3D printing with wax
Discover the 3D Wax Printing Process
Additive manufacturing offers the possibility to 3D print using a wide range of materials from plastic to resin and metal. But what about wax 3D printing? There are actually different ways to print wax.
We are going to tell you about 3D printed wax processes and applications. Here is everything you need to know about wax 3D printing!
Wax 3D Printed Concept ModelsHow can wax be used for 3D printing?
There are actually different techniques to 3D print wax.
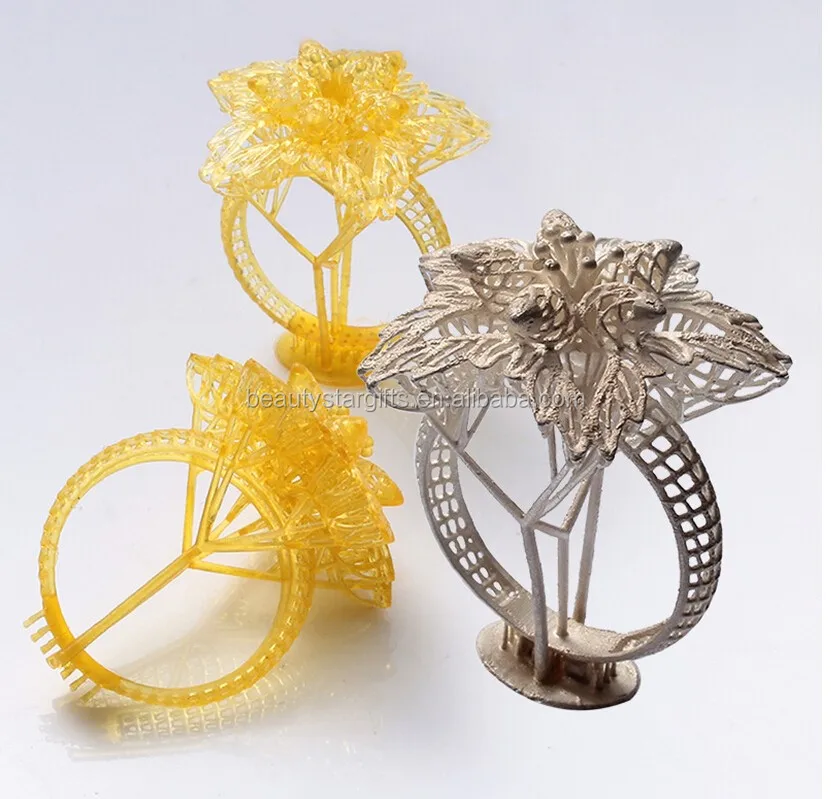
3D printing with wax is used to create a precise 3D mold out of a 3D file thanks to the 3D lost wax casting technique. 3D Lost wax casting (or investment casting) is a production process. The casting process mainly allows to produce customizable jewelry of very high quality and 3D design complexity in various printing materials, such as metals.
3D printing with wax is used to create a precise 3D mold out of a 3D file thanks to the 3D lost wax casting technique.
3D Lost wax casting (or investment casting) is a production process. The cast process mainly allows to produce customizable jewelry of very high quality and 3D design complexity in various printer materials, such as metals.
The idea is to create concept models with 3D modeling and then 3D Print wax patterns of the desired object thanks to a wax 3D printer. Then, by adding a refractory material around this model we obtain a mold. Melting the wax filament inside the mold creates an empty space that is filled with the 3D printers material, molten metal. The only remaining step is to break the mold to obtain the final object. Variable finishing options for this 3D printing technology are then available
Lost wax casting technique (or investment casting) framework with 3d printed casting patterns 3D printed jewelry produced with Sterling silver thanks to the a 3d printed model with waxIn addition to the lost-wax casting process, it is possible to actually 3D print wax.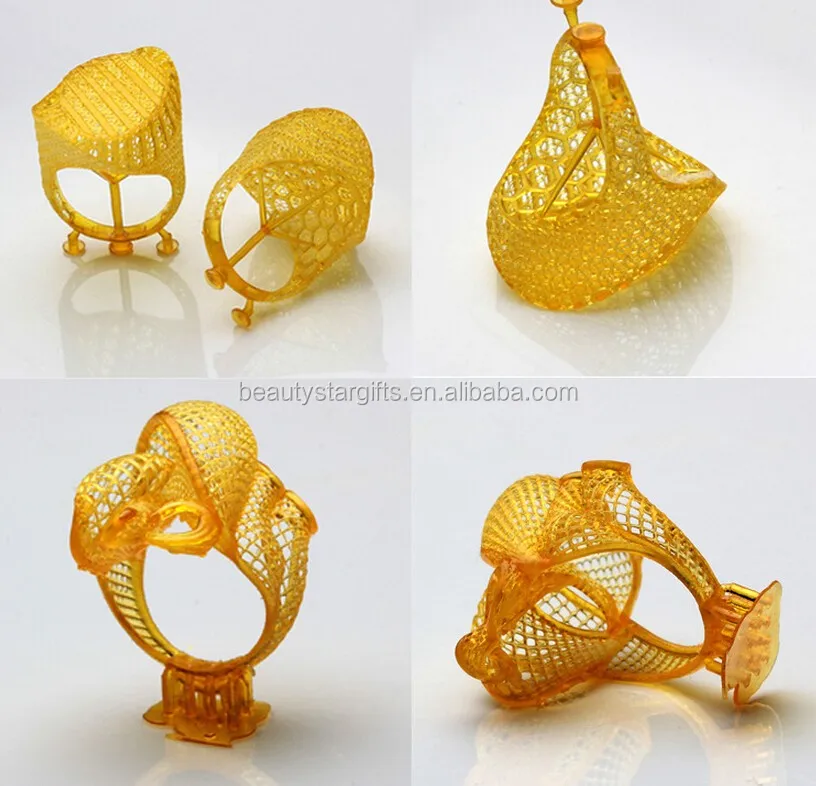 The material often used to print wax is not real natural wax, but it is a wax-like material, the mechanical properties of this material are then similar to wax.
The material often used to print wax is not real natural wax, but it is a wax-like material, the mechanical properties of this material are then similar to wax.
Wax 3D printing is made possible with technologies such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology. Using an FDM 3D printer, the 3D printing filament material will allow you to get great wax molds.
What is the 3D Printing Process for Last Wax casting?
In the Additive Manufacturing industry, wax 3D printing is made with multi jet printers like the Projet 3500 CPX HD printer that is used at Sculpteo. Unlike filament printing technique, multi jet modeling process (MJM) looks a lot like ink jet technology. Molten wax filament is deposited by nozzles on an aluminum build platform that moves down, layer by layer. 3D Printers are able to simultaneously 3D print with two wax types:
- The main one that melts around 70°C (depending on the wax type) and which actually creates the objects and the functional prototypes.

- The one that supports the wax product during creation has a lowest melting temperature. It is removed at the end by heating the overall piece.
This support wax enables the creation of almost any form, even the most complex product designs and the most complicated wax patterns.
This whole printing process can print products with an incredibly high resolution of 25 μm (0.025mm) between each layer which allows to create pieces with a virtually unlimited level of detail.
But, other 3D printing processes exist using wax such as DoD or Drop on Demand. During this printing process, the wax is deposited in dots instead of a continuous line as we can see with technologies such as inkjet 3D printing.
What are the properties of 3D Printed Wax?
Wax used for Additive Manufacturing is made of 100% pure castable wax but can have various colours and properties. This will also depend on the 3D printing wax process you will use. Moreover, using wax for casting process will allow you to get really detailed molds for products with an intricate geometry.
This will also depend on the 3D printing wax process you will use. Moreover, using wax for casting process will allow you to get really detailed molds for products with an intricate geometry.
How to use 3D Printed Wax?
Wax printing is mainly used to create dental molds and 3D printing jewelry. As a 3D printing service, we offer you a lot of different materials, technologies, and finishes to give life to all your projects. Among all of these possibilities we are offering you, you can choose to try lost-wax casting to start your jewelry business. Indeed, affording your own wax 3D printer might not be the most coherent and cheapest choice to develop your use of wax printing. Moreover, printing this material is a little bit more complicated to operate
Wax printing is mainly used to create dental molds and 3D printing jewelry. At Sculpteo, we are offering you the possibility to use our lost-wax printing process with our brass material and sterling silver material.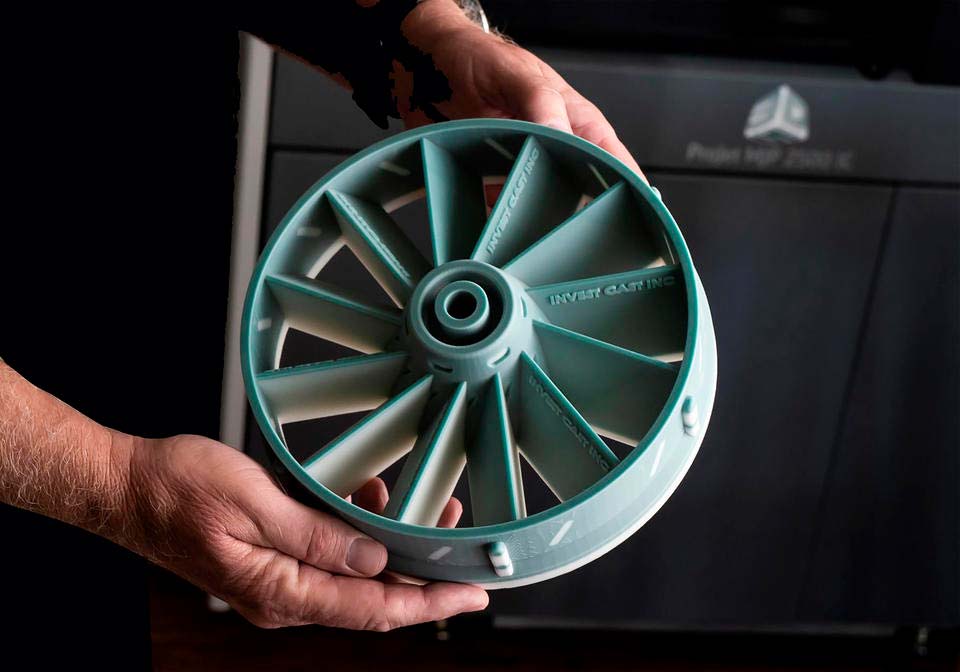 You can visit these material pages to see how you can use properly brass or silver as 3D printing material, to consult the safety data sheets and white paper for proper design guidelines, and to find their shipping info.
You can visit these material pages to see how you can use properly brass or silver as 3D printing material, to consult the safety data sheets and white paper for proper design guidelines, and to find their shipping info.
Are you convinced of the extraordinary potential of 3D printing with wax and want to order your personalized jewelry designs?
Getting started is easy if you have a design, upload it to Sculpteo to print it. Otherwise, browse our 3D printing marketplace where you can find a complete gift guide of our customers featured stories to find your dreamed gift.
In case you have any questions about 3D printing with wax or any other rapid prototyping technique, do not hesitate to contact customer support.
Best Wax 3D Printers & Filaments
- Author
- Recent Posts
Martin
Besides many test devices, Martin now has his fourth own 3D printer running and prints as a hobby for friends, family and himself.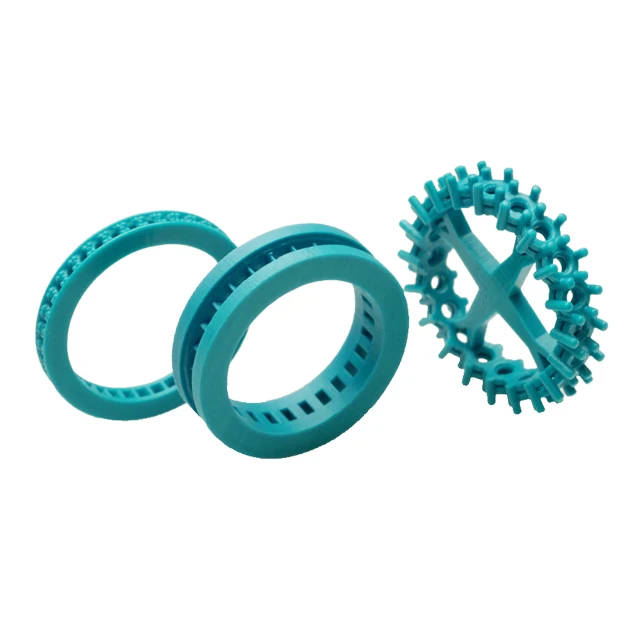 He is happy to share his experience with each new article.
He is happy to share his experience with each new article.
Latest posts by Martin (see all)
Disclosure: Links marked with * are Affiliate Links. I earn from qualifying purchases if you decide to make a purchase through these links – at no additional cost for you!
A wax filament 3D printer differs only slightly from conventional plastic filament printers. It has the conventional components such as an extruder, filament feed and printing plate.
Printing with wax is therefore practically identical in handling to the traditional plastic filament technique. The particularly good processability of wax filament also makes it possible to produce combination printers on which different materials can be processed. Alternatively, practically any conventional filament printer can be upgraded for processing wax material.
In addition to the proven layer-filament printing process, wax printing also offers “drop on demand” technology. Here, no continuous jet of liquid wax is processed, but the product is built up drop by drop. This technology impresses with excellent results but has so far only been available for high-quality printers.
This technology impresses with excellent results but has so far only been available for high-quality printers.
Besides the filament printer, there are also SLA resin printers with UV and laser light for wax printing. These have slightly higher printing speeds and the surface of the products becomes smoother. However, the liquid printers are much more expensive than the conventional coordinate-guided filament printers or, in the case of budget models, they have a very limited installation space.
In this article we will discuss the benefits of wax filaments and wax 3D printers and introduce you to the best printers and filaments for them:
The 5 best wax 3D printers:
- Anycubic Photon*
- ELEGOO Mars UV 3D Printer*
- Sindoh 3DWOX DP200 3D Printer*
- Peopoly Phenom MSLA 3D Printer
- Solidscape S300
The 4 best wax filaments:
- MOLDLAY*
- MakerJuice WaxCast resin*
- Formlabs Castable Wax
- Print2Cast
 (source: formlabs.com)
(source: formlabs.com)Table of Contents:
- 1 Wax Filament Cost
- 2 What Can You Do With a Wax 3D Printer?
- 3 Silicone Casting with Wax Printing
- 4 What Printing Materials are Available for Wax 3D Printers?
- 5 For Whom is a Wax 3D Printer Suitable?
- 6 Advantages and Disadvantages of a Wax 3D Printer
- 6.1 Advantages in Detail
- 6.2 Disadvantages in Detail
- 7 The Five Best Wax 3D Printers
- 7.1 Budget Model for Beginners: Anycubic Photon
- 7.2 In the Same League as the Photon: ELEGOO Mars
- 7.3 Affordable Large Format Printer: Sindoh 3DWOX DP200
- 7.4 Innovative Printing Process: Peopoly Phenom MSLA
- 7.5 High-End Wax Printing in 3D: Solidscape S300
- 8 The Four Best Wax Filaments
- 8.1 Standard Wax for Metal Casting: Moldlay
- 8.2 Low Priced but High Quality: MakerJuice WaxCast Resin
- 8.3 Expensive but Efficient: Formlabs Castable Wax
- 8.
 4 Low-Priced Starter Wax Filament: Print2Cast
4 Low-Priced Starter Wax Filament: Print2Cast
- 9 What Else You Need for Wax 3D Printing
- 10 Conclusion
Wax Filament Cost
If you now think that printing with wax is particularly suitable for test prints, we have to disappoint you: wax filament is surprisingly expensive.
If you can get plastic filament for as little as 8 dollars per kilogram, you have to reckon with almost 10 times that for wax filament.
Our Recommendation: MOLDLAY*Check Price at:
Amazon*
After all, printing with wax is good for your conscience: residual materials and waste are much less of a problem for the environment than plastic. But for the other advantages you have to look into the matter. Therefore, first of all: printing with wax is more a matter for specialists who know what they want to achieve.
Although you can try your hand at wax printing as a 3D printing beginner. However, you won’t have much fun with this printing technique, as the products are not very durable.
In contrast to plastic printing, durability is also not a specific goal of wax printing. Printing with this soft, temperature-sensitive material is only useful for very specific applications. But in these applications wax is the best you can take.
We have therefore compiled this comprehensive guide to 3D printing with wax. With the final buying advice for the suitable device and the best printer material, you too will find your way to the perfect wax print.
What Can You Do With a Wax 3D Printer?
A wax 3D printer does what a plastic 3D printer does. It builds up a 3D model of any shape layer by layer from a previously defined graphic.
Working speed, process and final result are very similar to plastic printing. Even this slight staircase structure of the surface is also present in wax printing. But here you already have a significant difference between the two printing materials.
While the finishing of a plastic surface is still a certain challenge, a wax model can be easily smoothed.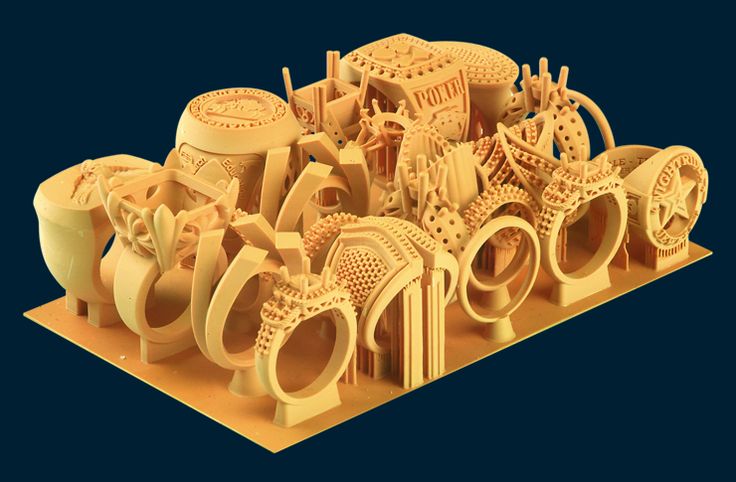 You have to be careful not to deform the model in your warm hand. With a little practice, however, you can get the unwanted layer structure away from the surface and get a nice, evenly smooth outer skin.
You have to be careful not to deform the model in your warm hand. With a little practice, however, you can get the unwanted layer structure away from the surface and get a nice, evenly smooth outer skin.
The special strength of a wax model lies in its temporary nature. This sounds paradoxical but is very advantageous for a very special application: metal casting. With a wax model, you can easily make casting molds with which you can cast metal products of any shape and form. Wax 3D printing can therefore become your entry into metal printing. The following metals are particularly suitable as casting material for beginners:
- Tin
- Lead
- Aluminium
Casting steel or copper would theoretically also work. However, these are particularly challenging because of their high melting temperatures. While tin melts at 231 °C, you need 1400 °C melting heat for steel.
Dealing with such hot liquid metal requires a lot of experience. We therefore advise you to use aluminum or tin. The results are very nice. Aluminum also becomes very stable and has high inherent strength.
The results are very nice. Aluminum also becomes very stable and has high inherent strength.
If you want to cast with lead, make sure you have sufficient ventilation and breathing protection. Lead fumes cause headaches and are harmful to your health.
Before you start, please take a close look at the subject of “casting metal”. Depending on the metal you have to consider different properties, for example shrinkage. When printing with your wax 3D printer, also make sure that the environment is cool enough. The filament is very sensitive to temperature and therefore deforms so easily that it becomes unusable for the printing process.
Silicone Casting with Wax Printing
An alternative to metal casting is the production of silicone products using a 3D wax printer. The printed product is not used as a casting core, but as a mold half. The special advantage of silicone casting in a wax mold is the smooth surface of the end product.
The low contact forces required for a clean silicone cast can be easily held by the wax. So if you need precisely shaped gaskets, anti-slip elements or other silicone products, 3D wax pressure is one of the best methods you can take. With the help of the mold halves, you are not limited to 1 piece. Carefully treated, you can make a small series of silicone products with a single wax mold. However, always make sure that the mold remains well cooled and therefore stiff.
What Printing Materials are Available for Wax 3D Printers?
For the normal user with a limited budget, conventional filaments are particularly suitable for wax printing. In addition to the filaments, there are also the wax-containing resins for SLA printing.
Liquid wax printers are much more economical and efficient, but the basic units cost a little more. Wax filament is up to 10 times more expensive than plastic filament. But it is also lighter. So you get more material on a roll.
There is a certain selection of wax colors. Since the final product is melted down again later anyway, a large selection of colors is rather irrelevant, as with plastic filaments. The smallest diameter of wax filaments is 1.75 mm.
Since the final product is melted down again later anyway, a large selection of colors is rather irrelevant, as with plastic filaments. The smallest diameter of wax filaments is 1.75 mm.
However, due to the material, it is not yet possible to produce thinner wax filaments. In addition to the 1 ¾ mm format, there are also particularly thick filaments with a diameter of 2.85 mm. However, you have to look at this relatively: Whatever is installed on the product first goes through a nozzle. There the wax is liquefied and converted into a thinner filament. The thickness of the filament therefore says nothing about the height of the individual layer with which your 3D model is built.
For Whom is a Wax 3D Printer Suitable?
There is hardly any useful application for a wax 3D printer other than metal casting. The casting cores made of wax are extremely sensitive and have only a very short lifetime.
Hobby printers who want to print out something from time to time are therefore not optimally advised to use a wax 3D printer. If you are interested in making jewelry out of metal, you can achieve outstanding results with a wax 3D printer. But you have to keep one thing in mind: metal casting with wax molds is always a “lost form process”. This means that the wax core is melted away from the hot metal and burnt.
If you are interested in making jewelry out of metal, you can achieve outstanding results with a wax 3D printer. But you have to keep one thing in mind: metal casting with wax molds is always a “lost form process”. This means that the wax core is melted away from the hot metal and burnt.
Ideally, however, you should melt the wax core out beforehand so that the metal can flow into the cavity undisturbed. If you want to cast several identical products, you need the appropriate number of cores.
It’s almost unfair what you can make with a wax 3D Printer! (source: formlabs)So before you spend a lot of money on a wax 3D printer, here’s what you can do: Make a plastic model and use it as a casting core for a separable plaster mold. Then use this plaster mold to make wax molds. You can now make as many of these as you want with your plaster mold. For simple forms this method is sufficient.
The special advantage of wax 3D printing, however, is that you can use it to produce extremely filigree casting molds. Especially the realization of inner cavities is not possible with the detour via a plastic casting core.
Especially the realization of inner cavities is not possible with the detour via a plastic casting core.
So you see: There are good reasons to add a wax 3D printer to your equipment. The results, especially if you have them as a successful metal casting, are very impressive.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Wax 3D Printer
You have the following advantages and disadvantages with a wax 3D printer:
Pro:
- Very filigree casting molds for impressive metal objects possible
- No “warping” during printing
- Environmentally friendly filament
- Detailed print
- Efficient use of print material
- No support material required
Contra:
- Expensive equipment
- Expensive filament
- Extremely fragile products with a limited life span
- Complicated handling
- Additional equipment may be required
Advantages in Detail
The manufacturability of filigree casting cores is certainly one of the biggest advantages of a wax 3D printer. The manufacturing process is known as “lost wax” offers the possibility to produce metal objects of any shape without the disadvantages of metal 3D printing.
The manufacturing process is known as “lost wax” offers the possibility to produce metal objects of any shape without the disadvantages of metal 3D printing.
As a primary molded casting, the metal objects are “monolithic”, i.e. made from a single casting. This makes them much more stable than the layered models from metal printing.
The flexible printing material produces practically no “warping” effect. This effect, which is particularly feared with plastic printing, has the consequence that the printed product deforms when the printing material cools down. The soft wax compensates the occurring tensions much better than the brittle plastic. With wax printing, you therefore always get what you want. Nasty surprises like “warping” are avoided with wax printing.
Wax printing does not produce problematic waste. You can also simply melt down the leftovers and make a candle out of them, for example.
Personalized 3D Printed Wax Candles. (source: 3dprintingindustry)The fine nozzles enable you to print wax with a particularly high level of detail.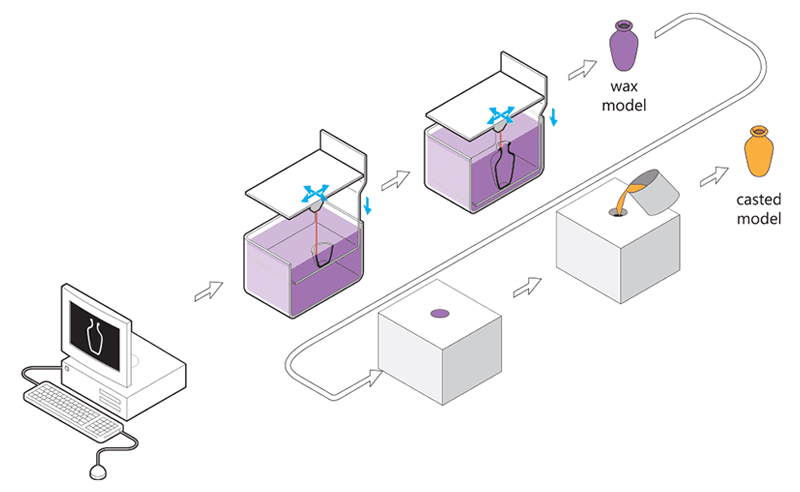 In this point the material is clearly superior to plastic. The nozzles also make optimum use of the filament so that you have practically no waste.
In this point the material is clearly superior to plastic. The nozzles also make optimum use of the filament so that you have practically no waste.
The lower density of the wax reduces the need for supports. The extremely light material has sufficient inherent stability during printing. This means that you can have even widely projecting details produced without additional support.
Related articles:
- Realize Complex Models with the Cura Tree Support
- Cura Support Blocker – How to Avoid Unnecessary Support
Disadvantages in Detail
Wax 3D printers are more expensive than normal plastic printers. Although the market and its prices are extremely dynamic, this is still the situation at the moment. The wax 3D printer is an oddity for which there is by far not as big a market as for the conventional 3D printers.
As with all other 3D printers, the market is strongly divided between consumer and professional devices. Interestingly, liquid printers for wax printing are available at a price of around 300 dollars. But in the professional sector, wax 3D printers quickly cost 10 to 100 times as much.
But in the professional sector, wax 3D printers quickly cost 10 to 100 times as much.
The filament is also almost 10 times more expensive than plastic. Although it is also lighter, so the usable length per kilogram is greater. However, this does not fully compensate for the higher price.
A particular disadvantage of wax 3D printing is the transience of its products. You have to keep the printed forms in the refrigerator to make them last a long time. But that’s not the point of 3D printing in the long run. So if you don’t want to use wax printing to make casting cores, this technology is not ideal for you.
The handling of filament, printer, products and the subsequent metal printing are very demanding. You need some experience to achieve really impressive results.
Finally, it may become necessary to upgrade your equipment for wax printing. Depending on the complexity and your demands on the results as well as the printers you use, you will need a lot of additional material to achieve the best possible quality. These include UV lamps, special heaters, cooling systems etc. However, the sensitivity and transience of the products is a constant problem.
These include UV lamps, special heaters, cooling systems etc. However, the sensitivity and transience of the products is a constant problem.
The Five Best Wax 3D Printers
It is comparatively difficult to really present a useful ranking for wax 3D printers. The market offers only very few models and these differ widely in price. Nevertheless, we would like to give you an overview of the five best wax 3D printers at the moment with this selection:
- Anycubic Photon*
- ELEGOO Mars UV 3D Printer*
- Sindoh 3DWOX DP200 3D Printer*
- Peopoly Phenom MSLA 3D Printer
- Solidscape S300
Budget Model for Beginners: Anycubic Photon
Anycubic Photon*The Anycubic Photon* is an SLA liquid printer. The model does not melt together dry filament but is building the object out of an immersion bath.
Like all SLA printers, AnyCubic Photon products have a very smooth surface. This saves a lot of rework. With a print size of 115 x 155 x 65 mm³, the print space is very limited. However, this space is sufficient for designing jewelry in the form of rings or bracelets.
But what makes the price-performance ratio a little less attractive is the meager equipment. Much of what you need for successful 3D printing is not included with this model.
Besides wax, you can also process resin with the Anycubic Photon. This gives you a solid 3D model that is temperature resistant.
Related article: Elegoo Mars vs. Anycubic Photon – Pro, Contra and Comparison
Anycubic Photon*Check Price at:
3DJake*
Amazon*
In the Same League as the Photon: ELEGOO Mars
ELEGOO Mars*The ELEGOO Mars* UV 3D printer is also an SLA printer. It is available at a similar price to the Anyubic Photon and has similar technical features. In handling it is slightly better than the cheaper model. In the test, it was noticed that the firmware can get a little confused during longer printouts. Basically, however, the ELEGOO Mars causes enthusiasm.
It is available at a similar price to the Anyubic Photon and has similar technical features. In handling it is slightly better than the cheaper model. In the test, it was noticed that the firmware can get a little confused during longer printouts. Basically, however, the ELEGOO Mars causes enthusiasm.
With both printers, it is noticeable that the formerly so expensive SLA technology is already available at very reasonable prices. Since it is clearly superior to the filament layer process in terms of surface quality, handling and material efficiency, this raises hopes for the general technological development in 3D printing.
ELEGOO Mars*Check Price at:
3DJake*
Amazon*
Affordable Large Format Printer: Sindoh 3DWOX DP200
CHECK PRICE*The higher price of the Sindoh 3DWOX DP200* is already justified by the fact that it offers a much larger installation space. At 210 x 200 x 195 mm, the printer offers 7 times the volume of the ELEGOO Mars or the Anycubic Photon.
At 210 x 200 x 195 mm, the printer offers 7 times the volume of the ELEGOO Mars or the Anycubic Photon.
This allows the production of very voluminous products. With its price, the Sindoh 3DWox DP200 is still in the budget of passionate hobby printers as well for semi-professional applications.
Overall, the printer is designed for easy operation, so that even laymen and beginners can quickly achieve good results.
CHECK PRICE*Check Price at:
Amazon*
Innovative Printing Process: Peopoly Phenom MSLA
Phenom by Peopoly (source: peopoly.net)The MSLA printing process is the evolution of traditional SLA printing. In case you didn’t know it yet: SLA printing was the beginning of 3D printing in the early 1990’s.
The difference between MSLA and SLA is that the former allows the resin or wax to cure layer by layer rather than point by point. This makes the printer not only faster but also more precise. The Peopoly Phenom MSLA 3D printer is the first of its kind to offer this technology at a very moderate price. This makes precise 3D printing with wax much more efficient.
The Peopoly Phenom MSLA 3D printer is the first of its kind to offer this technology at a very moderate price. This makes precise 3D printing with wax much more efficient.
The Phenom is thus on the threshold between semi-professional and industrial applications for wax 3D printing. The installation space is similar in size to the Sindoh 3DWOX DP200. This makes it particularly suitable for large products, quick printing of small molds or efficient multiple printing.
Phenom by Peopoly (source: peopoly.net)Check Price at:
Peopoly
High-End Wax Printing in 3D: Solidscape S300
The topic of this article is “The best 3D printers for wax”. That’s why we would like to introduce you to a device that is currently at the technological forefront. With its price, the Soldiscape S300 is definitely out of the budget of normal and semi-professional users.
With its price, the Soldiscape S300 is definitely out of the budget of normal and semi-professional users.
It is definitely a pure industrial device, which can provide excellent performance and corresponding turnover in prototyping, rapid forming or as a contract device. The Solidscape S300 is specifically promoted by the manufacturer as a wax printer for jewelry design. But in principle it is equally suitable for all other applications where wax models are required.
Check Price at:
solidscape
The Four Best Wax Filaments
If you would like to try the lost wax technique, we can recommend the following printing materials:
- MOLDLAY*
- MakerJuice WaxCast resin*
- Formlabs Castable Wax
- Print2Cast
Standard Wax for Metal Casting: Moldlay
CHECK PRICE*Moldlay wax filament* for 3D printing is the most widely used material for the lost wax process. It is also very suitable for making wax molds for silicone printing.
It is also very suitable for making wax molds for silicone printing.
Moldlay offers excellent and consistent quality from Germany. A particular advantage of Moldlay is that it makes practically no demands on the pressure equipment. The manufacturer states that the filament can be used on all 3D printers.
However, we would like to confirm this only under caution. For many devices, at least an adjustment of hardware and software will be necessary in order to process wax filament as reliably as plastic.
The Moldlay filament is available in the standard diameters of 1.75 mm and 2.85 mm. The material has a printing temperature between 170 °C and 180 °C. In principle, printing is also possible without an additional heating plate.
Like all wax filaments, Moldlay offers low warping with maximum stiffness and dimensional stability. The high wax content ensures that practically no residues are left in the mold during burn-out. However, rinsing with isopropyl alcohol is always recommended.
Check Price at:
Amazon*
Low Priced but High Quality: MakerJuice WaxCast Resin
CHECK PRICE*MakerJuice WaxCast resin* is an inexpensive printing resin for SLA printing with wax-like properties. It can be cured under UV light and is then very stable.
The manufacturer states that the wax is also suitable for demanding applications such as dentures. Furthermore, the MakerJuice WaxCast resin is also unreservedly recommended for all other applications:
- Jewelry production
- Prototype construction
- Technical models
Since SLA printers are becoming increasingly cheaper, the use of wax-resin, for example the MakerJuice WaxCast resin, can be a real alternative to filament printing, at least for small products.
In terms of surface quality, the SLA print is clearly superior. This is also reflected in the printing result.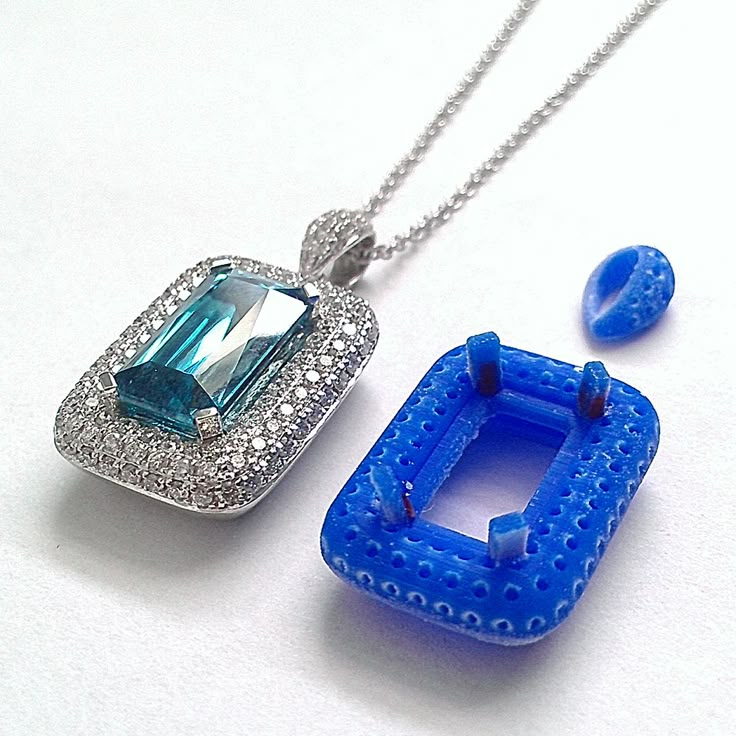 With untreated filament printing, the ugly stairs inevitably continue into the cast product. This is successfully avoided by using MakerJuice WaxCast resin and an SLA printer.
With untreated filament printing, the ugly stairs inevitably continue into the cast product. This is successfully avoided by using MakerJuice WaxCast resin and an SLA printer.
Check Price at:
Amazon*
Expensive but Efficient: Formlabs Castable Wax
Formlabs Castable Wax (source: formlabs)Formlabs Castable Wax is almost 6 times more expensive than the product from MakerJuice. This enormous price difference has its reason. The Formlabs Wax is optimized for use on the very expensive SLA printers from Formlabs*.
Its biggest advantage is that it enables very fast printing. In addition, the material is suitable for pronounced investment casting applications. This excellent material is particularly suitable for technical models where precision in internal cavities is required.
Formlabs Castable Wax (source: formlabs)Check Price at:
formlabs
Low-Priced Starter Wax Filament: Print2Cast
Print2Cast Filament (source: machinablewax)The Print2Cast wax filament surprises with a very reasonable price.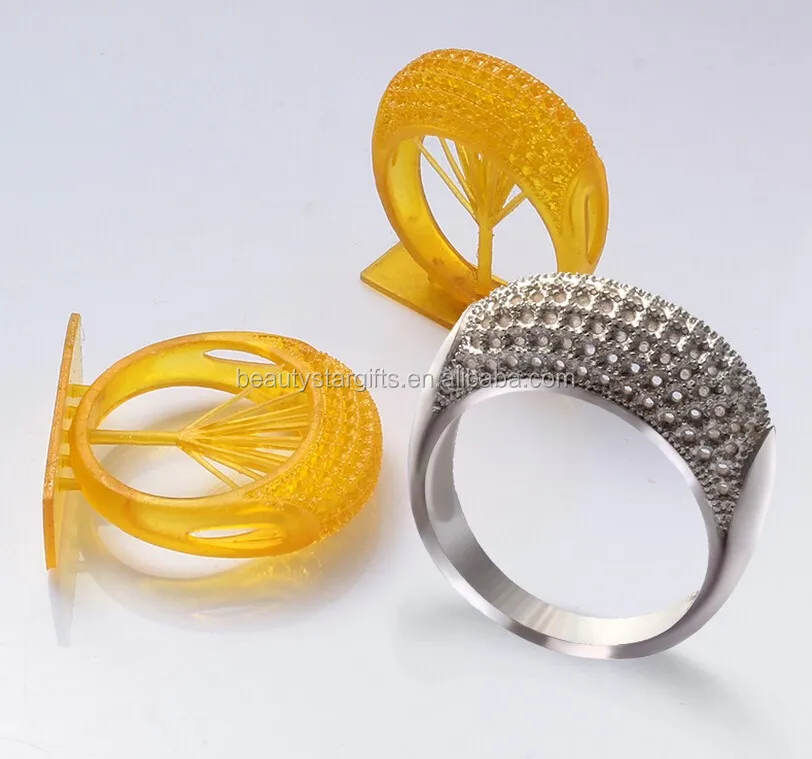
However, the low price is accompanied by certain reductions in quality. For beginners who want to take their first steps in the lost wax process, Print2Cast is completely sufficient. Enthusiastic hobby users, however, will quickly notice the difference to the somewhat more expensive Modlay.
Print2Cast Filament (source: machinablewax)Check Price at:
machinablewax
What Else You Need for Wax 3D Printing
Printing with wax practically always means that a lost wax process follows. Wax-based 3D printing is ideal for this purpose, but it is not suitable for any other typical 3D printing application. For good results, you’ll need the following add-ons and devices:
- UV light for curing
- Refrigerator for storage
- Molding material for lost wax (plaster, molding sand…)
- Cold- or hotboxes for sand casting
- Melting furnaces
- Equipment for metal casting (melting furnace, crucibles, protective equipment…)
Even if the wax theoretically melts or burns away immediately when the liquid metal is poured in, you will get better results with the previous melting out.
The metal simply flows more freely, which is very important in the casting process. If you want to cast your metal object in solid molds, for example hardened plaster, you have to clean the cavity beforehand. Isopropyl alcohol is suitable for this. You have to also make sure that the plaster mold is completely dry. Residual moisture in the mold will evaporate immediately due to the hot metal and form cracks.
However, these are just a few tips to keep in mind when pouring metal into pre-printed 3D molds. So please read the topic thoroughly before you start this beautiful but also dangerous hobby.
Conclusion
If you have prepared yourself sufficiently for the safe handling of liquid metal, today, with the available printers and materials, an inexpensive way for good results is open to you. For a start, you can convert your existing printer for processing wax filament.
Then with Moldlay* you already have good materials for first test prints.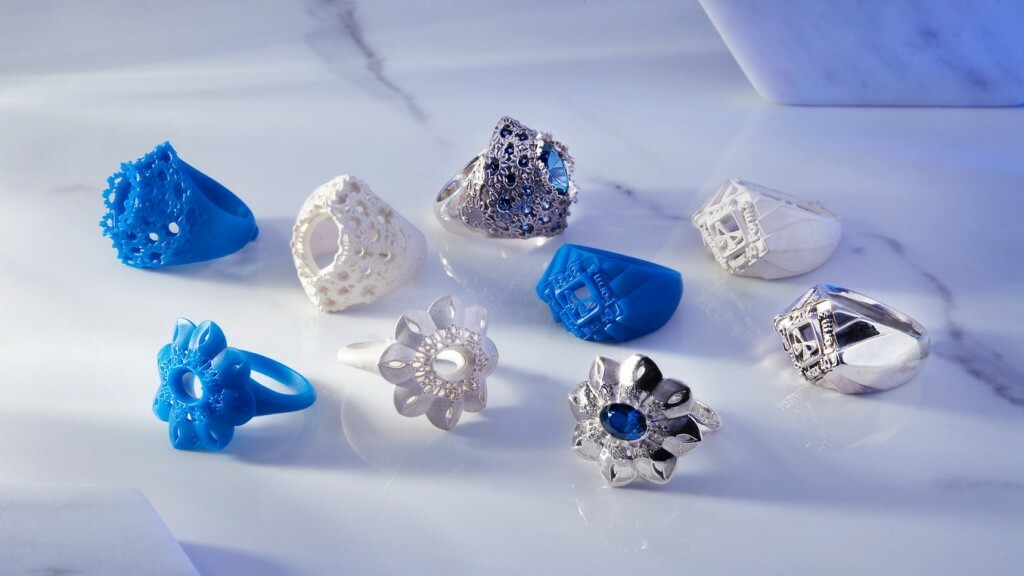 But if you want to produce really beautiful jewelry or precise investment castings, the SLA printers are simply better. The Peopoly Phenom MSLA offers you a very interesting combination of smooth surface, large installation space and innovative printing processes.
But if you want to produce really beautiful jewelry or precise investment castings, the SLA printers are simply better. The Peopoly Phenom MSLA offers you a very interesting combination of smooth surface, large installation space and innovative printing processes.
As a recommendation, we would therefore like to recommend this printer and Formlabs Castable Wax. This is quite expensive, but you don’t need a UV cabinet for it and you will get your results quickly.
Disclosure: This website is the property of Martin Lütkemeyer and is operated by Martin Lütkemeyer. Martin Lütkemeyer is a member of the Amazon Services LLC and other Affiliate Programs. These are affiliate advertising programs designed to enable websites to earn advertising revenue through advertising and linking to Amazon.com and others. Links marked with * are affiliate links.
3D wax printing: advantages, features, equipment
Basics of 3D
Casting
Jewelry industry
3D printers
Author: Viktor Naumov
Author: Viktor Naumov
Wax 3D printing vs traditional technologies | Wax 3D printers: advantages, disadvantages, applications | Wax 3D Printing Technology | FlashForge WaxJet: large-format machines for creating high-precision models | Order a consultation and printing services
Wax is an environmentally friendly, non-contact, soluble material commonly used in the manufacture of investment casting products. A casting mold is removed from the investment model, into which molten metal is then poured and the final product is obtained.
A casting mold is removed from the investment model, into which molten metal is then poured and the final product is obtained.
Wax 3D printing vs traditional technology
For traditional casting, as well as for other classical technologies, the advent of 3D printing was a turning point: additive methods immeasurably expanded the possibilities of production, making it possible to significantly optimize the technological cycle in enterprises of various industries.
Wax, characterized by good meltability (at temperatures above 60°C) and requiring simple post-processing, has become one of the most affordable and popular materials used in 3D printing. Today, even in a typical office or laboratory setting, you can install an additive machine and print high-quality wax models that closely match CAD models around the clock.
Thanks to the high performance of 3D wax printers, an enterprise can reduce the time it takes to make prototypes by several times, and sometimes even dozens of times, and, accordingly, reduce production costs. Models printed from wax are distinguished by high precision, perfectly even and smooth surfaces, as well as the finest detail, which makes it possible to create products of complex shapes and textures that cannot be made using traditional technologies.
How to make a casting mold in a week? Read the history behind wax and photopolymer 3D printed gas valve models.
Wax 3D Printers: Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications
Pluses
- High print speed.
- High level of detail for the production of geometrically complex products (printed layer thickness up to 16 microns).
- Ability to simultaneously manufacture parts of different configurations on the same platform.
- Perfect model accuracy (up to 0.
 1016 mm per 25.4 mm part size).
1016 mm per 25.4 mm part size). - Convenience and ease of use.
- Possibility of continuous operation.
Cons
-
Fragile and vulnerable to sunlight models.
-
Primarily functional prototyping.
-
High cost of consumables.
Wax models on the FlashForge WaxJet 400 build platform
Where is 3D wax printing used?
Wax 3D printing is used to create functional prototypes, tooling molds, and investment casting master patterns in areas such as jewelry, manufacturing, consumer goods, automotive, aviation, and medicine.
In particular, wax 3D printers are used to create:
- industrial components for the automotive and aerospace industries, mechanical engineering and instrumentation;
- items of jewelry and watch industry;
- prostheses and other medical devices;
- art objects, souvenirs.

Order a 3D test print of your product for free! Other services available - find out more and apply online:
Order service
Wax 3D printing technology
Wax 3D printers use multi-jet printing (MJP) technology. One of the features of this method is that the protruding parts of the product require supporting structures - they are easily removed at the end of the printing process or dissolve themselves.
When comparing wax and photopolymer, the latter wins in terms of the quality of the printed model, strength and cost, however, in terms of the quality of the final molded product, the advantage is definitely on the side of the wax.
MJP technology works in much the same way as conventional inkjet printing. The layer is applied by a print head with a large number of tiny nozzles through which the model material is fed onto a horizontal platform.
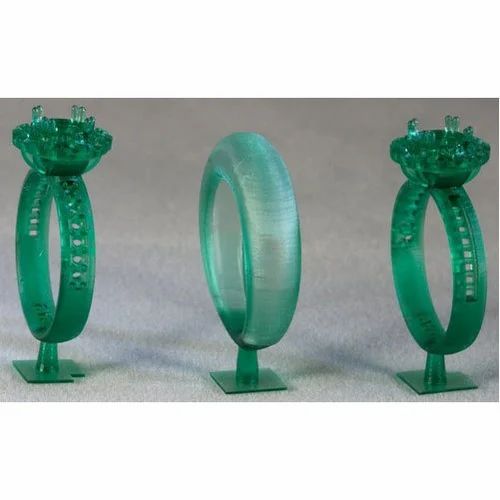
3D printed wax models and finished jewelry
Steps of the wax printing process
- The material is melted in a heated cartridge.

- The printhead applies wax to the build platform at the desired location.
- The build platform is lowered in the chamber by the thickness of the layer, and the process of applying the material is repeated layer by layer until the model is completely built.
- Wax solidifies immediately upon contact with the build platform.
- Models are removed from the build platform.
- Supports are removed with a special solution.
- The model is drying.
When printing with wax, two types of materials are used:
- harder (melting at about 70°C) - model wax for product printing;
- is softer or fusible - for creating supports.
Read on our blog: 3 Case Studies of Additive Manufacturing in Investment Casting
FlashForge WaxJet: Large Format Machines for Precision Modeling
Introducing professional MJP printers from the Chinese manufacturer FlashForge WaxJet 400 and 410.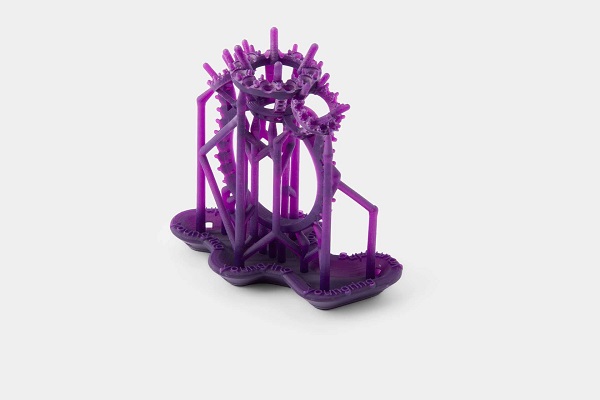 This is a line of large-format machines for printing high-precision and extremely smooth waxes up to 289 x 218 x 150 mm in size. The inclusion of WaxJet in the process will reduce production costs by 20-30% compared to a traditional casting cycle and create products 2.5 times faster than with classical methods.
This is a line of large-format machines for printing high-precision and extremely smooth waxes up to 289 x 218 x 150 mm in size. The inclusion of WaxJet in the process will reduce production costs by 20-30% compared to a traditional casting cycle and create products 2.5 times faster than with classical methods.
Benefits of the WaxJet 400 and 410
printers- Increased productivity: print up to 180 (WaxJet 410) or 360 (WaxJet 400) items per day.
- High resolution 1200 x 1200 x 1600 dpi and a layer thickness of only 16 microns.
- An ideal choice for printing jewelry, industrial tools, watches and souvenirs, as well as investment casting in aviation.
- Automatic material loading system.
- Stable material supply due to the immobility of the main print module with a movable build platform.
- An enclosed build chamber that isolates the printing process from external influences such as dust, microscopic debris, or excessive moisture.

- Compatible with two kinds of materials: 100% purple wax and white support wax material.
- Easy management and maintenance of 3D printers.
Read our review of WaxJet wax printers
WaxJet 400 3D printer example: impeller
Print time: 4 hours 38 minutes
Wax Model Weight: 7.18g
Application: For In713c
Alloy Turbine Casting Benefits compared to the traditional process: 80% faster time to market, 45% less labor
So, wax 3D printing will allow your business to achieve better efficiency by saving time and money on designing and manufacturing prototypes and master models for casting.
Are you convinced by the benefits of wax 3D printing?
Learn more about implementing 3D technologies, get detailed advice, order a demonstration of equipment or 3D printing services you can contact iQB Technologies : we have been successfully implementing 3D solutions for industry and business since 2006. Contact us: +7 (495) 223-02-06, [email protected] .
Contact us: +7 (495) 223-02-06, [email protected] .
Article published on 05/19/2022, updated on 09/23/2022
3D printing with wax on an FDM 3D printer. Recommendations and settings on the example of 3D printer PICASO Designer X.
- 1. First, a little history of
- 2. What is Filamentarno Wax Base?
- 3. Which printer is suitable for printing?
- 4. Why is Picaso Designer X good for Wax Base printing?
- 5. Preparing Picaso Designer X before printing Wax Base
- 6. Printing process
- 7. Result and output
Hello friends, 3DTool is with you!
Investment casting is a fairly popular method of manufacturing metal products. Most of the jewelry is produced in this way, this method is used to create parts of mechanisms, cases and other elements and assemblies that require increased strength. The starting point in the casting process is the original model or ready-made matrix, from which a copy is made from wax or other easily melted material to create shell molds into which the metal is already poured. But what if we bypass the initial model creation phase and make an immediately meltable wax model? This is where 3D printing and new material from 9 come to the rescue.0215 Filamentarno - Wax Base .
But what if we bypass the initial model creation phase and make an immediately meltable wax model? This is where 3D printing and new material from 9 come to the rescue.0215 Filamentarno - Wax Base .
1. A little history first
The idea of printing wax on a 3D printer is far from new, initially, the technology appeared in the camp of photopolymer 3D printers, was used, and is still used today, for example, by such giants as 3D Systems and Solidscape . Entire lines of devices have been honed to produce high-precision lost wax printouts with a perfect surface. However, such printers had and still have one tangible disadvantage - what if the desired object is much larger than the size of the working area of the device, and the quality of the surface, in general, does not matter much within reasonable limits? The first thing that comes to mind is to find a device with a larger working area, however, among the photopolymer printers, there are negligible models that meet this requirement and, basically, they are sharpened precisely for high quality and miniaturization. Or too expensive to maintain. What to do? But what if you use FDM for these purposes?
Or too expensive to maintain. What to do? But what if you use FDM for these purposes?
Photo from open sources, site sapr.ru
The first experiments with FDM 3D-printed/lost-waxed models used PLA and PMMA, the relatively low ash content of which, in theory, promised to achieve good casting quality, and some enthusiasts actually achieved quite good results. Instead of smelting, however, the technique of burning the material was used. However, widespread practice has shown too high a dependence of the result on the quality of the material, the presence or absence of a dye, the correct temperature regime and a strong limitation on the equipment and materials forming the shell form, not all of which withstand subsequent annealing and do not burst. Moreover, the crust-forming compound is able to transfer even the smallest defects and artifacts on the surface and any spills, cavities and flaws immediately appear on the final result. And avoiding the formation of unwanted gases when burning PLA is very difficult.
Photo from open sources, site sapr.ru
And if large-format casting in industrial, factory conditions allows the use of PLA and PMMA, due to the complication of production technology (there is a wide practice of using such giants of the world of FDM printers as BigRep for these purposes), then medium-sized workshops and small studios equipped with conventional boilerclaves require more flexible approach. And it is in this case that the Wax Base is perfect for them.
2. What is Filamentarno Wax Base?
Filamentarno WAX Base is a filament for 3D printing using FDM technology for subsequent investment casting from metals, the bulk of which is real jewelry wax. Of course, the composition contains other impurities to stabilize the rod and meet its characteristics in accordance with the requirements of fdm 3d printing, however, the final result is fully compatible with any melting techniques of conventional wax compositions and is easily glued to them, for example, to form sprues.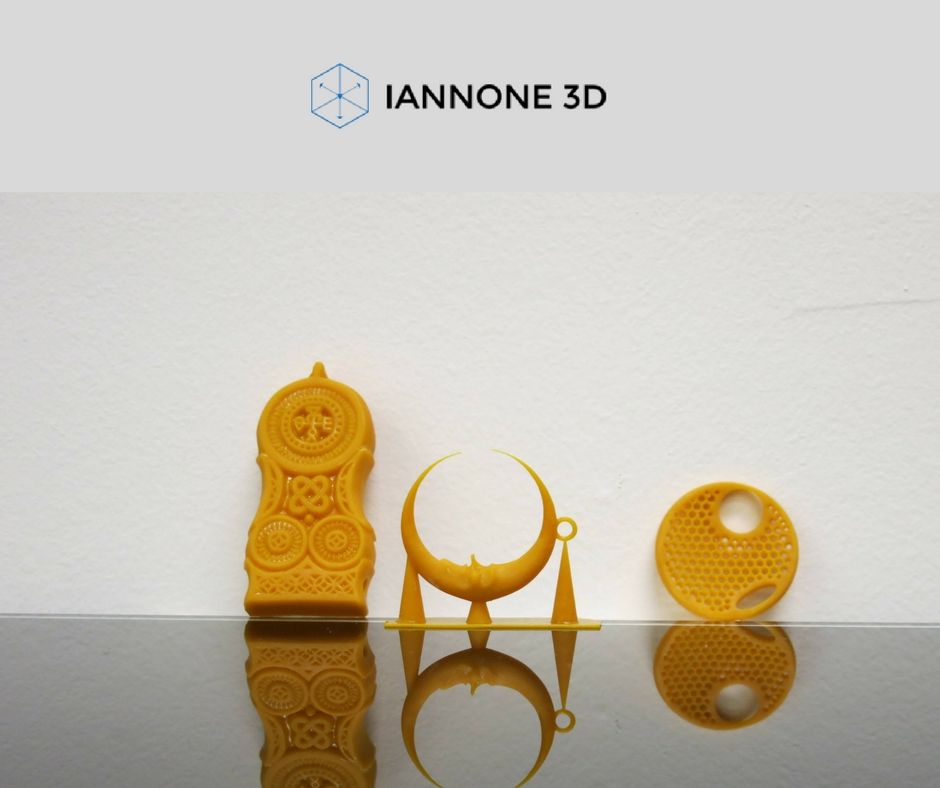
The company F ilamentarno took a long time to produce this material, the idea appeared a relatively long time ago, but the results were achieved only in the last couple of years, nevertheless, the sensation was such that the company even had to open a small 3D printing studio in order to gain experience applications and respond to the market demand since there were no analogues to this material before.
The material turned out to be promising, among its advantages there is a sharp increase in the maximum possible size of wax waxes, and printing speed, as well as the ability to greatly reduce costs, because the cost of melted wax in the form of a thread turned out to be much more profitable than photopolymer, not to mention the price of photopolymer 3D printers.
This material also has certain features that can hardly be called obvious disadvantages, but they impose strict requirements on the device on which it is planned to print.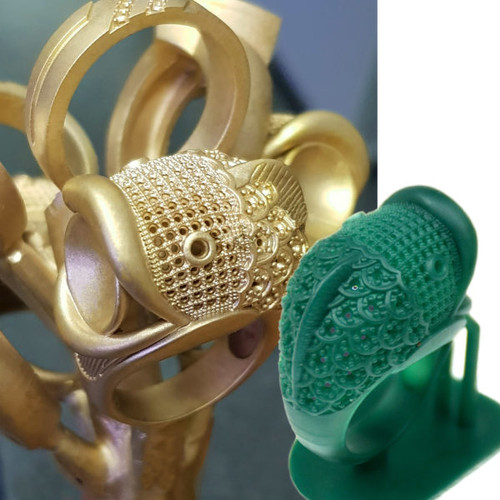 More about them below.
More about them below.
3. Which printer is suitable for printing?
Due to the physical characteristics of the raw material, Filamentarno Wax Base is printed at significantly lower temperatures than other materials. Softening occurs already at ~ 45 degrees, and melting, from ~ 95 degrees Celsius. Because of this, it can be easily smoothed out in post-processing using hot air guns, torches or soldering stations. The recommended print range is from 110 to 130 degrees, while most standard 3D printers do not allow the extruder temperature to drop below 190, less often 170 degrees Celsius, which is excessive in the case of Wax base .
Owners of simpler and cheaper models of 3D printers, as a rule, have the opportunity to correct the corresponding parameters in the printer's hardware firmware, or lower the temperature using special control commands. Meanwhile, expensive brands usually do not provide such opportunities and completely close both the firmware and the “console” commands from users from changes. Here is what the manufacturer writes on its website in the description of the material in this case:
Here is what the manufacturer writes on its website in the description of the material in this case:
“Most often printing on a 3D printer with a nozzle temperature below 170°C is prohibited by the printer firmware. To bypass this limitation, use the G-Code command: "M302 S80" - it can be inserted into the starting G-Code in the slicer settings. This command will lower the print temperature limit to 80°C."
Also, since the material is quite easily torn, soft and melts easily even at low Cold End heating temperatures, you will need to use a direct extruder drive (Direct) for printing, a remote (Bowden) broaching mechanism will not cope with the task and, at best, will “jam » material.
Nevertheless, at least one manufacturing company that took care of printing with low-temperature materials “out of the box” and has printing units equipped with direct drive, we can definitely name. Of course, we are talking about the manufacturer of 3D printers Picaso3D and line of 3D printers Designer Series X .
Let's take a look at the benefits of the Series X line for wax printing using the Picaso 3D Designer X as an example .
4. How good is Picaso Designer X for Wax Base printing?
In addition to the ability to set extremely low extruder temperatures for FDM 3D printing in material profiles, the Series X platform has a number of additional features that make working with the Wax Base easier.
First of all, it is the adjustable temperature of the cold zone (thermal barrier) of the printing unit. It has another temperature sensor that allows you to monitor and adjust peak performance by increasing and decreasing the cooling cooler speed.
This feature prevents the formation of plugs in the extruder tube above the melt zone. The special structure of the receiving "neck" in the pulling mechanism also plays into the hands, which eliminates the bending of the material during filling and printing.
In addition, the system of active “purging” of the working area, thanks to several turbine fans, allows you to quickly cool the material during printing, which also has a positive effect on the quality of the surface when printing roundings and overhanging elements.
And sensors for the presence of filament and control of the upper layer will help prevent damage to many hours of printing in the event of a break or end of the thread.
5. Preparing Picaso Designer X for printing Wax Base
To confidently print Wax Base on your device, you need to stock up on a clean, preferably new, extruder block with a new or carefully cleaned copper nozzle with a diameter of at least 0.4mm. In our case, the most suitable in the Picaso Designer X line is the 0.5 nozzle.
It is also necessary to take into account the following nuances:
-
A rubber scraper is installed on Picaso 3D printers to clean the PG - when printing WAX, it smears the material and harms rather than benefits, it must be removed.

-
For normal adhesion, the heating table on the first layer must be heated to 85-90 degrees, subsequent layers must be set to 0-30 degrees so as not to deform the wax. To do this, you need to have two different material profiles.
-
Airflow - required when printing overhanging elements, the main thing is not to overdo it, otherwise the layers will not bake well.
-
Wax, like many elastomers, does not like retracts, this parameter must be set to 0.
-
Refilling plastic takes place in two stages. The first is refueling at an elevated temperature of 190-200 degrees, to eliminate a possible wax plug. The second stage is filling at the extrusion temperature - 110-130C
-
It must be remembered that plastic is very sensitive to extrusion temperature, too high clogs the nozzle, too low gives poor interlayer adhesion. The optimum temperature for picaso designer x is 115 degrees for the first layer, 120-125 degrees for subsequent ones.

-
Periodically, it is necessary to check whether the plastic thread wound on the spool does not stick to itself, this can cause material slippage, because. it pulls out easily.
-
It is very important to correctly set the height of the nozzle above the table, because if the nozzle is pinched, a plug will quickly form in the extruder, which can be eliminated only by refilling the plastic again.
Before printing for the first time, be sure to replace the entire hot end or nozzle with a new / clean one, otherwise the desired result will not be achieved.
When preparing a 3D model for printing at Polygon X , you must adhere to the following rules, try not to make the outer wall very thin, the material may burst. The ideal option is 2 perimeters, approximately 1.2 mm, with a nozzle of 0.5
Percentage of filling, not less than 15%, if the geometry of the model allows.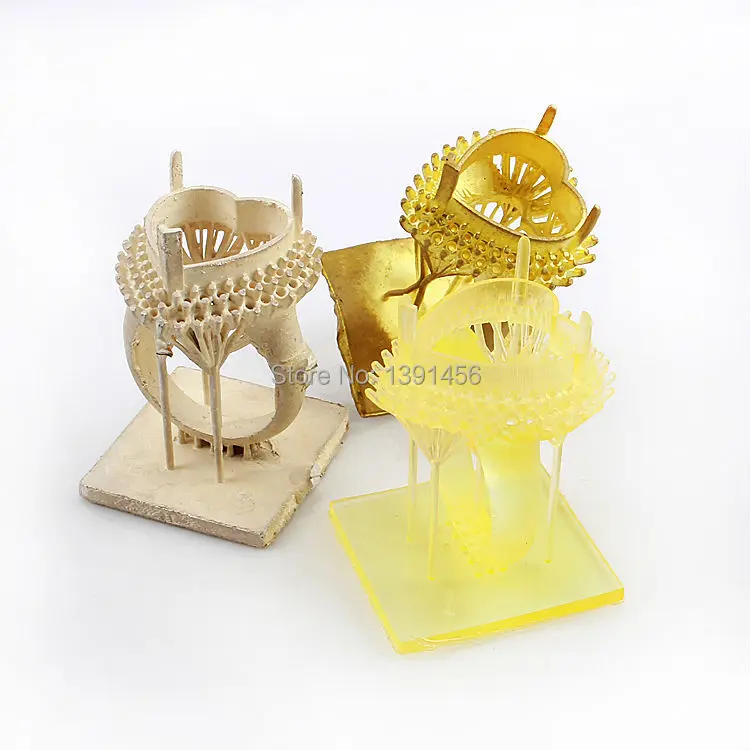
Otherwise, the requirements for the material are the same as for conventional plastics. It should be noted that the supports come off very easily and, if necessary, the attachment point can be treated with a burner or a building hair dryer in order to achieve a smooth surface.
We printed the current models at the following settings (pictured above).
It remains to create two print profiles for printing the first and subsequent layers, send them to the printer and wait for the print results.
6. 3D printing process
Before printing, be sure to thoroughly rinse the glass stage bed and apply fresh adhesive to it. In our case, a regular spray is suitable - glue from PICASO 3D , however, the manufacturer also offers a proprietary adhesive:
Next, you need to prepare two print profiles according to the following settings, experimentally they showed the best result when printing.
Wax3D_F - profile for subsequent layers, Wax3D(1Layer) for the first.
When rendering the model, be sure to manually set a pause after the second layer in order to have time to switch print profiles.
If you have previously printed with wax on the current printer, you need to start another profile with a higher temperature and load the material only after the old material has “melted through”.
Leaving material in the nozzle at high temperatures is not recommended. This is fraught with traffic jams.
7. Result and conclusion
When printing, we encountered several times the delamination and peeling off of the material from the heating table during the printing process and the selection of parameters.
As you can see in the photo, the material diverges in layers and it may feel that the temperature is insufficient for sintering. However, this is not the case, because when the temperature rises, the material does not extrude, but flows out of the die, which disrupts the layer structure, and the wax does not have time to cool. The difference is clearly visible in the photo below, on the left the temperature is too high.
However, this is not the case, because when the temperature rises, the material does not extrude, but flows out of the die, which disrupts the layer structure, and the wax does not have time to cool. The difference is clearly visible in the photo below, on the left the temperature is too high.
However, after several reprints, we managed to achieve good print quality. Both with and without support.
The material withstands rather steep angles of inclination "perfectly", as can be seen from this flange in the photo.
The artistic approach is not alien to the material, we printed the head of this character for about a day and, as you can see, the result is excellent.
In general, when printing products with low detail, it is best to select a slow (quality profile) or medium (standard profile) print speed setting so that the material has time to properly form and cool during extrusion. Otherwise, sagging "pulling" of the thread may form.