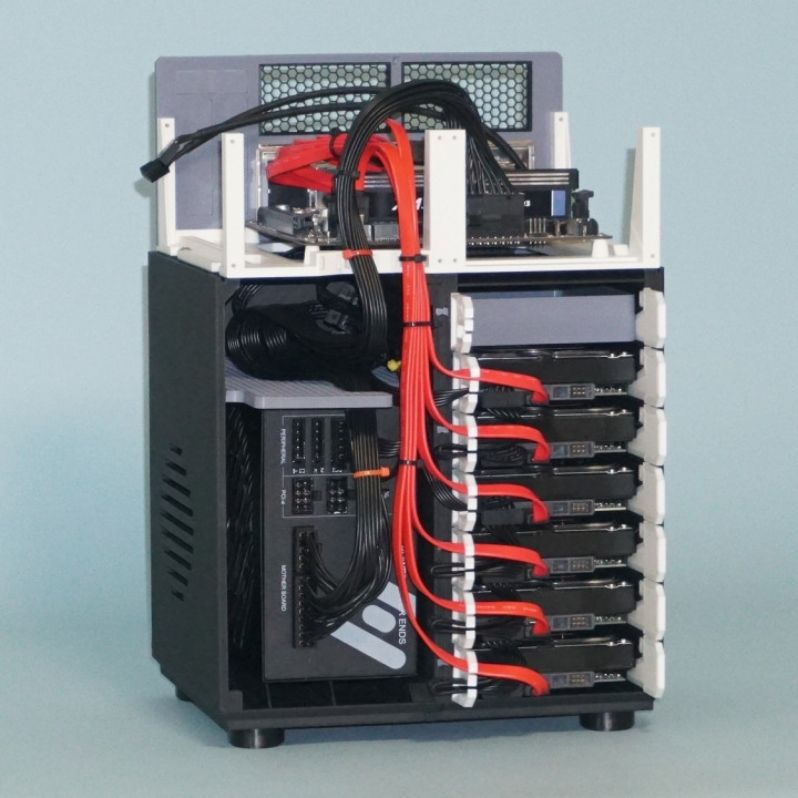
Reddit budget 3d printer
The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
While we'd hesitate to call 3D printing a mature technology, you might say it has reached its teenage years. Through their first decade-and-change, 3D printers have come down in price, grown easier to set up and operate, and become more reliable. And you may pay less than you expect: Many once-high-end features have migrated down to inexpensive models.
PC Labs has been reviewing 3D printers since 2013. Today, the state of 3D printing is strong, but that wasn’t always the case. For the first several years, it was often an adventure getting one of these printers up and running, let alone successfully through our testing regimen. Issues with filament-based—aka fused filament fabrication (FFF) or fused deposition modeling (FDM)—printers were abundant.
Filament feeders had to be coaxed into delivering filament from the spool to the extruder. Print beds had to be manually aligned. The extruder or hot end had to be positioned just right to minimize the gap between the nozzle and the build plate (the flat surface on which the object is printed). Objects frequently stuck to the build plate, and required careful, sometimes unsuccessful, efforts to pry them off. These and other issues required painstaking effort to resolve, often combined with calls to tech support.
Not so much anymore. While they can still be rebellious at times, 3D printers have grown up a lot, and achieving the 3D printer basics has gotten a lot less likely to end in a shouting match over small things. And they've gotten a lot more affordable, too, for curious DIY-ers and hobbyists to try.
If you're in the market for a beginner or low-cost 3D printer, it's important to know how lower-end models differ. Read on for mini-reviews of the top budget 3D printers we've tested. After that, we go into more detail on understanding the 3D printer specs and tech relevant to beginning buyers. Ready to take the plunge? Read on.
Original Prusa Mini
Best Overall Budget 3D Printer
4.5 Outstanding
Bottom Line:
It requires assembly and calibration care (plus shipping from the Czech Republic), but the Original Prusa Mini is a compact, open-frame 3D printer that consistently produces superb-quality output for a great price.
PROS
- Top-notch object quality
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Useful, professionally printed user guide
- Great support resources
- Versatile, user-friendly software
CONS
- First-layer calibration can be tricky
- Only includes starter packets of filament
- Requires monitoring if young children or pets are around
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | $399.00 | $399.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Original Prusa Mini Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Mini
Best Budget 3D Printer for Schools, Community Centers
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Mini is a consumer-oriented 3D printer that provides a winning combination of low price, ease of setup and use, solid print quality, and smooth, misprint-free operation.
PROS
- Very low price.
- Reasonably priced filament.
- Good print quality.
- No misprints in testing.
- Easy setup and operation.
- Quiet.
- Prints over a USB or Wi-Fi connection.
CONS
- Occasional problems in trying to launch prints.
- Removing printed objects from the print bed is sometimes tricky.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walmart | $199.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Amazon | $199.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Mini Review
Toybox 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Children
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
The Toybox 3D Printer works well as a model designed for children, offering reliable printing from a browser or mobile device and a few thousand toys to print, plus creative options to output drawings or photos. Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
Just bear in mind the tiny build area.
PROS
- Reliable, misprint-free printing
- Easy setup
- One-touch operation
- Well-composed help resources
- Access to more than 2,000 printable toys and projects
- Lets you create your own printable designs
CONS
- Tiny build area
- Not ideal for importing 3D files created elsewhere
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Toybox Labs | $379.00 | $299.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Toybox 3D Printer Review
Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Beginners, Non-Techies
4.0 Excellent
Bottom Line:
3D printing gurus will be intrigued by the Monoprice Mini Delta V2's use of the delta rather than Cartesian coordinate system, but beginners will just enjoy its low price, ease of use, and speedy printing.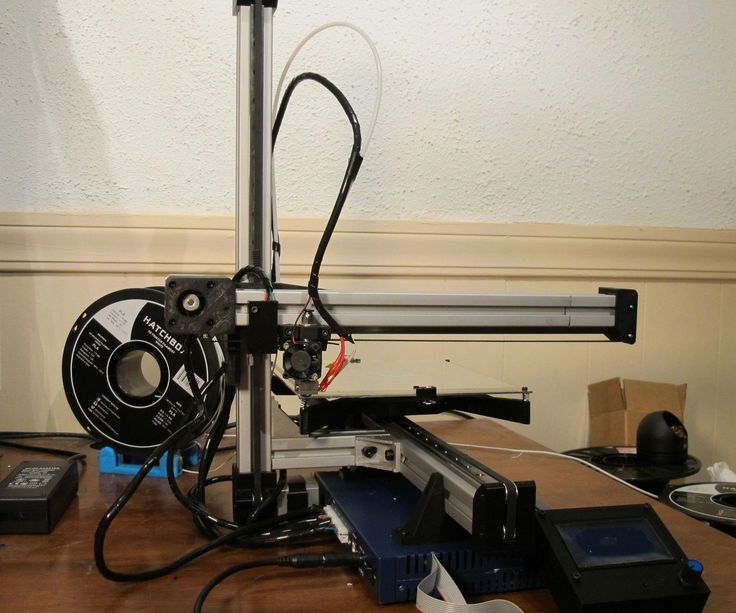
PROS
- Sub-$200 price
- Quick, nearly misprint-free printing
- Easy setup and operation
- Sturdy steel-and-aluminum frame
- Supports multiple filament types
CONS
- Tiny build area
- So-so print quality
- Mere one-year warranty
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $323.98 | $323.98 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer Review
Anycubic i3 Mega S
Best Budget 3D Printer With an Open Design, Big Build Area
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Anycubic i3 Mega S, an inexpensive open-frame 3D printer, produced decent-quality prints in our testing. To get the most out of it, though, may require precise calibration.
PROS
- Modestly priced
- Large build area for an inexpensive printer
- Supports a variety of filament types
- Generally solid print quality
- Uses well-known Cura software
CONS
- Finicky print-platform alignment
- Supported coils of filament are small
- Poorly placed spool holder
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $229. 98 98 | $229.98 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $279.00 | $279.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic i3 Mega S Review
Anycubic Vyper
Best Budget 3D Printer for the Biggest Build Area Possible
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Anycubic's modestly priced Vyper whips up large 3D prints on its open-frame design, and provides automatic print-bed leveling. Just know that some minor assembly is required—and printed objects may require a bit of cleanup.
PROS
- Relatively large build area
- Automatic bed leveling
- Simple assembly
CONS
- Short (one-year) warranty
- Includes only a small starter filament coil
- Using Cura software with the Vyper requires tweaking a couple of settings
- Test prints showed some "hairy" filament residue
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $429.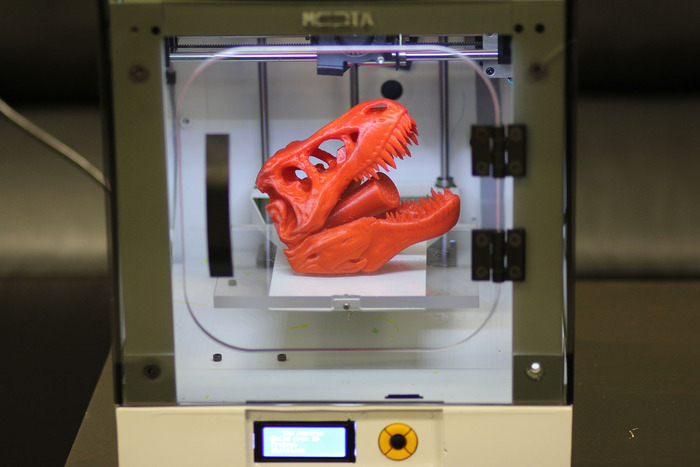 99 99 | $429.99 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| AnyCubic | $369.00 | $319.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Anycubic Vyper Review
Creality Ender-3 V2
Best Budget 3D Printer for Tinkerers and DIY Types
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
Hands-on tweaking defines Creality's budget-price Ender-3 V2, an open-frame 3D printer that you build from a kit. It produces generally above-par prints, but its print bed can be tricky to keep leveled.
PROS
- Inexpensive
- Slightly above-average print quality
- Good-size build area for its price
- Supports several filament types
CONS
- Manual print-bed leveling can be tricky
- Setup instructions could be deeper, more legible
- Questionable quality control on some parts
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299. 00 00 | $246.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Creality Ender-3 V2 Review
Flashforge Finder 3D Printer
Best 3D Printer for the Very Tightest Budgets
3.5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Flashforge Finder 3D Printer is moderately priced and offers good print quality, but it proved tricky to get up and running in our tests.
PROS
- Quiet.
- Good print quality.
- Connects via USB 2.0 cable, USB thumb drive, or Wi-Fi.
- Reasonably priced.
CONS
- Some objects pulled off the platform during testing.
- Poor documentation.
- Modest build volume.
- Limited to printing with polylactic acid filament (PLA).
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $729.00 | $729.00 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Flashforge Finder 3D Printer Review
Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Dabbling in Small Objects
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer is a compact, stylish 3D printer with above-par overall print quality, but, alas, a tiny build area for the money.
PROS
- Small, lightweight for a desktop 3D printer.
- Easy to set up and use.
- Supports PLA, PETG, and wood composite filaments.
- Multiple-color support.
- Wi-Fi camera monitors print jobs.
- Prints from USB drives, SD cards, or mobile devices.
CONS
- High price for its capabilities.
- Small build area.
- Too-brief warranty.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $699.00 | $699.00 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Polaroid PlaySmart 3D Printer Review
XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro
Best Budget 3D Printer With Closed Design, Roomy Build Area
3. 5 Good
5 Good
Bottom Line:
The XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro is a moderately priced closed-frame 3D printer with a large build volume and overall good performance, but a potentially balky filament-feeding system.
PROS
- Spacious build area
- Works with third-party filaments
- Self-leveling print bed
CONS
- Build plate is not heated
- Limited to PLA- and PETG-based filaments
- Guide tube is prone to detaching
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $299.95 | $199.95 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Best Buy | $449.95 | $449.95 | Check Stock (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our XYZprinting da Vinci Jr. 1.0 A Pro Review
Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer
Best Budget 3D Printer for Cheap Filament
3. 0 Average
0 Average
Bottom Line:
The Monoprice Voxel is an under-$400 3D printer that's easy to set up and use. It exhibits generally good print quality, but it was unable to print two of our test objects.
PROS
- Easy to set up and use.
- Budget price for printer and filament spools.
- Supports PLA, ABS, and several composite filament types.
- Versatile software.
- Prints over Ethernet or Wi-Fi, or from a USB thumb drive.
CONS
- Frequent misprints on certain test objects.
- Slightly balky touch screen.
| Sold By | List Price | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | $449.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
| Walmart | $429.99 | $369.26 | See It (Opens in a new window) |
Read Our Monoprice Voxel 3D Printer Review
Buying Guide: The Best Cheap 3D Printers for 2022
How to Buy a Cheap 3D Printer
The biggest changes to 3D printers over the last few years have come to the cheaper models. Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
Nowadays, many of those classic, ornery 3D-printing issues have been resolved (most of the time, anyway), even for consumer and bargain-priced 3D printers. Automatic print-bed leveling is the norm, and you can usually remove 3D-printed objects from heated and/or flexible build plates with a minimum of coaxing. And most 3D printer manufacturers have either developed and refined their own software, or have adapted an open-source printing platform such as Cura(Opens in a new window).
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
What separates more expensive 3D printers from cheap ones ("cheap" defined as $500 or less, for the purposes of this article) is often a select group of features. These include the build volume, the type of frame, the varieties of supported filament, the software, and the connectivity mix. Let's run through those in turn.
What's the Right Build Volume for a 3D Printer?
A 3D printer’s build volume is the maximum dimensions (HWD) of a part that it can print. (We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(We say “a part” because a 3D-printed object can consist of multiple parts that are printed, then glued or otherwise pieced together.) While the smallest build volume of any 3D printer we have tested is 3.9 by 3.9 by 4.9 inches, we consider any build volume smaller than 6 by 6 by 6 inches to be small, any between that and 10 by 10 by 10 inches as medium, and any printer with at least one build dimension of more than 10 inches as having a large build volume.
(Credit: Molly Flores)
As a general rule, inexpensive 3D printers have small build volumes, while more expensive ones have larger build volumes. This depends in part on the type of printer. Closed-frame 3D printers—and most semi-open models, which have a rigid top, base, and sides but are open in front and, often, back—tend to have small build volumes, while open-frame printers, lacking as rigid a physical structure, often have relatively large build volumes for the price. You'll want to weigh the build volume against the kinds of objects you will print.
Should I Get an Open-Frame or Closed-Frame 3D Printer?
Which brings us to the frame "form factor" question: open-frame versus closed-frame. Closed-frame 3D printers are boxlike devices, with a rigid base, walls (with a see-through door in front), and top. Among their advantages? They muffle the operating noise, as well as reduce the odor from melted filament (which is potentially an issue with ABS plastic), and they provide some protection for people or pets who might inadvertently touch the hot extruder. A downside: They tend to have smaller build volumes than open-frame 3D printers, which have fewer (often, no) walls to constrict them.
(Credit: Zlata Ivleva)
Low-cost 3D printers include both open-frame and closed-frame models, as well as a few stereolithography printers. If a relatively large build volume is a priority, you’re likely to get more bang for the buck with an open-frame model. Open-frames do have some clear downsides by definition: They tend to be noisy, emit odors when certain plastics are melted, and provide little protection for someone who might touch the hot extruder.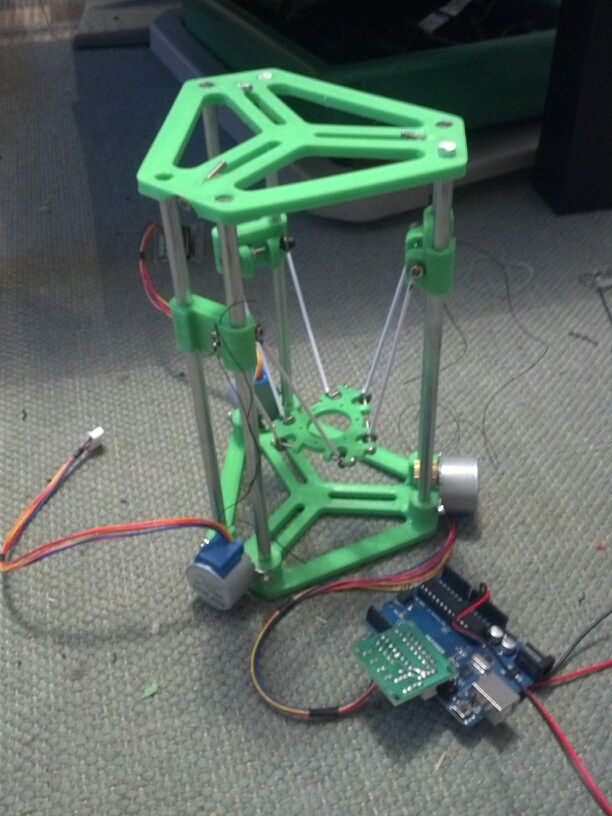
(Credit: Molly Flores)
Also, recognize some potential negatives of open frames, depending on the model. Some require assembly, being essentially kits, and most require more setup care than a closed-frame printer, plus more maintenance to keep them running smoothly. Still, these very traits should not deter—and may even appeal to—hobbyists and DIY folks.
What Should I Look for in 3D Printer Software and Connectivity?
Gone are the days when tinkerers had to cobble together several different programs to get a 3D printer to run. Manufacturers either include their own 3D printing program or modify an existing platform such as the open-source Cura.
3D printing software performs three main functions: processing an object file (resizing, moving, rotating, and in some cases duplicating it), slicing it (into virtual layers, based on your chosen resolution), and printing it. These are almost universally combined into a seamless process. Some high-end printers have software that supports a wider range of settings you can tweak, but even the basic suites work at least reasonably well.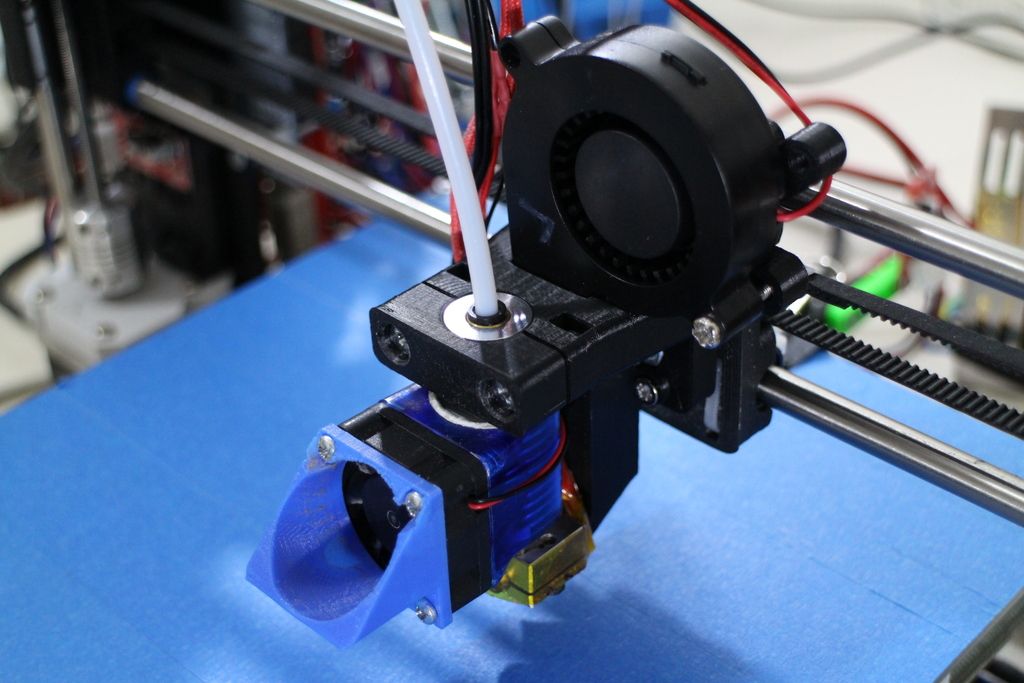
More likely to vary among the cheaper set is the array of connection options from model to model. Nearly all have a USB Type-A port to fit a thumb drive for printing from document files. Most also have a USB Type-B port for connecting directly to a computer, and some offer Wi-Fi, too (or as an alternative), while a handful let you connect via Ethernet to share the printer across a local network.
Some printers support storing 3D files on an SD or microSD card (which may also contain the printer’s system files). Most 3D printer manufacturers (even the discount ones) have a mobile app to launch and monitor print jobs, and a few provide access to cloud services from which you can print.
While high-end 3D printers tend to have an abundance of connection choices, discount models vary widely in their choices. Some are generous and some are basic, so it pays to assess what a given model offers.
What Should I Look for in Filament Support?
Filament support tends to be a key area that separates the cheaper models from the higher-end ones.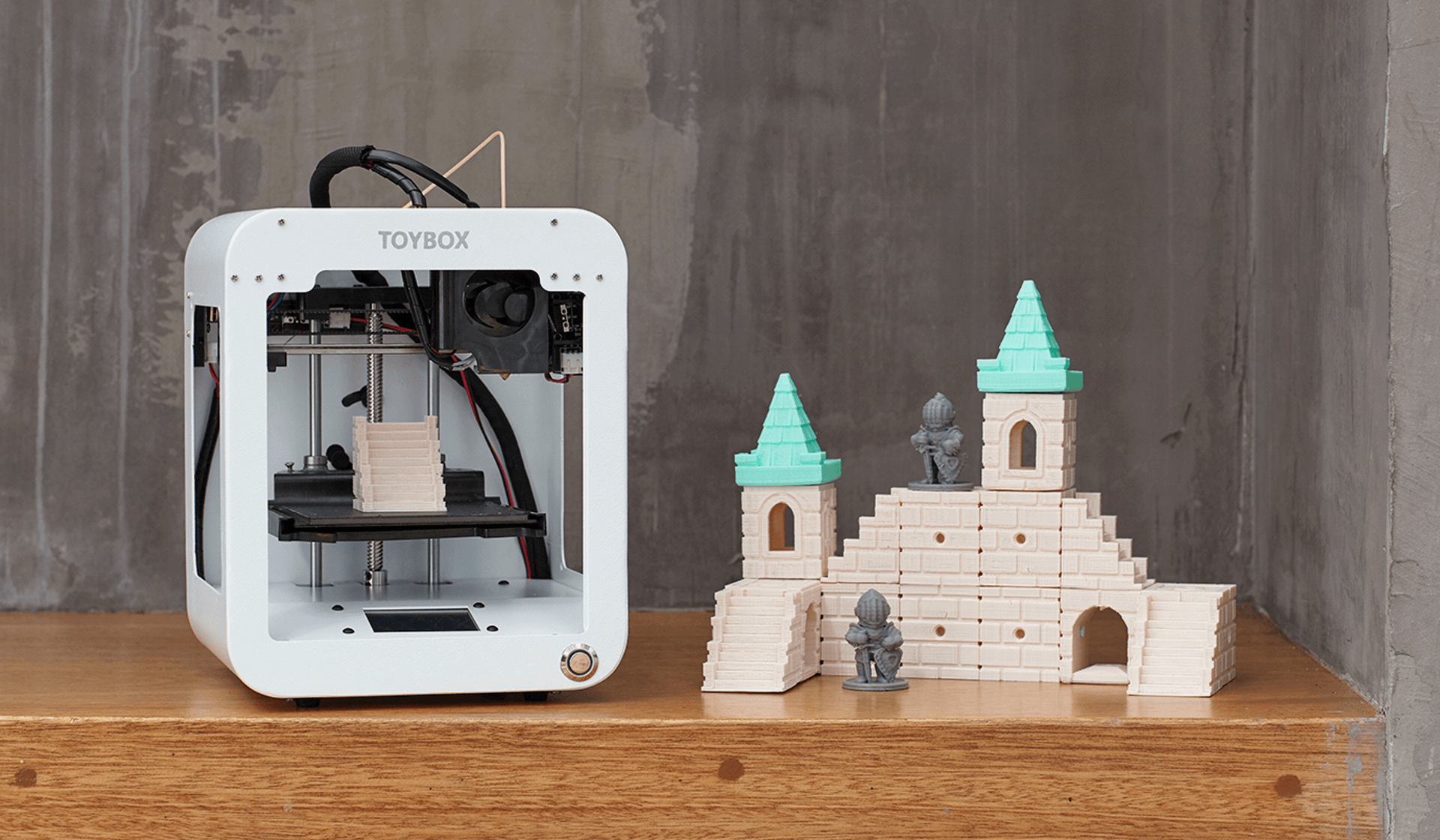 (See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
(See our guide to understanding 3D printing filaments for more particulars.) Inexpensive 3D printers tend to support a limited number of plastic filament types, some of them only PLA and/or ABS.
Recommended by Our Editors
3D Printing: What You Need to Know
3D Printer Filaments Explained
(Credit: Molly Flores)
PLA (polylactic acid) is a biodegradable, plant-based polymer, while ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the same tough plastic that Legos are made from. Objects printed from ABS are durable and nontoxic, though the material can be tricky to work with. ABS can emit an acrid, unpleasant odor during printing, and the bottom corners of objects being printed with it have a tendency to curl upward a bit, especially if you are using a non-heated print bed. This can lead to unsightly prints, and/or prints prematurely pulling off the build plate, ruining them.
Many entry-level and low-price 3D printers stick exclusively to PLA. If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
If you want to experiment with a larger variety of filaments—which include water-soluble filament, wood- and metal-laced composites, and both tough and flexible varieties—you may have to pay more, although a few discount models support a wide range of materials.
Should I Consider a 3D Printing Pen Instead?
Although they aren’t printers per se, inexpensive 3D pens are close kin to 3D printers—using the same filament types and a similar extrusion system—and we include them in the 3D printing category. Rather than tracing out a programmed pattern, you use the 3D pen much like a normal pen, except that you draw with molten plastic. You can trace a pattern or draw freehand, and even draw in three dimensions as the plastic quickly solidifies and hardens once extruded.
(Credit: 3Doodler)
Most 3D pens cost less than $100, and some cost $50 or less. At a glance, 3D pens may appear to be toys, but some artists and craftspeople have taken to them, as it is possible to make quite complicated and beautiful objects with them. If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
If your aim in 3D printing is something closer to freehand design and free expression than computer-centric, structured, and repeatable output, you might give one a try.
So, What Is the Best Cheap 3D Printer to Buy?
Buying a budget 3D printer needn’t mean a world of sacrifice. Plenty of capable and reliable models sell at less than $500, and while they may not be as feature-rich as their more expensive cousins, there's no sense in paying for things you don’t need.
Many casual 3D-printing experimenters will be fine with printing over a USB cable or from a thumb drive, and sticking to PLA may be the best choice for a starter 3D printer. If you focus just on the features you want, you may be pleasantly surprised at what you find. Below, check out a spec breakdown of the best under-$500 3D printers we have reviewed, paralleling our picks above. Also, for a look at the broader market, see our guide to our favorite 3D printers overall.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Great for beginners
Tom's Guide Verdict
The Monoprice Delta Mini V2 is an excellent 3D printer for the price, and a good way to get started in 3D printing if you don’t want to pay up for the Monoprice Voxel or Polaroid PlaySmart.
TODAY'S BEST DEALS
Pros
- +
Low cost, fully-featured 3D printer
- +
Prints PLA, ABS, PETG, and other materials
- +
Excellent print quality for the price
Cons
- -
The software has some rough edges
- -
Prints are limited to 4.3 inches in diameter
- -
Can’t work with flexible materials
Why you can trust Tom's Guide Our expert reviewers spend hours testing and comparing products and services so you can choose the best for you. Find out more about how we test.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer: Specs
Price: $199.99
Type: Delta Fused Filament Deposition (FFD) 3D printer
Filament Size: 1.75mm
Filament Type: PLA, ABS, PETG, Other
Interfaces: USB, WiFi
Storage: Micro SD
Size: 9.75 x 8.5 x 14.5 inches
Weight: 2. 2 pounds
2 pounds
Even though it sports an unusual look for a 3D printer, there’s something familiar about the Monoprice Delta Mini V2. That’s because this is actually the second version of this device — we reviewed the original Monoprice Mini Delta a while back when it was a low-cost if flawed way to get started in 3D printing.
Does the new version address those flaws, which included unreliable USB connections and printing modes along with other bugs? Our Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review finds a much improved device, though software remains a weak spot.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Price
You can get the Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer for $179, a very attractive price for entry-level printers. Consider that our top rated choice for best 3d printer — the Monoprice Voxel — costs $449, that’s quite a bargain.
The Monoprice Delta Mini V2 is available directly from Monoprice .
The Monoprice Delta Mini V2 is a cute little printer, measuring just 14. 5 inches high. While most 3D printers use left-right and forward-back rails that the print head slides along, the Delta 2 uses three spider-like arms, with the print head attached in the middle. Move one of these legs up, and the print head moves in that direction. By coordinating all three legs, the Monoprice Delta Mini V2 can move the print head anywhere in the print area.
5 inches high. While most 3D printers use left-right and forward-back rails that the print head slides along, the Delta 2 uses three spider-like arms, with the print head attached in the middle. Move one of these legs up, and the print head moves in that direction. By coordinating all three legs, the Monoprice Delta Mini V2 can move the print head anywhere in the print area.
It’s a rather compelling motion to watch, but it does have one limitation: the print area is circular and is smaller than a more standard printer of the same size. For the Mini Delta 2, the print area has a diameter of just over 4.3 inches and a height of just over 4.7 inches. That’s a total of about 81 cubic inches, which is somewhat smaller than the 107 cubic inches provided by the Polaroid Playsmart.
(Image credit: Monoprice)The Delta Mini V2 features several ways to connect to the outside world, including a micro SD card slot, a Micro USB port and a Wi-Fi interface. The latter option is of limited use, though — you can’t control the printer over a web interface or connect to it directly with a slicing app to send files. Instead, Wi-fi only works through a rather poor mobile app.
The latter option is of limited use, though — you can’t control the printer over a web interface or connect to it directly with a slicing app to send files. Instead, Wi-fi only works through a rather poor mobile app.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Controls
You’ve got several options for controlling the Delta Mini V2 — an on-device display, the PoloPrint Pro app, or through a slicer app such as Cura.
The small touch screen on the printer itself can be used with a fingertip or with an included plastic stylus. The latter is preferable, especially for precise jobs like entering a Wi-Fi password via the on-screen keyboard. Fingertips are fine for simpler jobs like pressing the start button, though.
(Image credit: Monoprice)The pre-release version of the PoloPrint Pro app that I tried is available for both iOS and Android. It’s a bit rough around the edges: I found that it often crashed or failed to connect to the printer. When it did work, I was able to start a print from the micro SD card or from the online library and monitor the print progress, although there is no camera in this low-cost printer that lets you see the print in progress.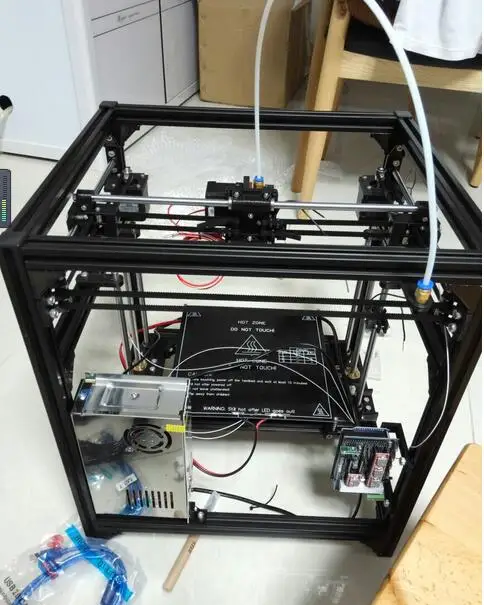 Another omission here is the ability to load your own models and print them from the app; Monoprice told us that this might be added at a later date.
Another omission here is the ability to load your own models and print them from the app; Monoprice told us that this might be added at a later date.
The best way to set up a print is with a slicing app such as Cura. A customized version of this open-source program for Windows and Mac is included on the micro SD card that comes with the Monoprice Delta Mini V2, and that is what we used to print in our tests. This doesn’t support connecting to the printer over WiFi, but it does support USB or saving a print file to the micro SD card. So, if you are using Cura to prepare prints, you have to use USB or micro SD to print.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Print process
The Delta Mini V2 is a pretty simple printer to use. Once you’ve created your print file in Cura or another program and copied it onto the micro SD card, you hit the print button in the on-screen menu and select the file to start printing.
The first thing the Delta Mini does is automatically level the print bed, touching the print head to the bed in three places to press a switch underneath it.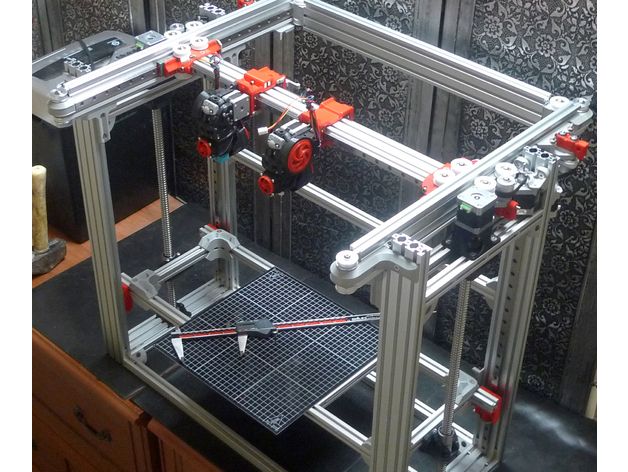 That lets the printer know exactly where the print bed is— an important step for laying down an even first layer. Once ready, the Delta Mini lays down the first print layer on the heated print bed, then moves up to do subsequent layers.
That lets the printer know exactly where the print bed is— an important step for laying down an even first layer. Once ready, the Delta Mini lays down the first print layer on the heated print bed, then moves up to do subsequent layers.
I found that prints worked well, with few errors and no major failures. If anything, prints stuck to the print bed a little *too* well, as I usually had to pry the final print off the bed with a paint scraper.
The Delta Mini V2 can handle multiple filament types including PLA, ABS, and PETG. You’re not restricted to filament from any one source, as the Monprice 3D printer can use 1.75mm filament from any manufacturer. We tested the Delta Mini with both PLA and ABS material and found it produced excellent results with both.
Your biggest limitation will be the maximum temperature of the print head and the print bed (250℃ and 100℃ respectively). The Delta Mini V2 also can’t handle flexible materials, as these require a different style of print head.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Print speed
The Delta Mini V2 is a pretty fast printer in draft mode: it cranked out a 3.5-inch high Thinker figure in a little more than 3.5 hours in this mode, which uses a 0.2 mm layer height. The 3D printer is a blit slower if you run it in normal quality, as my print took 7 hours and 10 minutes. This mode halves the height of each individual layer to 0.1mm.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Print quality
We use several test models to test 3D printers, including a scan of Rodin’s Thinker statue, a set of gears and a geometric sculpture. I was impressed with the quality of the prints that the Delta Mini 2 produced, thanks to the excellent detail.
Image 1 of 3
(Image credit: Tom's Guide)(Image credit: Tom's Guide)(Image credit: Tom's Guide)Our Thinker test print came out looking very nice, with smooth, natural curves on his shoulders and good detail on the face. There was some noticeable layering, though in both the draft and normal modes.
Image 1 of 3
(Image credit: Tom's Guide)(Image credit: Tom's Guide)(Image credit: Tom's Guide)Our gears test model also came out well: All we had to do to fit the gears together was to remove them from the raft that they were printed on. We didn’t need to do any other trimming, cutting, or tweaking to produce a set of gears that turned smoothly and evenly.
Image 1 of 2
(Image credit: Tom's Guide)(Image credit: Tom's Guide)The geometric sculpture is a difficult print, which is why we use it in our 3D printer testing. It involves printing a lot of sharp edges at angles, which taxes the ability of the printer to precisely control the flow of the molten filament. The Delta Mini V2 handled it without issues, producing a print that had sharp, well-defined edges and points. Once we had trimmed off the support material that held the print in place during the printing process, we were left with a very well printed, spiky sculpture.
Monoprice Delta Mini V2 3D printer review: Verdict
The Monoprice Delta Mini V2 is a simple printer that does an excellent job.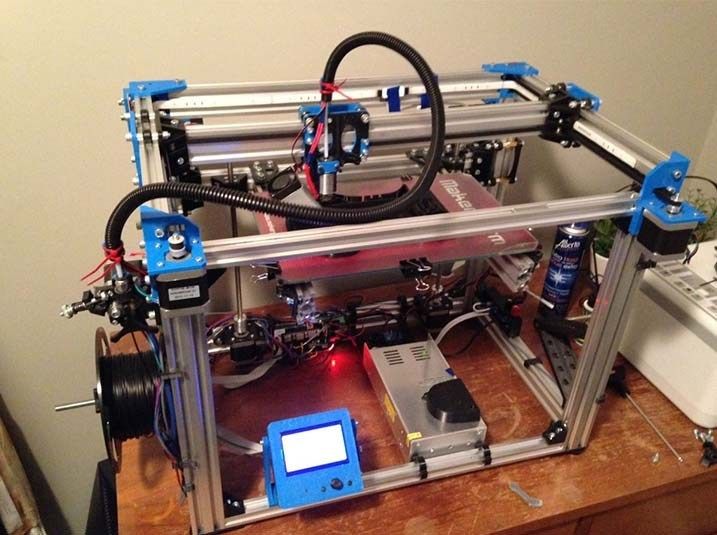 It prints quickly in high quality and can handle a wide range of different materials. The only limitation is the size of the print bed: with a diameter of 4.3 inches, it can’t print anything wider than that or more than 4.7 inches high. That is plenty big for most users, though, and at the price, you can’t beat the value the Delta Mini V2 offers.
It prints quickly in high quality and can handle a wide range of different materials. The only limitation is the size of the print bed: with a diameter of 4.3 inches, it can’t print anything wider than that or more than 4.7 inches high. That is plenty big for most users, though, and at the price, you can’t beat the value the Delta Mini V2 offers.
The mobile software issues still prove to be frustrating, but it’s hard to find a better printer at this low of a price. The da Vinci Nano from XYZprinting hovers around $200, but it can be hard to find these days. For that reason, beginners would be wise to give 3D printing a try on a low-cost option like the Monoprice Delta Mini V2.
Monoprice Mini Delta V2 3D Printer: Price Comparison
No price information
Check Amazon
powered by
Richard Baguley has been working as a technology writer and journalist since 1993. As well as contributing to Tom's Guide, he writes for Cnet, T3, Wired and many other publications.
As well as contributing to Tom's Guide, he writes for Cnet, T3, Wired and many other publications.
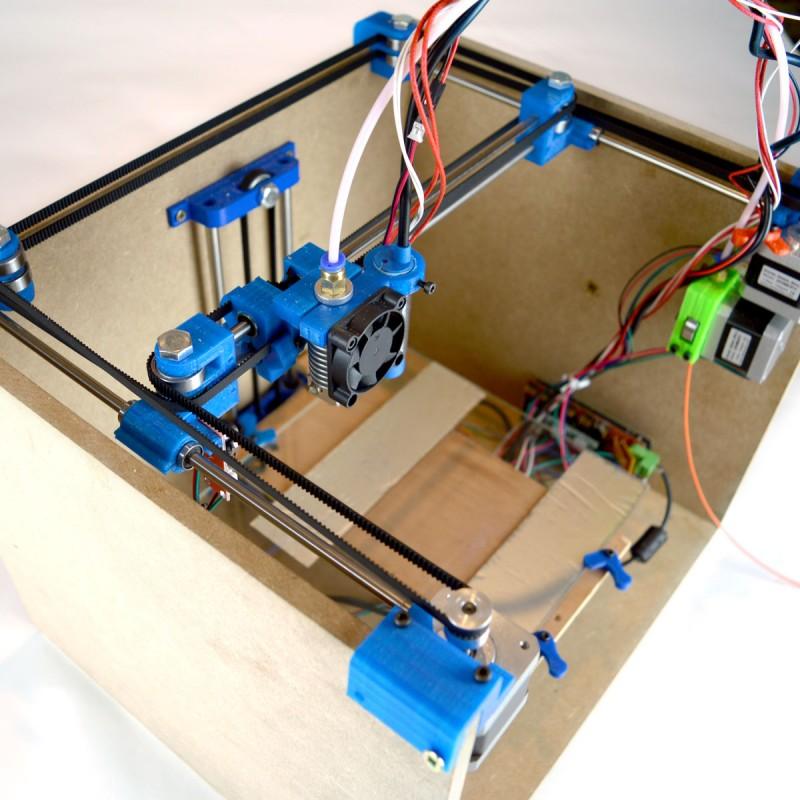
Building a home 3D printer with your own hands: recommendations from personal experience
3D printing and assembly of 3D printers is my hobby and passion. Here I will not share detailed diagrams and drawings, there are more than enough of them on specialized resources. The main goal of this material is to tell you where to start, where to dig and how to avoid mistakes in the process of assembling a home 3D printer. Perhaps one of the readers will be inspired by applied engineering achievements.
Why do you need a 3D printer? Use cases
I first came across the idea of 3D printing back in the 90s when I was watching the Star Trek series. I remember how impressed I was by the moment when the heroes of the cult series printed the things they needed during their journey right on board their starship. They printed anything: from shoes to tools. I thought it would be great someday to have such a thing too. Then it all seemed something incredible. Outside the window are the gloomy 90s, and the Nokia with a monochrome screen was the pinnacle of progress, accessible only to a select few. nine0003
Then it all seemed something incredible. Outside the window are the gloomy 90s, and the Nokia with a monochrome screen was the pinnacle of progress, accessible only to a select few. nine0003
Years passed, everything changed. Around 2010, the first working models of 3D printers began to appear on sale. Yesterday's fantasy has become a reality. However, the cost of such solutions, to put it mildly, discouraged. But the IT industry would not be itself without an inquisitive community, where there is an active exchange of knowledge and experience and who just let them delve into the brains and giblets of new hardware and software. So, drawings and diagrams of printers began to surface more and more often on the Web. Today, the most informative and voluminous resource on the topic of assembling 3D printers is RepRap - this is a huge knowledge base that contains detailed guides for creating a wide variety of models of these machines. nine0003
I assembled the first printer about five years ago. My personal motivation to build my own device is quite prosaic and based on several factors. Firstly, there was an opportunity to try to realize the old dream of having your own device, inspired by a fantasy series. The second factor is that sometimes it was necessary to repair some household items (for example, a baby stroller, car elements, household appliances and other small things), but the necessary parts could not be found. Well, the third aspect of the application is "near-working". On the printer, I make cases for various IoT devices that I assemble at home. nine0003
My personal motivation to build my own device is quite prosaic and based on several factors. Firstly, there was an opportunity to try to realize the old dream of having your own device, inspired by a fantasy series. The second factor is that sometimes it was necessary to repair some household items (for example, a baby stroller, car elements, household appliances and other small things), but the necessary parts could not be found. Well, the third aspect of the application is "near-working". On the printer, I make cases for various IoT devices that I assemble at home. nine0003
Agree, it is better to place your device based on Raspberry Pi or Arduino in an aesthetically pleasing "body", which is not a shame to put in an apartment or take to the office, than to organize components, for example, in a plastic bowl for food. And yes, you can print parts to build other printers :)
There are a lot of scenarios for using 3D printers. I think everyone can find something of their own.
A complex part in terms of drawing that I printed on my printer. Yes, it's just a figurine, but it has many small elements
Ready solution vs custom assembly
When a technology has been tested, its value in the market decreases markedly. The same thing happened in the world of 3D printers. If earlier a ready-made solution cost simply sky-high money, then today acquiring such a machine is more humane for the wallet, but nevertheless not the most affordable for an enthusiast. There are a number of solutions already assembled and ready for home use on the market, their price range ranges from $500-700 (not the best options) to infinity (adequate solutions start from a price tag of about $1000). Yes, there are options for $150, but we, for understandable, I hope, reasons, will not dwell on them. nine0003
In short, there are three cases to consider a finished assembly:
- when you plan to print not much and rarely;
- when print accuracy is critical;
- you need to print molds for mass production of parts.

There are several obvious advantages to self-assembly. The first and most important is cost. Buying all the necessary components will cost you a maximum of a couple of hundred dollars. In return, you will receive a complete 3D printing solution with the quality of manufactured products acceptable for domestic needs. The second advantage is that by assembling the printer yourself, you will understand the principles of its design and operation. Believe me, this knowledge will be useful to you during the operation of even an expensive ready-made solution - any 3D printer needs to be serviced regularly, and it can be difficult to do this without understanding the basics. nine0003
The main disadvantage of assembly is the need for a large amount of time. I spent about 150 hours on my first build.
What you need to assemble the printer yourself
The most important thing here is the presence of desire. As for any special skills, then, by and large, in order to assemble your first printer, the ability to solder or write code is not critical. Of course, understanding the basics of radio electronics and basic skills in the field of mechanics (that is, "straight hands") will greatly simplify the task and reduce the amount of time that needs to be spent on assembly. nine0003
Of course, understanding the basics of radio electronics and basic skills in the field of mechanics (that is, "straight hands") will greatly simplify the task and reduce the amount of time that needs to be spent on assembly. nine0003
Also, to start we need a mandatory set of parts:
- Extruder is the element that is directly responsible for printing, the print head. There are many options on the market, but for a budget build, I recommend the MK8. Of the minuses: it will not be possible to print with plastics that require high temperatures, there is noticeable overheating during intensive work, which can damage the element. If the budget allows, then you can look at MK10 - all the minuses are taken into account there. nine0032
- Processor board. The familiar Arduino Mega is well suited. I didn't notice any downsides to this solution, but you can spend a couple of dollars more and get something more powerful, with a reserve for the future.

- Control board. I'm using RAMPS 1.4 which works great with the Arduino Mega. A more expensive but more reliable board is Shield, which already combines a processor board and a control board. In modern realities, I recommend paying attention to it. In addition to it, you need to purchase at least 5 microstep stepper motor controllers, for example - A4988. And it's better to have a couple of these in stock for replacement.
- Heated table. This is the part where the printed element will be located. Heating is necessary due to the fact that most plastics will not adhere to a cold surface. For example, for printing with PLA plastic, the required surface temperature of the table is 60-80°C, for ABS - 110-130°C, and for polycarbonate it will be even higher
There are also two options for choosing a table - cheaper and more expensive. Cheaper options are essentially printed circuit boards with preheated wiring. To operate on this type of table, you will need to put borosilicate glass, which will scratch and crack during operation. Therefore, the best solution is an aluminum table. nine0032
Therefore, the best solution is an aluminum table. nine0032 - Stepper motors. Most models, including the i2 and i3, use NEMA 17 size motors, two for the Z axis and one each for the X and Y axes. Finished extruders usually come with their own stepper motor. It is better to take powerful motors with a current in the motor winding of 1A or more, so that there is enough power to lift the extruder and print without skipping steps at high speed.
- Basic set of plastic fasteners.
- Belt and gears to drive it. nine0051
Examples of elements appearance: 1) MK8 extruder; 2) Arduino processor board; 3) RAMPS control board; 4) motor controllers; 5) aluminum heated table; 6) NEMA 17 stepper motor; 7) a set of plastic fasteners; 8) drive gears; 9) drive belt
This is a list of items to be purchased. Hardcore users can assemble some of them themselves, but for beginners, I strongly recommend purchasing ready-made solutions. nine0003
nine0003
Yes, you will also need various small things (studs, bearings, nuts, bolts, washers ...) to assemble the case. In practice, it turned out that using a standard m8 stud leads to low printing accuracy on the Z axis. I would recommend immediately replacing it with a trapezoid of the same size.
M8 trapezoid stud for Z axis, which will save you a lot of time and nerves. Available for order on all major online platforms
nine0002 You also need to purchase customized plastic parts for the X axis, such as these from the MendelMax retrofit kit.Most parts available at your local hardware store. On RepRap you can find a complete list of necessary little things with all sizes and patterns. The kit you need will depend on the choice of platform (we'll talk about platforms later).
What's the price
Before delving into some aspects of the assembly, let's figure out how much such entertainment will cost for your wallet. Below is a list of parts required for purchase with an average price. nine0003
Below is a list of parts required for purchase with an average price. nine0003
Platform selection
The community has already developed a number of different platforms for assembling printers - the most optimal case designs and the location of the main elements, so you do not have to reinvent the wheel.
i2 and i3 are key platforms for self-assembly printer enclosures. There are also many modifications of them with various improvements, but for beginners, these two classic platforms should be considered, since they do not require special skills and fine-tuning. nine0003
Actually, illustration of platforms: 1) i2 platform; 2) i3 platform
On the plus side of i2: it has a more reliable and stable design, although it is a little more difficult to assemble; more opportunities for further customization.
The i3 variant requires more special plastic parts to be purchased separately and has a slow print speed. However, it is easier to assemble and maintain, and has a more aesthetically pleasing appearance. You will have to pay for simplicity with the quality of printed parts - the body has less stability than i2, which can affect print accuracy. nine0003
You will have to pay for simplicity with the quality of printed parts - the body has less stability than i2, which can affect print accuracy. nine0003
Personally, I started my experiments in assembling printers from the i2 platform. She will be discussed further.
Assembly steps, challenges and improvements
In this block, I will only touch on the key assembly steps using the i2 platform as an example. Full step by step instructions can be found here.
The general scheme of all the main components looks something like this. There is nothing particularly complicated here:
I also recommend adding a display to your design. Yes, you can easily do without this element when performing operations on a PC, but it will be much more convenient to work with the printer this way. nine0003
Understanding how all components will be connected, let's move on to the mechanical part, where we have two main elements - a frame and a coordinate machine.
Assembling the frame
Detailed frame assembly instructions are available on RepRap. Of the important nuances - you will need a set of plastic parts (I already talked about this above, but I'd better repeat it), which you can either purchase separately or ask your comrades who already have a 3D printer to print.
The frame of the i2 is quite stable thanks to its trapezoid shape.
This is how the frame looks like with parts already partially installed. For greater rigidity, I reinforced the structure with plywood sheets
Coordinate machine
An extruder is attached to this part. The stepper motors shown in the diagram above are responsible for its movement. After installation, calibration is required along all major axes.
Important - you will need to purchase (or make your own) a carriage for moving the extruder and a mount for the drive belt. Drive belt I recommend GT2. nine0003
The carriage printed by the printer from the previous picture after it has been assembled.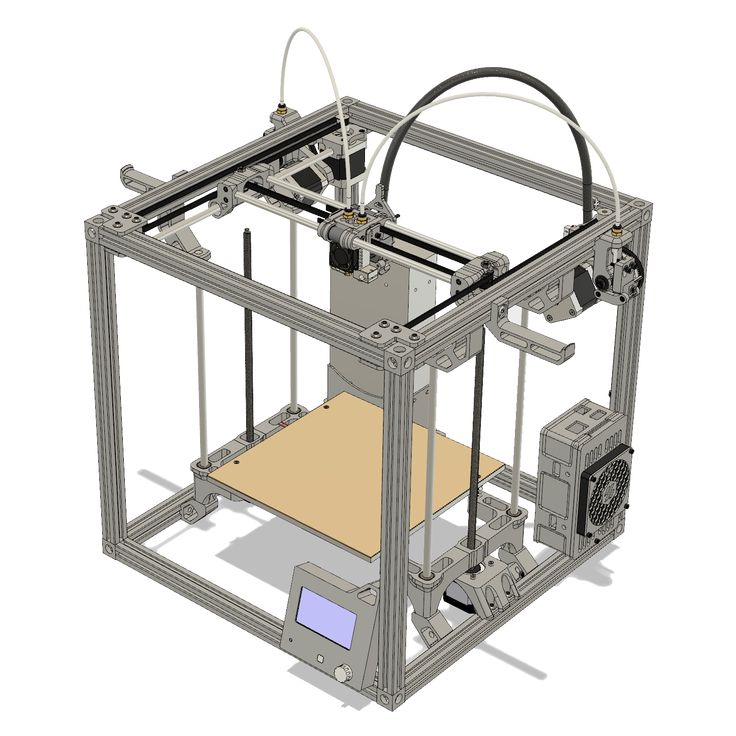 The part already has LM8UU bearings for guides and belt mount (top)
The part already has LM8UU bearings for guides and belt mount (top)
Calibration and adjustment
So, we completed the assembly process (as I said, it took me 150 hours) - the frame was assembled, the machine was installed. Now another important step is the calibration of this very machine and extruder. Here, too, there are small subtleties.
Setting up the machine
I recommend calibrating the machine with an electronic caliper. Do not be stingy with its purchase - you will save a lot of time and nerves in the process.
The screenshot below shows the correct constants for the Marlin firmware, which must be selected in order to set the correct number of steps per unit of measure. We calculate the coefficient, multiply it, substitute it into the firmware, and then upload it to the board.
Marlin 9 firmware constants0022
For high-quality calibration, I recommend relying on larger numbers in measurements - take not 1-1. 5 cm, but about 10. So the error will be more noticeable, and it will become easier to correct it.
5 cm, but about 10. So the error will be more noticeable, and it will become easier to correct it.
Calibrating the extruder
When the frame is assembled, the machine is calibrated, we start setting up the extruder. Here, too, everything is not so simple. The main task of this operation is to correctly adjust the supply of plastic.
If underfeeding, the printed test item will have noticeable gaps, like test die 1. Conversely, the result will look bloated if plastic is overfed (dice 2)
Getting Started Printing
It remains for us to run some CAD or download ready-made .stl, which describe the structure of the printed material. Further, this structure needs to be converted into a set of commands understandable to our printer. For this I use the Slicer program. It also needs to be set up correctly - specify the temperature, the size of the extruder nozzle. After that, the data can be sent to the printer.
Slicer interface
As a raw material for printing, I recommend starting with regular ABS plastic - it is quite strong, products made from it are durable, and it does not require high temperatures to work with.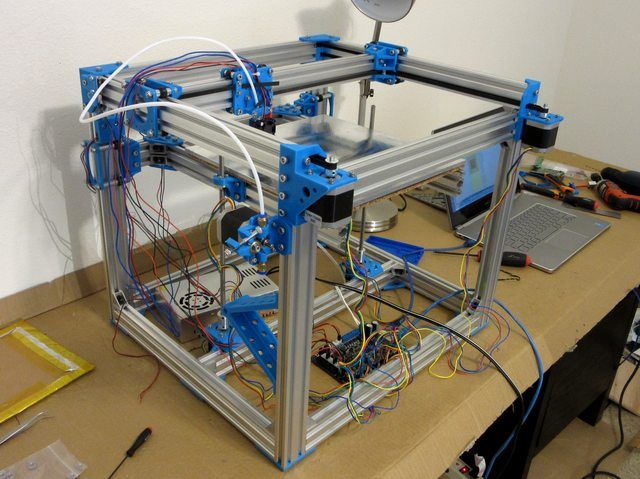 For comfortable printing with ABS plastic, the table must be heated to a temperature of 110-130 ° C, and the extruder nozzle - within 230-260 ° C.
For comfortable printing with ABS plastic, the table must be heated to a temperature of 110-130 ° C, and the extruder nozzle - within 230-260 ° C.
Some important details. Before printing, calibrate the machine along the Z axis. The extruder nozzle should be approximately half a millimeter from the table and ride along it without distortion. For this calibration, a regular sheet of A4 paper inserted between the nozzle and the surface of the heated table is best suited. If the sheet can be moved with little effort, the calibration is correct. nine0003
Another thing to keep in mind is the surface treatment of the heated table. Usually, before printing, the surface of the table is covered with something that hot plastic sticks to well. For ABS plastic, this can be, for example, Kapton tape. The disadvantage of adhesive tape is the need to re-glue it after several printing cycles. In addition, you will have to literally tear off the adhering part from it. All this, believe me, takes a lot of time. Therefore, if it is possible to avoid this fuss, it is better to avoid it. nine0003
Therefore, if it is possible to avoid this fuss, it is better to avoid it. nine0003
An alternative option that I use instead of scotch tape is to apply several layers of ordinary light beer, followed by heating the table to 80-100 ° C until the surface is completely dry and re-applying 7-12 layers. It is necessary to apply the liquid with a cloth moistened with a drink. Among the advantages of this solution: ABS plastic separates from the table on its own when it cools down to about 50 ° C and is removed without effort, the table does not have to be peeled off, and one bottle of beer will last you for several months (if you use the drink only for technical purposes :)). nine0003
After we have collected and configured everything, we can start printing. If you have an LCD screen, then the file can be transferred for printing using a regular SD card.
The first results may have bumps and other artifacts - do not worry, this is a normal process of "grinding" the printer elements, which will end after a few print cycles.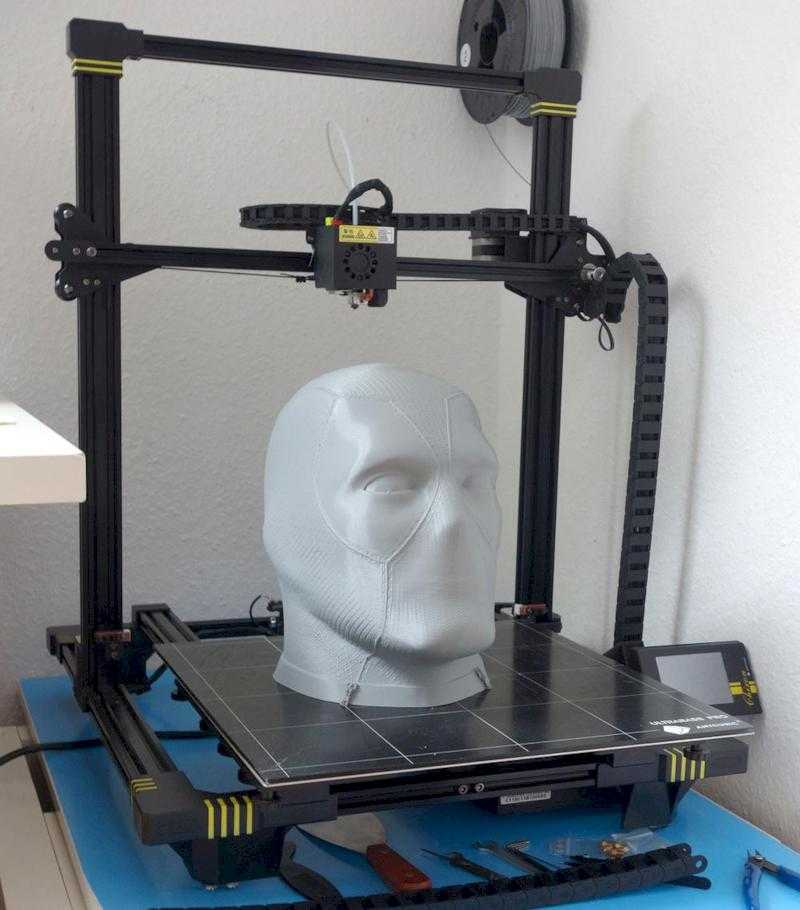
Tips to make life easier (and sometimes save money)
In addition to the small recommendations given in the text above, in this section I will also give a short list of tips that will greatly simplify the operation of a 3D printer and the life of its owner. nine0003
- Do not experiment with nozzles. If you plan to immediately print from materials that require high temperatures, then it is better to immediately take the MK10 extruder. On MK8, you can "hang" special nozzles that support high-temperature conditions. But such modifications often cause difficulties and require special experience. It is better to avoid this fuss on the shore by simply installing the right extruder for you.
- Add starter relay for heated table. nine0051 Improving the power supply system for this important printing part with a starter relay will help solve the known problem of RAMP 1.4 - overheating of the transistors that control the power of the table, which can lead to failure of the board.
 I made this upgrade after having to throw away a few RAMPS 1.4s.
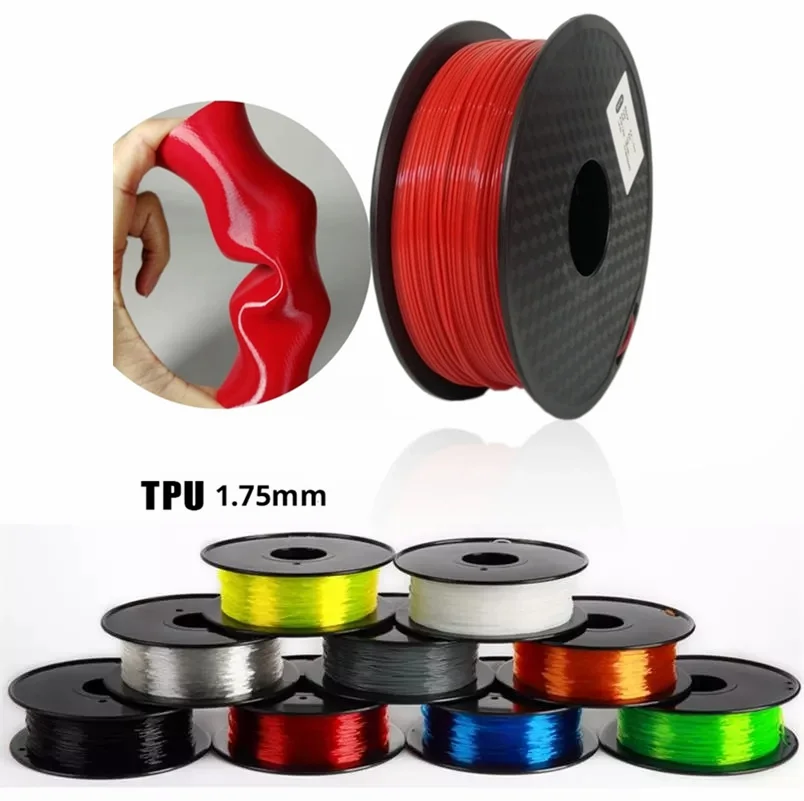
I made this upgrade after having to throw away a few RAMPS 1.4s. - Select the correct filament diameter for printing. I recommend using 1.75mm plastic for MK8 and MK10. If we take plastic, for example, 3 mm, then the extruder simply does not have enough strength to push it at an acceptable speed - everything will be printed much longer, and the quality will drop. ABS plastic is ideal for MK8, MK10 will be able to produce products from polycarbonate. nine0032
- Use only new and precise X and Y guides. Print quality will be affected. It is difficult to count on good quality with bent or deformed guides along the axes.
- Take care of cooling. During my experiments with various extruders, the MK10 showed the best results - it prints quite accurately and quickly. The MK10 can also print plastics that require a higher print temperature than ABS, such as polycarbonate. Although it is not as prone to overheating as its younger brother MK8, I still recommend taking care of its cooling by adding a cooler to your design.
 It must be permanently enabled, this option can be configured in Slicer. You can also add coolers to keep the stepper motors at an acceptable temperature, however, make sure that their air flows do not fall on the printed part, as this can lead to its deformation due to too rapid cooling. nine0032
It must be permanently enabled, this option can be configured in Slicer. You can also add coolers to keep the stepper motors at an acceptable temperature, however, make sure that their air flows do not fall on the printed part, as this can lead to its deformation due to too rapid cooling. nine0032 - Consider heat retention. Yes, on the one hand, we are struggling with overheating of the elements. On the other hand, a uniform temperature around the printer will contribute to high-quality printing (the plastic will be more pliable). To achieve a uniform temperature, you can put our printer, for example, in a cardboard box. The main thing is to connect and configure the coolers before that, as described above.
- Consider insulating your desk. Heated table heats up to high temperatures. And if part of this heat leaves properly, heating the printed part, then the second part (from below) just goes down. To concentrate the heat from the table onto the part, you can perform an operation to insulate it.
 To do this, I simply attach a cork mouse pad to its bottom using stationery clips. nine0032
To do this, I simply attach a cork mouse pad to its bottom using stationery clips. nine0032
Pins
I am sure that during the assembly process you will encounter a number of difficulties specific to your project. Neither this text nor even the most detailed guides will insure against this.
As I wrote in the introductory part, the above does not claim the status of a detailed assembly manual. It is almost impossible to describe all the stages and their subtleties within the framework of one such text. First of all, this is an overview material that will help you prepare for the assembly process (both mentally and financially), understand whether you personally need to bother with self-assembly - or give up on everything and buy a ready-made solution. nine0003
For me, assembling printers has become an exciting hobby that helps me solve some issues in home and work affairs, take my mind off programming and do something interesting with my own hands. For my children - entertainment and the opportunity to get unusual and unique toys. By the way, if you have children whose age allows them to mess around with such things, such an activity can be a good help for entering the world of mechanics and technology.
By the way, if you have children whose age allows them to mess around with such things, such an activity can be a good help for entering the world of mechanics and technology.
For everyone, the vectors of using 3D printers will be very different and very individual. But, if you decide to devote your personal time to such a hobby, believe me, you will definitely find something to print :)
I will be glad to answer comments, remarks and questions.
What to read/see
- what can be printed;
- 3D printer forum;
- RepRap community site with model descriptions and assembly instructions;
- printer that prints electronics.
Subscribe to the Telegram channel "DOU #tech" so you don't miss new technical articles.
Topics: DIY, embedded, tech
12 common 3D printing mistakes from simple to complex. How to avoid them? nine0001
1. Underestimation of the importance of the first layer. 2. Don't ask the 3D printing communities for help. 3. Random entanglement of the filament. 4. Fast assembly of your 3D printer. 5. Incorrect table and nozzle height calibration. 6. Using the wrong slicer settings. 7. Using a high % infill to reinforce details instead of walls/shells. 8. Don't use support when needed. 9. Never replace worn parts. 10. Lack of 3D printing monitoring. 11. Neglect of safety rules in 3D printing. 12. Buying a bad 3D printer out of over-enthusiasm. Output. nine0003
Don't ask the 3D printing communities for help. 3. Random entanglement of the filament. 4. Fast assembly of your 3D printer. 5. Incorrect table and nozzle height calibration. 6. Using the wrong slicer settings. 7. Using a high % infill to reinforce details instead of walls/shells. 8. Don't use support when needed. 9. Never replace worn parts. 10. Lack of 3D printing monitoring. 11. Neglect of safety rules in 3D printing. 12. Buying a bad 3D printer out of over-enthusiasm. Output. nine0003
There is nothing worse than 3D printing for days, weeks, months and years only to find out that you are making common mistakes.
We're sure many of you are familiar with that feeling, which is why we've written this post to get you back on the road to success by outlining some common mistakes to avoid on your 3D printing journey.
Here you will find both small errors that you did not pay attention to before, as well as serious errors that can lead to a complete cessation of 3D printing. nine0003
nine0003
Join our research to identify the most common 3D printing mistakes, as well as simple solutions to fix them quickly.
1. Underestimation of the importance of the first layer.
Too often 3D printing fails in the middle of the process due to poor adhesion of the first layer.
Definitely keep this important factor in mind if you want a successful print.
This is a mistake that is made too often, and it causes people to chase ghosts, trying to figure out what the problem is. nine0003
All this time, the reason was the bad first layers, which did not have a strong enough connection with the working platform.
Although your first layer is held at the start of printing, adhesion decreases as the print head moves. It is likely that your print may shift or fall off after a few hours if the first layer was not well extruded.
Solution .
- Make a few test prints ahead of time and see how well the material adheres.
 nine0032
nine0032 - Use an adhesive such as 3D Printer Varnish or at least a glue stick.
- Increase the flow rate (extrusion multiplier) for the first layer so the material has a better chance of sticking to the printer bed.
2. Do not seek help from the 3D printing communities.
Every user of a 3D printer has encountered a problem that required some effort to fix. Some people took on entire projects just to solve a 3D printer problem, when the solution was easy to find. nine0003
3D printing communities are known for helping people solve their problems, so be sure to check out these free resources. From 3D printing forums to Facebook groups and YouTube surveys of other 3D printer users, the options are endless.
When we first started exploring 3D printing, we noticed that many people mention how helpful other 3D printer users are, so we immediately registered on all kinds of Russian and English resources, Facebook and Reddit communities and joined this space .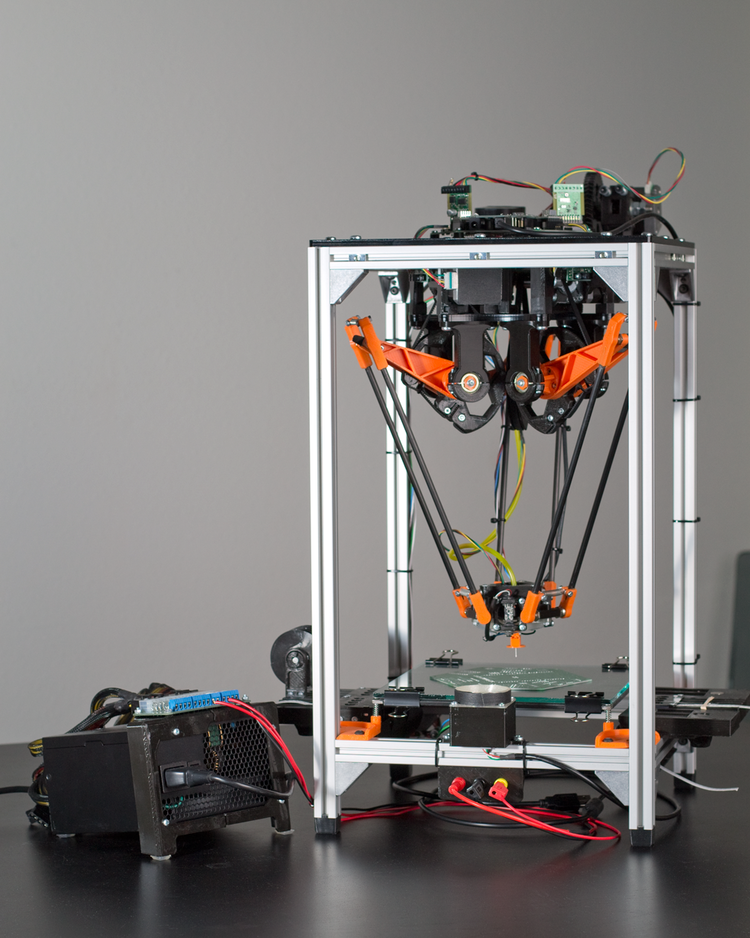 nine0003
nine0003
In most cases, people will offer the right solution and will be happy to help you try various troubleshooting options.
Not only can they help you with troubleshooting, but they can point you to some fun projects to try, as well as some of the latest innovations in the world of 3D printing.
Solution .
- Join active Facebook groups on 3D printing and your specific 3D printer. nine0032
- Subscribe to news feeds of authoritative 3D printing resources.
- Be sure to check out YouTube 3D printing bloggers who post new and interesting content on a regular basis.
- Find groups in Viber and Telegram. This is the fastest way to get an answer to your question.
3. Random entanglement of the filament.
We read a lot of reviews about 3D printer materials including PLA, ABS, PETG, etc. and some of the negative reviews mention tangled filament. nine0003
Unfortunately, in most cases, the thread becomes tangled due to the fault of users.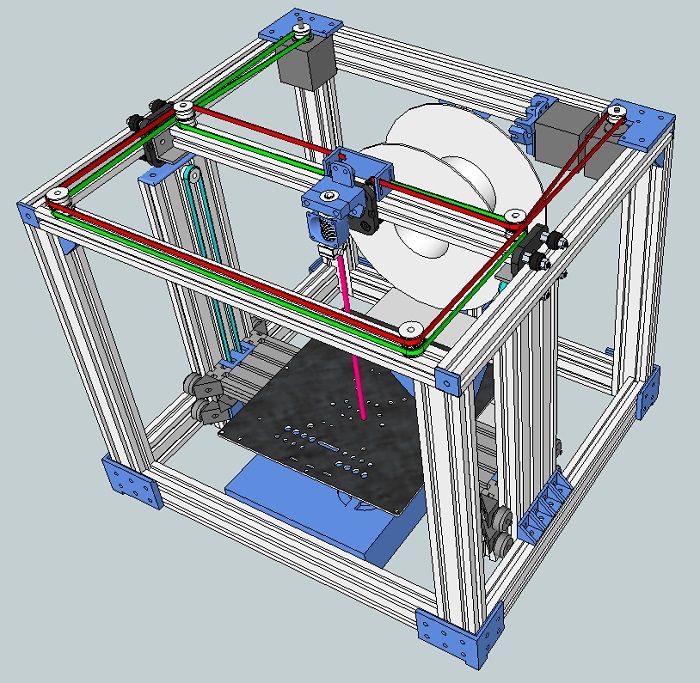
As a general rule, when the thread is wound onto the spool, there is very little chance of tangling, much more often after you take the spool out of the package.
If you loosen the windings in the winding and then wind the deflated windings back on the spool, you could accidentally wind them unevenly and create an overlap that will ruin your prints.
Solution .
When storing the filament, make sure that the end is securely fastened and cannot be easily loosened.
If there are already tangles on the spool, unwind enough thread and wind it tightly again so that it does not cross over.
If you are still unlucky, and you have purchased plastic of inadequate quality, during the production of which all technological cards were violated, then here is our advice: buy plastic for a 3D printer from trusted brands. The $100 price difference is infinitesimal compared to all sorts of other 3D printing costs. nine0003
However, this 100 UAH will save you not only from problems with overlaps, but also provide a stable diameter and color along the entire length, the absence of ovalities and smooth feeding.
4. Quickly assemble your 3D printer.
We were all very excited when we got our first 3D printer and it came to building it, but being overly excited can cause your 3D printer to build too quickly, resulting in poor print results.
This may not be immediately noticeable and you will get good quality prints within a few months. nine0003
What can happen gradually is wear due to incorrect assembly.
Ask yourself these questions before starting your first print.
Was your belt tight? Did you properly and securely fasten each wire? Is the Bowden tube installed correctly?
When it comes to a 3D printer, every little detail counts, so don't fall prey to 3D printing problems because of a quick and careless build.
Solution .
Find an authoritative YouTube video tutorial from an experienced 3D printer operator and follow assembly. nine0064 There are always a few little tricks they advise you to do for durability and high quality prints.
Even if you've already built your 3D printer, there are a few things you can fix that you may have missed.
The correct and high-quality assembly of a 3D printer actually leads to higher quality prints.
See also: How to set up your new 3D printer.
5. Incorrect table and nozzle height calibration.
Of all the layers in your 3D print, the first layer is the most important and it depends a lot on how well you leveled your platform and set your nozzle height. nine0003
It's not as easy as uploading a 3D model, sending it to an SD card and starting printing.
The software side of things is important, but the hardware side is just as important.
Many 3D printers come with manual platform calibration, so you have to raise or lower each corner yourself.
Your 3D printer doesn't have a perfect feedback system, which means it can't always check where the print head is.
The best he can do is use the X, Y and Z limit switches to make sure the printhead is 0. 00mm in each axis. nine0003
00mm in each axis. nine0003
What your 3D printer is very good at is extremely precise movements in the X, Y and Z axes, but if the nozzle height is not set properly at the beginning, everything falls apart.
The Z axis is height, so the nozzle must be properly adjusted so that it smoothly extrudes the filament along the surface of the build, neither too high nor too low.
Solution .
- Learn how to manually calibrate the table.
- Once your table is properly calibrated and the nozzle height adjusted, you can expect good prints. nine0032
- It might be a good idea for you to invest in an auto leveling system like BLTouch. We at our 3D printing studio in Odessa prefer manual calibration.
6. Using incorrect slicer settings.
The slicer settings you use for printing are some of the most important things when it comes to successful 3D printing.
Of the hundreds of setting changes you can make, one wrong setting is enough to ruin your print. nine0003
nine0003
Fortunately, there are printer profiles and default settings that give people a basic starting point for printing.
After a few prints, you will start experimenting with different settings such as temperature, line width, flow rate, and so on.
Some of the misapplied misconfigurations are related to changing materials.
Whether PLA or ABS or PLA of different brands and/or colors, temperature recommendations will vary. nine0003
Make sure you set them correctly.
Slicer settings can either help you or break your 3D printing, so use them wisely, preferably with some kind of guide.
In most cases, when you load a model from Thingiverse, for example, designers create a list of settings that generally work well, but don't blindly follow them and be careful.
For example, if you replaced a brass nozzle with a hardened steel nozzle, you would need to slightly increase the nozzle temperature because hardened steel does not conduct heat as well as brass.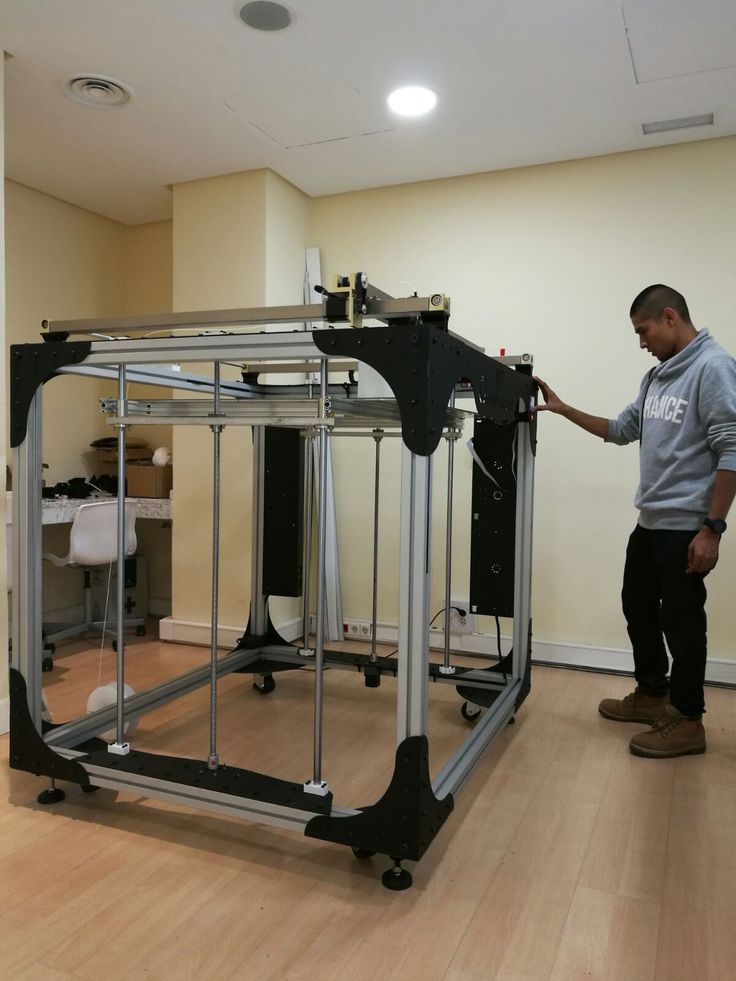 nine0003
nine0003
Another example is your work surface.
If you have added a glass substrate to your 3D printer, you should increase the table temperature to allow for the extra layer of heat transfer material.
Solution .
- Use calibration models such as speed and temperature towers for each new material.
- Spend a little more time looking at the slicer options to make sure you know what changing a setting will do. nine0032
- Repetition is the mother of learning. The more often you type, the faster you will become a pro.
Read also: The best models for 3D printing testing.
7. Using high % infill to reinforce details instead of walls/shells.
For years, most people have tried to reinforce their 3D printed parts with infill. This method definitely does the job, but there is a much more efficient method that has been proven to work much better. nine0003
Instead of wasting a lot of material and extra time printing the infill, you should use shells/walls to make the 3D printed part stronger.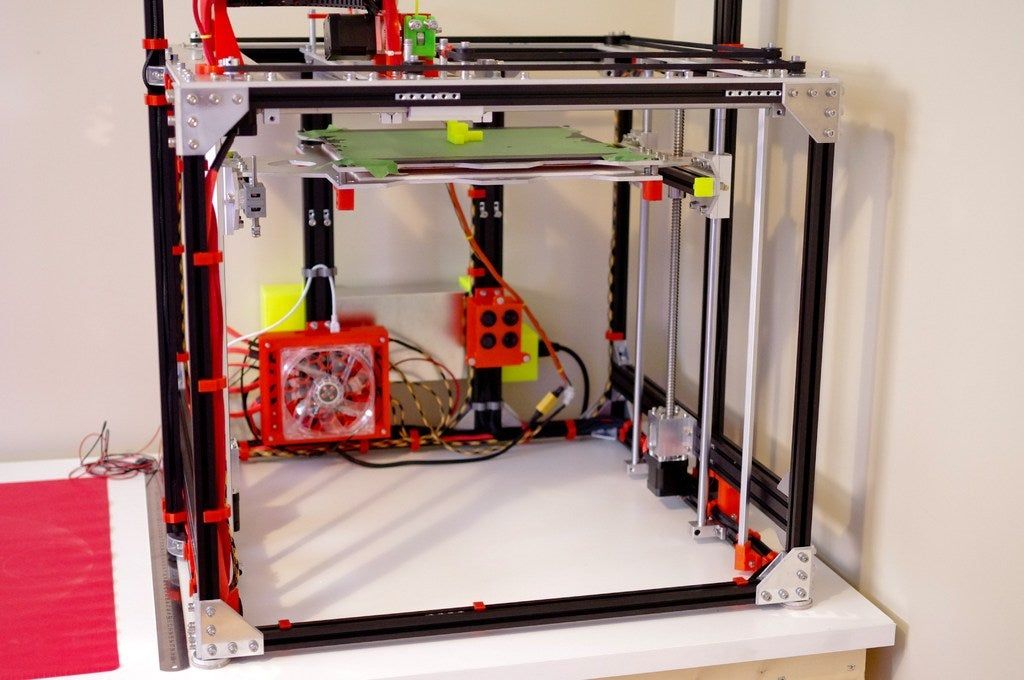
In some cases, increasing the percentage of filling does not provide the necessary margin of safety, while increasing the wall thickness makes it possible to produce truly reliable and impact-resistant products.
Solution.
- Instead of adding more infill, add more shells/walls to your prints to make them stronger. nine0032
- For a functional 3D printed part requiring strength, it is recommended to use about 4-6 walls.
8. Do not use supports when necessary.
Most people try to avoid the use of auxiliary supports to save time and material, but there are times when their use is necessary.
You can try tilting the prints in a certain way and moving them around the print bed, but sooner or later there will come a point when this approach doesn't work. nine0003
Many models are specially designed not to use support for successful printing, which is very convenient.
On the other hand, some designs are too complex to print without support.
3D printers cannot print in the air and large ridges definitely need support structures to extrude the material onto.
Most often you can do without supports on 45° or lower overhangs, but for anything higher it is recommended to use supports. nine0003
This is more of a visual skill that, with time and experience, allows you to understand when models need supports and when you can do without them.
Some slicers may not show support in preview, so you'll have to judge for yourself.
Solution.
- Make sure you don't avoid supports when they are needed, because in this case you will just lose overall. nine0032
- Use proper part orientation to ensure that your prints use as little support material as possible.
9. Never replace worn parts.
Although the profile, power supply and stepper motors of your 3D printer are designed to last for several years, other parts are consumables.
These are parts such as belts, nozzles and bearings. Make sure you replace these parts as they wear out.
Make sure you replace these parts as they wear out.
You may notice a decrease in print quality over time, and wear and tear on certain parts can definitely be the cause, so check these consumables and replace them as needed. nine0003
If you are printing with materials such as ABS, PA12, PC or glow-in-the-dark plastics, the brass nozzles wear out much faster than when printing with traditional materials.
Switching to a hardened steel nozzle is a good idea if you want to print with abrasive materials.
The disadvantage is that it does not have the same level of thermal conductivity as brass nozzles.
Here is a short list of 3D printer parts that wear out over time:
- Thermal barrier;
- PTFE tube;
- Fans;
- Wires/connectors;
- Thermistors;
- Belts;
- Glass platforms;
- Bearings;
- Heating block;
- Motherboard.
You can buy accessories for 3D printers in the corresponding section of our catalog.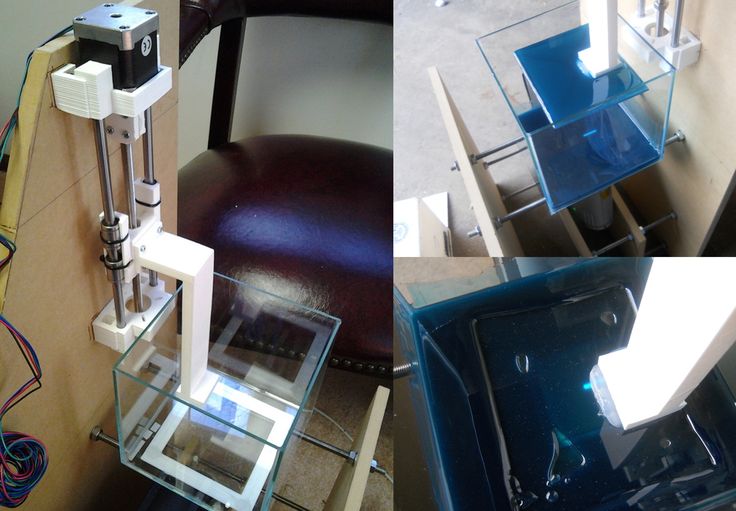
Solution.
- Be aware that some parts will not last forever, so check these parts from time to time and replace them as needed. nine0032
- Make sure these components are installed in a way that reduces wear.
- Keep a set of replacement parts on hand in case they fail (nozzles, belts, wiring, PTFE tubing).
- Purchase high quality parts designed for long life.
10. No 3D printing monitoring.
Whether you have a premium or budget 3D printer, any of them can fail. They can fail within the first few minutes when the first layer is not printing well, or a few hours after printing starts. nine0003
In our practice, there have been a few cases when checking our printers after a night shift, we found a mess on the work surface and the printer continued to extrude spaghetti plastic.
Monitoring is not a panacea for all problems, but with its help you can stop the process in time and avoid waste of plastic and electricity.
It is recommended to constantly monitor your 3D printers throughout the printing process to make sure everything is in order. nine0003
What we make sure to do is monitor the first coat and then come back 15 minutes later to make sure everything is going according to plan.
After that, checking the printers every hour or so is a good idea to control your prints.
Solution.
- Check the 3D print from time to time to make sure everything goes smoothly.
- Use the camera for remote fingerprint verification in conjunction with remote power control. nine0032
- Be sure to teach others how to stop your 3D printer if necessary.
11. Neglect of safety regulations in 3D printing.
Basic precautions are based on burn and fire hazards, mechanical hazards, and injury from tools or melted plastic.
The risk of fire is very rare these days because 3D printers are usually equipped with overheating protection.
Pay attention to burns from hot nozzle or print bed. nine0003
We've also heard stories of injuries from the sharp edges of the printer's scraper.
This can be easily avoided if you are careful in your actions.
Removing supports is not the most pleasant and interesting thing to do, but getting cuts or scratches when cleaning parts is even worse.
It is recommended to check the wiring, bolts, belts and all moving parts from time to time so that a potential malfunction can be detected in the future. nine0003
Connectors can sometimes fail, so be sure to check these aspects to ensure the 3D printing process runs smoothly and safely.
Solution.
- Be aware of your surroundings and be safe.
- Do not put your hand too close to the nozzle.
- Do not keep your hand on the platen when taking the print.
- Provide good ventilation.
12. Buying a bad 3D printer out of over-enthusiasm.
 nine0005
nine0005 We are regularly contacted by clients who, on a wave of enthusiasm, bought a cheap 3D printer on Aliexpress or other market place, and this printer does not work.
Spontaneous cheap purchases do not give you time to analyze and compare 3D printer models. In other words, you are making your choice unconsciously.
People have experienced a number of problems, such as the SD card slot not working along with serious difficulties in transferring files over Wi-Fi.
Other options included poorly insulated wires, crooked frames and platforms. nine0003
Deformed threaded screws, cheap hot ends, broken parts, poor shipping packaging, poor assembly at the factory are also common when buying cheap "NoName" printers.
You may end up spending most of your time repairing, fixing poor print quality issues, and just getting frustrated with 3D printing.
If you've been one of those unlucky ones, you've probably learned to take your time buying a 3D printer.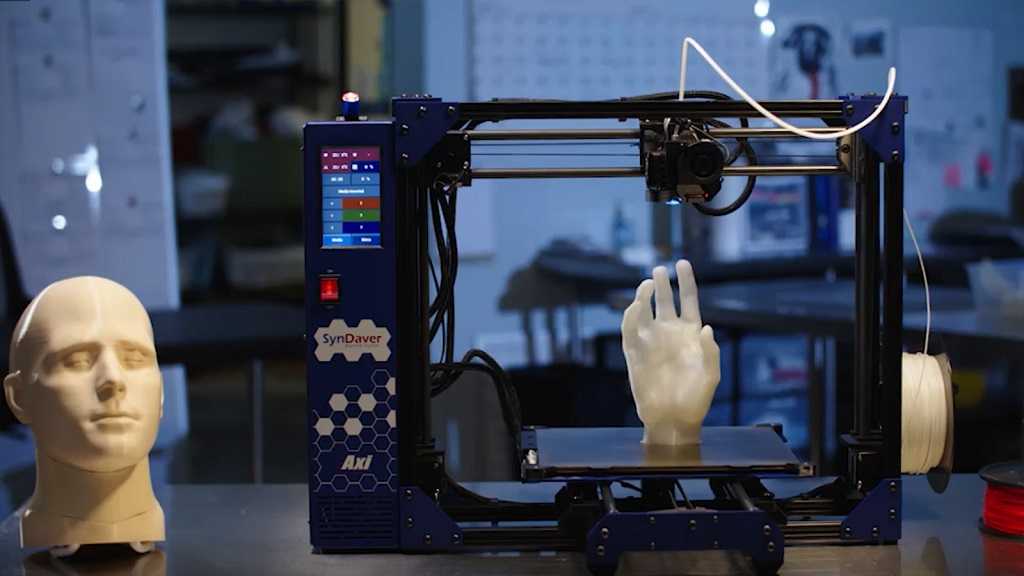 nine0003
nine0003
One of the most popular manufacturers of inexpensive 3D printers around the world is Creality, and their top product Ender-3 v2.
This 3D printer has been tested many times by users around the world, and its popularity proves to be the perfect combination of price and quality.
Every 3D company is a team that buys parts and builds a printer, but some do it much better than others and more consistently.
Some people who buy a bad printer either give up 3D printing, do a complete costly rebuild, or buy a better 3D printer much later. You might as well start by buying a good 3D printer! nine0003
Solution.
Choose a reliable 3D printer with a good reputation and avoid 90% of avoidable problems. We know a lot of stories about people going through the same thing, so save yourself the hassle.
We have never seen anyone call the Ender 3 Pro or the Voxelab Aquila X2 a bad first 3D printer because it really is a very good buy.