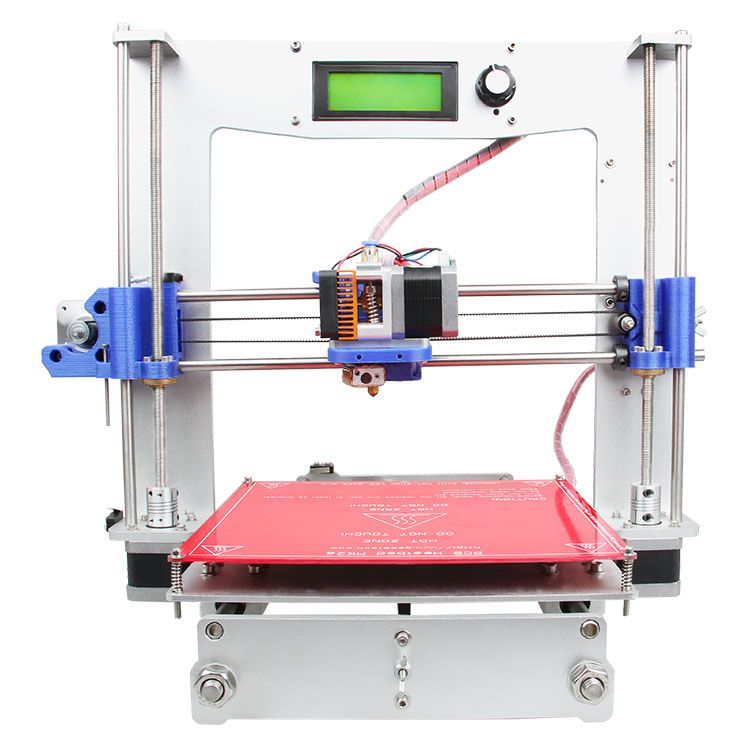
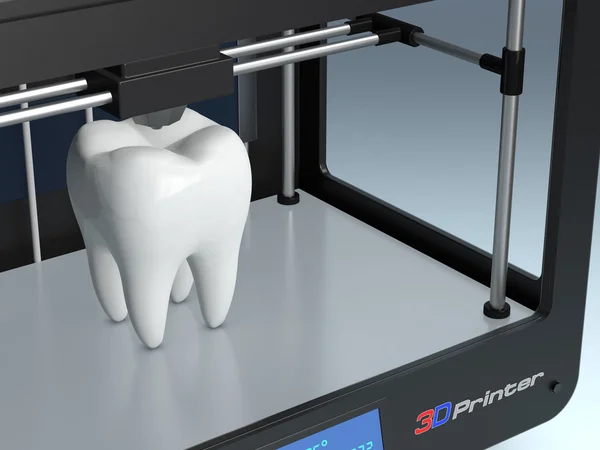
Public 3d printers
3D Printing | 3D Print Services
Find a 3D Printing Location
Print Functional Prototypes
You can use 3D printing for prototypes or one-of-a-kind items. Let The UPS Store® bring your ideas to life. We can even use your 3D CAD file.
Construct Manufacturing Jigs and Fixtures
We understand when you do your own manufacturing, jigs and fixtures are critical for insuring high-quality and efficiency during assembly and testing. Our 3D printer can create complex parts so you are not dependent on a CNC machine.
Create Custom Accessories
Want to design your own smartphone case or money clip? Most items that are smaller than a breadbox and can be made out of single color of plastic are perfect for 3D printing.
Build Architectural Models
You can work in just about any 3D architectural design program and then export to common 3D CAD file types. The finished product is ready to show off or you can sand and paint your building to give it just the right look.
3D Printing Services Expanded Across Nation
The UPS Store continues to expand 3D printing services nationwide to meet the growing demands of its small business customers. 3D printing now available at approximately 20 The UPS Store locations. Use the interactive map below to find a participating location near you, or check out the full list of all The UPS Store locations offering 3D printing services.
3D CAD and 3D Scanning Services
The UPS Store 3D print locations can now also offer you 3D CAD and 3D scanning services through HoneyPoint3D. Getting a custom 3D print has never been easier - you dream it, HoneyPoint3D designs it, The UPS Store prints it. Enjoy the HoneyPoint3D benefits of an easy quoting process, affordable and quality engineering, online viewing of your 3D files, and efficient turn-around times. Get your 3D CAD or scan quote today!
Netfabb® at The UPS Store®
Participating The UPS Store 3D print locations are utilizing Netfabb software for 3D print file preparation and customization. Services available at these locations include:
Services available at these locations include:
- File fixing
- Text labeling
- Logo labeling
- Cutting
Contact or visit these Netfabb locations to learn more about their advanced 3D offerings.
3D Printing Frequently Asked Questions
Here a few questions we frequently hear about 3D Printing.
Please feel free to contact your local The UPS Store for any other questions you may have
-
What is 3D printing?
-
3D Printing is a manufacturing process that uses a digital file to create three-dimensional objects one layer at a time. We run a system that uses ABS plastic and soluble supports to create realistic prototypes and marketing models.
-
What kinds of things can I 3D print?
-
Small business owners and aspiring entrepreneurs will have the opportunity to print prototypes as part of the new product development process. With this printer, The UPS Store locations will be equipped to produce items like engineering parts, functional prototypes, acting props, architectural models, fixtures for cameras, lights and cables.

-
How long does it take to print?
-
The time it takes to print an object will depend on the complexity of the design. A simple object may take 4-5 hours, while a complex object may take 24 hours.
-
Which UPS Store locations are offering 3D printing?
-
The UPS Store is in the process of rolling out nearly 100 3D printing locations across the country. Visit /print/3d-printing/locations for more information.
3D Printing in the Denver Public Library ideaLABs
We've made some changes to the way we offer 3D printing!
We're excited to let you (yes, you!) get more hands-on with the printers and run your print job yourself. This does mean we are no longer running a print queue or accepting submissions for printing - but now you will have the chance to run the entire process yourself, from design to finished print.
Use of the 3D printer is by reservation - please drop in or call the branch to reserve time. You will need a Denver Public Library card to make a reservation in advance. The maximum time you can reserve is two hours. We ask that people only make one reservation per week so as many people as possible can use the printers. Please read the full 3D Printer Policy below for details. We also have an FAQ below that for general questions about 3D printing.
You will need a Denver Public Library card to make a reservation in advance. The maximum time you can reserve is two hours. We ask that people only make one reservation per week so as many people as possible can use the printers. Please read the full 3D Printer Policy below for details. We also have an FAQ below that for general questions about 3D printing.
Every ideaLAB has at least one Lulzbot printer. Visit your neighborhood lab to learn more! Please note that the ideaLAB at the Central Library will remain closed due to on-going renovations to the building.
Denver Public Library ideaLAB 3D Printer Policies
As the ideaLBs reopen, the use of tools may look somewhat different than in the past. One of the big changes we’re making is to give customers more of a hands-on experience using the 3D printer.
In order to help you use the 3D printer successfully (and safely), we ask that you read through the following policies:
- Please try to read through the 3D Printing Guide before your first visit if you can.

- Use of the 3D printer is by reservation only. For the present, a reservation gives you the right to use the printer for two hours, once per week. We ask that families and groups not make multiple or back-to-back reservations under different accounts - that makes it much harder for other people to get access to the 3D printers.
- Please know that if you don't show up within 10 minutes of your reservation time, the system will automatically cancel it.
- If the printer is broken when you have a reservation, we'll do our best to let you know ahead of time, but sometimes that may not be possible.
- You must check in with ideaLAB staff before using the machines so you can get the material you're using approved by lab staff and get the 3D printer toolkit. We want to make sure everyone is safe and that you're comfortable with the equipment.
- We're sorry, but you can't bring in your own filament. We want to keep jams and fumes to a minimum for everyone.
 We will provide free PLA+ filament, but we can't change out colors for each customer nor guarantee you a specific color.
We will provide free PLA+ filament, but we can't change out colors for each customer nor guarantee you a specific color. - We'll give you some basic troubleshooting tips, but if something goes wrong, please don't do anything that involves disassembling printer hardware. Doing so will result in loss of privileges to use the machine. Please let us know if a problem pops up and we'll help!
- Things happen. Occasionally extruders will jam, beds will get scorched, and minor disasters will occur - these are understandable, and part of the process of learning how to use the printer, and will not affect your ability to reserve and use the machines. If you do something intentionally dangerous or that we've asked you not to do - using unapproved filament, removing parts from the machines, etc. - you will lose your privilege to use the machines..
- DPL printers can not be used to print out any weapons (if it's for cosplay, talk to staff and we'll try to figure it out). Outside of that, most things should be fine, but the Library retains the right to refuse any print request for any reason.

- Set-up and clean-up time is part of your 2 hour reservation, so please plan accordingly! Please finish your 3D printing jobs at least 10 minutes before the session ends so you can clean up materials and station. Jobs can not be left running overnight or past the end of your 2 hour reservation.
3D Printing FAQ
What is 3D printing?
Start with this definitive guide where you’ll find everything you need to know about 3D printing, beginning with the very basics before diving deeper.
How much does it cost?
3D Printing is currently free at Denver Public Library!
What can be printed?
All printing is done with PLA, a bioplastic made of corn. It might get a little melty if you leave it on your car dashboard, and you may not want to use it to make shelving mounts for your prize kettlebell collection. It's possible to make your model a little bit stronger by making it's walls thicker or requesting more infill. Ask us about it and we'll try to help you out. But if the piece you're printing is really mission critical in some way, use it at your own risk.
Ask us about it and we'll try to help you out. But if the piece you're printing is really mission critical in some way, use it at your own risk.
What cannot be printed?
Due to demand and limited resources, we can't print any job that will take over two hours. If you have something you'd like to print that will take longer than that, we're happy to help you try to figure out how to break up your model into smaller jobs, scale your print, or point you to one of the many paid 3D printing services. We also will not print out any weapons. Outside of that, most things should be fine, but the Library retains the right to refuse any print request for any reason.
Who can operate the printer?
Anyone who goes through an orientation with a staff member can! Read through the 3D Printer Policy above to learn how.
How To Get Your Object Printed
-
Create a file
- You can download an object file from a site like Thingiverse, Bld3r or use some of the lab's free modeling software like Tinkercad, Blender or SketchUp to make your own designs.

- Export your object as a .stl or .obj file. Need help? Just ask!
- You can download an object file from a site like Thingiverse, Bld3r or use some of the lab's free modeling software like Tinkercad, Blender or SketchUp to make your own designs.
-
Make your reservation
- Reserve time by coming by the branch, calling, or come into the ideaLAB during our open hours. You can reserve up to two hours on the machine.
-
Print out your creation
07.04.2021
Content
-
- What is a food 3D printer
- Field of use
- used raw materials
- 9000 9000 9000 9000
- Top 10 Best Food Printers: A List of the Most Current Models
- 1. PancakeBot 2.0
- 2. Wiiboox Sweetin
- 3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
- 4. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus Food 3D Printer with Cooling Chamber
- 5. byFlow Focus
- 6. Chefjet Pro
- 7. Foodini
- 8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer Commercial ArtcakesOT7 .
 90BOT Printer F5
90BOT Printer F5 - 10. ZMorph VX
- What is a food 3D printer
- Selection guide
- Output
A food printer is a high-tech device that is used to create culinary masterpieces. The decorative design of food products has reached a new level thanks to the use of modern technologies: high-quality and large-format printing is carried out on cakes, waffles, pancakes and even coffee. Here are the top best 3D food printers in different price categories for people who are fond of cooking. nine0003
What is a 3D food printer
The main feature of a food 3D printer is the raw materials used: instead of printing ink, the device is filled with edible ingredients. The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer. nine0003
Application
Futuristic 3D Printed Sugar Candy
Cookies printed with icing
Chocolate logos of famous companies
Cream Photo Print
Buying a food 3D printer is worth the owners of coffee houses, author's bakeries and private workshops.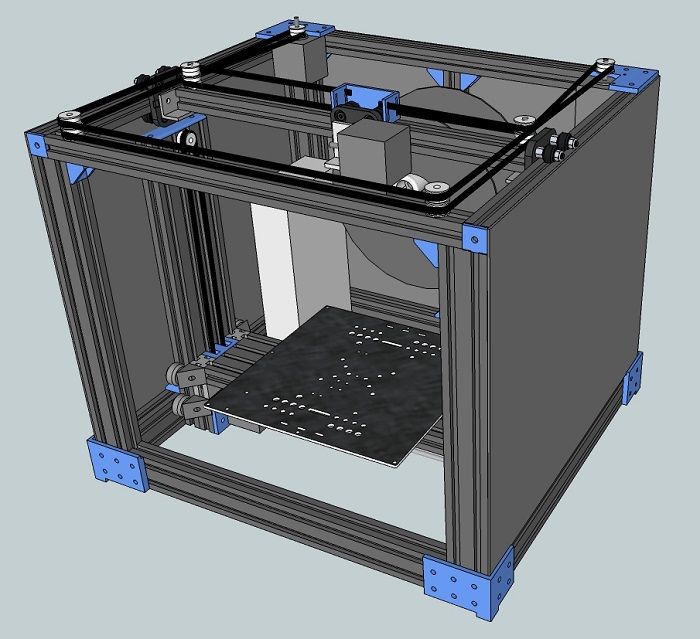 The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products. nine0003
The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products. nine0003
Raw materials used
The following ingredients are used as raw materials:
-
Chocolate without additives and impurities;
-
Mastic;
-
Sugar;
-
Whipped cottage cheese;
-
Vegetable and fruit pastes; nine0003
-
Fish and meat pates;
-
Flour;
-
Cheese, etc.
The confectionery pattern is applied to sugar, wafer or shock transfer paper. The first type has a sweetish aftertaste and aroma of vanilla. Due to the snow-white surface, no additional coating is required: the drawings look bright and clear. The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used. nine0003
The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used. nine0003
Interesting! Food printers are involved in waste reduction. Unattractive fruit and confectionery leftovers are used in the preparation of printing mixes. This makes it possible to use the means of production more efficiently.
Types of 3D food printers
Cooking enthusiasts can take advantage of the following food printing devices:
-
Food 3D printers are devices that print dishes whose recipes are listed in a database. The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges; nine0003
-
Confectionery printers are used to transfer images onto specialty paper or to design small confectionery products such as candies.
 Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer;
Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer; -
Food plotters transfer the image not to paper, but directly to the finished product. For example, a plotter is used to transfer an image directly onto a cake. nine0003
There are several types of food 3D printers:
-
Extrusion - paint is applied to the surface before the dish is created. The process is controlled by the computer with the loaded image. The system has an extruder that heats the food mixture, and the distribution of raw materials depends on the print head. The raw material is loaded into a syringe placed in the head. This means that in order to combine different shades, you have to periodically stop printing and change the syringe; nine0003
-
A carousel-type food 3D printer also has an extruder, but its main feature is the method of feeding raw materials: the containers rotate around the working surface, the supply and dosage of the material used depends on the recipe specified in the program.
 The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
Popular brands
Eminent manufacturers offer the best value for money food 3D printer. Quality devices provide accurate printing, high speed, durability, simplicity and ease of use.
Wiibox
This company manufactures 3D printers with high build quality and high productivity. These are universal mechanisms that fill both chocolate paste and mashed potatoes. Numerous positive reviews confirm the high quality of Wiibox products. nine0003
byFlow
The Dutch company byFlow specializes in food printing technology. The pursuit of excellence helps the company open up new horizons: the technique prints products from spinach, meat emulsion and other materials. High build quality, ease of use and durability - all these characteristics are applicable to the products of this company.
Choc Edge
Choc Edge is committed to revolutionizing the world of chocolate making. Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Attention! Printing dishes helps save time on cooking: instead of culinary worries, the user can simply activate the printing process and get on with other things.
nine0134Free shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Available on credit. To checkout, add the product to the cart and follow the instructions Go nine0003
Manufacturer Wiiboox Free Shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Top 10 Best Food Printers: List of the Most Current Models
Before you buy a food 3D printer, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular devices on the world market.
The top is based on ratings and customer reviews. nine0003
1. PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 is easy to use, which means it's suitable for inexperienced users too. Users can choose from suggested designs in the software, or create their own. Used to print pancakes.
Pros:
Ease of operation;
A wide range of proposed projects; nine0003
High speed.
Cons:
2. Wiiboox Sweetin
Buying a food printer from Wiiboox is worth not only for confectionery lovers, but also for ordinary chefs: the device prints cakes, cookies and even mashed potatoes. The main raw materials can be meat, cheese, chocolate, jam, mashed potatoes, dough and much more. A convenient touch panel helps to set the desired mode of operation, and a stylish appearance complements the interior of any establishment. nine0003
Pros:
Versatility: the ability to print not only sweet dishes, but also side dishes;
Attractive appearance;
High build quality;
Convenient control by touch panel.

nine0173 Cons:
High price.
3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
When talking about which chocolate 3D printer to buy, it is worth mentioning the numerous advantages of Choc Creator V2.0 Plus. The new model has become more perfect: the developers have worked hard to eliminate the shortcomings of the previous version. The modern model has small dimensions, thanks to which it can be used in any kitchen, and the uniform heating of the syringe ensures high-quality and uninterrupted operation. In practice, the chocolate printer has shown tremendous potential: it prints complex figures from chocolate. nine0003
Pros of :
Attractive appearance;
Uninterrupted work;
Durability;
The ability to create durable and beautiful chocolate figures.
Cons :
4.
Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
The new version of the Choc Creator V2.0 Plus printer is equipped with cooling chambers by popular demand. Users say that maintaining the optimal temperature in the room to preserve the integrity of chocolate figures is too problematic: therefore, the new device cools the raw materials. The price of a food 3D printer with a cooling system is slightly higher than a classic one, but the high performance of the final product justifies any costs. nine0003
Pros of :
Availability of a cooling system for finished products;
High printing precision;
Long service life;
Ease of use: You can turn the fans on and off with the side buttons.
Cons :
High price.
Attention! Confectionery food 3D printers are often used by artists to create edible masterpieces.
This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef.
5. byFlow Focus
Food printer from the Dutch company byFlow, which specializes in 3D printing of food. The compact high-tech device is used for the bakery industry, and the cartridges are suitable for the application of any pasty ingredients. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
6. Chefjet Pro
Buying a ChefJet Pro food printer is a must for people who dream of making bright and stylish sweets. The device is created on the principle of inkjet printing: sugar-containing powder materials are used instead of paints. The final product is made by powder layering. The printer is suitable for combining different shades and creating gradients. nine0003
Pros:
The ability to create unique flavors;
Neat and bright printing;
Aesthetic appearance of the device.

Cons:
- nine0015
High price.
7. Foodini
The 3D food printer from Foodini works on the principle of a stationary printer, but instead of printing inks, layer-by-layer imposition of edible raw materials is used: dough, cream, chocolate, cream, etc. The device is versatile: the user himself can choose the material, or use ready-made cartridges with products.
Pros:
Practicality; nine0003
High build quality;
Attractive appearance;
Availability of an online platform with unique recipes.
Cons:
8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer
The closed MMuse 3D printer is suitable for chocolate printing. Chocolate beans are used as raw materials: they are heated in an extruder and fed to the work surface through the print head.
nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
9. ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5
ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5 3D Printer
A food printer from Chinese manufacturers is used in the process of making pancakes of various shapes. Ease of operation allows the device to be used by children under adult supervision. nine0003
Pros:
Ease of operation;
High build quality;
Affordable cost.
Cons:
10. ZMorph VX
A multifunctional 3D printer capable of printing not only food, but also rubber, ABS plastic, polylactide, PVA, nylon, elastic and metal materials. The product is able to print with chocolate, butter, cookies, icing and other ingredients. In addition, there is a function of engraving and CNC milling. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
High price.

Selection guide
The modern market offers a wide range of food printers. Before making a purchase, you need to carefully study the characteristics of each model and build on your own preferences. Experts have created several recommendations for choosing: nine0003
In case you want to create realistic images for confectionery 3D printing, pay attention to the diameter of the nozzle: the narrower it is, the more accurate the image will be;
- nine0007
It is better for people living in regions with a warm climate to purchase chocolate 3D printers with a cooling system: such devices ensure that the figurines are kept at the optimum temperature;
The possibility of self-refilling the cartridge is the most practical and economical way to operate the printer;
Print speed is an important consideration for restaurant owners. Large batches of dishes must be produced quickly, and for home use this is not a very strict selection criterion.

Output
In the catalog of our online store, you can choose the best food printers from famous brands to create culinary masterpieces. Explore our range, learn about the characteristics of each printer and make great purchases. nine0003
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
What is 3D printing in 2021
3D printing technology has changed the manufacturing process of everything that surrounds us. From children's toys and clothes to prostheses, implants, etc.
The 3D printing process is also known as additive manufacturing. In simple terms, a computer program tells the printer where to lay thin layers of material that gradually turn into a solid object. nine0003
Types and processes of 3D printing technologies
The first mention of 3D printing technology appeared in the late 1980s.
They were called rapid prototyping technologies. The name refers to a process that was conceived as a faster and more cost-effective method of prototyping in product development. The very first patent application for this technology was filed by Dr. Hideo Kodama in May 1980. But, unfortunately for the inventor, the full patent specification was not submitted until one year after the application was filed. Kodama used ultraviolet light to cure plastic and create an AM object. nine0003
Years later, the American Scott Crumb developed the most common type of 3D printing today - FDM (Fused deposition modeling). This technology stands for deposition modeling. This type is characterized by the fact that the thermoplastic material is heated to a liquid state and extruded through the nozzle layer by layer.
Charles Hull, co-founder of 3D Systems, was one of the inventors of the 3D printing technology known as stereolithography. The technology is based on photochemical processes. nine0003
But Kodama, Crump, and Hull weren't the only ones to develop 3D printing techniques.

WINBO 3D printer at Art-Up Design Studio
Here are some other types of 3D printing in use today:
- FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is by far the most common method of producing thermoplastic parts and prototypes today. Based on the melting of the filament in the nozzle with its subsequent laying in layers. It is also the most economical way of 3D printing due to the availability of a wide range of thermoplastic materials with different technical characteristics, which allow generating both functional parts of mechanism prototypes and volumetric cases, as well as any free spatial decorative forms. nine0012
- SLA (Stereo Lithography Apparatus) is based on the layer-by-layer curing of a liquid photopolymer material under the influence of UV study. Can print objects in multiple colors and materials with different physical properties, including rubber-like parts. The high printing accuracy of this method makes it more expensive and not optimal for simple plastic structures.

- DLP (Digital Light Processing) cures polymers using a light projector rather than an ultraviolet laser. This allows you to create a whole layer in one exposure, thus increasing the speed of production. nine0012
Metals too have their own 3D printing techniques. The type of technology is selected depending on the features of the object.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is based on layer-by-layer sintering of polymer powder particles using laser radiation. The nylon powder melts into a strong, hard plastic. Due to the peculiarity of the technology, the surface of the part is not ideal, but very functional for use in prototypes with hinges and latches. nine0012
- SLM (Selective Laser Melting) is based on layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder under the action of a laser beam. Used in the manufacture of decorative items. Therefore, it is useful for applications in medicine and lightweight structures. Often this method is used in conjunction with traditional metal casting technology to create prototypes or final products.
- EBM (Electron Beam Melting) is based on layer-by-layer melting using an electron beam. The printing uses electromagnetic coils to superheat the metal powder in a vacuum. nine0012
How 3D printing works
3D printing is the process of layering one on top of another. Every 3D printed object starts life as a 3D model in a computer program.
You can create your own design in programs such as Maya, Blender, ZBrush, CATIA, Solidworks. In addition, ready-made 3D models of parts can be downloaded from sites such as Thingiverse or CGTrader.
When you have a 3D model obtained in one way or another, you “run” it through the “slicer” program (from the English word “to slice”), which converts the original 3D model in STL format into print layers. The information received is eventually converted into a special data format called G-code for further printing on a 3D printer. nine0057 Such programs usually come with the 3D printer, or they can be freely downloaded, such as the Cura program.
What these softwares have in common is that they create thousands of lines of code for layers. This code tells the printer how to print.
Next, you need to set up your 3D printer, select the print quality and the correct settings for the material. To start printing, you load your "sliced" part into the printer via a USB stick, SD card, or send directly from your computer. And the printer starts a slow additive layering process. nine0003
Photograph of Christian Reil from Pixabay
Materials used in 3D printing
The materials available for 3D printing have come a long way. Currently, there is a wide range of materials that differ both in properties, types, and in the states supplied (powder, threads, granules, resins, etc.).
Some materials are developed for specific applications to perform special tasks. For example, the medical sector, where special photopolymer resins (SLA 3D printing technology) are used, the properties of which make it possible to print implants, casts, and so on.
nine0003
Some of the most commonly used materials:
- Plastics. Sintering (SLS) typically uses polyamides or nylon supplied in powder form. It is a strong, flexible and durable material. It is white in color, so it needs to be tinted before or after printing. The most common 3D printing technology today is FDM, which uses ABS or PLA plastic filaments. These plastics are available in a wide range of colors. Compared to PLA, ABS plastic has higher strength characteristics. But PLA is biodegradable, so it's as widespread as ABS. nine0012
- Metals. More and more metals and metal composites are finding their way into industrial 3D printing. The most common of them are derivatives of aluminum and cobalt. Due to its strength characteristics, stainless steel is often used in powder form in 3D printing technologies such as sintering, melting, EBM. In the last couple of years, silver and gold have been added to the list of metals suitable for printing. This made it possible to significantly expand the possibilities of jewelry production.
nine0012
- Ceramics. A relatively new group of materials used in 3D printing. The peculiarity of printing with these materials is that the printed ceramic parts must go through the same processes as ceramic products made by traditional methods - firing and glazing.
- Biomaterials. Currently, a large number of studies are being conducted aimed at exploring the possibility of 3D printing from biomaterials for the needs of medicine. This includes the printing of human organs for transplantation, external tissues for replacement of body parts. To do this, leading institutions research living tissues. nine0012
- Food. Over the past few years, there has been an increase in experimentation with food 3D printing extruders. Chocolate printing is the most widely used. There are 3D printers that use sugar, pasta, meat, dough.
Photo of mebner1 from Pixabay
What 3D printing is used for
If you can think of an item, then most likely you can print it.
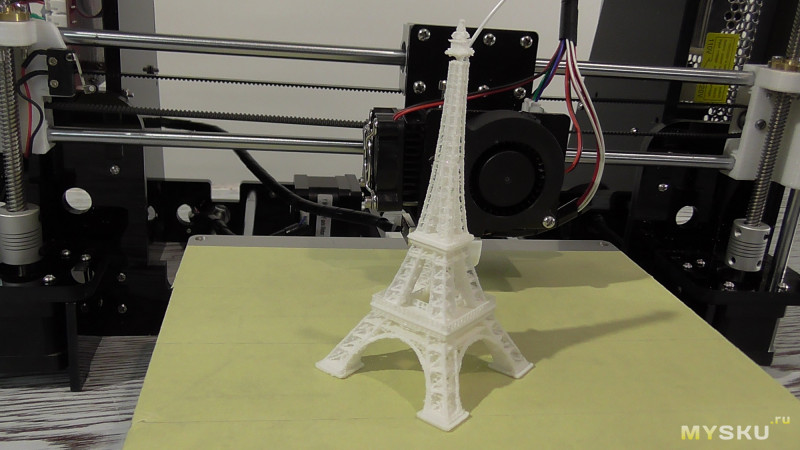
Children's toys, jewelry, phone cases and much more are already being printed by enthusiasts on 3D printers. Some use 3D printing for fun. Fun projects already exist: a printed guitar, a loom, and an intricate sculpture created from a combination of laser-fused glass and nylon. 3D printing has already moved beyond its origins in plastic printing and has moved into the use of metal, rubber, wood, synthetic fabrics, and ceramic resins. Functional 3D-printed human organs have not yet been created, but scientists say that this is a matter of the near future. nine0003
Because additive manufacturing of complex objects is faster and cheaper than traditional molding and casting methods, it has found its way into industry and the arts. The possibilities of this technology are almost limitless, but 3D printers are not perfect machines. In addition to all the advantages, there are also reasons for concern.
Ethical issues in 3D printers
3D printers consume a lot of energy and emit ultra-light plastic particles into the air, which are then inhaled by humans.
These harmful emissions can be compared to a cigarette lit indoors. nine0003
While humanity is trying to reduce the use and consumption of plastic, 3D printers are another technology heavily dependent on it. This presents a problem for all ecosystems, in particular for the already suffering oceans with their floating islands of plastic.
A few years ago, the news of the first 3D printed firearm caused a media frenzy. The creation of untraceable weapons by a private individual remains a modern security problem. nine0003
From a legal point of view, there is no clear answer to the question of who is responsible in the event of harm to health caused by a printed object. Indeed, in most cases, the developer of a 3D model, the manufacturer of a 3D printer, and the one who printed it are different people or organizations. Determining liability for potential injury and death is a new challenge.
At the same time, the use of 3D printing technology in the medical field to print tissue raises a number of ethical and moral questions.
These issues are similar to the talk of stem cell research and gene editing that has been going on for decades. nine0003
On the other hand, we have a powerful tool in our hands that is changing the way we create and produce things. We still don't fully understand what this means for our future.
Potential effect on the global economy
If 3D printing continues to develop at the same pace as it is now, then its use could potentially affect the global economy. The transition of production and distribution from the current model to localized custom manufacturing can reduce the imbalance between exporting and importing countries. nine0003
3D printing is creating new industries and new professions. Professions related to the production of 3D printers or, for example, a vacancy for a rapid prototyping technician at the Cartier jewelry house. New professional services are emerging, such as supply of materials, printer operator, legal services in dispute resolution and intellectual property issues.
With the development of 3D printing technology, the issue of "piracy" becomes an urgent problem.
The impact of 3D printing on developing countries is a double-edged sword. The positive effect for such countries is the reduction in the cost of production through the use of recycled and other local materials. But the loss of manufacturing jobs could hit these economies hard, and it will take time to find a balance. nine0057
Where can I use a 3D printer
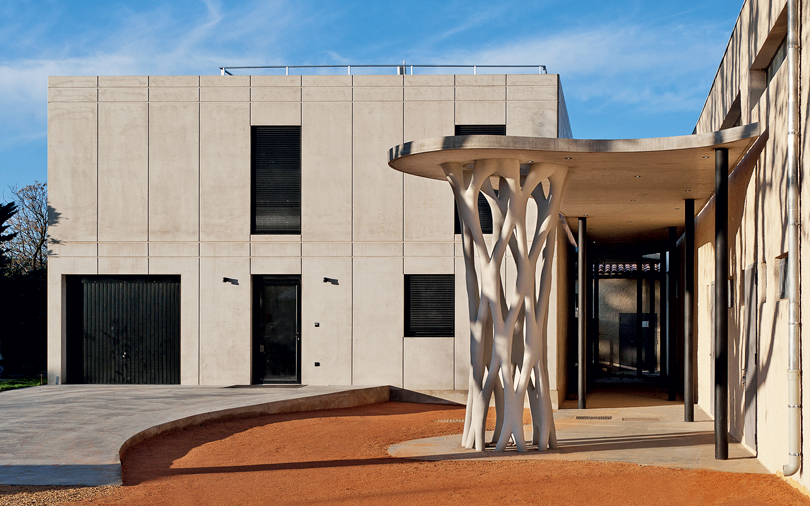
Owning a 3D printer with the necessary software and materials can still be expensive for individual needs, so public 3D printers are becoming more common.
There are places like labs and 3D printing shops. You can send your design and pick up the finished part in a couple of days. Some companies, such as ART AP Design Studio, also do 3D printing. nine0003
If you are a student or student, 3D printing services may be available at your school.
Printed products in Art-Up Design Studio
Where can I learn how to use a 3D printer
For those who already have the specialty of an engineer, there are advanced training programs (Additional education) from the Russian Academy of Crafts, designed for 36 or 72 academic hours.

Learn more