Best 3d printer under 1000 australia
The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
While we'd hesitate to call 3D printing a mature technology, you might say it has reached its teenage years. Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
PC Labs has been reviewing 3D printers since 2013. Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
Filament feeders had to be coaxed into delivering filament from the spool to the extruder. Print beds had to be manually aligned. The extruder or hot end had to be positioned just right to minimize the gap between the nozzle and the build plate (the flat surface on which the object is printed). Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Not so much anymore. While they can still be rebellious at times, 3D printers have grown up a lot, and achieving the 3D printer basics has gotten a lot less likely to end in a shouting match over small things. And they've gotten a lot more affordable, too, for curious DIY-ers and hobbyists to try.
If you're in the market for a beginner or low-cost 3D printer, it's important to know how lower-end models differ. Read on for mini-reviews of the top budget 3D printers we've tested. After that, we go into more detail on understanding the 3D printer specs and tech relevant to beginning buyers. Ready to take the plunge? Read on.
How to Buy a Cheap 3D Printer
The biggest changes to 3D printers over the last few years have come to the cheaper models. Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura.
Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura.
What separates more expensive 3D printers from cheap ones ("cheap" defined as $500 or less, for the purposes of this article) is often a select group of features. These include the build volume, the type of frame, the varieties of supported filament, the software, and the connectivity mix. Let's run through those in turn.
What's the Right Build Volume for a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer’s build volume is the maximum dimensions (HWD) of a part that it can print. (We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together. ) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
As a general rule, inexpensive 3D printers have small build volumes, while more expensive ones have larger build volumes. This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.
Should I Get an Open-Frame or Closed-Frame 3D Printer?
Which brings us to the frame "form factor" question: open-frame versus closed-frame. Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
Low-cost 3D printers include both open-frame and closed-frame models, as well as a few stereolithography printers. If a relatively large build volume is a priority, you’re likely to get more bang for the buck with an open-frame model. Open-frames do have some clear downsides by definition: They tend to be noisy, emit odors when certain plastics are melted, and provide little protection for someone who might touch the hot extruder.
Also, recognize some potential negatives of open frames, depending on the model. Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
What Should I Look for in 3D Printer Software and Connectivity?
Gone are the days when tinkerers had to cobble together several different programs to get a 3D printer to run. Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
3D printing software performs three main functions: processing an object file (resizing, moving, rotating, and in some cases duplicating it), slicing it (into virtual layers, based on your chosen resolution), and printing it. These are almost universally combined into a seamless process. Some high-end printers have software that supports a wider range of settings you can tweak, but even the basic suites work at least reasonably well.
More likely to vary among the cheaper set is the array of connection options from model to model. Nearly all have a USB Type-A port to fit a thumb drive for printing from document files. Most also have a USB Type-B port for connecting directly to a computer, and some offer Wi-Fi, too (or as an alternative), while a handful let you connect via Ethernet to share the printer across a local network.
Some printers support storing 3D files on an SD or microSD card (which may also contain the printer’s system files). Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
While high-end 3D printers tend to have an abundance of connection choices, discount models vary widely in their choices. Some are generous and some are basic, so it pays to assess what a given model offers.
What Should I Look for in Filament Support?
Filament support tends to be a key area that separates the cheaper models from the higher-end ones. (See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
(See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable, plant-based polymer, while ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the same tough plastic that Legos are made from. Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Many entry-level and low-price 3D printers stick exclusively to PLA. If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
Should I Consider a 3D Printing Pen Instead?
Although they aren’t printers per se, inexpensive 3D pens are close kin to 3D printers—using the same filament types and a similar extrusion system—and we include them in the 3D printing category. Rather than tracing out a programmed pattern, you use the 3D pen much like a normal pen, except that you draw with molten plastic. You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
Most 3D pens cost less than $100, and some cost $50 or less. At a glance, 3D pens may appear to be toys, but some artists and craftspeople have taken to them, as it is possible to make quite complicated and beautiful objects with them. If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
So, What Is the Best Cheap 3D Printer to Buy?
Buying a budget 3D printer needn’t mean a world of sacrifice. Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Many casual 3D-printing experimenters will be fine with printing over a USB cable or from a thumb drive, and sticking to PLA may be the best choice for a starter 3D printer. If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Below, check out a spec breakdown of the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed, paralleling our picks above. Also, for a look at the broader market, see our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
The Best Printers for 2022
Choosing a printer may sound easy. But once you start diving into all the available features, making a choice can quickly get daunting. Do you need a basic printer just to print, or do you want to scan and copy as well? And what about faxing, or scanning to and printing from the cloud, or even scanning and sending an email? How do you choose between inkjet and laser technology? What’s the real difference between a $200 model and a $500 model?
Don't fret: We've got you covered on all fronts. PC Labs tests dozens of printers every year, across everyday consumer models, big business machines, pocket-size photo printers, and more. Scroll down for our top tested picks across all these categories, then read on for a comprehensive guide to how to buy a printer.
PC Labs tests dozens of printers every year, across everyday consumer models, big business machines, pocket-size photo printers, and more. Scroll down for our top tested picks across all these categories, then read on for a comprehensive guide to how to buy a printer.
How to Buy a Printer
Printers vary widely based on whether they’re for home use or business use (or dual use in a home and home office), what you intend to print with them, and whether you need color printing or just monochrome. In particular, text, graphics, and photos each require different capabilities to print at high quality. Even if you print just one kind of output most of the time, you also may want a printer that can do other things well. So be clear on the full scope of your printing needs before you buy.
Most printers are designed with either business (usually office) or home use in mind. Generally, business models are geared toward outputting text if they are mono printers, and both text and graphics if they are color models. Home printers (typically inkjets) favor photos and often graphics, as well.
Home printers (typically inkjets) favor photos and often graphics, as well.
Special-purpose options include label printers, portable printers, and dedicated and near-dedicated photo printers. (Even among specialty printers, 3D printers are a special case, and beyond the scope of this discussion.)
Should I Get an All-in-One Printer, or a Single-Function Model?
Most printers today add extra functions beyond printing. The additions always include scanning, which can be convenient and economical if you have light- to moderate-duty scanning needs. If you don't need scanning or related features like copying and faxing at all, however, or your scanning needs are heavy-duty, you might be better off with a single-function printer and a separate scanner.
Most lasers, and some inkjets, with extra functions include "multifunction printer" or "MFP" in the name, while most inkjets, and some lasers, use "all-in-one" or "AIO." The two terms, and their acronyms, are interchangeable. Along with scanning, the additional functions almost always include some combination of standalone copying, standalone faxing, faxing from your PC, standalone emailing, emailing through your PC, and standalone copying to and printing from online systems.
Along with scanning, the additional functions almost always include some combination of standalone copying, standalone faxing, faxing from your PC, standalone emailing, emailing through your PC, and standalone copying to and printing from online systems.
Office MFPs typically include an automatic document feeder (ADF) to handle multipage documents and legal-size pages. Many ADFs can handle two-sided documents—either by scanning one side and flipping the page over to scan the other side, or by employing two sensors to scan both sides of the page in a single pass. Some single-sided ADFs let you scan one side of a stack of pages, flip the stack manually to scan the other side, and then automatically interfile the pages in the right order.
Some inkjet AIOs offer additional printing options, including printing on optical discs. Many let you print documents and images from, and scan to, mobile devices. Some models let you email documents to the printer from anywhere in the world, then print them out. Our roundup of the best all-in-one printers will help you sift through the many options out there.
Our roundup of the best all-in-one printers will help you sift through the many options out there.
What Are the Most Common Types of Printer?
Generally, business models use laser or similar technology (more on that shortly) and are geared toward text, or text and graphics, while home printers are generally inkjets and favor photos and graphics. Within each printer category, quality for each kind of output varies widely. Some business printers can handle all three types well enough for in-house printing of brochures and other marketing materials, for example.
The two most common technologies, laser and inkjet, increasingly overlap in capabilities, but there are still differences. Most lasers and LED printers (which are identical to lasers other than using LEDs for a light source) print higher-quality text than most inkjets, and almost any inkjet prints higher-quality photos than most lasers. However, some inkjets today print text that's nearly laser quality, except for a tendency to smudge if they get wet, while some lasers print photos at what's known as business quality, which translates to good enough for a trifold brochure.
Beyond questions of technology and output type, there are several more finely grained categories of printer.
Home printers (approximate price range: $50 to $250) are almost exclusively inkjets (with the exception of some small-format dedicated photo printers). They are built for low-volume printing, tend to be slow, and also tend to have high ink costs. They typically print photos better than text, and may or may not print graphics well. Almost all of them are all-in-ones. If your budget is tight, and you want a single printer for text, graphics, and photos that handles photos reasonably well, this is where to start looking for an inexpensive printer.
Home-office printers ($100 to $400) are largely inkjets or inexpensive mono lasers, and are built for low- to mid-volume printing. Most inkjets in this category are all-in-one printers, geared primarily toward text and graphics printing, though some also handle photos well, while most lasers are printers only.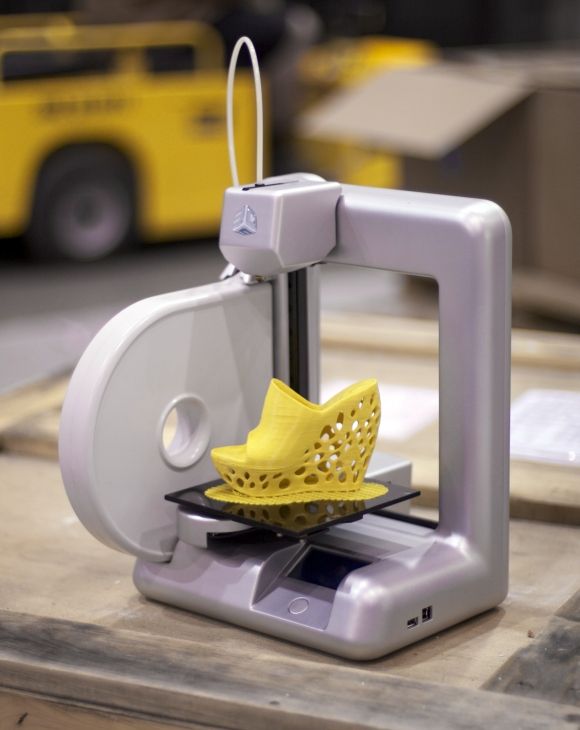 Paper capacity starts at about 100 sheets, though higher-end models can hold up to 500 sheets. Most of these printers are also suitable for micro offices (with up to five people), and many are perfectly fine choices for households, especially for students printing a lot of documents for school.
Paper capacity starts at about 100 sheets, though higher-end models can hold up to 500 sheets. Most of these printers are also suitable for micro offices (with up to five people), and many are perfectly fine choices for households, especially for students printing a lot of documents for school.
Home-office printers are a subset of business printers ($100 to $2,500 or more), which range from compact models for low-volume use to gigantic floor-standing units that can anchor a department. Most business printers are lasers (though inkjets have been making inroads into that market for years), and many are monochrome, intended primarily for text rather than graphics and photos. Most are multifunction devices. For many businesses, speed and paper capacity are paramount, and security is important as well, which is why many business printers offer security features such as password-protected printing. Some even employ accessories such as an encrypted hard drive or an ID card reader to limit access to documents.
Regardless of which home or business category a printer is in, cost can be a key factor. In general, the more expensive the printer, the lower its per-page printing costs, while the lower the ink price, the more expensive the printer will be. Whether you'll save more with a low-cost printer or low-cost ink depends on how much you print (more on this later). Some printer makers also offer ink subscription programs that can lower running costs, particularly if you print close to the number of pages included in the plan.
Near-dedicated photo printers ($400 to $2,000) are designed for professional photographers and photo enthusiasts, but almost all of these photo printers are just as useful for graphic artists, since they also print high-quality graphics. Some are wide-format printers designed to print on paper as large as supertabloid size (13 by 19 inches), and many can print on paper rolls as well. For precision color, they use up to a dozen ink cartridges. With these, ink cost per page is much higher than for office printers, due to the amount of ink they use.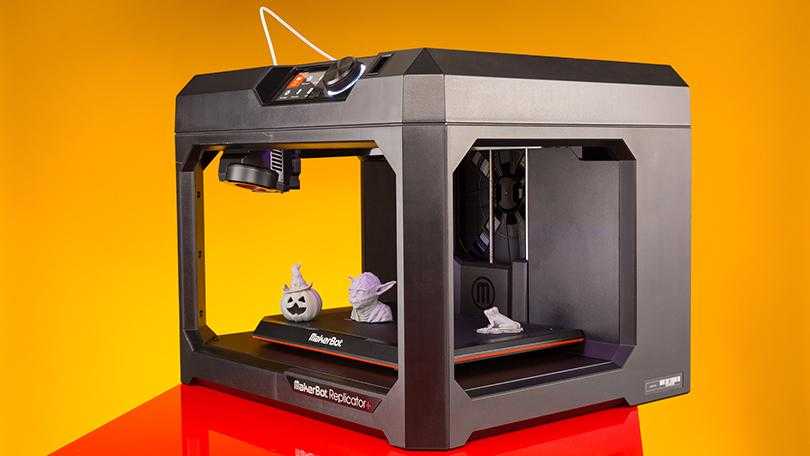 Total cost per page is higher still, because their inks are designed to print on a range of expensive, high-quality papers, each of which can give the image a somewhat different look.
Total cost per page is higher still, because their inks are designed to print on a range of expensive, high-quality papers, each of which can give the image a somewhat different look.
Small-format photo printers ($80 to $250) are dedicated devices built strictly to... you guessed it, print photos, especially from smartphones. Print sizes can range from wallet-size to 5 by 7 inches, and many models can print only a single size. Most are highly portable, and either come with a battery or accommodate one that you can buy separately.
Tabloid- and supertabloid-size, printers ($150 desktop printers to multi-thousand-dollar floor-standing beasts) are another subset of business printers. These wide-format machines come in all the same potential variations as other office printers, from mono-only or color-capable, to printer-only or MFP, to inkjet or laser. The difference is they can handle printing on up to tabloid (11-by-17-inch) or supertabloid (13-by-19-inch) size paper. Note that the least expensive in this group are limited to accepting only one large sheet at a time, making them useful for printing at this size in small quantities only, and only occasionally.
Note that the least expensive in this group are limited to accepting only one large sheet at a time, making them useful for printing at this size in small quantities only, and only occasionally.
Label printers are built to churn out paper or plastic labels. Some include label-design software and connect to your computer, while others are standalone devices, letting you design and print labels using a small, built-in keyboard. Manufacturers of either kind of label printer typically offer a variety of label colors, types, and sizes.
Portable business printers aren't common, but they can be useful for applications like printing a proposal for a potential customer while sitting in their office or at their kitchen table, or printing the latest version of a handout for a potential client while sitting in your car, just before a meeting. Typical models in the portable printer category are compact and light, and use inkjet or thermal technologies to print. And most come with a rechargeable battery.
How Much Do You Plan to Print?
If you print only a few pages a day, you don't have to worry about how much a printer is designed to print, as defined by its recommended (not maximum) monthly duty cycle. To define those terms? Maximum duty cycle is the absolute most a printer should be allowed to print per month without affecting the maximum number of pages it can print in its lifetime. The recommended duty cycle is usually how much it can handle on a regular basis and still last as many years as it was designed for. It may also be based on the paper capacity and how frequently you can conveniently refill the trays.
If you print enough for the duty cycle to matter, don't buy a printer that doesn't include that information in its specifications. Figure out how much you print by how often you buy paper and in what amounts. If you usually print on both sides of the paper, count each sheet as two pages in your calculations. Then pick a printer designed to print at least that much.
What Paper Types and Sizes Do You Print On?
Be sure to consider the minimum and maximum paper size you print on, paper thickness, and whether you need a duplexer to print on both sides of the page. If you often print on more than one type of paper—switching to envelopes, checks, or letterhead for example—look for a printer with multiple drawers, or at least a single-sheet bypass tray, so you don't need to constantly unload regular paper and load your specialty media then reload the regular paper. You'll also want a paper capacity that won't require adding paper more often than feels comfortable. A good rule of thumb is that you shouldn't have to refill paper more than once a week, on average.
How Much Will a Printer's Total Cost of Ownership Be?
The high cost of printer ink is a traditional sore spot for both home and business customers, which has led to the major manufacturers introducing ways that users can lower their per-page ink costs. But the companies are also preserving their own revenues, which means you need to think in terms of the total cost of ownership —the initial cost plus the total cost of ink over the printer's lifetime—to know which printer will be less expensive in the long run.
Depending on how many pages you print, paying a high cost per page for a low-cost printer can actually be the less expensive choice. (Our primer How to Save Money on Your Next Printer shows how to calculate the total cost of ownership for inkjets. The same logic works for any printer.)
If you print enough to make a high-cost printer with low-cost ink the more economical choice, note that Epson’s EcoTank and SuperTank printers, Canon's MegaTank printers, and HP's Smart Tank Plus printers use inexpensive bottled ink that you pour into internal tanks, while Brother’s INKvestment models ship with high-capacity ink cartridges—in some cases, several sets of them—that offload ink into reservoirs within the printer. HP's Neverstop laser printers offer a similar approach, just with bulk laser toner. With any of these models, you'll pay extra up front for the printer, but the included ink will last a long time, and additional bottles or cartridges are notable for their low price. (See more about how to save on printer ink.)
(See more about how to save on printer ink.)
Ink subscription programs are another way to lower ink costs. HP Instant Ink is the big one here, along with Brother Refresh EZ Print and Canon Pixma Print Plan. All offer owners of select printers the option to pay a monthly fee for printing up to a certain number of pages. The same fee applies for either black or color printing, and each company automatically sends you more ink when you run low. These programs can save you a considerable amount of money, particularly if you print mostly in color and print close to the number of pages included in the plan.
How Fast Do You Need to Print?
If you print only one or two pages at a time, you don't need a speed demon. In fact, most home printers are not built for speed, and most lasers with high page per minute (ppm) claims leave out the first page when calculating the rating, giving the much slower first-page-out (FPO) time separately. If you print a lot of longer documents, however, the fast speed starting with page 2 is more important, which means you probably want a laser printer.
As a rule, laser printers will be close to their claimed speeds for text documents, which don't need much processing time. Inkjets often claim faster speeds than more expensive lasers, but they usually don't live up to these claims. However, inkjet printers have been getting faster, and a few recent high-end models (sometimes dubbed "laser alternative" inkjets) can hold their own against comparably priced lasers for speed. (See how we test printers.)
How Are You Going to Connect Your Printer?
USB ports remain ubiquitous on printers. Most office printers, and an increasing number of home printers, also include an Ethernet jack, Wi-Fi wireless connectivity support, or both, which let you to share the printer with your home or office network. (If you're having trouble with this feature on your current printer, here's how to troubleshoot your printer's Wi-Fi connection.) Printers that offer Wi-Fi Direct (a peer-to-peer protocol that sometimes masquerades under a different name) can connect directly to most Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
Most major printer companies now provide mobile apps so you can snap a photo with your phone and print it out directly, without needing to transfer it to a computer first. Small-format photo printers often support Bluetooth for connecting mobile devices and more. A few printers can connect to a mobile device for printing via Near-Field Communication (NFC) merely by tapping the phone or tablet to a particular spot on the printer, but the NFC fad seems to be fading.
Do You Need Printer Security Features?
Printer security is often overlooked, but at your peril. Hackers can gain access to a network through the printer, and in any office printer that you're not right next to, sensitive documents in the paper tray can be seen by prying eyes before you get to them. Many business-centric models include a private printing feature, so that after you send the print job to the printer, you have to enter a PIN at the printer's control panel to actually print it.
For business printers in particular, firmware should be kept updated, as it often repairs vulnerabilities, and any printer hard drives should be encrypted. Many manufacturers offer administrative tools to help IT departments ensure printer security.
Many manufacturers offer administrative tools to help IT departments ensure printer security.
How Do You Gauge Size and Weight?
To a large extent, a printer's size and weight are dependent on the paper handling features you need, but even so, there are considerable variations. Make sure the printer will fit in its allotted space (in all three dimensions, including paper feeders and output trays that may need to extend), and isn't too heavy to move around if you decide to renovate. Very compact printers are available for people who live and work in dorm rooms or other tight spaces.
Printers: Frequently Asked Questions
Should you buy third-party ink or refill kits?
For inkjet tank printers and bulk toner laser printers, ink or toner from the printer manufacturer doesn't cost enough to be an issue. For cartridge-based printers, third-party ink often costs significantly less. But be aware that it can also come with a whole tank full of issues.
First, there’s no guarantee that you’re going to get the same quality ink from a third party that you would when buying the manufacturer-branded product. Also, using ink that isn’t approved by the manufacturer can violate your warranty. And don’t think you can get away with secretly using that renegade ink: If your printer has an internet connection, it may well report your violation to the manufacturer. Sometimes, with firmware updates, we've seen the use of third-party ink "deauthorize" the use of the aftermarket cartridge.
Many printer manufacturers now offer ink subscriptions, so new ink shows up at your door when you need it. If that's available for your model, it can often be the best way to go.
Should you buy cheap paper? What about recycled paper?
For everyday printing, store-brand 20-pound weight paper will usually serve nicely. However, you'll often get better looking output if you step up to a higher-quality paper. For lasers, as well as for inkjet text and graphic printing, that means a heavier weight, and possibly a brighter white level. For photos on inkjets, it means getting matte presentation paper or photo paper. Getting photo or matte paper that's the same brand as your printer will usually be the best choice; printer manufacturers design ink and paper to work together and often offer a variety of presentation and photo papers.
For photos on inkjets, it means getting matte presentation paper or photo paper. Getting photo or matte paper that's the same brand as your printer will usually be the best choice; printer manufacturers design ink and paper to work together and often offer a variety of presentation and photo papers.
Recycled paper also offers acceptable quality, and you can find 100% post-consumer-content recycled paper for many uses, including cover stock and bright white paper suitable for business use. There are other kinds of eco-friendly paper as well, such as all-purpose paper made from sugar cane and photo paper made from cotton. Do your small part to save a tree and research eco-friendly media options. Any modern printer will handle them well.
What is the best printer for home use?
What kind of printer you get for your home depends on what you plan on printing. As a general rule, if you print text only, or text and graphics that don't need color, a mono laser printer will do the trick. If photos are on your agenda, you need an inkjet or dedicated small format photo printer. If the only color output you print is graphics, you probably want an inkjet as well, but if you print infrequently, an inexpensive color laser may be the better choice. Laser printers have the advantage of being able to sit for months without being used, and then simply turn on and work, without the clogged nozzles or wasted ink for cleaning them that inkjets sometimes need. If you plan on doing any scanning or copying, but not so much that you need a standalone scanner, you should look to an all-in-one or multifunction printer. Decent AIOs aren’t that much more expensive than their printer-only counterparts.
If photos are on your agenda, you need an inkjet or dedicated small format photo printer. If the only color output you print is graphics, you probably want an inkjet as well, but if you print infrequently, an inexpensive color laser may be the better choice. Laser printers have the advantage of being able to sit for months without being used, and then simply turn on and work, without the clogged nozzles or wasted ink for cleaning them that inkjets sometimes need. If you plan on doing any scanning or copying, but not so much that you need a standalone scanner, you should look to an all-in-one or multifunction printer. Decent AIOs aren’t that much more expensive than their printer-only counterparts.
Should you buy a refurbished printer?
Printers have reached the point where improvements are infrequent and incremental, so buying a printer that’s a few years old isn’t going to mean sacrificing any groundbreaking technology. That said, if you buy a refurbished or used printer, get it from a trustworthy source, make sure it's been recertified by the manufacturer, and look for a reasonable warranty and return period. Here's what to know before buying refurbished electronics.
Here's what to know before buying refurbished electronics.
So, Which Printer Should I Get?
Based on our advice above, and our key picks for various usage cases below, you should be ready to shop. Keep in mind what you need to print, how many pages you need to print, and how much you're willing to pay up front and per page, and you'll be sure to find the right printer for you. If you're replacing an old printer, recycle or donate it so it can become someone else's refurbished bargain.
If money's tight, start with our picks for the best cheap printers, and check out how to save money on ink. If you're shopping for a business, we've got the best business printers rounded up for you as well.
Top 20 Inexpensive 3D Printers ($199 to $1000)
3DPrintStory Reviews Top 20 Inexpensive 3D Printers ($199 to $1000)
Just 10 years ago, a 3D printer cost over $100,000. Today, you can easily find a cheap 3D printer for under $200. This is amazing.
Today, you can easily find a cheap 3D printer for under $200. This is amazing.
Naturally, the lower the price, the more restrictions. Some of the printers on our list will not have a heated bed and the workspace will be small. Naturally, the quality of most of the models presented below cannot compete with more expensive counterparts.
But with a little patience and diligence, it is quite possible to achieve high-quality 3D printing on a printer that costs half the price of a flagship smartphone. And it's really cool!
Important note : All 3D printers in this top are supplied assembled by the manufacturer. If you have free time and want to spend less money, you can buy DIY kits and assemble the 3D printer yourself according to the instructions.
List of the best cheap 3D printers in the price range from $ 200 to $ 1000
| 3D Printer | Material Material | Working space (mm) | Price | 459 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flashforge Finder | PLA | 140 x 140 x 140 | 499 |
XYZPRINING DA vinci jr. 1.0 Pro 1.0 Pro | PLA | 150 x 150 x 150 | 499 |
| XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. Mix 2.0 | PLA | 150 x 150 x 150 | 599 |
| Printrbot Simple | |||
| Dremel Idea Builder | PLA | 230 x 150 x 140 | 899 |
| Printrbot Simple Pro | PLA | 200 x 150 x 200 | 999 |
| Prusa i3 MK2 | PLA, ABS, exotic | 250 x 210 x 20022 | |
In the article we are considering unfinished, but high -quality 3D printers from AM etc.
If you want to buy them, even if you live in large cities such as Kyiv, Moscow, St. Petersburg, Minsk, it may turn out that these models will not be in the online stores of your city, or they may be with a decent mark-up relative to the cost that indicated in the article.

Since most of them are European / American, it is possible that they will not be in stores at all.
Therefore, before making a choice, I recommend looking directly at eBay, Amazon, Aliexpress, etc. - many sellers on these planforms deliver to the CIS countries within 1-4 weeks on average.
It is especially worth monitoring these platforms during the discount period - Black Friday or Chinese New Year (Aliexpress or Gearbest) - prices on such days can be 2 or more times lower than usual and it is worth waiting for a few weeks.
Monoprice MP Select Mini ($199)
Probably the best 3D printer on our list. Why? Because the Monoprice MP Select Mini is an impressive development with a thoughtful, compact design at a very low price. This model has a quick-change steel material feed wheel, a cooler for cooling the nozzle, a color LCD screen, a heated table, plus the ability to transfer models for 3D printing via microSD or USB.
The heated bed and wide temperature range of the extruder are especially pleasing, because for such a small price you get the opportunity to print in different materials: from ABS B to PLA or exotic materials like conductive PLA plastic, wood, metal-based composites and PVA.
For those who are worried about the lack of a guarantee - for such a price it is possible without it. This model is upgradeable. For example, you can install a new nozzle, change the table and add WiFi connectivity.
Small working space - 120 x 120 x 120 mm. Over time, this will definitely not be enough for you.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Monoprice MP Select Mini
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: ABS, PLA, exotic;
- Working space: 120 x 120 x 120 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- 3D printing speed: 55 mm/s;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: SD card, USB.
Back to the list of 3D printers
M3D Micro Retail ($249)
The M3D Micro 3D printer hit the market thanks to Kickstarter.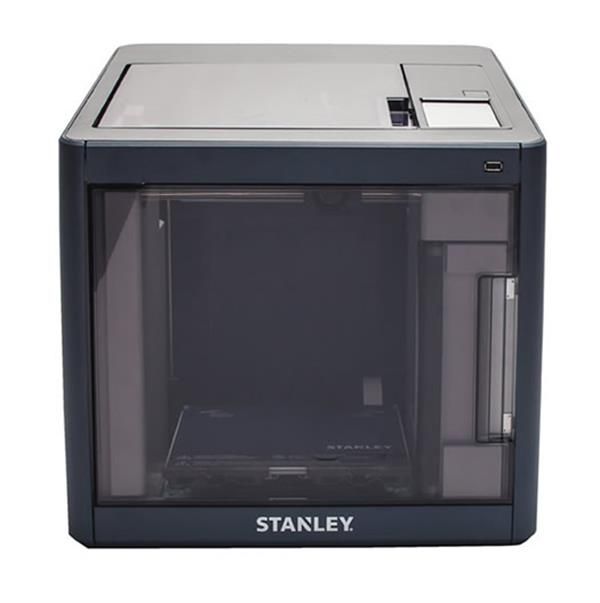 This model was presented with an incredible price of $349.
This model was presented with an incredible price of $349.
The working space of the M3D Micro is 109 x 113 x 166 mm. There are several body color options. The company has implemented "Micro Motion Technology" - a set of innovative solutions - thanks to which you get excellent quality 3D printing at a small price.
Today, this inexpensive 3D printer already costs even less than the price announced on Kickstarter. You can buy it for $249 with a 12 month warranty. By the way, it is already possible to pre-order the next "pro" version.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer M3D Micro Retail
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 116 x 109 x 113 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 50 microns;
- Maximum layer height: 350 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- XY accuracy: 15 microns;
- Open Source: no;
- 3D printing speed: 55 mm/s;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: no;
- Connection: USB.
Back to 3D printer list
XYZprinting da Vinci Mini ($289)
Da Vinci Mini is a successful attempt to make the 3D printer user-friendly. This model has only one button and 5 multi-colored indicators that reflect the current status of 3D printing. In addition, this affordable 3D printer is WiFi capable so you can control it over a network in your home, office or lab.
Unfortunately, you can only use the manufacturer's own 3D materials. On average, they cost 20% more than usual. However, the company also argues that the materials used (PLA) will be 100% non-toxic.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer XYZprinting da Vinci Mini
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 150 x 150 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: no;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, WiFi.
Back to 3D printer list
Monoprice Maker Select V2($299)
The next cheap 3D printer with a good reputation is the Monoprice Maker Select V2.
This model is an analogue of the Wanhao Duplicator i3, which, in turn, borrowed the design from the Prusa i3. But this does not affect the quality, as the Monoprice Maker Select V2 is easy to use and gives excellent 3D printing results.
Monoprice Maker Select V2 design feature is that the power supply and control panel are placed outside the 3D printer. The working space of this model is 200 x 200 x 180 mm. And this is really a good indicator for the money.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Monoprice Maker Select V2
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: ABS, PLA, exotic;
- Working space: 200 x 200 x 180 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.
Back to the list of 3D printers
New Matter MOD-t ($299)
New Matter is a young startup that offers a 3D printer MOD-t - An interesting design with a minimalistic design. This cheap 3D printer is WiFi enabled so you can manage print settings and print from your computer, tablet or smartphone. The working space is 150 x 150 x 125 mm. Thanks to the case, the noise during its operation is reduced. But the most interesting and attractive thing about MOD-t is the price. Only $299. In general, this is an interesting, high-quality model.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer New Matter MOD-t
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 150 x 100 x 125 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: no;
- Connection: USB, WiFi.
Back to the list of 3D printers
Printrbot Play ($399)
The Printbot Play is a very popular budget 3D printer that is often used in education. This inexpensive, reliable model, which is almost entirely made of metal.
The working space is 100 x 100 x 130 mm. Printbot Play has an extruder manufactured by the company itself - Alu Extruder v2. The body is made of powder coated steel and aluminium. SD slot provided.
You can upgrade the basic design of the Printrbot Play with a heated stand or increase the Y-axis stroke.

Back to 3D Printer List
Wanhao Duplicator i3 Plus ($459)
The Wanhao Duplicator i3 Plus is an upgraded version of the popular Wanhao Duplicator i3 (which in turn is based on the Prusa i3).
The main features of this cheap 3D printer are a large working space of 200 x 200 x 180 mm, a steel frame, electronics integrated into the design itself (previously it was taken out separately), a slot for a full-size SD card and a touchscreen display for control.
Wanhao Duplicator i3 Plus Cheap 3D Printer Specifications
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: ABS, PLA, exotic;
- Working space: 200 x 200 x 180 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: design and software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.

Back to the list of 3D printers
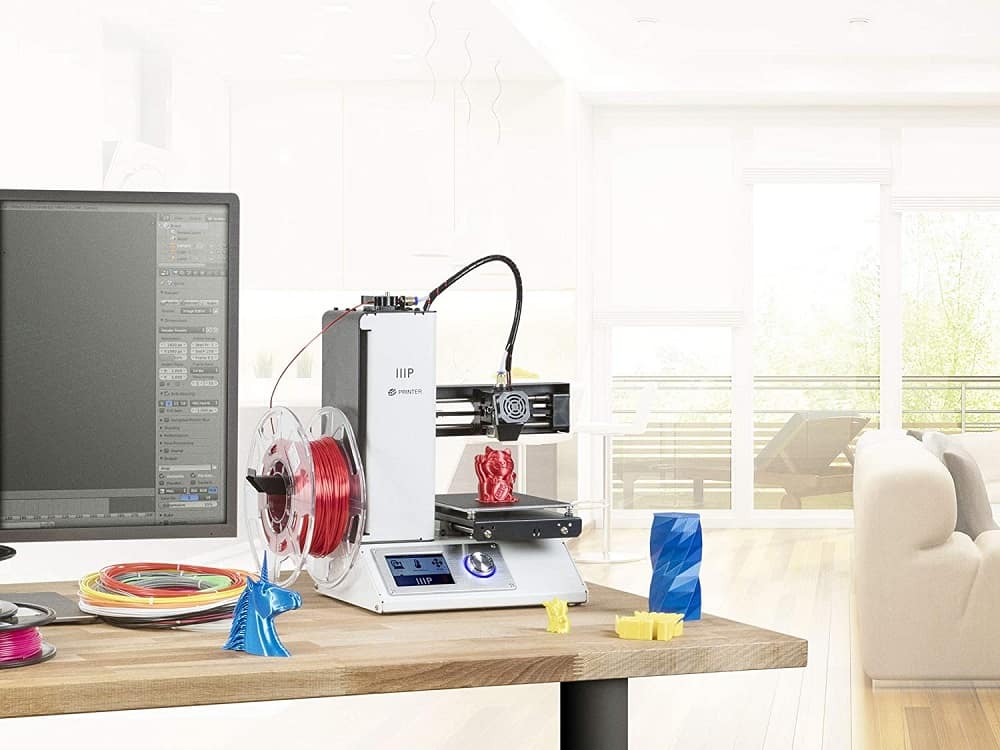
Flashforge Finder ($499)
FlashForge Finder is one of the newest 3D printers on our list. This affordable 3D printer offers an average working space of 140 x 140 x 140mm.
This Finder features a transparent sidewall design so you can view the 3D printing process from any angle. A color display is installed, it is possible to transfer data via WiFi network. The printer comes with some supplies and a USB flash drive, so you can start 3D printing almost immediately.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer FlashForge Finder
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 140 x 140 x 140 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- XY accuracy: 11 microns;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, WiFi.
Back to 3D printer list
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 Pro ($499)
What's so special about the da Vinci Jr. 1.0 pro? This is a new model from XYZPrinting, which includes many advanced features, such as support for printing materials from other manufacturers and increased speed of 3D printing.
Also features an auto-calibration mechanism, a closed chamber with a unique cooling system, and a 0.3mm nozzle option for high-quality printing of fine model details. All in all, this is a great 3D printer with a lot of useful features and at a low price.
Specifications for cheap 3D printer da Vinci Jr. 1.0 Pro
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 150 x 150 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
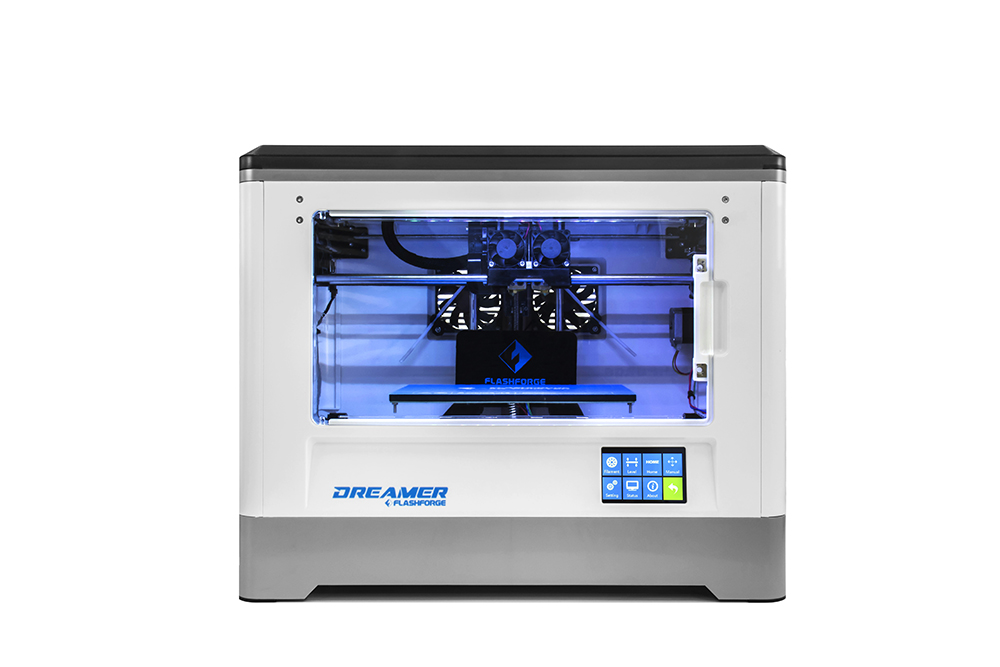 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.
Back to 3D printer list
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. Mix 2.0 ($599)
XYZprinting provides a wide range of low cost 3D printers. And paying attention to each model is quite difficult, although many of them are very interesting.
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. Mix 2.0 stands out because it can print with two different materials and mix them to create multi-colored models. This dual-color 3D printing technology is rare in this price range ($500 to $1,000), so if you're interested in experimenting with multicolor printing, XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. Mix 2.0 is a great choice.
However, there is a drawback. This 3D printer is not compatible with materials from other manufacturers, so you will have to buy special materials from XYZprinting (as we mentioned above, they cost 20% more, but are not toxic).
Specifications of cheap 3D printer XYZprinting da Vinci Jr.
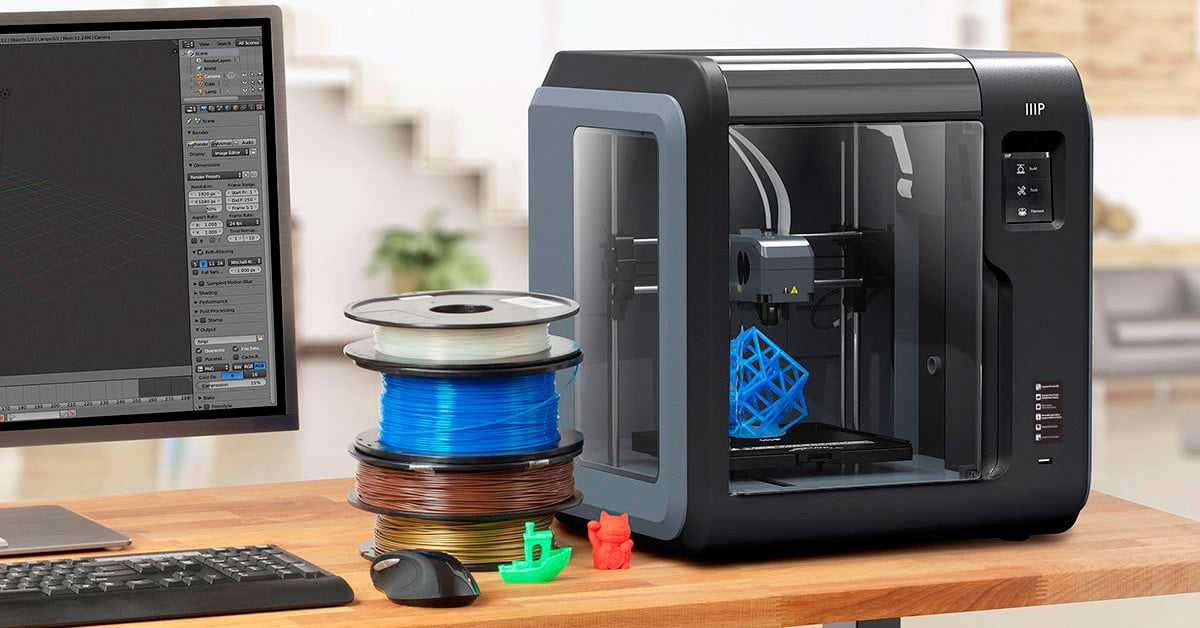 Mix 2.0
Mix 2.0 - Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 150 x 150 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 200 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: no;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card, WiFi.
Back to 3D printer list
Printrbot Simple ($599)
Printrbot Simple is the flagship of the Printbot empire. This model has a great open design with a solid aluminum frame and a working space of 150 x 150 x 150mm. This inexpensive 3D printer comes fully assembled at a very good price. As you need and want to experiment, you can add a heated table and expand the workspace in the horizontal plane.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Printrbot Simple
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 150 x 150 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- 3D printing speed: 80 mm/s;
- Open Source: design and software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: optional;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: no;
- Connection: USB.
Back to the list of 3D printers
UP mini 2 ($599)
The UP mini 2 is a low cost 3D printer that packs in impressive design and functionality. For starters, it has a touch screen panel and the ability to connect via WiFi.
But the most interesting is further. Implemented power failure protection system. 3D printing will continue after the emergency stop. Built-in HEPA air filtration system. Automatic detection of the height of the extruder nozzle. A separate, closed container for the material, thanks to which it does not deteriorate under the influence of moisture from the environment.
Great 3D printer for a small price. The only thing that upsets me a little is the small working space - 120 x 120 x 120 mm.
Specifications of cheap UP mini 2 3D printer
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA, ABS;
- Working space: 120 x 120 x 120 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 150 microns;
- Maximum layer height: 350 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, WiFi.
Back to 3D Printer List
Monoprice Maker Select Ultimate ($699)
The Monoprice Maker Select Ultimate is an extraordinary beast that combines elements from two leaders in the world of 3D printing - Zortax and Ultimaker. The Monoprice Maker has an aluminum perforated printing table, which was offered in the Zortax M200 (thanks to this table, the grip of the base of the model with the table is much better), and the software part is almost identical to Ultimaker 2 (very user-friendly interface and functionality).
This model uses a "Bowden extruder", i.e. the feed units and nozzle are separated, unlike the direct feed. This improves reliability and reduces the likelihood of 3D printing errors (although, most likely, it was necessary to sacrifice printing speed, as the weight of the printing unit increases). Given the cost, this is a good model, the analogues of which are much more expensive.
Specifications of cheap UP mini 2 3D printer
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA, ABS, exotic;
- Working space: 200 x 200 x 175 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 20 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.
Back to the list of 3D printers
Robo C2 ($799)
The Robo C2 is a small 3D printer with tons of connectivity options. Using a specialized application, you can monitor the status of 3D printing from your smartphone or tablet. It can be connected to a Chromebook. Thanks to the built-in slicing program, you do not need to install additional printing software.
Probably the most impressive is the integration with Amazon Alexa. Users can stop, cancel and check the status of 3D printing in real time using voice commands.
What does this inexpensive 3D printer offer? Working space 127 x 127 x 150 mm. The 3D printing speed is 300 mm/s and the resolution is 20 microns. There is a built-in 3.5'' color touch screen, a system for monitoring the amount of remaining material for printing, automatic calibration and a removable self-aligning print platform. The only drawback is that the table is not heated, so you have to use PLA plastic.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Robo C2
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 127 x 127 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 20 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, WiFi.
Back to the list of 3D printers
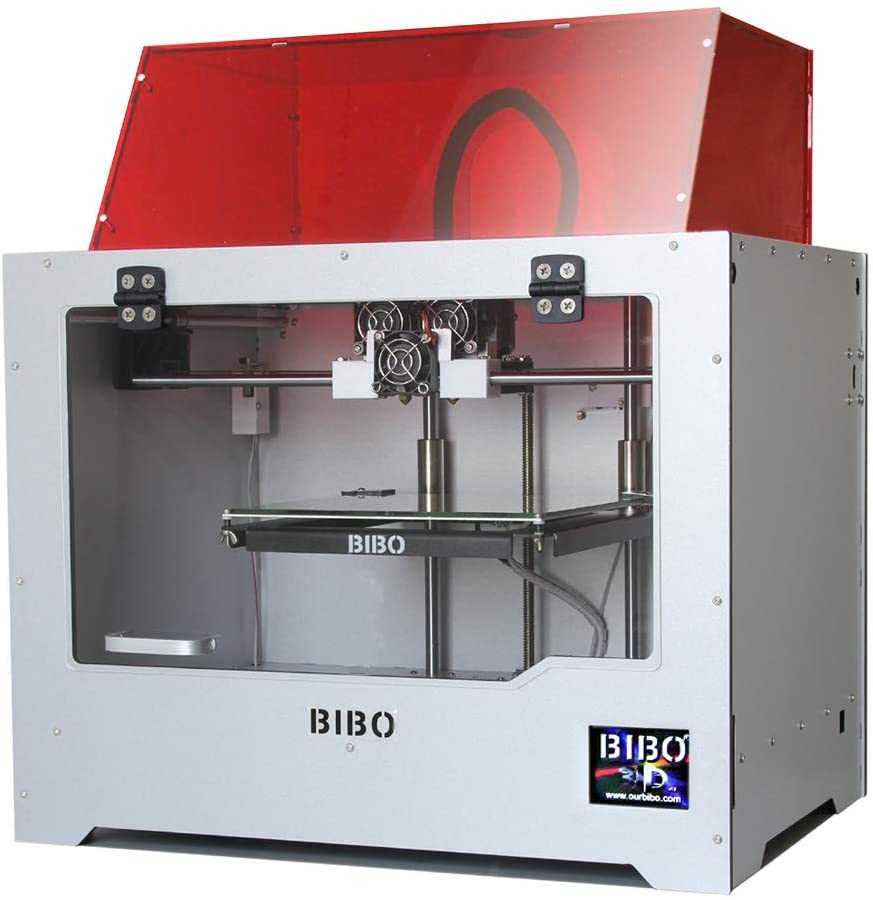
Wanhao Duplicator 4S ($829)
The Duplicator 4S has 2 extruders. It's essentially a copy of the MakerBot Replicator. Behind the steel body is the MK10 material feed mechanism, which is currently the easiest to use and most sought after in the market for 3D printer components.
It's essentially a copy of the MakerBot Replicator. Behind the steel body is the MK10 material feed mechanism, which is currently the easiest to use and most sought after in the market for 3D printer components.
One of the features of this model is a high-precision material feed wheel, which ensures the same filament feed speed. The Duplicator 4S is equipped with a 0.4mm precision nozzle.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Duplicator 4S
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: ABS, PLA, exotic;
- Working space: 225 x 145 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Maximum layer height: 500 microns;
- Number of extruders: 2;
- XY accuracy: 11 microns;
- 3D printing speed: 40 mm/s;
- Open Source: software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 0.4 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.

Back to the list of 3D printers
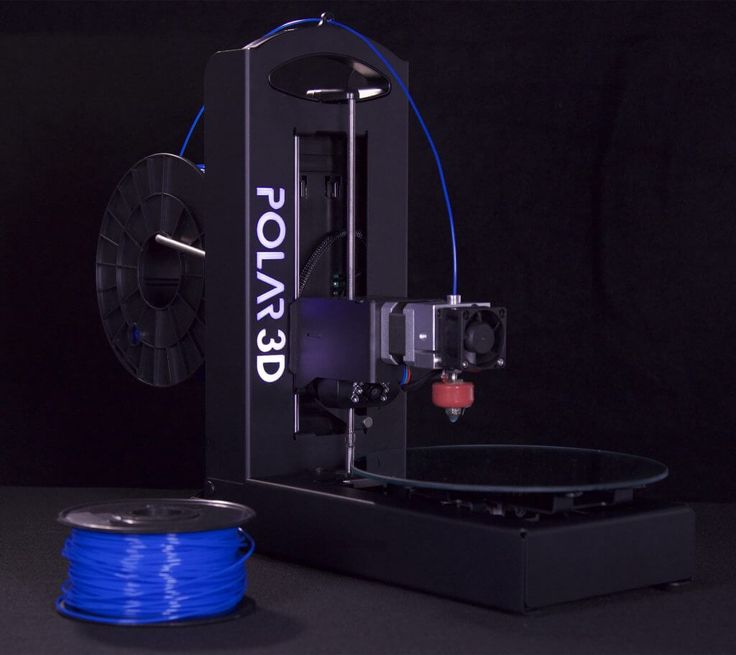
Polar 3D Printer ($899)
Polar 3D belongs to a separate category of 3D printers in this top, since this model implements the polar coordinate system. This causes the table to rotate and the print head to move up, down, right, and left.
Thanks to the polar coordinate system, this 3D printer is powered by two stepper motors, so it consumes less power. In addition, it turned out to realize a larger size of the working area: 203 (table diameter) x 152 (Z coordinate) mm.
Nominal price $899, but there are special discounts for educational institutions. The discounted price is only $599.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Polar 3D
- Printer type: FDM;
- Materials for 3D printing: PLA;
- Working space: 203 (table diameter) x 152 (Z-coordinate) mm;
- Minimum layer height: 50 microns;
- Maximum layer height: 400 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- 3D printing speed: 40 mm/s;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: no;
- Connection: USB, WiFi, SD card.
Back to 3D printer list
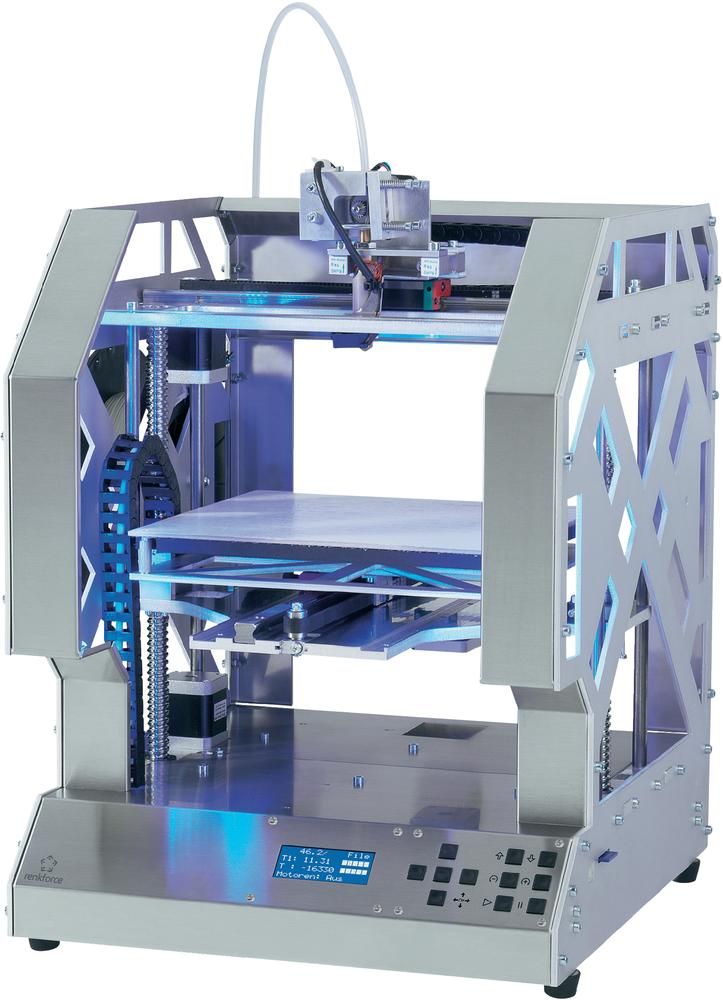
FlashForge Creator Pro ($899)
You've probably heard of this 3D printer. FlashForge Creator Pro is very similar to Makerbot Replicator 2X. This inexpensive 3D printer has 2 extruders, it has a steel closed body.
Other features include a table sizing system, and a guide screw that makes the guide system more stable and durable. The design is nothing special, but this model has earned positive reviews from the 3D community due to its reliability, versatility and ease of use.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer FlashForge Creator Pro
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: ABS, PLA, exotic;
- Working space: 225 x 145 x 150 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Maximum layer height: 500 microns;
- Number of extruders: 2;
- XY accuracy: 11 microns;
- 3D printing speed: 40-100 mm/s;
- Open Source: design and software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.
Back to 3D Printer List
Dremel Idea Builder ($899)
The Idea Builder is plug and play. This 3D printer is designed by Dremel. It has a color touch screen display. Sufficiently large working space - 230 x 150 x 140 mm. Unfortunately, the table is not heated. On the other hand, since only PLA plastics can be used, this model is great for classrooms and teaching labs.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Dremel Idea Builder
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 230 x 150 x 140 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: no;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: no;
- Heated table: no;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, SD card.

Back to the list of 3D printers
Printrbot Simple Pro ($999)
Printrbot Simple Pro is a significant upgrade from the original Simple. Same open design, no body. Like its predecessor, the Printrbot Simple Pro is compact and portable. All-metal construction for excellent vibration damping and shock resistance.
The main difference is the built-in color touch screen, the ability to connect via WiFi and free cloud service (optional), which greatly improves the 3D printing process. Simple Pro has a 32-bit processor, which ensures smooth and fast movements. And at the same time, this model is included in our top 20 cheap 3D printers, since its cost is $999.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Printrbot Simple Pro
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: PLA;
- Working space: 200 x 150 x 200 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 50 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- Open Source: design and software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: optional;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.
 75 mm;
75 mm; - Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: USB, WiFi.
Back to 3D printer list
Prusa i3 Mk2 ($999)
This is one of the best 3D printers you can buy in this price range. All nodes are open-source licensed and part of the Rep-Rap project, so there are many copies around ... but all replicas are worse than the original.
The Prusa i3 Mk2 is equipped with a heated table that has technology to compensate for temperature differences in the center and corners. There is an automatic calibration system. And of course, amazing documentation. This is an extremely versatile 3D printer that you will 100% appreciate when you start printing with unusual materials such as PLA, PET, HIPS, Flex PP or Ninjaflex, etc.
The Prusa i3 Mk2 is a 3D printer that is constantly being developed and supported by the manufacturer. Its developer Josef Prusa regularly adds new features, software and design improvements (for example, the ability to color 3D print). If you look for quality competitors in the 3D printing market, then the cost of their equipment will be in the region of $2000 - $3000.
If you look for quality competitors in the 3D printing market, then the cost of their equipment will be in the region of $2000 - $3000.
The only drawback is that if you decide to buy a Prusa i3 Mk2, you will have to wait about 2 months, as the company cannot keep up with the high demand.
Specifications of cheap 3D printer Prusa i3 Mk2
- Printer type: FDM;
- 3D printing materials: ABS, PLA, exotic;
- Working space: 250 x 210 x 200 mm;
- Minimum layer height: 100 microns;
- Number of extruders: 1;
- 3D printing speed: 50 mm/s;
- Open Source: design and software;
- Compatible with materials from other manufacturers: yes;
- Heated table: yes;
- Nozzle diameter: 1.75 mm;
- Control panel on 3D printer: yes;
- Connection: SD card.
Best 3D Printers Under $1000 in 2021 (Review and Buyer's Guide)
Nowadays, 3D printing technology is becoming more and more accessible to any user.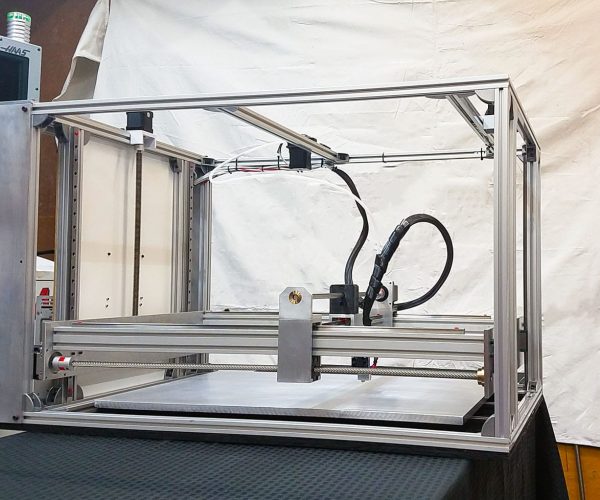 Not only because they are being made more intuitive and user-friendly, but also because their prices are significantly reduced to match the economic opportunities of a wide audience in the market.
Not only because they are being made more intuitive and user-friendly, but also because their prices are significantly reduced to match the economic opportunities of a wide audience in the market.
The thing is, 3D printer prices vary a lot, and if you ask us, we will definitely go for printers under $1,000 but no less than $250. This is the ideal price point where you can find many 3D printer models that can compete with other high quality models. They usually come with a lot of impressive features that might surprise you. For example, the Creality Ender 5 Plus has an astounding maximum build volume of 350 x 350 x 400mm. At this price, it's a very pleasant choice that makes it popular with enthusiasts and professionals who are interested in printing huge models. If you're familiar with the YouTube videos we've reviewed, you've probably come across this model more than once. We often see it being chosen by various generalists and 3D artists for printing life-size helmets onto masks and more.
Of course there are many other options to consider; especially now, when every year there are many, many new models from leading brands. Some of them come from Flashforge, ANYCUBIC, FLSUN and Snapmaker. The fact is that choosing a 3D printer is not just a game of picking aesthetically pleasing fruit from a low tree. This requires you to evaluate your knowledge as a 3D printer user and the features that will benefit you the most. For example, while the Creality Ender 5 Plus is a great choice, it's not exactly 101% beginner-friendly. For best results, adjustments and correct (AND DETAILED) tuning are required. The same goes for the ANYCUBIC Photon Mono X, which is famous for its detailed prints.
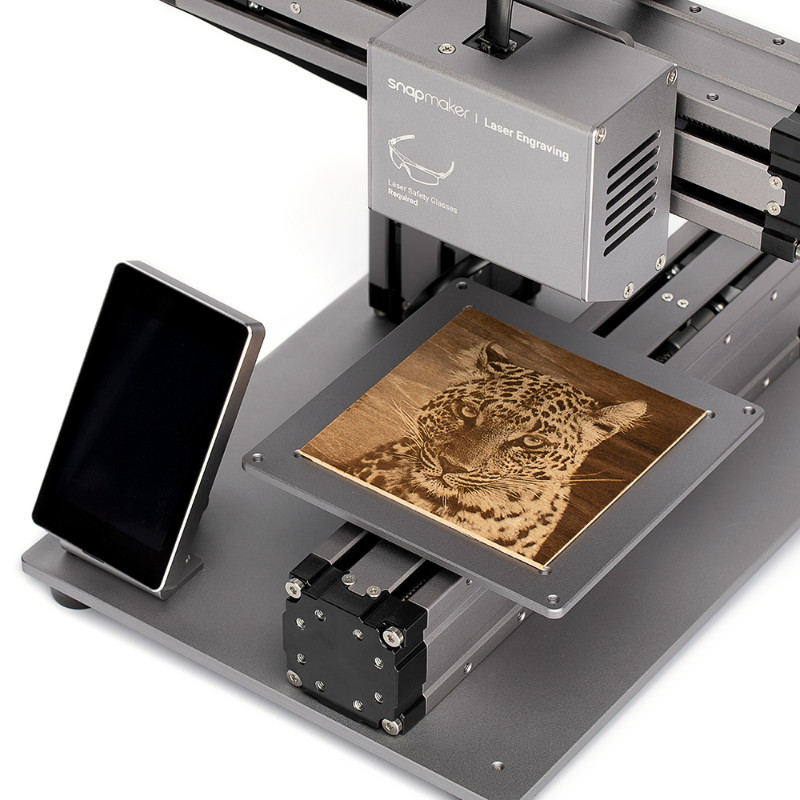
There are also certain technologies you might be interested in. If you're tired of regular FDM printers, a delta model like the FLSUN QQ-S Pro might be a good choice. There are models that are equipped with amazing features such as a laser engraver and Snapmaker Original 3-in-1 CNC carving features. The IDEX Flashforge Pro 2 system also deserves attention.
The IDEX Flashforge Pro 2 system also deserves attention.
In order to provide you with more detailed information about them, we conducted a study with the help of our team's experts. After what seemed like an eternity of arguing about which 3D printer is the best, we have prepared a comprehensive review for you. After a series of comparisons and personal observations of the devices, we hope to give you their best moments to help you decide which one to choose. Let's get started:
Print speed
200 mm / s, but decreases to 80 mm / s
Custom
Functions
Ease in use
Cost Extension
Cost.
Pros :
- Offers better print volume.
- Offers a great feature set at a great price.

- Comes with a stable print platform and the print quality is consistent.
- The glass print platform is great.
- Can serve larger projects.
Cons:
- Very loud printer.
- Not for beginners; its setup is quite complex and some tweaking (electronics and tubes) is needed to achieve the best results.
Final take:
To get the Creality Ender 5 Plus on our list, our team had a hard time comparing it to the brand's newer model: the Creality Ender 6. It's true that its successor offers more striking aesthetics, but when it comes to comes down to practicality, we really think the Creality Ender 5 Plus offers a higher value.
First, the Creality Ender 5 Plus has a more impressive and exceptionally high print volume.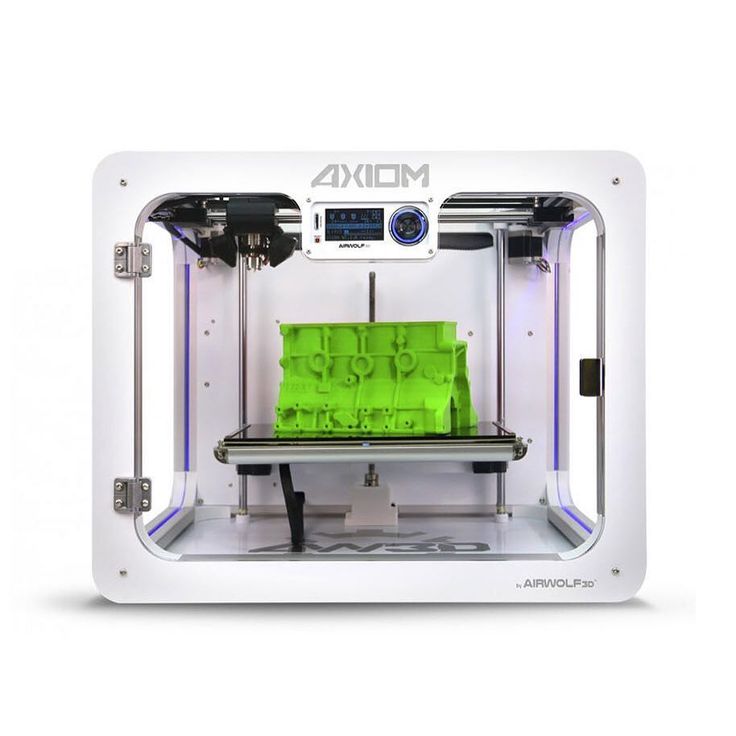 It offers a maximum build volume of 350 x 350 x 400mm, which is relatively better than the Ender 6's 250 x 250 x 400mm build volume. With it, you can print large models in the Ender 5 Plus, such as helmets and busts, which seems to be simply not possible in other small 3D printers.
It offers a maximum build volume of 350 x 350 x 400mm, which is relatively better than the Ender 6's 250 x 250 x 400mm build volume. With it, you can print large models in the Ender 5 Plus, such as helmets and busts, which seems to be simply not possible in other small 3D printers.
They have almost all the same parts like 1.75mm filament diameter, 110°C max print bed temperature, 260°C max extruder temperature, filament types, slicing software and more. Printing accuracy and quality of both models are also practically the same. Apart from the fact that both have a printing accuracy of 0.1 mm, they are also the same in terms of layer thickness from 0.1 to 0.4 mm.
However, in terms of speed, the Ender 6 is a step ahead as it is 3 times faster than the Ender 5 Plus. The latter has a maximum print speed of 200mm/s, which drops to 80mm/s when set for precise models. The Ender 6, on the other hand, delivers a solid print speed of 150mm/s, which is absolutely fast and still acceptable for high quality prints. Hence, if speed is not an issue for you, the Creality Ender 5 Plus is still a good choice.
Hence, if speed is not an issue for you, the Creality Ender 5 Plus is still a good choice.
What's more, the Creality Ender 5 Plus offers a better feature set that we feel is far more convenient than what the Ender 6 offers. speed up printer setup. This is contrary to manually leveling the Ender 6 using the adjustment screws. That being said, if you already have a Creality Ender 5 Plus, there really is no need to upgrade to Ender 6. And if you're planning on choosing between the two, we'd still recommend the Ender 5 Plus because of its amazing features.
Print speed
100 mm / s max.
performance and quality
Functions
Ease in use
The price ratio
pluses :
- is delivered in the collected form and work with the rest of the building is quite simple.

- The lid is plastic, but there is a solid metal frame underneath that is undeniably durable.
- Has a compact design.
- Has a maximum print speed of 100mm/s.
- You can print two identical models at once.
- Still available with compact body.
Cons:
- Removing the print is quite difficult.
- The filaments are located on the back of the printer and there is no notification feature to tell you if you are out of filament.
Final double:
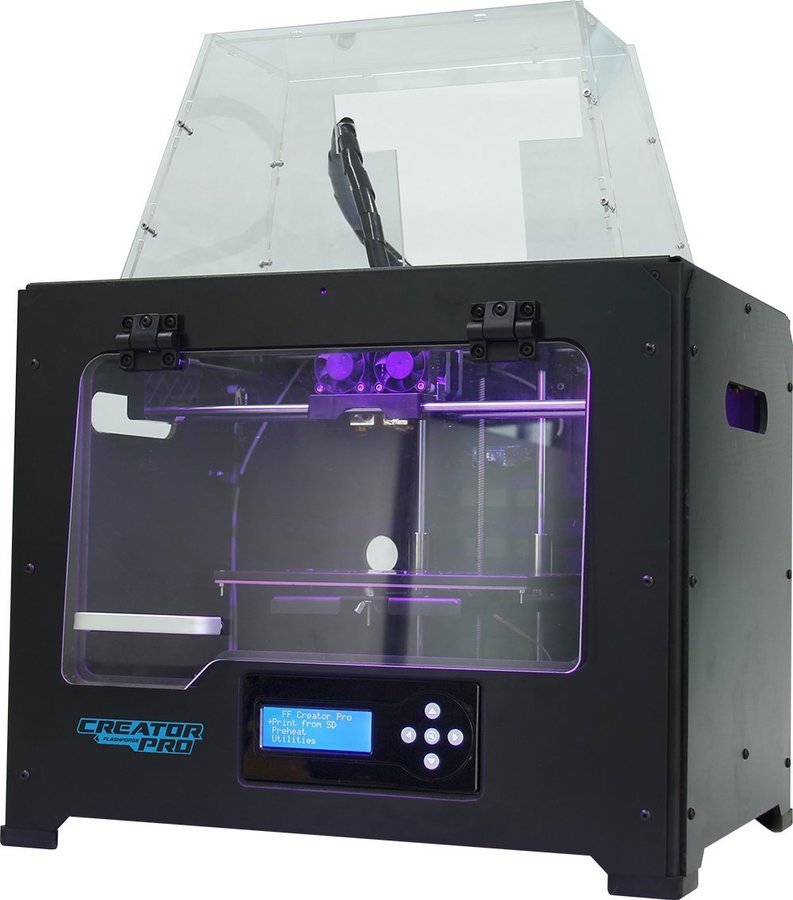
There's just so much to love about Flashforge Pro 2 that sets it apart from its predecessor. Flashforge Creator Pro.
First, it boasts an IDEX system or an independent dual extruder, which you will not see in any other printer on the market. This is a big upgrade from the old model attachments that are attached to each other. Don't get us wrong. We all still love Flashforge Pro dual extrusion, but IDEX Pro 2 is simply unbeatable. Thanks to this feature, which offers you two independent extruders, you can print two identical models at the same time. He can do it even in mirror mode! What's even better is that you can print them in 2 different colors since the machine uses 2 spools of filament at the same time. Sick!
This is a big upgrade from the old model attachments that are attached to each other. Don't get us wrong. We all still love Flashforge Pro dual extrusion, but IDEX Pro 2 is simply unbeatable. Thanks to this feature, which offers you two independent extruders, you can print two identical models at the same time. He can do it even in mirror mode! What's even better is that you can print them in 2 different colors since the machine uses 2 spools of filament at the same time. Sick!
What's more, the Pro 2 still has valuable features and details that we still love in the old version. This includes the closed design of the printer, which makes the printing process still safe and quite attractive. As for the heated aluminum print bed, it's the same as the Creator Pro.
On the other hand, you're getting a huge upgrade in terms of user interface since the Pro 2 now comes with a touch screen feature. The system is quite simple and excellent. All the settings you need can be accessed at once, and the icons and commands are intuitive. No complications.
No complications.
However, we sincerely think that the main drawback of this model is the brand's initiative to create Creator printers with more updated features. For example, it only comes with a maximum nozzle temperature of 240 degrees, which limits its ability to serve other fiber types.
The Pro 2's small build size is also a bit problematic, especially now that it uses IDEX technology. It has a 200 x 148mm base plate with a print height of 150mm. If you use two extruders in mirror mode, this means that the build volume will be reduced even more due to the space between the extruders while working on the X axis at the same time. This gives a maximum width of 80mm for each model. However, this volume should be sufficient for most 3D printing projects. First of all, given the efficiency of printing two models in just one run, you still have a pretty competitive 3D printer with this bad boy.
Press speed
to 60 mm / h at a layer height of 0.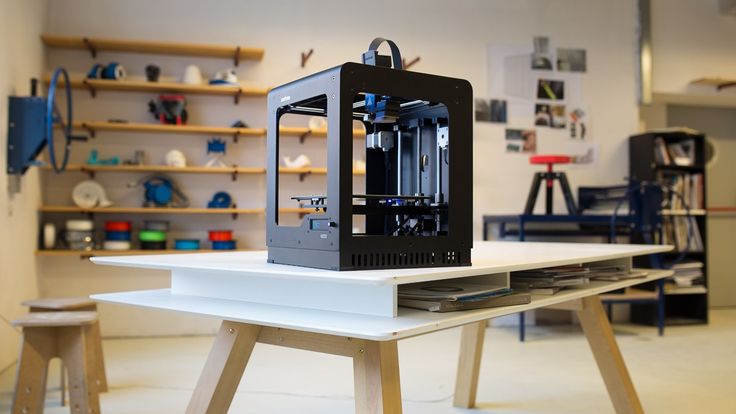 05 mm
05 mm
6
Custom
Functions
simplicity in the use of
Pros :
- Relatively quieter than other printers.
- Build plate alignment is largely undemanding.
- Print speed up to 60 mm/h at 0.05 mm layer height.
- Provides 50 micron XY resolution.
- Supplied with large assembly volume.
Cons:
- Not exactly for beginners, especially since 3D printing results require a steep learning curve.
- The wireless antenna is placed next to the resin tank, which may cause some problems in the future.
Final double:
If FDM isn't your thing and you need more detailed performance, this MSLA printer is worth considering. After all, this is one of the largest printers in its category, with a build volume of 192 x 125 x 245mm. Hence, it can work great with small to medium projects including busts and masks. Good news? Given the nature of the printing process, it can print several tiny models in the entire 192 x 125mm print area. Hence, it can be used to print multiple models at the same time, not to mention faster curing times.
After all, this is one of the largest printers in its category, with a build volume of 192 x 125 x 245mm. Hence, it can work great with small to medium projects including busts and masks. Good news? Given the nature of the printing process, it can print several tiny models in the entire 192 x 125mm print area. Hence, it can be used to print multiple models at the same time, not to mention faster curing times.
The reason for this is quite simple: it is equipped with new features that make it different from the old one. MSLA printers. First up is the 8.9-inch monochrome LCD display, which means improved light transmission, cutting curing time from 6 seconds to 1.5-2 seconds per coat. Also, since the LCD can weaken over time when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, the device allows you to adjust the light so you can extend its lifespan. Apparently this also means longer curing times in each of your projects, and if that's not an issue for you then this feature is a great addition.
In terms of print detail, its 4K resolution with 3840 x 2400 pixels on screen gives it a great experience. In addition, the Z-axis boasts a dual linear guide to keep the printer stable during the printing process. As a result, you will get the highest possible detail on MSLA printers with a smooth surface. Basically, you will get most of what you expect if your sliced model is decent.
However, as is the case with other 3D printers, Mono X is not only about the sun and the rainbow. First, it uses resin to make models that can get really messy, especially if you're trying this type of printer for the first time. Secondly, no offense, adding "wireless" control to the device is almost useless. Yes, we really appreciate the fact that this will allow you to control the printer via your phone via the Anycubic mobile app. This includes starting and pausing the printing process, as well as changing some settings. However, this is similar to controlling the device with built-in controls. Also, setting up the app is tedious, which is why we really think it's almost impractical. However, the great features of this 3D printer can be equated to this small problem.
Also, setting up the app is tedious, which is why we really think it's almost impractical. However, the great features of this 3D printer can be equated to this small problem.
Press speed
120 mm / sec
performance and quality
Functions
Cost ratio
pluses :
- coating for easy removal of prints.
- Platen heated to 110°C.
- Assembly is quite simple and easy.
- Can handle tall models and can print fast.
- Very affordable compared to other options.
Cons:
- Does not offer a glow sensor.
Final take:
The FLSUN QQ-S Pro is way out of the budget range of the other printers on the list. it's a lot cheaper than them, but after looking at the other types of printers on this list (and the possibility that some readers might want us to include a delta printer), we decided to include it.
it's a lot cheaper than them, but after looking at the other types of printers on this list (and the possibility that some readers might want us to include a delta printer), we decided to include it.
Delta printers are not as popular as their Cartesian counterparts, but in some ways they can offer a number of advantages when it comes to speed. Compared to others, their lightweight printheads allow them to move freely and faster. This is the reason why FLSUN QQ-S Pro provides a reliable print speed of 120mm/s, which is relatively close to the performance of the famous Ender 6.
Another distinguishing feature of such a delta printer is the height. In the case of the QQ-S Pro, it has a large Z-height, which means it is capable of printing tall models. It also measures 255 x 365mm, which is impressive given its price compared to other printers.
We also really like that, considering its price range, it has an automatic bed leveling. Its print head is equipped with an automatic alignment sensor. On the plus side, bed leveling is not only effortless, it also needs to be leveled once, since the machine bed does not move.
On the plus side, bed leveling is not only effortless, it also needs to be leveled once, since the machine bed does not move.
The printer uses a titanium extruder that attaches to the frame and feeds filament through a Bowden tube. It provides a maximum temperature of 270°C, allowing you to work with a significant number of fiber types. This includes ABS, PLA, PVA, HIPS, wood and the like, which are relatively flexible. However, this is where we see the main problem with this delta printer model (in fact, this is a problem for all FLSUN printers): there is no filament sensor at all. Luckily, the filament can be easily controlled as it is located at the top of the printer compared to Flashforge Pro 2.
Press speed
100 mm / sec
Custom
Functions
Ease in the use of
9000 9000 9001 value and feature set.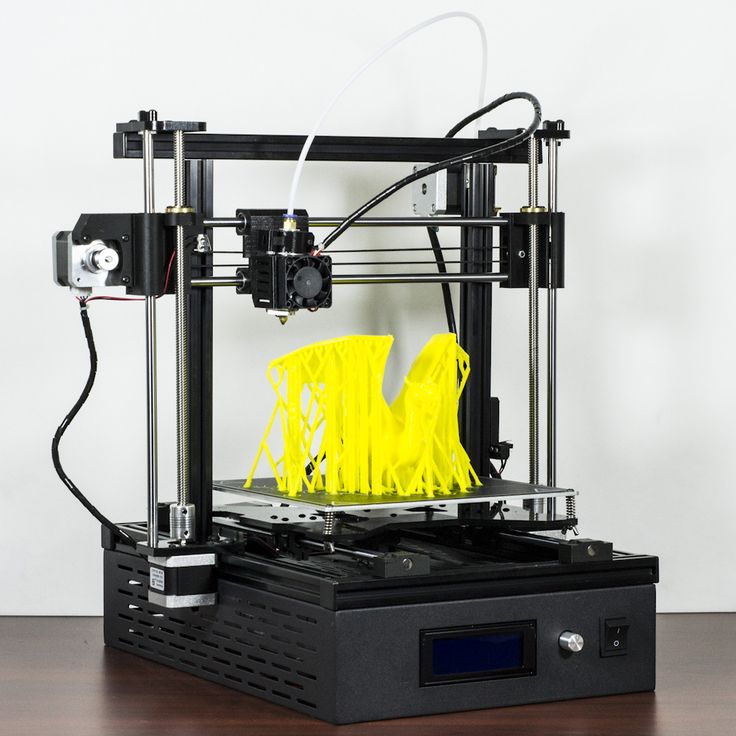
Cons:
- The 3D printing feature has limited build volume.
- Thread function is very loud.
Final take:
If innovation and extra features are the main criteria to consider, then the Snapmaker Original 3-in-1 truly is a winner. This 3D printer is one of the most funded 3D printing projects on Kickstarter due to its great features. It will not only be a 3D printer, but also a laser engraver and a CNC carving machine. This is the reason many people like it, especially 3D enthusiasts who want to explore other kinds of projects.
This is the reason many people like it, especially 3D enthusiasts who want to explore other kinds of projects.
The general concept of this multifunctional machine is quite simple. It works through the use of three modules, each offering a specific feature. They are easy to replace next to the appropriate beds/platforms needed for the job. The modules are secured with 4 hex head screws and you only need to work on unplugging/plugging in the specific cables you need. In a couple of minutes, you can switch from 3D printing to engraving and cutting.
The device's 3D printing feature is not as competitive as other options like the Creality Ender 5 Plus or Flashforge Pro 2. It only has a 125mm square volume. This means that it is only intended for very small projects such as printing small accessories and models.
The maximum print head travel speed is 100mm/s, although actual printer performance may vary. However, the nozzle can generate heat up to 250°C, allowing the 3D printer to process a significant number of fiber types. The layer resolution of the 3D printer is between 50 and 300 microns, and the accuracy of 3D printing is quite decent.
The layer resolution of the 3D printer is between 50 and 300 microns, and the accuracy of 3D printing is quite decent.
The 125 x 125mm working area laser engraving module provides a spindle speed of 19,000 RPM which produces excellent details when used with compatible materials such as wood, acrylic, printed circuit boards and carbon fiber sheets. According to our observations, the spindle works differently depending on the material used in the process. While it works great with carbon fiber sheets, it can work more with softwood materials.
The same applies to the laser engraver function for selected compatible materials. It uses a wavelength of 405 nautical miles and a power of 200 mW. It can work well with a wide range of materials, including wood, bamboo, leather, plastic, fabric, paper, opaque acrylic, and more. However, for higher performance, users can have an upgraded 1600mW module for the device.
Check Price
Best 3D Printers Under $1,000 Buyer's Guide
print volume
This is a must, especially if you often work with 3D prints of different sizes. Medium-sized devices like the FLSUN QQ-S Pro and Flashforge Pro 2 should be enough for most everyday projects, but if you think you need something for larger projects, we recommend the Creality Ender 5 Plus. It can provide a maximum build volume of 350 x 350 x 400mm. While not as fast as its successor, the Ender 6, it can deliver consistent results. The FLSUN QQ-S Pro is also a good choice, especially for vertically long and tall prints considering it's a delta model.
Medium-sized devices like the FLSUN QQ-S Pro and Flashforge Pro 2 should be enough for most everyday projects, but if you think you need something for larger projects, we recommend the Creality Ender 5 Plus. It can provide a maximum build volume of 350 x 350 x 400mm. While not as fast as its successor, the Ender 6, it can deliver consistent results. The FLSUN QQ-S Pro is also a good choice, especially for vertically long and tall prints considering it's a delta model.
FDM printing technology is undoubtedly the most convenient technology in the world of 3D printing. Not only because models are usually easy to assemble or because of the unusual features that you often find in such models, but also because of the threads used in them. No mess and no extra steps like resin curing. With SLA printing, the opposite is true. However, while often despised due to the sticky material used in the printer, it should keep you from considering SLA 3D printers. The reason is simple: SLA is very good when it comes to details. That is why it is often used not only by enthusiasts, but also by professionals, especially in the field of medicine, who require detailed printouts of objects.
The reason is simple: SLA is very good when it comes to details. That is why it is often used not only by enthusiasts, but also by professionals, especially in the field of medicine, who require detailed printouts of objects.
features
It's true that there is no perfect 3D printer on the market, but as we often tell our readers, it's all about finding the right set of features that will give you the most benefit...and the best value for money . It is on this principle that we have made the Creality Ender 5 Plus the leader of our list. There is a newer and "higher" model than this one, the Ender 6. However, after carefully looking at the things the latter loses in order to achieve a more modern look, we think the Ender Plus 5 is still much more practical to have. The printing ability is the same in terms of accuracy. But what really helped was the auto leveling and the sheer volume of printing that most of us often need.
There are other 3D printer models that come with other enticing features such as the IDEX system in Flashforge Pro 2, the detailed ANYCUBIC Photon Mono X resin prints, the awesome print height of the FLSUN QQ-S Pro, and numerous Snapmaker features.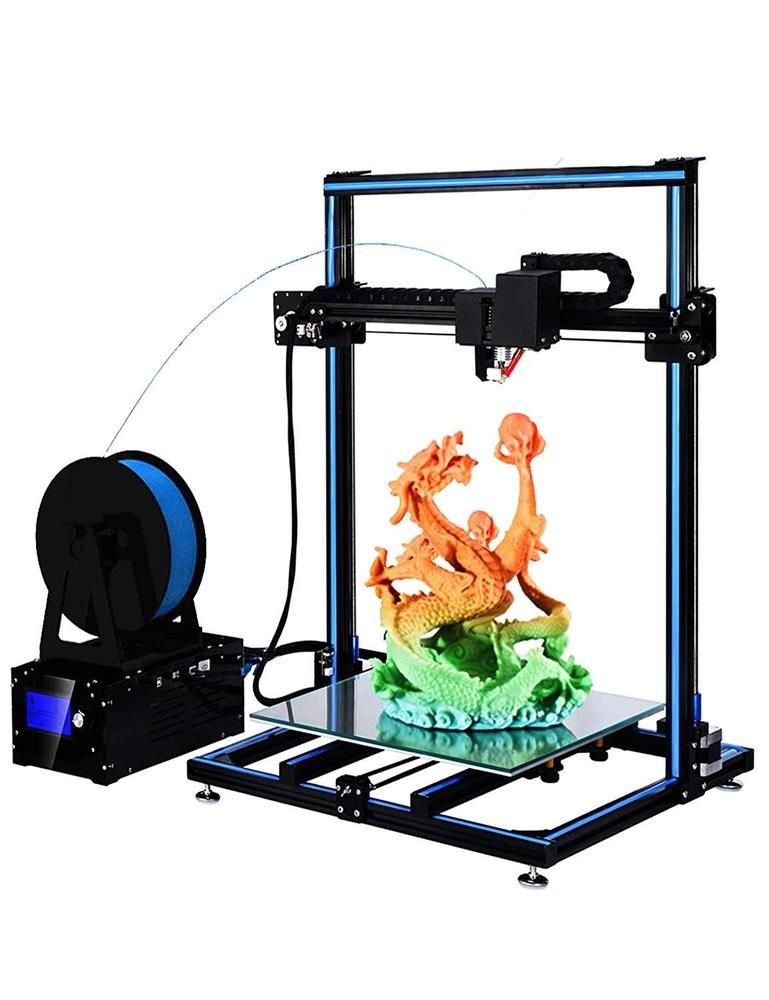 Original 3-in-1. In addition, each model is complemented with other details that enhance their convenience, from a closed print area to wireless connectivity. However, the bottom line is to find a model that offers the best set of parts that will satisfy you.
Original 3-in-1. In addition, each model is complemented with other details that enhance their convenience, from a closed print area to wireless connectivity. However, the bottom line is to find a model that offers the best set of parts that will satisfy you.
As mentioned, 3D printers under $1,000 often have great deals for you. They are often equipped with the right set of features to suit most of your project needs. However, it's certainly a good idea to make sure you get the most out of everything. For example, although Ender 5 Plus is an older version, it has a relatively higher price than Ender 6. However, this does not mean that the latter can give you better performance and value. You can add about $30 to enjoy the good old Ender 5 Plus model, but it's worth it in the long run considering it can handle larger projects. So yes, that's the point. Don't mind spending or adding a little more to your budget if you think this model will really benefit you.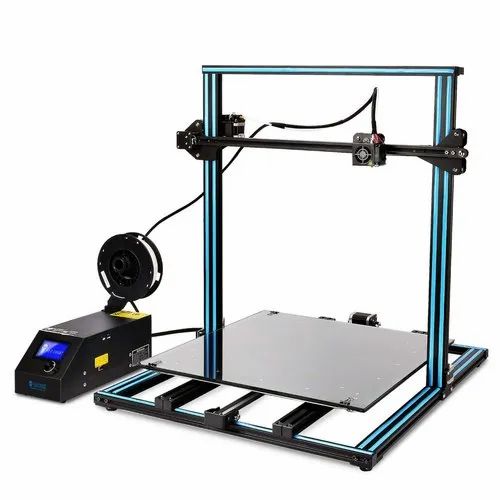
Best 3D Printers Under $1,000 FAQ
Are 3D Printers Expensive?
There are entry-level 3D printer models that range from $200 to $500. They should offer the most basic features you need to 3D print models, but there are better options that cost upwards of $500, like the Creality Ender 5 Plus. However, there are other high-end options from $1,500 to $6,000.
Which filament should I use for my 3D printer?
This depends on the maximum heating power of the device and its compatibility with certain fiber types. However, the most commonly used fibers are PLA and ABS.
Can I leave my 3D printer overnight?
It is never recommended to leave the 3D printer running overnight or unattended. In addition to the danger that the printer may pose to curious children and pets, it may encounter some electronic problems that could lead to a fire.