What does the extruder do in a 3d printer
3D Printer Extruder: Basic Buyer's Guide
The 3D printer extruder is a crucial piece of equipment in your 3D printer.
FDM printers work by depositing filament layer by layer to build a model. The extruder is the tool that moves, heats, and pushes the filament out of the printer. The type of extruder and hotend that you use can change the quality and style of your print, so it’s no wonder that this is considered an essential part of any 3D printer.
In this article, we’ll review the basic information you need to know about 3D printer extruders and hotends.
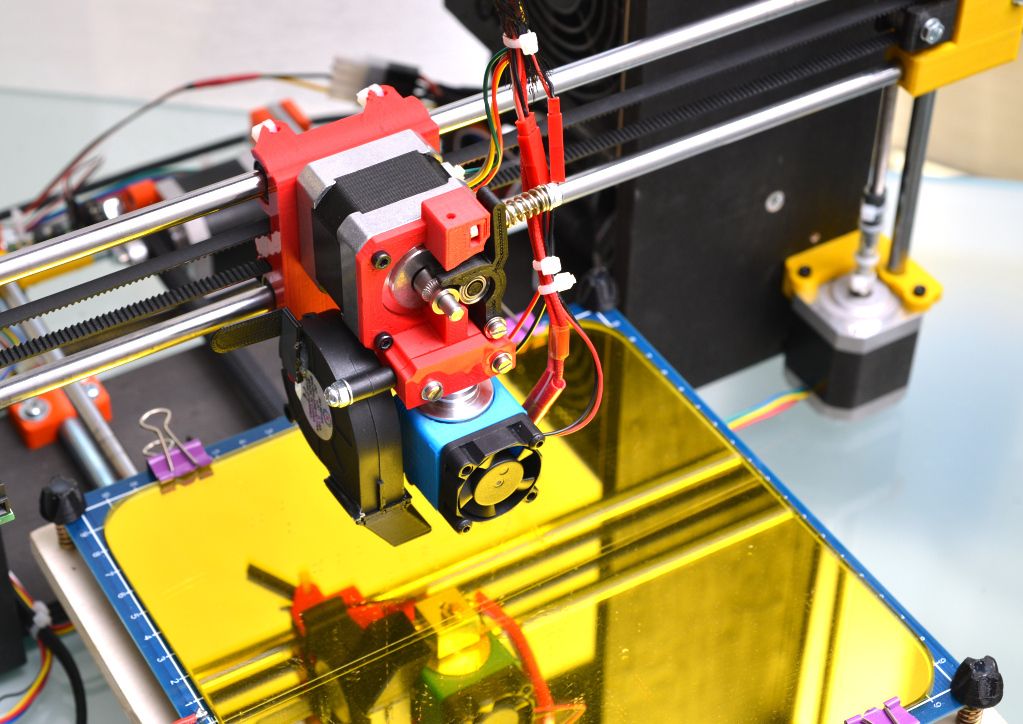
What is a 3D Printer Extruder?An extruder is the part of the 3D printer that is responsible for pushing the filament along, melting it, and placing it on the bed to build the model. A 3D printer extruder is made up of many different tools that do a combination of different jobs. Namely, there is a coldend and a hotend.
For the sake of this article, we will refer to the extruder as the entire piece of the 3D printer that moves, melts, and deposits filament – essentially, the coldend and the hotend. Others may refer to the extruder as simply the piece that moves the filament, and the hotend as the piece that melts.
- The cold end is responsible for moving the filament along to direct it to the hotend. A motor and gear work to guide filament, either through a PTFE tube or directly into the hotend. There are two different types of coldends that work a little bit differently, which we’ll review in the next section.
- The hotend heats, melts and extrudes the material layer by layer through a nozzle. Two of the most important components within the hotend are:
- The heater, which heats and melts the filament.
- The nozzle, which directs the filament as it is extruded.
There are two main types of extruders that you will find on professional 3D printers: Direct and Bowden. Some types of 3D printers also feature a dual extrusion.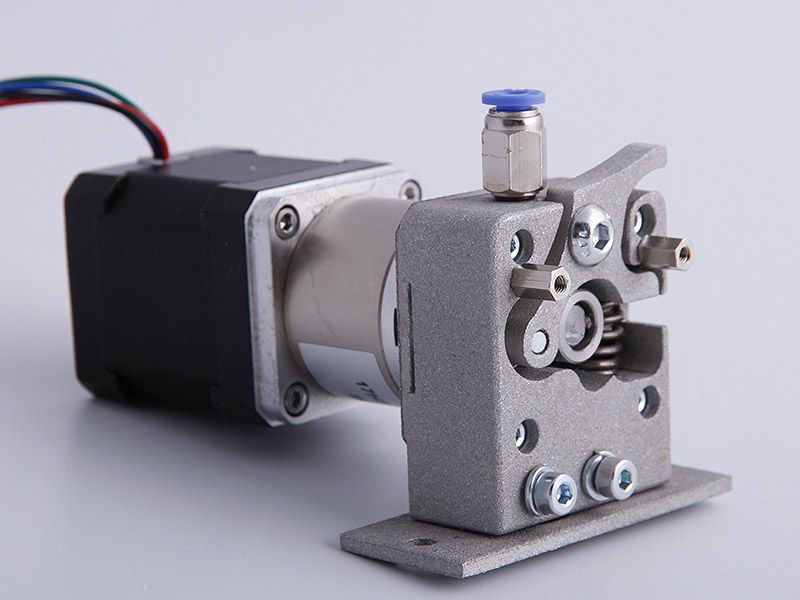 Let’s review the difference between all three.
Let’s review the difference between all three.
In a direct extruder, the filament runs from the cog, to the coldend, to the hotend, all in one piece. This means that the drive and the gear that moves the filament along is directly above and attached to the hotend.
Because the extruder sits directly on top of the hotend, the extruder itself is heavier and slower. However, many prefer to print flexible 3D filaments using a direct extruder. With a direct extruder, the filament has less distance to travel before getting melted and deposited. Consequently, there’s less opportunity for issues during the extrusion process.
Bowden ExtruderIn a bowden extruder, the coldend and the hotend are separated by a PTFE tube where the filament runs along. Instead of the coldend sitting directly on top of the hotend, a tube separates the two pieces.
As opposed to a direct extruder, a bowden extruder is much lighter and faster, because the only moving part is the hotend.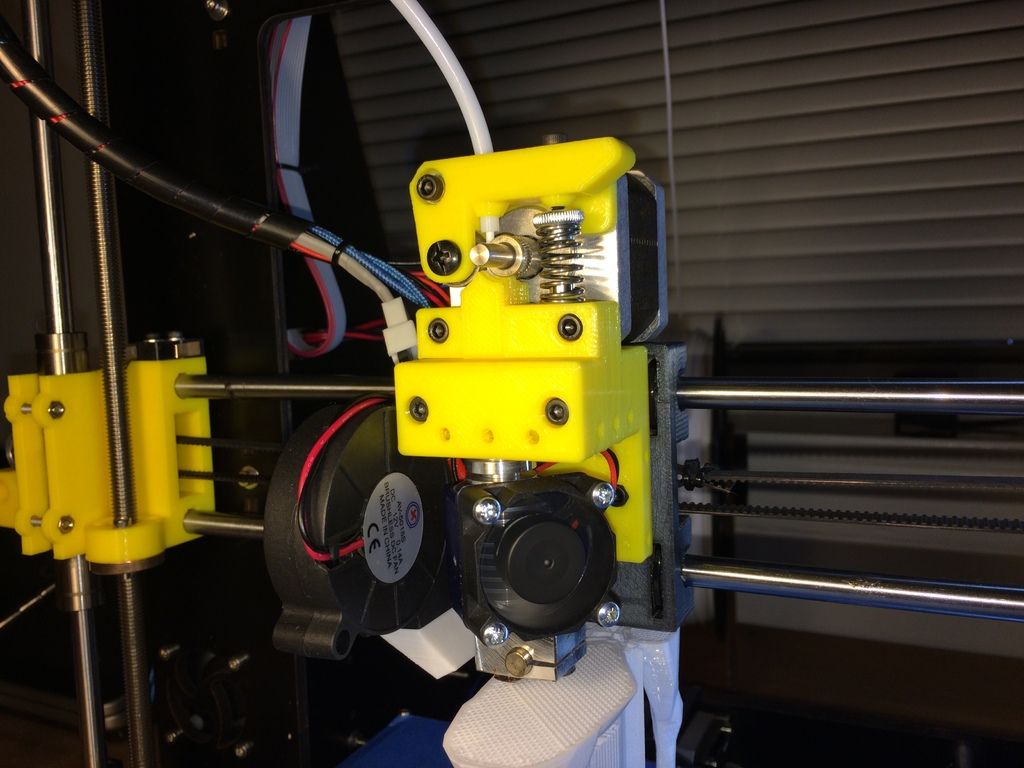 The coldend, with the drive, is positioned on a fixed point on the printer.
The coldend, with the drive, is positioned on a fixed point on the printer.
Bowden extruders print high-quality models and are great for printing models that feature long, continuous designs. It used to be said that flexible materials can’t be used with a bowden extruder, but that is an outdated thought. As long as there is no room for the filament to move or wiggle, it will be able to move just fine through the tube into the hotend.
Dual ExtrudersAlong with different styles of extruders, some printers can also be equipped with two or more extruders.
Dual extruders allow you to print multiple materials at once, or even print two models at the same time. Dual extrusion allows you to accelerate your printing process because there are now two tools moving, melting, and depositing filament.
The dual extruders can also feature an independent dual extrusion system (IDEX). That means the extruders work independently from one another. So, even though typical dual extruders move together at the same time, IDEX extruders function freely from each other. As a result, they are opening the possibilities of increased efficiency, higher productivity, and time-saving.
As a result, they are opening the possibilities of increased efficiency, higher productivity, and time-saving.
We can’t talk about extruders without touching on the hotend. As mentioned before, hotends are the piece of the extruder that is responsible for melting and extruding the filament onto the bed.
You can customize your hotend depending on the nozzle you attach. Because the filament is pushed through the nozzle, the size and type of nozzle you choose will have a major impact on the style and effectiveness of your model.
There are many different types of nozzles you can choose and place on your 3D printers, depending on the type of material you’re printing or the design you have in mind. This topic is so extensive, that we’ve dedicated an entire article to it, which you can read here.
Should you run into troubleIf you’re experiencing difficulties regarding these printer parts, it’s most likely to be down to the most common printing issue in 3D printing: underextrusion.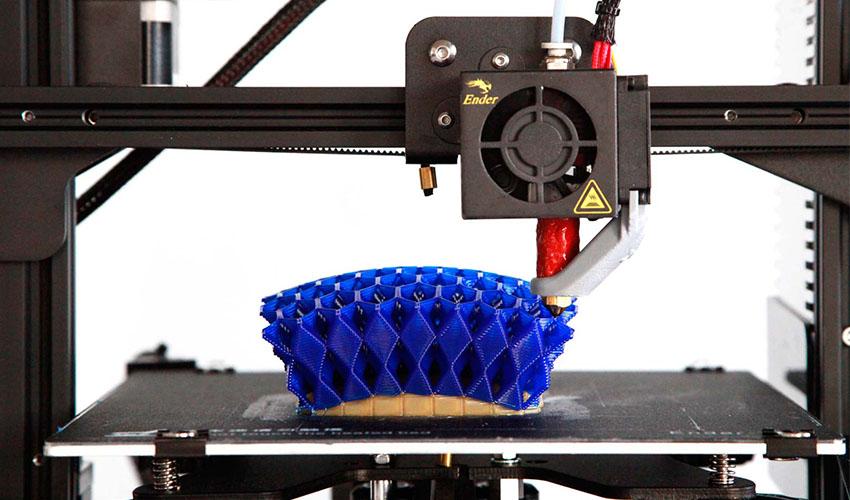 This pesky problem is when there’s a lack of extruded material in the printed part that presents itself as either no filament being extruded from the hotend, missing layers or spongy prints. Underextrusion occurs due to one of the following faults:
This pesky problem is when there’s a lack of extruded material in the printed part that presents itself as either no filament being extruded from the hotend, missing layers or spongy prints. Underextrusion occurs due to one of the following faults:
- outdated software
- wrong choice of material
- the state of your bowden tubes
- a lack of cooling
- issues with the hotend
- issues with the extruder board
- the extruder motor failing to push the filament properly
For more information on how to combat each of these contributing factors, have a read of this article featured on our BCN3D Knowledge Base, which is crammed full of tips and tricks to get you through the trickiest of print jobs.
How much does a 3D Printer Extruder cost?In BCN3D we offer two types of extruder motors: the Extruder Motor R and the Extruder Motor L, plus the extruder kit where both are included. Prices go from 130€ each to 180,15€ for the kit.
Prices go from 130€ each to 180,15€ for the kit.
Moreover, here you can find a wide variety of hotends and their prices.
Lastly, BCN3D offers an extruder board for the price of 15€.
Final ThoughtsNext time you look at your 3D printer, you’ll feel a little more appreciative of all the work going on in that small piece of equipment called an extruder. As with many other aspects of 3D printing, understanding this tool and its work will help you become a more efficient user and significantly improve the quality and properties of your prints.
essential part of a 3D Printer
While using additive manufacturing, and especially when you are 3D printing by yourself with a desktop 3D printer, you might be confronted with an extruder. This component of 3D printers plays a great role in your additive manufacturing projects, that is why we think you should know everything about it!
The 3D extruder is the part of the 3D printer that ejects material in liquid or semi-liquid form in order to deposit it in successive layers within the 3D printing volume. In some cases, the extruder serves only to deposit a bonding agent used to solidify a material that is originally in powder form. Let’s discover the function of the 3D printer extruder, a little but essential part, required for some additive manufacturing processes
In some cases, the extruder serves only to deposit a bonding agent used to solidify a material that is originally in powder form. Let’s discover the function of the 3D printer extruder, a little but essential part, required for some additive manufacturing processes
What is an extruder?
The 3D extruder is the part of the 3D printer that ejects material in liquid or semi-liquid form in order to deposit it in successive layers within the 3D printing volume. In some cases, the extruder serves only to deposit a bonding agent used to solidify a material that is originally in powder form.
The different 3D printing technologies that require an extruder
Found in 3D Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printers, the extruder is also required for proper operation of machines using Binder Jetting or Polyjet technologies, and even 3D Systems’ CPX machines. These are additive manufacturing machines that need to deposit material before transforming it either by adding a bonding agent to it (Binder Jetting) or by changing the chemical properties (Polyjet and CPX). These technologies are explained in our guide about the different kinds of 3D printing.
These are additive manufacturing machines that need to deposit material before transforming it either by adding a bonding agent to it (Binder Jetting) or by changing the chemical properties (Polyjet and CPX). These technologies are explained in our guide about the different kinds of 3D printing.
What are the differences and advantages of 3D printer nozzles, depending on the 3D printing technologies?
- For FDM / FFF printers
The filament extruder on a FDM printer is the part that extrudes the plastic filament in a liquid form and deposits it on a printing platform by adding successive layers. The printing head is made of many distinct parts including a motor to drive the plastic filament and a nozzle (or extruder) to extrude the plastic.
Some 3D FDM / FFF printers are now equipped with two extruders. This enables you, in particular, to print two materials simultaneously in order to obtain 3D prints in two colours. The presence of two extruders also allows support material to be extruded, which can be removed afterward using a solvent.
To regulate the plastic cooling process, some printers are enclosed. This helps maintain a uniform temperature in the manufacturing chamber, ensuring greater consistency in the print result.
- For printers operating with Binder Jetting
The most common kinds of Binder Jetting printers are probably the Projet printers from 3D Systems. These printers have an extruder that projects a bonding agent (or colour) onto a powder material. It’s the action of projecting this bonding agent onto successive layers of powder that creates the object.
- For Polyjet printers
Polyjet technology, originally developed by Objet (which is now owned by Stratasys), is also based on the projection of resin in the form of droplets onto the printing platform. Once the droplets are projected, UV polymerises the resin.
Cold end and hot end: What are these components?
The cold end is the cold part in the upper portion of the 3D printer extruder. At this point, there is no heating of the filament. This is just the part with the motor and gearing, pushing the 3D printer filament into the hot end. Different systems actually exist, there is usually a combination of gears and hobbed bolts, dictating the movement of the printing filament.
At this point, there is no heating of the filament. This is just the part with the motor and gearing, pushing the 3D printer filament into the hot end. Different systems actually exist, there is usually a combination of gears and hobbed bolts, dictating the movement of the printing filament.
The hot end is the part where the filament is transitioning from solid to liquid, while extruded on the building plate. But how is the filament melting? Indeed, something has to be hot enough to melt materials and as we want to print an accurate part, the temperature between the cold filament, the hot end, and the final cold and solid part has to be perfectly managed. The heat break, in combination with the heat sink, maintains a boundary at which the filament is confronted with high temperatures. There is, in the system, a heater cartridge that is getting hot, transferring heat to the nozzle via the heater block in aluminum.
Most desktop 3D printers ship with 0.4mm nozzles as standard, but there are many other sizes available. Brass is usually used for 3D printer nozzles, but there are also several options. For some materials, stainless steel can be prefered.
Brass is usually used for 3D printer nozzles, but there are also several options. For some materials, stainless steel can be prefered.
Direct or Bowden extruder: Which one to choose?
There is not a single extruder type, your choice will depend on the kind of 3D printer that you have, on the materials that you will use, and on the printing speed and accuracy that you need.
There are two different possibilities: Direct or Bowden extruders. The nature of your projects will determine which extruder you need to use. First, all extruders have motors, but there are also geared extruders to control your print speed. It is not essential, but it can help you to customize your setups in order to improve your print quality.
Direct extruders are directly attached to the hot end, while a Bowden extruder (or remote extruder) has a tube to link the hot end and the extruder body. For direct extruders, the gear rotates by a stepper motor driving directly the filament to the extruder hot end. The filament path is shorter, that is why Direct extruders are better to 3D print flexible materials than Bowden extruders You can totally 3D print flexible filament with a Direct extruder, but it is not really convenient.
The filament path is shorter, that is why Direct extruders are better to 3D print flexible materials than Bowden extruders You can totally 3D print flexible filament with a Direct extruder, but it is not really convenient.
With Bowden extruders you can 3D print your projects faster. It is easier to accelerate or decelerate because there is just the printing head to move, not the whole extruder hot end.
They both can have a direct drive system. Indeed, for both of them the filament drive mechanism can be mounted to the motor shaft, directly.
Moreover, keep in mind that there are extruders for all filament thickness, for 3mm filament, 1.75mm filament, etc.
Extruder-related problems in 3D printers
The main problems encountered with 3D printer extruders are the same as with inkjet printers, which is poor maintenance or the use of the wrong materials leading to deterioration or fouling the nozzle that projects the material.
In the particular case of 3D FDM printers, the main problem stems from print nozzles that are blocked by hardened plastic unable to leave the extruder or by slack or space in the plastic extrusion axis, causing discontinuous extrusion.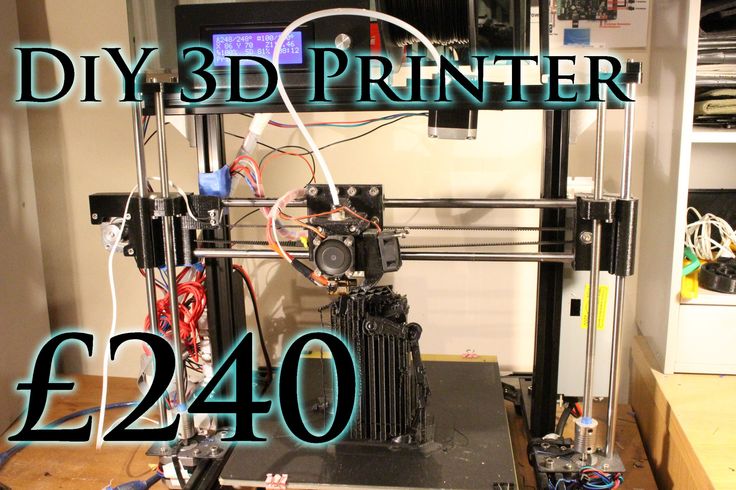
Sculpteo provides a 3D printing service that enables you to verify your file and order a 3D print in a few clicks. To try our service, begin by uploading a 3D file.
Related glossary pages
Extruder for 3d printer: what does it consist of and how to choose it?
03.10.2017
Any printer for three-dimensional printing has certain features in its design. The main component of each is an extruder for a 3d printer. In simple terms, this is a print head that creates new items. Its principle of operation is simple: a special nozzle squeezes out plastic through it, from which a 3D pattern is formed.
3d printer extruder design
A standard 3D printer uses filamentous plastic. There are many varieties of it, but ABS and PLA are commonly used. Although the materials may differ, the design of the extruder is made according to the same principle.
Any extruder for a 3d printer consists of two parts:
- cool-end block is responsible for feeding the filament.
 Its design includes a drive from an electric motor, a clamping mechanism, gears. Due to the rotation of the gear, a thread of plastic comes out of the coil, which passes into the heater. There, the thread becomes viscous under the influence of high temperatures. This helps to squeeze it through the nozzle and turn it into the desired shape. nine0028
Its design includes a drive from an electric motor, a clamping mechanism, gears. Due to the rotation of the gear, a thread of plastic comes out of the coil, which passes into the heater. There, the thread becomes viscous under the influence of high temperatures. This helps to squeeze it through the nozzle and turn it into the desired shape. nine0028 - hot-end block is a nozzle with a heating element. It is usually made of aluminum or brass, as these materials have good thermal conductivity. The heater consists of a nichrome coil, several resistors and a thermocouple. During operation, this block heats up, which contributes to the melting of plastic. The thermal insulating insert between the blocks is responsible for cooling the working surface.
How to choose an extruder? nine0010
In order for a 3D printer to work efficiently, you need to choose a print head of the same quality. How to choose an extruder for a 3d printer is a difficult question, but there are a few points that will help you make the right decision when buying:
-
Material type.
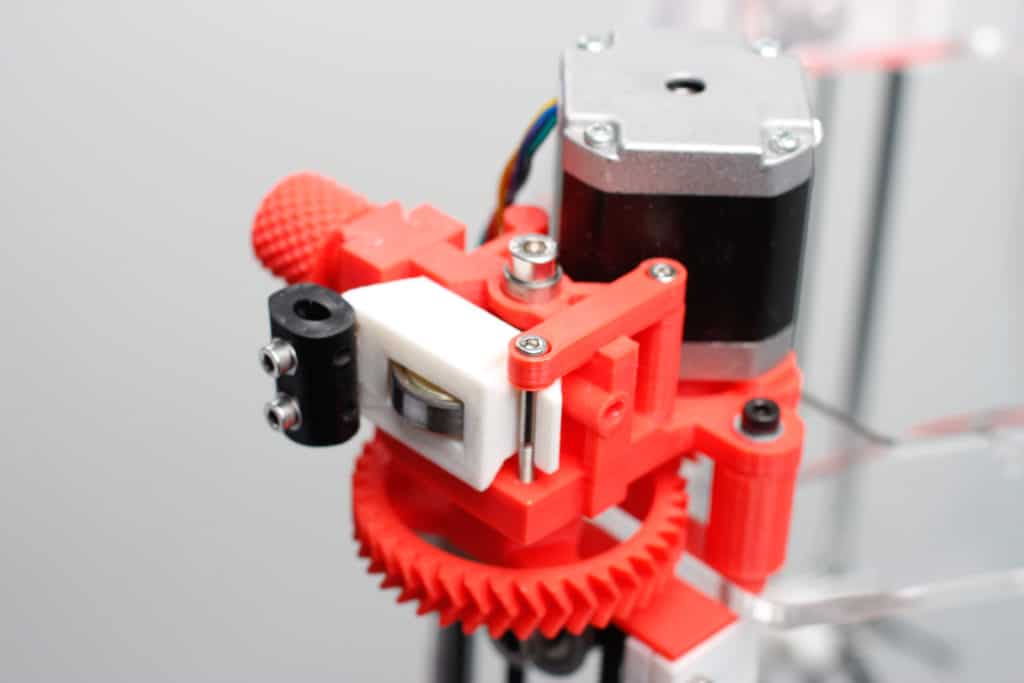 Modern extruders are either created using 3D printers or equipped with cast elements. The second option will be more durable in use, which is important for heavy loads. The advantage of printed heads is low cost. nine0003
Modern extruders are either created using 3D printers or equipped with cast elements. The second option will be more durable in use, which is important for heavy loads. The advantage of printed heads is low cost. nine0003 -
Filament feeding method. This detail is very important, since the thread is fed through it to the heater. The whole process must be neat and smooth so that the plastic does not get tangled when fed to the nozzle.
-
Feed roller view. Quite often it happens that due to poor adhesion of the material to the feed roller, the thread begins to slip. Most often this happens with nylon threads.
-
Nozzle parameters. The print head can be equipped with nozzles of various sizes. The diameter of the nozzle will depend on what shape we want to get in the end. nine0003
Learn more at 3D Print Expo 2017
Please rate the news:
Share:
Back to news
Subscribe to receive the latest news
Techno Print 3D Company
This is our first review of the most popular and inexpensive 3D printers for 2020. The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The list will include the best-selling devices in two price ranges (up to 30 tr and up to 60 tr). Printers working with both plastic filament (FDM) and photopolymers (LCD/DLP) will be presented. This list will always be up to date, as it is periodically updated and supplemented. Read more→
The Chinese company Dazz3D announces the launch of the project on KickStarter and accepts pre-orders for Dazz3D Basic and Dazz3D Pro 3D printers. These revolutionary new devices are aimed at both the professional and amateur markets. Read more→
We all know that precise calibration of the 3D printer desktop is the foundation and the key to successful printing on any FDM printer. In this article we will talk about the main and most popular ways to level the "bed". So, as mentioned above, 3D printing without desktop calibration is impossible. We face this process Read more→
It's hard to go through a day today without hearing about 3D printing technology, which is bursting into our lives at an incredible speed. More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
More and more people around the world are becoming addicted to 3D printing technology as it becomes more accessible and cheaper every day. Now almost anyone can afford to buy a 3D printer, and with the help of Read more→
The FormLabs Form 2 and Ultimaker 3 are perhaps the most popular 3D printers today, capable of high quality printing with incredible surface detail. Moreover, these two devices use completely different technologies, and therefore, there are a lot of differences between them. Many will say that it is wrong to compare them or Read more→
XYZprinting, best known for its daVinci line of desktop 3D printers, is bringing five new devices to the professional and industrial environment. One will use laser sintering technology, the second full color inkjet printing and three DLP machines. First of all, the novelties will be of interest to dentists and jewelers. Read more→
Cleaning the nozzle of a 3D printer is a fairly common process that any user of such a device has to deal with.