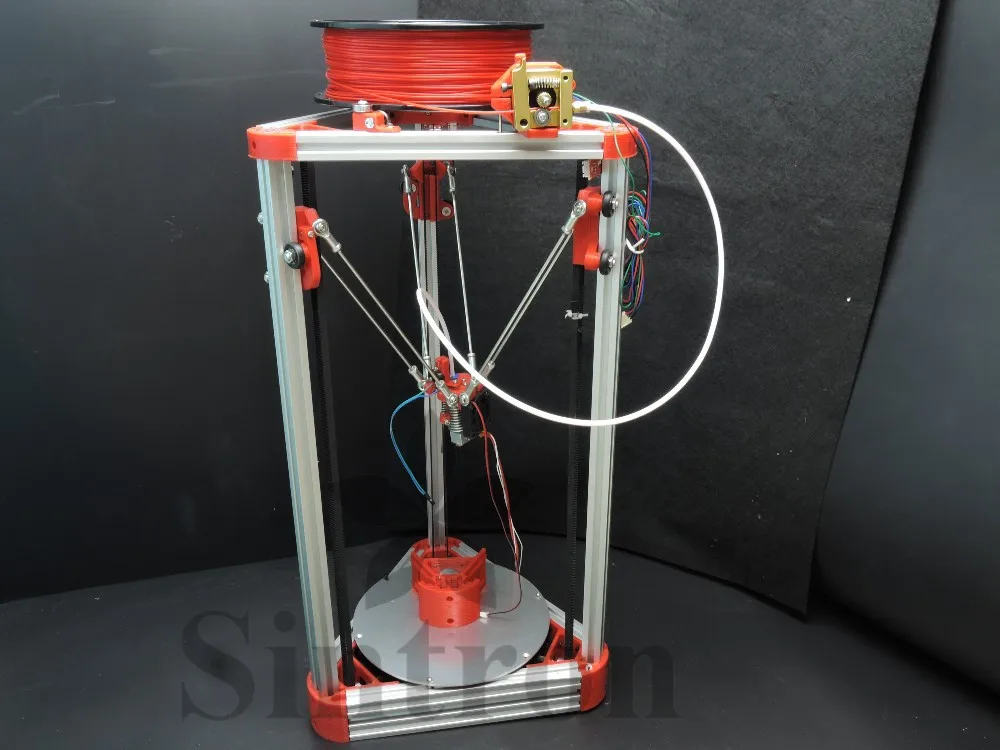
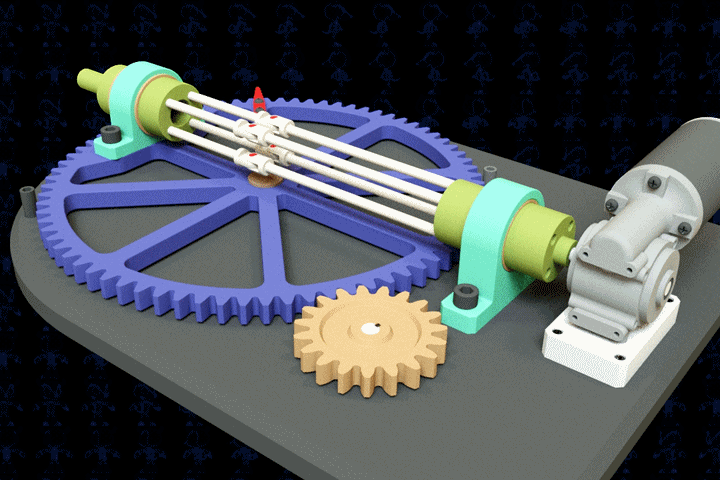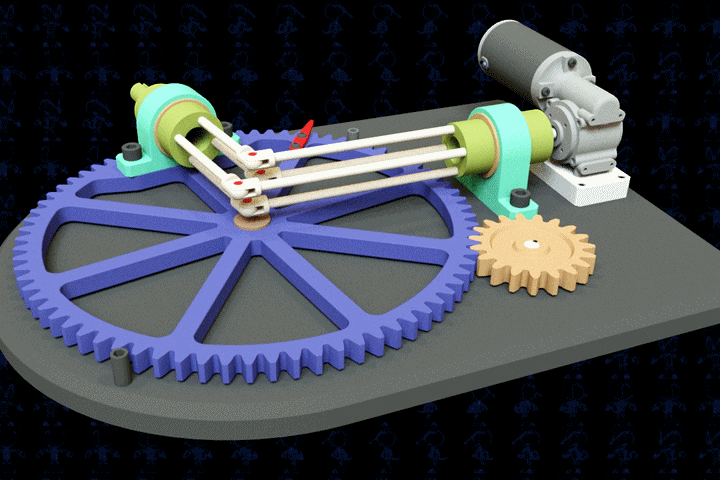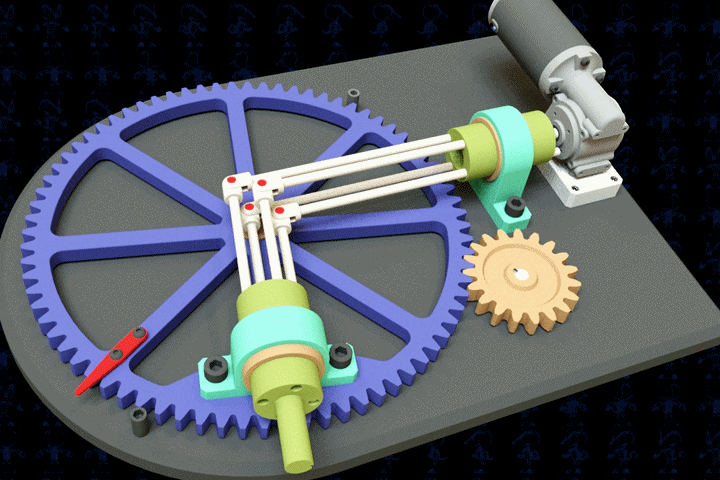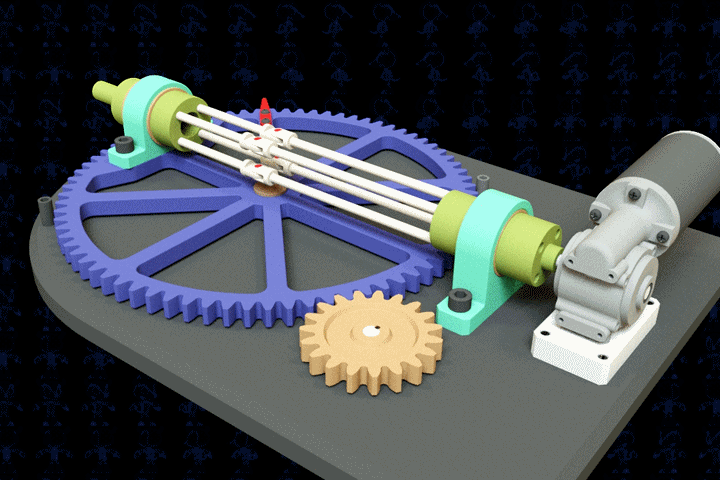
Why 3d printing is the future
Why is 3D Printing an Important Part of the Future?
3D printing is already making a difference in our world. We don’t have to look far back, in order to have a good example of that. During the pandemic crisis, when ventilator parts were missing, to respond to the high demand in hospitals, regular people with 3D printers, helped manufacture some from their home, thanks to plans that they were provided with. Here is more on the importance of these futuristic printers.
Manufacturing Techniques will take Less Time
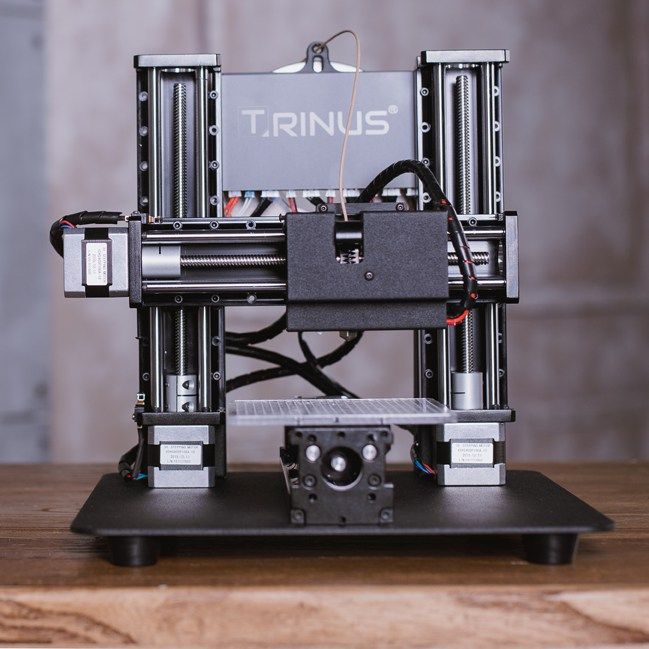
You may not know this, but the first 3D printing machine manufacturer saw the light of day, all the way back in 1983. Of course, the technology has changed a lot since then, and it will continue to do so in the years to come, making 3D printing machines, more and more useful and practical, in a large variety of ways. It is predicted that by 2030, the industry will have completely changed, through innovations. But for now, the first thing that 3D printing has been doing, in the field of manufacturing, is gain time. Before, to create a prototype, you had to build a mold, which would then be used to manufacture the sample. That was expensive and took some time. Now, with a 3D printing machine, you insert the plan in its memory, and it goes to work. Within minutes or hours (depending on the workload), you have your prototype in hand.
It is also true about creating customized pieces, one at a time, which was impossible before, without going through a long and expensive process. If you liked a product but wanted to have a few modifications on it, a few years ago, the situation would have been looking at a salesman that started laughing. He would then explain, in details, why it was almost impossible to do, unless you had a fortune to spend. Now, with 3D printing, the engineer prepares the modifications and enters them inside the information that he will feed the 3D printer. Then, the unique piece can be processed right away.
Capacity to use a Variety of Materials
When the 3D printing machine came out on the market, many wanted to see it have as many flaws as possible. This is quite normal, since it was about to become a strong competitor, as time and cost would be reduced, like we explained before. One of the faults that people said it had, was that it could only work with plastic materials. In fact, most people today still think that this is true. But this is a misconception. One of the most important innovations of this technology is when it started to print with metal. The automotive industry saw the advantages immediately, and many started integrating it in their manufacturing plant, in one way or another. The industry of 3D printing is now focussing on creating machines that will be able to print with materials such as polymers, new alloys, glass, ceramics, photosensitive resins, and composites. But the wildest idea out there, right now, is the capacity to print with food… Did we mention that 3D printing machines were going to be an important part of the future, already? Now, you know why.
This is quite normal, since it was about to become a strong competitor, as time and cost would be reduced, like we explained before. One of the faults that people said it had, was that it could only work with plastic materials. In fact, most people today still think that this is true. But this is a misconception. One of the most important innovations of this technology is when it started to print with metal. The automotive industry saw the advantages immediately, and many started integrating it in their manufacturing plant, in one way or another. The industry of 3D printing is now focussing on creating machines that will be able to print with materials such as polymers, new alloys, glass, ceramics, photosensitive resins, and composites. But the wildest idea out there, right now, is the capacity to print with food… Did we mention that 3D printing machines were going to be an important part of the future, already? Now, you know why.
In manufacturing, according to the technique you are using to produce objects, you may find yourself with problems, when it comes to precision. In such cases, it would then be impossible to create objects that are complex in their structure. Then, you would have to change technique, which would raise the cost. But that is not an issue with 3D printing. In fact, it can be as precise as you need it to be, printing elements that other modes of production could not. Any geometric complexity will not be a problem to these new machines.
In such cases, it would then be impossible to create objects that are complex in their structure. Then, you would have to change technique, which would raise the cost. But that is not an issue with 3D printing. In fact, it can be as precise as you need it to be, printing elements that other modes of production could not. Any geometric complexity will not be a problem to these new machines.
Already Helping in Medicine and Humanitarian Efforts
This is just a start, but the technology has already been helping into these two very important fields of life. In the first case, it can print parts of medical instruments, but also customized prosthetics and implants. In the second, it now takes a lot less time to build a refuge, in situations of natural disasters. Much less then having to fly a refuge kit to be built on site, since the printers are already on the ground.
Why is 3D printing the future of manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing and the future
Looking at stories from the media, there are many predictions that 3D printing is an integral part of the future of manufacturing.
Currently, the technology is rapidly being adopted in many areas of industry and as time moves forward, we shall start seeing the technology being implemented in many use cases not only limited to organisations.
The excitement for the technology is mainly stemming from one simple old economic term which is “Economies of scale“.
Similar to many technologies before it, most of the innovations begin in large institutions and then as the proliferation of the technology grows, economies of scale come into play.
You only have to look at the history of computing itself to see this trend. The first machines were large and clunky and as time went on, more and more developments lead to cheaper methods of production which lead to costs decreasing and finally the computer becoming affordable to the average home.
In terms of current historical comparison, we are at the syndication stage, where the largest adopters of 3D printing technology are institutions and early adopters are aiming to create more value from the technology.
Being a product that is catered to the manufacturing field, this is the logical focus of the market currently. Despite the largest segment being hobbyists, organisations will receive the most value from 3D printing in a number of ways.
Firstly, 3d printing gives companies the capability of in-house manufacturing at the fraction of the price.
Building hardware is hard and the biggest in the initial stage is being able to quickly build prototypes at a reduced cost. 3D printing eliminates many factors, such as expensive machining tools or the route that many companies take which is outsource parts out.
The disadvantage of this approach is simply costs that can arise from reiterations in design and also time, where companies need to compete with other companies that have also orders from the same outsourced firm. In addition, the process of delivery of the request prototype adds to the total lead time of the product development cycle.
The different 3D printing techniques.

There are a several 3d printing technologies that are used widely in the manufacturing world. We shall focus on the top 3 3D printing techniques and why organisations decide one over another.
Learn more about the 3d printing techniques
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)
Also known as Fused Filament Fabrication, this 3D printing technique is the most widely used technique. Its based on spools of plastics or a composite material that is melted and extruded out to create layers.
Companies use this technique due to it being the most user friendly method and that its the only method that offers production-grade thermoplastics like PLA, NYLON and others.
This means parts produced with FDM have in some cases better mechanical properties than other printing methods. Parts produced with FDM have better heat, impact and chemical resistance than other plastic based 3d printing techniques.
Additionally FDM printers in general are less expensive and the materials for the printing process are easily sourced and affordable.
Companies can produce both visual prototypes, functional parts for prototypes and in many cases, tooling for many manufacturing firms.
The disadvantage of FDM is that parts have less detail than other printing techniques, so uses for highly detailed small objects is a little more difficult to reproduce with FDM.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography is the oldest printing technique that offers a few different use cases and also operates slightly in the polar opposite of FDM.
SLA uses liquid resins and creates a sliced section of an object that is then hardened using a UV laser.
SLA parts are more accurately produced and offer great tolerance advantages to 3d printed parts.
They are best used for creating highly detailed prototypes for companies that require it, however their costs for both printer and material is higher than FDM.
A further challenge is the use of toxic liquid resins which offer parts that have less mechanical properties than other methods.
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering uses a powder material that is then hardened with a laser.
Each cross section is built up in the same fashion as SLA but the difference is that SLS machines (DMLS) have also the option of metallic parts that then require a sintering step to harden the finished part.
Parts produced have great mechanical properties and this method can create visual prototypes,functional prototypes and end-use parts.
The disadvantage however is its only used for short production runs due the extreme high cost of both the printer and materials. Additionally, the handling of the powder material can be dangerous if not stored properly.
So, why are so many companies adopting 3D printing?
There are a number of reasons and the biggest is when we look at the concept of economies of scale (where savings are generated by the more you produce).
We see that 3D printing has lowered the minimum efficient scale of production, which is a game-changer for manufacturers.
The minimum efficient scale in manufacturing can be surmised as the lowest amount that an organisation needs to manufacture but still being able to benefit from economies of scale by being able to offer the product at a competitive price.
A simple example would be, if a car company were to produce a small number of vehicles, the average cost of a car would be immensely high because of fixed costs, such as labour costs, rent and others.
If the car manufacturer were to produce a large number of vehicles, then the cost per unit would be lower since fixed costs are spread across the larger number of units.
To better understand this, we need to then look at the relationship between unit average cost and marginal costs.
Marginal costs put simply is the cost associated with producing one extra unit and the change it produces to total costs for that product.
Expanding on the car manufacturing industry, a car company factory at full capacity would need another production line to produce one extra car which would mean the new line being categorized as a marginal cost. By adding the extra line, the cost of producing extra cars would decrease.
By adding the extra line, the cost of producing extra cars would decrease.
This is a key important figure for many manufacturers because it helps them determine the optimal production number for their business.
How does 3D printing relate to the economy?
3D printing is a technology that has a lower efficient scale due to a few properties.
Firstly, 3D printing reduces labour costs because it can be highly automated, where a small team can run a line of printers easily without overseeing each element, affording them to work on other tasks. Secondly, 3D printing can produce highly complex geometric parts in a single process.
What does this mean? Looking at standard production methods, such as injection modelling or CNC machining, many of these technologies require multiple steps to produce items that have complex shapes and in many cases, these technologies cannot achieve the same complexity as 3D printing.
Many parts would require multiple production runs to get the desired results which would increases costs.
Additionally, to be able to create these objects, organisations need highly trained staff which also adds to their fixed costs.
3D printing can produce parts, allow for changes without requiring extra tools or equipment in comparison to other methods.
The future possibilities are exponential and this is why the world is fixated on the technology.
3D printing turns the head on standard manufacturing. Most production innovations since the industrial revolution have been incremental and have been catered to improving upon the previous generations.
Improvements were created through what others had done before, improving production lines, improving inventory systems and other standard manufacturing processes.
3D printing, on the other hand, looks at the physics of producing items, where one machine can produce items simply, quicker and easier than before without using systems of the past.
This is the reason why many companies are focusing on technology and why its potential is highly valued in the manufacturing industry.
Latest tesitmonials
what lies ahead for 3D printing
The prospects for 3D printing
Even now, the prospects for 3D printing are extremely promising. Scientists are actively developing existing 3D printing techniques, developing new technologies and types of materials, and finding new areas of application. Many call 3D printing the technology of the future, and for good reason. The technique is able to completely turn the usual way of life, changing the way most things are produced. In fact, a 3D printer is a real multifunctional factory, small and compact. Due to this, the future of 3D printing can definitely be called successful.
3D printers can significantly reduce production costs, thereby reducing the cost of products. Judging by the growing trend towards the popularization of 3D technologies, raw materials for 3D printing will become the main commodity unit in the future. In general, the prospects for 3D printing are defined for many areas. And now we will try to reveal them as much as possible.
And now we will try to reveal them as much as possible.
The Future of 3D Printing
If you try to imagine the future of 3D printing, your imagination paints a rather interesting picture. Given the great interest of scientists in the 3D bioprinting technique, which is one of the most promising 3D printing technologies, the production of artificial organs on a 3D printer is not far off. It is also safe to say that the future of 3D printing will bring us dramatic changes in areas such as:
- Construction. 3D printing of houses, or contour construction, attracts many with its futurism and simplicity. The first steps in this direction have already been taken. The pioneers in 3D printing of houses were the Chinese, followed by the government of Dubai who discovered contour building. The first 3D printed office building has already been built in this city of the future, and an entire block is planned to be printed in the near future. And just recently, the first printed house in Europe was created on a 3D printer;
- Electronics.
 When listing the prospects for 3D printing, this point should be given special attention. Scientists believe 3D printing of electronics is the future of digital device manufacturing, and with good reason. Graphene properties and its application in additive manufacturing are currently being actively researched. A huge breakthrough in this area is the creation of a graphene battery with an unlimited service life on a 3D printer;
When listing the prospects for 3D printing, this point should be given special attention. Scientists believe 3D printing of electronics is the future of digital device manufacturing, and with good reason. Graphene properties and its application in additive manufacturing are currently being actively researched. A huge breakthrough in this area is the creation of a graphene battery with an unlimited service life on a 3D printer; - Automotive and aerospace industry. The future of 3D printing is largely based on its ability to reproduce almost any element of varying complexity. In this regard, 3D printing is already widely used in the development of aircraft, machines and satellites. The ISS even has its own 3D printer, not to mention a number of successful 3D printing of cars.
- Pharmaceutical industry. Yes, yes, you can imagine. The future of 3D printing is in the manufacture of tablets and other medicines. This is confirmed by epilepsy pills legalized in the USA, made according to a special technique.
 The essence of this perspective of 3D printing is the gradual release of active substances, so that instead of many tablets, you can drink just one.
The essence of this perspective of 3D printing is the gradual release of active substances, so that instead of many tablets, you can drink just one. - Food industry. 3D food printers are gradually gaining space in cafes and restaurants. While this is probably one of the most raw 3D printing technologies out there, it has potential. Food 3D printers are especially interesting for the possibility of making food for astronauts, as well as the freedom to display culinary talent. This is confirmed by the amazing 3D-printed desserts of our compatriot.
Other questions and answers about 3D printers and 3D printing:
- Finance Which 3D printer manufacturers are best?
- Finance Which 3D printer is better to buy?
The future of 3D printers
Now let's try to imagine the future of 3D printers. There are several important points to be noted here. Below we list the most likely scenarios for the future of 3D printers.
- Improving the reliability and quality of devices. Surely, many users are looking forward to this, because most of the existing models of 3D printers cannot boast of uninterrupted operation and the absence of printing errors;
- Large-scale distribution. It is certain that the future of 3D printers will please us with their popularization. Even now, one can observe a growing trend towards the use of 3D printing in almost all areas of industry. In parallel with the fact that more and more users learn about the possibilities of technology, the demand for desktop 3D printers is also growing;
- Availability. In continuation of the previous paragraph, it is worth noting that the growing demand for 3D printers will lead to lower prices for these devices. The use of 3D printing for domestic purposes is gaining momentum, which brings new equipment manufacturers to the market. Naturally, such a step will entail a reduction in the cost of devices;
- Enlargement of the construction area.
 3D printing of large-sized objects has long occupied the minds of developers. Of course, this applies to industrial 3D printers, because the functionality of 3D printing at this scale will allow you to create full-fledged components, for example, cars and aircraft;
3D printing of large-sized objects has long occupied the minds of developers. Of course, this applies to industrial 3D printers, because the functionality of 3D printing at this scale will allow you to create full-fledged components, for example, cars and aircraft; - Expanding the range of available materials. The future of 3D printers depends a lot on 3D printing materials, because more means more possibilities. The development of special equipment and related materials is being carried out by many companies, and news about the release of new polymers is constantly appearing.
3D technologies of the future
Summing up, it remains to consider only 3D technologies of the future. These include various futuristic scenarios that, to one degree or another, are already beginning to develop today. These include the technique of virtual reality, 3D scanning to create the perfect clothes and shoes, 3D printed makeup, and more. In a way, 3D technologies of the future also include bioprinting.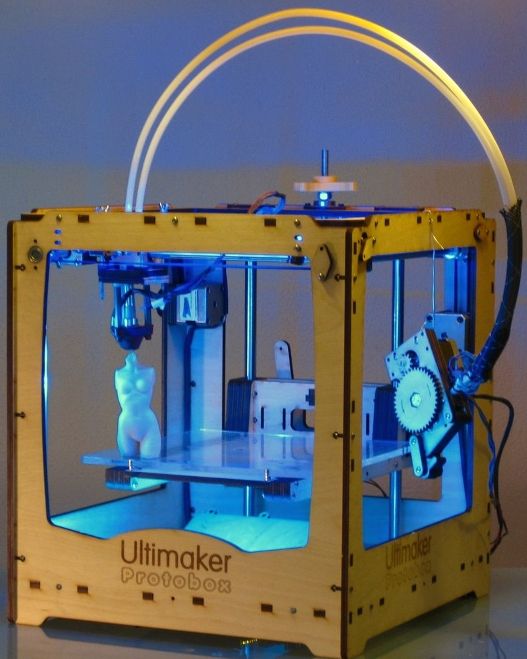 By the way, scientists are talking about building the first 3D printed settlement on the Moon and Mars, so the prospects for 3D printing are also relevant outside the Earth.
By the way, scientists are talking about building the first 3D printed settlement on the Moon and Mars, so the prospects for 3D printing are also relevant outside the Earth.
This was a list of the main scenarios for the future of 3D printing. Let's see how they are destined to come true. If you have additional questions that we have not covered, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add your questions! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
Our store offers a wide range of 3D printers, 3D scanners, 3D plastics and resins, as well as other accessories at the best prices on the Ukrainian market with delivery to all cities (Kharkiv, Nikolaev, Dnepropetrovsk, Lviv, Zaporozhye, Kherson, Donetsk, Odessa ). We also provide 3D printing, 3D scanning and 3D modeling services. For all questions, please contact us in any way convenient for you. Contacts are listed here. We look forward to collaborating!
Back to Home
Perspectives, development and the future of 3d printers
3D printing is an extremely promising technology that has the potential to change how many things are made. In addition, the use of 3D printers will significantly reduce the production time of various products and reduce their final cost. Let's consider in which areas the use of 3D printing is most promising, what is the future of this technology and how quickly it will develop.
In addition, the use of 3D printers will significantly reduce the production time of various products and reduce their final cost. Let's consider in which areas the use of 3D printing is most promising, what is the future of this technology and how quickly it will develop.
Relevance of 3D printing
3D printing technology is relevant due to its ease of use and saving time spent on the production of various types of products.
Printing of 3D objects also provides high-precision reproduction of the necessary shapes and details of a particular object. At the same time, manual labor is practically reduced to zero, which means that the cost of the operator and maintenance of the 3D printer will be minimal. Subsequently, this will reduce the cost of the finished product.
Thanks to these benefits, 3D printing is successfully used in many industries and everyday life.
The promise of 3D printers in various fields
3D printing technology has quite a lot of promise when applied correctly. The following areas of activity are most in need of 3D printing services:
The following areas of activity are most in need of 3D printing services:
- Construction. In the construction industry, 3D printing can be a powerful addition to traditional construction methods. Since this technology does not require the involvement of a large number of people to perform hard work. A few operators and craftsmen are enough to service the construction 3D printer. The first successful experiments in the manufacture of building parts and the construction of houses have already been carried out in China and the United Arab Emirates.
- Electronics. In the manufacture of digital devices, 3D printing will reduce the time for the manufacture of labor-intensive parts, microcircuits and hardware electronics. In particular, 3D printing is already developing the first samples of graphene batteries that have an unlimited service life.
- Mechanical engineering and automotive industry. In this area, with the help of three-dimensional printing, experimental models of future spare parts and parts are created, which later allow the production of products of perfect quality.
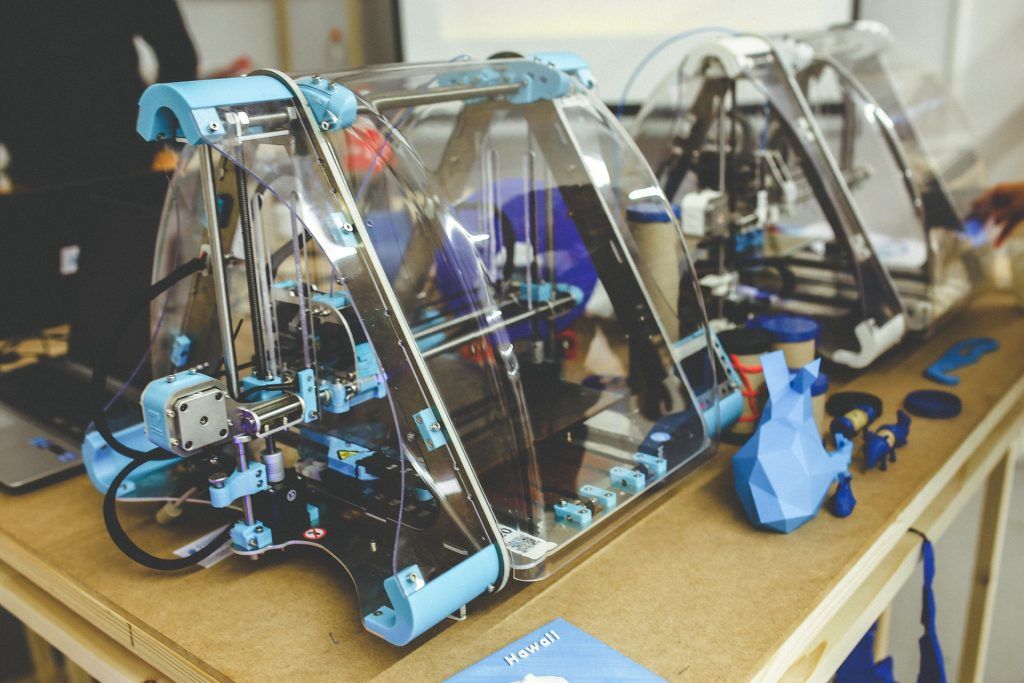 This is possible due to the detailed study of a three-dimensional object during its creation and printing of a finished computer model, which has a high level of detail.
This is possible due to the detailed study of a three-dimensional object during its creation and printing of a finished computer model, which has a high level of detail. - Aerospace industry. The use of 3D printing in this industry is explained by the ability to create innovative designs of any complexity. Details of satellites, rockets and other space objects are printed from metal, polymers and other types of heavy-duty materials.
- Medicine and pharmaceuticals. In medicine, 3D printing technology is extremely important. Therefore, in this industry it is studied in great detail. With the help of a 3D printer, it is possible to print prototypes of human organs, prostheses, bone tissue implants. Even the first steps are being taken to develop and print real organs that will take root well in the human body. In the pharmaceutical industry, 3D printing is mainly used to create tablets that will gradually release active substances after ingestion.
- Advertising.
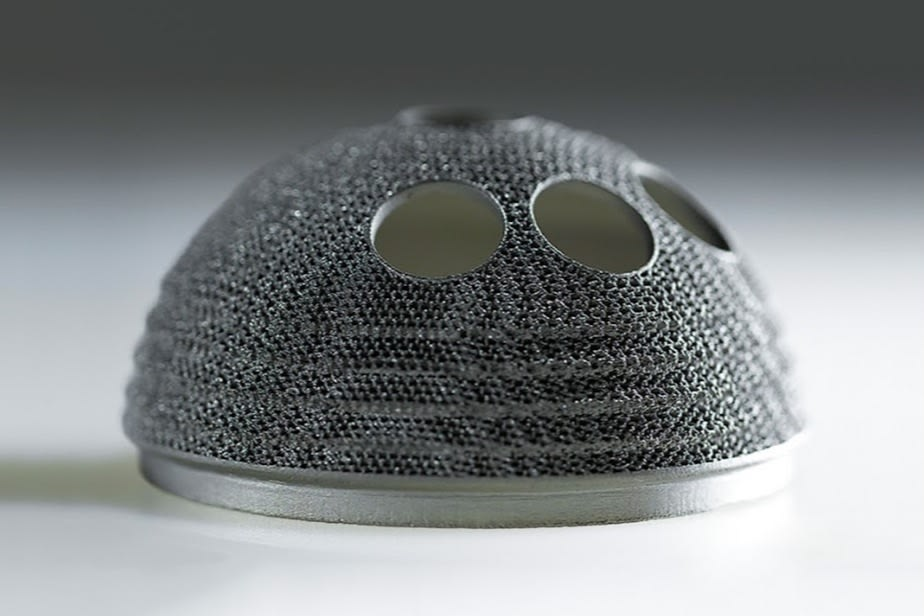 For advertising purposes, 3D printers print prototypes of various products, demonstration and handouts.
For advertising purposes, 3D printers print prototypes of various products, demonstration and handouts. - Food industry. 3D food printers are especially interesting because they allow you to create edible objects from familiar foods. 3D printing makes it possible to create unique decorations and complex multi-color objects with high detail.
The future of 3D printing
3D printing, if properly developed and explored, will be more accessible in the future. Since 3D printers will be common as a work unit in many areas. At the same time, prices for such equipment are likely to fall. Since they will be produced by various companies in large quantities to satisfy the demand of all buyers.
The growing demand for 3D printing will lead to the development of new types of 3D printers and materials for creating products.
Also for larger 3D printing, large-scale equipment will be created that will allow printing very large products for construction needs, engineering and other industries.
Unexpected possibilities of 3D printing
In addition to the standard creation of three-dimensional objects, the development and 3D printing of unique and customized products is also available on a 3D printer. Their shape, structure and design features are limited only by the user's imagination. It is possible to produce unusual products. For example, non-melting ice sculptures, curly perfectly fried pancakes or fine jewelry.
Who is the future of 3D printing?
Primarily, the future of 3D printing depends on inventors who create new types of printers and develop new printing technologies depending on the type of material used. Most often, 3D printing novelties appear in research centers, industrial enterprises and technical departments of various universities. This is due to the fact that people working in such institutions are interested in the development of new technologies. Since innovation will help to improve and improve the processes of creating products in specific areas. In addition to researchers and students, a large number of developments are carried out by children and 3D printing enthusiasts. For example, the invention of the first 3D-printed prosthesis belongs to 17-year-old Easton LaChapelle.
In addition to researchers and students, a large number of developments are carried out by children and 3D printing enthusiasts. For example, the invention of the first 3D-printed prosthesis belongs to 17-year-old Easton LaChapelle.
In addition to inventors, organizations that sponsor new developments are also responsible for the continued development and improvement of printing methods.
Help. Three companies are considered the most famous in the field of 3D printing: Shapeways, Sculpteo and Materialize. They are engaged in the professional development and release of new models of 3D printers, materials, as well as the improvement of existing technologies and the creation of new ones.
What's in store for 3D printing in the next few years?
Experts in the field of 3D printing in 2021 make the following forecasts for its development:
- The spread of 3D printing will be massive. Studios for creating three-dimensional objects will be distributed in much the same way as studios for photocopying and printing materials.
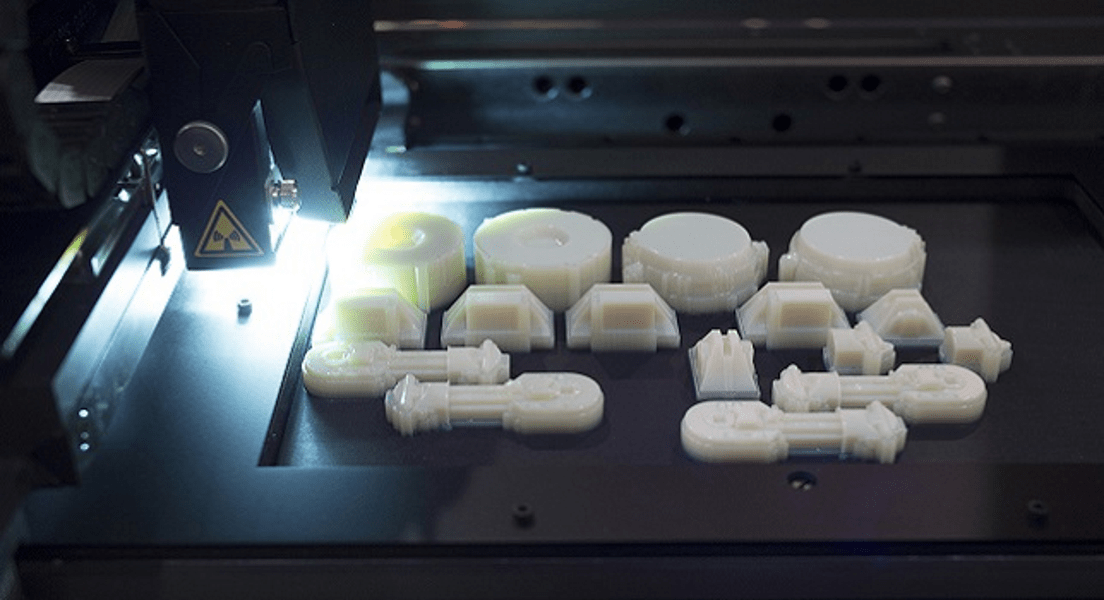 3D printing will be carried out both on standard models and on individual projects.
3D printing will be carried out both on standard models and on individual projects. - Small-scale production of various products will completely switch to 3D printing technology. This will help to significantly reduce the price of finished products.
- Medical scientists will master the creation of full-fledged and fully compatible organs on a 3D printer, which will be printed from dividing human cells.
- With due diligence confirming the safety of 3D printing for construction purposes, many companies in the industry will start using powerful industrial printers to create the required building elements. At the same time, the time to build houses will be reduced and the proportion of hired workers who perform hard work will decrease.
A revolution in materials
A standard 3D printer uses plastic materials as a filament. However, technology development continues at an accelerated pace. Thanks to this, innovative materials appear on the market, such as:
- Metal powder.
 This material is mixed with a polymer during printing and is used in the technology of laser sintering of metals. Products printed from a mixture of polymer and metal powder have increased strength comparable to real metal.
This material is mixed with a polymer during printing and is used in the technology of laser sintering of metals. Products printed from a mixture of polymer and metal powder have increased strength comparable to real metal. - Graphene. This carbon material is being used experimentally to develop a new composite. Ideally, a 3D-printed graphene sheet would be one molecule thick. By weight, the material will be lighter than air, but its strength properties will be very high - the sheet is ten times stronger than steel.
- Ceramic foam. Such material has flexible characteristics that can be changed depending on the purpose of use. From ceramic foam on a 3D printer, you can print both a very light figure and a heavy monument. In theory, development already exists. But it requires a series of tests and stabilization of functional properties.
What are the unusual technology projects of the future?
Among the unusual 3D technologies of the future, special attention should be paid to:
- creation of individualized clothes and shoes, which will be produced on the basis of 3D body scanning;
- make-up created by special portable 3D printers, which is very fast and yet very precise in fine details;
- bioprinting with living cells and creation of tissues and organs from hydrogel.

Learn more