3D printing online india
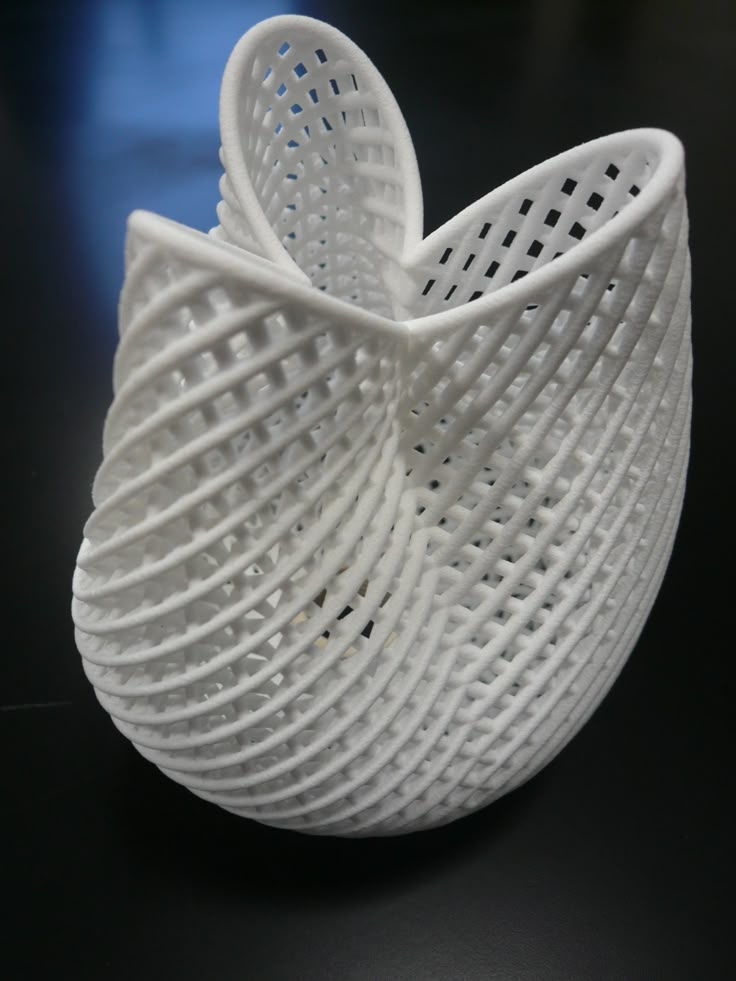
Online Jewellery 3D Printing Service
LEARN MORE
1. What is Jewellery 3D Printing Service?
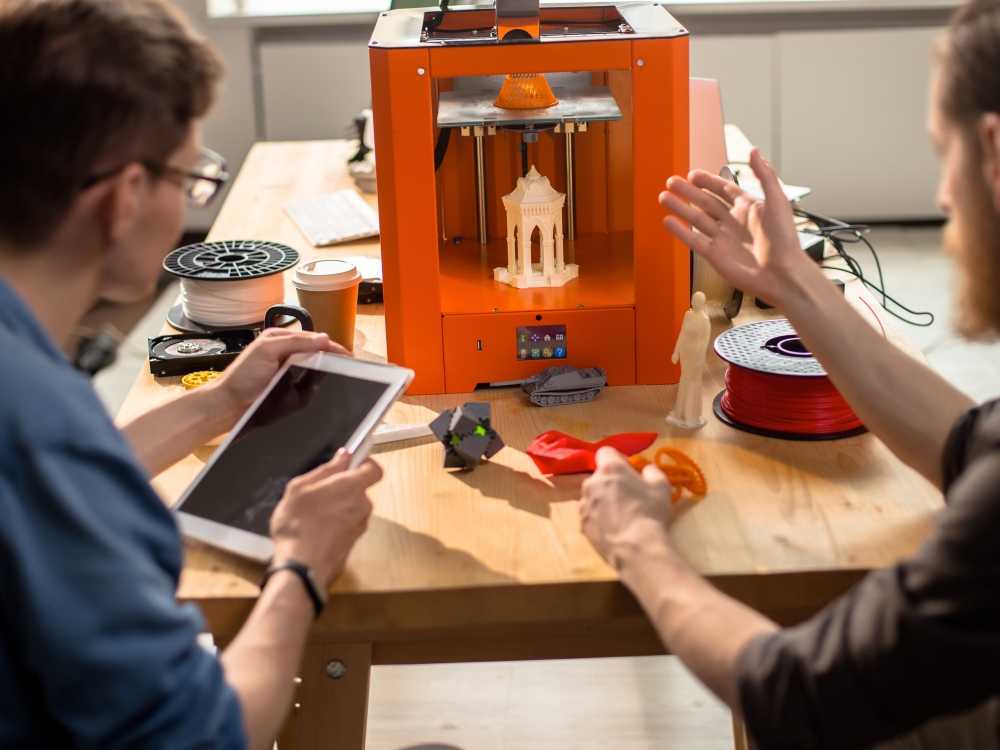
Jewellery 3D Printing Service allows you to fabricate various kinds of jewellery models within a matter of a few hours. The outputs are non-toxic, ready for hand-modeling, and extremely accurate.
2. Why should you opt for Jewellery 3D Printing Service?
Jewellery 3D Printing Service allows jewellery desginers, and jewellery shop owners to make realistic prototypes that can be cast or produced for end-usage. This method is faster, cheaper, and more accurate.
3. What is Digital Jeweller?
When you 3D print jewellery models using online services such as Makenica then you become a digital jeweller instead of a traditional jeweller who use traditional casting methods for jewellery making.
4. What is Digital Jewellery?
Digital Jewellery is the scientific name when using additive manufacturing services for jewellery and fashion applications. These services include SLA, DLP, among many others.
5. How does Digital Jewellery or Online Jewellery 3D Printing works?
Once the CAD/CAM design is completed, you can share the designs with us or upload it here. Once we receive the design, we start production as per your requirements. Apart from that, in order to produce end parts, here are a few steps that will help:
Step 1: Prototyping (using jewellery 3d printing services like Makenica.com)
Multiple iterations of a design are 3D printed with standard resin.
Step 2: Fitting & Customer Feedback
3D printed models are used for fitting and gathering customer's feedback.
Step 3: Investment pattern
Castable resin is used to 3D print an investment pattern of the final design.
Step 4: Casting (can be done using traditional method or jewellery 3d printing services)
The pattern is used to make a mold for the target material.
6. What are the Jewellery 3D Printing Service tolerances?
Here are some of the Jewellery 3D Printing Services tolerances:
| Distance Dimensions | +/- 25 microns accuracy on either side is typical. |
| Shrink Mitigation | A shrinkage rate of +/-0.15% can be expected due to the thermal expansion of the liquid, and the response of the flexible mold. |
| Surface Quality | The surface finish is externally smoothed to a glossy, satin, or matte surface. |
| Feature Definition | Extreme sharp corners and small text may appear slightly rounded. |
| Size Recommendation | Parts can be as large as 500mm on any one side. |
7. What is the minimum order quantity for Jewellery 3D Printing Services?
There is no minimum order quantity for ordering online. Although you can get cost benefits when you order in larger quantities.
8. What are the size limitations for Jewellery Casting Service?
| Maximal part size | 500 mm (40in) |
| Minimal part size | 0.1 mm (100 microns) |
| Minimal diameter | 0.1 mm (100 microns) |
9. What is the assurance on the output quality of the 3D Printed Jewellery Parts?
What is the assurance on the output quality of the 3D Printed Jewellery Parts?
Every Jewellery 3D Printing service order includes our standard inspection file that includes reports and certifications such as:
- Critical dimensions
- Quantity of parts
- Removal of sharp edges and burrs
- Number of parts inspected
- Surface finish
- Threads and tolerances
- Full dimensional inspection report
- Resin material test report
- ISO9001, ISO14001, ISO27001, and IATF 16949 certifications
10. Which cities do we provide Jewellery 3D Printed Services or 3D Dental Dentistry Services in?
Makenica provides Jewellery 3d printing services in all tier-1,2 & 3 cities.
TIER-1 CITIES:
Bangalore
Chennai
Delhi
Hyderabad
Kolkata
Mumbai
Ahmedabad
Pune
TIER-2 CITIES:
Agra
Ajmer
Aligarh
Amravati
Amritsar
Asansol
Aurangabad
Bareilly
Belgaum
Bhavnagar
Bhiwandi
Bhopal
Bhubaneswar
Bikaner
Bilaspur
Bokaro Steel City
Chandigarh
Coimbatore
Cuttack
Dehradun
Dhanbad
Bhilai
Durgapur
Erode
Faridabad
Firozabad
Ghaziabad
Gorakhpur
Gulbarga
Guntur
Gwalior
Gurgaon
Guwahati
Hamirpur
Hubli–Dharwad
Indore
Jabalpur
Jaipur
Jalandhar
Jammu
Jamnagar
Jamshedpur
Jhansi
Jodhpur
Kakinada
Kannur
Kanpur
Kochi
Kolhapur
Kollam
Kozhikode
Kurnool
Ludhiana
Lucknow
Madurai
Malappuram
Mathura
Goa
Mangalore
Meerut
Moradabad
Mysore
Nagpur
Nanded
Nashik
Nellore
Noida
Patna
Pondicherry
Purulia Prayagraj
Raipur
Rajkot
Rajahmundry
Ranchi
Rourkela
Salem
Sangli
Shimla
Siliguri
Solapur
Srinagar
Surat
Thiruvananthapuram
Thrissur
Tiruchirappalli
Tiruppur
Ujjain
Bijapur
Vadodara
Varanasi
Vasai-Virar City
Vijayawada
Visakhapatnam
Vellore
Warangal
3D Printing Services in Bangalore
1. What is 3D printing and how does it work?
What is 3D printing and how does it work?
3D printing Bangalore is the process of creating a three-dimensional, physical object from a digital model. 3D printing service is sometimes referred to as “additive manufacturing,” although this term is used more frequently within the manufacturing industry to describe online 3D printing’s role in the industrial process.
3D printing in Bangalore begins with a 3D CAD model that is sliced into fine layers. The software turns these layers into instructions for your 3D printer, which deposits material layer by layer until the model is replicated. Excess material is removed post-process, leaving the user with a complete physical object. The software and materials that are used vary depending on the user’s intended application for the product.
2. What materials can be used in 3d printing?
Below are the materials used for 3D Printing in Bangalore:
ABS
ABS is a low-cost material, great for printing tough and durable parts that can withstand high temperatures while 3D Printing online.
Flexible
Flexible filaments, commonly referred to as TPE or TPU, are known for their elasticity allowing the material to easily stretch and bend for 3D Printing in Bangalore.
PLA
PLA is the go-to material for most users due to its ease-of-use, dimensional accuracy, and low cost.
HIPS
HIPS is a lightweight material most commonly used as a dissolvable support structure for ABS models in online 3D Printing India.
PETG
PET and PETG filaments are known for their ease of printability, smooth surface finish, and water resistance.
Nylon
Nylon is a tough and semi-flexible material that offers high impact and abrasion resistance. It is an ideal choice for printing durable parts.
Carbon Fiber Filled
Carbon fiber filaments contain short fibers that are infused into a PLA or ABS base material to help increase strength and stiffness.
ASA
ASA is a common alternative to ABS and is great for outdoor applications due to its high UV, temperature, and impact resistance for 3D Printing in India.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is known for its strength and durability. It has very high heat and impact resistance making it an ideal choice for tough environments.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene is great for high-cycle, low strength applications due to its fatigue resistance, semi-flexible, and lightweight characteristics.
Metal Filled
Metal filled filaments are made by mixing a fine metal powder into a base material, providing a unique metallic finish, and added weight.
Wood Filled
Wood filaments combine a PLA base material with cork, wood dust, or other derivatives, giving the models a real wooden look and feel.
PVA
PVA is commonly known for its ability to be dissolved in water and is often used as a support material for complex prints in 3D Printing Bangalore.
3. Is 3D printing the future?
In short, Yes. 3D printing in Bangalore provides the design freedom to experiment with more effective and efficient part shapes, with fewer potential points of failure improving the management of a sensitive thermal environment. As product development cycles shrink across every industry, these capabilities give manufacturers a level of design, production, and supply chain flexibility previously unobtainable.
4. Why is 3D printing not popular?
3D printing Bangalore is an upcoming technology, and it is already a part of INDUSTRY 4.0 . But on par we have to accept the fact that it is not commonly used except for the industrialists down the lane. According to us, a few reasons for its reduced popularity:
- 3D printers are costly ones but a one time investment.
- Basic CAD knowledge is necessary for working with 3D printing in Bangalore.
- Above all there are no predetermined properties for the printer materials i.
 e., we do not know the performance of 3D printed materials
e., we do not know the performance of 3D printed materials - Any breakage caused by the whole component has to be replaced . It cannot be repaired unlike steel components.
5. Limited raw materials, not all material can be 3d printed with 3D Printing Bangalore.
5. Is 3D printing time consuming?
The quantity of parts being produced also has an impact on the amount of time it takes to complete a 3D printing Bangalore job. However, the reduction in print time is not as greatly reduced for more complex parts with short layers as the actual printing process is still fairly time-consuming.
6. How popular is 3D printing in Bangalore?
With the help of 3D Printing Bangalore, you can print anything from electronics to jewellery just sitting at home. Yes, that is what 3d printing service does! It has been in use in the industrial setting for almost 30 years and now it is advancing towards consumer as well as small scale-oriented businesses in Bangalore.
7. What can 3D printers make?
There’s much more on the list of applications for 3D printing in Bangalore, all happening now in myriad industries using a variety of innovative technologies and materials. Think dentistry, eyewear, prosthetics, furniture design, archaeology, palaeontology, and forensic sciences, to name just a few. And you can be sure that the creative and diverse uses for 3D printing Bangalore will continue to grow — and continue to improve the way we live and work.
8. Is nylon good for 3D printing?
Yes. When it comes to 3D printing materials, Nylon has to be mentioned as one of the most popular materials for professional users. This can be attributed in large part to its popularity outside of 3D printing Bangalore. Nylon has a wide range of applications thanks to its unique properties and the benefits of 3D printing in Bangalore mean that parts can be made on the fly easily and inexpensively.
9. Is there a Limitation to what shapes you can 3D print?
No limits in terms of shapes, but no information on manufacturability. One of the principal advantages of 3D Printing Bangalore is that it is possible to imagine all shapes without the limits of the constraints of the plastics industry, such as undercuts, hollowness, respect for thicknesses, etc.
One of the principal advantages of 3D Printing Bangalore is that it is possible to imagine all shapes without the limits of the constraints of the plastics industry, such as undercuts, hollowness, respect for thicknesses, etc.
10. How can Makenica help me?
Makenica offers 3D Printing services in India with which it is possible to print complex geometric shapes and interlocking parts that require no assembly. It is also possible to produce single objects, in small quantities, at low cost and fast delivery. This technology of 3D Printing Bangalore at Makenica also helps in the reduction of production-related material loss.
11. Why to Choose Our 3D Printing Service in Bangalore?
Here are the reasons why 3D Printing Bangalore with Makenica is popular:
- Flexible Design
- Rapid Prototyping
- Print on Demand
- Strong and Lightweight Parts
- Fast Design and Production
- Minimising Waste
- Cost Effective
- Ease of Access
- Environmentally Friendly
- Advanced Equipment
12. What types of 3D printers are there?
What types of 3D printers are there?
The seven different types of 3D printers used for 3D Printing in Bangalore are:
Fused deposition modelling (FDM)
Stereolithography(SLA)
Digital Light Processing(DLP)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Laminated object manufacturing (LOM)
Digital Beam Melting (EBM)
13. Which Cities Makenica Service in India ?
Makenica, with a significant presence, is the country's greatest pool of 3D Printing expertise, with competent professionals. Makenica has five facilities in Bangalore, with headquarters in the United States. This broad reach has enabled us to provide excellent service to a large customer base. The online 3D Printing services available at Makenica range from personalised to one-of-a-kind bespoke solutions. Each customer is guided on their route to quality production by our team of specialists.
Printed food, car, home… What can we expect from 3D printing technology in the near future?
In recent years, 3D printing has been one of the hottest topics in global technology news. As the technology fan base grows, there are more and more skeptics about the future of the 3D printing industry. Especially for our regular column “Expert”, we spoke with Alexey Lartey, co-founder of Toyze, a 3D printing company, and found out how 3D printing can change our lives in the very near future.
As the technology fan base grows, there are more and more skeptics about the future of the 3D printing industry. Especially for our regular column “Expert”, we spoke with Alexey Lartey, co-founder of Toyze, a 3D printing company, and found out how 3D printing can change our lives in the very near future.
Alexey Lartey, co-founder of Toyze
Alexey, today the 3D printing industry is still in its infancy and is a rather narrow field of activity. Will the time come when a 3D printer will be as indispensable an element of human life as, say, a phone, a computer or a regular printer, or will it still remain a device for design professionals, engineers, etc.
To begin with, all 3D printers are divided into several categories: industrial printers that have been used in production for many years, and desktop 3D printers for ordinary consumers, which, in my opinion, will become just as familiar in the near future phenomenon, like a conventional printer. In general, 3D printers by and large follow the path of first inkjet and then laser printers. After all, if you remember, the first inkjet printers also cost a lot at first, because at that time the technology itself was quite expensive. Even now, 3D printing technology is still quite expensive, but there are already a number of models on the market that are available to ordinary consumers. Although the price for them, of course, is still high - from $ 500 for the most basic model to 4-5 thousand dollars for more advanced versions. There are top models and for 10 thousand dollars.
In general, 3D printers by and large follow the path of first inkjet and then laser printers. After all, if you remember, the first inkjet printers also cost a lot at first, because at that time the technology itself was quite expensive. Even now, 3D printing technology is still quite expensive, but there are already a number of models on the market that are available to ordinary consumers. Although the price for them, of course, is still high - from $ 500 for the most basic model to 4-5 thousand dollars for more advanced versions. There are top models and for 10 thousand dollars.
Still, it's hard to imagine how a 3D printer can be useful in everyday life. In your opinion, will the printing industry 3 D- be able to find an application that will allow the printer to become truly widespread?
Indeed, today a 3D printer is more of a companion device that does not carry a serious payload for the average user. One of the use cases for a 3D printer in everyday life, in which it can turn into a device of everyday use, can be food printing. By the way, such experiments are being actively carried out, and the first tests are already underway. There are already 3D printers that can make different sweets. Just imagine - you can simply print the dish you like and generally no longer approach the stove.
One of the use cases for a 3D printer in everyday life, in which it can turn into a device of everyday use, can be food printing. By the way, such experiments are being actively carried out, and the first tests are already underway. There are already 3D printers that can make different sweets. Just imagine - you can simply print the dish you like and generally no longer approach the stove.
Yes, in this case, many people would certainly want to buy this device. In fact, this is your personal chef who makes a dish from scratch right at your arrival home.
Something like that. Of course, this technology is still at a very early stage, but in principle, a scenario is quite possible when a person, through an application on his phone, while sitting at work, sets the parameters of what he wants for dinner and at what time. And by the time the person comes home, dinner is already printed on the printer.
In which areas of human activity will the 3D printer be the most in demand over the next 10 years?
First of all, this is medicine, where 3D printing technology is already being used to create human tissues. For example, elements of an artificial heart and dentures are already being created on a 3D printer. In addition to medicine, 3D printers will be increasingly used in the automotive industry. For example, Koenigsegg has successfully created a turbine for its car, as well as rims on a 3D printer. There is even a fully printed car already. Now active research work is underway to create a 3D printer for printing building concrete blocks. In Singapore, the task was set to create a 3D printer in the next three years, which will be used in the construction of municipal housing, which will help to significantly reduce the cost of work.
For example, elements of an artificial heart and dentures are already being created on a 3D printer. In addition to medicine, 3D printers will be increasingly used in the automotive industry. For example, Koenigsegg has successfully created a turbine for its car, as well as rims on a 3D printer. There is even a fully printed car already. Now active research work is underway to create a 3D printer for printing building concrete blocks. In Singapore, the task was set to create a 3D printer in the next three years, which will be used in the construction of municipal housing, which will help to significantly reduce the cost of work.
If we talk about the main barriers to the mass distribution of 3D printers, what are these barriers? High cost of device, consumables, or both? What do you think is more likely to decline - the cost of devices or consumables?
The main barrier is the high cost of printers. It so happened that there are two companies on the market today that produce 3D printers, and they are essentially monopolists in the market - these are 3D Systems and Stratasys. These are the two main players in the world of industrial 3D printers and due to the lack of competition they have a very high margin business. An industrial 3D printer costs from 70.000 €, while a 3D printer is similar in price to a car, that is, you buy a printer in a basic package and can add various options to it as you wish. 3D Systems and Stratasys worked successfully for many years and made very good money doing b2b business, but at some point they decided to enter the b2c segment as well. And since these are American companies with a lot of money, they just started buying out small startups that dealt specifically with 3D printers for consumers.
It so happened that there are two companies on the market today that produce 3D printers, and they are essentially monopolists in the market - these are 3D Systems and Stratasys. These are the two main players in the world of industrial 3D printers and due to the lack of competition they have a very high margin business. An industrial 3D printer costs from 70.000 €, while a 3D printer is similar in price to a car, that is, you buy a printer in a basic package and can add various options to it as you wish. 3D Systems and Stratasys worked successfully for many years and made very good money doing b2b business, but at some point they decided to enter the b2c segment as well. And since these are American companies with a lot of money, they just started buying out small startups that dealt specifically with 3D printers for consumers.
This is partly why the expected price reduction did not occur, but at the same time, an understanding came to all market players: the technology is no longer so new that prices remain at the same high level.
Therefore, I think that in the next year or two, the cost of desktop 3D printers will fall, and this will encourage people to be able to buy and use them more massively. By the way, as far as I know, Canon is going to release its first 3D printer this year, which should be much cheaper than the competition. And as for consumables, there are more and more of them now, so the price is also slightly reduced.
You are one of the founders of Toyze, which popular online game characters. How did you come up with this idea? Which characters are the most popular?
Our Toyze app allows users to create, with maximum customization, real action figures of online game characters exactly as they appear in the game. Our team has quite a lot of experience in the gaming industry, so initially the choice fell on it. As for the most popular characters, this is, of course, Om Nom from Cut the rope, talking Tom from My Talking Tom and a character named Poo from the Pou game of the same name, which is now insanely popular in South America.
How does a 3D printer work in general, and how does the 3D printing process itself work?
At Toyze, we use a special material for printing, which is essentially an analogue of gypsum. In English it is called multicolor plaster. The model itself is created by bonding the adhesive to the plaster material in the form of powder. That is, the printer is given a design, and then the printing process starts. The printer head goes around in circles and simply mixes the glue with the powder, determining the shape of the object. Each 3D printer has its own print cycle, on average it is 4 hours. It does not matter how complex the design or how large the model is.
After the model is printed, does it harden immediately or does it take some time?
The printed model must cool for some time, after which the so-called post-processing begins: the model is dipped in a special solution in order to finally fix the plaster and then it can be coated with varnish or a special matting composition.
Well, we just have to wait a bit and, who knows, just like you print online game character figures today, we will be able to print almost any thing we need in the near future. Wait and see. Thanks for the interesting conversation!
Pharmacy 3D printing | Remedium.ru
Magazine "Remedium" №9, 2020
DOI: 10.21518/1561-5936-2020-9-58-60 Ph.D. This direction can be used to develop drugs with controlled release of active substances; preparations containing combinations with fixed doses, as well as for the creation of orodispersible dosage forms. The global 3D drug market is still largely at the research stage, but is expected to grow rapidly in the next decade [1].
3D printing in pharmacy
Yuliya Prozherina, Cand. of Sci. (Bio.),
RM Analytics
3D printing of drugs is an innovative and cost-effective technology, which is a major step towards personalized medicine. This technology can be used for the development of controlled-release drugs; fixed-dose combination drugs, as well as for the creation of orodispersible dosage forms. The global 3D drug market is still largely at the research stage, but its rapid growth is expected in the coming decade [1].
This technology can be used for the development of controlled-release drugs; fixed-dose combination drugs, as well as for the creation of orodispersible dosage forms. The global 3D drug market is still largely at the research stage, but its rapid growth is expected in the coming decade [1].
FROM CARS TO DRUGS
3D printing was developed in the late 1980s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) as a rapid prototyping method. Currently, it has become widespread and is actively used in industries such as automotive, healthcare (primarily in dentistry and orthopedics) and retail.
Important steps are also being taken towards the development and implementation of 3D medicines into clinical practice. By the way, issued by Therics, Inc. (Princeton, New Jersey) at 19The '94 license covers the use of 3D printing for the production of various products, including medicines (MPs). The application of these technologies in the field of drug delivery has been actively investigated, and in 2015 it was implemented in the United States. In August 2015, the first 3D-printed and FDA-approved LP was produced on an industrial scale. It was the orodispersible antiepileptic drug Spritam (levetiracetam) from Aprecia Pharmaceuticals. The creation of this drug laid the foundation for the 3D future in pharmaceuticals, demonstrating the possibilities of 3D printing for the production of complex dosage forms. Research and development in this area is still ongoing [2].
In August 2015, the first 3D-printed and FDA-approved LP was produced on an industrial scale. It was the orodispersible antiepileptic drug Spritam (levetiracetam) from Aprecia Pharmaceuticals. The creation of this drug laid the foundation for the 3D future in pharmaceuticals, demonstrating the possibilities of 3D printing for the production of complex dosage forms. Research and development in this area is still ongoing [2].
IMPORTANT ADVANTAGES
3D drug printing technology becomes an important step in the development of personalized medicine, as it allows implementing the principle of individual selection of components and their dosage depending on the needs of the patient. In addition, when creating a dosage form (DF) according to the presented technology, it is possible to adjust the release profile of the active ingredient depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. Particularly relevant is the creation on the basis of this technology of easily and quickly soluble orodispersible drugs in the oral cavity.
3D printing of drugs may also be in demand in the orphan drug segment, since these drugs are produced in small quantities.
From a technological point of view, the advantages of additive methods in drug development are the ability to accurately control the spatial distribution of pharmaceutical substances, create complex geometries, precipitate small amounts of pharmaceutical substances, reduce waste, and speed up the production of various compositions for screening studies or the manufacture of individualized drugs. The manufacturing benefits associated with LP printing are moving away from traditionally complex, slow and costly production chains and enabling more personalized products without the need for high volume production [2]. To some extent, 3D printing can become a continuation of the pharmacy tradition of manufacturing medicines based on individual recipes, but at a technologically new level and implemented in a slightly different way.
WORLDWIDE 3D
According to Maximize Market Research, the global 3D medicine market reached $245 million in 2019 and is expected to grow to $456 million by 2027 (CAGR 8 . 07%).
07%).
The key drivers of market growth are innovations in 3D printing technologies, as well as an increase in diseases such as epilepsy, schizophrenia, for which the use of instantly soluble dosage forms in the oral cavity is important. On the other hand, unforeseen technological difficulties, the need for large investments in further research, the introduction of various regulation scenarios for this industry segment, as well as the likelihood of side effects of drugs manufactured by this method can hinder further market growth [1, 3].
The global 3D printed medicines market can be segmented by dosage form, manufacturing technology and geography.
Based on dosage form, the market is categorized into tablets, capsules, multi-drug implant, nanoparticles, solutions, nanosuspensions, encapsulated polymer and implant [1].
In terms of applied 3D drug manufacturing technology, the market is divided into inkjet printing, direct-write, zip dose, thermal inkjet (TIJ), deposition modeling (FDM), powder printing and stereolithography (SLA) [1]. Despite the fact that over the past 15 years a large number of different 3D printing technologies have been introduced into the LP prototyping industry, inkjet printing is still the most popular [2].
Despite the fact that over the past 15 years a large number of different 3D printing technologies have been introduced into the LP prototyping industry, inkjet printing is still the most popular [2].
Geographically, the market is divided into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), South America, and the Middle East and Africa (MEA). The Asia-Pacific region holds the leading market share in the 3D printed medicine market, accounting for 34.1%. It is expected to act as a further growth driver for the segment (CAGR 18.2%). At the same time, countries in the Asia-Pacific region, such as China and India, will grow at the highest rates thanks to huge investments in both R&D and the pharmaceutical industry. In the European region, growth in the development of this technology is also predicted [3].
Drawing. Global 3D Printed Medicines Market, by Region: 2020-2027
Source: Maximize. Market Research PVT. LTD [3]
There are still few players in the global market for 3D printed medicines. The key ones are GlaxoSmithKline PLC and Aprecia Pharmaceuticals LLC, Fabrx Ltd [1]. Merck, Hewlett Packard Caribe, BV, LLC, 3D Printer Drug Machine, Cycle Pharmaceuticals, etc. are actively engaged in development in this direction [4]. In order to stay in the competitive market, the leading players use various strategies such as acquisitions, mergers, expansions, joint ventures and products. For example, GlaxoSmithKline PLC (GSK) has been investing in 3D printing technology for several years. The R&D department of the 3D printing company uses it in a variety of ways, from drug prototyping to drug packaging. The goal of Fabrx Ltd and GSK is to develop approaches to individualized medicine for each patient using 3D printing [1].
The key ones are GlaxoSmithKline PLC and Aprecia Pharmaceuticals LLC, Fabrx Ltd [1]. Merck, Hewlett Packard Caribe, BV, LLC, 3D Printer Drug Machine, Cycle Pharmaceuticals, etc. are actively engaged in development in this direction [4]. In order to stay in the competitive market, the leading players use various strategies such as acquisitions, mergers, expansions, joint ventures and products. For example, GlaxoSmithKline PLC (GSK) has been investing in 3D printing technology for several years. The R&D department of the 3D printing company uses it in a variety of ways, from drug prototyping to drug packaging. The goal of Fabrx Ltd and GSK is to develop approaches to individualized medicine for each patient using 3D printing [1].
Work on the creation of LP using 3D printing technology is also underway in our country. For example, scientists at the St. Petersburg Chemical and Pharmaceutical University plan to create a technology for individual drug dosages using 3D printing. The university has a Russian-made Picasso 3D printer. Another promising project in the field of bioprinting for the university is the creation of drugs with controlled release [5].
Another promising project in the field of bioprinting for the university is the creation of drugs with controlled release [5].
DRIVER – COVID
While the creation of 3D medicines still requires more research, the production of medical devices and various parapharmaceutical products is progressing more rapidly. In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic has only accelerated this process. So, for example, in many countries of the world this spring, medical products designed to protect against coronavirus were printed on 3D printers. Printed medical masks in the UK were provided by iMark, and in Russia by Temporum (a resident of the Nagatino technopark). Carbon has been actively printing face shields. In Spain, Consorci de la Zona Franca, HP Inc., Leitat and CatSalut have developed the first 3D printed emergency ventilation device. Devices printed on a 3D printer were actively purchased by hospitals in Italy [6]. And this is not the limit of the possibilities of using additive technologies. According to Forbes, the coronavirus pandemic could be a truly high point for 3D printing [7].
According to Forbes, the coronavirus pandemic could be a truly high point for 3D printing [7].
References
- 3D Printed Drugs Market Research and Forecast 2018-2027. available at: https://www.omrglobal.com/.
- Blynskaya E.V., Tishkov S.V., Alekseev K.V. 3D printing technologies for the production of dosage forms. Drug development and registration . 2018;(24):10–19.
- Global 3D Printed Drugs Market–Industry Analysis and Forecast (2020-2027) – By Scenario, End User and Region. Available at: https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/.
- 3D Printed Drugs Market 2019 Top Key Players are 3D Printing Systems, Aprecia Pharmaceuticals, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, GlaxoSmithKline PLC and Forecast to 2025. Source: Available at: https://www.medgadget.com/.
- Using 3D printing technology, it is possible to control drug release in the body. Access mode: https://gxpnews.net/.
- 3D printing in medicine.

Learn more












