3D printer simulator open source
Open source 3D printing toolbox
What is Slic3r?
Features
Compatible with your printer too. RepRap (Prusa Mendel, MendelMax, Huxley, Tantillus...), Ultimaker, Makerbot, Lulzbot AO-100, TAZ, MakerGear M2, Rostock, Mach4, Bukobot and lots more. And even DLP printers.
Fast G-code generation is fast. Don't wait hours for slicing that detailed model. Slic3r is about 100x faster than Skeinforge. It also uses multithreading for parallel computation.
Lots of input/output formats. Slic3r reads STL, AMF and OBJ files while it can output G-code and SVG files.
Do you like the graphical interface or command line? All the features of the user-friendly interface are also available from command line. This allows to integrate Slic3r in your custom toolchain and batch operations as you like.
Open source, open development. Slic3r is open source software, licenced under the AGPLv3 license. The development is centered on GitHub and the #slic3r IRC channel on FreeNode, where the community is highly involved in testing and providing ideas and feedback.
Dependencies? Nah. Slic3r is super-easy to run: download, double click and enjoy. No dependencies needed. Hassle-free. For MacOS X, Windows, Linux.
Print with dual multiple extruders. Print beautiful colored objects, or use your secondary extruder to build support material. Or put a larger nozzle on it and print a faster infill.
Use brim for the best adhesion. This unique feature improves built plate adhesion by generating a base flange around your objects that you can easily remove after printing.
Microlayering: save time, increase accuracy. You can choose to print a thicker infill to benefit from low layer heights on perimeters and still keep your print time within a reasonable amount.
Compose a plate but print one object at time. Use the built-in plating interface that allows to place objects with drag-and-drop, rotate and scale them, arrange everything as you like. The sequential printing feature allows to print one complete object at time in a single print job.
Use the built-in plating interface that allows to place objects with drag-and-drop, rotate and scale them, arrange everything as you like. The sequential printing feature allows to print one complete object at time in a single print job.
Cool cooling strategies. A very smart cooling logic will regulate your fan speed and print speed to ensure each layer has enough time to cool down before next one is laid on it.
Manage multiple printers, filaments and build styles. The configuration handling system was designed for people working with multiple machines and filaments: you can save configurations as presets for each category avoiding to multiply your saved configurations.
Enjoy support material. Automatic generation of support material for overhangs.
Gallery
Links
The RepRap Project
The 5 Best G-Code Simulators for Machining and 3D Printing
A good G-Code simulator can make the difference between a successful manufacturing process or an expensive failure. Here are some of the best simulators.
Here are some of the best simulators.
Debugging is a vital part of any programming task. This is certainly true with programs that will interact with the physical world like those used to control CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics.
Any mistake in the programming of these physical machines could cause real damage to the environment, the machine itself, and even to human workers in the case of some robots.
G-Code simulation is probably the best way to ensure that you have written your program to a high standard. Although very few people these days write G-Code by hand — we tend to use CAM programs — there is still a huge benefit to checking your program in a simulator before loading it into your physical machine.
Here is a list of some of the best types of G-Code simulator that you can use these days.
What is a G-Code Simulator?
A G-Code simulator is a type of software tool that provides a virtual representation of a CNC machine’s tool path made by following the instructions in a G-Code file.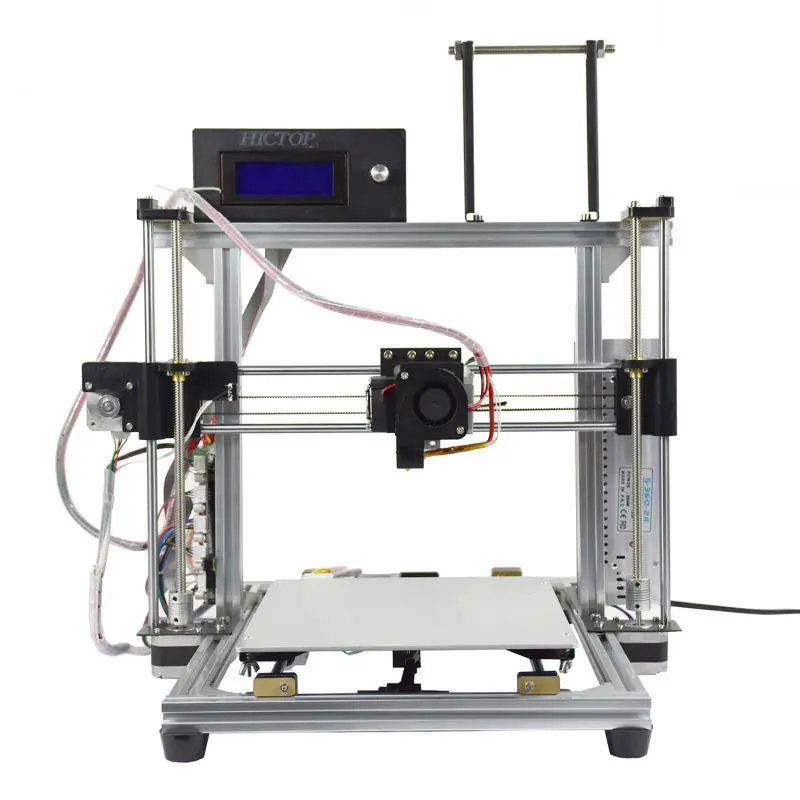 They range from simple simulators that output a single image of the tool path to complex tools that can detect collisions and plot the path in 3D.
They range from simple simulators that output a single image of the tool path to complex tools that can detect collisions and plot the path in 3D.
The basic purpose of a G-Code simulator is to give you a way to see how the machine tool will move. Without this, the only way to debug your program is to test it out on the machine itself… and by then it’s too late to avoid disaster.
G-Code simulators have experienced a resurgence in popularity over recent years thanks to the rise of 3D printing. Hobbyists and professionals alike need a way to see a 3D printed item before they spend hours printing it. A good simulator provides a quick and easy way to achieve this.
The 5 Best G-Code Simulators for Machining and 3D Printing
There are quite a few options for simulating your G-Code out there. Some of them are okay, others are a waste of time.
Here are 5 types of G-Code simulator that are all good in some situations. Which you pick depends on your unique needs for this machining or 3D printing application:
1.
 Stand-alone G-Code Simulator
Stand-alone G-Code SimulatorThere are some simple software tools available that will quickly simulate your G-Code file and show you the path. In general, they don’t interface with CNC machines or 3D printers, but they at least give you the confidence that your program “draws the shapes” that it’s supposed to.
Some notable examples include:
- NC Viewer a handy online tool for quick visualization.
- CAMotics an open-source simulator for 3-axis machining.
- G-Code Q’n’dirty another open-source web tool.
2. Slicer Software (for 3D printing)
If you are using G-Code to program a 3D printer, your Slicer software may be able to give you a visualization of what the final printed item will look like.
A Slicer is a software tool that turns your CAD model into G-Code.
For example, RoboDK users often use the free tool Slic3er when they are using robotic 3D printing. This tool allows them to visualize the item that they are going to print before they send it to the robot.
Slic3r can also perform some of the functions of a dedicated G-Code simulator, such as estimating the time it will take to print the object and repairing incomplete 3D files.
3. RoboDK for Robotic Machining and 3D Printing
If you are considering using a robot for your machining or 3D printing, probably the best option is RoboDK (of course, we would say that, wouldn’t we?… but it’s also true).
RoboDK’s machining and printing wizard works with G-Code.
You can load a G-Code file into the software then easily simulate the path. Then, with the same software, you can send the program directly to the robot’s controller, without having to do any robot programming at all!
Not familiar with robotic machining? Check out our introductory post.
Didn’t know robots could do 3D printing? Here’s a video:
4. Libraries (e.g. MATLAB or Python)
There are some situations where you might want to perform some more advanced analysis on your G-Code or link with your own programming. Perhaps you are using the code as part of a research project or you are developing your own 3D printer.
Perhaps you are using the code as part of a research project or you are developing your own 3D printer.
In such cases, it could be helpful to use a G-Code library for your preferred programming language.
For example:
- G-Code Reader is an extension for MATLAB.
- PyCNC is a library for Python.
- Gsim is an open-source 2D simulator written in Python.
5. Your Favorite CAM Package
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) programs are how many of us generate our G-Code files in the first place.
Popular CAM packages (which also include plugins for RoboDK) include:
- MasterCAM
- Inventor
- Fusion 360
Many of the leading CAM packages also have the capacity to simulate your G-Code. Often, if you want to link the software directly with your CNC machine or 3D printer, it will require you to purchase an extra add-on license, so weigh up the pros and cons beforehand. However, simple simulation can usually be achieved within the CAM software itself.
How to Pick the Best Software for You
There are clearly several ways to simulate G-Code!
But, which is going to be the best software for you? The answer depends on your situation.
If you are a hobbyist who is just using G-Code to program your home 3D printer, for example, one of the open-source, stand-alone simulators or Slicer software will probably be the best option.
If you are a researcher or programmer looking to delve deep into the simulation, one of the MATLAB or Python libraries might be worth checking out.
Finally, if you are working in industry, however, you will want a piece of software that is easy to use, robust and won’t give you any unnecessary headaches. For robotic machining or 3D printing, RoboDK is a good option. For all other CNC, look at a decent CAM package.
What questions do you have about G-Code simulation? Tell us in the comments below or join the discussion on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Instagram or in the RoboDK Forum.
Top 20 Free 3D Printing & 3D Printing Software
Looking for 3D printing software? We've rounded up the top 20 software tools for beginners and professionals alike. Most slicers are free.
What is a slicer? This is a program for preparing a digital model for printing. Models for 3D printing are usually distributed in STL files. To turn an STL file into G-code (a language that a 3D printer understands), a slicer program is required. It is called a slicer because it cuts (to slice - English) a 3D model into many flat two-dimensional layers, from which a 3D printer will add a physical object.
Which slicer should I choose? In this article, we will tell you which slicer is best for 3D printing for each stage of your work. Which one is better for preparing a 3D model for printing? But what if you need to create a 3D model from scratch? And if you are only taking the first steps in 3D?
Don't be afraid: we've answered all of these questions, including the required skill level for each program and where you can download it. The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
- Cura
- CraftWare
- 123D Catch
- 3D Slash
- TinkerCAD
- 3DTin
- Sculptris
- ViewSTL
- Netfabb Basic
- Repetier
- FreeCAD
- SketchUp
- 3D Tool
- Meshfix
- Simplify3D
- Slic3r
- Blender
- MeshLab
- Meshmixer
- OctoPrint
#1: Cura
For beginners who need a slicer to prepare STL files for 3D printing
Cura is the default slicer software for all Ultimaker 3D printers, but can be used with most others , including RepRap, Makerbot, Printrbot, Lulzbot and Witbox. The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
This program is very easy to use and allows you to manage the most important 3D printing settings through a clear interface. Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings. If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings. If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Cura can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: Cura
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#2: CraftWare
3D printers by the Hungarian startup CraftUnique to support their CraftBot crowdfunding machine. However, the program works with other printers.
Like Cura, CraftWare allows you to switch from "Easy" to "Expert" mode, depending on how confident you feel. It's a colorful app that features a visual G-code visualization with each function represented by a different color. But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
Please note, however, that this program is still in beta, so bugs may occur.
Download: CraftWare
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#3: 123D Catch
-systems, smartphones and tablets, which allows you to convert images of objects into a 3D model. Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
You need many photos of an object from different angles - the more the better - after which they will be compiled into a 3D model.
123D Catch is more of a fun app than a professional 3D printing tool, but after some tambourine dancing, you can get good results, especially when paired with an STL editor like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Android, iOS, Windows Phone
#4: 3D Slash
and surprisingly simple, and refreshingly new. With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
You can start with a large block and, like a virtual sculptor, remove small cups from it with tools such as a hammer or drill, or start from empty space and build a model from cubes and other shapes. You can paint with flowers or use template pictures.
Other features worth mentioning are tools for creating logos and 3D text. The Logo Wizard imports an image and creates a 3D model, while the Text Wizard allows you to enter and format text, and then turn it into 3D.
Recommended!
Download: 3dslash.net
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux, Browser
#5: TinkerCAD
- A computer-aided design (CAD) system for 3D printing, which is a good starting point for beginners. Since its capabilities are limited compared to Blender, FreeCAD and SketchUp, many users switch to more powerful tools after some time.
As in 3D Slash, here you can build models from basic shapes. At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
Come in: Autodesk TinkerCAD
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#6: 3DTin
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
another easy and intuitive online tool choice for beginners in 3D modeling. All you need is a Chrome or Firefox browser with WebGL enabled.
Choose from a huge library of 3D shapes and add them to your sketch. All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
Enter: 3DTin
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#7: Sculptris
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
clay. This is a fantastic 3D modeling program if figurines are your main task. For example, you can make a bust of your favorite video game or comic book character. Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Download: Pixologic Sculptris
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#8: ViewSTL
For beginners who want to view STL files
ViewSTL is the easiest way to view STL files . Simply open a web page and drag the STL onto the dotted box.
The STL online viewer allows you to display the model in one of three views: flat shading (for a quick view), smooth shading (for a high-quality image), and wireframe.
Enter: ViewSTL
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#9: Netfabb Basic
some nice features that allow you to analyze, "repair" and edit STL files before moving on to the model cutting stage.
A good choice if you need more than just a slicer and want to be able to quickly fix STL files without having to learn programs like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Don't let the 'Basic' in the title fool you, Netfabb Basic is actually a very powerful 3D printing tool. It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
Download: netfabb.de
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
No. 10: Repetier
For advanced to prepare STL files for 3D printing
9002 the next level of 3D printer slicer software, but if you want to stay open source, you should look into Repetier. It is the great grandfather of 3D printing software and a favorite of the RepRap community. To date, the program is moving by leaps and bounds from the level for beginners to advanced users. Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
What's more, Repetier Host works remotely via Repetier Server, so that the 3D printer can be controlled via a browser, tablet or smartphone.
Download: Repetier
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#11: FreeCAD
The program is a great option for developing your design skills. More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
Download: freecadweb.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#12: SketchUp
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
SketchUp is the perfect combination of simplicity and the perfect combination functionality, with a user-friendly interface and a relatively flat learning curve (i. e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
The Make SketchUp version is free and will include everything you need for 3D modeling if you also download and install the free STL exporter. There is also a professional edition for architects, interior designers and engineers.
Download: sketchup.com
Price: Free (SketchUp Make), $695 (SketchUp Pro)
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#13: 3D-Tool Free Viewer
view and validate STL files
3D-Tool Free Viewer is a sophisticated tool that, among other things, allows you to check the structural integrity and printability of your file. With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
Download: 3D-Tool
Price: Free
Systems: PC
#14: Meshfix
your model for errors.
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#15: Simplify3D
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing print. A flexible algorithm checks the model for problems, fixes them, shows a preview of the printing process (ideal for identifying potential problems), and then slices it.
This slicer offers the best infill pattern options in the competition. For models that require supports, Simplify3D will create the appropriate structures on its own and give you full control over their placement. For printers with a dual extruder, when printing with different materials, the Dual Extrusion wizard will help, as a result of which, for example, it will be easier to remove the dissolving filament.
Simplify3D supports 90% of today's commercially available desktop 3D printers and is compatible with Marlin, Sprinter, Repetier, XYZprinting, FlashForge, Sailfish and MakerBot firmware. Simplify3D can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: simplify3d.com
Price: $149
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#16: Slic3r
source code, which has a reputation as a carrier of super new functionality, which you will not find anywhere else. The current version of the program is able to show the model from multiple angles, so that the user gets a better preview experience.
There's also an incredible 3D honeycomb infill, the first of its kind that can extend over multiple layers rather than repeating itself like a stamp. This significantly increases the strength of the internal filling of the model and the final printout.
Another option is direct integration with Octoprint. Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Download: Slic3r
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#17: Blender
For professionals who want to create 3D printable models
Blender is a popular computer-aided design (CAD) system with a steep learning curve. Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
In short, Blender is one of the most powerful tools out there. Its community is always ready to help, there are a lot of educational materials. It's also open source, so enthusiasts often write extensions to make it even better and more powerful.
Download: blender.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#18: MeshLab
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing
MeshLab - advanced editor. It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#19: Meshmixer
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing files. It's especially good for identifying potential problems and fixing them automatically. For example, it will show paper-thin walls that can lead to problems with 3D printing. Meshmixer is part of the Autodesk family of 3D printer software, so it should work well with tools like TinkerCAD.
For example, it will show paper-thin walls that can lead to problems with 3D printing. Meshmixer is part of the Autodesk family of 3D printer software, so it should work well with tools like TinkerCAD.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#20: OctoPrint
start, pause or interrupt 3D print jobs. Combined with Wi-Fi capable devices, it makes for a great monitor for remotely monitoring the 3D printing process.
Octoprint understands the G-codes of almost all 3D printers and slicers and includes a gCodeVisualizer to visualize this code before or during printing.
If you want to work away from your 3D printer and control it remotely, Octoprint is the best you can find.
Download: octoprint.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
Source
Top 10 Free 3D Modeling Software of 2019
3D Modeling Has Many Uses: Thanks to it computer graphics, realistic video games are created, tests are carried out, prototypes are created. Every year 3D-modelers are becoming more and more in demand - but where to learn it?
Every year 3D-modelers are becoming more and more in demand - but where to learn it?
We've rounded up the top 10 free programs with the latest tools in 2019 to help you practice creating 3D models.
3D Slash is a 3D modeling software that allows you to create models using a simple building block concept.
This service is much simpler than its counterparts: users create 3D structures by working on a cuboid using a variety of 3D modeling tools: Hammer, Spatula, Chisel, Wood and Drill - for many, the creation process models in 3D Slash are somewhat reminiscent of Minecraft. 3D designing with these tools will be easy even for beginners. 3D projects in the program can be imported and modified.
However, note that by default the tools will give the model "pixel prints". If you prefer crisp edges and smooth surfaces, select tool sizes below your printer's resolution.
LibreCAD is a free and open source 3D modeling software. Contains the basic tools you will need to model and modify projects. The user interface of LibreCAD is not overloaded, so this 3D modeling software is suitable for beginners.
The user interface of LibreCAD is not overloaded, so this 3D modeling software is suitable for beginners.
It should be noted that the service only displays 2D views, so the size of the source file will be only 30 MB. Also, in addition to 2D, the service can display isometric images.
Meshmixer 3.0 is a program that allows you to design 3D prototypes by combining several models. Users can cut the desired parts from the models and paste them into others.
In addition, the program allows you to create sculptures and prepare your prototypes for printing. The program is available on Windows and OS X.
SculptGL is the perfect option if you want to learn how to create organic 3D sculpting. The whole process of building models in this program resembles clay modeling.
Using dynamic topology modifiers, you can subdivide a 3D model to create more complex details, and importing a base mesh can save you a lot of time.
The software runs on WebGL, so it opens without problems in most browsers. It also has limited functionality - just a couple of brushes that mimic real sculpting tools. But in this case, it's more of a plus than a minus.
It also has limited functionality - just a couple of brushes that mimic real sculpting tools. But in this case, it's more of a plus than a minus.
The intuitive AutoDesk 123D software offers a variety of 3D modeling and CAD tools. In addition, it supports 3D printing and laser cutting technology. The software is available on Windows, MacOS X and iOS.
Houdini Apprentice is a free version of Houdini FX with fewer tools. It is suitable for artists, students and amateurs who create three-dimensional models. Houdini Apprentice has a simple and intuitive interface, so the program will be useful for beginner 3D designers as well.
TinkerCAD is software that helps you create complex designs effortlessly. Recently, the TinkerCAD development team has added the ability to design objects using Codeblocks, allowing for more technical parametric modeling. Thanks to him, the quality of 3D models will not depend so much on how well you use the mouse and keyboard.
Wings 3D is a simulation program with many tools to create realistic prototypes. With its help, you can texture models - the built-in AutoUV tool helps with this.
The program does not support animation and represents only one OpenGl render, so it is often used in combination with other programs. Wings 3D uses the Erlang programming language and is available on Windows, Linux, and MacOS X.
This free software includes many common CAD modeling tools, but they are beyond the beginner's grasp. The user interface is clearly inspired by AutoCAD, so DesignSpar is a good alternative for 3D modelers who would like to use this software but can't afford it.
While the basic features of this software are free, the publisher charges for additional features such as advanced import/export and rendering options.
Like some other programs, DesignSpark connects to online services. In particular, it allows you to load 3D models directly into free CAD software, as well as print and mail designs.