3D print service london
3DPRINTUK | 3D Printing Service London
PROFESSIONAL PLASTIC PART MANUFACTURE. HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
I NEED TO PRODUCE A BATCH OF PARTS
Low Volume Batch Production
Order Parts when Required!
1 – 10,000 Parts
No Tooling Costs, No Set Up Fee
Price Breaks for Higher Volume
I HAVE AN STL FILE & NEED A QUOTE
If your model is ready to go, upload your stl file for an automatic adjustable quote. Our system will choose the cheapest pricing structure for you.
HERE TO HELP YOU SAVE ON PART PRODUCTION COSTS
Refer a Friend
Once your friend places an order
you both get a 10% discount token
Volume Price Breaks
We have designed our pricing structure with aggressive price breaks to benefit those who need higher quantities
ADDITIVE FOR MANUFACTURE
3DPRINTUK are specialists in low volume production using state of the art SLS and MJF 3D printing systems. Our aim is to bridge the void between prototype and injection moulding. If tooling costs are prohibitively expensive for your product or you don’t require the volume demanded by injection moulding it’s time to email us or give us a call.
Our aim is to make you the best plastic parts possible using state of the art 3d printing systems. With over 10 years experience, 3DPRINTUK have mastered the process of printing parts using both SLS and MJF technology, with no need for support material, virtually no layer lines and short turnaround times, you are guaranteed robust, accurate parts, time and time again.
We can produce one off rapid prototypes if that’s what you require or production runs of tens of thousands of parts, on demand.
Call or email us to discuss your project.
OUR SERVICES INCLUDE
MORE ABOUT 3DPRINTUK
Additive manufacture with 3DPRINTUK can save you £1000’s
Enter your tooling costs and quantity required into our low volume calculator and it will tell you at what point SLS is viable for manufacture and how much you can save in part production costs.
We want to save you money on part production costs, check out our tips and tricks video
Contact
Call: 0208 692 5208
Email:
General Enquiries - [email protected]
OFFICE HOURS:
Mon-Friday 9.00am - 5.00pm
Daily cut off for new orders: 3.00pm
WE ARE SOCIAL
SEARCH
Search for:Unit D9
Leyton Industrial Village
Argall Avenue
London
E10 7QP
NEWSLETTER
Sign up to our Newsletter for the latest
service updates and special offers
OUR PRICING APP
GENERAL
SERVICES
3D PRINTING
PRICING
ABOUT US
3DPRINTUK Portal
3DPRINTUK is introducing its ‘Price Beat Promise’ for customers who have received a cheaper quote from one of our competitors. You can request a quote review for any part, within any order, on a like-for-like part basis.
You can request a quote review for any part, within any order, on a like-for-like part basis.
Parts will be reviewed by our team and 3DPRINTUK promises to explore all options to beat or match a competitors quote.**
All you have to do is send us a PDF copy of the quote you would like us to review and we will adjust our quote to reflect the discount.
Instructions:
Start a new quote
Upload all of your parts and fill in all the details to get your quote
Click the Price Beat Promise button in the quote navigation bar
Follow the instructions to attach the pdf of the quote you’d like to match
Click send. That’s it!
Your request will be checked as soon as we can and your quote will be adjusted.
** Before you submit a request, please read our full Price Beat Promise Terms and Conditions.
Loading...
Unfortunately, there is an issue loading our payment provider Stripe.
This error is extremely rare and may be caused by a firewall or plugin blocking the payment script.
How to resolve:
Please try a hard refresh of the page as described here.
If you continue to see this message, please call 0208 692 5208 or email [email protected] and we can attempt to take payment over the phone.
Log in
or Create an account
Editing / parts
Material (optional)
Texture (optional - material must be selected first)
Colour (optional- material + texture must be selected first)
Quantity (optional)
Hi, how can we help?
09/01/2023, 07:21:45
-
Upload new parts
Select or drag and drop your . STL files
STL files
*By uploading your files to 3DPRINTUK, you agree to our Terms of Service.
User anonymous
User anonymous
| Group name | Quantity |
|---|
Deleting a tag will remove it from any associated parts.
| Tag name | Delete |
|---|
No saved tags
Standard View
Controls
left mouse
right mouse
middle mouse / mousewheel
Closing or reloading the page will interrupt this process
Extra Small (xs)
Small (sm)
Medium (md)
Large (lg)
X-Large (xl)
XX-Large (xxl)
3D printed organs have taken root
Image copyright, Wake Forest
Image caption, Almost any replica of a human organ can be made using 3D technology nine0014 published in the journal Nature Biotechnology the results of the development of American scientists .
Breakthrough opening allows the use of living tissue to repair damaged organs.
A medical professor at University College London called the new technology "the goose that lays the golden eggs."
The idea of integrating individual human stem cells into a 3D printed replica of a damaged organ could revolutionize regenerative medicine. nine0005
Replacing a broken jaw, damaged heart muscle, or restoring a missing ear to a person is easy with this technology.
Today, the main problem of transplantation of artificially regenerated organs is the difficulty of maintaining their viability - tissues over 0.2 mm thick lack oxygen and nutrients.
Sponge
A team from the American medical center Wake Forest has developed a new technique that allows you to make a living tissue penetrated by microchannels using a 3D printer. The fabric has a sponge-like base, which allows nutrients and neural networks to penetrate into its structure. nine0005
nine0005
Image copyright, Wake Forest
Image caption,An integrated regenerative system is used to 3D print body parts
The technology is an integrated system, part of which is responsible for tissue growth, the other is for making an exact copy of the replaced organ on a 3D printer .
The starting material consists of a biodegradable plastic that forms the outer structure of the replicated organ and a water-based gel that contains the cells and stimulates their growth. nine0005
Animal testing has shown that after implantation, the plastic is gradually degraded and replaced by a natural structural matrix of proteins produced by the cells.
Blood vessels and nerves are rotated directly into the implants.
Powerful possibilities
According to Professor Anthony Atala, lead researcher at the Wake Forest Center, it is now possible to print human tissue, but scientists want to wait until animal tests are completed to understand how durable the recreated organs are. nine0005
nine0005
Image copyright Wake Forest
Photo captionThis is what a broken jawbone looks like on a CT scan
Whatever the case, 3D printing opens up new possibilities for medicine. “Let’s say we have a patient with a jaw injury that is missing part of it. We do a tomography on the patient, then we send the data to the printer, and it will create the missing part of the jawbone that will completely fit the patient,” he told the BBC.
image copyrightWake Forest
Image caption,And so, the missing fragment made using a 3D printer
Technologies using biodegradable materials, which are then soaked in a solution with stem cells, are already being used.
Two years ago, Wake Forest Medical Center experimented with transplanting lab-grown female genital organs, but in general, the possibilities of such procedures are limited due to problems with maintaining cell viability.
According to Professor Atala, their recent experiment created a wide variety of tissues - muscles, soft cartilage and hard bones - which indicates the vast possibilities of the new technology. nine0005
nine0005
Golden Goose
Professor Martin Birchall, a surgeon at University College London, says the results of the study are striking.
"The prospect of using 3D printing of human tissues and organs for implantation was real, but, I confess, I did not expect to see such rapid progress. What they managed to create can be called a goose that lays golden eggs!" - the doctor was delighted.
He also believes that more testing is needed before the new technology can be used in humans, but he hopes it will take a little time. nine0005
"Given the scale of this breakthrough research, advances in other areas, the resources available to Wake Forest scientists, and the pressing needs of public health, I believe that in less than a decade, surgeons like myself will be able to operate on printed organs. and fabrics. I can't wait," adds Martin Birchall.
What does it cost us to build everything! The most interesting 3D printing projects / Software
It is possible that the invention of 3D printing will go down in history as one of the most revolutionary inventions in human life. Just think - any thing that used to take days, weeks or even months to create can now be done in a matter of hours. And when technical barriers are overcome, a person will be able to create almost any object - from furniture to electronic devices. Already, individual enthusiasts and entire research centers are creating a variety of devices using 3D printers. The most interesting of them will be discussed below. nine0005
Just think - any thing that used to take days, weeks or even months to create can now be done in a matter of hours. And when technical barriers are overcome, a person will be able to create almost any object - from furniture to electronic devices. Already, individual enthusiasts and entire research centers are creating a variety of devices using 3D printers. The most interesting of them will be discussed below. nine0005
⇡#3D printing: a good start
Despite the fact that 3D printing has begun to change our lives only in recent years, it was not invented a year or even ten years ago. Her father is Chuck Hull (Charles W. Hull). Today he is over 75 years old, but the inventor of the very first 3D printing technology - stereolithography - does not think of retiring. “I'm old enough to retire, but I'm so interested that I won't do it,” Chuck says, laughing. His name is not very well known to the public, but Chuck's contribution to the development of 3D printing is simply enormous. The name of Chuck Hull is put on a par with such names as Thomas Edison or Steve Jobs. Chuck Hull owns over 60 US patents and is also the inventor of the versatile STL 3D printing format. nine0005
The name of Chuck Hull is put on a par with such names as Thomas Edison or Steve Jobs. Chuck Hull owns over 60 US patents and is also the inventor of the versatile STL 3D printing format. nine0005
More than thirty years ago, Chuck managed to print the first object in his laboratory - a small cup. He was so delighted with his creation that, despite the late hour, he woke up his wife and showed her the first 3D print. The sleepy wife in pajamas looked at her husband's creation and frankly admitted that she expected something better. But neither Chuck, nor even his wife, could imagine what this discovery would lead to.
The method tested by the scientist was very simple. Liquid photopolymer fills some capacity. An ultraviolet beam moves along the surface of the material, which causes the material to become hard in the right place. Layer by layer, the polymerization process forms a solid object. nine0005
Three decades later, Hull admitted in an interview that he did not expect his invention to have an impact on medicine. But today there is no doubt that the rapid production of robotic prostheses, glasses, assistive devices for people with disabilities, not to mention artificial organs, all this means a revolution in medicine and the discovery of new approaches to treatment.
But today there is no doubt that the rapid production of robotic prostheses, glasses, assistive devices for people with disabilities, not to mention artificial organs, all this means a revolution in medicine and the discovery of new approaches to treatment.
⇡#3D printing and medicine
The production of implants using 3D printing is one of the most promising areas in modern surgery. With a frequency of a day or two, news appears that this or that organ has been grown with the help of three-dimensional printing or a new prosthesis has been made. nine0005
A future where 3D printing is present in every home seems futuristic and incredible. But even stranger is a world where medicine has gone to the next level and is using 3D printing to bring the handicapped back to full life. Moreover, some experiments conducted by scientists today suggest that 3D printing will change the person himself.
⇡#Human Upgrade
Belgian scientists from the University of Hasselt implanted the jaw of an 83-year-old woman. It was created in just a few hours, while previously such a part would have been made in several days. The jaw was 3D printed from a special titanium alloy. Now, somewhere in distant Belgium, a happy granny with titanium teeth chews hams right with the bones and cracks walnuts on a dare. Joking aside, the pace at which doctors are getting closer to creating a Cyberman is mind-boggling. nine0005
It was created in just a few hours, while previously such a part would have been made in several days. The jaw was 3D printed from a special titanium alloy. Now, somewhere in distant Belgium, a happy granny with titanium teeth chews hams right with the bones and cracks walnuts on a dare. Joking aside, the pace at which doctors are getting closer to creating a Cyberman is mind-boggling. nine0005
Doctors have already learned how to create artificial bones and joints by printing them on a 3D printer. And this is no longer the technology of the future, today hundreds of people walk around the planet who can live thanks to printed implants. So, in March of this year, British doctors returned to normal life Stephen Power, whose skull was crushed as a result of an accident. First, X-ray images of the face were carefully examined, and then artificial parts of the skull were printed on a 3D printer, taking into account all the anatomical features of the patient. After a complex operation, doctors from Wales placed the printed parts of the skull on Stephen, restoring facial symmetry. Looking at this man a few months after the operation, you can’t even believe that he survived such a terrible accident. nine0005
Looking at this man a few months after the operation, you can’t even believe that he survived such a terrible accident. nine0005
At the same time, another unique operation was performed at the Utrecht University Medical Center: a young girl had almost her entire skull replaced with a printed plastic copy. This was extremely necessary, since the thickness of the girl’s own skull was constantly increasing due to illness, which created a real threat to life. At the time of surgery, the girl had loss of vision and severe headaches. The operation lasted 23 hours, and the result exceeded all expectations. After only a few months, the girl has already gone to work and feels much better than before the operation. Her sight has returned, and nothing reminds her that her life hung in the balance. nine0005
But even this is not as impressive as the prototypes of bionic implants that biologists constantly demonstrate. For example, McAlpine, assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Princeton, last year showed a printed artificial ear that allows you to hear radio waves.
The finished ear consists of a helical antenna inside a cartilaginous structure. Two wires lead from the base of the ear and wrap around the helical "cochlea" - the part of the ear that allows a person to perceive sound. If you connect it to the electrodes, in theory, you can not only restore hearing, but also make it sharper, as well as expand the perceived frequency range. nine0005
⇡ # How to print a house
As soon as it became obvious that the future belongs to three-dimensional printers, architects rushed to develop models of buildings that could be folded from printed blocks. This task at first glance seemed not so difficult. Building a house with printed parts is as easy as folding a LEGO brick. So thought builders-printers of future houses. For example, in 2013, an architect named Janjaap Ruijssenaars of Universe Architecture confidently claimed that he could showcase the world's first printed building as early as 2014. But just a few months after the first sensational statements in the media, the terms were called much more distant. According to the architect, the erection of such an ambitious creation already took at least a year and a half. nine0005
According to the architect, the erection of such an ambitious creation already took at least a year and a half. nine0005
And, as always, China was drawn into the race for the right to be called the first. While American and European builders colorfully described their projects and anticipated the publicity hype that would accompany the opening of such projects, Chinese enterprising businessmen were one step ahead.
Winsun New Materials, a little-known Chinese firm in Suzhou County, Jiangsu Province, has developed a new approach to building simple one-story buildings. With the help of a huge 3D printer, Chinese builders promise an unprecedented speed of building houses - up to ten buildings in 24 hours! To design such a super-useful construction tool, Chinese businessmen invested $3.2 million. The printer itself for building houses was developed by engineers for 12 years. nine0005
No less interesting is the material used in the construction of new houses. Winsun New Materials uses unclaimed construction waste to make homes that are environmentally friendly and incredibly cheap—only $4,800 to build. China bribed everyone with cheapness, proving that 3D printing in modern construction is no longer expensive pampering and exotic.
China bribed everyone with cheapness, proving that 3D printing in modern construction is no longer expensive pampering and exotic.
The only detail that the Chinese have not yet learned how to print on a printer is the roof. The builders explain that at this stage it is impossible to erect this part of the building for technical reasons. nine0005
Curiously, a Chinese construction firm could have completed many more large projects if it weren't for bureaucratic delays. In one of the interviews, representatives of Winsun New Materials complain that the construction of buildings using this technology requires appropriate regulations, which officials simply do not have time to approve.
⇡#3D printing over the Internet
The development of 3D printing technologies stimulates the emergence of startups that are somehow related to 3D printing. All these decisions lie on the surface, and clever businessmen do not miss the chance to earn. Three-dimensional printers have not yet become as common peripherals as inkjet or laser printers. Therefore, web services for printing 3D objects through online orders can bring a fairly large income to their owners. nine0005
Therefore, web services for printing 3D objects through online orders can bring a fairly large income to their owners. nine0005
One of the most successful projects in this area is the Shapeways service, which allows you not only to order your layouts remotely, but also to use a number of additional services, such as using special types of coatings for printed products, organizing the sale of your layouts, etc.
⇡#Bumpy Photo: Bumpy Photo
In addition to services like Shapeways, other 3D printing projects are already available online. An example of such a “timely” service is the Bumpy Photo project. nine0005
Simultaneously with the growing popularity of 3D printing, users began to show more and more interest, so to speak, in everything 3D. Someone has discovered a whole world of 3D graphics and is now using a 3D editor to develop and visualize their ideas by printing a prototype on a printer. Other users began to look for easier ways to create 3D, in order to print their ideas again, implementing them in the form of layouts. Just for this category of people, the Bumpy Photo service made a bet. nine0005
Just for this category of people, the Bumpy Photo service made a bet. nine0005
When a person looks at a photograph, he subconsciously determines the volume of objects in the picture, sees the depth of the scene in the frame. Bumpy Photo experts have come up with a way to determine the bulge of objects in a flat image. Using a special algorithm, the selected image is analyzed, and a so-called relief map is compiled for it, which determines the near and far points in the picture. If these points are shifted in the image, a normal photo will get a pseudo-stereoscopic effect. nine0005
The creators of the service rightly assumed that there would be many who would like to receive such a printed bas-relief. Portraits of loved ones, as well as photographs of beloved animals, can be given a second life and become a little more realistic if they are turned into a 3D surface. The illusion will become even more noticeable if the light source is correctly placed near such a three-dimensional photograph.
⇡#Minockio: print yourself out
A person likes to look at himself from the side — in a photo, video, in a mirror. Perhaps that is why there are so many projects among 3D printing services that allow you to print yourself. One such service is called Minockio. Using a simple online designer, you can design a cartoon character that will look like a specific person. The design is then sent for printing, and the result is a four-inch figurine with familiar features that shakes its head in a funny way. nine0005
⇡#Shapify.me: attack of the clones
The Shapify.me web service is similar to the previous one, but it no longer creates a cartoonish, but quite realistic 3D copy of a person. The process of creating a three-dimensional model is extremely simple and effective. To get a 3D model, you must use a Microsoft Kinect device with an Xbox 360 game console or a Windows computer. With the help of a camera, the system scans a person from different angles. Based on the images taken, a three-dimensional model is formed, which can be sent for printing. In this case, you do not need to have the skills of three-dimensional modeling and know the features of the work of three-dimensional editors. Everything is simple and fast, and the finished result, a small figurine, can be sent to someone as a gift or put on your table and enjoy. nine0005
In this case, you do not need to have the skills of three-dimensional modeling and know the features of the work of three-dimensional editors. Everything is simple and fast, and the finished result, a small figurine, can be sent to someone as a gift or put on your table and enjoy. nine0005
⇡ # How to print sound
Speakers sometimes have a completely amazing look - they can look like a pair of parallelepipeds, they can be shaped like a horn or resemble sea shells. But the geometry of acoustic systems is not only the result of the designer's imagination. In order for this device to give the listener a natural sound, the designer must follow the laws of physics, experimenting with form and materials. By and large, this is a whole science in which there are many interesting solutions and unusual approaches. And in this matter, 3D printing accelerates the pace of creative research. nine0005
⇡# 3D printed speaker
The heart of any speaker system is the speakers. No matter how hard engineers try to improve the sound of acoustics, there is a limit that is determined by the technical characteristics of these parts. However, perhaps 3D printing can help improve these characteristics in the future. Last year there were several attempts to create a speaker using 3D printing technologies. The first such experiment was carried out by the New Zealand designer Simon Ellison (Simon Ellison). nine0005
However, perhaps 3D printing can help improve these characteristics in the future. Last year there were several attempts to create a speaker using 3D printing technologies. The first such experiment was carried out by the New Zealand designer Simon Ellison (Simon Ellison). nine0005
Simon Ellison - designer, music lover and fisherman
He managed to create a speaker design that is 90 percent plastic. The only element that had to be left was a magnet with a winding. The glass dome speaker with the printed speaker, which Simon ended up showing off, looks amazing, just as good as the expensive systems from big names.
The designer used a combination of different materials for the best sound quality. It took nine hours to print the components, and the designer spent several more hours assembling the product. It's hard to say how good the speaker system sounds, but it looks spectacular. nine0005
Following Simon, a similar experiment was conducted by Cornell University researchers Apoorva Kiran and Robert MacCurdy. True, their loudspeaker had a rather mediocre sound and looked much more modest than Simon's device.
True, their loudspeaker had a rather mediocre sound and looked much more modest than Simon's device.
Perhaps the most unusual project for the production of acoustics using 3D printing was proposed by a group of researchers at Disney Research. Ordinary loudspeakers consist of two obligatory parts - a magnet and a winding. When these elements interact, vibration occurs, which is transmitted to the membrane, which gives rise to sound. The new technology proposed by the experts is based on the electrostatic design of the speaker. In this case, the sound is produced by a membrane that is sandwiched between two conductive surfaces. When a signal is applied to these conductive surfaces, the air between them acquires a charge, and the membrane deforms, that is, sound is generated. Considering that 3D printers are increasingly using multiple materials and there are already separate devices that allow printing with conductive material, creating such speakers will soon be a breeze. This technology opens up new possibilities for acoustic designers, because the speakers can be of any shape. nine0005
nine0005
⇡#Music that was printed
It may seem strange, but the sound itself can also be "sent to print". To do this, you need nothing at all - to give the technique into the hands of the artist. These people think outside the box and use the tool in their own way. For example, the Swedish artist Rickard Dahlstrand learned how to materialize sound. He picked up a 3D printer and listened to its sound. Like any other technique, this device makes a characteristic sound during operation. The tone and timbre of the sound depend on the positioning of the print head. Rickard Dahlstrand tried to print music by making the head move in the right direction. It turned out to be such a “kalyaka-malyaka”, to look at which people line up. nine0005
For example, at Music Hack Day 2013, which was held in Stockholm, Ricard organized a whole gallery of printed musical works - from the overture to Rossini's "William Tell" to Beethoven's Fifth Symphony and Mozart's masterpieces. And, of course, the Imperial March from Star Wars did not go unnoticed.
Sample video
⇡#Clothes sewn by the printer
Designers of all stripes, regardless of occupation, are showing an increased interest in the new 3D printing technology. Are no exception and those who are engaged in the development of clothing. At a fashion show, the most famous fashion designers do not consider it shameful to demonstrate clothes made from non-standard materials. Often on the podium you can see amazing robes made of wood, metal, plastic - beautiful and completely impractical clothes that are rather symbolic. But if you approach the issue of creating dresses, trousers and shirts in this way, then why not use a 3D printer? Especially since 3D printing can do what a fashion designer can only dream of - almost instantly provide a result. nine0005
⇡#Dress sewn according to the formula
One of the first who set out to print clothes on a printer was designer Michael Schmidt. His first creation is a one-of-a-kind dress made entirely with the help of the Shapeways web service (not counting the decorative Swarovski crystals that adorned the finished outfit).
For an unusual dress, an unusual way of designing it was also used. The dress was literally programmed and calculated. Fashion designers are usually far from science, so the help of another person who would have a technical mindset was needed. Michael turned to his friend, the architect Francis Bitonti. After conferring, they came to the conclusion that the surest way to derive a formula for a dress is to refer to the golden ratio, which is easily described by the Fibonacci number sequence. Around this famous mathematical calculation, disputes have long been ongoing. The Fibonacci sequence is interesting because it can be found in the most unexpected creations of nature. Fibonacci numbers can describe the arrangement of seeds in a sunflower, the placement of leaves on a tree, and much more. And yet, according to a popular hypothesis, many man-made masterpieces became such precisely because the rules of the golden section were observed during their creation. Many designers tend to assume that this rule allows you to get the harmony of form. Michael Schmidt was of the same opinion. The curves drawn using the Fibonacci sequence were superimposed on the contours of the female figure, as a result of which the “ideal” topology of the dress was obtained, from which the layout for printing was drawn up. nine0005
Michael Schmidt was of the same opinion. The curves drawn using the Fibonacci sequence were superimposed on the contours of the female figure, as a result of which the “ideal” topology of the dress was obtained, from which the layout for printing was drawn up. nine0005
We can't claim that the golden section rule worked 100%, but the printed version of the clothes really looks good. It contains more than three thousand fastened movable elements that give the dress some elasticity.
⇡#3D shoes
While others are only exploring the possibilities of using 3D printing to produce outfits, renowned sportswear and footwear manufacturer Nike has taken 3D printing to the industrial scale. This brand has announced a new technology for the production of sports boots, which will allow the company to abandon the long process of creating template molds. nine0005
nine0005
The most important thing in sports shoes is maximum grip on the ground. If we consider shoes as a construction, then the main part responsible for the sporting characteristics of the model is the sole. The results demonstrated by the athlete directly depend on the shape of the spikes, their number and the variant of their location on the shoe. Nike has developed a new outsole shaping principle based on selective laser sintering technology.
According to the company, soon the shape of the sole on the shoe can be corrected in a matter of hours, releasing models taking into account the individual characteristics of the athlete. The company's designers are delighted with the new approach. Now you can experiment with 3D printing every day and not languish in anticipation of the next protector prototype being received and tested. nine0005
⇡#3D printer as a sewing machine
A 3D printer developed at Carnegie Mellon University in collaboration with a team of scientists from Disney Research in Pittsburgh is able to create three-dimensional models from . .. soft yarn. The operation of such a 3D printer is somewhat reminiscent of a sewing machine. Along the base moves the needle combined with the print head, which forms the geometry of the printed model by felting. The first thought that comes to mind when you see such a device is that you can easily make soft children's toys with it. And in this sense, the fact that specialists from the ubiquitous Disney company had a hand in creating the printer seems very symbolic to us. nine0005
.. soft yarn. The operation of such a 3D printer is somewhat reminiscent of a sewing machine. Along the base moves the needle combined with the print head, which forms the geometry of the printed model by felting. The first thought that comes to mind when you see such a device is that you can easily make soft children's toys with it. And in this sense, the fact that specialists from the ubiquitous Disney company had a hand in creating the printer seems very symbolic to us. nine0005
⇡#3D printing for driving and flying
Printed supercars
The main material used in most 3D printing devices today is ABS plastic (sometimes PLA is used - biodegradable plastic). Products made with it can be coated with paint, varnish. Visually "disguised" plastic in such models can sometimes even be confused with some other material, such as metal. This material has many advantages..jpg) ABS material is non-toxic, impact resistant, can contact with water, resistant to alkalis, does not react with fats, gasoline, lubricants, hydrocarbons. nine0005
ABS material is non-toxic, impact resistant, can contact with water, resistant to alkalis, does not react with fats, gasoline, lubricants, hydrocarbons. nine0005
Swedish supercar manufacturer Koenigsegg has taken advantage of all these qualities in the production of the new Koenigsegg One:1. This machine has amazing features. The power of 1360 horsepower alone (which equates to one megawatt) is enough for the car to be considered the world's first representative of a new class of cars - megacars. By the way, the very name of the new car has a hidden meaning, “one to one” means the ratio of power and weight of the car, which, thanks to the careful selection of materials, is only 1340 kg. nine0005
Designing this machine, the Swedish company's specialists regularly turned to 3D technologies. Before the approval of a particular component of the car, preliminary testing of a part printed on a 3D printer was often carried out. Sometimes Swedish designers used three-dimensional scanning, which made it possible to quickly create a basic model of a particular part.
In addition to ABS, which was ideal for prototyping, the engineers also used printing of titanium structures. So, for example, components of a new turbocharger with variable geometry were printed on a 3D printer. A titanium exhaust tip was also made, reducing the weight of the structure by 14 ounces (400 grams). nine0005
3D technology has made it possible to significantly speed up the process of developing the design of components and in some cases even reduce the cost of production (the retail price of the machine was two million dollars in the end).
If you find Swedish supercar manufacturer Koenigsegg's masterpiece beyond your means, don't be discouraged. There is a great way to save money. Pay attention to another supercar - from a small American company Rezvani Motors.
The cost of a sports car from this manufacturer is much lower - from $124 900. But the design of this sports car also used printed parts. These are mainly small elements - fragments of the lighting system, mirrors, etc. In addition, three-dimensional models of the car were used at the design stage of the car body, which was eventually made of carbon fiber.
In addition, three-dimensional models of the car were used at the design stage of the car body, which was eventually made of carbon fiber.
⇡#A flying 3D printer that prints nests and fights radiation
An unusual project was also demonstrated by the Air Robotics Laboratory at Imperial College London. Through the efforts of engineers, a flying 3D printer was created. The main goal of roboticists was to create a device that can be used to clear the area of radioactive debris, for example, in an accident at a nuclear power plant. nine0005
Scientists have combined a printer with a quadcopter and developed a special program that determines the behavior of this quadcopter. With the help of sensors, the first flying quadcopter identifies the source of radioactive contamination, after which it flies up and starts printing on the surface of the object with a sticky substance. Next, the robot sends a signal to its partner, which flies up and lands on a sticky "nest". After a while, the substance solidifies, and the second porter robot flies away, carrying away the cargo contaminated with radiation. The prototype is capable of lifting a weight of up to two and a half kilograms, but British specialists intend to build an enlarged copy of these robots in the near future, which will be able to pick up loads of up to forty kilograms. nine0005
The prototype is capable of lifting a weight of up to two and a half kilograms, but British specialists intend to build an enlarged copy of these robots in the near future, which will be able to pick up loads of up to forty kilograms. nine0005
⇡#Porthole printing
Since 2010, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration has been working on the development of 3D printing technologies in low gravity conditions. During this time, NASA specialists managed to achieve good results. So, in July 2013, a pair of rocket engine injectors were successfully tested, which were subjected to high pressure and temperature (3316 degrees Celsius). The purpose of the ongoing research is to study the possibilities of 3D printing in space and extreme conditions. The presence of such tools on board the space station can significantly reduce the cost of flights, since the crew members will be able to create the spare parts necessary for repairs on their own, and not transport them from Earth. nine0005
nine0005
⇡#Printing under maple syrup: food on a 3D printer
Oddly enough, but one of the first prototypes of 3D printing devices can be considered... a confectionery syringe. Long before the advent of computer technology, confectioners deftly “printed” delicious patterns from cream and dough. But then a lot depended on the individual skill and skill of a person in the kitchen. And with the advent of 3D printers, the task has become easier. It was enough to equip the printer with edible material, correct the printing principle, and the result was a tool for edible masterpieces. nine0005
Modern 3D printers can print all sorts of delicious things. For example, one of the major chocolate corporations, The Hershey Company, uses 3D printing to produce confectionery. And the help and technical support of the “chocolate printer” is provided by 3D Systems, the same company that was founded by the inventor of three-dimensional printing, Chuck Hull.
But besides the industrial machines for the production of sweet things, there are many more small interesting food 3D printing projects. nine0005
nine0005
Miguel Valenzuela, for example, built a 3D printer for his three-year-old daughter back in 2010, using the popular Lego children's set. Miguel once read an article about a British designer, Adrian Marshall, who used Lego to build a miniature pancake machine for a client. When Miguel had the imprudence to tell his eldest daughter Lily about this, she listened to her father, and then turned to her younger sister and said: “Maya! Dad is going to make a pancake machine!” When a three-year-old child demands a pancake machine, it's better not to argue, Miguel decided, and began designing such a device. He spent six months to create this miracle, but the efforts of the head of the family were more than justified. The children were delighted with the cooked pancakes and ate them with increased appetite. It looked like this. nine0005
Miguel built an invented device on the Arduino platform, it was called PancakeBot and printed pancakes beautifully. By pouring batter according to a given pattern, the PancakeBot pancake printer can make any shape, such as “build” the Eiffel Tower or draw the silhouette of an animal.
By pouring batter according to a given pattern, the PancakeBot pancake printer can make any shape, such as “build” the Eiffel Tower or draw the silhouette of an animal.
⇡#Fly in the ointment: printed weapons and a threat to health
3D printing has many advantages, however, in addition to the benefits it promises, this technology can bring harm to humanity. It all depends on the purpose for which a person will use it. You can print cases for gadgets, you can design prostheses, or you can use 3D printing to make jewelry. And you can set a goal to create a weapon aimed at the destruction of other people. Unfortunately, this thought quickly crossed the man's mind. And as soon as 3D printers became available to the average user, there were enthusiasts who immediately offered their designs of plastic weapons. nine0005
⇡#Printers in service
The first model of a pistol that could be easily printed on a 3D printer was the Liberator. It was invented by a Texas student named Cody Wilson. Interestingly, at the time of the appearance of the first printed pistol, Cody had a license to develop firearms.
Interestingly, at the time of the appearance of the first printed pistol, Cody had a license to develop firearms.
The Liberator's first single-shot pistol made of plastic
The Liberator was made entirely of standard consumables, with the exception of one small detail - the pistol's firing pin had to be metal. However, this is not a problem at all, since this part of the gun can simply be made from an ordinary nail. nine0005
As soon as Cody demonstrated his development, it was immediately subjected to a flurry of criticism from officials. Less than a week later, the US government passed a law restricting free access to blueprints for such devices.
However, it is almost impossible to control the 3D printing of weapons today. Anyone with a 3D printing device can make firearms at home.
Israel's Channel 10 reporters conducted an experiment that only added fuel to the controversy surrounding the unexpected problem of controlling the production of new weapons. They smuggled an unopened pistol into the Knesset without any difficulty and were able to pass, along with the weapon, within a few steps of Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. nine0005
They smuggled an unopened pistol into the Knesset without any difficulty and were able to pass, along with the weapon, within a few steps of Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. nine0005
Other Daily Mail journalists Simon Murphy and Russell Myers similarly demonstrated the extent of the problem. They unsealed the gun from documentation from the Web and, with no concealment of their cargo, were able to take the Eurostar train at rush hour and travel from London to Paris. The security service did not notice the threat, and the metal detectors could not fix the components of The Liberator, which Simon Murphy assembled without problems in a single structure in the train lavatory. nine0005
3D weapon production and distribution scandals continue unabated. One of the latest incidents took place in Japan, where gun laws are known to be very strict. Local resident Yoshimoto Imura, to his misfortune, posted a video on YouTube showing a weapon printed on a printer. After some time, the police raided his house, who confiscated several ready-made pistols.
A 27-year-old Japanese man feigned surprise and stated that he knew nothing about the illegality of his actions. He bought the printer quite legally, paying almost $600 for it, and downloaded all the necessary documentation from the Internet. Of course, Yoshimoto was cunning, because he, as a lover of weapons, should have been well aware that it was the Japanese government that had a very strict policy regarding the possession of firearms. Firearms Act of 1978 years prohibits the Japanese from owning any firearms, with very rare exceptions. Japanese citizens are allowed to own rifles or shotguns, but only if they hold a hunting license. The licensing procedure in Japan is very strict and obtaining a license is a lengthy process. This incident is interesting, first of all, because the law was first applied to unsealed weapons.
Production of things using 3D printing technologies is dangerous not only because scientific progress can turn to the "dark side" for the production of weapons.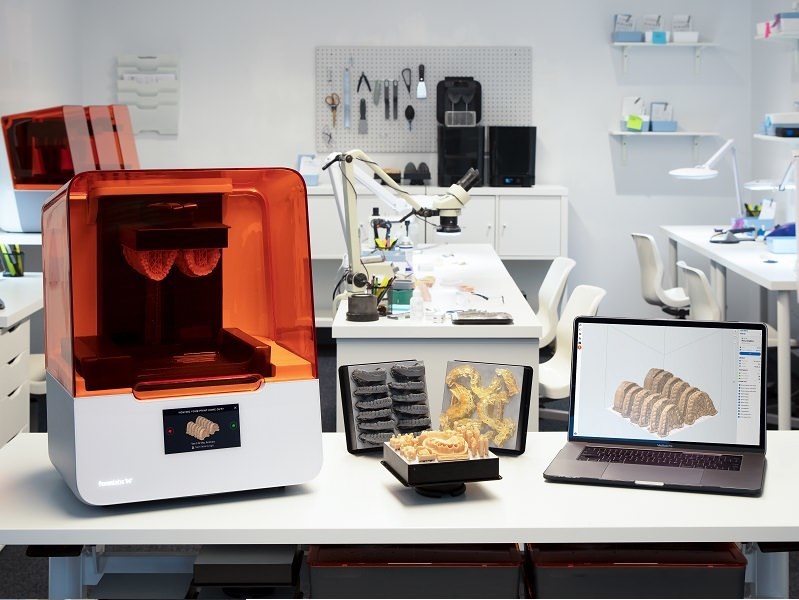 Infected with the idea of easy creation of things, many do not pay any attention to the safety precautions that must be observed by the user when working with a 3D printer. nine0005
Infected with the idea of easy creation of things, many do not pay any attention to the safety precautions that must be observed by the user when working with a 3D printer. nine0005
⇡#Watch out, 3D printing in progress!
According to researchers at the Illinois Institute of Technology and scientists at the National Institute of Applied Sciences in Lyon, 3D printers may pose a health risk when used at home. In 2013, a team of scientists conducted a series of studies, and it was found that when plastic is heated during the printing process, it emits up to 20-200 billion ultra-small particles into the air per minute. Their entry into the lungs and blood poses a threat to human health, especially for those who suffer from asthma. nine0005
Also, heating acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS plastic) releases by-products that are toxic to mammals. Of course, the degree of negative health impact largely depends on the 3D printing technology used, the design of the device, the presence of a hood, and other factors. However, in any case, it is best to print in a well-ventilated area, and the machine itself should ideally be hermetically isolated from the user during operation. At the moment, there are many artisanal designs of printers that are sold under the do-it-yourself scheme. Often these are Chinese assembly kits, where elementary security measures are not provided at all. nine0005
However, in any case, it is best to print in a well-ventilated area, and the machine itself should ideally be hermetically isolated from the user during operation. At the moment, there are many artisanal designs of printers that are sold under the do-it-yourself scheme. Often these are Chinese assembly kits, where elementary security measures are not provided at all. nine0005
⇡#3D printing: what's next?
Mix of materials: printing anything
It is easy to predict the near future. Devices for three-dimensional printing will master more and more new types of materials. The development of technology can be strongly influenced by some new discovery, which we simply cannot predict. The only thing that can be said with certainty is that the scope of three-dimensional graphics will become wider.
The day is not far off when the owner of a 3D printer at home will be able to print not only plastic parts, but also complex electronic devices. One of the most requested features is support for printing with multiple materials at the same time. In the future, the possibility of combining different materials opens up simply fantastic opportunities for the production of objects for various purposes. One of the prototypes of such a device is a printer called Rabbit Proto, created by graduates of Stanford University. nine0005
In the future, the possibility of combining different materials opens up simply fantastic opportunities for the production of objects for various purposes. One of the prototypes of such a device is a printer called Rabbit Proto, created by graduates of Stanford University. nine0005
The design of this "pilot" printer includes two modules - a module for standard ABS 3D printing and an additional head that works as a nozzle for precise injection of conductive ink. This combination makes it possible to literally create electronic devices. As an example, the creator of Rabbit Proto demonstrates how easy it is to make a Nintendo-like game controller using such a 3D printer.
The designer guarantees the compatibility of its nozzle with most modern RepRap printers. It is assumed that a completely ready-to-use Rabbit Proto printer will cost $ 2,500. The developer made his project open. Anyone can read the technical documentation of the device on GitHub. nine0005
3D printing, 3D scanning, 3D copying: ALL IN ONE
It is likely that the process will become more advanced and the functionality of 3D printers will expand.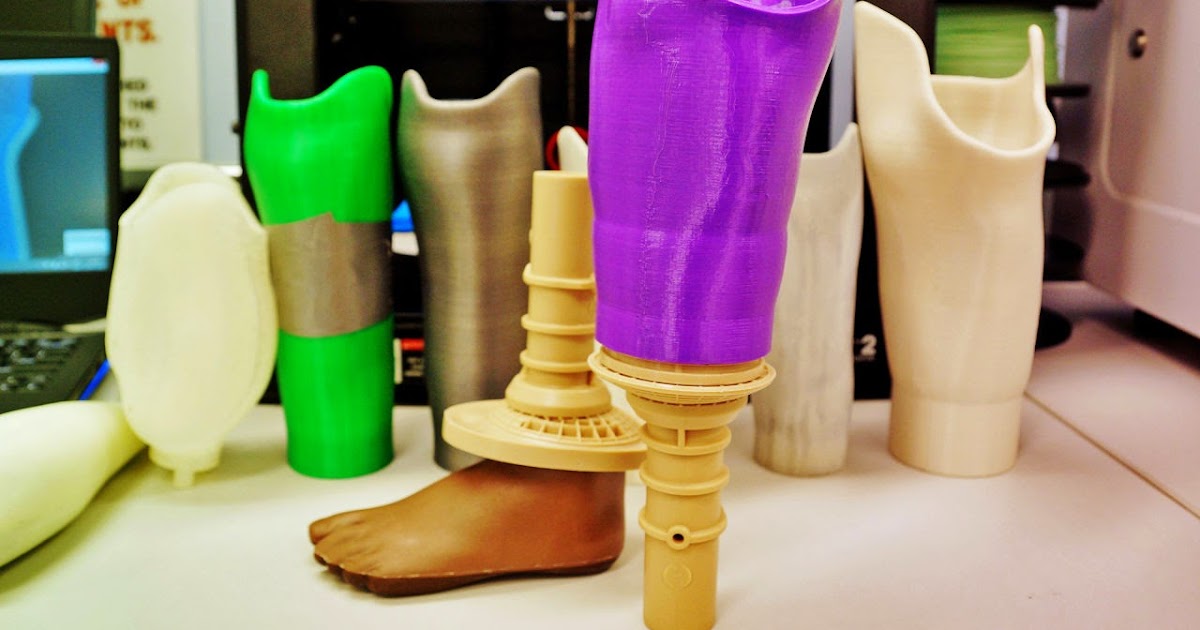 Already now we see the first hint of the evolution of these devices. In the same way that conventional printers have become MFPs with the ability to scan and copy, 3D printers will also learn to digitize the geometry of objects on the fly. This idea has already begun to be implemented by the engineers of the American company AIO Robotics. nine0005
Already now we see the first hint of the evolution of these devices. In the same way that conventional printers have become MFPs with the ability to scan and copy, 3D printers will also learn to digitize the geometry of objects on the fly. This idea has already begun to be implemented by the engineers of the American company AIO Robotics. nine0005
ZEUS All-In-One 3D Printer
Most recently, they showed a model of a multifunctional device. A device called ZEUS All-In-One 3D Printer can print, scan, copy models. In addition, this device supports the Fax mode of operation, which allows you to transfer the model geometry to a remote print station (to a similar printer).
ZEUS 3D Printer should go on sale this summer. It is equipped with a seven-inch color display, can perform auto-calibration and model grid alignment, and is very easy to operate. Scanned space 9inches (diameter) x 5 inches (height), and the printable space is 8 x 6 x 5.