3D printed meals
The Top Applications in Food 3D Printing
Published on June 24, 2022 by Alexandrea P.
What might have once seemed a fantasy, is quickly becoming a reality. Food 3D printing has been growing rapidly in the past few years and already we are seeing 3D printed food being sold and even offered in universities and there are more and more 3D printers designed specifically for food 3D printing. From meat to desserts and everything in between, initiatives mixing 3D technologies and food are increasingly common as they allow for not just more complex and original shapes and innovative recipes, but also adapt to specific diets. For your convenience, we have gathered some of the applications we have seen in food 3D printing including food and gadgets. Check out the list which is in no particular order, if it is used in the realm of cooking, you will find it below!
3D Print Liquids and Fruits with Dovetailed Design Studio
We previously told you have Dovetailed Design Studio’s efforts to make a 3D printer that could make fruit using spherication. Well, since then, the technology has advanced. Dovetailed’s nufood 3D printer is what they consider to be the world’s first liquid-based 3D printer and it allows for the creation of small flavor bursts, including of course for fruit. Indeed, one of the first applications was with the combination of fruit juice and sodium alginate powder for the creation of different fruits. Now, fruit flavored droplets are still being made by the company for luxury food and cocktails. The company hopes the printer will add playfulness and joy to cooking.
Photo Credits: Dovetailed Design Studio
Barilla Makes 3D Printed Pasta
The renowned Italian company Barilla, which specializes in pasta, developed the first 3D printer for fresh pasta in collaboration with the Dutch company TNO in 2016. With it, they have managed not only to offer good quality to the dishes around pasta, but it can also be used to create unique shapes. Now the company has announced that on its website it is already selling at least 15 different 3D printed pasta models. Some famous chefs are said to be already using some of these pastas in their kitchens.
Some famous chefs are said to be already using some of these pastas in their kitchens.
3D Printed Meat is Now Available
Additive manufacturing has now made it possible not only to produce meat substitutes such as those from Nova Meat or Redefine Meat, but even “real” meat products can be 3D printed. This is achieved by means of a process in which viable animal cells are used in the 3D printing process. In the future, this could put an end to factory farming with the help of additive manufacturing, which makes it possible to produce muscle as well as fat cells with pinpoint precision and industrial production speed. Hybrid products that combine the advantages of animal and vegetable protein are also well received by consumers, as the cooperation between the two companies Meatech and Enough shows.
The 3D Printed Seafood Making Waves
In the food 3D printing sector, the Austrian start-up Revo Foods has recently been making the news.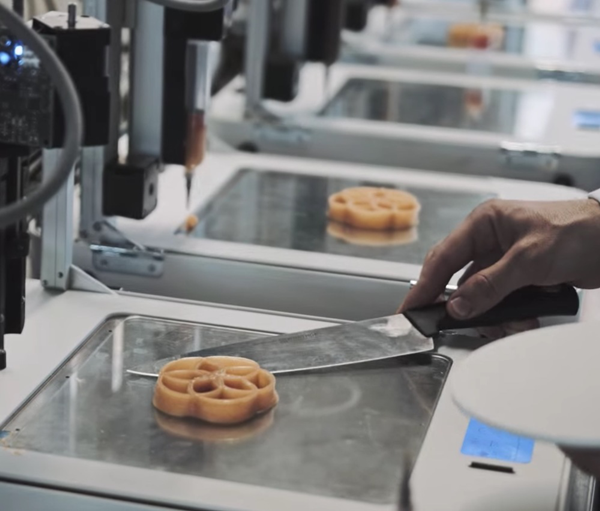 Using various plants, the startup aims to 3D print several seafood products, such as salmon slices. While Revo Foods currently offers products in the form of spreads that have not been 3D printed, in the near future the company hopes to take advantage of 3D technologies to develop an automated production line and 3D print more salmon, in all its forms!
Using various plants, the startup aims to 3D print several seafood products, such as salmon slices. While Revo Foods currently offers products in the form of spreads that have not been 3D printed, in the near future the company hopes to take advantage of 3D technologies to develop an automated production line and 3D print more salmon, in all its forms!
Photo Credits: Revo Foods
3D Printed Food Based on Seaweed
In Chile, nutrition experts have developed foods designed from algae through additive manufacturing. Filled with important nutrients and attractive shapes, these foods were developed from Cochayuyo algae, a plant found in Chile that is an important source of plant protein. Because of the advantages of 3D printing, the teams in charge of this project have developed edible figurines designed to attract children. In this way, they hope to make children want to eat plant proteins. Regarding the printing process, if the technology used is not specified, the experts confide however to be able to 3D print an edible figurine in only 7 minutes.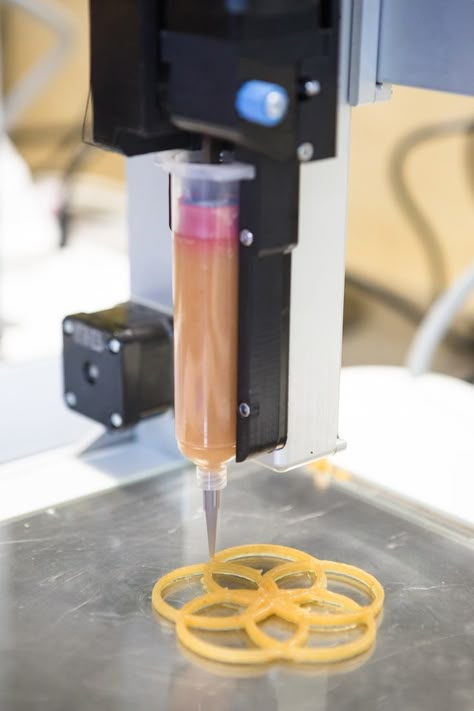
Restaurants Serving 3D Printed Food
It is clear that 3D printing plays and will increasingly play a very important role in our lives. A clear example of this is the number of new developments in the food sector related to this technology. 3D printed food has all the advantages brought by using 3D manufacturing but applied to the culinary world. Therefore, there are many chefs around the world who are already turning to the technology in their kitchens. That being said, having a 3D printer in a restaurant is an expensive option and therefore many restaurants cannot afford it. Others use 3D printers as way to attract consumers, as is the case of the restaurant Cocina Hermanos Torres, a Michelin-starred restaurant.
3D Printed Chocolate is Gaining in Popularity
Currently, there are a lot of companies that are dedicated to 3D printing chocolate, in fact, there are universities that are studying how to find the perfect crunchy chocolate through topological optimization. Multiple companies are looking to reinvent chocolate and adapt it to the digital age. To do this, master chocolatiers are combining additive manufacturing technologies with their traditional techniques. In this way, they successfully develop different ranges of chocolates with unique shapes and exclusive flavors. One example is Mona Lisa 3D Studio, a company that 3D prints your creations or designs in chocolate scale.
Multiple companies are looking to reinvent chocolate and adapt it to the digital age. To do this, master chocolatiers are combining additive manufacturing technologies with their traditional techniques. In this way, they successfully develop different ranges of chocolates with unique shapes and exclusive flavors. One example is Mona Lisa 3D Studio, a company that 3D prints your creations or designs in chocolate scale.
3D printing skips processing steps, such as mold design, mold making and mold testing (photo credits: Mona Lisa 3D Studio)
3D Printed Beverages and Cocktails
As unlikely as it may sound, 3D printing has now even found its way into the beverage market. The abundance of possibilities, that are enabled by using 3D printing, gave new beverage printing companies innovative ideas to print drinks in many ways, making them a new trend. Amazing ideas such as 3D polycapsules at the bottom of biodegradable cups, that are activated with the addition of water to make smart energy drinks, or 3D artwork, created inside a glass filled with a cocktail, the options are endless! With additive manufacturing making its debut and just barely scratching the surface of what is possible in the beverage industry, it is highly likely that we will see many new and exciting projects emerge in the near future.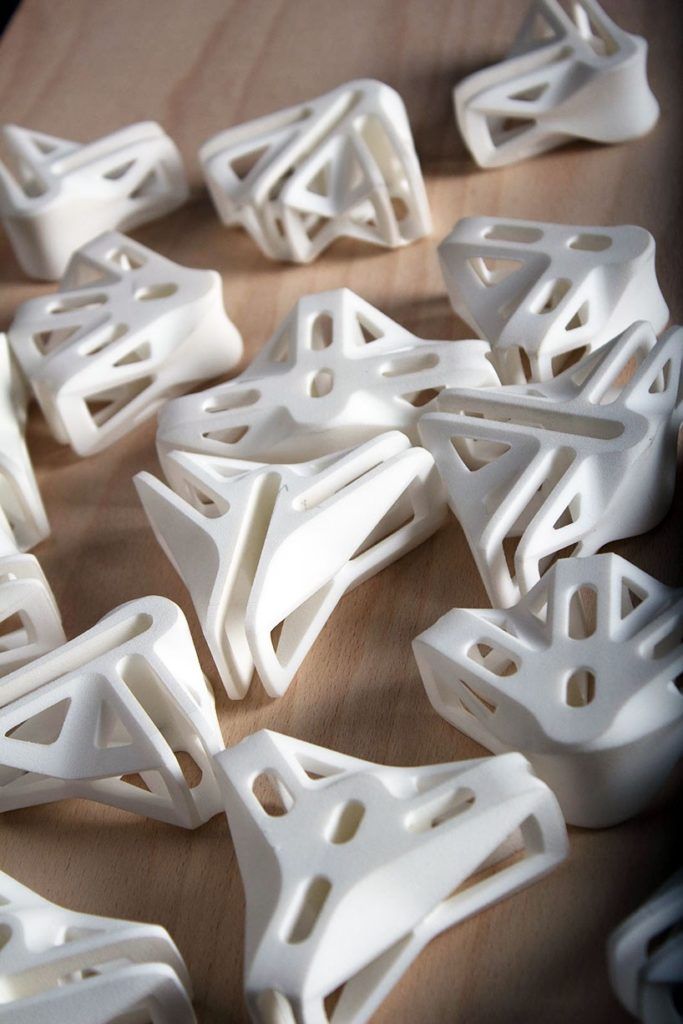
Cake Made Using 3D Printing
As you might have guessed from the 3D printed chocolate, desserts can also be created with the use of additive manufacturing! For those with a sweet tooth, there are a number of 3D printed cakes that look as good as they taste. For example, Nina Métayer decorated this cake with the rose window of the Notre Dame de Paris, which was reproduced perfectly using 3D printing. But making Mont Blanc in cake form is no problem either, as Chef Francisco Migoya has shown. Using milk chocolate, marron glacé pieces, crispy meringues, heavy freeze-dried cream, and a crumbled vanilla cookie as a substitute for the pie crust, he conjured up this pie, printing out a 3D model of the famous mountain for the purpose.
Kitchenware from the UAUProject
UAUProject, which originates from a studio in Warsaw, Poland, has set itself the goal of generating no waste and no emissions and placing a particularly strong focus on the aspect of sustainability. The products, which are based on personalizable and individual kitchen utensils, are produced by 3D printing from plant-based bioplastics such as PLA and are fully recyclable and compostable in industrial plants. In order to counteract overproduction, the UAUProject has focused on production to order in order to be able to act sustainably in a more targeted manner.
The products, which are based on personalizable and individual kitchen utensils, are produced by 3D printing from plant-based bioplastics such as PLA and are fully recyclable and compostable in industrial plants. In order to counteract overproduction, the UAUProject has focused on production to order in order to be able to act sustainably in a more targeted manner.
Photo Credits: UAUProject
Turning Food Waste into 3D Printed Cutlery
In addition to the interesting projects previously mentioned, the use of 3D printing in the circular economy within the gastronomic field is also worth mentioning. And yes, although it may seem strange, there are also many projects dedicated to the reuse of food waste for use with 3D printing. Companies like Upprinting Food, based in the Netherlands, seek to take advantage of food waste to give it a second life by creating sustainable and uniquely designed food. But not only can food be created anew, there are also other initiatives that use these leftovers to create everyday objects. For example, the Barbara Gollackner studio launched last year an original 3D printed tableware made from industrial food waste. Called Wasteware, the tableware includes plates, cutlery and even bowls – interesting initiatives to promote recycling and the circular economy!
For example, the Barbara Gollackner studio launched last year an original 3D printed tableware made from industrial food waste. Called Wasteware, the tableware includes plates, cutlery and even bowls – interesting initiatives to promote recycling and the circular economy!
On the right, a plate made by the startup Upprinting Food. On the left, part of the Wasteware tableware,
Objects to Preserve Your Food
When buying fruits and vegetables, it’s not always easy to ensure proper preservation – you’ve probably thrown away overripe or even rotten produce. To prevent this food waste, designer Lea Randebrock came up with the “Clay Pantry” collection: these are 3D printed objects made from clay that help preserve food. And to make it work, the objects have been designed to be watered, like plants -; clay is a porous material that will allow water to evaporate and thus cool the food inside. The collection includes several pieces that can all be integrated into smaller or larger living spaces.
What do you think of food 3D printing? Will you adopt it in your kitchen? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!
What in the World is 3D Food Printing?
Revo Foods’ plant-based seafood alternatives are developed with the help of 3D food printing technology. A group of specialized food technologists and engineers constantly experiment with new recipes to create new revolutionary products that are both delicious and nutritious. And they achieve that with the help of state-of-the-art 3D food printers, and 3D food printing is one of Revo Foods’ unique selling propositions.
Now you may be wondering… “what in the world is 3D food printing; do you download fish images and print them on paper?” – we get the confusion. Here is everything you need to know about 3D food printing.
What is 3D Printing?
Also called “additive manufacturing”, 3D printing is the process of making three-dimensional objects from a digital file. As the name suggests, the creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. That means that the object is created by laying down layers of material on top of each other.
As the name suggests, the creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. That means that the object is created by laying down layers of material on top of each other.
This process differs from traditional printing methods. When printing a file from your computer via a regular printer, you simply print an image of it on paper. When, however, you print a file with a 3D printer, you create a replica of it with the materials of your choice. Imagine seeing an object in your computer screen and having it in your hands a few minutes or hours later. Quite fascinating, isn’t it?
Δείτε αυτή τη δημοσίευση στο Instagram.
Η δημοσίευση κοινοποιήθηκε από το χρήστη Revo Foods (@revo_foods)
This revolutionary method was first imagined by writers and creatives in the 1940s.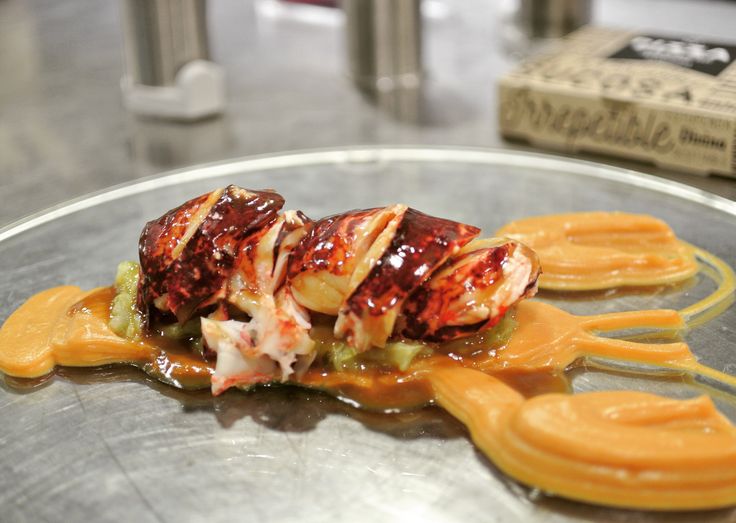 Writer Murray Leinster had written a story named “Things Pass By”, where he described a futuristic production method that “makes drawings in the air following drawings it scans with photo-cells. But plastic comes out of the end of the drawing arm”. It took over 40 years to materialize these revolutionary ideas. Early additive manufacturing equipment and materials were developed in the 1980s. But it was the 2010s that helped 3D printing gain massive popularity. That is partly because Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)* printing process patents expired in 2009.
Writer Murray Leinster had written a story named “Things Pass By”, where he described a futuristic production method that “makes drawings in the air following drawings it scans with photo-cells. But plastic comes out of the end of the drawing arm”. It took over 40 years to materialize these revolutionary ideas. Early additive manufacturing equipment and materials were developed in the 1980s. But it was the 2010s that helped 3D printing gain massive popularity. That is partly because Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)* printing process patents expired in 2009.
What is 3D Food Printing?
Although 3D printing mostly focused on the production of products made of plastic, it became quite handy in food manufacturing. Believe it or not, NASA has been looking into the technology to limit food waste and to make food that is designed to fit an astronaut’s dietary needs. Additive manufacturing of food is being performed by depositing food, layer by layer, into three-dimensional objects.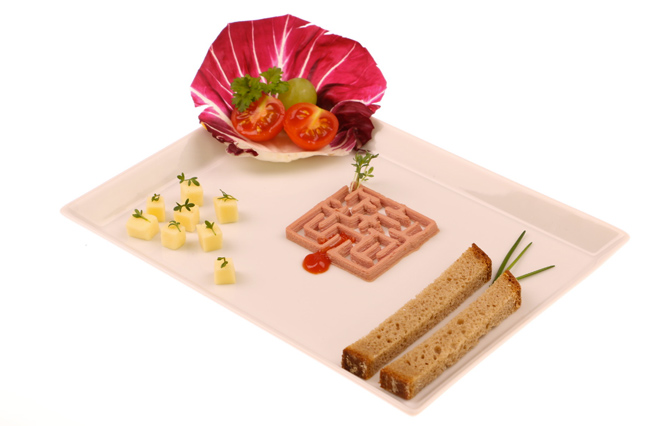 The most common way of doing that is by using food-grade syringes to hold the printing material, which is then deposited through a food-grade nozzle layer by layer. This is not too unusual from other food production methods, which today already often can produce in a 3D shape. The main novelty with 3D food printing is that is can be performed in a much more controlled way, leading to products which could not be produced otherwise (such as plant-based fish fillets).
The most common way of doing that is by using food-grade syringes to hold the printing material, which is then deposited through a food-grade nozzle layer by layer. This is not too unusual from other food production methods, which today already often can produce in a 3D shape. The main novelty with 3D food printing is that is can be performed in a much more controlled way, leading to products which could not be produced otherwise (such as plant-based fish fillets).
This method offers endless possibilities in terms of texture and flavor, which can come in handy when developing meat and fish substitutes. Since 2020, Revo Foods has been using this technology to develop high-quality seafood alternatives, such as smoked salmon slices made of peas and algae extracts!
The Benefits of 3D Printing Food
- Unlimited design freedom
- Texture variety
- Food waste reduction
- Time-saving
- Personalized nutrition (in the future)
- Less inventory
About Revo Foods
Revo Foods is an Austrian start-up that develops and produces plant-based seafood alternatives with the goal of ending overfishing.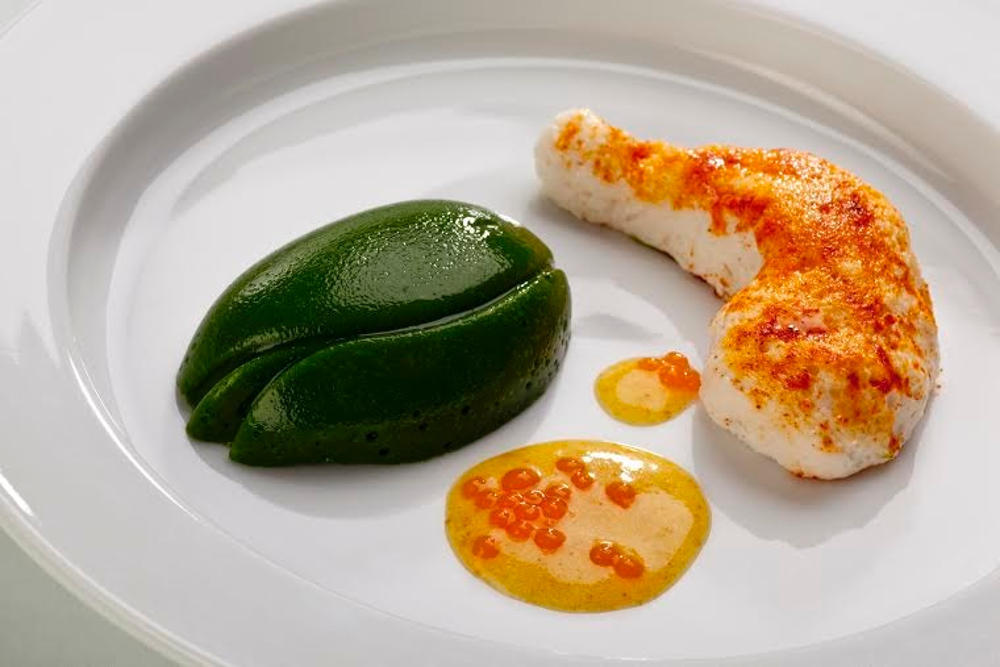 Our first product, Revo Salmon, is already available in more than 15 European countries. In June 2022, the first texturized salmon fillet by Revo Foods was presented at “Have a Taste of the Future” tasting event in Vienna. It is worth mentioning that 3D food printing has played a major role in the development of our revolutionary products.
Our first product, Revo Salmon, is already available in more than 15 European countries. In June 2022, the first texturized salmon fillet by Revo Foods was presented at “Have a Taste of the Future” tasting event in Vienna. It is worth mentioning that 3D food printing has played a major role in the development of our revolutionary products.
*FDM is an additive manufacturing technology that creates 3D components using a continuous thermoplastic or composite material thread in filament form.
Startup byFlow served a five-course 3D printed meal in a pop-up restaurant
News
Do you think 3D printed food has a future? While some criticize today's 3D food printers for being limited and wondering if they're needed at all, innovators from the Danish company byFlow will showcase the technology's potential at the 3D Food Printing Conference in Venlo, the Netherlands.
 On April 12, six lucky people got the chance to try a five-course 3D printed meal. All the food was made on byFlow 3D printers in a pop-up restaurant by Spanish chef Mateo Blanca.
On April 12, six lucky people got the chance to try a five-course 3D printed meal. All the food was made on byFlow 3D printers in a pop-up restaurant by Spanish chef Mateo Blanca. The 3D Food Printing Conference was held for the second time. Visitors were invited to taste unusual dishes, among which were a chicken printed in the shape of an octopus and steamed, 3D-printed sheep's cheese, and even meat that was previously dissolved in champagne to be passed through an extruder.
But the most exquisite delicacies were prepared for six guests. Especially for them, a five-course menu was compiled, among which was even carpaccio with guacamole sauce. All dishes were given an unusual shape using a 3D printer, after which they were carefully decorated. This gastronomic delight is made possible by the efforts of Spanish chef Mateo Blanca, who owns the recently awarded Michelin star restaurant La Boscana. Also, the idea of a pop-up restaurant was realized with the participation of 3D Samba, 3DChef and London-based 3DFP Ventures. Together with byFlow, they have achieved a truly masterful result that combines delicious food with next-generation technology. Similar pop-up restaurants that will serve 3D printed food are already planning to open in Dubai, Seoul, Rome, Las Vegas, Paris, Toronto, Berlin and Singapore.
True, the founders of startup byFlow say that the goal of this restaurant was as simple as possible: to showcase the variety of 3D printed food and the capabilities of the amazing Focus 3D 3D printer. The company is currently owned by siblings Floris and Nina Hoff, their father Fritz and friend Janine Hendrix. According to Nina, the success of the event proves that 3D food printing has a future, because it can be used to create fun, unusual and delicious dishes. True, she later added that a 3D food printer is not just a device for preparing funny dishes. “There are huge practical possibilities in 3D food printers,” she said. – For example, they will become indispensable for people who have difficulty chewing and swallowing food. Usually they have to eat foods boiled to a state of porridge, which are still driven through a blender. Such food looks disgusting, while all these processing processes completely kill its flavors and nutritional value.
Usually they have to eat foods boiled to a state of porridge, which are still driven through a blender. Such food looks disgusting, while all these processing processes completely kill its flavors and nutritional value.
Conference attendees noticed that 3D printed food not only looks delicious. She retained the aroma, taste and nutritional value. “If necessary, you can even cook dishes with a certain number of calories and add vitamins,” said Nina. From her point of view, this is an excellent solution to the problem of malnutrition.
The 3D printer was designed and built by Floris. At this stage, it is able to print different types of products thanks to a smart system of interchangeable print heads. “Freeze-dried vegetables and fruits retain all of their nutrients. We grind them into powder and add agar-agar. The result is a paste for 3D printing,” explained Nina. Chicken, for example, is mixed with herbs and also turned into a paste. After printing, products that a 3D printer can give some unusual shape can be fried in a pan, baked in the oven or steamed.
After printing, products that a 3D printer can give some unusual shape can be fried in a pan, baked in the oven or steamed.
But work on the Focus 3D 3D printer is not yet complete. “We have been developing this technology for a long time and now we are seriously engaged in preserving the taste of products,” Nina explained. To preserve the flavor and structure of the products, byFlow collaborates with several chefs, including Hans van Wolde. The company is optimistic about the future and firmly believes that we are on the threshold of a new era in the history of cooking, which is approaching by leaps and bounds. “Large food corporations will leave the market if they ignore this technology,” Nina concluded.
Source
Follow author
Follow
Don't want
8
More interesting articles
6
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
REC, one of the leading Russian manufacturers of consumables for FDM/FFF 3D printer. ..
..
Read more
four
Follow author
Subscribe
Don't want
Experts from the Institute of Light Materials and Technologies (ILMT) of the united company RUSAL developed...
Read more
sarkazm
Loading
04/01/2016
39825
68
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
News from the world of printing in a short line
FDplast announced the release of a free...
Read more
where and how they are already used / Habr
3DS Culinary Lab
3D Systems is the world's first innovative culinary center for 3D printing, located on the corner of Melrose and Highland, the epicenter of the Los Angeles culinary community.
The 3DS Cooking Lab opened this summer as a space for cooperative learning, collaboration and research - a place where the industry can experience the ChefJet Pro (Professional Food Printer) and where chefs, mixologists and culinary innovators can experiment with the combination of traditional culinary craft and 3D printing. This innovative hub will also frequently host events for leaders in the hospitality industry, gatherings of culinary communities, as well as symposiums and workshops that will explore and shape the range of 3D printed dishes.
Duff Goldman, Charm City Cakes
Chef Duff Goldman's "Ace of Cakes" is the original cake-making reality show. Duff can still be seen on his new show Duff Till Dawn and as a host at Sugar High. By the time Duff first got to the 3DS Cooking Lab, he was already experienced in 3D scanning brides and grooms for his cakes! Together we decided to develop a multi-tiered cake that would look like a traditional wedding cake.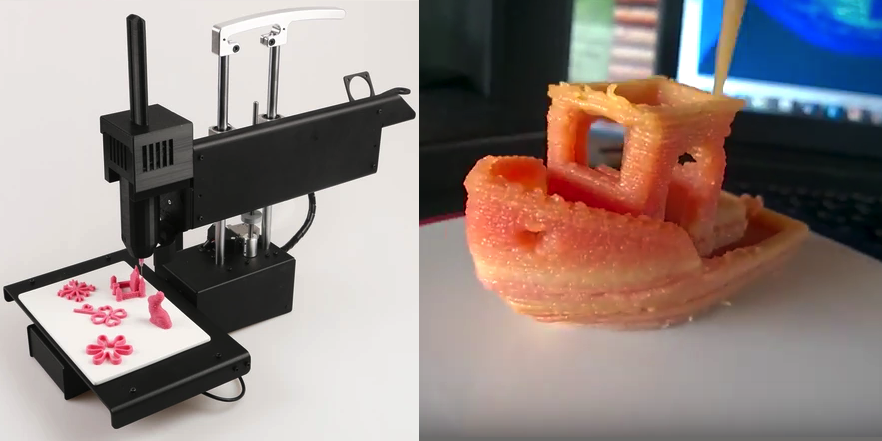 Clear geometric patterns decorate each tier, giving a completely unique look to the culinary masterpiece:
Clear geometric patterns decorate each tier, giving a completely unique look to the culinary masterpiece:
Matthew Biancaniello, Eat Your Drink
Matthew Biancaniello, industry renowned cocktail specialist and former mixologist at the Roosevelt Hotel's Liberty Bar, will be releasing his first cookbook, Eat Your Drink, this fall. As for the composition of drinks, which is highly dependent on the seasonal market and local ingredients, Matthew's cocktail creations rely heavily on savory. To test 3D Systems, he decided to create a cocktail that would whimsically combine the aromas of dried camphor milk mushrooms, bergamot and chamomile with tequila, kiwi fruit and freshly squeezed lemon juice. As a result of 3D printing, we got an acorn-shaped vase with miniature chamomile flowers and twigs around the edges:
Mei Ling
Season 12 winner of the Bravo reality show Top Chef, Mei Ling partnered with 3D Systems to create a 3D printed component to create an intricate dessert based entirely on the flavors of Hawaii and inspired by the beauty of the passion fruit flower.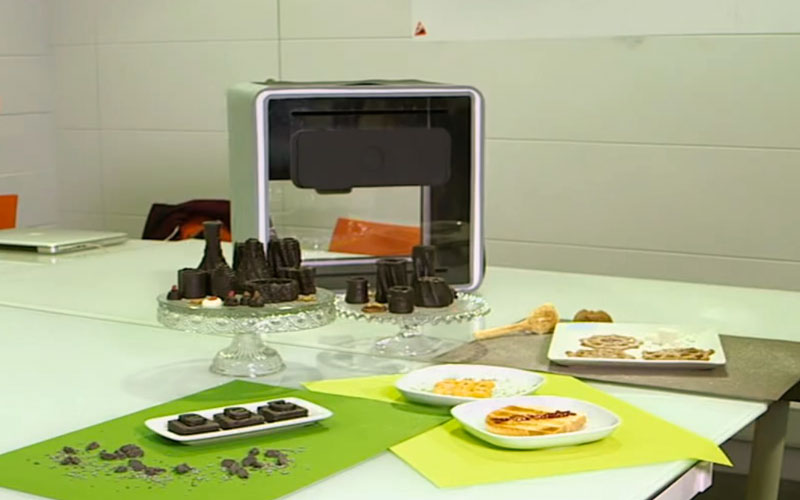
The dish consisted of passion fruit pulp, caramelized banana English cream chilled to an ice cream consistency with liquid nitrogen, freeze-dried strawberry powder, bee pollen, yogurt, and sliced fresh bananas and strawberries. A thin perforated 3D printed interpretation of the passion fruit flower, flavored with the fruit itself, topped each serving. Mei suggested that guests crush the fragile passion fruit flower with spoons to combine flavor and texture in each bite.
Josiah Citrine, Melisse Restaurant
Chef and co-owner of Mélisse, a 2-star restaurant (according to the Michelin guide) in Santa Monica, Josiah Citrine and chef Ken Takayama partnered with 3D Systems to create the appetizer. Chef Citrine was particularly interested in adding a certain flavor to the dish, and in an unexpected way, they decided to create an innovative version of the classic dish - French onion soup.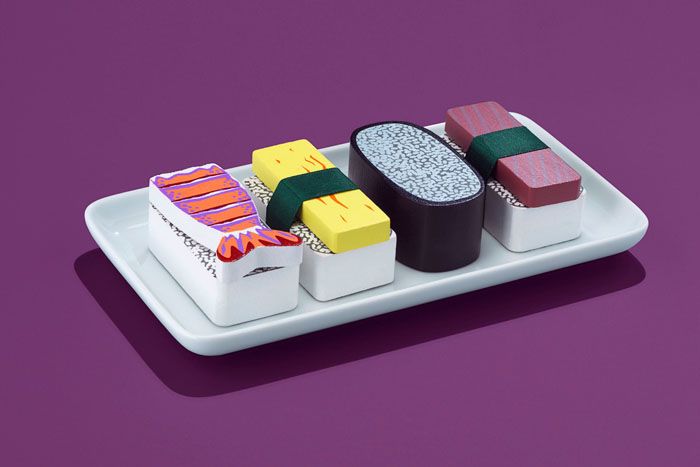
3D printing was tested on a traditional component, toast, which was printed using aromatic onion powder. Chef Citrine combined a small bundle of onion petals and burrata cheese along with printed croutons and garnished everything with skoroda flowers and battered onions. To this was added oxtail broth, which turned the rich beef consommé into an incredible interpretation of the classic French onion soup.
Culinary Institute of America
The Culinary Institute of America (CIA), the nation's preeminent culinary education institution, is partnering with 3D Systems to explore the intersection of 3D printed food and traditional artisan cooking methods. Beginning with the establishment of a 3D food research lab at their Hyde Park campus using a ChefJet Pro 3D food printer, the partnership will also include a series of conferences and workshops for the KIA community, as well as fellowships and fellowships at the 3DS Culinary Lab in Los Angeles.