3D printer dimensions
3D Printers Dimensions & Drawings
Digital
>
Digital Products
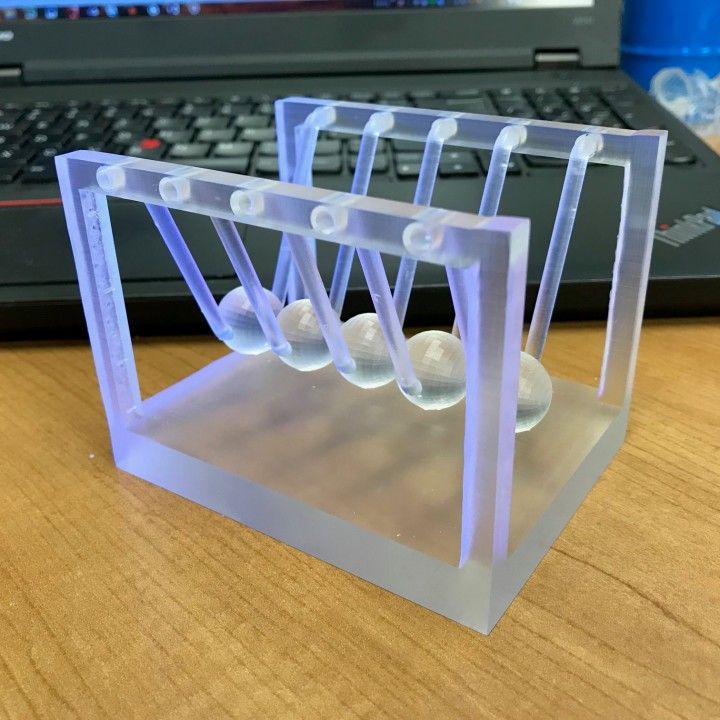
A 3D Printer is a square or rectangular machine which is able to create 3D objects out a variety of materials. An object is first modeled in a 3D program, and then sent to the 3D printer. The printer then splices the 3D object into layers, and is able to print from the bottom of the base to the top of the object over many hours. Depending on the machine, 3D printers typically utilize ABS, PLA, or PVA Filaments to print objects with. 3D Printers can often be found in design offices, schools, and even for the hobbyist in the occasional creative household.
What are the different types of 3D printers available?
Currently, there are 9 basic types of 3D printers available. The different types of 3D printers include Fused Deposit Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Digital Light Processing (DLP), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). The other types of 3D printers are Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Electron Beam Melting (EMB), Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM), Binder Jetting (BJ), and Material Jetting/Wax Casting.
Who invented the 3D printer?
The 3D printer was invented by Charles Hull in the mid-1980s. Charles Hull, later went on to fund the company 3D Systems, a company that sells 3D printers with a variety of technologies. These 3D printing technologies range from entry-level kits to advanced commercial 3D printing systems.
How can you make money with a 3D printer?
You can make money with a 3D printer by making pre-made 3D prints, offering specialized training on 3D printing, starting a 3D printing business, or even selling an online 3D printing course. You could also start a YouTube channel and create content on 3D printing or offer 3D scanning services.
3D Printers Guides
Browse through our curated 3D Printers Guides for additional categorizations, tips, details, variations, styles, and histories of 3D Printers. Guides provide additional insights into the unique properties and shared relationships between elements.
Guides provide additional insights into the unique properties and shared relationships between elements.
Sort by
Thank you! Your submission has been received!
Oops! Something went wrong while submitting the form.
15.7” | 39.9 cm
—
19.1” | 48.5 cm
—
13.2” | 33.5 cm
—
15.7” | 39.9 cm
—
—
19.8 lb | 9 kg
—
—
Dremel 3D20
39.900
48.500
33.500
9.000
1200
3D
16” | 40.6 cm
—
20.25” | 51.4 cm
—
15.9” | 40.4 cm
—
—
—
43.6 lb | 19.8 kg
—
—
Dremel 3D40
40.600
51.400
40.400
19.800
400
3D
16” | 40.6 cm
—
20.25” | 51.4 cm
—
15.5” | 39.4 cm
—
—
—
35 lb | 16 kg
—
—
Dremel 3D40 Flex
40.600
51.400
39.400
16.000
5
3D
16” | 40.6 cm
—
20.25” | 51.4 cm
—
15. 9” | 40.4 cm
9” | 40.4 cm
—
—
—
47.5 lb | 21.5 kg
—
—
Dremel 3D45
40.600
51.400
40.400
21.500
1750
3D
18” | 45 cm
—
12” | 30 cm
—
11” | 28 cm
—
—
—
18 lb | 8 kg
—
—
Formlabs Form 1+
45.000
30.000
28.000
8.000
200
3D
20.5” | 52 cm
—
13.6” | 34.5 cm
—
13” | 33 cm
—
—
—
28.5 lb | 13 kg
—
—
Formlabs Form 2
52.000
34.500
33.000
13.000
5200
3D
20.9” | 53 cm
—
15.9” | 40.5 cm
—
14.8” | 37.5 cm
—
—
—
38.5 lb | 17.5 kg
—
—
Formlabs Form 3
53.000
40.500
37.500
17.500
2500
3D
28.9” | 73.5 cm
—
30.5” | 77.5 cm
—
20.5” | 52 cm
—
—
—
120 lb | 54 kg
—
—
Formlabs Form 3L
73. 500
500
77.500
52.000
54.000
10
3D
25.6” | 64.9 cm
—
17.2” | 43.7 cm
—
16.3” | 41.3 cm
—
—
—
65 lb | 29.5 kg
—
—
MakerBot Method
64.900
43.700
41.300
29.500
1000
3D
33.9” | 86.1 cm
—
19.4” | 49.3 cm
—
22.2” | 56.5 cm
—
—
—
90 lb | 41 kg
—
—
MakerBot Replicator Z18
86.100
49.300
56.500
41.000
700
3D
16.2” | 41 cm
—
20.8” | 52.8 cm
—
17.4” | 44.1 cm
—
—
—
40.4 lb | 18.3 kg
—
—
MakerBot Replicator+
41.000
52.800
44.100
18.300
2500
3D
19.2” | 48.8 cm
—
13.5” | 34.2 cm
—
14” | 35.7 cm
—
—
—
27.1 lb | 12.3 kg
—
—
Ultimaker 2 Extended+
48.800
34.200
35.700
12. 300
300
200
3D
15.3” | 38.8 cm
—
13.5” | 34.2 cm
—
14” | 35.7 cm
—
—
—
24.9 lb | 11.3 kg
—
—
Ultimaker 2+
38.800
34.200
35.700
11.300
2400
3D
15.3” | 38.9 cm
—
13.46” | 34.2 cm
—
14.96” | 38 cm
—
—
—
23.4 lb | 10.6 kg
—
—
Ultimaker 3
38.900
34.200
38.000
10.600
9700
3D
19.25” | 48.9 cm
—
13.46” | 34.2 cm
—
14.96” | 38 cm
—
—
—
24.9 lb | 11.3 kg
—
—
Ultimaker 3 Extended
48.900
34.200
38.000
11.300
700
3D
16.46” | 41.8 cm
—
15.5” | 39.4 cm
—
14.96” | 38 cm
—
—
—
31.7 lb | 14.4 kg
—
—
Ultimaker S3
41.800
39.400
38.000
14.400
70
3D
20.5” | 52 cm
—
19. 5” | 49.5 cm
5” | 49.5 cm
—
18” | 45.7 cm
—
—
—
39.7 lb | 18 kg
—
—
Ultimaker S5
52.000
49.500
45.700
18.000
2900
3D
47.1” | 119.7 cm
—
19.5” | 49.5 cm
—
19.5” | 49.5 cm
—
—
—
92.4 lb | 41.9 kg
—
—
Ultimaker S5 Pro Bundle
119.700
49.500
49.500
41.900
5
3D
Related Digital Collections
Digital
View the CategoryMore
Understand Units and Sizes for your 3D printing Dimensions
3D Learning Hub
See all categories
Contents:
- Introduction
- How to Choose a Unit of Measure for your CAD File
- Dimension, Weight and Size Constraints of a 3D printing
- Modify the Size of Your 3D Printed Object
Introduction
Designing for 3D printing requires to keep in mind that your object will be a physical object with weight, size and constraints. Even if your object is coherent and seems to be at the dimensions you wish on the screen, it is really important to check if the 3D printed object will match your expectations and the machine constraints. Here are some tips to help you manage the units and size for 3D Printing with Sculpteo.
Even if your object is coherent and seems to be at the dimensions you wish on the screen, it is really important to check if the 3D printed object will match your expectations and the machine constraints. Here are some tips to help you manage the units and size for 3D Printing with Sculpteo.
How to Choose a Unit of Measure for your CAD File
Whether you use the metric system or not, you need to know the exact size and dimension of your model.
Quite frequently, when you create a new file or scene in your CAD software, you are asked what unit of measure you want to use for this modeling project.
If not, you can modify it in the software settings. We wrote tutorials for the most used CAD software, that you can discover here.
On Sculpteo the default measure unit set is the millimeters, but you can choose, before you upload your file, between Millimeters, Centimeters and Inches as unit of measure for your 3D print.
Be careful however because if you designed your model in centimeters in your CAD software, when you’ll upload it on Sculpteo and choose millimeters, your object’s unit of measure will be changed.
For example, a cube of 10x10x10cm will become a 10x10x10mm cube. That’s why it’s extremely important to choose the same unit on our platform as you did on your CAD software.
If you forget to choose the unit of measure before uploading your file, don’t worry! You can still do it afterwards.
In the 3D printing settings tab, under Review and Checkout, you can see a recap of the options you chose before placing your order. If the measure unit doesn’t match your CAD file settings, modify it. As you change the settings, the price will automatically adjust (as you can see on the image below).
Dimension, Weight and Size Constraints of a 3D printing
The 3D printing process observes some constraints depending on the material you choose and the associated 3D printer.
The printing surface is indicated on the material page of our Learning Center.
For example, 3D printing in white plastic polyamide (PA11) with raw finish involves a maximum size of 677 x 368 x 565 mm.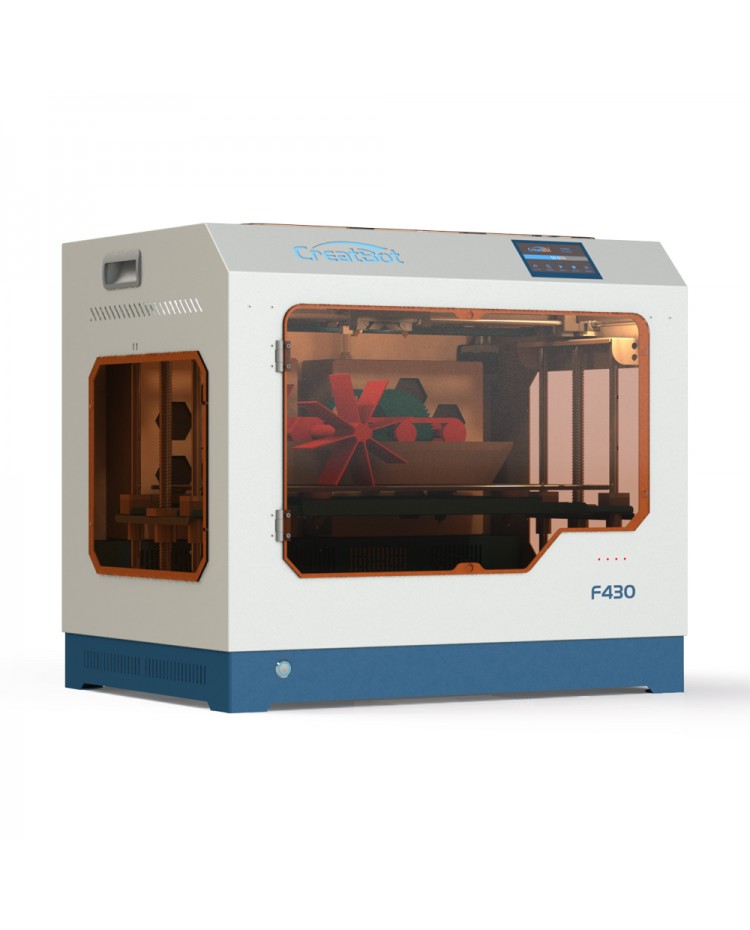
Depending on your material, finish and needs, the size plays a great role in the success of your 3D printing project.
To learn more about the material sizes of each material, you can visit our Learning Center.
The weight of your model also plays a role in the price and the size of your object. A bigger object involves more raw material, which leads to a more expensives and heavy object.
To counter this effect, you can hollow your model in your CAD software or directly on Sculpteo with our automatic Hollowing tool.
You just have to place two holes on your model to allow the unfused material to be evacuated, your model to become lighter, and its price to be reduced in real time on the platform.
Modify the Size of Your 3D Printed Object
As you are going to transform a digital model (you CAD file) into a physical object (the 3D printed object), it is quite important to control the size of what you designed.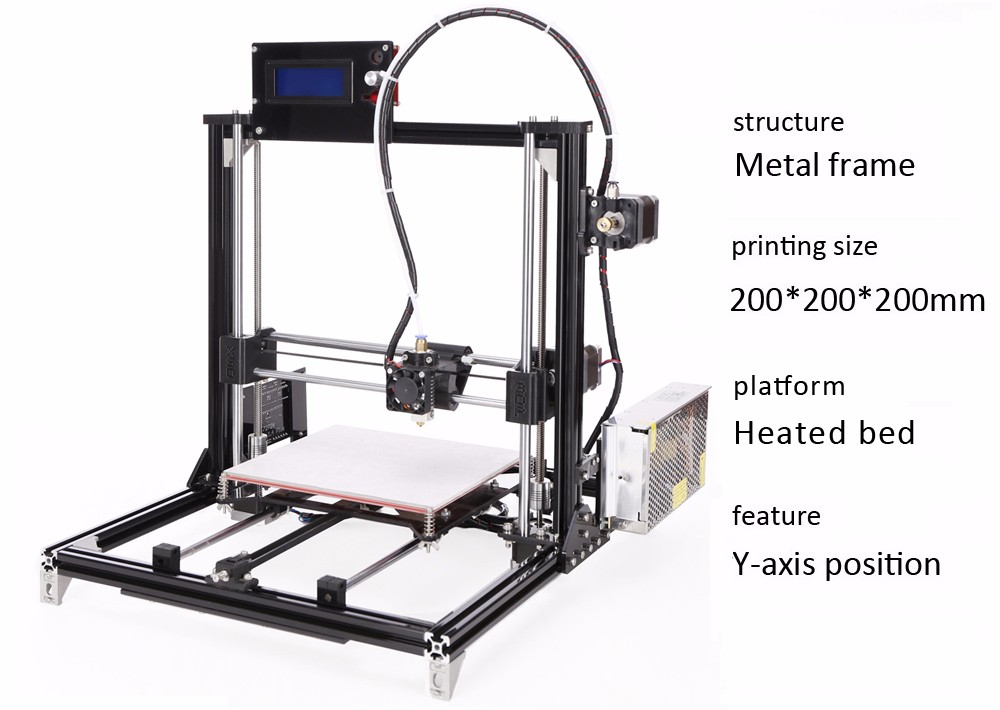
To modify the size of your object in your CAD software, you can see our tutorials on how to prepare your CAD file for 3D printing.
The method consists in using a measure tool on each part to check if the object is at the right size. Another technique is to create a cube you know the dimensions of outside of your model. When your object is inside of the cube, you obtain the approximative area occupied by your object in the machine’s tray.
We did a video to show you step by step how to control the size of your object in 3Dstudio Max.
As you can see, this method is slow and specific. To simplify the process, we decided to provide a scaling tool directly on Sculpteo that allows you to modify the global scale of your object and see the impact on the price.
To use that tool, you just have to go in the 3D Printing Settings and modify the scale values. The online tool scales the object proportionally in every axis to keep its proportions.
Be careful however to not oversize your object as it has to fit in the machine’s tray. A message will display if the object size exceed the machine’s capacity.
A message will display if the object size exceed the machine’s capacity.
On the contrary, do not reduce too much the scale of your object as finest parts may not be 3D printed. Our online solidity check tool will verify if the thinnest parts could be printed or not and warn you about it. If parts of the model are too thin, our thickening tool could fix the issue directly online.
To learn more about the help tools to optimize your file, you can visit our Learning Center and upload a file
Related Topics
- Return to Top
Get the latest 3D printing news delivered right to your inbox
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to hear about the latest 3D printing technologies, applications, materials, and software.
3D printer print size - 1.2 x 1.5 x 1.8 m. by Sprint 3D.
Rapid prototyping of large-scale art products
In the minds of many contemporaries, 3D printing is a technology that can create extremely small objects - spare parts, souvenirs, various kinds of models, and so on. Moreover, many believe that it takes many hours. In the meantime, a whole car has already been created through 3D printing. And it didn't take weeks. Let's consider which print size 3 D printer is possible today and what print speed 3 D print is currently being achieved. But first, a few words about prototyping.
Moreover, many believe that it takes many hours. In the meantime, a whole car has already been created through 3D printing. And it didn't take weeks. Let's consider which print size 3 D printer is possible today and what print speed 3 D print is currently being achieved. But first, a few words about prototyping.
Rapid prototyping of 3D models is a process of rapid creation of mock-ups of models (prototypes), which will later be used to improve and finalize design solutions. In some cases, such prototypes can also be used as finished products.
Satellite 3D Printer 500x500x800 cm
Modern 3D Printer Capabilities
3D printing equipment has made a huge leap forward in recent years. One of the brightest representatives of the new generation of printers for rapid prototyping of dimensional art products is the 3D printers that we use in our work.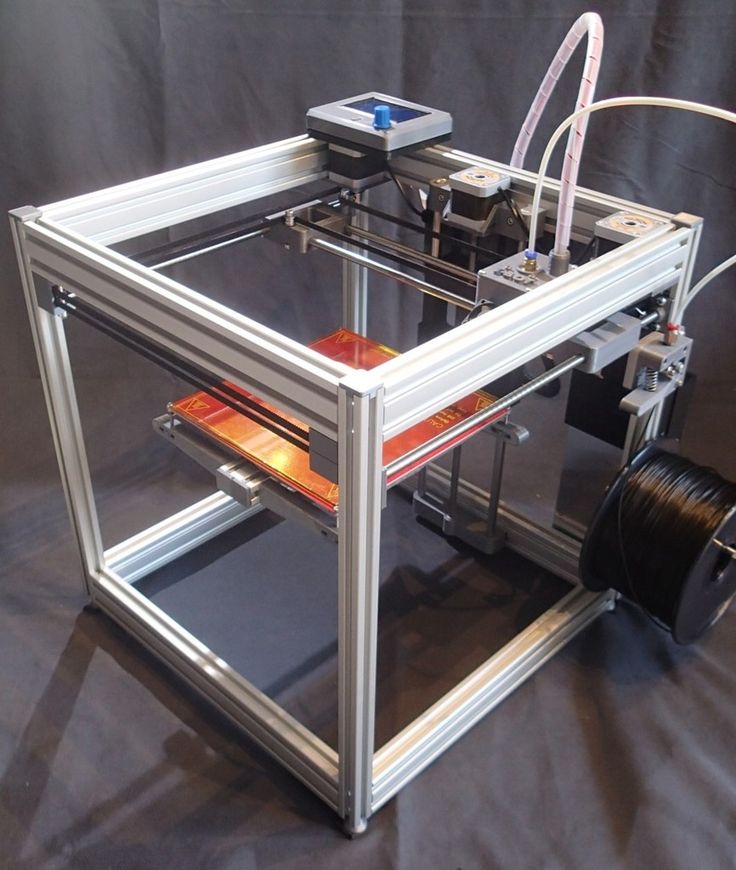
Main equipment features:
- Working area - up to 1.2x1.5x1.8 m.
- Speed 3 Printing D of along the Z axis (in height) - 35 cm / hour.
How do you achieve high print speeds and the ability to produce large items? First of all, due to the use of special photopolymer gel compositions with a high degree of viscosity, as well as due to the rationalization of the placement of supporting structures. The so-called GDP-technology (Gel Dispensed Printing) is used. It is based on the use of liquid light-sensitive compounds that quickly harden under the influence of ultraviolet lamps. Those are located directly above the print heads and act directly on the material. This system ensures fast curing.
Due to the fact that the GDP technology cures faster than other technologies, it is not necessary to use supports for horizontal surfaces. Obviously this saves time. And at the same time, the materials of production.
Also note that 3D printer models and some analogues use two printheads that work independently of each other. This allows you to create two objects at the same time in one workspace or separate components of one large product. Accordingly, print size 3 D of printer in this case, when gluing, it increases at least twice and can exceed 3 meters.
Large-scale 3D printing: how much more difficult it is than small-sized
In fact, print size 3 D of the printer practically does not affect the complexity of production and subsequent post-processing. If in older models of printers there could be cases when the material clogged the nozzle and the work done simply went down the drain, then modern equipment is devoid of such shortcomings. You don’t have to worry that something will go wrong in the many hours of printing and you will have to redo everything from the beginning, wasting time and a lot of resources.
Separately, we note the simplicity of the post-processing process. After hardening, the gel lends itself perfectly to a wide variety of processing. It is perfectly painted and varnished, which opens up the widest possibilities for creating a wide variety of dimensional objects: stands, product models, models of equipment and much more. Everything is fast, convenient and at the same time quite inexpensive. The printing process itself and finished products meet the requirements of environmental friendliness and safety of use. During production, no harmful and dangerous substances are emitted, and the printed products fully comply with modern environmental standards and are hypoallergenic. This is a particularly important factor at the present time.
How does 3D prototyping work? A physical structure is built according to a previously prepared mathematical model.
The advantages of prototyping are obvious:
1. Visibility of the whole process;
2.
 Minimization of the time required for preparation of production;
Minimization of the time required for preparation of production; 3. Reduce engineering and design costs.
The first step in prototyping is mathematical modeling, which creates a mathematical model in STL format. After that, prototypes are finalized to create the necessary surface textures. Prototyping also includes the development of technologies, the production of specific models and their finishing. Everything is almost identical to small-sized printing, although products are made with many times larger sizes.
Advantages of rapid prototyping in large-scale printing:
- Accurate and fast verification of the conformity, function and form of the printed design.
- Extensive design flexibility and versatility with the ability to quickly transition between different stages of production.
- Increased speed 3 D print and no waste of materials that are already used in large quantities.

- Ability to quickly test the properties of specific products in order to further develop new materials and at the same time obtain new properties of finished products.
- Minimize the risk of any design errors and improve the quality of finished products.
If printing on a 3D printer with a working area of 1.2x1.5x1.8 m is also relevant for you, SPRINT3D is at your service. Modern technological equipment for dimensional printing, high-quality materials and professionalism at all stages of production - all this the SPRINT3D team provides to each client.
Still have questions? Use the feedback form on the website or call + 7 (929) 680 27 76.
8 nuances worth paying attention to / Habr
Sooner or later, everyone learns about 3D printing. And only a few lucky people, imbued with the opportunities that 3D printing opens up, catch themselves thinking that they want to purchase a 3D printer. The desire gradually develops into a serious decision and the search for the right option begins. And here the potential buyer is faced with the fact that he does not fully understand what to choose among the whole variety of 3D printers. We will try to answer this question in as much detail as possible.
The desire gradually develops into a serious decision and the search for the right option begins. And here the potential buyer is faced with the fact that he does not fully understand what to choose among the whole variety of 3D printers. We will try to answer this question in as much detail as possible.
What to pay attention to and how to make a choice? We want to offer a small checklist of the nuances that you need to pay attention to when choosing a 3D printer.
You need to decide for yourself what tasks you will use this technique for? What capabilities should a 3D printer have to solve your problems?
Point 1: Decide on a 3D printing technology
The first step is to decide on the technology of 3D printing. There are two main paths here.
If you are faced with the task of manufacturing high-precision and miniature products, such as jewelry, then 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology are suitable for you. Such printers are specially designed for the manufacture of high-precision models. 3D printing in these printers occurs using a laser beam that illuminates the photopolymer resin. Hence the accuracy of the models.
Such printers are specially designed for the manufacture of high-precision models. 3D printing in these printers occurs using a laser beam that illuminates the photopolymer resin. Hence the accuracy of the models.
Prominent representatives of this segment: Form 2 3D printer or B9Creator 3D printer
If you are faced with a wider range of tasks, and functionality, part size, and low manufacturing cost are more important, then an FDM printer will suit you. 3D printing on this equipment involves layer-by-layer melting of plastic.
If everything is clear for SLA printers. The scope of their application is jewelry, dentistry, high-precision prototypes of small parts. Then we will dwell on FDM printers in more detail. There is a lot more variety of different options for implementing printers.
Nuance 2: Evaluate your needs
Of course, you always want to get all the best and with maximum opportunities. Do you need all this to solve your current problems?
What can be an example? For example, the size of the working area of the FDM 3D printer.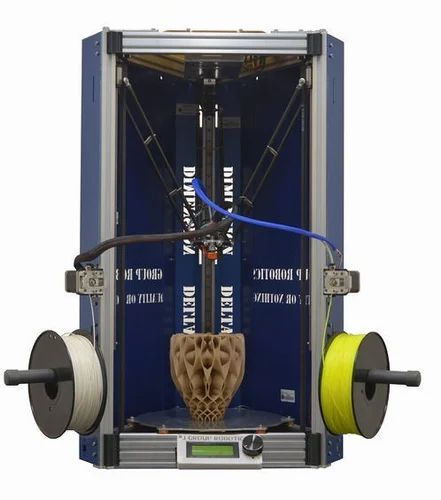 There are printers on the market with a large print area (1m x 1m x 1m), and with a very small one (100mm x 100mm x100mm). But for most tasks, a certain standard has already developed. This is the printable area within 200 x 200 x 200 mm. With slight fluctuations in size in one direction or another. Most 3D printers have exactly this size of the working area. This volume is enough to solve 95% of any tasks.
There are printers on the market with a large print area (1m x 1m x 1m), and with a very small one (100mm x 100mm x100mm). But for most tasks, a certain standard has already developed. This is the printable area within 200 x 200 x 200 mm. With slight fluctuations in size in one direction or another. Most 3D printers have exactly this size of the working area. This volume is enough to solve 95% of any tasks.
But options are possible...
If you plan to make small parts, then a smaller size may be enough for you. But if your work will be related to manufacturing, for example, a master model for casting, or large prototypes, then only then it makes sense to pay attention to a printer with a large print area.
In other cases, the size of the printable area larger than the standard is nothing more than a nice bonus. But as they say, you have to pay for everything. Therefore, most often it makes sense to focus on the “standard” print area. And even if the part you need to print is larger than the working area of your 3D printer, you can always cut it in a special editor, and then print 2 parts of the model and glue them together.
Point 3: Decide on the complexity of the products
You should decide for yourself how complex models you will print on a 3D printer. If you plan to manufacture complex prototypes, or complex art models, then you need a 3D printer that can print with two materials. This is necessary so that your printer can print supports from soluble material. If the models are not the most complex, then you can get by with one extruder and save the budget. A complex model is a model with a large number of elements suspended in the air, or a model whose elements have angles greater than 30 degrees.
Point 4: Decide on the list of materials used.
Another important point. You must immediately determine for yourself a list of possible materials with which you are going to print. This primarily applies to materials with a high degree of shrinkage, such as ABS and Nylon. In order to print with such materials, a heated table is clearly required in a 3D printer. And it is very desirable to have a closed case to provide a thermal circuit around the model.
And it is very desirable to have a closed case to provide a thermal circuit around the model.
If you plan to print with PLA only. You don't need a heated table.
But still it is better that the printer has a heated table. Now the difference in the cost of printers with a heated table is practically the same as the cost without it. But you get a universal solution with which you can perform a full range of tasks facing a 3D printer.
One more thing. Possibility of printing with flexible materials.
Quite a number of 3D printers face the problem of printing with flexible materials. Of course, printing with various Flexes and Rubbers is very interesting at first glance. But the use of these materials in life is not very common.
Usually, for most people, this happens like this:
A couple of models are printed, the understanding comes that this is not a fast and rather complicated process. And this is where the acquaintance with flexible materials ends. Therefore, it makes sense to demand such an opportunity from the printer if printing with such materials is very necessary.
Therefore, it makes sense to demand such an opportunity from the printer if printing with such materials is very necessary.
Point 5: Construction and kinematics
Next, you need to pay attention to the design of the 3D printer. Even if you are not a great specialist in technology, you can immediately see that some printers have an open design. And others are closed. As they like to be called in the Russian-speaking community "cubes". What does the appearance say?
Printers with an open design, usually have kinematics with a horizontally moving table (based on Prusa 3D printers). This kinematics has some inherent flaws. Such as, not the highest print speed and possible print quality problems associated with the complexity of the settings. First of all, this is the so-called wobble.
Also, the lack of a closed housing can cause print quality problems with high shrink plastics (ABS, Nylon).
The main advantage of printers of this design is their price. It is usually lower. But as you know, you have to pay for everything. In this case, the worst performance. The so-called "cubes" today, is the main design, which is represented by leading manufacturers on the market. Such printers are built according to the scheme with a lifting table. And they lack most of the shortcomings that are inherent in printers from the previous group. “Cubes” usually have a closed body, which allows the highest quality printing with plastics with a high degree of shrinkage.
It is usually lower. But as you know, you have to pay for everything. In this case, the worst performance. The so-called "cubes" today, is the main design, which is represented by leading manufacturers on the market. Such printers are built according to the scheme with a lifting table. And they lack most of the shortcomings that are inherent in printers from the previous group. “Cubes” usually have a closed body, which allows the highest quality printing with plastics with a high degree of shrinkage.
Closed case printers are more rigid. This results in better quality printing.
Print head movement kinematics, available in various designs. They have their pros and cons. But most of them have advantages over moving table printer circuits.
Point 6: Diameter and changeable nozzle
Most 3D printers on the market come with 0.3-0.4mm nozzles. This is enough to solve the vast majority of tasks facing a 3D printer.
Some of the printers have the ability to install a nozzle of a different diameter, others do not. As we wrote above, the need to print with nozzles with a diameter other than 0.3-0.4 mm arises very infrequently. This mainly concerns, or personal experiments, or some very specific tasks. If you do not plan to do this, then this opportunity is not so necessary.
As we wrote above, the need to print with nozzles with a diameter other than 0.3-0.4 mm arises very infrequently. This mainly concerns, or personal experiments, or some very specific tasks. If you do not plan to do this, then this opportunity is not so necessary.
What do we mean by specific tasks?
This is especially true for large prints where it is important to reduce print times. This can be achieved by using large diameter nozzles. For example, with a diameter of 0.6-0.8 mm, or even a diameter of 1 mm. For printers with a large printable area, the ability to change nozzles is already a vital necessity.
So, just like with the heated table, the ability to change nozzles is a nice bonus. It is not mandatory, but very useful if you do not have to pay extra for it.
Point 7: Print thickness
It is important to understand that most models on a 3D printer are printed with a layer of 0.1-0.2 mm. These are the optimal values that allow you to achieve quality and acceptable print speed. There are a certain number of printers that allow you to print with a layer of less than 0.05 mm, and get very high quality prints. But then there is the problem of a sharp increase in print time. And if such print quality is important to you, then it probably makes sense to turn your attention to 3D printers, which we talked about at the very beginning of the article. These are 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology.
There are a certain number of printers that allow you to print with a layer of less than 0.05 mm, and get very high quality prints. But then there is the problem of a sharp increase in print time. And if such print quality is important to you, then it probably makes sense to turn your attention to 3D printers, which we talked about at the very beginning of the article. These are 3D printers using SLA or DLP technology.
Point 8: Extruder type
Today there are two main types of extruder. This is a direct extruder in which the bar feed motor is located in the printhead itself. And the so-called Bowden extruder, where the plastic feed motor is located on the body. And the plastic itself is fed to the extruder through a fluoroplastic tube.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of each type of extruder?
Bowden extruder, due to the absence of a motor on the print head, has a lower weight. And therefore, it has greater positioning accuracy, which affects the print quality. And a higher speed of movement, which, accordingly, has a positive effect on the speed of printing. But it has one drawback. It is usually quite difficult to print with flexible plastics on a Bowden extruder. Such as Rubber or Flex.
And a higher speed of movement, which, accordingly, has a positive effect on the speed of printing. But it has one drawback. It is usually quite difficult to print with flexible plastics on a Bowden extruder. Such as Rubber or Flex.
This extruder reveals all its positive features when using plastic with a diameter of 2.85-3.00 mm. But this type of plastic is less common than the now standard plastic with a diameter of 1.75 mm. And therefore, users of printers with such plastic are often deprived of the opportunity to use new types of materials. Which are primarily produced in the most common form factor of 1.75mm.
Direct extruder usually does not have such big problems with flexible plastics. Easier to set up, but due to the greater mass of the print head, it is inferior to the Bowden extruder in terms of speed and positioning accuracy.
Which do you prefer? This is the user's choice. We just wanted to talk about the pros and cons of these extruder types.
Of course, there are many more nuances when choosing a 3D printer. But we think that even our small list will force you to look and study some points that you may not have thought about more closely.
But we think that even our small list will force you to look and study some points that you may not have thought about more closely.
And will save you time and money when choosing a 3D printer.
3Dtool company has extensive experience in the 3D equipment market. We work with leading Russian and foreign manufacturers, offering high-quality equipment for a reasonable price. Our service center is staffed by highly qualified specialists who are able to solve any problem in the shortest possible time, and all offered 3D printers come with a 1-year warranty.
In our assortment you can always find 3D printers for your tasks:
1) Budget 3D printers
2) Business 3D printers
3) Large area 3D printers
4) SLA and DLP 3D printers
Do you have any questions? Call by phone: +7 (499) 992-72-23 (Moscow) and 8 (800) 775-86-69 (free of charge within the Russian Federation) or write to the mail: [email protected] and our employees will be happy to give you a detailed consultation on any topic of interest.