Strongest 3d printer filament 2023
What is the Strongest 3D Printing Filament That You Can Buy? – 3D Printerly
People used to consider 3D printed objects weak and brittle, but we have made some serious strides in the durability of these models.
We can create a strong 3D printer filament that stands up to very harsh conditions. This made me wonder, what is the strongest 3D printer filament that you can actually buy?
The strongest 3D printer filament you can buy is polycarbonate filament. Its mechanical structure is unlike many others, where strength tests have shown the excellent resilience and strength of this filament. Polycarbonate is widely used for engineering and has a PSI of 9,800 compared to PLA’s 7,250.
I will describe some interesting details about 3D printer filament strength, as well as give you a researched list of the top 5 strongest 3D printing filament, plus more, so keep on reading.
What is the Strongest 3D Printer Filament?
Polycarbonate (PC) filament is the strongest filament of all the known printing materials in the market. It is used for bullet-proof glass, riot gear, phone & computer cases, scuba masks and much more. The durability and rigidity of PC outweighs other printing materials easily.
The glass transition temperature rate offered by Polycarbonate filament is much higher than most other plastics filaments, meaning it has a high temperature resistance.
One of the tough competitors is ABS filament but you will be amazed to know that Polycarbonate filament can withstand 40°C more than ABS, making it a very strong filament.
Even at room temperature, thin PC prints can be bent without cracking or bending. Wear and tear doesn’t affect it as much as other materials, which is great in many 3D printing applications.
PC has amazing impact strength, higher than that of glass and several times higher than acrylic materials. On top of its incredible strength, PC also has transparent and lightweight qualities which make it a serious contender for 3D printing materials.
The Polycarbonate filament has a tensile strength of 9,800 PSI and can lift weights of up to 685 pounds.
Depending on the different types of 3D printers and its components, Polycarbonate filament has an extruding temperature of almost 260°C and requires a heated bed of around 110°C to print properly.
Rigid.Ink has a great article detailing how to print with Polycarbonate filament.
All these statistics are far better and efficient than any other filament tested until now. In a nutshell, Polycarbonate filaments is the king of the 3D printing filament when it comes to strength.
Top 5 Strongest 3D Printing Filament
- Polycarbonate Filament
- Carbon Fiber Filaments
- PEEK Filaments
- ABS Filament
- Nylon Filaments
Polycarbonate Filament
When it comes to the strongest filaments, polycarbonate filament will always be seen at the top of the list as described above. Many amazing features and reasons are contributing to making it to float above the other filaments but some of the most appreciated features of Polycarbonate filaments include:
Many amazing features and reasons are contributing to making it to float above the other filaments but some of the most appreciated features of Polycarbonate filaments include:
- PLA usually begins to deform at a minor temperature of about 60°C but Polycarbonate filament can resist the heat up to amazingly 135°C.
- It is durable with impact and high shatter resistance.
- Electronically, it is non-conductive.
- It is transparent and highly flexible.
You can’t go wrong with some PRILINE Carbon Fiber Polycarbonate Filament from Amazon. I’d thought it would be a lot pricer but it actually isn’t too bad! It also has great reviews that you can check out.
One user actually tested how much carbon fiber was in the PRILINE Carbon Fiber Polycarbonate Filament and they estimated it was around 5-10% carbon fiber volume to plastic.
You can print this on an Ender 3 comfortably, but an all-metal hotend is recommended (not required).
Carbon Fiber Filament
Carbon fiber is a thin filament composed of fiber that contains carbon atoms. The atoms are in a crystalline structure that provides high strength which makes it an ideal choice for industries like automotive.
Markforged state that their carbon fiber filament has the highest strength-to-weight ratio, where in their flexural strength three-point bending test, illustrated that it is 8x stronger than ABS and 20% stronger than the yield strength of aluminum.
Their carbon fiber has a flexural strength of 540 MPA, which is 6 times higher than their nylon-based onyx filament and it’s also 16 times stiffer than their onyx filament.
You can purchase 2KG of carbon fiber PETG for around $170 from 3DFilaPrint which is very premium for 3D printer material, but a great price for high quality filament.
It is light and has excellent resistance to chemical degradation and corrosion. Carbon fiber has better dimensional stability because of its strength that helps in mitigating the chances of colliding or shrinking.
Carbon fiber has better dimensional stability because of its strength that helps in mitigating the chances of colliding or shrinking.
The stiffness of carbon fiber make it a top contender for the aerospace and automotive industries.
PEEK Filament
PEEK filament is one of the most reliable and trusted materials in the huge 3D printing industry. PEEK stands for its composition which is Polyether Ether Ketone, a semi-crystalline thermoplastic.
It is well known for its excellent strength and high-end chemical resistance. During its manufacturing, a process is followed known as phased polymerization at a very high temperature.
This process makes this filament highly resistant to organic, bio, and chemical degradation in any type of environment with a useful operating temperature of 250°C.
As PEEK filaments reduce the amount of moisture absorption and make the process of sterilization easy, medical fields and industries are adopting PEEK filaments for 3D printer rapidly.
It does get pretty pricey so keep that in mind!
ABS Filament
ABS comes in the list of the strongest filaments because it is a hard thermoplastic material that can resist impact gracefully.
This filament is widely used in printing processes such as engineering purposes, technical printings, etc. It is one of the most cost-effective as compared to other major types of fiber filaments.
This is the fact that makes this filament ideal for the users who are bound to a budget but want to have a high-quality strong filament for 3D printing.
ABS is a perfect choice if you are going to print things that will have the stress of will include high functionality. As this filament is heat and water-resistant, it provides users with a smooth and attractive finish to the product.
You also have the ability to easily work with the material, whether that’s sanding, acetone smoothing, or painting.
Nylon Filament
Nylon is an excellent and strong material that is used in most of the 3D printers. It has an amazing tensile strength of almost 7,000 PSI which is more than most of the other 3D filaments.
This filament is highly resistant to the chemicals and heat which makes it one of the ideal options to use in industries and major organizations.
It is strong but comes after ABS although, the nylon industry is moving forward to bring improvements using mixtures of particles from fiberglass and even carbon fiber.
These additions can make the nylon filaments more strong and resistant.
NylonX by MatterHackers is a perfect example of this composite material for some amazing 3D printed strength. The video below shows a great visual of this material.
TPU Filament
Although TPU is a flexible filament, it has some serious strength in the impact-resistance, wear and tear resistance, chemical and abrasion resistance, as well as shock absorption and durability.
As shown in the video titled ‘The Ultimate Filament Strength Showdown’ above, it showed to have amazing material strength and flexibility. The Ninjaflex Semi-Flex withstood 250N of pulling force before snapping, which in comparison with Gizmodork’s PETG, gave a force of 173N.
Which Filament is Stronger ABS or PLA?
When comparing the strength of ABS and PLA, the tensile strength of PLA (7,250 PSI) is greater than the tensile strength of ABS (4,700 PSI), but strength comes in many forms.
ABS has more flexible strength since PLA is brittle and doesn’t have as much ‘give’. If you expect your 3D printer part to bend or twist, you would rather be using ABS over PLA.
If you expect your 3D printer part to bend or twist, you would rather be using ABS over PLA.
The all-famous Legos are made from ABS, and those things are indestructible!
In hotter environments, PLA doesn’t hold its structural strength very well so if heat is a factor in your area, ABS is going to hold up better. They are both strong in their own rights but there is another option.
If you want a filament which meets in the middle of the two, you want to look towards using PETG, which is easy to print like PLA, but has a little less strength than ABS.
PETG has more natural flex than PLA and should keep its shape longer.
PETG can also withstand higher temperatures than PLA, but you want to make sure your 3D printer has the correct capabilities to reach the necessary temperatures to print it.
What is the Strongest 3D Printer Resin?
Accura CeraMax is considered as the provider of the strongest 3D printer resin. It guarantees full capacity temperature resistance as well as the highest strength for heat and water resistance.
It can be used efficiently to print the perfect composite like prototypes, ceramic-like components, jigs, tools, fixtures, and assemblies.
What is the Stiffest 3D Printing Material?
PLA filament is also known as Polylactic Acid and is one of the most used filaments in 3D printers.
It is considered as a standard filament material that is widely being used because it can print clearly at a very low temperature without requiring a high heated bed.
It is the stiffest 3D printing material and is ideal for the beginners because it makes 3D printing easy as well as it is very inexpensive and produces parts to be used for a variety of purposes.
After being the stiffest 3D printing material it is also known as the most environmentally friendly material to be used in 3D printers. As an amazing property, PLA emits a pleasant smell while printing.
What is the Weakest 3D Printing Filament?
As it is mentioned above that simple nylon or some PLA filaments are considered as the weakest 3D printing filaments in the 3D industry. This fact is only valid for previous or old versions of the nylon filaments.
However, the new updates such as filled nylon filaments with Onyx or nylon carbon fiber filaments come in the list of top strongest filaments for the 3D printers.
What's the Strongest 3D Printer Filament? MatterHackers Attempts to Find Out - 3DPrint.com
There is an overwhelming amount of material to choose from in 3D printing – even just when it comes to desktop FDM printers. For the casual maker, printability and appearance are often all that matters, particularly if you’re mainly printing decorative items. But when you’re trying to create a functional object, how do you know what material is going to best fit your needs? That’s not an insignificant question, particularly if the item you’re printing is going to be responsible for any weight-bearing functions. How do you know if your filament will be strong enough?
But when you’re trying to create a functional object, how do you know what material is going to best fit your needs? That’s not an insignificant question, particularly if the item you’re printing is going to be responsible for any weight-bearing functions. How do you know if your filament will be strong enough?
That’s a question that MatterHackers gets asked frequently. The retailer carries one of the largest selections of filament in the 3D printing industry, so their team knows a lot about filament and filament strength. After being asked again and again about what type of filament is the strongest, MatterHackers decided to do some testing to find out the answer.
“‘Strength’, however, is a bit vague as it can refer to a few different mechanical properties – tensile strength, yield strength, fatigue strength, compressive strength, and impact strength – so it’s a difficult question to answer without more information,” Taylor Landry from the MatterHackers team cautions.
“…We’re not a testing lab and we can’t perform any scientific tests of those mechanical properties, and we surely didn’t find a Young’s Modulus. What we can do is perform a comparative test – putting 3D printed parts through the same test, and seeing how filaments compare to each other.”
To test different materials, MatterHackers decided to 3D print an object that better be as strong as possible: a carabiner. They scaled their model to approximately the same size as a typical aluminum carabiner you can find at the hardware store, rated for 150 lbs. They printed each test model on a Rostock Max with a 0.4mm nozzle at 0.25mm layer height and 50% triangle pattern infill, with five perimeters and five solid top and bottom layers.
The team then rigged up a force gauge to a block and tackle pulley system with a 8:1 ratio, meaning that for every one pound applied to one side of the system, eight pounds were applied to the other side. They tested each carabiner by attaching it to the pulley system and applying tension with a ratcheting cable until the carabiner failed. The force gauge recorded the peak force for each one.
The force gauge recorded the peak force for each one.
The results are as follows:
“Somewhat surprisingly, Taulman 645 failed at the lowest weight of any filament we tested, but it was the only filament that didn’t break,” MatterHackers states. “Because it’s not very rigid, it just bent and deformed until it came off the test rig. This toughness is obviously a very useful characteristic, but it’s not an ideal material for something like this carabiner.”
PLA, unsurprisingly, performed poorly, with PETG not faring much better. NylonX, however, was a welcome surprise, showing itself to be 100% stronger than PLA and 60% stronger than ABS on average. Polycarbonate also performed well, but was also the most challenging material to print with, requiring thorough drying before printing and having a tendency to warp.
The team also tried printing a few carabiners on a Markforged 3D printer. Markforged is well known for its fiber-reinforced nylon 3D printing materials, and MatterHackers printed two carabiners with fiberglass-reinforced material and two with carbon fiber reinforcement. Surprisingly, all four of the parts performed worse than the NylonX and Polycarbonate parts, for reasons that aren’t quite clear yet, according to MatterHackers – they’re planning to explore the matter further in the near future, having gotten incredibly strong parts from Markforged materials in the past.
Surprisingly, all four of the parts performed worse than the NylonX and Polycarbonate parts, for reasons that aren’t quite clear yet, according to MatterHackers – they’re planning to explore the matter further in the near future, having gotten incredibly strong parts from Markforged materials in the past.
Of course, the tests weren’t just straightforward measurements of tensile strength, the team came to realize. Stiffness was also a factor.
“While we were applying tension to the 3D printed carabiners, we weren’t just measuring tensile strength. We found that the integrity of the latch and the ability of it to stay closed as long as possible was a huge factor in the max load before failure. The more flexible the filament is, the more easily the latch unseats/opens, and this leads to failure more quickly.”
Thus, while Taulman 645 performed poorly, that doesn’t mean it isn’t a strong filament – in fact, it essentially returned to its original shape after the weight was removed, rather than breaking. What MatterHackers’ test may have proved most of all is that strength is a complicated thing to gauge, and that what works best for one application might be completely wrong for another. Also, a 3D printed carabiner is a cool way to carry around your keys, but if you’re going mountain climbing, you’d best buy an aluminum one from the sporting goods store. Discuss in the MatterHackers forum at 3DPB.com.
What MatterHackers’ test may have proved most of all is that strength is a complicated thing to gauge, and that what works best for one application might be completely wrong for another. Also, a 3D printed carabiner is a cool way to carry around your keys, but if you’re going mountain climbing, you’d best buy an aluminum one from the sporting goods store. Discuss in the MatterHackers forum at 3DPB.com.
Stay up-to-date on all the latest news from the 3D printing industry and receive information and offers from third party vendors.
Tagged with: 3d printed carabiners • 3d printer filament • high strength materials • markforged • material testing • Matterhackers • NylonX filament • PETG • pla • taulman 645 • tensile strength
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
What is the most durable material for 3D printing?
3DPrintStory 3D printing process What is the most durable material for 3D printing?
While the 3D printing process seems like a great alternative to traditional manufacturing methods, the parts produced can be fragile and unusable. As a rule, this is the result of using standard materials that are not designed for strength and durability. But there is a solution: use durable materials! Durable 3D printing materials can greatly enhance your options, as you can print parts and assemblies for small projects without fear of breakage.
In this article, we'll take a look at the three most durable types of 3D printing materials. However, before that, we will take a closer look at what strength means in terms of filament materials.
However, before that, we will take a closer look at what strength means in terms of filament materials.
What is strength and how do we evaluate it?
The strength of a material can be measured and evaluated in different ways. In this article, we will mainly use tensile strength (stress before something breaks). We will list the tensile strength of each 3D printing material in pounds or pounds per square inch (PSI).
Despite the obvious number of pounds the material can support, there is still a margin of error depending on how the part was printed. We've compiled research from a variety of sources to make sure these three materials are the strongest.
You must also understand that the material itself is not the only factor that affects the strength of the finished product. The design itself, post-processing and the 3D printing process also affect the strength of the part.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC) is considered by many manufacturers and reviewers to be the strongest 3D printing filament available. In particular, it is possible to achieve high strength of polycarbonate products by 3D printing with an all-metal hot end and a 3D printer in a case that is isolated from the influence of the external environment.
In particular, it is possible to achieve high strength of polycarbonate products by 3D printing with an all-metal hot end and a 3D printer in a case that is isolated from the influence of the external environment.
Some Numbers
Airwolf 3D has come to the conclusion after many filament tests that polycarbonate is the best choice of durable filaments for desktop 3D printers. They were able to hang up to 685 pounds on a polycarbonate printed hook and found that this material had a tensile strength of 9800 psi. In contrast, the same part printed in PLA could only support 285 pounds.
Using a similar test, MatterHackers studied the tear strength of this type of thread, as well as a number of other materials. They were able to hang an average of 409 pounds on the polycarbonate hook, while the PLA parts had a significantly lighter average weight of just 154 pounds.
Finally, renowned 3D printing YouTuber Thomas Sunladerer reviewed several polycarbonate materials and gave very positive feedback on the strength of the material.
3D printing with polycarbonate
It is worth noting that the quality of 3D printing with polycarbonate is not very good. Compared to other materials, protrusions and small details may not turn out as well as using the same PLA.
According to Rigid.Ink, polycarbonate is mostly sold in clear. This 3D printing material has excellent heat resistance as well as impact resistance. But note that you will have to print at high temperatures. As mentioned above, it is better to use an enclosed 3D printer and a solid metal hotend.
Pros of polycarbonate : extra strong, excellent thermal and impact resistance.
Cons of polycarbonate : does not cope well with protrusions and small details of a 3D model, requires a body and an all-metal hot end, a limited number of colors.
Nylon
Next on our list of durable 3D printing materials is nylon. This material is considered by many to be the most reliable for desktop 3D printers.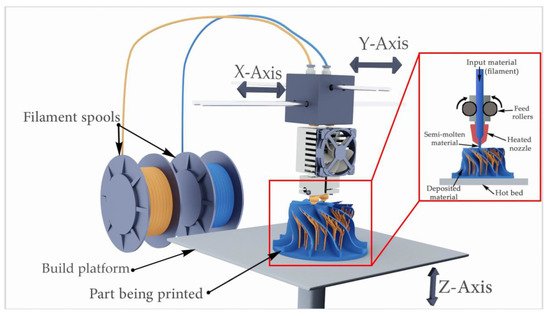 Nylon is inferior in strength to polycarbonate, but still clearly stronger than other competitors such as PLA and ABS.
Nylon is inferior in strength to polycarbonate, but still clearly stronger than other competitors such as PLA and ABS.
Some numbers
A hook printed with nylon (910) thread had a breaking strength of 7,000 psi, while the same ABS hook only had a strength of 4,700 psi, according to Airwolf 3D. Airwolf 3D also noted that the nylon filament-printed clip holds 485 pounds.
MatterHackers posted similar results and noticed that a hook printed with their NylonX material can hold an average of 364 pounds before it breaks. Rigid.Ink also reviewed some nylon threads and gave them a four out of five rating for strength and a five for durability. For comparison: the strength and durability of PLA is three conventional units.
Nylon 3D printing
Nylon is slightly easier to print than polycarbonate, but it's still not PLA. Nylon filament is quite hygroscopic, so it must be kept dry and requires a high printing temperature of 220-270°C. This material is prone to slight warpage, but is also resistant to impact, fatigue, and high temperature.
Nylon pros: impact resistance, fatigue resistance, heat resistance, easier to print than polycarbonate.
Nylon 9 cons0042 : hygroscopic, warping, very high hot end temperature required.
Composites
Finally, composite threads, although not essentially a single material, can be extremely strong. Composites are threads with certain additives that affect the properties of the material, including to increase strength. The names of these threads usually have the words "pro", "reinforced" (reinforced) or "infused" (infused), since they are usually a mixture of different materials.
For this reason, it is impossible to assess where the composite fibers are compared to the two previous materials. Some composites, such as Carbonyte, can compete with nylon threads for strength, while some composites are less durable.
It all depends on what the composite thread consists of. Durable is usually a high strength material such as nylon impregnated with another high strength material such as carbon fiber or glass.
Speaking of carbon fiber, this is also a very strong filament that is sometimes used for 3D printed bicycles. However, some composite fibers are stronger than many pure carbon fibers, so they are not in the top three, but deserve special mention as composite fibers.
Some numbers
We will use carbon fiber nylon and glass fiber nylon threads as examples. MatterHackers has determined that hooks printed on these materials can hold an average of 349and 268 pounds respectively.
Rigid.Ink gave the fiberglass nylon filament four out of five ratings for strength and five for durability. They also gave the carbon fiber nylon a five out of five rating for both strength and durability. In comparison, PLA and ABS were in the top three for strength.
3D printing with composites
Composites vary in the way they are 3D printed, but they are generally relatively similar to their base material. Durable composite fibers are usually made from nylon, so you'll have to print at fairly high temperatures. These threads are also quite expensive.
These threads are also quite expensive.
Advantages of composites : This is a combination of several materials to achieve the best possible properties, durable.
Cons of composites: Expensive, requires high 3D printing temperatures.
Printer accessories | kaup24.ee
Buyers rate Kaup24.ee!
Buyers rated: 4.6/5
13,487 ratings. See all
As with any technical device, various consumables are required for normal operation of printers. Since today there are several types of printers: inkjet, laser, 3D printers for bulk printing, label printers, each type requires its own consumables. In the assortment of our e-shop you will find accessories for printers different types. So for printing on a 3D printer, we have a large selection of bobbins with multi-colored threads made of PLA, PETG and ABS thermoplastic. For various models of laser printers, there are accessories necessary for their normal operation, such as containers for collecting waste toner. In addition, here you can buy label printers, as well as cartridges with self-adhesive tape for them.
In addition, here you can buy label printers, as well as cartridges with self-adhesive tape for them.
Show more Show less
FilterView product listCheapest on topMost expensive on topDelivery timeHighest rating
RETURNING KAUP24-EURO
8 20 € / month 107 00 €
Add to cart
Oki
RETURNING KAUP24-EURO
7 10 € / month 92 39 € 138 59 €
Add to cart
Oki
Consumables for laser and 3D 3D printers, such as containers for waste toner, multi-colored rolls of plastic threads, ribbons for label printers, are offered in our online store.
Accessories for various types of printers
- Waste toner containers are a consumable item for many laser printers. Timely replacement of the container ensures high quality printing and extends the life of the printer.
- Embossed label printer suitable for indoor and outdoor labeling. Adhesive, non-stick metal and aluminum strips can be used for it.
- Cartridge with self-adhesive label tape. The tape is easy to remove without leaving marks, sticks to almost all clean flat surfaces, the inscription does not fade in the sun.
- Rolls of threads of different colors from PLA, PETG, ABS, ABS + thermoplastic in a vacuum bag - for 3D printing on a 3D printer. The main advantages of ABS thermoplastic are elasticity and impact resistance. PLA thermoplastics melt very well and have lower printing temperatures. PETG is more flexible than PLA and easier to print than ABS.
Looking for 3D printer accessories? In the online store Kaup24.
Learn more