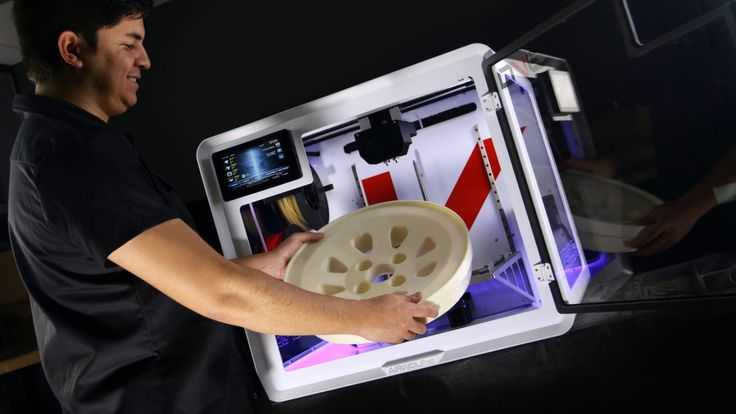
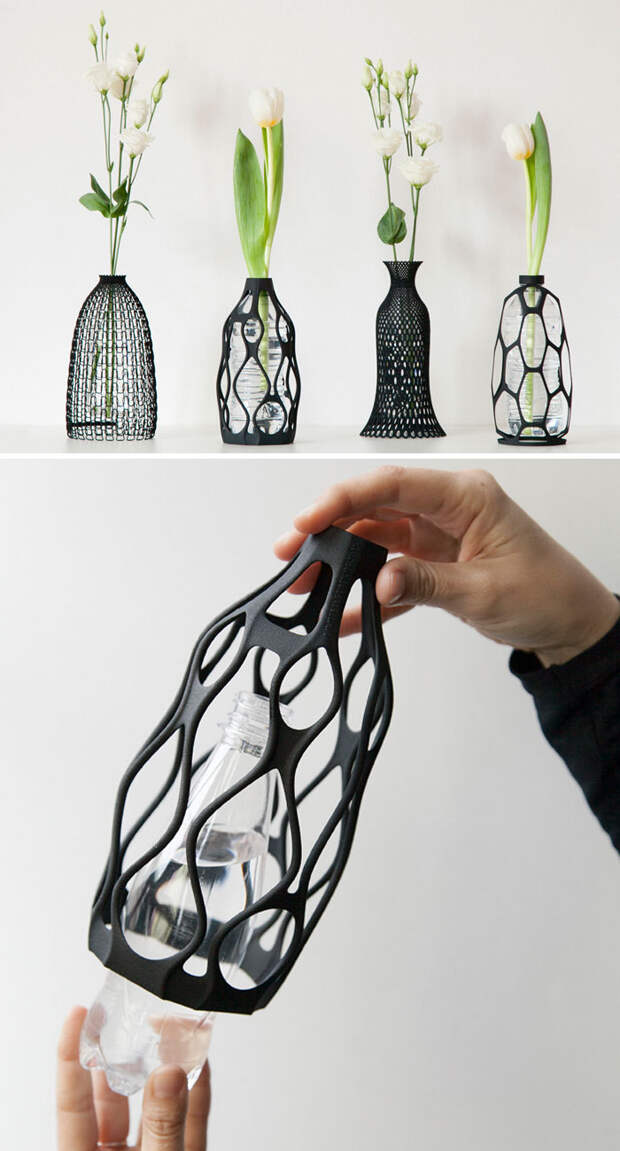
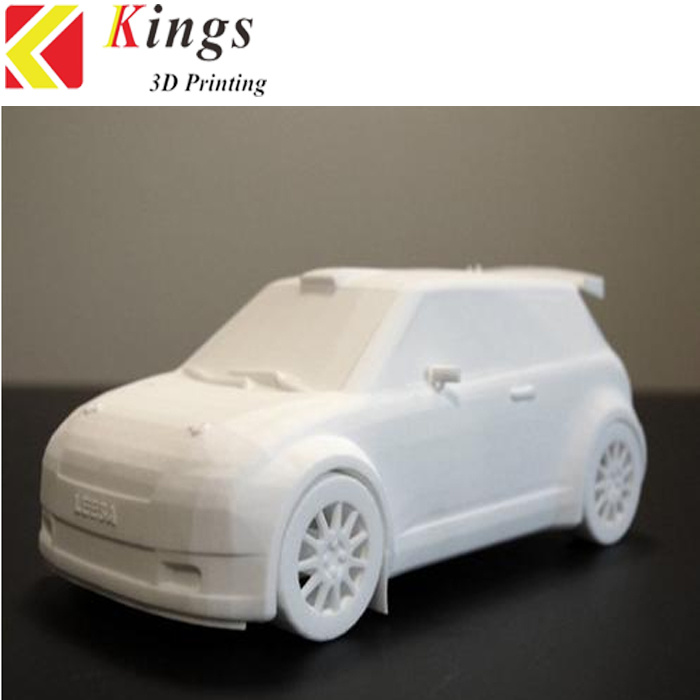
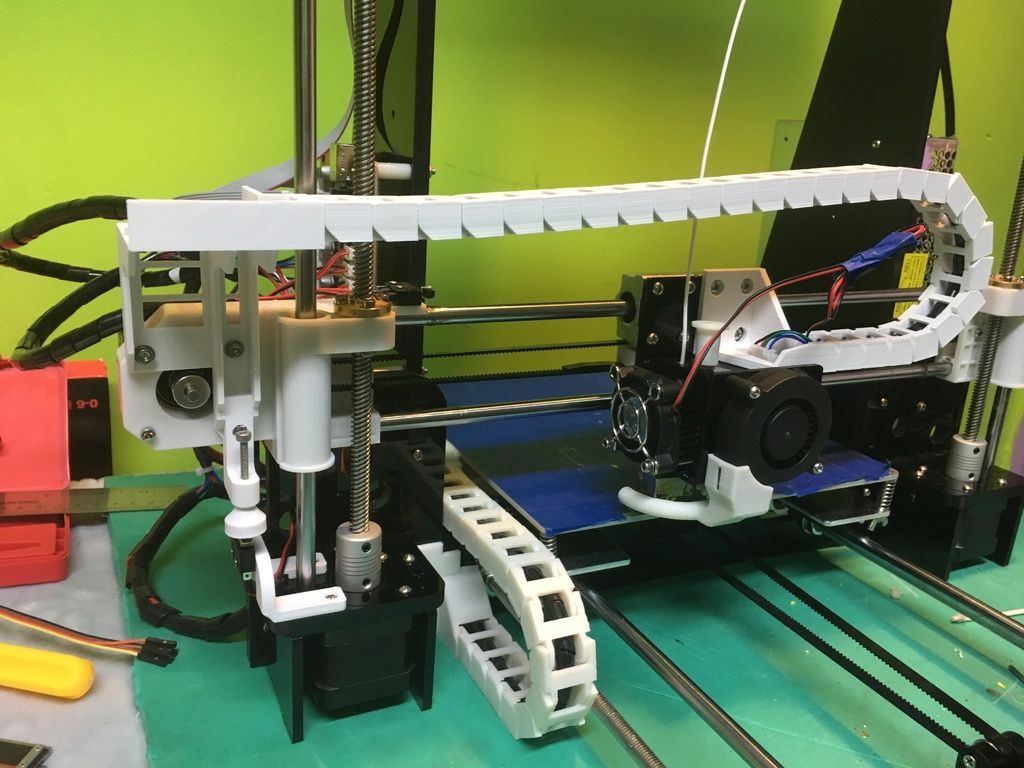
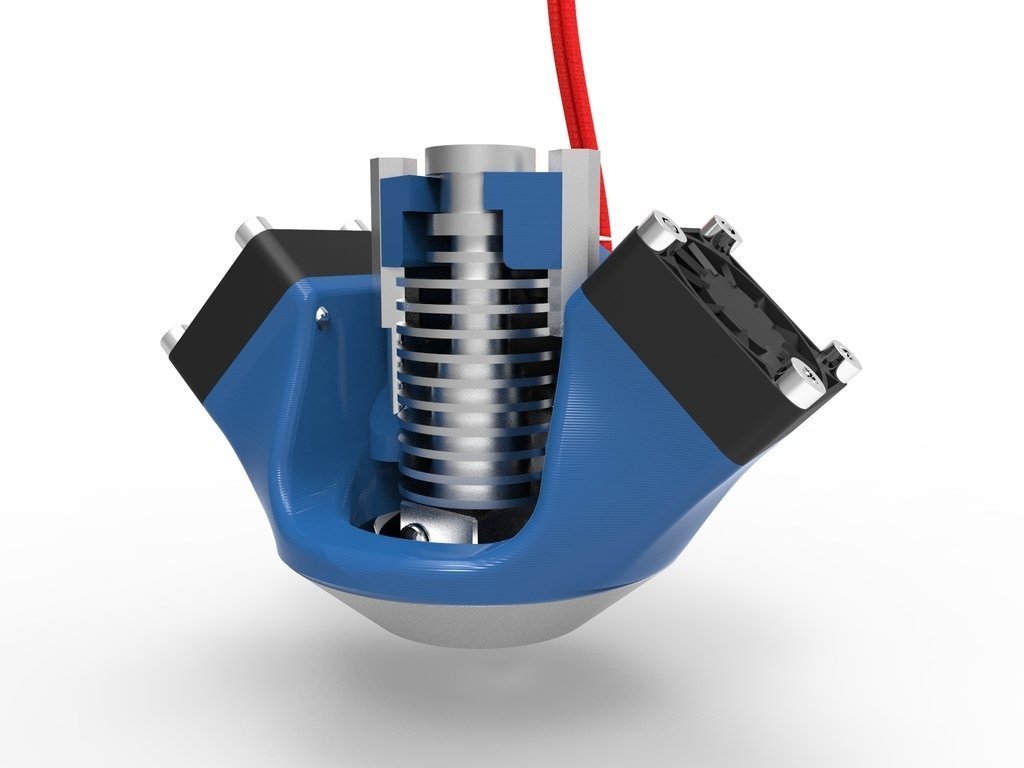
What is a 3d printing engineer
Making it work: 3D printing and engineering
Adam Kohut12 December 2019
Applications
Engineering is about creating designs that work as efficiently as possible. Wasted time is wasted money, and to have a project stall because of an unforeseen design flaw or a delay in the supply chain can be as frustrating as it is costly. That’s why control is so valuable – control of your time, control of your costs, control of your entire process. And 3D printing is all about control.
Using 3D printing, engineers can create new prototypes – even those with complex internal structures and geometries – address problems, and find solutions, without ever leaving their working environments. The right 3D printer holds the potential to shrink development time from months to days, encourages collaboration between peers, and enables the creation of rapid prototypes and end-use parts – ensuring that projects are finished on deadline, within budget, and bring about desired results.
Design flexibility
When creating custom parts for small bore motorcycles, engineers at MNNTHBX (Man in the Box) know that the design and testing phases both have the capacity to be time-consuming and expensive, especially when using materials such as aluminum.
Using Ultimaker 3D printers, MNNTHBX is able to increase the flexibility of its designs and improve product test phases. It has also seen a marked increase in its return on investment, saving upwards of $1,000 per printed part.
A 3D print mounted on a part created by small-bore motorcycle parts manufacturer MNNTHBX
“Our printer basically paid for itself the first time we saw a product through prototyping. Being that we prototype roughly 15 products annually, the cost savings become apparent,” Greg Hatcher, Owner of MNNTHBX, said. “3D printing on Ultimaker mitigates risk and opens the door to creating working concepts on extremely low investment. Long gone are the days of spending thousands of dollars running multiple prototypes through traditional CNC machining methods. When we take a design to the machine shop, we know before we start that it’s a fully functional design meeting our standards.”
Proof of concept
It’s one thing to create a bold new design – it’s another entirely for that design to work as intended.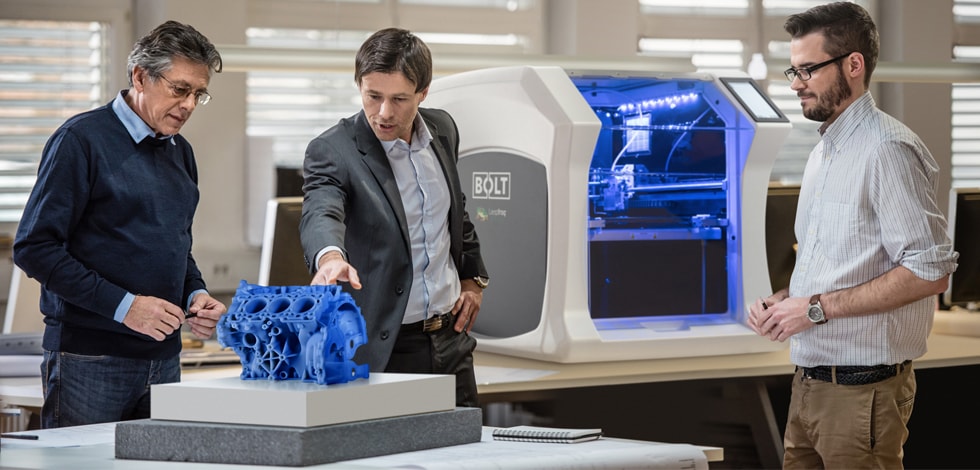 Sending those designs into space adds an additional level of complexity. Honeybee Robotics has contributed critical planetary analysis technology incorporated into three of NASA’s Mars mission, including planetary drills and sampling systems on the Curiosity rover.
Sending those designs into space adds an additional level of complexity. Honeybee Robotics has contributed critical planetary analysis technology incorporated into three of NASA’s Mars mission, including planetary drills and sampling systems on the Curiosity rover.
Honeybee Robotics’ projects demand complex, load-bearing metal parts that can survive harsh environments. Using 3D printing, engineers were able to quickly and cheaply test concepts and establish project parameters, rather than relying fully on methods of outsourced fabrication, which were slower and more costly.
A soil scooper partially created with 3D printing by Honeybee Robotics
“A lot of what we do is to build subsystems and then test their performance,” says Yoni Saltzman, Project Engineer, said. “How fast they are, things like that. So physically building key elements of the robot is what the printer allows us to do cheaply and quickly.”
End-use parts
At a Heineken brewery in Seville, Spain, Ultimaker printers are used to create parts in-house, which are then implemented on its bottling line, replacing metal parts that are heavy, and tend to knock bottles over.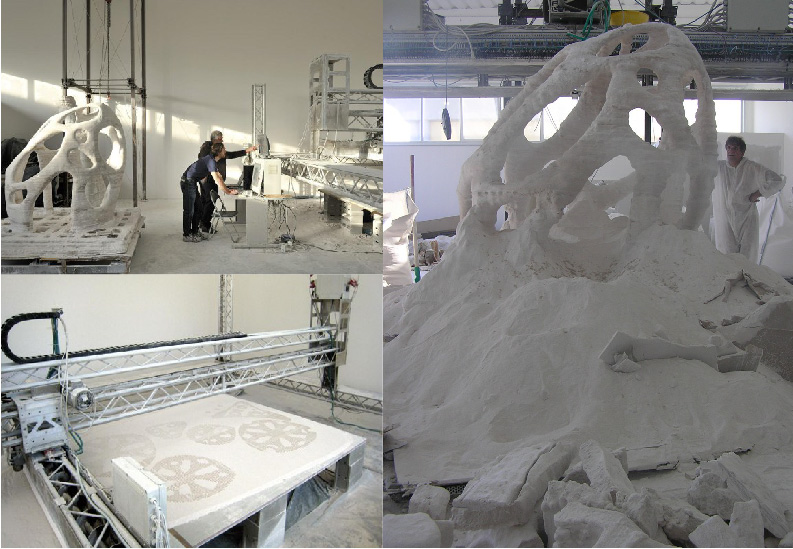 The redesigned 3D printed parts are lighter and cheaper alternatives, and now play active roles in Heineken’s manufacturing environment.
The redesigned 3D printed parts are lighter and cheaper alternatives, and now play active roles in Heineken’s manufacturing environment.
“3D printing has proven to be a technology that helps us, brings value to us, and enables our people to work more efficiently,” Juan Padilla, Packaging Manager at the plant, said.
Watch the videoLow-volume production
3D printing can also play a part in low-volume production of complex parts. IMI Precision Engineering is a world leader in motion and fluid control technologies. It needed a new additive manufacturing technique that would allow the creation of geometrically complex parts. By turning to 3D printing and the Ultimaker S5, the firm saved thousands of dollars in part creation – and nearly 2,000 hours per year in labor.
A finished complex print created by IMI Precision Engineering
“The Ultimaker S5 offered the best value, with the size and materials we needed to print all the parts,” Kathryn Jones, an IMI Graduate Engineer, said.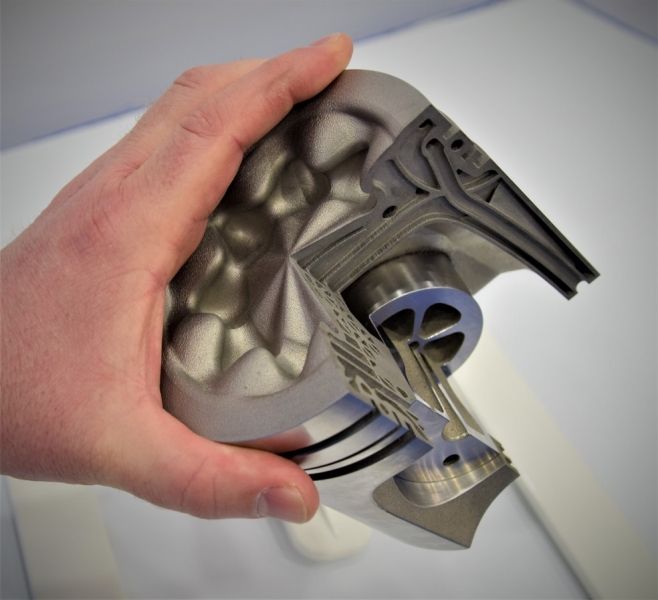 “It added new capability to another 3D printer that we had purchased last year, with lower costs for low volume parts and improved manufacturing efficiency.”
“It added new capability to another 3D printer that we had purchased last year, with lower costs for low volume parts and improved manufacturing efficiency.”
Ready to introduce 3D printing into your workflow?
Discover Ultimaker 3D printers
How 3D Printing Will Change Your Engineering Degree
In recent years, 3D printing has truly begun to capture the imagination of the masses, as low cost printers for personal use begin to make it possible for hobbyists and aspiring designers to create objects designed in CAD software right on their desks.
3D printing is also triggering a change in the way both small businesses and industry giants build and design their products. This is starting to be reflected in today’s engineering degrees and as this technology changes and matures, so will the future of engineering and the engineering degree. So what changes can you expect 3D printing to bring to engineering over the next ten years? And what do these changes mean to you and your engineering degree in the future?
The Future Of 3D Printing
Three dimensional printing, or additive manufacturing, goes beyond the capability of printing in the traditional sense of ink on paper, allowing for 3D objects to be physically printed before your very eyes. 3D printers allow you to create prototypes, models and products out of materials such as plastics and metals. The printers do this by creating layer upon layer of your design in your chosen material until the final product is formed. 3D printing allows companies and individuals to rapidly prototype ideas for new parts or products and also promises to cut down costs on the creation of products through savings in supply-chains, product waste and storage.
3D printers allow you to create prototypes, models and products out of materials such as plastics and metals. The printers do this by creating layer upon layer of your design in your chosen material until the final product is formed. 3D printing allows companies and individuals to rapidly prototype ideas for new parts or products and also promises to cut down costs on the creation of products through savings in supply-chains, product waste and storage.
The benefits of 3D printing are likely to revolutionise many industries. The automotive and aerospace industries benefit from much shorter lead times than with associated traditional engineering methods such as casting or machining, allowing for much faster development and testing of components. In the future, it may even be possible for large components or even entire cars to be entirely 3D printed, as recently demonstrated by Local Motors at the 2014 International Manufacturing Technology Show in Chicago, USA.
The ability to print electronic circuitry points to a future of consumers being able to 3D print electronic consumer products such as mobile phones, or the possibility of producing highly customized products based on individual consumer preferences.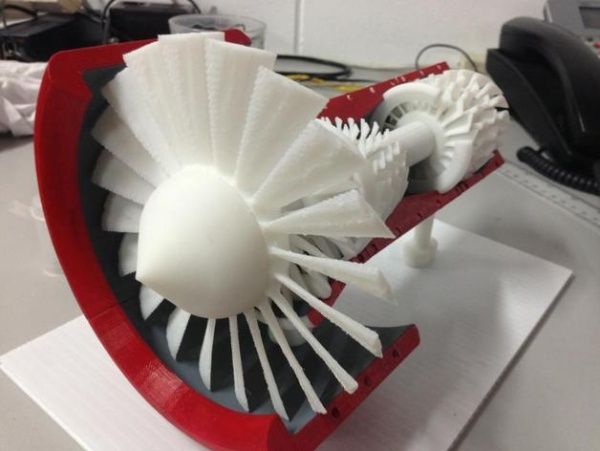 Google has recently partnered with 3D Systems to develop Project ARA, a modular phone which will allow customised 3D printed personalised features, which could point to a future of consumer electronics highly shaped by 3D printing.
Google has recently partnered with 3D Systems to develop Project ARA, a modular phone which will allow customised 3D printed personalised features, which could point to a future of consumer electronics highly shaped by 3D printing.
The food industry is also set for a revolution thanks to 3D printing. NASA has invested in the technology in the hope that one day its astronauts will be able to print their food whilst in space. Whilst printers currently exist that allow for 3D creations of foodstuff such as chocolate and pasta, 3D printing may in the future be able to allow fine control of the nutritional content of many types of food, which in turn could help tackle several health problems such as obesity and diabetes or even world hunger.
Healthcare is also set to benefit hugely from developments in 3D printing. 3D printing has already found use in preparing dental prosthetics, hearing aids and bespoke scaffolding for joint replacement and reconstructive cosmetic surgeries. The promise of printing functional human tissues could lead the way for 3D printing organs such as kidneys to help test new drugs and even directly replace failing organs.
Degrees That Will Push The Future Of 3D Printing
As 3D printing itself is a relatively new industry in its own right, there are not yet many degrees available that focus solely on 3D printing, but there are a select few already in existence.
One such degree is a Masters degree in 3D Bioprinting that will appeal to postgraduate students with an interest in regenerative medicine. Offered in partnership by Queensland University of Technology and the University of Wollongong (both in Australia) and University Medical Center Utrecht of the Netherlands and the University of Würzburg in Germany, this degree will focus on the biofabrication of new body parts.
There are many types of engineering degrees that will give you a background that is directly applicable to the world of 3D printing, and some even encompassing different subjects areas that will give you direct access to the techniques used in additive manufacturing processes. To name a few:
- Materials & Chemical Science
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electronic Engineering/Mechatronics
- Civil Engineering
- 3D Modelling/Industrial Design
Materials & Chemical Science
Material science is one of the most important areas for innovation in 3D printing.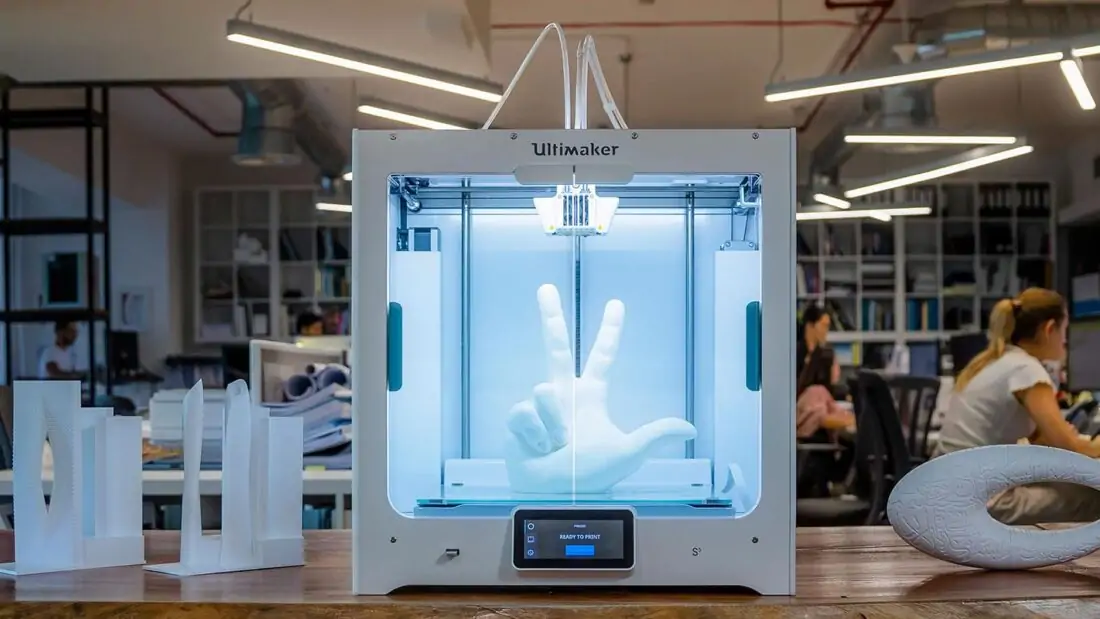 Additive manufacturing processes exist for a range of different materials already such as plastics, metals, foodstuffs, wood and concrete. For 3D printing to fulfill its potential to revolutionise different industries, material science has to progress what is possible in terms of printing material.
Additive manufacturing processes exist for a range of different materials already such as plastics, metals, foodstuffs, wood and concrete. For 3D printing to fulfill its potential to revolutionise different industries, material science has to progress what is possible in terms of printing material.
Studying a degree incorporating material science and technology will help you to develop materials that a more durable, lighter, safer and more environmentally friendly to use.
The need for modern, low cost and durable printing materials also extends to chemical science, where advances will lead to more advanced plastics for use in products. In the health industry, it is hoped that advances in 3D printing and chemical processes will lead to molecule level printers that are able to print drugs on demand. So look for degrees in chemical engineering to get involved in this area.
Mechanical Engineering
3D printing makes it possible to produce objects with much more complex structures than traditional manufacturing methods and is likely to become the go-to manufacturing process for many different areas in manufacturing.
By studying a degree in Mechanical Engineering you will be able to equip yourself with knowledge of the latest developments in industry and you will be well placed to make your career in revolutionising manufacturing processes.
SEE MORE: Mechanical Engineering Degrees
Electronic Engineering/Mechatronics
Studying a degree in electronic engineering or mechatronics will allow you to apply yourself to the integration of electronic components and circuitry in 3D printed components, or even study the electronics and robotics that will control the manufacturing processes of the future.
SEE MORE: Electronic Engineering Degrees
Civil Engineering
3D printing is poised to have a dramatic impact upon architecture, building design and manufacturing, with entire houses already produced in China with giant 3D printers. 3D printing allows building designers to experiment with shapes and geometries in design that may not be financially viable with existing building techniques.
By studying a Civil Engineering degree you will learn how engineers approach industrial problems and how 3D printing can improve upon existing solutions.
SEE MORE: Civil Engineering Degrees
If you are more interested designing objects to create in 3D than the printing process itself, degrees in 3D modelling and Industrial design will both give you the technical and creative skills you need to make a career in designing items for manufacturing. Talented 3D modellers and Industrial designers that know how to design products to harness the capabilities of 3D printing will be help to drive innovation of additive manufacturing.
There are many different areas of Engineering that will benefit in the future from the advancements in 3D printing. Our advice is to pick the area of engineering that interests you the most to study and if you can apply what you learn to 3D printing, then you will help to drive the manufacturing revolution.
If you want more information about Engineering Degrees you can check out our Engineering Directory here.
description, where to get in Russia, prospects
Higher education in Synergy: leading university, all forms of education, star teachers
Apply
Advertising
Category: Physical and technical sciences and technologies
Promising
The profession of 3D printing engineer is relatively new in the labor market. Such specialists are engaged in maintenance of equipment designed for 3D printing of physical objects, software development, installation and adjustment of 3D printers. Also, a 3D printing engineer can be engaged in research activities in his field. nine0005
Close
advertising
On the profession
Universities 15
What USE submit
Courses Link
salaries: how much does an engineer 3D printing
* 9000 9000 9,000Experienced: 50000 per month
Professional: 70000 per month
Salary in a particular region or company may differ from those given.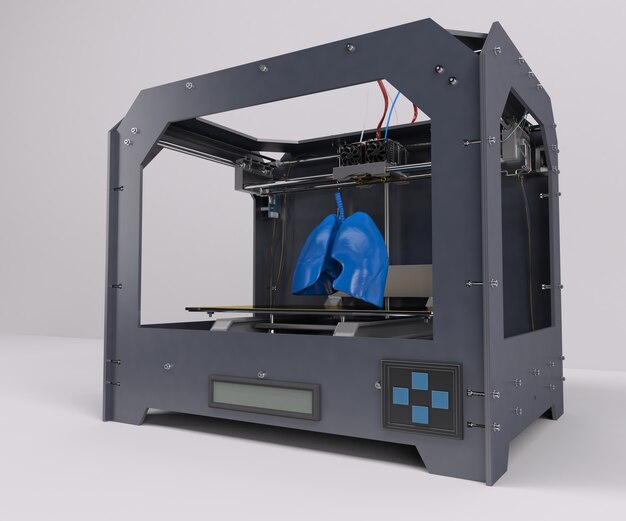 Your income is greatly influenced by how you can apply yourself in the chosen field of activity. Income is not always limited only by the fact that you are offered vacancies in the labor market. nine0005
Your income is greatly influenced by how you can apply yourself in the chosen field of activity. Income is not always limited only by the fact that you are offered vacancies in the labor market. nine0005
Demand for the profession
The market for 3D printing services is developing unevenly. There are certain areas where such specialists are in high demand. However, as a rule, very strict requirements are imposed on applicants in terms of qualifications and professionalism. It seems that over time the need for 3D printing engineers will increase significantly. Many areas of activity, from medicine to industrial production, will attract such specialists. Prospects for the profession are wide. nine0005
Who is the profession for?
A 3D printing engineer is focused on working with complex computer technology. Such a profession makes special demands on the personal qualities of a specialist.
The profession can be recommended to those who:
- Interested in technology, computers, programming;
- Purposeful and organized;
- Can formulate problems and build algorithms for solving them;
- Comprehensively developed, erudite, has a large vocabulary; nine0066
- Interested in innovation, adapts easily to new technologies;
- Able to work in a team.

Career
Career growth is not obvious, this profession is not yet widespread in the labor market. Such specialists work in rather specific organizations that provide narrow-profile services. However, a qualified 3D printing engineer is a highly qualified specialist in the field of programming and the use of computer systems. Such engineers will be able to achieve good positions in related professions, in large industrial and commercial structures. Most often, a young engineer is expected to occupy the position of a specialist in a scientific or industrial organization. nine0005
Responsibilities
Being a highly specialized specialist, a 3D printing engineer performs the entire range of maintenance and operation of 3D printers.
His duties include:
- Installation and adjustment of equipment for 3D printing;
- Development, installation, maintenance of 3D printer software;
- Perform routine maintenance, minor repairs of equipment;
- Adaptation of the terms of reference to the specific conditions for the manufacture of 3D printing products; nine0066
- Control of geometric and physical parameters at all stages of product manufacturing;
- Purchase of additional equipment and consumables.

Rate the profession: 12345678910
The profession is more suitable for those who like the following subjects at school: physics and informatics
Similar professions
-
Atomic physicist (nuclear physicist)
nine0065 -
R&D Engineer
-
Metrology Engineer
-
Operations Engineer
-
Compressor station maintenance engineer
-
Astrophysicist
-
Astronomer
-
Astrochemist
-
Automotive mechatronics engineer
nine0065 -
Physical Testing Technician
-
Thermal Engineer
-
Thermal engineer
- nine0006 Nanophysicist
-
Optician
Quality Control Engineer
Space Ballistic
3D printing engineer - description of the profession, obtaining a specialty, job duties and salary in Moscow
3D printing engineer - description of the profession, obtaining a specialty, job responsibilities and salary in Moscowhome
Professions nine0005
Engineering
3D printing engineer
- Geodesy, cartography
- Mining, mine surveying, geology, resource extraction, excavations
- office work
- Design
- Journalism, writing, criticism
- Engineering nine0066
- Art, cinema, theater, sound work
- IT, programming
- Personnel, work with personnel
- Logistics, merchandising
- Marketing, advertising, PR
- Medicine, health care, medical supplies manufacturing
- International relations, linguistics
- fashion, beauty nine0066
- Scientific specialties
- Pedagogy
- Nutrition, gastronomy
- Working with animals, agriculture and nature management
- Working specialties
- Craft, printing, industry
- Sport
- Construction, design, property management nine0066
- Transport, auto industry
- Tourism and entertainment
- Management of organizations and personnel, administration
- Economics, business, consulting, insurance
- Jurisprudence
- Other
3D printing engineer is engaged in technical support, work with equipment, software, creation of 3D models. Specialists must have in-depth knowledge of engineering, programming and mathematics. The profession is connected with future specialties. nine0252 The profession is suitable for people interested in physics and mathematics (see
Specialists must have in-depth knowledge of engineering, programming and mathematics. The profession is connected with future specialties. nine0252 The profession is suitable for people interested in physics and mathematics (see
choice of profession, which is important for school subjects).
Brief description
The profession of a 3D printing engineer has appeared quite recently, but its value and social significance cannot be underestimated. Thanks to 3D printing, unique products are used today that are used in the field of medicine and industry. Mathematicians and engineers are constantly developing more advanced technologies that allow them to create spaces, anatomical models, memories, homes, and prostheses using this type of printing. And the printers used to print biomaterials make it possible to create human skin, a step forward in the treatment of injuries, injuries, accelerating the rehabilitation period. The engineer, who is an excellent programmer, technician, biologist and even a chemist, is in full control of the introduction of 3D printing, as the profession makes him feel the composition and characteristics of various materials. To work in this area, you need to have a technical education, attending IT courses, model conferences will be an advantage. The specialist must be able to independently design a 3D model, select the necessary materials, calculate all the risks, and then print, create products for the medical, aviation, industrial, etc. industries. nine0005
To work in this area, you need to have a technical education, attending IT courses, model conferences will be an advantage. The specialist must be able to independently design a 3D model, select the necessary materials, calculate all the risks, and then print, create products for the medical, aviation, industrial, etc. industries. nine0005
Performance characteristics
3D printing engineers use a variety of materials, computer programs and industrial 3D printers for their work. Today, these specialists need medical centers, industry, aerospace, engineering and other industries. There are few specialists, their work cannot be named simply because the duties of a 3D printing engineer include: choosing new materials, conducting tests, using modern software to improve and adjust the parameters of a 3D printer; development of layouts, development of raster images for subsequent printing; full control over the letter; Studying new technologies; Knowledge of certification rules, requirements for 3D models and finished products.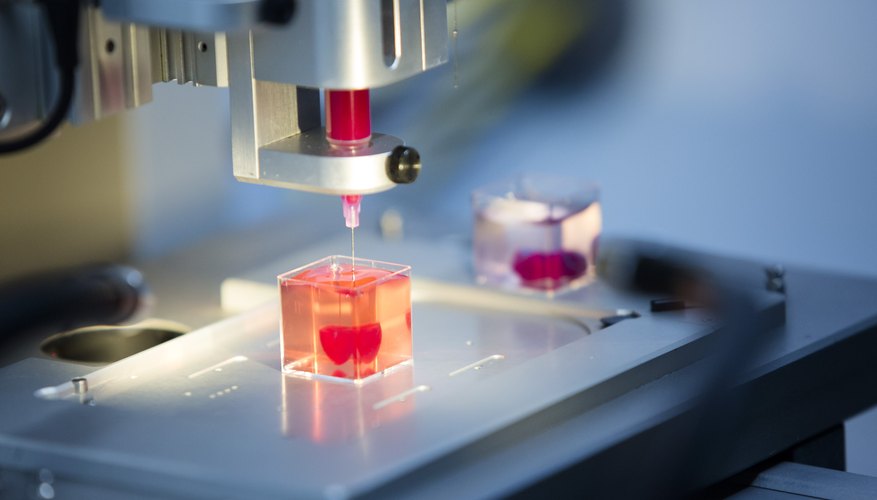 documentation development, software debugging; selection of new equipment, training of other employees; equipment maintenance. Responsibilities vary by location, but a 3D Printing Engineer must be a broad-based specialist who is willing to quickly learn new technologies and then successfully apply them in practice. Employers have strict engineering requirements because the salary of such specialists is significant. They must have at least 3 years of practical experience, it is important to have technical knowledge of a foreign language. A 3D printing engineer must know the basics of economics and marketing, because his duties include optimizing workflows aimed at reducing the cost and speed of printing. nine0005
documentation development, software debugging; selection of new equipment, training of other employees; equipment maintenance. Responsibilities vary by location, but a 3D Printing Engineer must be a broad-based specialist who is willing to quickly learn new technologies and then successfully apply them in practice. Employers have strict engineering requirements because the salary of such specialists is significant. They must have at least 3 years of practical experience, it is important to have technical knowledge of a foreign language. A 3D printing engineer must know the basics of economics and marketing, because his duties include optimizing workflows aimed at reducing the cost and speed of printing. nine0005
Pros and cons Pros An important profession that will help save millions of lives in the future, improve the environment, it is advisable to let you waste natural resources. 3D printing engineers today are unique specialists. demand in different areas. The specialist will not have problems finding work in megacities. The salary is stable and high. An experienced engineer can open his own production for the production of souvenirs or other products. You can study in Russia and register at a technical university. Lack of physical activity Disadvantages: Seated work, but not monotonous. Irregular working day, because the production of a large product may take more than 5 hours. The cost of industrial 3D printers is high, so in order to organize your own production, think about the initial capital or look for an investor. Any mistake made by a 3D printing engineer is full of huge financial losses. Difficulties in finding work in small towns. Working on a computer leads to visual impairment. Important Personal Qualities A 3D printing engineer is the bearer of a large amount of professional knowledge, so he must be an erudite person with an excellent memory. In nature, this rare specialist should be responsible, curiosity, creativity. The engineer is obliged to study, welcome and constantly study science and linguistics, since further instructions, books and technical documentation are also created mainly in foreign languages.
The salary is stable and high. An experienced engineer can open his own production for the production of souvenirs or other products. You can study in Russia and register at a technical university. Lack of physical activity Disadvantages: Seated work, but not monotonous. Irregular working day, because the production of a large product may take more than 5 hours. The cost of industrial 3D printers is high, so in order to organize your own production, think about the initial capital or look for an investor. Any mistake made by a 3D printing engineer is full of huge financial losses. Difficulties in finding work in small towns. Working on a computer leads to visual impairment. Important Personal Qualities A 3D printing engineer is the bearer of a large amount of professional knowledge, so he must be an erudite person with an excellent memory. In nature, this rare specialist should be responsible, curiosity, creativity. The engineer is obliged to study, welcome and constantly study science and linguistics, since further instructions, books and technical documentation are also created mainly in foreign languages.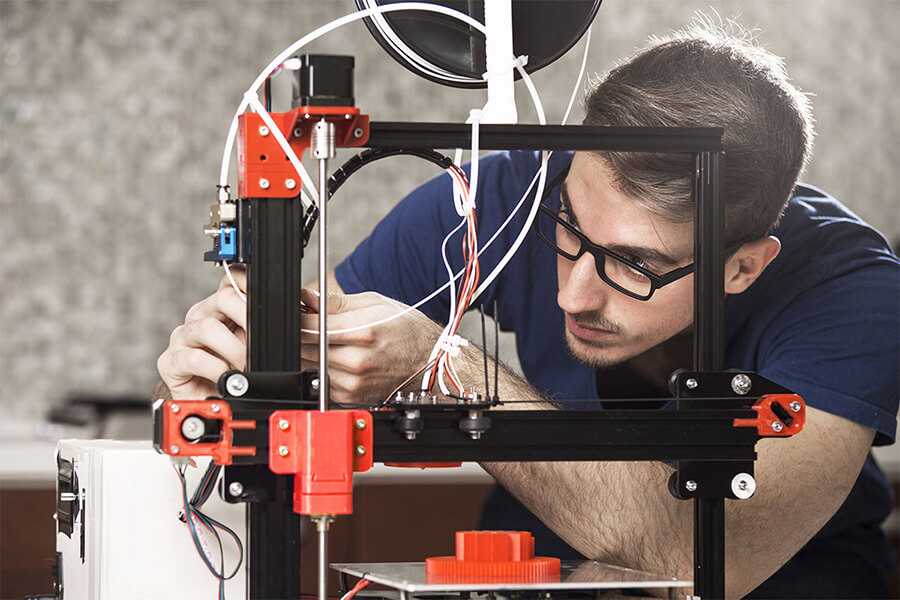 nine0252
nine0252
Additional education courses
| The Interregional Academy of the Construction and Industrial Complex (MASPK) invites specialists to professional retraining and advanced training courses developed under the guidance of leading specialists in the most demanded industries. Distance learning at professional retraining courses in the direction of "Product Engineering Engineer" will allow you to receive a document confirming your qualifications without interrupting your work. nine0005 |
Place of work
3D printing engineers will be able to work in agencies involved in the production of consumer goods. They are in demand by architectural firms, factories, medical centers and nanolaboratories, clothing design and production agencies. 3D printing is used in all areas of life, so a young college student can choose an interesting and useful direction.