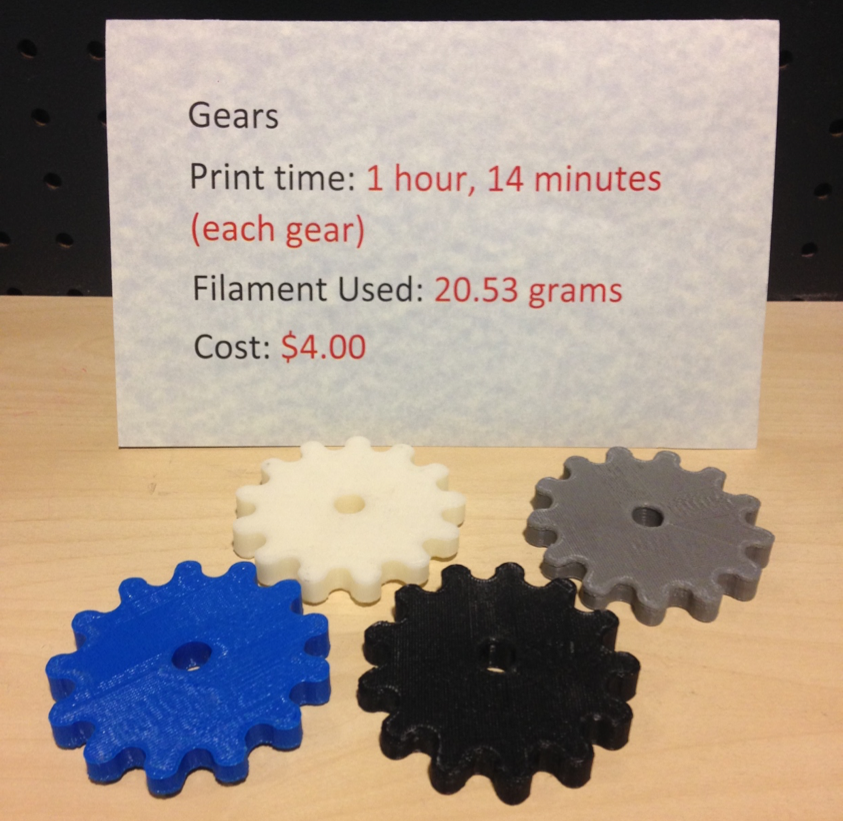
Calculating 3d printing costs
How to calculate 3D printing costs?
We often see online discussions about the price of 3D prints, or more specifically: how to calculate the price for having something 3D printed. Since there are many myths floating around, we figured out that many people will be interested in a deep dive into various aspects of this field. So, how do you set the right price for a 3D print? We’ll take you through the main aspects of 3D printing pricing that affect the price, however, if you’re not really keen on learning every single detail, feel free to scroll down to the end – we have a small surprise for you there.
Let’s imagine a purely hypothetical example of a certain Josef from Prague (any similarities to actual persons or places are purely coincidental), who bought three 3D printers to make some profit: he has the Original Prusa i3 MK3S, Original Prusa MINI, and the Original Prusa SL1.
A customer ordered this test object from Josef and wishes to know the price of the object printed on the printers mentioned above. It should be printed with Prusament PLA Orange (MK3s and MINI) and with Prusa Orange Tough resin (SL1).
Material costs
Josef already knows that the most expensive aspects are manpower and filament (or resin). Filament and resin prices depend on the manufacturer’s pricing, which makes counting the material costs very simple. 1kg of Prusament PLA Orange costs 24.99 USD (without tax and shipping) and according to PrusaSlicer, one tree frog model consumes 6.27 g of filament (basic settings – 0.15mm layer height, 15% gyroid infill).
Josef simply calculated (24.99 / 1000 * 6,27) that material for one tree frog on the MK3s or MINI will cost him 0.15 USD. Printing a tree frog without supports on the SL1 (0.05mm layer height) will consume 10.43 ml resin – this costs 0.6 USD. If the customer wants to print it with other materials, the price could rise a lot. There are filaments with a price exceeding 90 USD/kg and resins more expensive than 315 USD/kg.
There are filaments with a price exceeding 90 USD/kg and resins more expensive than 315 USD/kg.
The bottom line here is pretty simple: Material cost = filament price / filament weight (g) * model weight (g)
Manpower costs
Josef values his work at 9.50 USD/hour (calculated from average wage in the Czech Republic for the year 2020). He already knows that print preparation (including slicing) takes him approximately 5 minutes (10 minutes in case the resin in the SL1 needs to be changed). Therefore, he calculated the work on one treefrog to 0.8 USD for MK3s/MINI and 1.6 USD for SL1. It’s not too expensive to prepare small models downloaded from the internet. However, it’s important to know that plenty of models require more difficult print preparations. Even slicing alone can take even 30 minutes or more – e.g. preparing supports for SLA printing using manual supports can take a long time.
The price for human labor can, in many cases, reach dozens of USD, especially in cases when something completely new has to be designed. Even a relatively simple technical part can take several hours to draw, which increases the price dramatically.
Even a relatively simple technical part can take several hours to draw, which increases the price dramatically.
3D printer operation costs
Another thing that Josef calculated was 3D printer operation costs. He started with electricity: according to the local electricity distributor’s rates, 1 kWh costs from 0.07 USD to 0.09 USD. Let’s work with 0.09 USD. The printer input power depends on several factors, however, most of the time it needs around 100-150 W. Printing a tree frog on the MK3s takes 1h 16 min, 1h 10min on the MINI, and 1h 48 min on the SL1. With 150W power input (usually it’s not that much), electricity for printing one tree frog will be less than 0,023 USD. Such a low price is practically negligible.
On the other hand, Josef would like to recoup the money he spent on buying his printers within 6 months (4392 hours) of printing. This led him to add a fixed fee to printing hour costs. The fee (based on our actual printer prices) is 0. 21 USD/hour for the MK3S, 0.1 USD/hour for the MINI, and 0.36 USD/hour for the SL1.
21 USD/hour for the MK3S, 0.1 USD/hour for the MINI, and 0.36 USD/hour for the SL1.
3D printer operation costs = Printer price / required investment return time (h) * print time (h)
Electricity cost = negligible
Margin
Josef is still afraid that his investment might not return with these prices. There are other factors coming into play as well: for example, a printing accident could occur, causing the loss of filament. Or there may be extra maintenance costs. The most common issues are usually print quality problems (e.g. printing large ASA-based objects can lead to warping etc.). You can head over to our older articles about print quality and troubleshooting.
In other words, it’s not easy to calculate a price that would cover all potential issues and/or mistakes. It largely depends on the user’s experience and many other factors. In this case, Josef has to observe what percentage of prints tend to fail over a long period, and what do these failures cost him. However, for starters, he set the margin to be 30% of the material (filament or resin) price.
However, for starters, he set the margin to be 30% of the material (filament or resin) price.
So, let’s sum up the order: Josef charged the customer the following prices: 1.3 USD (MK3s), 1.16 USD (MINI), and 3.15 USD (SL1), tax not included. Certainly, there will be many people who see it differently – there are customers who won’t pay larger sums of money and there are makers who don’t see it profitable enough.
The purpose of this guide is to give you an overview of all things you should take into account when calculating the costs. Basically, you need to include the material costs, time spent on print preparations, and some kind of “failure insurance”, plus general running costs. The price for energy consumed is almost negligible. Really long prints will be around a dollar, tops. Obviously, we did not include taxes – if you want to start a business with commissioned 3D printing, you need to check your country’s laws regarding this kind of work.
Here’s a complete recap of Josef’s order:
Material: 0.15 (MK3s) + 0.15 (MINI) + 0.6 (SL1) USD
Labor: 0.8 (MK3s) + 0.8 (MINI) + 1.6 (SL1) USD
Printer operation: 0.27 (MK3s) + 0.12 (MINI) + 0.65 (SL1) USD
Margin (30% of material cost): 0.05 (MK3s) + 0.05 (MINI) + 0.18 (SL1) USD
Total: 5.42 USD
Finally, let’s see how the price would change if the customer wanted to have a truly large and complex model printed on the MK3s. Again, it’s a downloaded model, which is pretty much ready to print, however, it takes 1 day, 17 hours, and 48 minutes to finish. The material of choice is a non-standard carbon fiber composite material XT-CF20, which costs 49.99 USD and we will need 756 g to finish the print. Other values necessary for the calculation remain the same:
Material: (49.99 / 750) * 756 = 50.39 USD
Labor: 0. 8 USD
8 USD
Printer operation: 0.21 * 41.8 + 0.023 * 41.8 = 9.74 USD
Margin (30% of material cost): 50,39 * 0,3 = 15,12 USD
Total: 76.05 USD
It comes as no surprise that larger objects and expensive materials also mean much higher final prices, even though the price for labor stays the same. Printer running/maintenance costs gradually increase with printed hours. Similarly, the price can increase even with seemingly simple parts, if it needs more of Josef’s time (for example drawing the part, manual editing of supports etc.).
3D print calculators
We know that there’s a lot of things to cover, so this is why we made this handy 3D Printing Price Calculator! It’s incredibly easy to use: just fill in the data and it will give you the result immediately! You can set every necessary attribute there and you can share your results with other people. The calculator can also import existing G-codes, saving you even more time. Give it a go!
Give it a go!
Do you use 3D printing to make a living? Share your experience with pricing and general thoughts in the comment section – we’re sure that many others will find it useful!
Happy printing!
3D Printing Cost Calculator
Created by Bogna Szyk
Reviewed by Małgorzata Koperska, MD and Adena Benn
Last updated: Oct 19, 2022
Table of contents:- How much does it cost to 3D print?
- 3D printer filaments
- FAQ
Whether you're just starting out or running a professional 3D printing business, this 3D printing cost calculator and our paper thickness calculator will surely come in handy. After inputting a few basic parameters, you will be able to determine accurately what you should charge for any job.
Naturally, if you don't own a 3D printer and are trying to figure out how much it costs to 3D print, this calculator is also a tool for you! Keep reading to understand the fundamental principle behind it or to find out which filament type is the best for your project.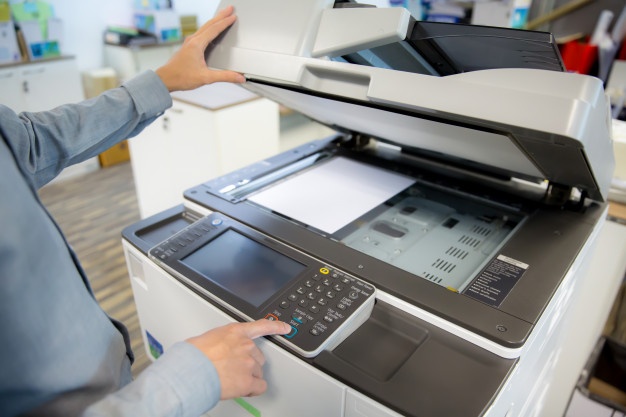
If you are serious about starting a printing business, you should also explore our paper quantity converter to learn more about the terms associated with buying paper in bulk and the amount contained within. Additionally, our pixels to print size calculator will help you to learn more about what it takes to create good-quality images when printing. This is something anyone serious about building a printing business should know.
How much does it cost to 3D print?
Our 3D printer calculator splits the total cost of a 3D printing job into two parts: the material cost, corresponding directly to the material that will be used, and labor cost, associated with the time of printing. Additionally, you can add a markup to ensure you're getting at least some profit on each item you print.
We calculate the material cost according to the following formula:
material cost = ρ π × (d/2)² × L × price
where
- ρ is the density of the material;
- d is the diameter of the filament;
- L is the length of the filament used for printing; and
- price is the cost of material per unit weight (per kilogram or pound).
Once you know the material cost, it's time to find out what is the labor cost:
labor cost = time × hourly rate
where
- time is the time needed to finish the job,
- hourly rate is the cost per one hour of 3D printing.
At the end of calculations, our 3D printing cost calculator adds the markup) to account for the profit:
final price = (material cost + labor cost) × (100% + markup)
Voilà - you just found the total price of a 3D printing job! Be sure to experiment with the result, for example, by changing your hourly rate or by adding half an hour to printing time to simulate a jammed extruder that you need to fix.
3D printer filaments
You probably noticed that the material cost depends on three main factors: the volume of the material, its density, and its price. While the volume depends solely on the project you're about to print, the other two are associated with the type of filament.
In our 3D printing cost calculator, you can choose between the six most common filament types. If you're using a different one, open the advanced mode to manually input its density.
filament type | full name | density (g/cm³) | |
|---|---|---|---|
ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene | 1.05 | |
PLA | Polylactic Acid | 1.27 | |
PETG | Polyethylene Terephthalate | 1.25 | |
PETT | T-Glase filament | 1.45 | |
HIPS | High Impact Polystyrene | 1.04 | |
TPU | Thermoplastic Polyurethane | 1.30 | |
FAQ
How much does it cost to 3D print per inch?
It costs $0. 35. However, It highly depends on the material cost. Omnicalculator tool 3D printing cost calculator can help you analyze between different options.
35. However, It highly depends on the material cost. Omnicalculator tool 3D printing cost calculator can help you analyze between different options.
- We need to choose the material type. For example, ABS with a density of 0.6069 oz/in3 and a price of $20.
- Considering density, we need to print 0.6069 ounces.
- Our 3D printer calculator indicates that 3d printing one inch will cost $0.35.
How to calculate the 3d print cost?
You can use Omnicalculator 3D printer calculator or do as follows:
- Define your 3d printer material type and get its price per kilogram. Also, find out its density
- Calculate the volume of your 3d print model. Use your design software for increased preciseness.
- Get the mass of your model by multiplying its volume per material density.
- Multiply the obtained mass by the material price per kilogram. The result represents your material 3D print cost.
 Do not forget to add labor costs such as electricity and designing time.
Do not forget to add labor costs such as electricity and designing time.
Can you make a business with a 3d printer?
Yes, you can, and Omnicalculator tool 3D printing cost calculator can help you with it. To be successful with it, follow the subsequent recommendations:
- Dedicate proper time to material selection since quality/usability matter the most.
- Do not forget to add labor costs such as electricity, and manpower costs, among others.
- Add a markup price which will be your profit over your costs.
How to 3d print?
Once you have covered how much it costs to 3D print and you have a 3d printer at home plus printing material, do as follows:
- Create or find a design of your interest. Save it as an STL file in a portable memory.
- Adjust the nozzle and the printer bed position to be parallel and close enough.
- Preheat the bed, and check any other manufacturer recommendations.
- Print!
Bogna Szyk
Cost of material
Material type
Filament diameter
Filament length
Filament weight
Material cost
$
Labor cost
Printing time
Cost per hour
Labor cost
$
Final price
Markup
Final price
$
Check out 31 similar tech and electronics calculators 💻
Amdahl's lawBattery capacityBattery life… 28 more
3D printing cost calculation
Although I posted the link in the discussion of the parallel topic of comrade 3D_MPL (Cost of 3D printing. Calculator for calculating from 3D-MPL), I thought it would be better to make a separate post to get feedback.
Calculator for calculating from 3D-MPL), I thought it would be better to make a separate post to get feedback.
So please make constructive (!) suggestions. I will answer any questions on the topic.
.
So.
Again and again the question arises of how to calculate the payment of your labor as correctly as possible. Although some of the details seem simple, they often require a lot of brain effort, which MUST be paid. Well, the time spent too.
.
Some people think that it is enough to take into account the weight of the part - I think this method is simply fundamentally wrong, because, for example, printing a vase / box with a 1mm nozzle and a 0.6mm layer will be faster than printing some highly detailed bracket in a car or a souvenir with a 0.2mm nozzle and a 0.05mm layer. So, with the same weight, the time can be many times (tens of times) longer! Yes, and draw a different bracket, you must be able to!
Moreover, we want our many hours of work to be adequately paid.
A typical example from my practice is a kettle handle.
The detail is shapeless, you don't know how to approach it in order to draw it. The result - 7 hours of modeling, 4 hours of printing, an hour of post-processing, 57 (total!) Grams of plastic. And now, imagine, a customer comes to you, 'Why is it so expensive??? It's only 57 grams!!!'. And you lost a whole day (work shift).
.
So, I think that the main resource that should be paid for is time!
.
And here, in fact, is the table.
Link to Yandex Disk: https://yadi.sk/i/oy1r3v_dA-8E1w
.
By the way, I update the table from time to time! I recently discovered an inaccuracy in the calculation of the cost of the material, corrected it. So follow the link and check it out.
.
Some characteristics:
Time is written conveniently - in hours and minutes.
Modeling and post-processing cost per hour.
Separately, the weight and cost of the coil are written - no need to calculate the cost of a kilogram (for lazy people).
The so-called 'difficulty factor' is missing from the table. The complexity itself will be formed from: modeling time (mostly), printing time (necessary detailing), post-processing time (picking out supports from hard-to-reach places, painting, etc.).
Substitute the values that are convenient for you. I don't insist on these. Columns 'Prices' and 'Costs'.
The white numbers in the 'Total' column are reference numbers, just for convenience.
Depreciation is calculated from the time of direct operation of the printer (more work - more wear). I take half a dollar.
The price of the first part differs from the subsequent ones only by taking into account the simulation time.
Printer power is taken to the maximum - pennies still come out.
Currency - rubles. You can change to yours.
When you write the price for a reel, you must also take into account the cost of delivery! (In our outback, the delivery of one coil is 500 rubles!) I can add the 'delivery' item for convenience, if you want.
.
I advise you not to show this table to the client. Unless if he thinks that it is too expensive, it must be recalled that he would not agree to work for 100 rubles / hour (or how much you put). And you yourself know that the client wins if he buys one spare part instead of a whole expensive unit. See for yourself.
Sometimes, on the contrary, it is possible to raise the price for the same reasons)))
.
Let me add a little about the cost of the actual filament.
Even the most expensive filament does not affect the final cost so much. Substitute in the table, for example, Bestfilament PLA (1350 rubles / kg) or Filamentarno CF-5 (3300 rubles / kg).
Here is a well-known detail. Bosch meat grinder safety clutch:
Its weight is 9 grams.
Calculate the cost of material only:
Bestfilament PLA - 7 rubles. (don't make such a thing out of it! :o)
Filamentafno CF-5 (as in the photo) - 30 rubles.
.
PS: The table is not designed for big business, but rather for a part-time job/money hobby.
.
Everything for everyone!
Online calculator for calculating the cost of 3D (3D) printing
You are here
Home » Our services
How to calculate the cost of 3D printing
- load the model in STL format into the calculator;
- get a cost estimate and recommendations;
- change the print settings or leave the default;
- if you are ready to order 3D printing on a 3d printer, click the "Order printing" button, fill in the contact details and send an application.
test model used for illustration purposes. To calculate your model, download it. The calculation takes place automatically.
Load STL file?Click the "Load" button and select the 3d model file. This is an STL file, such as 3dmodel.stl. The calculator will automatically calculate the cost immediately. You can go directly to the calculation below or change the 3D printing settings
This is an STL file, such as 3dmodel.stl. The calculator will automatically calculate the cost immediately. You can go directly to the calculation below or change the 3D printing settings
Characteristics of the model, recommendations and cost of 3D printing
Volume, cm 3 : - Area, cm 2 : - Dimensions, mm: - Plastic consumption, cm3: - Plastic consumption, gr: -
Recommendations: -
Preliminary cost of printing: -
Set your own 3D printing settings? Press if no special print settings are required, rather than the default settings*optimum settings for price/performance ratio). The default settings are marked with *.
Select material:? This is the material that will be used for 3D printing. Simply put, ABS is suitable for gears, housings and similar technical details, PLA is suitable for figurines and souvenirs, for the rest, see the material comparison table in the FAQ section.
ABS*ABS is strong and durable, suitable for printing housings, gears and stressed parts. We print by default.
PLAPLA has low print shrinkage, prints small fragments well, can print overhanging elements. Also, since PLA is made from corn, it can be used in food production.
PET-GPET-G is stronger than ABS, has less shrinkage, and is chemically resistant. This plastic has excellent interlaminar adhesion. Food grade plastic
CarbonCarbon is a nylon with added carbon. Very durable and wear-resistant, has low shrinkage and deformation during printing. In addition, after printing, the parts have a rough surface, on which the layering is not visible.
FlexFlex is an excellent rubber-like material. Unlike similar TPU (polyurethane), it is chemically resistant to engine oil and gasoline, can be used as gaskets and flexible hoses in the automotive industry
PhotopolymerPhotopolymer resin is indispensable for printing small and precise parts. Advantages: layer thickness up to 1 micron, no visibility of layers, the ability to print transparent models, coloring before printing with coloring pigments
ABS-LikeABS-Like is a type of photopolymer that is close to ABS in strength, so that ABS-Like can be used to print heavy duty and strong parts. Combined with ultra-high precision printing, it is indispensable for printing small gears and machine parts
Combined with ultra-high precision printing, it is indispensable for printing small gears and machine parts
Select infill density:? This parameter characterizes how much the part will be filled with plastic. Often it is not necessary to completely fill the part, partial filling can be used to save plastic
10%
20%*
33%
50%
100%
Select layer thickness (height):? This parameter characterizes the quality. The thinner the layer thickness, the better the printing will be, but the longer the printing time and its cost
0.05mm
0.1mm
0.15mm
0.2mm
0.25mm*
Print order
test model
Hold the left mouse button to rotate the model
Use middle mouse button or Shift and left mouse button to zoom
Use Alt and left mouse button to move the model
Order print
The print operator will receive a request with a 3D model and selected print characteristics and will contact you.
Download model STL
Read more
- Maximum file size: 120 MB .
- Allowed file types: stl .
Telephone
Order comment
Data
Add filesAdd new file
Read more
- Maximum file size: 100 MB .
- Allowed file types: stl obj .
FDM thermoplastic 3D printing:
-
Eco-friendly PLA strength detail smoothness flexibility Environmental friendliness
2923 RUB/cm 3 Ordering
Ecoplastics PLA is made of corn and therefore, completely eco -friendly and therefore is completely eco -friendly and is completely eco -friendly as accusations and therefore is completely eco -friendly.
 for printing culinary molds, bottles and children's toys. Due to the peculiarities of the material (detailing, printing "on weight") figurines, souvenirs and various decorative elements are well obtained from it. Well processed and smoothed. Order printing
for printing culinary molds, bottles and children's toys. Due to the peculiarities of the material (detailing, printing "on weight") figurines, souvenirs and various decorative elements are well obtained from it. Well processed and smoothed. Order printing -
Popular ABS strength detail smoothness flexibility environmental
2919 rub/cm 3 Print order
Excellent price-quality ratio, made from oil.
 Well suited for printing cases, instruments, automotive components, gears and mechanisms, elastic and strong. Excellent mechanical and chemical processing. Order print
Well suited for printing cases, instruments, automotive components, gears and mechanisms, elastic and strong. Excellent mechanical and chemical processing. Order print -
Durable PET-G strength detail smoothness Environmental friendliness
3923 rub/cm 3 Order a printing
in PET-G.
 Excellent interlayer adhesion, which will be stronger than ABS parts. In addition, PET-G is chemical resistant and can be used in food production (common plastic bottles are made from PET). Order printing
Excellent interlayer adhesion, which will be stronger than ABS parts. In addition, PET-G is chemical resistant and can be used in food production (common plastic bottles are made from PET). Order printing 69 RUR/cm 3 Print Order
Carbon is a nylon with added carbon. Thanks to this combination, carbon has the super strength of nylon, but is spared its disadvantage - strong shrinkage. Carbon also has an amazing property: the surface of the part after printing is rough without visible layering, like other plastics. Therefore, it can be used not only for printing heavy-duty and loaded products, but also for decorative elements. Order print
You must have JavaScript enabled to use this form.
Order
Phone
Service type - Not specified -3D printing3D scanning3D modelingother
Choice of plastic - Not Specified -ABS/PLAPET-GCarbonFlexFotopolimerABS-Like
Upload drawing or 3d model File formats: obj, stl, max, doc, pdf, jpg, png, step, 3ds, zip, rar. The maximum file size is 120 MB. In the description, describe the terms of reference and the details of the task.
The maximum file size is 120 MB. In the description, describe the terms of reference and the details of the task.
Add new file
Read more
- Maximum file size: 120 MB .
- Allowed file types: obj stl max doc pdf jpg png step 3ds zip rar .
Notes
Many potential customers of our company who are considering our professional services think that 3D printing cost of is very high today. They say that new expensive equipment, not the cheapest materials and unique technology, which is not available on every corner, lead to an automatic increase in the cost of the service provided, which has only recently begun to be popular in our country. But such reasoning goes against the fundamental concept and philosophy of our company. From the first day of opening, we set ourselves the goal of bringing 3D printing technologies to the masses, making them the most affordable for everyone. And, in our opinion, on this path we have managed to achieve great success. The 3D printing cost calculator , posted on the official website of our company, will help you make sure of this.
And, in our opinion, on this path we have managed to achieve great success. The 3D printing cost calculator , posted on the official website of our company, will help you make sure of this.
The development of appropriate software has been one of the top priorities of our skilled programmers. We wanted to demonstrate to potential customers that 3D printing of can be quite affordable in its final price. And the best way to do this is by providing the opportunity to conduct your own calculations according to individual parameters, available to each visitor to our site. To take advantage of 3D printing cost calculator , you do not have to contact our managers, go through the registration procedure on the site or send your contact information anywhere. Just go to the site, go to a special page and take step-by-step actions, the end result of which will be to get the result you need in the form of the price of the ordered service.
How exactly is the calculation of the cost of 3D printing in the calculator on our website? This procedure boils down to making three basic steps .
- Download model
You will need a file of a three-dimensional model of the object, which you want to print by ordering the appropriate service from our company. The file must be in STL format, which is optimal both for the printing procedure itself and for carrying out the necessary calculations.
- 3D printing settings
These are advanced steps for specifying individual print process parameters. In particular, here you can determine the material of the printed object, the filling density of the object and the thickness of the printed layer. Each of these parameters, set in the corresponding windows of the online 3D printing cost calculator, will largely determine the quality of the final result. This is especially important for the thickness (height) parameter of the walls of the printed part, which will be the better, the thicker and stronger its underlying layer will be.
Please note that the defined parameters are already set by default, and you will have to change them as you wish in manual mode. As for the settings shown, they are suitable for the vast majority of our customers and their orders. We are talking about the use of reliable ABS plastic, a 20% filling density of the printed object, as well as a layer thickness of 0.25 millimeters. If these parameters suit you, you can safely skip the second paragraph and proceed to the third step of using the 3D printing cost calculator.
- Get result
When you upload the correct 3D model file, our calculator will quickly make the necessary calculations and then display the price on your screen. At the same time, the main characteristics of the printed object will be calculated and visually indicated, and recommendations will be provided regarding the possible need to change the order parameters in order to achieve a better result. Online calculation of the cost of 3D printing in the calculator starts immediately after you upload a three-dimensional model.