Presentation about 3d printing
How 3D Printing Works in the Real World
Informative News & Exciting Updates!
PromoAmbitions
Recent News & Updates
How is 3D Printing Used in the Real World?
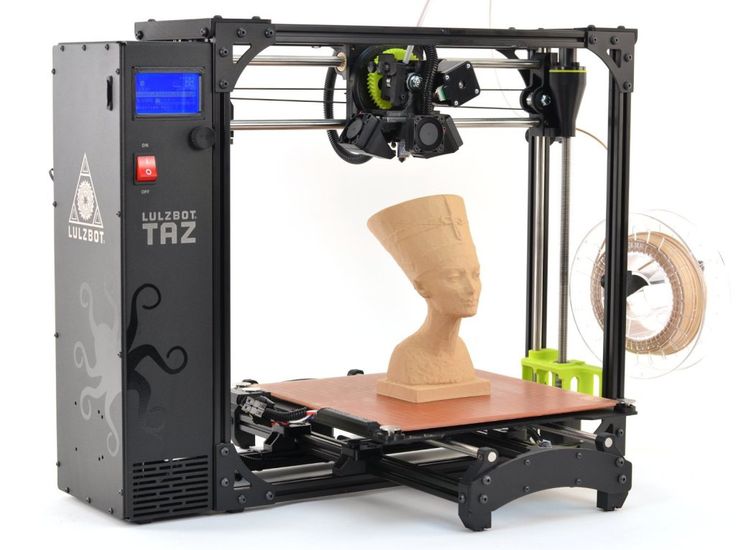
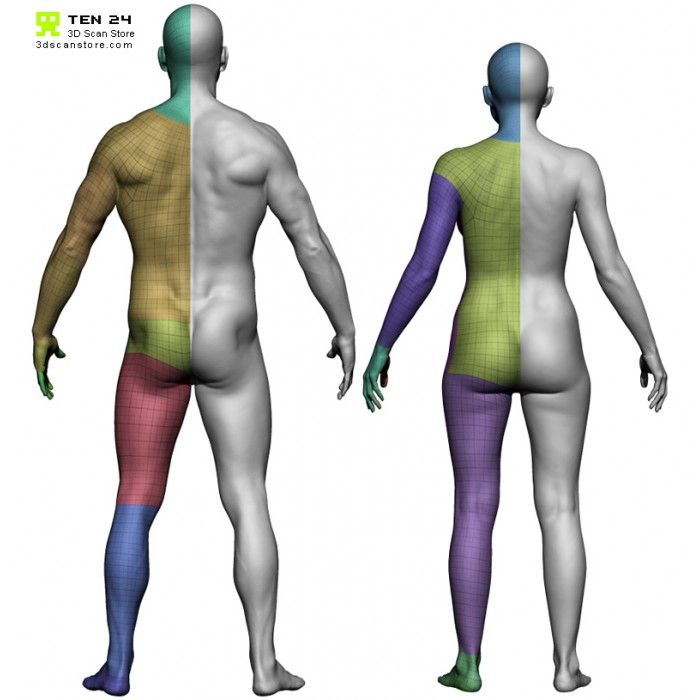
Additive manufacturing has been revolutionizing industries across our planet for several decades now. What was originally intended for speedy prototypes, has now become integral to the manufacturing process; many even suggesting that we are experiencing the fourth industrial revolution thanks to this technology. From body parts, animal prosthetics, cars, homes, food and nearly everything in between, this technology is helping to enhance people’s quality of life, make the manufacturing process more efficient, and foster innovation across virtually all industries. The below presentation serves to illustrate all of this and more.
How 3D Printing is Changing the World Part 1How 3D Printing is Changing the World Part 2We’re excited to announce that we’ve decided to release our entire additive manufacturing presentation! We used to present this in school systems across the tri-state area and beyond, but while the world is on pause, we do not want to deprive students, instructors and enthusiasts from utilizing this learning resource. If you are an instructor using this for your class curriculum, then please consider donating at the link below so that we can continue making more of these presentations.
In Part 1 we do our best to explain the 3D printing process in the simplest way possible using real life examples and distinguishing between two and three-dimensional creations. We discuss how Computer-Aided Design programs are utilized to design the idea in three dimensions and then show time lapse videos to exemplify the creation process. We also dive into transferring of files and post-processing including a detailed explanation of why supports are utilized and how they are typically removed prior to a finished product is presented. The two most popular additive manufacturing methods – Material Extrusion and Stereolithography are discussed.
To illustrate how this innovative technology is revolutionizing industries across the world, we provide a plethora of real-life examples in Part 1 and Part 2 of this video series:
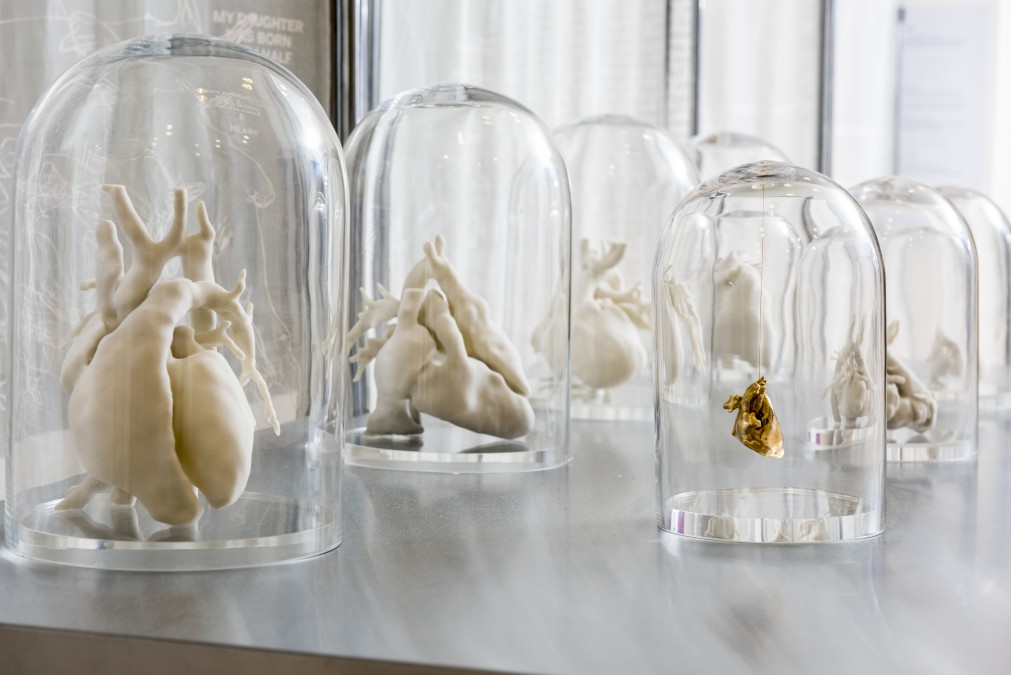
- Tissue, Body Parts, and Organs
- Casts, Orthotics, and Prosthetics
- Sustainable homes built in 24 hours
- Vitamins and Medication
- Garments and Jewelry
- Impressive Cars
- Motorcycles and bikes
The Negative Aspects of 3D Printing
Yes, Additive Manufacturing does have negative disadvantages and far-too-often these get overlooked because of the plethora of benefits and revolutionizing aspects of additive manufacturing across virtually all industries. In this video, we aim to educate you on some of the limitations and downsides attributed to this technology.
In this video, we aim to educate you on some of the limitations and downsides attributed to this technology.
Topics covered in the video include:
- Labor: Many lower income manufacturing jobs that are especially relied upon in third world countries will be rendered obsolete by additive manufacturing.
- Weapons: It has been proven that both guns and bomb parts can effectively be created using this technology and the implications of digital blueprints for these weapons being disseminated to millions through open-source platforms is troubling. This being an international issue and the topic of plastic weapons having the ability to bypass metal detectors is also explored.
- Unhealthy Air Emissions: The melting of material during the creation process releases very small particles and volatile organic compounds into the air. The health consequences along with some helpful measures to avoid this issue are discussed.
- Learning Curve: We dive into the difficulty level and common problems associated with this technology that is preventing it from being a common household item which families can rely on for printing necessities. The 3D Printing workflow process challenges are mentioned.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Infringement on design patents, trademarks, and creative commons licenses is highlighted and the risk posed to original designers and businesses that rely on original designs is discussed.
Please support the release of this Workshop Presentation for free use by educational institutions all over the world as well as the creation of future videos by making a donation below…
The Future of 3D PrintingThe Future Applications of 3D Printing Technology
Additive Manufacturing has only been around for a few decades now, but has already been integrated into the supply chain of most industries. As the process becomes more affordable and print times exponentially faster, there will be a boom in innovation and new possibilities for the adaptation of this technology in many sectors.
As the process becomes more affordable and print times exponentially faster, there will be a boom in innovation and new possibilities for the adaptation of this technology in many sectors.
Topics covered in the video include:
- On-Demand Solutions in Operating Rooms – a tech medical professional will have a station set up to scan and print body parts on command for surgical solutions.
- Custom Clothing Stations – Kiosks will exist in malls where individuals can get scanned and measured precisely and then on a digital screen can try out different clothing and customize it to their unique preferences.
- Custom Medications in Pharmacies – 3D Printers in pharmacies will give pharmacists the ability to print meds in custom dosages with unique delayed-release properties.
- Personalized Vitamins – After a quick vitamin profile test, ideal custom-made multivitamins will be created for customers.

- Future Home Solutions – More prevalent use of 3D Printed homes across impoverished countries will occur.
- Custom Shoes for a Perfect Fit – scanned and created for personalized use with desired brand, shape, design, etc.
- At-Home Dental Guards – There will be affordable at-home bio-compatible dental guard solutions.
- Custom Jewelry & Accessories Kiosks – One will be able to customize the design, the message, the intricate pattern and have your finger scanned for the perfect fit
- Integration into the School Curriculum – CAD and other 3D software will be taught to students from elementary school onwards causing them to be proficient by graduation.
Please support the release of this Workshop Presentation for free use by educational institutions all over the world as well as the creation of future videos by making a donation below..
paypal.me/EddiKhaytman
Share this post
Share on facebook
Share on twitter
Share on linkedin
Share on pinterest
Share on print
Share on email
Presentation best 3D printing models・Cults
Hand Business Cards Holder 3D print model
€10
STENCIL PLATING #1 - CHEF, FOOD, DISHES MEAL PRESENTATION ART spiral - EMPLATED
€4. 61
61
STENCIL PLATING #5 - CHEF, FOOD, DISHES MEAL PRESENTATION ART - PLATING
€4.77
Harry Potter wand holder
€0.70
Best 3D Printer in the World
€0.62
3D Printing presentation, sign Bathroom, WC
€0.62
HOME
Free
Unlocked car
€1.50
Card holder
€1.94
Turntable with ball bearings, speed controller and motor
€3.80
INTERROGATION/QUESTION SYMBOL
€2.50
POLYMER CLAY ALPHABET MODEL SET
Free
BASE-SQUARE-002
€3
Semaphore H0 - 1/87, 1/72 detailed, working mechanism
€4
Inter-Raptor Presentation
Free
Centerpiece leaf
€1.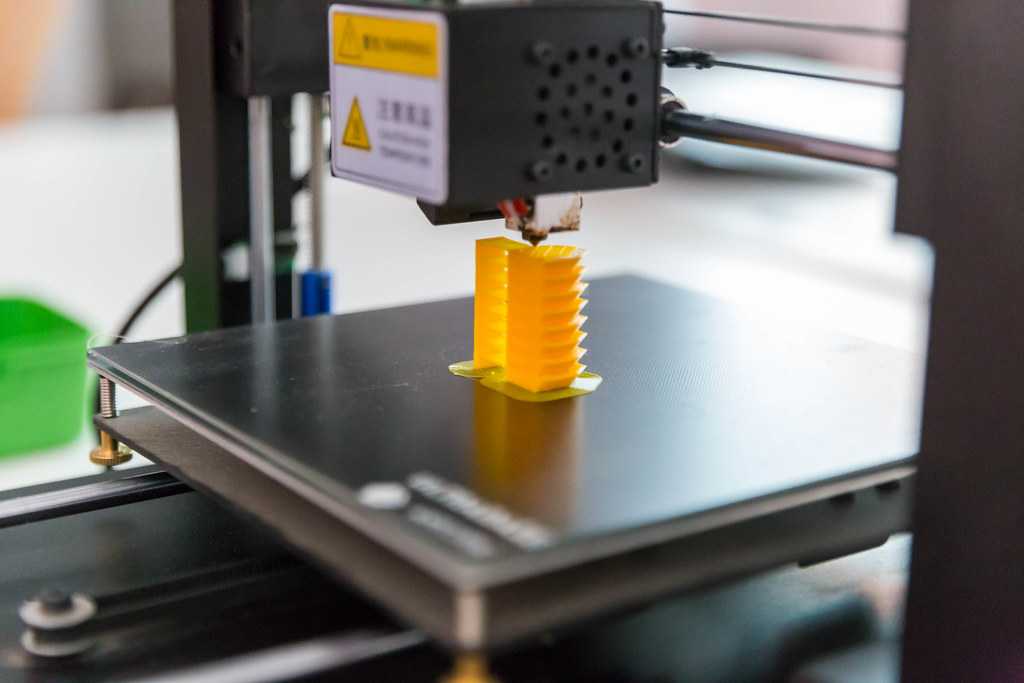 04
04
Wine holder
Free
Led table
€5.06
Phone holder freehand: Ego shot movie maker for presenting printed items
Free
BASE-ROUND-002
€2
shift gear 4speed
Free
Miniature Display Case
€4.10
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa / Save Cards (Dent, Dientes, Tooht) / boîte
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa (Guitarra Fuego) / Save Cards (Guitar Fire) / boîte
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa (Guitar) / Save Cards (Guitar) / boîte
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa (Pajaro) / Save Cards (Bird) / boîte
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa (Perro) / Save Cards (Dog) / boîte
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa (Planta) / Save Cards (Plant) / boîte
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa / Save Cards (Batman) / boîte
€1. 15
15
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa / Save Cards (Cangrejo) / boîte
Free
GUARDA CARJETAS CON TAPA (Música) / SAVE CARDS (Music) / BOÎTE
Free
Guarda Tarjetas Con Tapa / Save Cards (Pikachu) / boîte
Free
Save Cards With Lid / Save Cards
Free
Phone Holder with Amplifier and Charging station 3D print model
€2.49
Display stand for Vinyl
€4
Wicked Marvel Avengers Captain America 3d Bust: STL ready for printing FREE
Free
3D Business card nature
Free
Presentation Stand
Free
Skateboard wall mount with backlighting
€1
divider - internal locker for the "kasseby" showcase of a large Swedish furniture manufacturer group
Free
Modernist architecture masterpiece, concrete structure of station shelter H0/other scales
€3
H0/other scales bridge tower building model
€1. 50
50
Vase flowerpot FDO
€0.65
Tripod Table Adapter
€0.50
design document holder / office display cabinet .
€1.50
StarScan_Dub_Turntable
Free
kamden suit with monk strap shoes 3D model
Free
BASE-SQUARE-001
€3
3D printing - online presentation
Similar presentations:
3D Printing Technologies and Trends
Additive technologies: 3D printing
Additive manufacturing technologies
3D printing
3D printing technologies at the enterprise "3D Techno"
Methods and technologies for prototyping products. (Lecture 7)
Control of technological processes based on computer CAD systems in mechanical engineering. (Lecture 7)
(Lecture 7)
Additive manufacturing
Additive technologies in mechanical engineering
Additive technologies
3D printing
3D printer
3D printer (fabber, Rapid Prototyper) is a peripheral device that uses the
method of layer-by-layer creation of a physical object from a digital 3D model.
Charles Hull - founder of 3D Systems Corporation
3D printing - additive manufacturing
Application:
• prototyping (rapid prototyping),
• production of finished products (fast production).
Printer resolution - thickness
applied layers (Z-axis) 16-200 microns.
Accuracy
printer
-
accuracy
positioning of the print head in
horizontal plane (along the X and Y axes)
10-100 microns.
Two types of materials:
support materials.
Structural
and
Method
Extrusion
Technology
Fusion Deposition Modeling
(FDM or FFF)
Wireframe
Free Form
Electron Beam Melting (EBFȝ)
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Powder
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
Titanium Alloys, Cobalt Chromium Alloys
Stainless steel, aluminum
Heat selective sintering (SHS)
Thermoplastic powders
Laser selective sintering (SLS)
Thermoplastics, metal powders,
ceramic powders
Gypsum, plastics, metal powders,
sand mixtures
Paper, metal foil,
plastic film
Photopolymers
Photopolymers
Inkjet
3D Inkjet Printing (3DP)
Lamination
Object Fabrication
Lamination Lamination (2S9025) Digital LED Projection (DLP)
Polymerization
Materials used
Thermoplastics (such as polylactide
(PLA), acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
etc. )
)
Almost any metal
alloys
Almost any metal
alloys
Titanium alloys
products by layer-by-layer laying of the melted
thread from the fusible working material.
Developed by S. Scott Trump in the late 1980s
Trademark of Stratasys Inc.
FDM variant
Testing of a device prototype
operating on EBFȝ technology
Laser sintering of powder materials
(Selective Laser Sintering, SLS)
SLS
additive manufacturing technology
for the production of models, prototypes and finished products
from fusible powder material
(plastic, metal ) by melting it under
laser radiation.
Designed by Carl Deckard and Joseph Beeman,
University of Texas at Austin Mid 1980s.
Acquired in 2001 by competing
company 3D Systems.
The last of the SLS
technology patents was filed on January 28, 1997,
expired on January 28, 2014, and
technology is publicly available.
Rapid Prototyping
Solutions
Five Star Plastics
New Balance
uses
SLS technology to create
footwear
Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
Developed by the Institute for Laser Technology (ILT)
Fraunhofer Aachen and F&S
Stereolithographietechnik GmbH in Paderborn.
Today the technology belongs to SLM
Solutions GmbH and ReaLizer GmbH
A variation of SLS
technology The process takes place in a working chamber filled with
inert gases (argon). Oxygen-free
avoids oxidation of consumable
(can be printed with metals).
J2-X rocket engine part printed by NAS
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Developed by EOS, Munich
A variation of Selective Laser Sintering or SLS
and Selective Laser Melting or SLM.
DMLS allows the
to create solid
metal parts.
print resolution ~20 µm
DMLS setup
Rocket engine parts
Super Draco
Elon Musk, Space X
Nickel-chromium material
Inconel superalloy
Electron beam melting (EBM)
A variation of SLS and SLM
The main difference is the use of electronic emitters instead of lasers
Titanium implant obtained using EBM
Industrial EBM machine manufactured
by the Swedish company Arcam AB
Craniofacial
implant manufactured using
using EBM technology
Selective heat sintering ( SHS)
A variant of SLS technology
Used for fusible materials
Desktop SHS printer - Blueprinter
Models printed with SHS method
• Institute for Problems of Laser and Information Technologies
RAS.![]()
Resolution
down to 15 microns
Desktop
stereo lithography
OWL printer
Nano
Digital LED projection (DLP)
A variation of SLA technology
Difference - the use of LED projector
Helisys Inc.
LOM
-
technology
forming
layer-by-layer bonding (heat, pressure)
thin
films
working
material
with
cutting (using a laser beam or
cutting tool
)
corresponding
contours on each layer.
Mcor 3D Printer
Matrix Plus
3D Inkjet Printing (3DP)
Developed by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)
, 1993
Name Variations:
• Ink Jet Modeling
• Multi-Jet Modeling, MJM,
• Poly25, 900 • Drop-On-Demand-Jet, DODJet.
support materials - wax,
modeling materials
-
gypsum,
metal powders, sand mixtures
plastics,
Powder bonding technology (Binding
powder by adhesives)
Manufacturing company: Z Corporation.
1-2 - the roller applies a thin layer of starch and cellulose powder to the work surface;
3 - inkjet printhead prints with drops of binding liquid on the powder layer,
locally reinforcing part of the solid section;
4 - process 1-3 is repeated for each layer until the model is ready, the remaining powder is
removed
UV irradiation through
photomask (Solid Ground Curing, SGC)
Manufacturer: Cubital Inc
English Russian Rules
3D printing and 3D printer presentation, report
3D printing and 3D printer
Authors of the presentation: Salatina E. A., Salatin S. A.
3D Printer
is a peripheral device that uses a layer-by-layer method to create a physical object from a 3D digital model. In foreign literature, this type of device is also called fabber, and the 3D printing process is called Rapid Prototyping.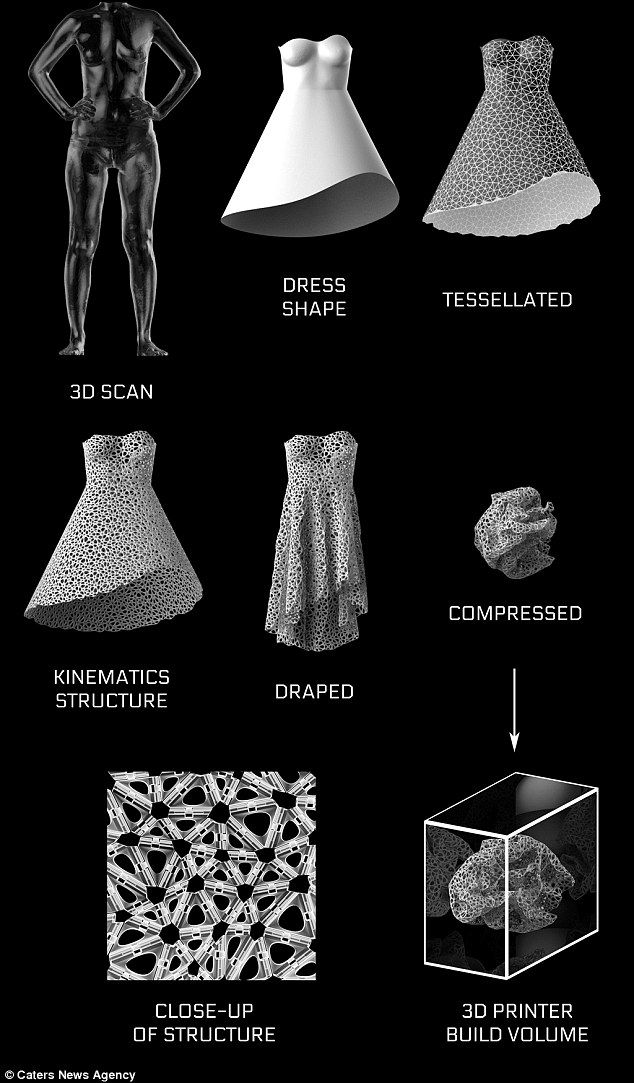
What is a 3D printer?
The principle of operation of a 3d printer is based on the principle of gradual (layered) creation of a solid model, which, as it were, is “grown” from a certain material. The advantages of 3D printing over the usual, manual methods of building models are high speed, simplicity and relatively low cost.
Technologies
There are various 3D printing technologies. The difference between them lies in the way the product layers are applied.
The most common are SLS (selective laser plexus), HPM (molten material overlay) and SLA (stereolithiography).
The most widely used technology due to the high speed of building objects is stereolithography or SLA.
SLA technology
The technology works like this: a laser beam is directed at a photopolymer, after which the material hardens.
The photopolymer is a translucent material that deforms when exposed to atmospheric moisture.
Once cured, it can be easily bonded, machined and painted. The working table (elevator) is in a container with a photopolymer. After the laser beam passes through the polymer and the layer hardens, the working surface of the table moves down.
SLS technology
Laser beam sintering of powder reagents - aka SLS - is the only 3D printing technology that is used in the manufacture of molds for both metal and plastic casting.
Plastic models have excellent mechanical properties which make them suitable for making full-featured items. SLS technology uses materials that are similar in properties to the brands of the final product: ceramics, powdered plastic, metal.
The 3D printer device looks like this: powder substances are applied to the surface of the elevator and sintered under the action of a laser beam into a solid layer that corresponds to the parameters of the model and determines its shape.
DLP technology
DLP technology is new to the 3D printing market. Stereolithographic printers are positioned today as the main alternative to FDM equipment. This type of printer uses digital light processing technology. Many people wonder what the 3d printer of this sample prints with?
Instead of a plastic filament and a heating head, photopolymer resins and a DLP projector are used to create three-dimensional figures.
Despite the intricate name, the device is almost indistinguishable from other desktop printers. Its developers, represented by
QSQM Technology Corporation, have already launched the first samples of high-tech equipment into a series. It looks like this:
HPM technology (FDM) HPM
Allows you to create not only models, but also final parts from standard, structural and high-performance thermoplastics. It is the only technology that uses production grade thermoplastics to provide unparalleled mechanical, thermal and chemical strength to parts.
It is the only technology that uses production grade thermoplastics to provide unparalleled mechanical, thermal and chemical strength to parts.
HPM Printing stands out for its cleanliness, ease of use and suitability for office use. Thermoplastic parts are resistant to high temperatures, mechanical stress, various chemicals, wet or dry environments.
Soluble auxiliary materials allow the creation of complex multi-level shapes, cavities and holes that would be problematic to obtain with conventional methods. HPM 3D printers create parts layer by layer by heating the material to a semi-liquid state and extruding it according to computer-generated paths.
When the 3D printer has finished creating the part, it remains to separate the auxiliary material mechanically, or dissolve it with detergent, after which the product is ready for use.
3D pens
Hand-printing pens are also popular these days. Moreover, it would be correct to call them not printing devices, but pens for drawing three-dimensional objects.
Moreover, it would be correct to call them not printing devices, but pens for drawing three-dimensional objects.
The pens are made in the same way as fusing printers. The plastic thread is fed into the pen, where it melts to the desired consistency and is immediately squeezed out through a miniature nozzle.
Applications for 3D printing
3D printing has opened up great opportunities for experimentation in areas such as architecture, construction, medicine, education, fashion design, small-scale production, jewelry, and even in the food industry. In architecture, for example, 3D printing allows you to create three-dimensional models of buildings, or even entire microdistricts with all the infrastructure - squares, parks, roads and street lighting.
Thanks to the cheap gypsum composite used, the cost of finished models is low. And more than 390 thousand CMYK shades make it possible to embody any, even the most daring, imagination of an architect in color.
3D printer: application in the field of construction
In construction, there is every reason to believe that in the near future the process of building buildings will be much faster and easier. Californian engineers have created a 3D printing system for large objects. It works on the principle of a construction crane, erecting walls from layers of concrete. Such a printer can build a two-story house in just 20 hours. After that, the workers will only have to carry out finishing work.
Medical Applications
In medicine, thanks to 3D printing technologies, doctors have been able to recreate copies of the human skeleton, which allows them to more accurately practice techniques that increase the guarantees of successful operations.
3D printers are increasingly being used in the field of prosthetics in dentistry, as these technologies allow much faster production of prostheses than with traditional manufacturing.