommended temperature, check the information on the packaging.
2. Measure thread . If you still can't get the desired result and filament separation remains a problem, use a caliper to check the filament diameter. After measurement, adjust the settings of the slicing software. ( author's note - if you have a bowden hotend, then you need to unscrew the fitting from the hotend, enter the command (for example, in Pronterface) M302 : Allow cold extrudes and extrude a meter of plastic. If more or less is extruded, then you have an incorrect number steps per mm for the extruder If you have a direct hotend, then you need to unscrew the nozzle ( the nozzle can only be unscrewed when it is hot! ). It is also worth noting that even with the correctly set steps per mm value, when retracting, the distance traveled will be less than when extruding. This is because more resistance is experienced when retracting )
3. Check print head . After starting printing, most printers lift the print head off the model base. Check if the nozzle is clean.
Check print head . After starting printing, most printers lift the print head off the model base. Check if the nozzle is clean.
4. Set the extrusion factor to . If there is no difference between the actual extrusion diameter and the software settings, check the extrusion multiplier settings (or flow rate or flow compensation), they may be too low. Each slicing application solves the problem differently, but try increasing the ratio by 5% and restarting the print process.
5. Open the Edit Process Settings window in Simplify3D and go to the Extruder tab - the extrusion factor should be set to 1.0 which corresponds to 100%. Open the Material tab in Cura and increase the Flow settings (you may need to enable Flow in the Preferences window).
Cheklist:
Description of the problem
Excessive extrusion means that the printer is supplying more material than needed.