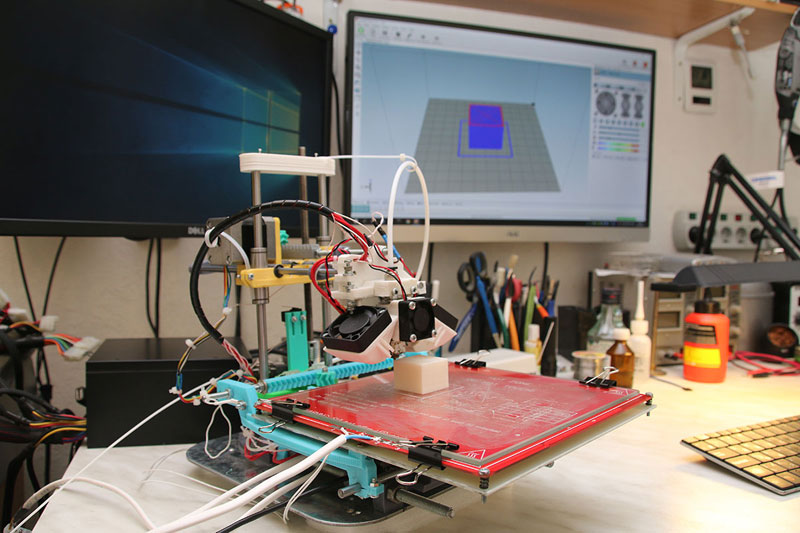
3D print bloodborne
Bloodborne best 3D printing models・Cults
Estus Flask - Dark Souls
€7.43
Bonfire - Dark Souls
€7.43
High Lord Wolnir chalice - Dark Souls 3
€11.14
Bloodborne Logo Keychan Key Chain
Free
Duelist monster hunter
€1
Bloodborne Board Game Card Holder
€0.50
Ludwik Bust
€23.46
Clock Face Hunt Track
€4.64
Bloodborne Clocktower
€13.93
3D Printable Hunter Dashboard
€9.29
3D Printable Fog Gates
€4. 64
3D Printable Bloodborne: The Board Game Tiles
€111.43
Bust of Lady Maria
€8.82
Lady Maria
€13.93
Bloodborne Ludwig Holy Blade (with sheath)
€15
Bloodborne Evelyn
€15
Church Pick - Bloodborne
Free
Bloodborne Hunter Pistol wrapped
€9.29
Bloodborne Blood Echoes Logo and keychain
Free
Starscourge Radahn
€6.38
Malenia, Blade of Miquella
€6.38
BLOODBORNE LAMP BLOODBORNE
€5. 73
73
Sekiro: Sekiro Shadows Die Twice (or three, or 4, or a thousand)
€6.38
Sekiro: Isshin, the Sword Saint
€6.38
Sekiro: Emma the Gentle Blade
€6.38
Laurence The First Vicar Miniature
Free
Grimwatch Hunters
€9.29
DOG POPE - ELDEN RING MIRIEL PASTOR OF VOWS TURTLE TORTOISE HI-POLY STL FOR 3D PRINTING
€1.85
Rakuyo´s Sword - Bloodborne
€9.29
3D models, digital. Lady Maria of the Astral Clocktower Accessories, Bloodborne - The Old Hunters. Video game, props, cosplay
€19.34
MALENIA HELMET
€2. 99
99
THE EVER BRILLIANT GOLD MASK
Free
RYKARD, LORD OF BLASPHEMY (HEAD)
€3.24
ACADEMY OF RAYA LUCARIA
€4.99
TORRENT (SPIRIT STEED)
€4.99
Sacred Relic Sword
€3.24
Teardrop Scarab
Free
Malenia Blade of Miquella
€4.99
Astel naturalborn of the void
€1.99
Fallingstar Beast
€4.48
Renna
€16.71
Evelyn Pistol from Bloodborne
€23.21
Radagon of The Golden Order
€6. 30
30
Queen Marika Statue
€6.27
Axe of Godrick
€2.49
Rakuyo blade from Bloodborne
€23.21
Maliketh the Black Blade (Elden RIng)
€3.71
Blaidd Sword, Royal Greatsword (Elden Ring)
€2.49
Bloodborne 3d - Etsy.de
Etsy is no longer supporting older versions of your web browser in order to ensure that user data remains secure. Please update to the latest version.
Take full advantage of our site features by enabling JavaScript.
Find something memorable, join a community doing good.
( 256 relevant results, with Ads Sellers looking to grow their business and reach more interested buyers can use Etsy’s advertising platform to promote their items. You’ll see ad results based on factors like relevancy, and the amount sellers pay per click. Learn more. )
You’ll see ad results based on factors like relevancy, and the amount sellers pay per click. Learn more. )
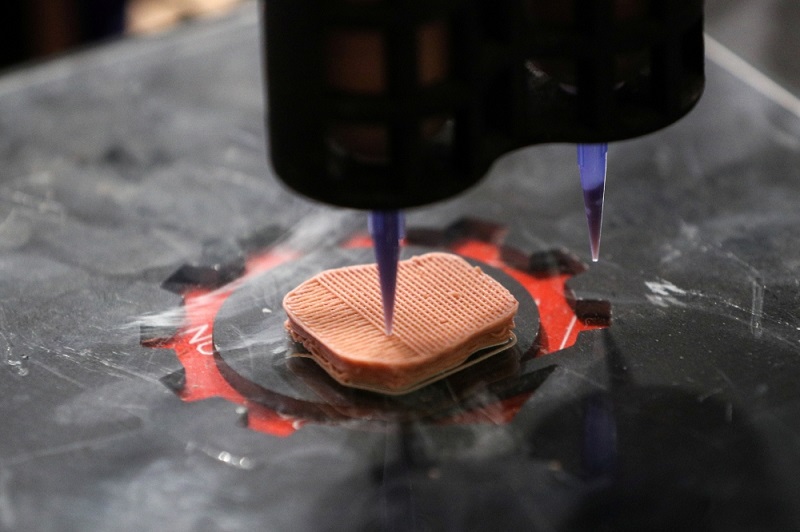
3D printing with "human blood" accelerated the healing of deep wounds
December 01, 2021 18:09 Olga Muraya
Up to 61% of the total blood volume is its plasma.
Pixabay Illustration.
Irish scientists have developed a technology for 3D printing implants based on patients' blood plasma. This method allows you to accelerate the healing of wounds on the skin, even those that are classified as severe.
A new study has shown that enriched blood plasma can be printed using a 3D printer. The resulting implant "magically" heals even the most severe wounds on the skin, including those left after surgical operations.
Platelet rich plasma (or PRP). Recall that platelets are responsible for blood clotting and play an important role in the processes of regeneration of damaged tissues.
In a recent study, scientists at the RCSI University of Medicine and Health in Ireland created PRP from the blood of a patient with a complex skin wound and then 3D printed it into a tissue repair implant.
Let us explain that PRP is created from peripheral blood collected from a person: the number of platelets in plasma is artificially increased several times due to various manipulations with blood.
The platelet-rich plasma obtained in this way was incorporated into a gelatin methacrylate (GelMA) hydrogel by the Irish specialists. So they got "bio-ink" for their printer.
The scientists then used them to 3D print a scaffold with an architecture specifically designed for skin wound healing.
In just one surgical operation, the implant was inserted into the patient's body, and it turned out that it really helps in the treatment of poorly healing skin wounds.
Research has shown that PRP-based implant accelerates wound healing by providing efficient vascularization (appearance of new blood vessels) and inhibition of fibrosis (tissue scarring).
"In addition to promising results in the field of skin wound healing, this technology has the potential to be used for the regeneration of other tissues. This will significantly affect the ever-growing markets for regenerative medicine, 3D printing and personalized medicine," notes the author of the development, professor of bioengineering and regenerative medicine Fergal O'Brien of RCSI.

The work of the Irish researchers was published on November 23, 2021 in the scientific journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Recall that we previously reported that scientists used 3D printing technology to create a functioning ovarian bioprosthesis. We also wrote about the technology of 3D printing of cartilage and even the cornea of the eye. We also talked about a 3D bioprinter for printing human skin, indistinguishable from real.
More news from the world of science and medicine can be found in the sections "Science" and "Medicine" on the media platform "Looking".
science medicine blood healing wound plasma news
Previously related
-
3D-printed steel-bronze product at Skoltech
-
In Stavropol, students created a house using a giant 3D printer
-
Invisible QR codes invented
-
Texas will have a huge block of 3D-printed houses
-
Chinese Startup 3D Printed Black Pig Meat
-
Rare beef 3D printed for the first time
Human blood can be used on a 3D printer to heal wounds
Scientists from Ireland healed a deep human wound using a 3D printer. They created biological ink from a patient's lab-enhanced blood and printed it into a structure to be placed inside an open wound. Because the ink was rich in wound-healing platelets, the man quickly recovered from his injury. According to the researchers, the technology they applied in the future will be able to restore other tissues of the human body - it will be possible not only to heal wounds, but also to correct other health problems. And in general, the experience gained had a good effect on the development of 3D printing technology in the field of medicine. Let's look into the details of this scientific achievement.
They created biological ink from a patient's lab-enhanced blood and printed it into a structure to be placed inside an open wound. Because the ink was rich in wound-healing platelets, the man quickly recovered from his injury. According to the researchers, the technology they applied in the future will be able to restore other tissues of the human body - it will be possible not only to heal wounds, but also to correct other health problems. And in general, the experience gained had a good effect on the development of 3D printing technology in the field of medicine. Let's look into the details of this scientific achievement.
Scientists fill a 3D printer with human blood and cure a serious wound
Interesting fact: 3D printers are currently used to create prostheses and implants. For example, doctors today can print and transplant people's auricles, bladders, and smaller organs like the cornea of the eye. In 2015, the FDA first approved the use of 3D printing for the production of an epilepsy drug. 
Blood-based 3D printer ink
Irish scientists shared their achievement in the scientific journal Advanced Functional Materials. Relatively recently, they faced the task of healing a person from a deep wound. To do this, they took a blood sample from a patient and created platelet-rich plasma (PRP) from it in the laboratory. Initially, in the peripheral blood of a person there are not so many platelets responsible for the rate of clotting and repair of damaged tissues. But researchers have been able to increase their numbers in the lab. How exactly this happens, it makes no sense to describe within the framework of this article - this is a complex process, which takes a lot of time to explain.
Platelets are responsible for blood clotting
Platelet-rich plasma was subsequently mixed with gelatin methacrylate hydrogel (GelMA). Thanks to him, the patient's blood became much thicker, which made it possible to use it as ink for a 3D printer. Using printing equipment, scientists have created a structure capable of repairing wounds. Unfortunately, it was not possible to find photographs of the printed design. So we can not say what size it is and what exactly it is. In a simple surgical operation, the structure was carefully placed in the patient's wound.
Unfortunately, it was not possible to find photographs of the printed design. So we can not say what size it is and what exactly it is. In a simple surgical operation, the structure was carefully placed in the patient's wound.
Unfortunately, there is no photo of the used 3D printer. But it should look something like this. In particular, they launched the process vascularization - the formation of new blood vessels. At the same time, they suppressed fibrosis, that is, they prevented tissue scarring. According to bioengineering professor Fergal O'Brien, in the future, the developed technology will be able not only to heal wounds, but also be used to restore other tissues. He did not give examples, but, most likely, we are talking about the treatment of human internal organs. If this is true, 3D printing technology will someday be able to save many lives.
In the future, 3D printing can help treat serious diseases
As I wrote above, today scientists are able to print full-fledged human organs. This process looks a little different than in the described case. In short, the researchers take live cell samples, place them on the surface of support structures, and multiply them. As a rule, the finest plastic threads serve as the basis for printing organs. After the formation of the desired organ, scientists expose the base to ultraviolet light and it is destroyed. It sounds very high-tech, but this method has several disadvantages, which I discussed in this article.
This process looks a little different than in the described case. In short, the researchers take live cell samples, place them on the surface of support structures, and multiply them. As a rule, the finest plastic threads serve as the basis for printing organs. After the formation of the desired organ, scientists expose the base to ultraviolet light and it is destroyed. It sounds very high-tech, but this method has several disadvantages, which I discussed in this article.
It is believed that the first 3D printer was invented by American Charles Hull in 1986. At that time, this device was very large, but today the size of the printing equipment has noticeably decreased. The same can be said about the cost - you can buy a 3D printer for a very affordable price.
Generally, home 3D printers are used to print simple knick-knacks. But, as we have already seen, in the future, these devices can save many lives. In addition to medicine, 3D printing is even used in construction - a couple of years ago we talked about the fact that a huge printer began to build an entire residential area.