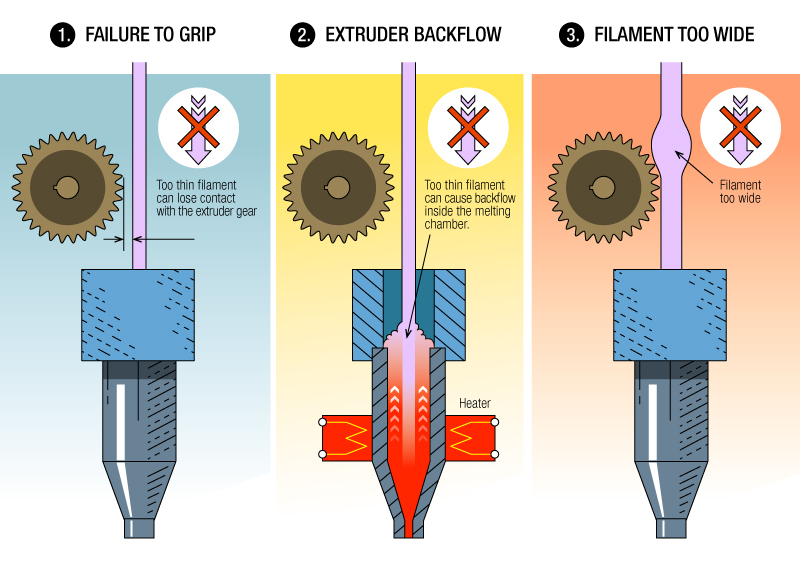
3D printer output device
Output Devices - Computer Science GCSE GURU
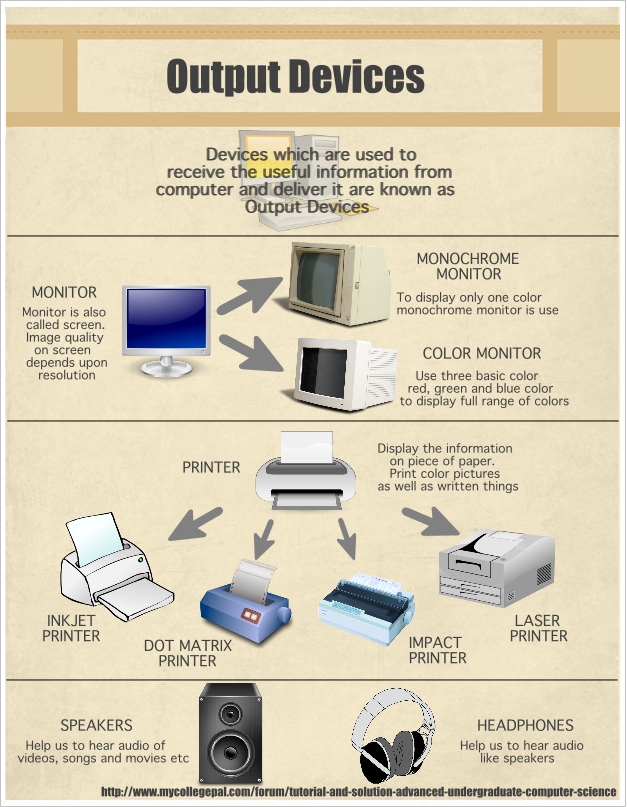
What is an output device?
Output devices are pieces of computer hardware used to communicate the results of data processing performed by a computer.
The objective of output devices is to turn computer information into a human friendly/readable form.
There are many examples of output devices, each with their own benefits and drawbacks.
Jump to a section on this page:
LCD & LED Flat Display Screens
What is a display screen?
Display screens are amongst the most common types of output device.
Thanks to the development of LCD technology, display screens now require less power and are lighter and thinner than their obsolete CRT ancestors.
LCD screens produce sharp high resolution images.
Most display screens are either LCD or LED. Details of these can be found below.
Typical applications for display screens- Phone and tablets
- Laptops and computer screens
- Televisions
- Gaming devices
- Cameras
- Household appliances
Benefits of display screens
- Low power consumption means that displays can be placed on battery powered devices
- Screens are now lighter and thinner – meaning they can be used in a variety of places
- Sharp high resolution images
- Vivid colours with good contrasts
- Reach maximum brightness quickly
- Reliable and long lasting
Drawbacks of display screens
- Keeping up with the absolute latest screen technology can be expensive
LCD Screens
LCD screens are made from millions of tiny blocks called pixels.
Each pixel contains a red, green and blue light filter which can be individually adjusted to create any colour when combined.
This is possible because the liquid crystals found in each pixel can be manipulated to allow all, some or none of the fluorescent tube back light through to the individual RGB filters at the front of the screen.
LED Screens
LED screens work in a similar way to LCD screens but with one major difference, the light source.
Small LED bulbs are used to provide light to the LCD pixels, not fluorescent tubes.
These LED bulbs either fill the entire back of the display unit, or on thinner models are just arranged around the edges.
A fully back lit LED display allows for localised diming of the screen, producing deeper blacks in parts of the screen where no light is needed.
Edge lit LED displays allow the screens to become even thinner than standard LCD displays.
In some situations LED screens are more power efficient than LCD.
LCD & DLP Data Projectors
What is a data projector?
Data projectors are output devices used to project the digital output from a computer device on to a large screen or wall.
The user can usually choose whether the projector mirrors their computer screen, extends it, or replaces it.
Projectors are ideal when training or presenting information to a large audience.
Prices are very reasonable for basic projectors, however, a data projector capable of showing cinema films or sports footage in a bar are far more expensive.
Data projectors come in two mains types, 3LCD and DLP. The differences between these are detailed below.
Typical applications for projectors- Presenting to a large audience
- Education and training environments
- Boardrooms
- Cinemas and bars
Benefits of projectors
- Projected content can be seen easily be a large audience
- Allow a wide range of media and ideas to be shared with others
- Entry level projectors are affordable
Drawbacks of projectors
- Top quality projectors are very expensive
- Some projectors do not work very well in natural light
LCD Projectors
The lamp light is split from white into red, green and blue using dichroic mirrors.
The RGB light channels are passed through separate monochrome LCD screens, one for each of the three colours.
The RGB light is then reassembled into a single light beam and magnified out of the projector using lenses.
It is the three LCD screens that therefore control how much red, green and blue is present in the final image.
DLP Projectors
DLP projectors work in a different way to LCD projectors.
Most affordable DLP projectors use a fast spinning colour wheel filter to sequentially split the lamp light into red, green and blue light.
The projected image is created by a bank (chip) of thousands of microscopic mirrors. Each mirror represents one pixel.
These tiny mirrors are carefully in sync with the colour wheel, turning towards or away from the RGB light as and when it is needed, thousands of times per second. So, if part of the projected image requires no red light, they face away from the light when the colour wheel filter is allowing red light through.
The reflected image from the mirrors is then magnified out of the projector using lenses.
Inkjet Printer
What is an inkjet printer?
Inkjet printers are output devices usually used in a home or small office for low volume printing.
A moving print head sprays ink droplets on to the paper from a cartridge filled with liquid ink. Thermal bubble technology is used to fire these microscopic ink droplets from the cartridge.
Because the bulk of the action happens in the high-tech ink cartridges, they are priced quite highly in relation to the price of the actual printers (which are often very affordable).
Inkjet printers are now commonly combined with a flatbed scanner to create an all in one solution.
Typical applications for inkjet printers- Low volume printing where speed isn’t critical
- High quality photographic documents
- Home and small office
- Printing on heat sensitive stationary, such as labels
Benefits of inkjet printers
- Entry model printers are very affordable
- Excellent photographic quality
- Can print on a variety of stationary as no heat is applied
Drawbacks of inkjet printers
- Generally slower at printing than compared to laser printers
- Ink cartridges can be expensive
- Printed text is nice and clear but laser printed text is still superior
Laser Printer
What is a laser printer?
Laser printers are output devices usually found in businesses and organisations.
Using static electricity, the way they work is completely different to inkjet printers.
Laser printers are ideal for high volume printing because they produce very high quality documents at fast speeds.
Laser printers use a powdered ink/toner cartridge, not liquid ink.
- The rotating printing drum is given a negative charge.
- A laser removes the negative charge from certain areas of the drum as it scans across it, creating a neutrally charged copy of the text/image to be printed.
- From an ink roller, negatively charged toner is attracted to the neutral spaces on the printing drum.
- The toner image/text then transfers from the printing drum to some positively charged paper.
- A fuser is used to heat the document and permanently melt the toner on to the page.
- High volume printing where speed is critical
- Shared printer for several users
- Predominantly text based documents
- Found in businesses and offices
Benefits of laser printers
- Very good at producing sharp text
- Fast high volume printing
- Large input trays to hold more paper
- Cost per page is generally lower than inkjet
Drawbacks of laser printers
- Good quality images, but inkjet images are superior
- Initial cost for printer can be expensive
- Heavy and bulky
- Toner is expensive but is replaced infrequently
Test your knowledge of output devices with our quick quiz.
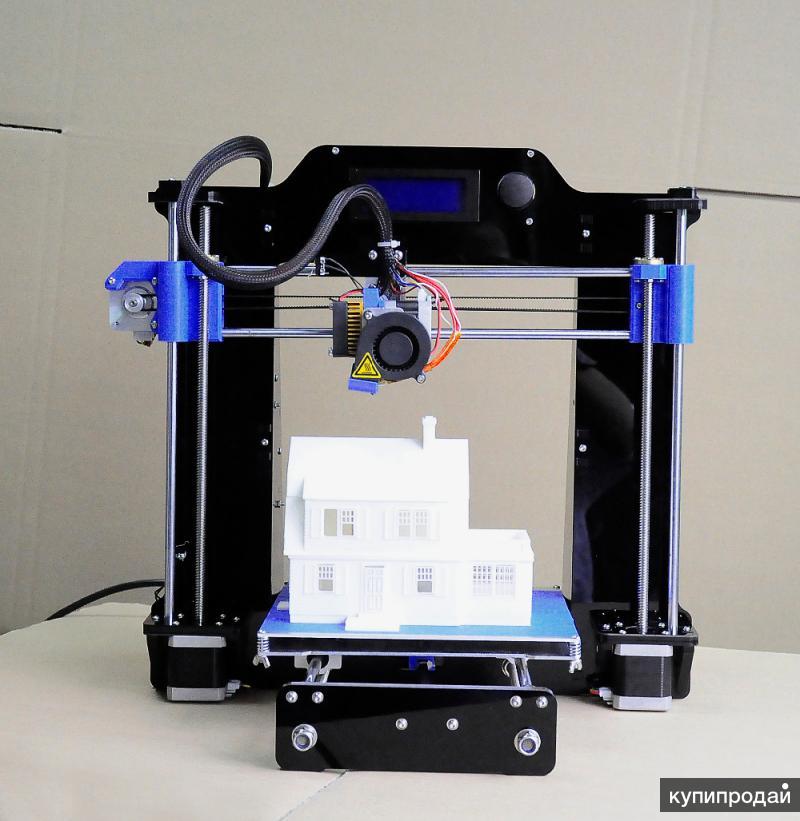
3D Printer
What is a 3D printer?
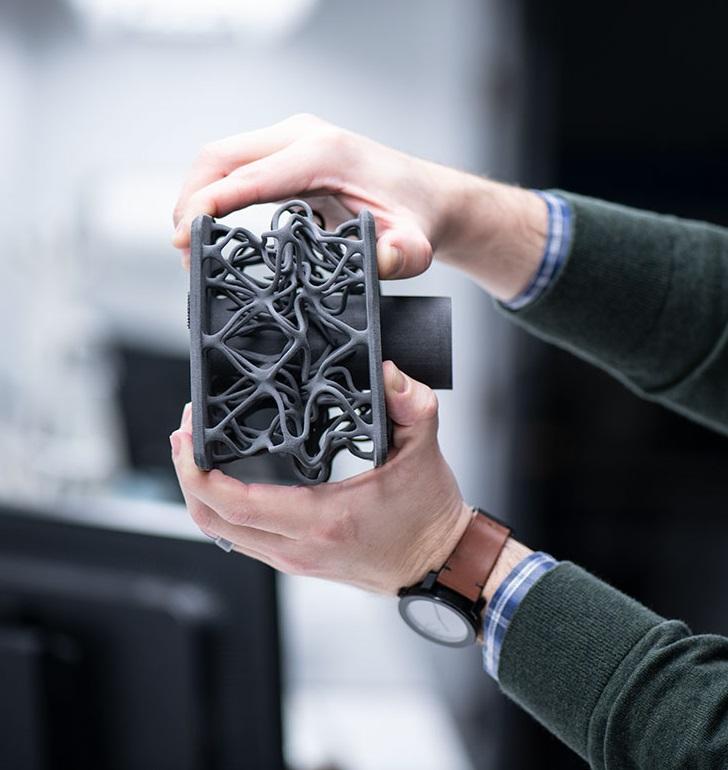
3D printers are output devices used to create three dimensional objects from a 3D computer model.
The computer model can be created by using a 3D scanner, or by hand using CAD modeling software.
Using a method called additive manufacturing, 3D objects are created by layering a material, layer by layer, from the ground up until the object is completed.
Typical applications for 3D printers- Home and commercial use
- Prototyping parts and solutions
- Human prosthetics
- Medical aids
Benefits of 3D printers
- Prototype objects can be created at a fraction of the cost of a factory
- A variety of intricate and “impossible” objects can be printed in a variety of materials
- Computer designs can be shared and printed by others
Drawbacks of 3D printers
- Expensive to buy although entry models are becoming more affordable
Wide-Format Printer
What is a wide-format printer?
A wide-format printer is an output device capable of large scale printing.
Most wide-format printers work in a similar way to inkjet printers, allowing for some flexibility with the materials that can be used.
Wide-format printing is economical when printing a larger item in small volumes as setting up a traditional print run can be expensive.
Typical applications for wide-format printers- Banners, posters, murals
- Vehicle image wraps
- Architectural drawings and construction plans
- Theatre and TV studio backdrops
- Signage
Benefits of wide-format printers
- Economical for small volume printing
- Can print in a variety of larger sizes, using continuous rolls of paper
Drawbacks of wide-format printers
- Initial cost is expensive
2D Cutter
What is a 2D cutter?
A 2D cutter is an output device capable of cutting holes or shapes into a flat 2D surface.
Examples range from inexpensive paper/card cutting machines used by craft enthusiasts, to industrial models used in manufacturing to cut through metal.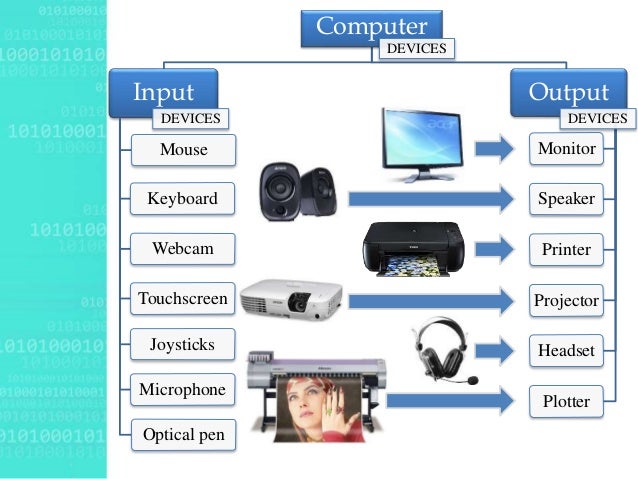
- Manufacturing (laser cutters)
- Craft projects (paper and card blade cutters)
Benefits of 2D cutters
- Fast and consistently accurate cuts can be made all day long
Drawbacks of 2D cutters
- Some industrial models can be expensive to setup and maintain
- Output is only as good as a the computer 2D model
3D Cutter
What is a 3D cutter?
A 3D cutter is similar to a 2D cutter except it is capable of rotating and cutting at many angles. This means that 3D objects can have cuts made to all of its surfaces, unlike 2D cutters that can only cut into a flat 2D surface.
3D cutters come in many varieties, some of which do not use lasers.
Typical applications for 3D cutters- Manufacturing
Benefits of 3D cutters
- Fast and consistently accurate cuts can be made all day long
- All sides of an object can be cut into
Drawbacks of 3D cutters
- Can be expensive to setup and maintain
- Output is only as good as a the computer 3D model
Speakers and Headphones
What are speakers and headphones?
Speakers and headphone are the output devices responsible for producing sounds.
Speakers and headphones convert digital signals into analogue sound waves that are audible to our human ear drums.
Speakers come as standard is most portable computing devices. Desktop computers usually require the purchase of separate speakers.
Speakers and headphones aren’t just for music, they also allow us to hear computer warning signals and other people when communicating via voice or video calls.
Typical applications for speakers and headphones- Headphones keep sound personal so as not to disturb others
- Speakers allow for sound that can fill the room
- Music
- Communications (phones, tablets, laptops)
Actuators
What is an actuator?
Actuators are the output devices responsible for creating real world movement. This could range from physically opening automatic shop doors to lowering the landing gears on a plane.
They are often used in a computerised control system, acting upon a signal sent by the microprocessor. Actuators include electric motors, pistons and pumps.
Actuators include electric motors, pistons and pumps.
3D Printer - Javatpoint
| next → ← prev What are printers?A printer is an electronic device that transfers the information and graphics from the computer to paper in the printed form. A printer can be used with mobile phones, personal computers, or laptops. The output document or a file can be in the form of only text information, graphics or images, or the combination of both text and graphics. We need to provide an input command to the printer attached to the device to produce the output. What are 3D printers?3D printers are the hardware devices that produce 3D printing outputs in paper instead of a product. It can also produce a 3D model from ready to print CAD files. It uses less material as compared to other manufacturing processes. The output is generally in the form of a 3D object. 3D printers use a different material, such as stereolithography materials, nylon, photopolymers, etc. The common uses of 3D printers are to produce a prototype, miniature models, etc., for testing or development. The term is generally confused with regular printers. But it is different from the traditional printers. Today, printers are available is wide sizes and prices according to the specific features. Here, we will discuss 3D printers, 3D printing, types of 3D printers, etc. Let's start. Printers are commonly classified as 2D printers and 3D printers. Let's first discuss 3D printers in detail. 3D printers do not require any ink for printing. As discussed, the output of the 3D printers is in the form of a 3D model, prototype, or object. Working on a 3D PrinterWe have discussed 3D printers. But, we must be confused about how the printing process works in a 3D printer. The input of a printer requires a file for printing. Various file formats can be used as an input file for a 3D printer. It means that the required input file should be a 3D file. We can also use any 3D software to convert a flat file into a 3D file. We can also say that the required file is a blueprint of the object to be formed. The file consists of related information, such as geometry, color compositions, structure, materials, etc. When a file is ready as per the requirements, we can send the file to a 3D printer. The printer uses raw materials, such as resins, thermoplastics, powders, melted solids, etc., to convert that 3D image into a 3D model. The printing process is quick and uses fewer materials than another manufacturing process to produce the same output. Let's discuss the differences between 3D printers and 2D printers. It will help us to understand the process and applications of both printers. 3D Printers vs. 2D Printers3D printers are considered better than 2d printers. Let's discuss the differences between 3D printers and 2D printers. It is listed in the below table.
3D PrintingMost of the 3D printing files are the output of the CAD modules created in the computer system. 3D printing produces a 3D model from a CAD file or other 3D file systems. Let's discuss the 3D printing technologies. It will help us to clearly understand the materials and the process of different 3D printing technology in various 3D printers. 3D Printing TechnologyVarious 3D printers vary as per the printer cost, quality, speed, etc. The 3D printers depend on the 3D printing quality of various printers. The different types of 3D printers are listed below:
Let's discuss this in detail. StereolithographySLA or Stereolithography 3D printers have various advantages, such as smooth and quality finish, great details, etc. It is the world's first 3D technology used for 3D printing. It was developed around 1986. SLA uses a solid-state laser to cure the part of the product. But, DLP (Digital Light Processing) can take a shorter time to trace the object's cross-section compared to SLA. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)FDM technology is based on thermal plastic materials for 3D printing. It is generally a spool of filament that is loaded inside a 3D printer. The brands that use FDM for manufacturing 3D objects are Nestle, BMW, etc. It follows the sanding process and finishing process after the printing. Such a printer also can extrude the objects. The extrusion is carried out through the nozzle and the base. Fused Deposition Modeling is popular for creating prototype and concept models. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)SLS works with a wide variety of materials, such as ceramics, metals, powders, etc. SLM (Selective Laser Melting)SLM is commonly used in mass production and building prototype. The primary difference between Selective Laser Sintering and Selective Laser Melting is the type of feedstock and the power material usage. Otherwise, both the processes are quite similar. SLS uses a different type of materials, while SLM is a process commonly for metals. LOM (Laminated Object Manufacturing)As the name implies, LOM uses heat and pressure to laminate or fuse plastic and paper parts. The product is further cut using the lasers into the desired shape. It is considered one of the fastest and inexpensive 3D printing processes to create a prototype model. BJ (Binder Jetting)The 3D printing process is a layering process. It means one layer is formed at a time. In the Binder Jetting process, a binder is used to fuse the areas. We can say that the binder acts as a bonding material. MJ (Material Jetting)Material Jetting printers work in a similar way to 2D printers. A layer is build using the printhead droplets (like the ink) that are cooled using UV light. The materials used in the droplets are the photosensitive material. It offers high accuracy with a smooth surface finish. DLP (Digital Light Processing)DLP is a similar technology to SLA. It was developed around 1987. DLP is also considered the oldest 3D technology used for 3D printing. It uses modern light sources, such as arc lamps. But, SLA uses an ultraviolet light source. It also prints faster as compared to SLA. EDM (Electron Beam Melting)As the name signifies, it uses an electron beam to fuse parts. The electronic beam originates from an electronic laser. The material used is generally metal rather than thermoplastics. Types of 3D PrintersHere, we will discuss the types of 3D printers that are based on the 3D technology discussed above.
Advantages of 3D PrintersThe advantages of 3D printers are listed below:
DisadvantagesThere are also some disadvantages of the 3D printers. Let's discuss some of the most common disadvantages.
Top Manufacturers of 3D Printers in IndiaThe manufacture of 3D printers in India has reduced transportation costs from abroad, such as China. Today, 3D printers are easily available in various designs and features.
Next TopicCardboard ← prev next → |
3D printers. Rapid prototyping technology for KOMPAS-3D models
ASCON actively cooperates with hardware manufacturers. We are confident that this cooperation will contribute to the development of modern technologies and their successful application in various sectors of the economy.
The ability to quickly and easily create physical prototypes of 3D models of new products or construction objects speeds up the development process, and we hope that users will appreciate our initiatives.
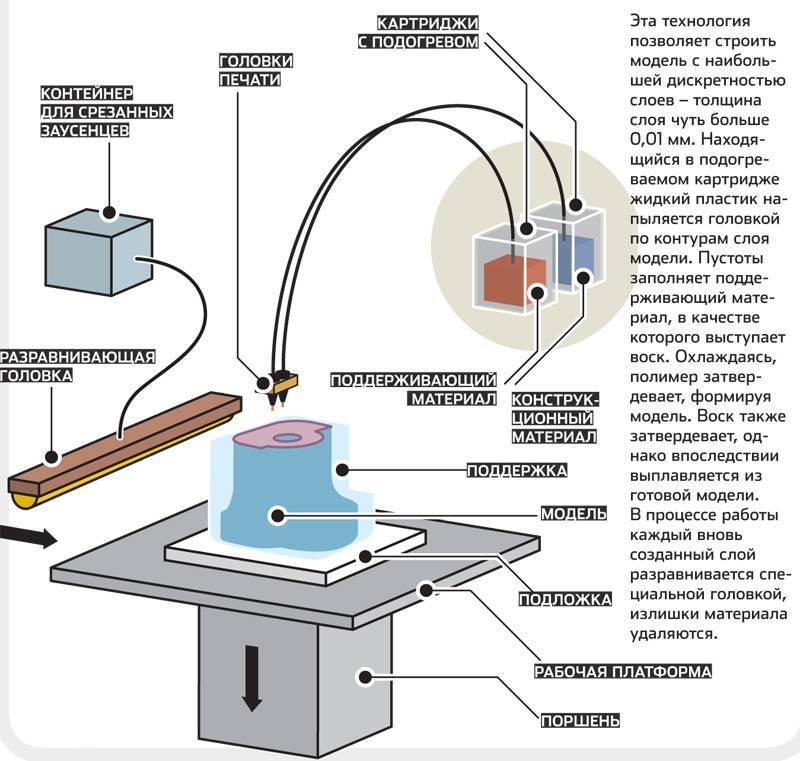
How does a 3D printer work?
A three-dimensional or 3D printer is a device for outputting three-dimensional data (usually three-dimensional geometry). The result of his work is some physical object, a prototype.
There are several 3D printing technologies, but all of them are based on the principle of creating solid geometry layer by layer.
Prototyping procedure
- Development of a 3D model in the KOMPAS-3D system.
- Export geometry to STL or WRL format.
Saving in *.Stl format.
Starting from version V15.1 in KOMPAS-3D, the dialog for setting saving parameters in Stl has changed. If earlier the setting depended on the accuracy parameters set for the part, then in the new version the dialog Stl export parameters appeared.
Parameters dialog for writing to STL format. Description.
The dialog appears on the screen when exporting a model to STL format. Surfaces existing in the model are transferred to the STL format as polyhedral surfaces with triangular faces. The process and result of constructing a finite number of non-overlapping triangles that join each other along common sides is called by triangulating . The segments connecting the vertices of the triangles are called edges .
Surfaces existing in the model are transferred to the STL format as polyhedral surfaces with triangular faces. The process and result of constructing a finite number of non-overlapping triangles that join each other along common sides is called by triangulating . The segments connecting the vertices of the triangles are called edges .
Triangulation parameters are configured in the dialog.
Description of controls
| Item | Description |
| Items | The group of options allows you to control the export of model objects. When the corresponding options are enabled, the following objects are exported:
|
| Coordinate system | The list allows you to select the CS that contains the coordinates of the vertices and normal vectors of triangular faces.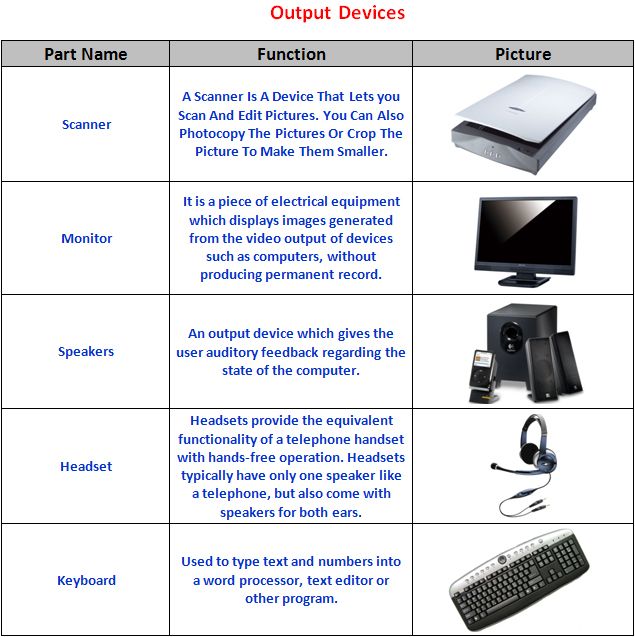 The list is not available if only the absolute coordinate system exists in the model. The list is not available if only the absolute coordinate system exists in the model. |
| Units of length | The list allows you to select a unit of length for recording the coordinates of vertices and normal vectors of triangular faces. |
| Approximation accuracy | Group of options that allows you to set approximation parameters. At least one option from the group must be enabled. |
| Maximum linear deviation | Enabling this option allows you to set the maximum allowable deviation along the normal of the triangular face of the transferred surface from the original surface. Deviation can be set using the "slider". To change the deviation value, move the "slider" on the scale between the extreme left ("coarse") and extreme right ("fine") positions. The range of allowable values depends on the dimensions of the model. The desired value can be entered manually in the field to the right of the scale. |
| Maximum angular deviation | Enabling this option allows you to set the maximum allowable angle between the normals of adjacent triangular faces of the transferred surface. Deviation can be set using the "slider". The range of allowable values of the angular deviation is 45–0.1 (in degrees). The desired value can be entered manually in the field to the right of the scale. The maximum allowable value is 90. |
| Maximum fin length | Enabling this option allows you to set the maximum edge length. The range of allowable values depends on the dimensions of the model. |
After completing the settings, click OK. To exit the dialog without writing the file, click the Cancel button.
Save results with different parameters for a ball with a diameter of 50 mm.
Microsoft 3D Builder is used to evaluate parameters
Maximum linear deviation
Maximum angular deviation
Maximum edge length
- Opening a file with geometry in a special program - a slicer that serves a 3D printer.

The main function of the slicer is to cut a solid object into many layers of small thickness and create a G-code - a set of commands for creating 2D images (sections) of each layer in a plane perpendicular to the Z axis.
If the model has a complex shape, the slicer can create supports - additional sections of material that are separated after the model is made.
In addition to cutting models into layers, the user can use additional functionality, for example, change the view, scale, rotate, label, multiply models.
- Send G-code to 3D printer.
Sending is carried out either via a network, or via cable, or by recording to a media (memory card). - Layer-by-layer "growing" of a three-dimensional model in the working chamber of a 3D printer.
- Removing the finished model from the printer.
- If necessary, separation of supports from the model and additional processing of the model.
- Hercules 3D printers
- 3D printers ZPrinter
- PICASO 3D 3D printers
3D printer - Computer device
| 3D printing is the construction of a real object based on a 3D model created on a computer. Then the digital three-dimensional model is saved in the STL file format, after which the 3D printer, to which the file is output for printing, forms a real product. The printing process itself is a series of repetitive cycles associated with the creation of three-dimensional models, applying a layer of consumables to the desktop (elevator) of the printer, moving the desktop down to the level of the finished layer and removing waste from the surface of the table. The cycles follow one another continuously: the next layer of material is applied to the first layer, the elevator is lowered again and so on until the finished product is on the working table. The principle of operation of a 3d printer is based on the principle of gradual (layered) creation of a solid model, which, as it were, is “grown” from a certain material, which will be discussed a little later. The advantages of 3D printing over the usual, manual methods of building models are high speed, simplicity and relatively low cost. For example, manually creating a 3D model or a part can take quite a long time - from several days to months. After all, this includes not only the manufacturing process itself, but also preliminary work - drawings and diagrams of the future product, which still do not give a complete vision of the final result. As a result, development costs increase significantly, the period from product development to its mass production increases. 3D technologies, on the other hand, allow you to completely eliminate manual labor and the need to make drawings and calculations on paper - after all, the program allows you to see the model from all angles already on the screen, and eliminate the identified shortcomings not in the process of creation, as is the case with manual production, but directly during development and create a model in a few hours. This virtually eliminates the possibility of manual errors. 1. Medicine. First of all, the stereolithography method has been used for quite some time now to obtain customized dental braces based on a patient's oral cavity scan. The material is a polymer that is harmless to humans. This method of orthodontics is used by Align Technology. Siemens, on the other hand, makes hearing aids that are perfectly compatible with the ears of patients. 2. 3D printing is used to manufacture the tubes used in the production of F-18 fighter jets. In fact, the first bioprinter has already been created by Invetech engineers and Organovo medical specialists. The material for products in it are very small clusters of cells, "fused" into one whole according to a given pattern. |


 that forms the output object.
that forms the output object.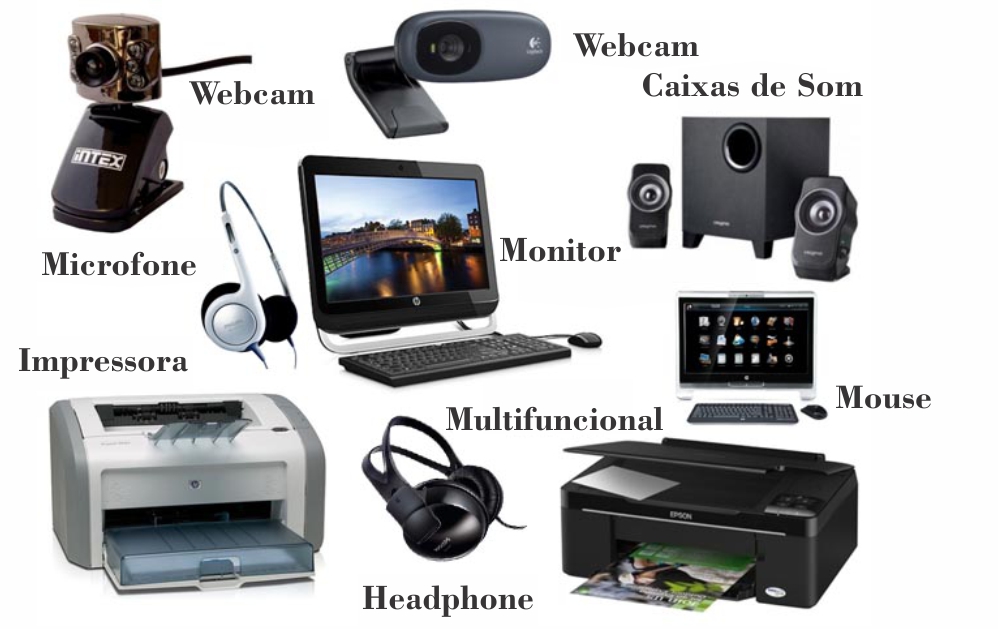 The input file is generally a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or STL (Standard Triangle Language) file.
The input file is generally a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) or STL (Standard Triangle Language) file.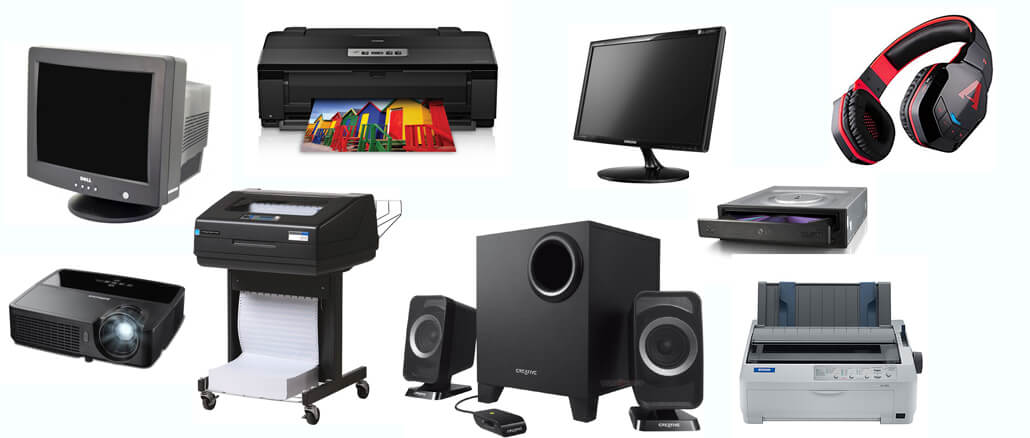 It is because 3D printers produce the output as a real 3D object rather than printing on paper. On the other hand, 2D printers are easily accessed by anyone to convert the soft copies into hard copies. It is cheap and affordable. But, 3D printers are mostly used in industries and are not affordable.
It is because 3D printers produce the output as a real 3D object rather than printing on paper. On the other hand, 2D printers are easily accessed by anyone to convert the soft copies into hard copies. It is cheap and affordable. But, 3D printers are mostly used in industries and are not affordable.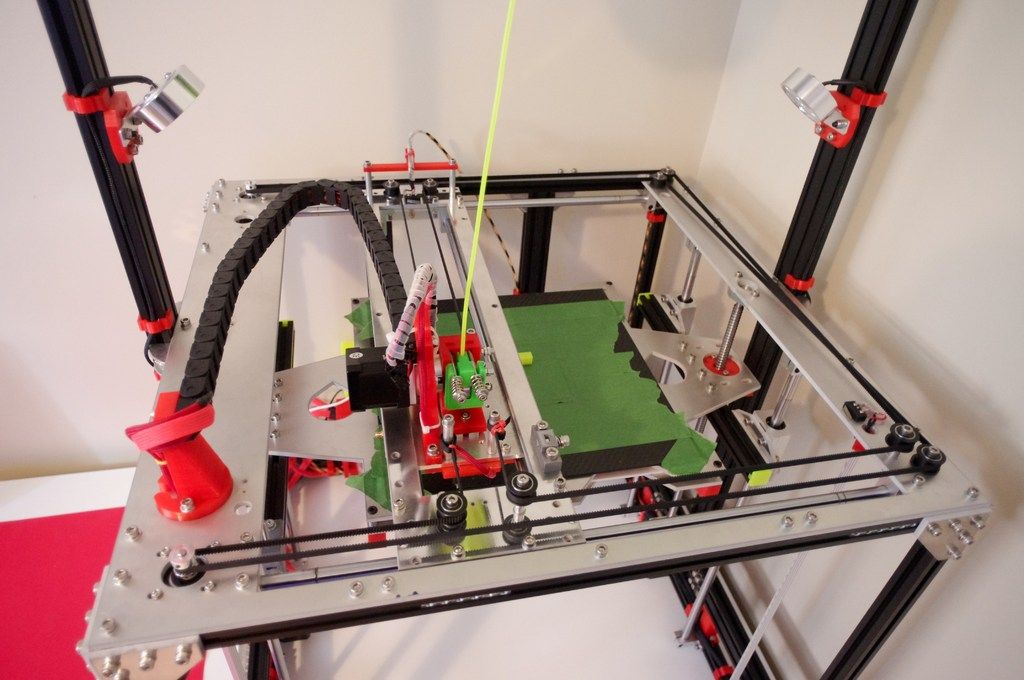 to produce the output 3D object.
to produce the output 3D object. The material is used to form a layer by layer structure, which further appears as a 3D model. 3D printing is generally a layering process. It means that the output produced is created layer by layer using a particular material. 3D printing can be performed using different materials, such as thermoplastics, powder, melted metals, etc.
The material is used to form a layer by layer structure, which further appears as a 3D model. 3D printing is generally a layering process. It means that the output produced is created layer by layer using a particular material. 3D printing can be performed using different materials, such as thermoplastics, powder, melted metals, etc.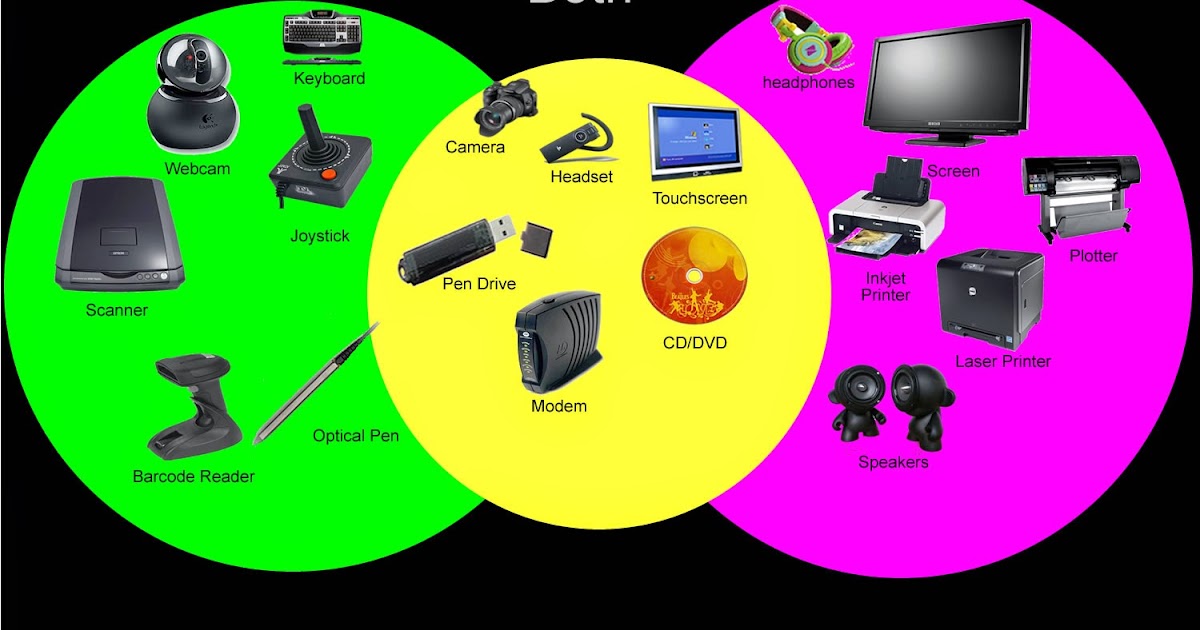
 SLS is generally preferred in aerospace manufacturing parts due to its high cost.
SLS is generally preferred in aerospace manufacturing parts due to its high cost. The common materials used by the BJ are metals, ceramics, etc. The applications of Binder Jetting include sand casting molds and the fabrication of color prototypes.
The common materials used by the BJ are metals, ceramics, etc. The applications of Binder Jetting include sand casting molds and the fabrication of color prototypes. Such a process takes place in a vacuum. It is because electron beams can collide with gas or air particles. EDM builds a layer of powder on the part and applies laser after the power is set. The electronic beam causes the powder to melt that further results in the joining of metal parts. 3D printing is a layering process. It continues till the final object is formed.
Such a process takes place in a vacuum. It is because electron beams can collide with gas or air particles. EDM builds a layer of powder on the part and applies laser after the power is set. The electronic beam causes the powder to melt that further results in the joining of metal parts. 3D printing is a layering process. It continues till the final object is formed.


 Let's discuss some of the top manufacturers of 3D printers in India.
Let's discuss some of the top manufacturers of 3D printers in India.