Russian 3d printing house
This Week in Tech: Russian Company 3D Prints House in 24 Hours
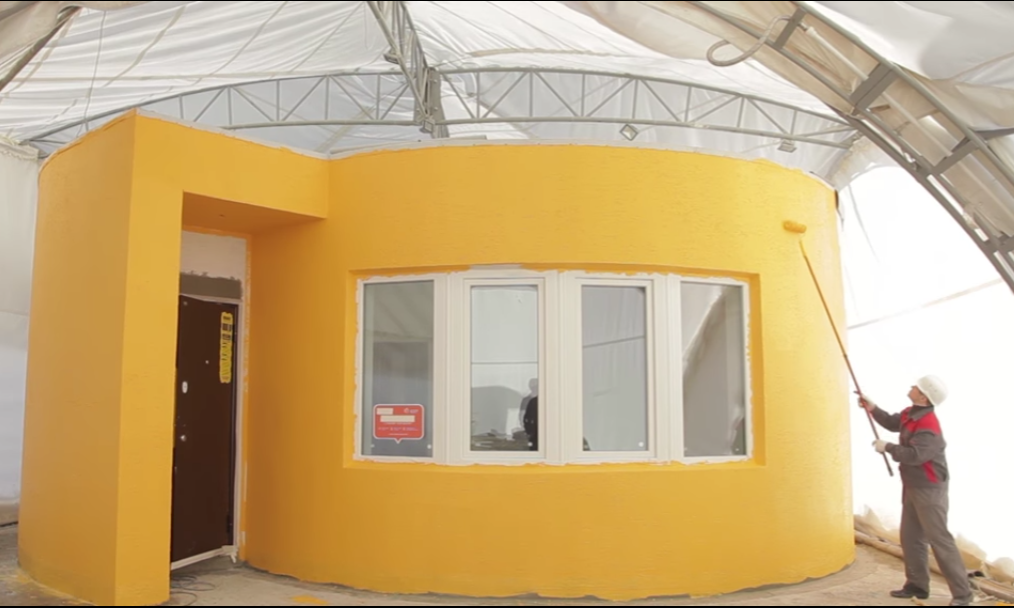
Construction company Apis Cor and Russian developer PIK group took one day to construct an on-site 3D-printed house in Stupino, Russia. Built by a mobile 3D construction printer with a concrete mixture as the ink, the single-story structure measures 38 square meters (about 410 square feet) and costs around $10,134 to build. Temperature and curing restrictions of the mixture—which can only be used above 5 C (about 41 F)—required the team to erect a tent around the construction zone to insulate the area. The house was finished with a layer of "mineral plaster [that] consists of white cement and ball-shaped marble and granite crumbs, so it can serve as an additional heat insulation and goes well with the thermal insulation systems," according to Apis Cor's website. [3DPrint.com]
Courtesy National GeographicThe island of Ta'u in American Samoa has converted its energy source from diesel to solar power. The island relied on diesel fuel for all of its electricity needs, but in November, SolarCity, a solar power company recently bought by Elon Musk and his Tesla company, completed the installation of a microgrid solar system comprising 5,328 solar panels with a 1.410 megawatts capacity. The energy generated can be stored in 60 Tesla Powerpack batteries that can retain power for up to three days without sun. [National Geographic]
Despite this project's scope, SolarCity let go 20 percent of its staff in 2016 due to slow growth in the industry, ending the year with 12,243 employees. [Reuters]
Courtesy Arielle Fragassi via Flickr Creative CommonsICYMI: A recent white paper by global architecture firm Perkins+Will with the Healthy Building Network suggests antimicrobial ingredients used to kill bacteria on countertops, floor tiles, and other building materials are doing more harm than good. [ARCHITECT]
Courtesy Hokkaido UniversityResearchers at Hokkaido University in Japan have developed fiber-reinforced hydrogel composite that is five times stronger than carbon steel. The scientists say this material is environmentally friendly, durable, and flexible, making it viable for fashion, manufacturing, and medical applications. [InHabitat]
The scientists say this material is environmentally friendly, durable, and flexible, making it viable for fashion, manufacturing, and medical applications. [InHabitat]
ICYMI: Next Progressives alum Geoffrey von Oeyen creates a mechanized awning for a California school using sailboat technology. [ARCHITECT]
Courtesy Hyperloop OneLos Angeles–based company Hyperloop One has begun initial talks with the Indian government about potentially constructing the ultra-fast transportation system in the country. "India turns out to be a massive opportunity obviously for the concept of Hyperloop, which is why there’s so much interest," says Hyperloop CEO Rob Lloyd in a Bloomberg article. The company is planning to source components such as steel locally and will decide whether to move forward with the project by the end of the year. [Bloomberg]
Courtesy New AtlasScientists at Cornell University and the University of Minnesota have discovered a way to combine polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) plastics together without compromising durability.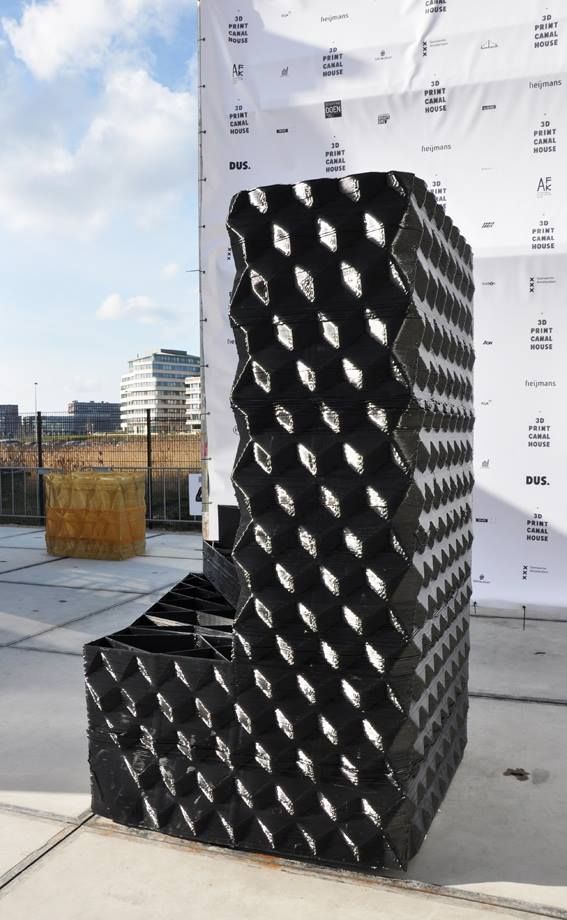 Usually incapable of creating a homogeneous mix, PE and PP plastics are limited in terms of what they can be recycled into together. However, using multi-block polymers, the team created a structurally strong plastic alloy that could potentially make it easier for manufacturers to recycle these two types of plastic waste. [New Atlas]
Usually incapable of creating a homogeneous mix, PE and PP plastics are limited in terms of what they can be recycled into together. However, using multi-block polymers, the team created a structurally strong plastic alloy that could potentially make it easier for manufacturers to recycle these two types of plastic waste. [New Atlas]
ICYMI: Tech and architecture join forces as IBM's question answering supercomputer Watson and design studio SOFTlab team up to conceptualize an installation inspired by Gaudi. [ARCHITECT]
In an effort to have its facilities run on more sustainable energy, Amazon announced that it will be installing solar arrays on the roofs of 15 global fulfillment and distribution facilities by the end of this year. The company—which has been criticized by Greenpeace for its higher usage of grid power as compared to other tech giants such as Facebook and Apple—hopes to install solar arrays across 50 buildings by 2020.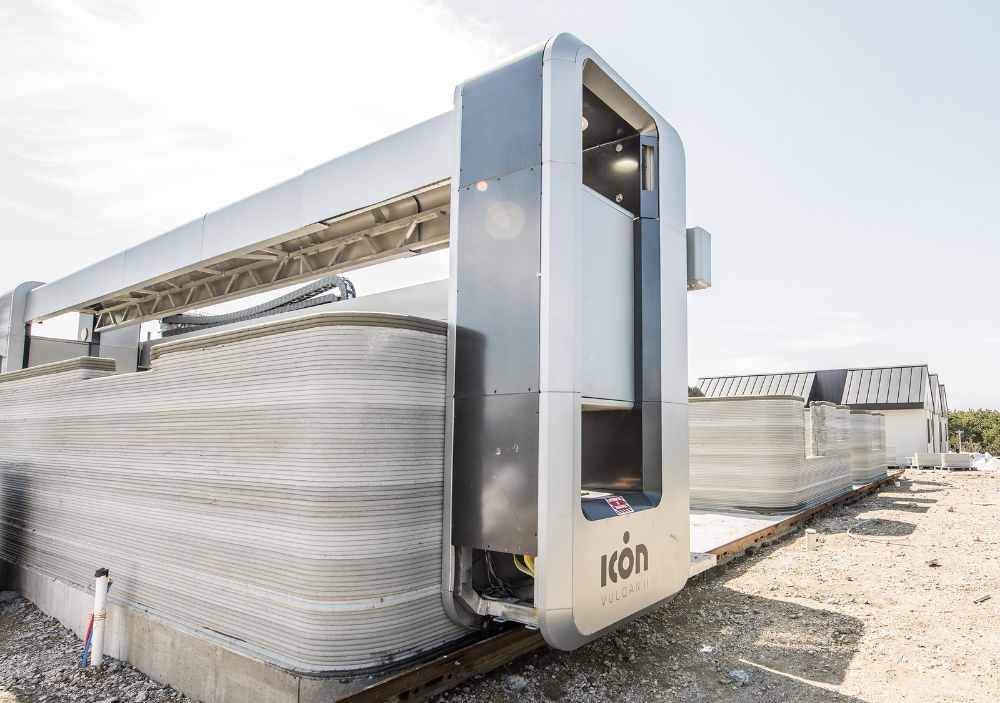 The arrays are expected to provide 80 percent of each facility's energy needs. [TechCrunch]
The arrays are expected to provide 80 percent of each facility's energy needs. [TechCrunch]
3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day
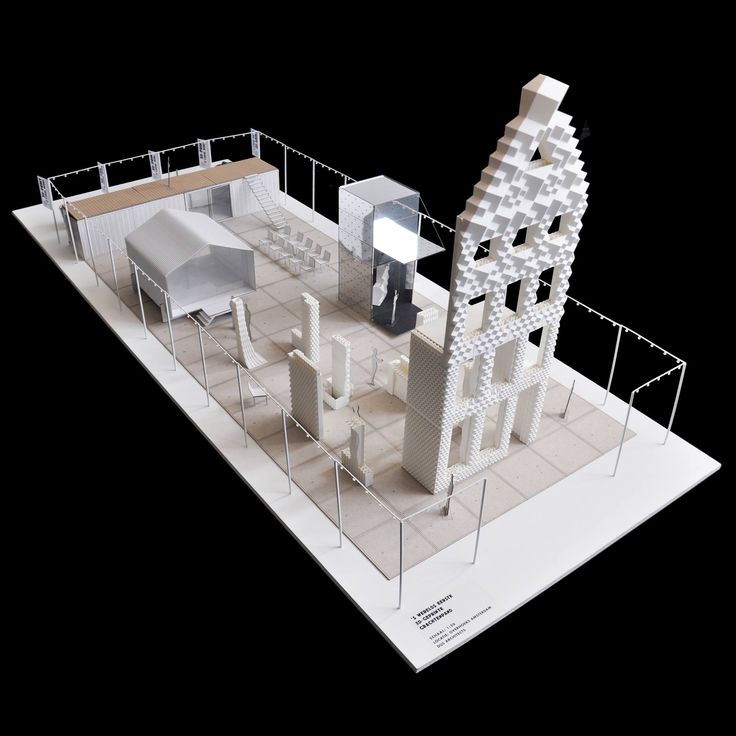
Wouldn’t it be wonderful for you to get home the next day you thought of owning one? Nowadays, 3D printing technology is invading many fields of industry, one of which is the construction business. The American 3D printing company Apis Cor and Russian real estate developer collaborated, earlier this year, in building the world’s first 3D printed house in only 24 hours. The 3D Printed House stands today in Stupino, a town close to Moscow, Russia.
Read More:
-
3D Printing Breakthrough: Dutch Researchers Develop New Algae-Based Bioplastic for 3D Printing
-
Why 3D Printing Is All the Talk Now in Architecture?
An automatic unit of mix and supply and a mobile 3D printer were utilized in building the residential house. They were developed by Apis Cor particularly for this purpose.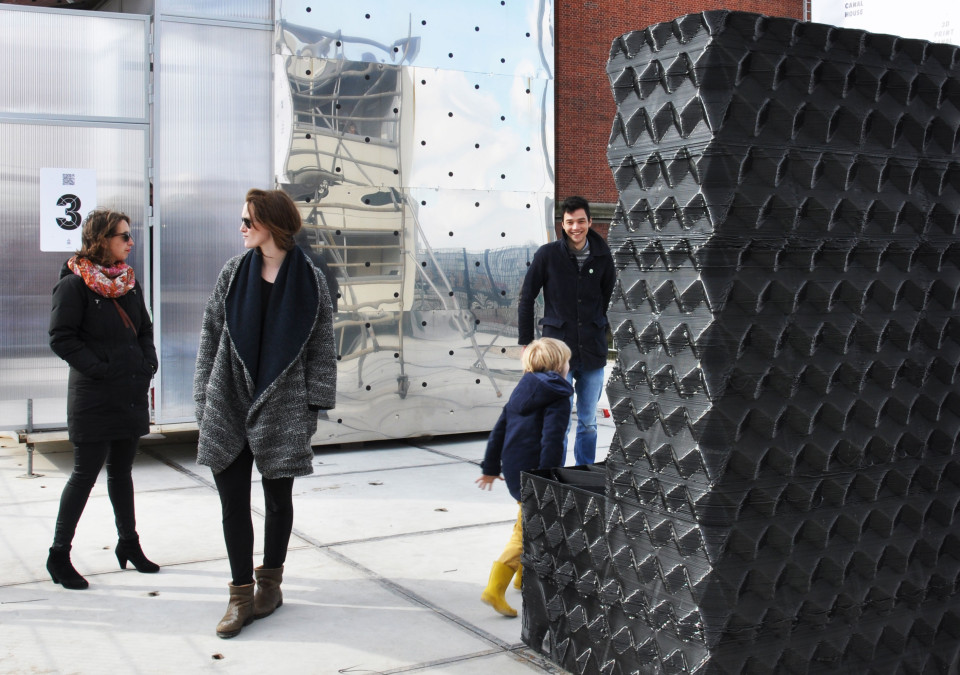 The printer, which acted similarly to a crane, built all the items of the house. It constructed the whole building as a single unit, from the exterior to the interior, including all the walls and partitions. That was in contrary to custom 3D printing which creates the building parts as separate pieces, in facilities away from the construction site. The separate panels are then brought back to be assembled and connected on-site. Apis Cor’s curved-shaped house has an area of 37 square meters (400 square feet). This particular shape was selected rather than others. It was chosen to highlight the magnificent capabilities of the 3D printer that can create any desired building shape. The house includes a living room, a bathroom, a kitchen, and a hallway. One of the five partners in this project is Samsung which supplied the house with all the needed appliances, among which was a curved TV to fit onto the curved wall of the living room. Although the roof is flat, it is capable of enduring snow load specifications for buildings.
The printer, which acted similarly to a crane, built all the items of the house. It constructed the whole building as a single unit, from the exterior to the interior, including all the walls and partitions. That was in contrary to custom 3D printing which creates the building parts as separate pieces, in facilities away from the construction site. The separate panels are then brought back to be assembled and connected on-site. Apis Cor’s curved-shaped house has an area of 37 square meters (400 square feet). This particular shape was selected rather than others. It was chosen to highlight the magnificent capabilities of the 3D printer that can create any desired building shape. The house includes a living room, a bathroom, a kitchen, and a hallway. One of the five partners in this project is Samsung which supplied the house with all the needed appliances, among which was a curved TV to fit onto the curved wall of the living room. Although the roof is flat, it is capable of enduring snow load specifications for buildings. That was achieved by using patches of polymer membranes, linked together utilizing hot air. Installation of doors and windows occurred after completion of the building process. One of the many advantages of the 3D printing process is that it is flexible and adaptable. It allows different kinds of installations as well as fittings to be included during the building process.
That was achieved by using patches of polymer membranes, linked together utilizing hot air. Installation of doors and windows occurred after completion of the building process. One of the many advantages of the 3D printing process is that it is flexible and adaptable. It allows different kinds of installations as well as fittings to be included during the building process.
courtesy of Apis Cor.
Construction of the Apis Cor House:
The weather, however, was not in favor of the construction process. The construction of the 3D printed house took place in the severe winter of Russia. Although the printer itself can function at temperatures down to -35 degrees Celsius, the concrete mixture it uses can only form at a temperature exceeding 5 degrees Celsius. Therefore, a tent was used to insulate the perimeter and to provide better temperature conditions for the concrete mixture. Geopolymers will enable construction companies in the future to build 3D houses at any season of the year.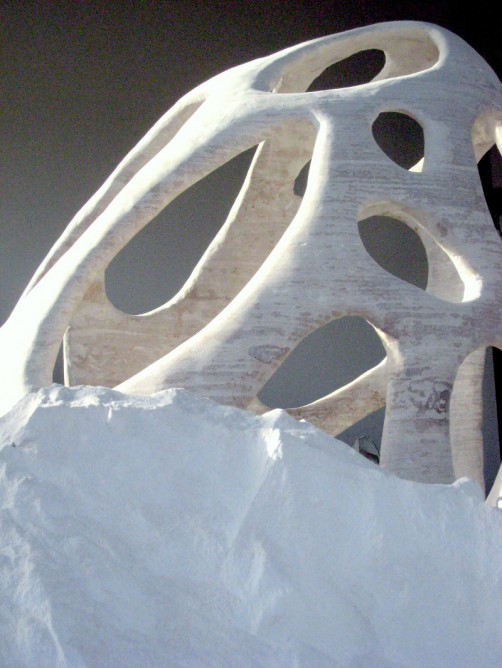 Another advantage of the new technique is the low cost of the created buildings as opposed to the ordinary block buildings. The novel method saves up to 70% of the construction cost. The 3D printed building produced by Apis Cor cost $10,134, which means $275 for every square meter. This cost includes every single aspect of construction exteriorly and interiorly like the roof, the insulation, the finishes, and of course the foundation. The doors and windows were the most expensive items of the house.
Another advantage of the new technique is the low cost of the created buildings as opposed to the ordinary block buildings. The novel method saves up to 70% of the construction cost. The 3D printed building produced by Apis Cor cost $10,134, which means $275 for every square meter. This cost includes every single aspect of construction exteriorly and interiorly like the roof, the insulation, the finishes, and of course the foundation. The doors and windows were the most expensive items of the house.
All images courtesy of Apis Cor.
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day11
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day6
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day10
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day2
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day7
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day3
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day4
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day5
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day8
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day9
Arch3O-3D Printed House by Apis Cor Entirely Created in One Day1
3DSLA.
 RU - Russian 3D printers®
RU - Russian 3D printers® Cost-effective additive manufacturing based on metal 3D printing systems, integration of additive approaches into existing technological processes, transfer of part of the processes to additive principles are current trends that are being thought about. These […]
On October 2, we participate as a technology partner in the Razvitie forum in Moscow (Holiday Inn Sokolniki Hotel, Rusakovskaya st., 24), We quote: Not only members of the consortium will take part in the exposition, […]
Russian 3D printers. What prevents the future from printing
I often use 3D printing for my production needs, but always the thought of making a video about how a 3D printed part went into business comes after everything is ready. Now […]
The Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation has prepared a catalog of domestic manufacturers of 3D printers. Link to the source: http://minpromtorg.gov.ru/common/upload/files/docs/katalog_additivity. pdf There are 81 sheets in the catalog, of which 11 sheets contain reference data and title pages. Of the remaining 70 sheets […]
pdf There are 81 sheets in the catalog, of which 11 sheets contain reference data and title pages. Of the remaining 70 sheets […]
3DSLA.RU polymer for LCD SLA 3D printers gives stable results and high quality when printing on LCD 3D printers such as Anycubic Photon and the like. For the convenience of our […]
Specialists of Kotlin-Innovator JSC reasonably treated the SLM process as one of the stages of the production chain and began to integrate it into their production processes. I will reserve the right to disclose details to my respected partners, but […]
Results of the Metalworking 2019 Forum» for the domestic market of additive technologies from Dmitry Trubashevsky.
On the first day of the Metalworking 2019 exhibition, Director of the Investment Engineering Department of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation M.I. Ivanov got acquainted with our products. The distinguished guests were presented with new 3D printing systems and consumables.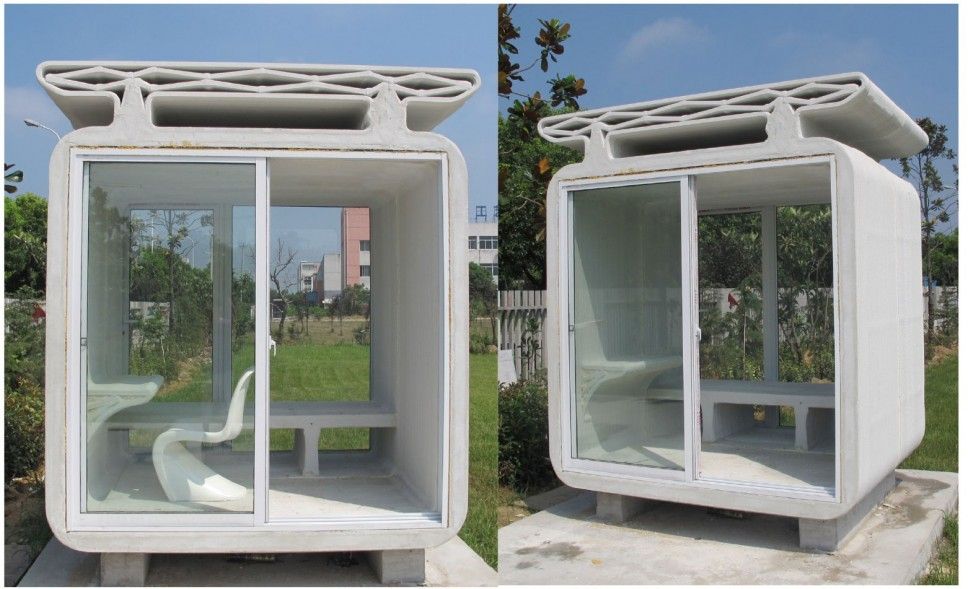
The production of medical devices for individual use by additive manufacturing is justified from an economic point of view, since almost all of them have a strictly individual shape and parameters. In the photographs, intervertebral disc prostheses (cage) with […]
Hello. Today, a novelty from the company 3DSLA.RU is next in line. This company has previously produced polymers and various printers. But, now they have invented 7 cool polymers, with a completely new composition. Polymers […]
Triangulatica 1.2.0.6 has been released. You can download the trial version at https://triangulatica.com/ru Trial: 10 fully functional cuts in the trial version. New: - Built-in calculation kernel calibration against correction tables for galvo (Use […]
From April 15, 2019, deliveries of a new series of our polymers will start, designed for 3D printing on affordable 3D LCD and SLA printers (Anycubic Photon, Whanhao D7, etc.).
On the morning of April 3, 2019, the main developer of our company, Denis Vlasov, attended a business breakfast at the invitation of the Minister of Economy, Innovation, Digitalization and Energy of North Rhine-Westphalia prof. Dr. Andreas Pinkquart, where already […]
Dr. Andreas Pinkquart, where already […]
We print cobalt-chromium caps and clasp prostheses for dental use on the RussianSLM FACTORY selective laser melting machine.
At the technical council on the introduction of additive technologies JSC Shipbuilding Corporation Ak Bars discussed the tasks, expressed opinions, debated, marveled at the scale of the enterprise and showed the achievements of #3DSLA.RU - Russian 3D printers and #Triangulatica. In the next […]
On the morning of November 28, 2018, at #PIIF, I presented our #RussianSLM FACTORY to the Governor of St. Petersburg A.D. Beglov, Chairman of the Board of OJSC "Rosnano" Chubais A.B., Vice-Governor of St. Petersburg Movchan S.N., Chairman of the Committee for Industrial Policy and Innovations of St. Petersburg Meiksin […]
TASS interview
Interview given by J'Son TV.
On October 17, 2018, we found our chief developer Denis Vlasov on the long list of RBC AWARD 2018 in the Innovator nomination. RBC SPB AWARD 2018
RBC SPB AWARD 2018
Triangulatica — our powerful slicer for all 3D printing technologies presented at INNOPROM 2018. Triangulatica has two great advantages - it supports all 3D printing technologies and fast math […]
RussianSLM® FACTORY and Triangulatica are presented to the Minister of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation D.V. Manturov Minister of the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation Denis Valentinovich Manturov visited the booth 3DSLA.RU and got to know our new products: 3D […]
3D printing — Worldskills Russia national team
“
3D printing technology was invented back in the 80s of the last century, but became popular not so long ago. With this printing method, the material is layered on top of each other, forming a finished product, and not just a two-dimensional image. Thanks to this, the possibilities of 3D printing are almost limitless: you can produce both a small high-precision part and an entire structure! In this tutorial, we'll walk through the entire 3D printing process from start to finish.
Glossary
To help you master the material, we recommend that you study the following concepts:
Apparatus that works on the principle of additive manufacturing. The finished product is, as it were, "grown" from a certain material
The principle of production, in which the finished product is formed by gradually adding material to the base
Programs that allow cutting STL models into layers and, based on this, generating a G-code in which commands are written for 3D printer
Video Lecture
Abstract
Additive Manufacturing Technologies
There is a huge variety of 3D printing technologies in the world today, from the oldest and simplest FDM technology to the emerging 3D bioprinting technology.
SLA (stereolithography)
Technology for the production of models from liquid photopolymer resins. The polymerization of the resin occurs due to irradiation with an ultraviolet laser at the points of contact of the material with the beam.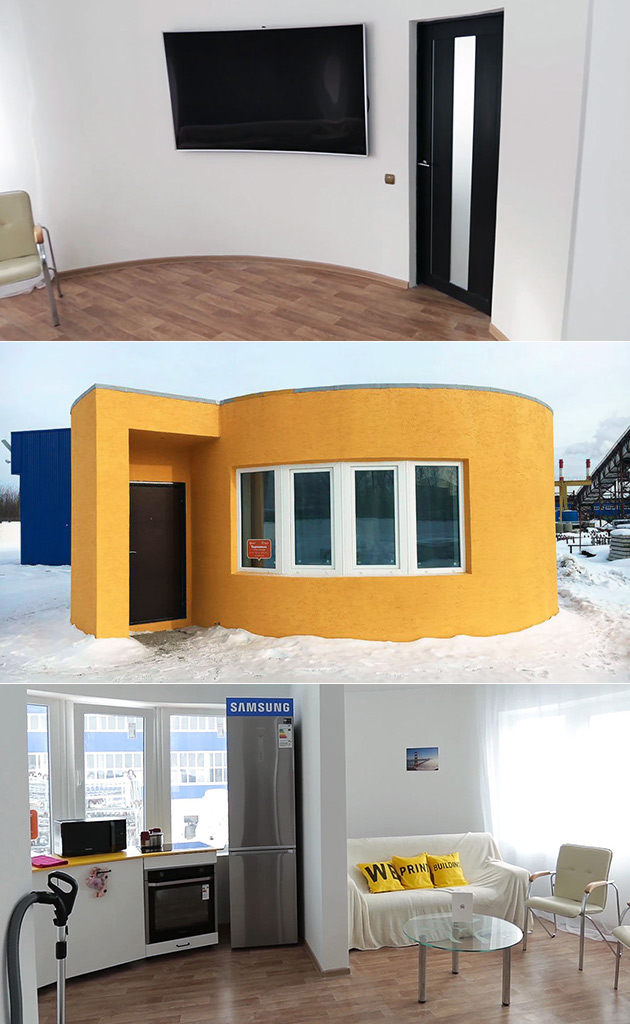 Upon completion of the contour construction, the working platform is immersed in a tank with liquid resin for a distance equal to the thickness of one layer. After leveling the surface of the liquid material, the process of building the next layer begins. The cycle is repeated until the complete model is built.
Upon completion of the contour construction, the working platform is immersed in a tank with liquid resin for a distance equal to the thickness of one layer. After leveling the surface of the liquid material, the process of building the next layer begins. The cycle is repeated until the complete model is built.
The main advantage of stereolithography is its high printing precision. The minimum layer height can be as low as 25 microns.
Among the shortcomings, it is worth noting the high cost of manufactured models due to the high price of consumables.
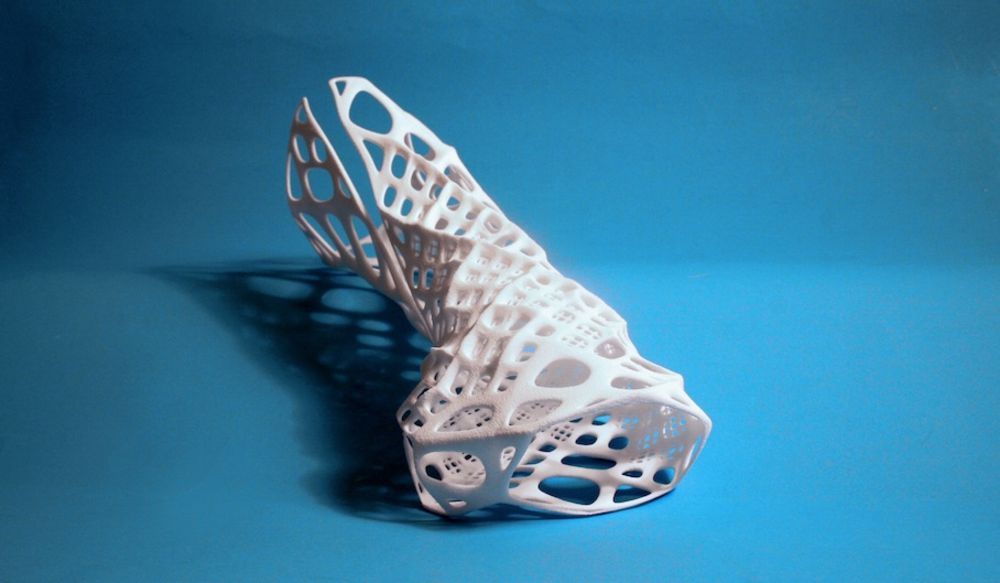
Here is an example of a printed part with mechanical supports.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
In this manufacturing process, a laser selectively sinters polymer powder particles, fusing them together to create layer after layer.
This technology provides high precision, detail and allows the production of parts with good and stable mechanical properties, unlike FDM and SLA.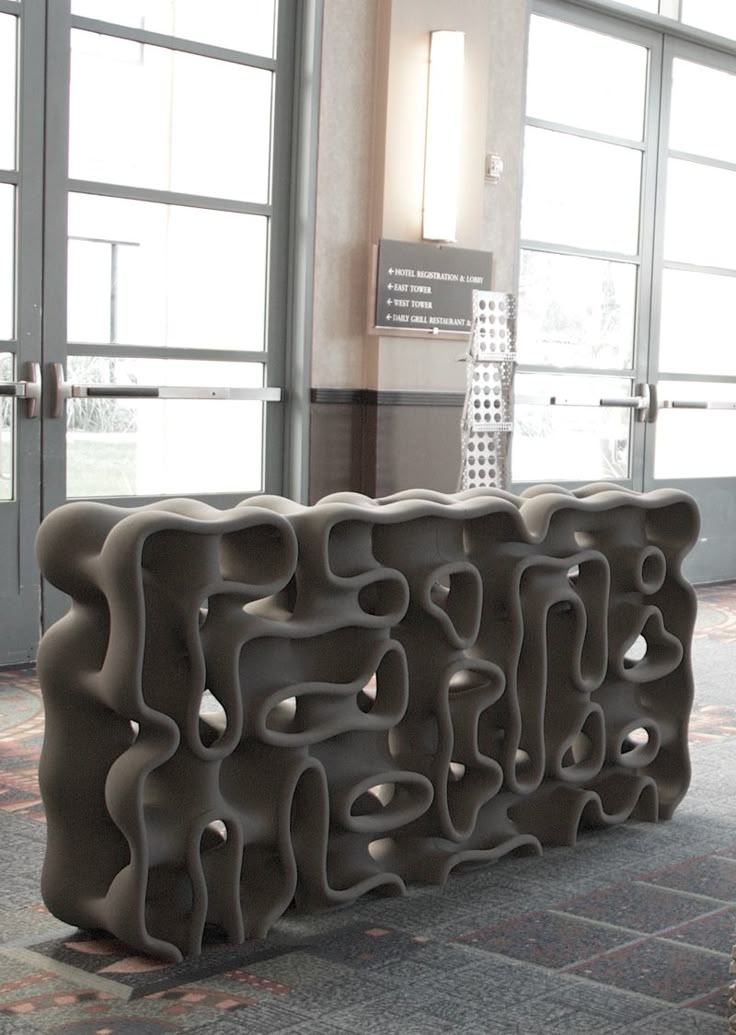 And printing in the volume of consumables allows you to print parts of even the most complex shape without mechanical supports.
And printing in the volume of consumables allows you to print parts of even the most complex shape without mechanical supports.
Here is an example of a part printed using this technique.
MJP (Multi Inkjet 3D)
This technology is based on layering an object from a wax-based photopolymer to build supports and a resin with properties selected for the part itself.
MJP is somewhat similar to SLA technology: both use photopolymer resins and UV lasers. But MJP is distinguished by more detailed printing and the presence of wax supports, which, in turn, allows you to completely get rid of the post-processing of the model.
This is what a part made using this technology looks like.
CJP (colour inkjet)
The principle of printing is to apply powdered materials layer by layer, after which a binder polymer is applied. The peculiarity of the technology is that polymers of different colors can be used, which makes it possible to create multi-colored and textured parts.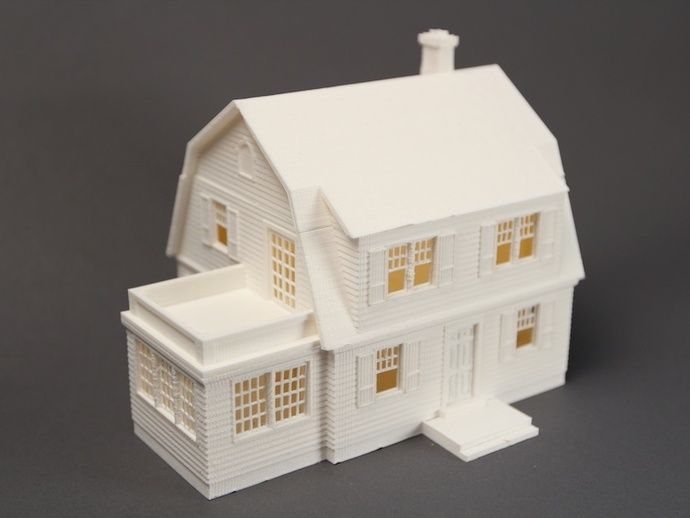
This technology is used to create realistic prototypes of buildings, clothes and shoes, human organs in medicine, and to make scanned human figures.
FDM (Fusion Deposition Modeling)
This technology is printed by fusing the material layer by layer.
Although FDM technology is the oldest printing technology, it has become widespread relatively recently. It includes ease of study and use, availability of additive technologies on the market, and an excellent balance between price and quality of finished products.
FDM technology allows you to use different types of media for printing. Each material differs in its properties and printing parameters. These can be:
- simple plastics: ABS, PLA;
- engineering plastics: PetG, ePeek;
- special materials: PVA, Hips, Flex.
Making a part on a 3D printer
Safety precautions
- During the operation of the 3D printer, do not reach into the working area where printing is being performed.

- Protective goggles and gloves must be worn when handling photopolymer printers that use photopolymer resin.
- Wear eye and respiratory protection when using printers that use powder media.
What We Need
3D Printer
3D Printing Plastic
Computer with Slicer 9004 3 148
USB flash drive
Special adhesive for 3D printing
Napkins
Making settings for printing
1.
2. We arrange the model so as to minimize the number of supports.
3. Set print options. Set the height of the layer. It should not exceed the diameter of the nozzle installed on the printer. The higher the layer height, the faster the print, but the surface quality of the model suffers.
4. Set the fill percentage. They affect the occupancy rate of the model: the higher the percentage, the stronger the model. But at the same time, material consumption and printing time increase.
They affect the occupancy rate of the model: the higher the percentage, the stronger the model. But at the same time, material consumption and printing time increase.
5. Perform support settings. The main ones are the gaps between the model and the support body during printing. When setting supports, you must take into account the height of the layer.
6. Perform adhesion settings. They allow you to create "skirts" around the models, which increase the contact area of the model with the table. The smaller the contact area, the wider the "skirt" should be.
7. After setting all parameters, press Slicing.
8. Save the job and send it to the printer.
Preparing the printer
1. Loading material into the printer.
2. In the program, go to the "Plastics" section, select the "Plastic Loading" item and set the type of plastic you want to load.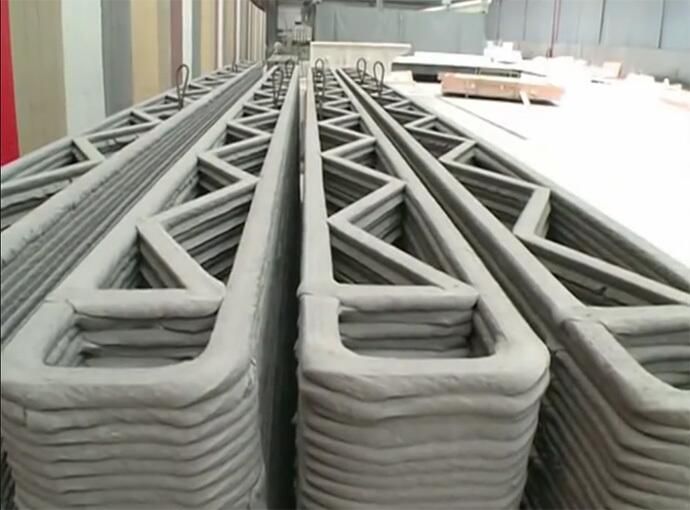
3. Calibrating the printer. To do this, go to the "Service" section, select the "Desk settings" item and follow the instructions on the screen.
4. The job can be run in one of the print speed profiles: Draft, Standard, or Quality. Each profile is labeled with an estimated print time. Select the required profile.
5. Apply the 3D printing adhesive to the napkin and spread it evenly on the table.
6. We start the job and wait for the part to be printed.
Finished product measurement and post-processing
1. Printing completed. Let the model cool down and remove it from the table.
Important
Do not remove the finished model from the table immediately, as this can ruin the model itself or even damage the table
2. We are reviewing the finished product. We take the dimensions of the physical model and compare them with the dimensions of the three-dimensional model.
We take the dimensions of the physical model and compare them with the dimensions of the three-dimensional model.
3. We evaluate the surfaces of the model. Very slight roughness is the norm for FDM printing. To achieve ideal surfaces, the model needs further post-processing.
“
In this lesson, we went through the entire path of a 3D printer operator and figured out the steps that go into it. And now consolidate your knowledge by completing a small task.
Interactive task
To reinforce your knowledge, take the test
| Let's start! |
| Further |
Sorry, you answered all the questions incorrectly
Read the lecture and watch the video again
| Go again |