Plastic handgun 3d printer
3D printed guns - what kind of gun can be 3D printed and how it works
3D printing, a considerable shake-up in the gun industry
Advanced customization and low production costs are among the advantages of 3D printing for making firearms. Note that it is possible to 3D print gun parts such as the magazine or the handle. 3D printing the most important parts like the chamber or the barrel is a challenge.
The most credible option for homemaking a gun is by crafting a lower receiver as demonstrated in the Wired video below. The machine capable to turn an aluminum block into a gun part is a lot closer to a milling machine than a 3D printer.
To prove their expertise, some companies like Solid Concepts made metal 3D printed guns. Metal 3D printing technology is far too expensive and complex for individuals nowadays.
The most notable 3D printed firearms
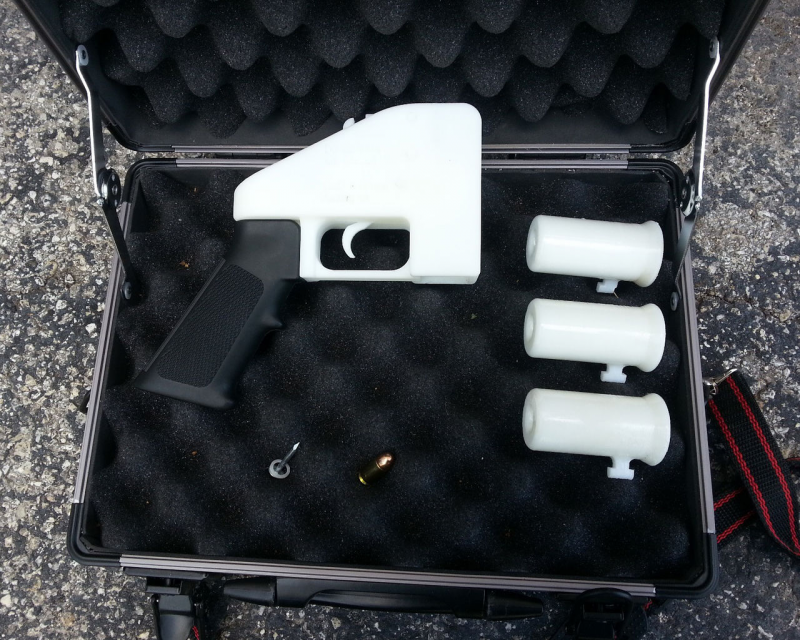
In May 2013, the first 3D-printed gun was test-fired by Cody Wilson. This plastic pistol was produced by internet activists Defense Distributed under the name ‘Liberator’.
The Liberator .038 is made out of 3D printed ABS, with the exclusion of a single nail used as the firing pin.
Cody Wilson, inventor of the 3D printed gun : “the Liberator”In August 2013, a Canadian man going by the name “Mathew” 3D printed an actual rifle, a Grizzly .22 Caliber Rifle model.
In September 2013, the Hexen organization produces the Reprringer Pepperbox .22 Revolver. The weapon can hold 5 bullets at once in its 3D-printed barrel.
In November 2013 Solid Concepts, now a Stratasys brand, 3D printed an operational metal gun.
The Browning 1911 Metal Replica fired more than 600 bullets without any damage to the gun.
In May 2014, Yoshitomo Imura 3D printed and fired a Zig Zag .38 Revolver. He was later arrested and convicted for owning four 3D-printed plastic pistols at his house.
Seized 3D printed plastic handguns displayed at Kanagawa police station in Yokohama, south of Tokyo, after Yoshitomo Imura’s arrest in 2014.In July 2014, a US citizen nicknamed “Buck O’Fama” 3D printed a receiver for a semi-automatic .22 Ruger Charger pistol.
The Ruger Charger accepts high-capacity mags holding 30 rounds or more. It is capable of shooting a full magazine without issues.
In May 2015, a man nicknamed Derwood, 3D printed the ‘Shuty’, a 9-mm semi-auto based on a combination of parts from a standard AR-15 and a P.A. Luty.
The design for the Shuty combines a metal bolt, an AR fire-control group, and the barrel of a Glock. The magazine, bolt carrier, upper and lower receivers are all 3D printed.
In September 2015, a college student named Chris, 3D printed a semi-automatic revolver called the ‘Yoshee Six Shooter’. The Yoshee Six Shooter is a revolver-style weapon that has multiple barrels and can fire multiple shots without reloading. It includes a 3D printed grip, hammer, spring, barrel, and barrel holder. A metal screw is used as a firing pin to strike the rim of the bullets.
The Yoshee Six Shooter is a revolver-style weapon that has multiple barrels and can fire multiple shots without reloading. It includes a 3D printed grip, hammer, spring, barrel, and barrel holder. A metal screw is used as a firing pin to strike the rim of the bullets.
In November 2015, an engineering student called James Patrick has built a 3D printable revolver that uses a rubber band and a nail to fire .22 bullets. The revolver called PM522 Washbear can hold six or eight bullets and can shoot them in a row. This is not the first 3D printed gun made by Patrick who also made a previous model (single shot) called the Songbird.
In January 2016, the now-famous Derwood, 3D printed a new gun of its design, the ‘Shuty MP-1’. This 3D printed gun is a 9 mm semi-automatic pistol made from 95% 3D printed parts.
However, the remaining components and most complex parts of the 3D printed gun are made of metal: store-bought Glock barrel, hammer, firing pin, bolts, and springs.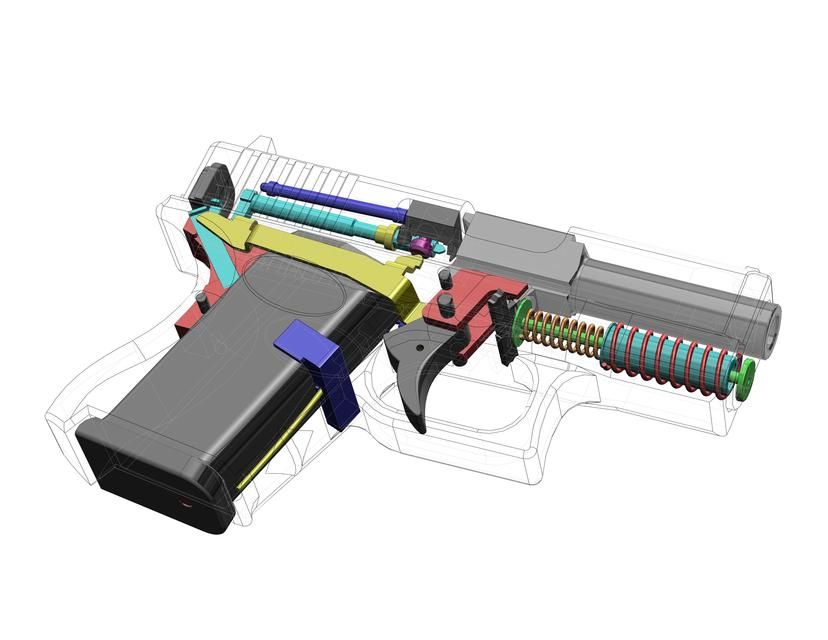 Derwood has been able to shot more than 600 hundred cartridges with his Shuty MP-1.
Derwood has been able to shot more than 600 hundred cartridges with his Shuty MP-1.
According to him, the plastic holding the barrel starts to melt after about 18 shots so it is better to let the gun cool off regularly.
The legal issues of 3D printing untraceable gun parts and 3D printing gun laws
Most gun parts (magazine, pistol grip, upper receiver) can be bought online without any tracking records. But the receiver stands out as one of the most complex and important parts.
The Ghost Gunner by Defense Distributed is a CNC milling machine capable of making AR-15 lower receivers. The AR-15 is like an AR-10 but uses smaller components for firing 0.223 caliber bullets. Like other CNC mills, the Ghost Gunner uses a digital file to carve objects out of aluminum.
The Ghost Gunner produces an unserialized AR-15 lower receiver from a pre-engineered aluminum part (called 80 percent lower) in a few hours.
As a consequence, the rifle itself is untraceable: it is a ghost gun. Which raises major legal and security issues…
Components of the AR-15 ghost gun made by Andy Greenberg, including the homemade lower receiver. Source: WiredIn 2013, the UK Home Office introduced stricter regulations on 3D printed guns and 3D printed firearms, making it highly illegal to create, buy, or sell them or 3D printed gun parts in Great Britain.
In November 2015, the parliament of the state of New South Wales, Australia, passed one of the strongest prohibition laws against 3D-printed guns. This law called Firearms and Weapons Prohibition Legislation Amendment Bill 2015, intends to penalize both physical and digital possession of 3D printable guns the same way as any illegally owned firearm holder. More information can be found in this 3D printing Industry article.
California passed a law in July 2016 requiring anyone who makes or assembles a homemade firearm to apply for a serial number or “other mark of identification” from the state Department of Justice.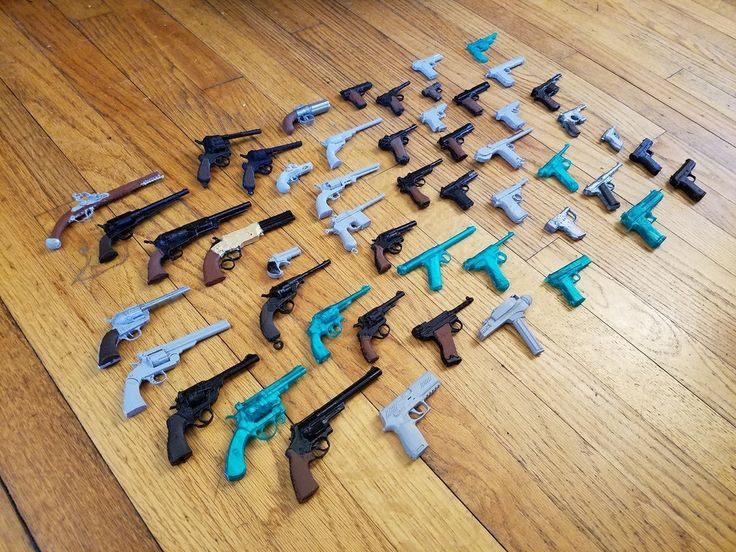
Around Asia, notable laws on 3D printed guns include Singapore, where possession of a 3D printed gun is punishable by death.
In 2017, China introduced the Chongqing regulation which required manufacturers involved in 3D printing to register with the government to help prevent 3D printing technology from being used to produce illegal items (including blueprints) such as firearms.
As of 1st August 2018, Defense Distributed is again allowed to publish designs for 3D printed guns after the US Department of State agreed to waive its prior 2015 restraint order against Cody Wilson and Defense Distributed. Therefore individuals are allowed to freely publish designs and other technical files about 3D printed guns in the United States.
I 3D-Printed a Glock to See How Far Homemade Weapons Have Come
ST.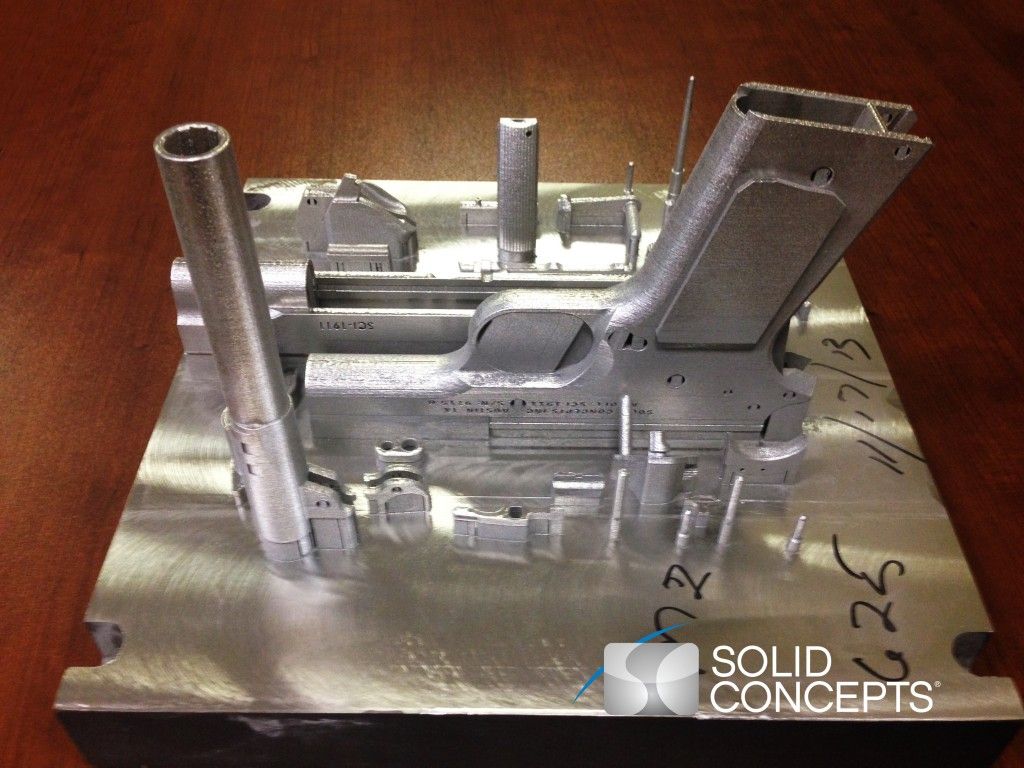 AUGUSTINE, Florida — The fully-automatic “Scorpion” submachine gun can burn through a 30-round clip of 9mm ammo in a matter of seconds with one steady pull of the trigger. It looks, feels, and shoots just like a factory-made gun—except part of this one came off a 3D printer.
AUGUSTINE, Florida — The fully-automatic “Scorpion” submachine gun can burn through a 30-round clip of 9mm ammo in a matter of seconds with one steady pull of the trigger. It looks, feels, and shoots just like a factory-made gun—except part of this one came off a 3D printer.
According to the Scorpion’s maker, the material used to 3D-print the frame (the heart of the gun, where the metal barrel and other parts all come together) is actually “on par or stronger” than the off-the-shelf equivalent. I’d never fired a full-auto weapon before—let alone one made partly of plastic—and when I took aim and squeezed the trigger, the Scorpion unleashed a wild spray of bullets that missed my target and thumped into a mound of dirt behind the firing range.
Advertisement
The Scorpion was one of many jaw-dropping weapons on display in late June at a Florida event dubbed the “Gun Maker’s Match,” the first-ever shooting competition exclusively for home-assembled firearms. Except for the machine gun, which requires a special federal license, these are a species of “ghost gun,” meaning there are no serial numbers and thus no easy way for authorities to track down the owner or manufacturer.
The shooting contest was put on by a non-profit called Guns For Everyone National, with help from the digital gun building collective Are We Cool Yet? or AWCY, which has been pushing the envelope of what’s possible with 3D-printed arms.
To meet these gunmakers and get a true sense of what 3D-printed guns are capable of these days, I decided to enter the shooting contest in Florida—and build my own ghost gun.
Although the technology has radically evolved in recent years, the best-known 3D-printed gun is still The Liberator, the first one ever created, in 2013. A single-shot, snub-nose pistol, The Liberator resembled a postmodern “Saturday night special,” something just as likely to blow your hand off as fire an actual bullet. These days, beyond the Scorpion, AWCY has created and released plans for a 3D-printed “battle rifle” and under-barrel flare guns that are just a few millimeters away from the military’s “RAMBO” model 3D-printed grenade launcher.
Advertisement
News
People Are Panic-Buying Untraceable ‘Ghost Guns’ Online in the Coronavirus Pandemic
Tess Owen
The most common and controversial ghost guns cost a few hundred dollars online and come “80 percent” finished in a box with all the necessary tools. The sudden proliferation of these cheap, mail-order ghost guns has prompted alarm among law enforcement nationwide. Nearly 24,000 “privately made firearms” were recovered at crime scenes from 2016 to 2020, according to a recently leaked Department of Justice report, and the number of cases where felons and other “prohibited persons” were found with such guns doubled in a single year.
Ghost guns have also turned up in the hands of white supremacists and far-right extremists. A self-proclaimed Boogaloo Boi pleaded guilty last month to possession of 3D-printed machine gun parts and a homemade silencer. The DOJ report, issued June 22 and verified by The Trace, warned of individuals with “racially or ethnically motivated violent extremist ideologies” sharing 3D-printed machine gun files.
Advertisement
To meet these gunmakers and get a true sense of what 3D-printed guns are capable of these days, I decided to enter the shooting contest in Florida—and build my own ghost gun.

Only ten states plus Washington, DC, have local laws that attempt to regulate ghost guns. They are virtually unregulated federally, but the Biden administration has proposed new rules that would require serial numbers on certain unfinished parts and restrict mail-order kits, which the president singled out in an April speech at the White House.
“The buyers aren’t required to pass a background check to buy the kit to make the gun,” President Joe Biden said. “Consequently, anyone from a criminal to a terrorist can buy this kit and, in as little as 30 minutes, put together a weapon.”
But building a 3D-printed gun from scratch, as I learned, takes a lot longer than half an hour. And while there’s evidence of extremists and criminals seeking to exploit the untraceability of ghost guns, there is also a nerdy group of designers and tinkerers who insist they are strictly abiding by gun laws and enjoying a “very loud” hobby.
Shopping for the Ghost Gun
Having never owned a 3D-printer or a gun, I started as a blank slate. Rob Pincus, a personal defense instructor and gun rights advocate, agreed to lend expertise and a 3D-printer. He warned the printing and building process would take at least two days, which he said contradicts the notion that it’s easy for people who want to misuse guns to simply 3D-print one.
Rob Pincus, a personal defense instructor and gun rights advocate, agreed to lend expertise and a 3D-printer. He warned the printing and building process would take at least two days, which he said contradicts the notion that it’s easy for people who want to misuse guns to simply 3D-print one.
“You have to want to do it this way,” Pincus said. “I don't know who the person is that falls into the weird zone where they don't want to buy a gun, they can't buy a gun, but they really want a gun and this is the path of least resistance, as opposed to finding somebody to buy a gun for them or buying a gun illegally out of somebody's trunk somewhere.”
Advertisement
My initial aim was to build AWCY’s Scorpion, which can be legally 3D-printed and assembled in semi-auto (one bullet per trigger squeeze) in most places. But Pincus dashed my Scorpion dreams.
For one thing, it takes multiple days of 3D-printing to make one, which was time I didn’t have before the match. There’s also a shortage of ghost gun parts on the internet—in part due to a recent buying spree amid the Biden’s administration efforts to tighten the laws.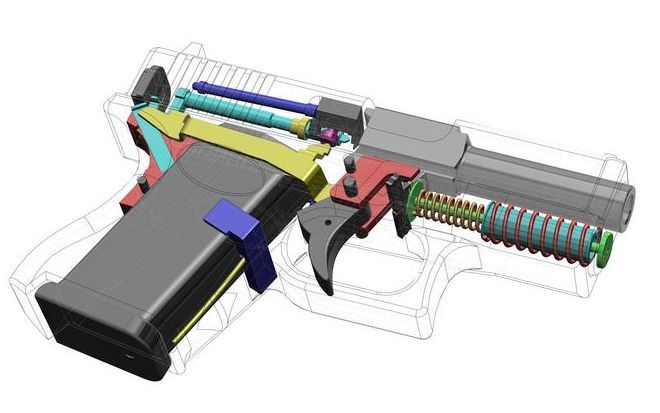
Without metal parts, the Scorpion would not work. While 3D-printed plastic is strong enough to serve as the frame of the gun, it won’t hold up as a barrel or bolt. It would also be illegal, since federal law requires guns to have at least one metal component.
The author's 3D-printed Glock 19 9mm pistol with the words "Ghost Gun" on the grip. (Photo by Keegan Hamilton / VICE News)
“You need the metal parts,” Pincus told me. “Technically, could you build one out of all plastic? Yes. Is it going to be reliable and awesome? Probably not.”
I ultimately settled on the Glock 19, as its essential parts were readily available online. The barrel, slide, trigger assembly, and other metal bits cost around $320, shipped directly to the gun range in Florida hosting the match, along with a $23 spool of PLA+ filament. That plus a standard 3D-printer and a couple boxes of 9mm ammo was almost all I needed.
Printing the Gun
The Glock design, along with plans for hundreds of other guns, is accessible through a website called DEFCAD. It’s hosted by a company called Defense Distributed, led by Cody Wilson, inventor of the first 3D-printed gun. The files can be found elsewhere online, but Wilson’s site makes the repository easy to browse in a store-like user interface, and users must pay a $50 annual membership for access.
It’s hosted by a company called Defense Distributed, led by Cody Wilson, inventor of the first 3D-printed gun. The files can be found elsewhere online, but Wilson’s site makes the repository easy to browse in a store-like user interface, and users must pay a $50 annual membership for access.
For years, the U.S. government tried to limit sharing of 3D-printed gun blueprints through the State Department’s powers over international arms exports. Wilson fought back on First Amendment grounds, and in April the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals issued a ruling that indefinitely lifted restrictions on publishing 3D-printed gun blueprints.
Advertisement
When I asked Wilson if U.S. authorities could ever hope to totally block the files from being shared online, he replied: “The government should invent a time machine and kill me seven years ago. It's far too late now. The equipment—the 3D printing, it's so cheap. You can make anything. You can design anything.”
For years, the U.
S. government tried to limit sharing of 3D-printed gun blueprints through the State Department’s powers over international arms exports.
Wilson is a polarizing figure in the gun world. In 2018, he was arrested and accused of sexually assaulting a 16-year-old girl he met through SugarDaddyMeet.com. He pleaded guilty to injuring a child, a third-degree felony, and received seven years of probation. In addition to hosting 3D-gun files, Wilson also sells a machine called The Ghost Gunner, which helps convert unfinished parts into AR-15s and other guns.
“The files are literally everywhere in a perfect fluid explosion on the internet,” Wilson said. “It's not supposed to be legal, and yet we found a way to make it legal.”
To get the files from Wilson’s site, I had to verify my identity and sign up for a membership, bringing the total gun budget to just under $400, still cheaper than a brand-new Glock. But when my frame came off the printer (a 16-hour process), there were a few glaring differences. For one, mine did not have a serial number; instead it had the words “Ghost Gun” literally printed on the handle. It was also rough around the edges, not yet ready for the metal parts to be inserted.
For one, mine did not have a serial number; instead it had the words “Ghost Gun” literally printed on the handle. It was also rough around the edges, not yet ready for the metal parts to be inserted.
Advertisement
It took another four hours and change to sand down the plastic using metal filing tools, a drill, and an electric Dremel grinder. Pincus patiently guided me as I stumbled through the process, which was harder than it seemed on the instructional videos I’d seen on YouTube. The finished product was white on the bottom (my “Ghost Gun”-emblazoned frame) and black on top, with a factory-made barrel and slide. Pincus assured me it was safe to test fire.
Shooting the Ghost Glock
On the shooting range, the plastic ghost Glock felt heavy in my hand. There are videos of 3D-printed guns splintering into pieces during test fires, and I was a little nervous as Pincus coached me on posture and grip. I squeezed the trigger and the first round pinged off a metal target 15 yards away. The gun worked, but not perfectly. All the grinding to make the metal parts fit together caused a jamming issue. More work with the Dremel tool helped, and after several more test fires, Pincus deemed the gun ready for competition.
The gun worked, but not perfectly. All the grinding to make the metal parts fit together caused a jamming issue. More work with the Dremel tool helped, and after several more test fires, Pincus deemed the gun ready for competition.
The match in Florida drew around 50 entrants, almost exclusively white and male, with a couple dressed in full-camo. The mood was more carnival than militia gathering, with everyone gawking at each other’s guns and some online-only friends meeting face to face for the first time. There were multiple contest categories, ranging from kit guns to weapons entirely 3D-printed with homemade metal components. Contestants were judged on a combination of speed and accuracy, maneuvering through courses and shooting at stationary targets.
Advertisement
“This is really what we want to be the first of many celebrations of what I call a freedom hobby,” Pincus said, addressing the crowd. “For some of us, it's, ‘Hey, I want to make my own gun. I don’t want the government involved. ’ For some of us, it's ‘I want a custom gun that has my logo or my name or my grip angle or whatever’... for other people, it's, ‘I want to create designs that never existed before and share them with all of Earth.’”
’ For some of us, it's ‘I want a custom gun that has my logo or my name or my grip angle or whatever’... for other people, it's, ‘I want to create designs that never existed before and share them with all of Earth.’”
Leading the push to create wholly unique 3D-gun designs is Darren “Derwood” Booth, a chain-smoking West Virginian who told me he likes living in a rural area because he can step out his front door and test-fire new designs whenever he pleases. His latest work is called the King Cobra, which is virtually indistinguishable to the untrained eye from a factory-made assault weapon. A 9mm “pistol caliber carbine” like the Scorpion, the King Cobra is totally original and homemade, emblazoned with a skull and lightning-bolts symbol Derwood borrowed from Quentin Tarantino’s film “Death Proof.”
Rob Pincus (right) and Xander Guetzloe, a moderator of the group Are We Cool Yet?, address the crowd at the "Gun Maker's Match" shooting competition in Florida in June 2021. (Photo by Keegan Hamilton / VICE News)
Derwood posts his files online for anyone to download or modify, and says he does not profit from his work. “I haven’t ever made a dime off of it,” he told me. “I've invested thousands just in the hobby, but no, I haven't made a red cent.”
“I haven’t ever made a dime off of it,” he told me. “I've invested thousands just in the hobby, but no, I haven't made a red cent.”
Derwood’s designs are showing up all over the world, including in countries where 3D-printing now threatens to undermine strict gun control laws. His work was the basis for another “pistol caliber carbine” called the FGC-9 (short for Fuck Gun Control 9mm), wielded last year by an anonymous masked man in a documentary about the rise of 3D-printed guns in Europe.
Advertisement
“I’m not so happy with that,” Derwood said. “Because, hey, they have laws over there. Obey your local laws. I’m not encouraging anybody to do anything illegal.”
Art That Can Kill
Some plastic gunsmiths argue their work is shielded not only by the right to bear arms but also the First Amendment’s right to freedom of expression, since their guns are works of art. The group AWCY, which organized the Florida shooting contest, handed out stickers with the silhouette of their 9mm Scorpion and the motto “Art is not meant to be contained. ”
”
Xander Guetzloe, a moderator for AWCY, brought a Scorpion to the Florida match that he modified to make it look like the barrel spits fire from a dragon’s mouth.
“Art is in the eye of the beholder, right? This is just a way of expressing ourselves,” Guetzloe said. “It's freedom of expression in a much louder way.”
Guetzloe estimated that AWCY has about 500 members, with 200 actively working on gun design projects in the group’s online forum. The members, he said, include “lawyers, technical writers, plumbers, electricians, just a little bit of everybody,” each lending their own expertise.
AWCY’s aesthetic is vaguely hipster and intentionally low-brow, with guns modified to look extra phallic or with Nerf-style neon colors. They tease new 3D-gun file releases on a well-curated Instagram feed, often finding inspiration in classic weapons that have cult followings. Guetzloe, who has a day job in IT, worked on creating a 3D-printed CETME, a “battle rifle” that’s seen combat in conflicts around the world.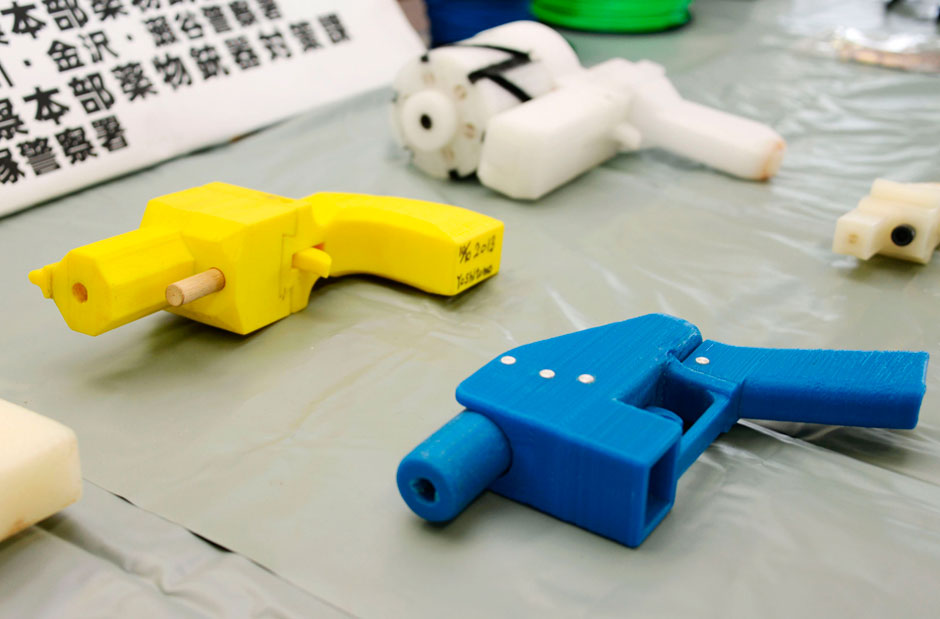
Advertisement
“Art is in the eye of the beholder, right? This is just a way of expressing ourselves,” Guetzloe said. “It's freedom of expression in a much louder way.”
When I pointed out that most art isn’t also a deadly weapon, Guetzloe replied, “It could be used for harm. But I feel like most people that are going to do that are going to go out and steal one. The amount of effort that you put into these, you're not going to do that just to go and do someone harm.”
Even after 22 hours of work, my gun didn’t work properly. At the competition, it jammed repeatedly, and I was unable to finish round one of the contest. Pincus suggested swapping on a Glock-brand slide and barrel, which he had on hand. The factory part plus a little bit of gun oil made all the difference.
I loaded a clip into the gun and racked the new slide, which smoothly locked into place. Taking aim at a target, I squeezed off a few rounds in a row. The spent shell casings popped out of the chamber and were instantly replaced by fresh bullets; my semi-automatic gun finally worked semi-automatically. To test what it could do, I unloaded the rest of the clip rapid-fire—boom-boom-boom-boom. There were no jams. It worked (almost) like a real Glock.
The spent shell casings popped out of the chamber and were instantly replaced by fresh bullets; my semi-automatic gun finally worked semi-automatically. To test what it could do, I unloaded the rest of the clip rapid-fire—boom-boom-boom-boom. There were no jams. It worked (almost) like a real Glock.
Law Enforcement Isn’t Thrilled With 3D Guns
Making a fully-functioning semi-auto handgun from plastic and a few metal parts, it turns out, is totally legal (at least in Florida), but there are other applications for 3D-printing beyond guns that are troubling for law enforcement. Federal gun laws are enforced by the Bureau of Alcohol Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives (ATF), and it’s the explosives aspect of the agency’s mission that is increasingly overlapping with 3D-printing.
John “J.D.” Underwood, the special agent in charge of the ATF’s National Center for Explosives Training and Research, told me that 3D-printed land mines are already a possibility. He showed me a 3D-printed “bomblet,” which could be attached to a drone and dropped from the sky.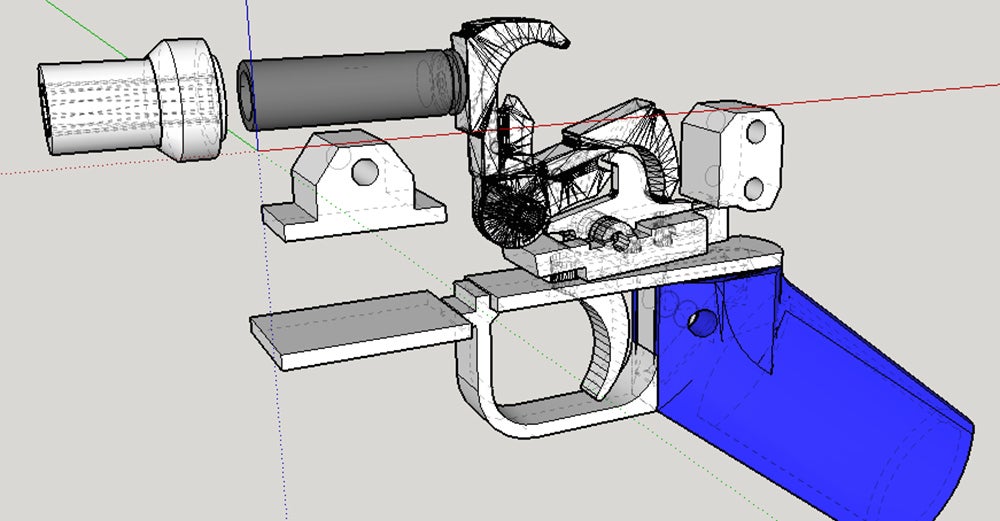 Such devices, he said, have already been used against U.S. troops in the Middle East.
Such devices, he said, have already been used against U.S. troops in the Middle East.
Advertisement
“Nobody or anything's stopping somebody from making this in the United States today,” Underwood said, holding up the miniature plastic bomb in his hand.
When I asked Guetzloe, the AWCY moderator, about the group’s 37mm launcher, he told me the sole purpose is for firing signal flares. But the under-barrel tube version looks very similar to the military equivalent, a 40mm grenade launcher adapted by the Army for 3D-printing in order to save taxpayers money by lowering production costs.
Underwood was impressed with the designs on display at the Florida shooting match, and he stressed that the ATF has no problem with law-abiding gunmakers using 3D-printers.
“As long as they're used for their intended purposes by people that legally can have firearms, I don't have an issue with that,” he said. “It's when people use those firearms for criminal purposes, that's when it becomes a problem. ”
”
Last December, ATF agents raided the offices of Nevada-based Polymer80, the largest ghost gun company and seller of a popular “Buy Build Shoot” kit. No charges were filed and no employees were arrested, and the company continues to advertise pistol kits, though all the options are currently out of stock.
Advertisement
Polymer80 also faces civil lawsuits, most recently from two Los Angeles County sheriff’s deputies who sued the company for selling an “untraceable home-assembled” Glock kit that was later used by a gunman who seriously wounded them in a Compton shooting. The deputies allege the company “purposefully sold their products without markings to make it difficult for law enforcement to trace the firearm.”
“Untraceable ghost guns are now the emerging guns of choice across the nation.”
The gun control group Everytown Law is also suing Polymer80 and other ghost gun makers. One case, which also involves the city of Los Angeles, accuses the company of creating a public nuisance and violating California’s business code. According to the LAPD’s chief, 700 ghost guns seized in the city last year were made from Polymer80 parts, including more than 300 in South LA, where homicides have been on the rise.
According to the LAPD’s chief, 700 ghost guns seized in the city last year were made from Polymer80 parts, including more than 300 in South LA, where homicides have been on the rise.
“Untraceable ghost guns are now the emerging guns of choice across the nation,” LA City Attorney Mike Feuer said when announcing the lawsuit in February. “Nobody who could buy a serialized gun and pass a background check would ever need a ghost gun. Yet we allege Polymer80 has made it easy for anyone, including felons, to buy and build weapons that pose a major public safety threat.”
Advertisement
A Polymer80 spokesperson did not respond to requests for comment.
The company’s website states there is “a strict policy against selling 80% lower receivers to persons known to us to be convicted felons or otherwise prohibited persons.”
It also says building a gun from a kit provides customers with “a fun learning experience and a greater sense of pride in their completed firearm.”
Melting the Ghost Gun
I’d be lying if I didn’t say I was slightly proud (and more than a little terrified) of my ghost Glock.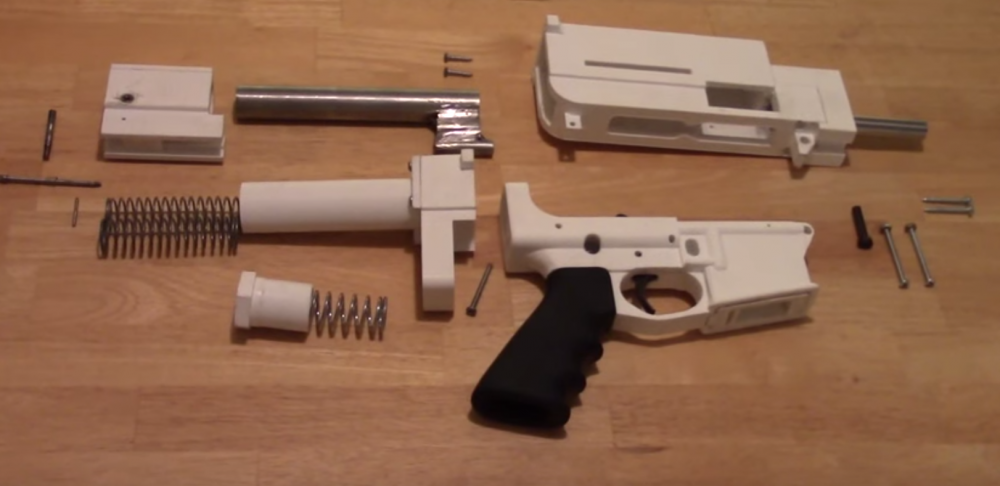 I somehow ended up taking third place in the 3D-printed pistol category. Just like me, some of my competitors seemed to spend more time behind a computer screen than at the firing range. I was told some shooting clubs prohibit ghost guns or 3D-printed guns, making it difficult to find a place for target practice. And reliability was clearly an issue, as many people—even the most advanced builders—suffered malfunctions and jams. The guns may look badass, but they don’t yet quite stack up evenly to the real thing.
I somehow ended up taking third place in the 3D-printed pistol category. Just like me, some of my competitors seemed to spend more time behind a computer screen than at the firing range. I was told some shooting clubs prohibit ghost guns or 3D-printed guns, making it difficult to find a place for target practice. And reliability was clearly an issue, as many people—even the most advanced builders—suffered malfunctions and jams. The guns may look badass, but they don’t yet quite stack up evenly to the real thing.
But as 3D-printing technology improves, making a 100% DIY ghost gun will become easier and easier. Even if there's a ban on “80 percent” kits, anyone with access to a printer, a few hundred dollars, and some free time will still be able to crank out a semi-auto pistol, one with no paper trail to identify the owner. In the eyes of Pincus and others at the shooting match, this is actually a good thing.
“I know this is counterintuitive for a lot of people, but the more people who have guns, the more normal gun ownership is, the more responsible the community will be and also the more educated the community will be in judging responsibility,” Pincus said. “I don't think everybody should have a gun. I think everybody who wants to be a responsible gun owner should have that option.”
“I don't think everybody should have a gun. I think everybody who wants to be a responsible gun owner should have that option.”
Since I live in California, one of the states that regulates ghost guns like other firearms, I would need to register my gun with local authorities. Such laws, however, have done little to contain ghost guns. Last week, the city of San Francisco sued three companies that sell do-it-yourself ghost gun kits, alleging they target buyers who are banned from owning guns and want to evade background checks.
“Ghost guns are a massive problem in San Francisco—they are becoming increasingly involved in murders, attempted murders, and assaults with firearms,” said San Francisco District Attorney Chesa Boudin. “We know that the rise in gun violence is connected to the proliferation of, and easy access to, guns that are untraceable, guns that are easier to obtain by people who would be otherwise prohibited by law from getting them.”
I have no interest in owning a handgun—let alone one with “Ghost Gun” on the handle—so I decided to melt down the frame and return the gun to its original form: molten plastic.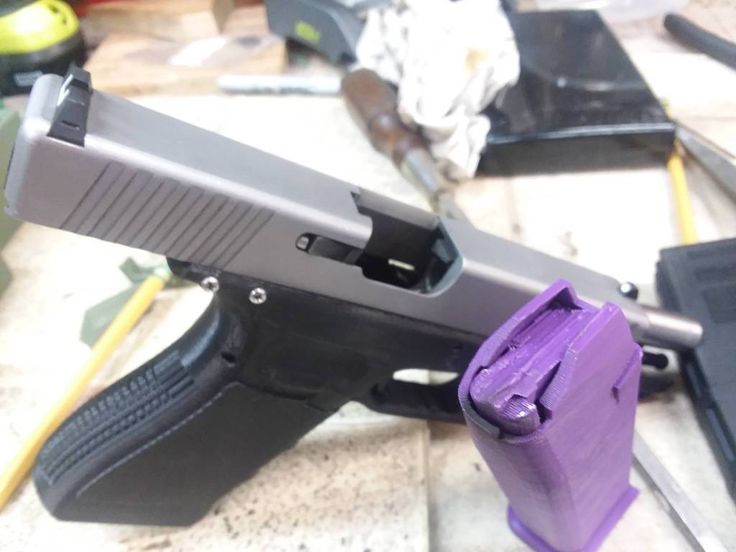
Miguel Fernández-Flores contributed reporting.
is it possible to print pneumatic and firearms
Is it possible to make a gun on a 3D printer and is it legal?
Today's 3D printers offer enormous possibilities. They can print products of almost any complexity. Until quite recently, it was difficult to even imagine that a plastic weapon could shoot. However, it is already possible to make a pistol on a 3D printer, which, although not reliable, still fires live ammunition. nine0003
Can firearms be 3D printed?
Back in 2013, a young American gun fighter proved that plastic guns could be 3D printed. He was the first in the world to make a pistol in this way, in which only the striker was made separately from metal. All other parts were printed on an FDM printer.
Today's 3D printers are capable of printing any CAD model, and these models of firearms have been available for over 10 years. If in previous years their printing required professional skills, now almost any user can master them. With a 3D printer and a finished model, it became quite possible to print a gun. Another thing is that such "creativity" is punishable by the laws of most countries. nine0003
If in previous years their printing required professional skills, now almost any user can master them. With a 3D printer and a finished model, it became quite possible to print a gun. Another thing is that such "creativity" is punishable by the laws of most countries. nine0003
The evolution of 3D printed weapons
Despite all the prohibitions and restrictions, the evolution of 3D printed firearms is moving at a great speed. The beginning was laid by the single-shot plastic pistol Liberator of the American K. Wilson, which appeared in 2013. It had a simple design and was chambered for 380 ACP. Already after 10-12 shots, this weapon became unusable. However, the very possibility of printing firearms served as an impetus for the development of the idea. The author of the first pistol himself founded the Defense Distributed company, which began to actively improve the technology. nine0003
One of the ways to increase the durability of weapons was to increase the number of their barrels. At the beginning of 2014, the Japanese Y. Imura makes a 38 caliber Zig Zag pistol. He was able to fire up to 6 shots non-stop. The author of the weapon was recognized as a criminal and convicted.
At the beginning of 2014, the Japanese Y. Imura makes a 38 caliber Zig Zag pistol. He was able to fire up to 6 shots non-stop. The author of the weapon was recognized as a criminal and convicted.
The next step was the production of a six-shot revolver by J. Patrick in 2015. The PM522 Washbear has been shown in action on YouTube. The weapon was noticeably safer for the shooter compared to previous versions, but still allowed to fire only a few dozen rounds. nine0003
The first semi-automatic pistol for a 9 mm bullet appeared in 2016 under the name Shuty-MP1. It was developed by a handicraft gunsmith who hid under the pseudonym Derwood. It wasn't exactly a plastic weapon. The author used some metal parts from factory pistols - a barrel, a firing pin, a bolt and several springs. This made it possible to ensure a rate of fire of more than 46 rounds / min. However, when changing the store, the plastic case had to be cooled. In 2017, the same master proposed an improved model - Shuty AP-9.
The main contribution to the development of 3D printed weapons technology was made by Defense Distributed, which united a group of like-minded activists. First, these enthusiasts won legal proceedings in the United States and obtained permission to 3D-print weapons, which greatly expanded their capabilities. Secondly, they were able to set up a professional business with product testing and quality control. As a result, in 2018–19 they developed numerous models of a variety of firearms - from pistols to carbines. They posted over 30 files for printing original gun parts. Most of them were plastic, and the metal parts were not made from purchased, ready-made elements, but from simple metal profiles (tubes, strips, etc.), which are sold in ordinary hardware stores. This made it possible to exclude the use of parts patented by gunsmiths. nine0003
At the moment, the semi-automatic carbine FGC-9, developed on the basis of the Shuty AP-9, has become the pinnacle of "creativity" of Defense Distributed. At the same time, there is not a single factory part in it. The barrel for the 9 mm cartridge is made of steel pipe using electrochemical processing.
At the same time, there is not a single factory part in it. The barrel for the 9 mm cartridge is made of steel pipe using electrochemical processing.
Where can I get drawings and what should I look for?
Gun manufacturing bans make it much harder to get blueprints and models of guns for 3D printing. The right to free placement of information was achieved only by Defense Distributed. Their website provides free access to drawings, models and technologies. Other information can be found on the Internet, but they are usually illegal. nine0003
When choosing a model, pay attention to the following information:
- material used;
- cartridge for which the model is designed;
- number of cartridges in the magazine, rate of fire;
- operating time before failure.
It is important to clarify which metal parts will need to be purchased separately, in addition to plastic for printing on a printer.
What does the law say in different countries?
The only country where firearms can be 3D printed is the United States. Gun Control Act 19 applies here68, giving Americans the right to make weapons, but only for personal use. Only one limitation is put forward: it must be determined by metal detectors, that is, it must have a metal element. In virtually all other countries, homemade manufacture and repair of weapons for any purpose is prohibited by law. In Russia, printing it on a 3D printer falls under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and is punishable by imprisonment.
Gun Control Act 19 applies here68, giving Americans the right to make weapons, but only for personal use. Only one limitation is put forward: it must be determined by metal detectors, that is, it must have a metal element. In virtually all other countries, homemade manufacture and repair of weapons for any purpose is prohibited by law. In Russia, printing it on a 3D printer falls under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation and is punishable by imprisonment.
Should we be afraid of plastic weapons?
The question of how dangerous a weapon printed on a printer is becoming increasingly important. Despite all the prohibitions, it is extremely difficult to control the spread of technology around the world. The availability of 3D printers and the increase in their functionality make it possible to master the production of plastic guns at home. How dangerous is such a weapon? nine0003
Most experts agree that currently printed weapons are more of an interesting toy. It is quite expensive and is designed to carry out only a few dozen shots. Moreover, such pistols are quite dangerous for the shooter himself with live ammunition, because they can explode in their hands.
Moreover, such pistols are quite dangerous for the shooter himself with live ammunition, because they can explode in their hands.
However, the danger cannot be underestimated. It is easier and cheaper for a "serious" criminal to buy illegal military weapons than to make them on a printer. At the same time, there may be "enthusiasts" who, for their own interest, can make a pistol and try it out in action. Such inadequate people represent an undoubted danger. In addition, the temptation is great for terrorists. Metal detectors do not detect a plastic gun, which means that it is easier to carry it, for example, on an airplane. nine0003
Important! Plastic weapons have a very small resource. At the same time, sometimes just one shot is enough to kill a person.
3D printed firearms have the following advantages:
- the ability to make military weapons at home;
- light weight;
- availability of materials;
- Ability to copy famous weapon models.
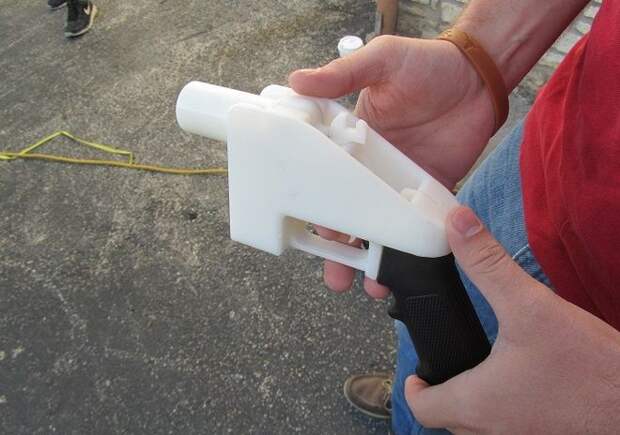

Always remember that there are significant disadvantages:
- illegal production;
- high cost of weapons;
- very small resource and limited rate of fire;
- danger to the shooter himself.
Currently, plastic weapons have more disadvantages than advantages, and most importantly, you can get a real prison term for making them.
Prospects for printing weapons
The potential for 3D printing of firearms is far from exhausted. The expansion of equipment capabilities and the development of innovative materials indicate that in the near future such weapons may approach military weapons in terms of characteristics. In the future - a significant increase in the resource and the provision of automatic firing. nine0003
Significantly increases the reliability of printed pistols and carbines SLS technology using metal powder. Such weapons already differ little from the factory metal models. While it is very expensive, which significantly limits the application. However, over time, the material will become cheaper, which means it will become more affordable.
However, over time, the material will become cheaper, which means it will become more affordable.
Printing firearms on a 3D printer has become a reality. Despite its extremely low performance and reliability, interest is growing in it. Experts predict that the printing of weapons will become widespread, and it is impossible to stop such production. There comes a time when measures should be taken at the legislative level to establish effective control over this process. nine0003
- March 21, 2021
- 4833
Get expert advice
3D printer gun | Weapons printed on a 3D printer
With the help of 3D printing, you can make not only harmless souvenirs and trinkets. People did not limit themselves to the necessary mechanisms and things. Legislators were seriously worried, because enterprising designers and inquisitive minds tried to print weapons. And not just a model for cosplay, but a real one, capable of firing live ammunition. But most importantly, they succeeded! Therefore, it was necessary to introduce restrictions at the legislative level for the safety of people. nine0003
And not just a model for cosplay, but a real one, capable of firing live ammunition. But most importantly, they succeeded! Therefore, it was necessary to introduce restrictions at the legislative level for the safety of people. nine0003
Weapons were printed not only by professional devices capable of metal printing. And quite ordinary ones, printing using FDM technology. At the same time, it was possible to print not only prototypes of existing weapon models, but also to develop completely unique models.
3D printed weapons - analogues
The most well-known variants of weapons analogues printed in whole or in part are:
- Сolt M1911 from Solid Сoncepts
- Replica of the grizzly .22 hunting rifle, made of plastic by a Canadian with the pseudonym "Matthew"
- Horns for AK 47 and AR-15 - Feinstein from Defense Distributed
- Parts for AK-47
Concept3d printable Solt M1911 printer. For this, an alloy of chromium, nickel and molybdenum called Inconel 625 was used.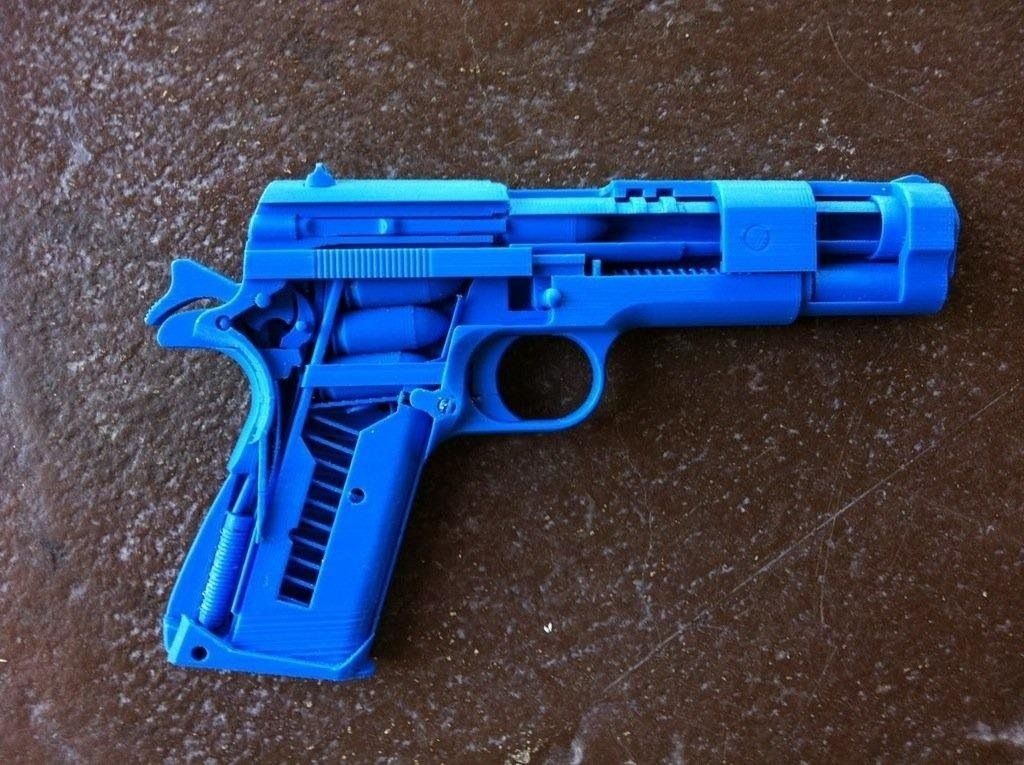 2000 shots can be fired from this weapon. In this case, the number of misfires will be minimal.
2000 shots can be fired from this weapon. In this case, the number of misfires will be minimal.
A grizzly .22 plastic hunting rifle capable of firing 14 rounds, after which its barrel becomes unusable. The weapon was built through trial and error on a Stratasys Dimension 1200e. nine0003
Other legally restricted options are hybrid systems of existing firearms.
New Designs
Many have gone further and have not tried to print existing models of weapons, but have tried to create new unique models. The most famous among them are:
- Liberator and Lulz Liberator
- Shutu-MP1
- Reprringer Pepperbox
The very first additive pistol was the Liberator. This iconic weapon appeared in 2013. It is completely printed on a Stratasys Dimension SST 3D printer, and its cost is about $10. The drawings of this device were freely available. The disadvantages of this weapon were that it gave a lot of misfires, and was only capable of one shot. The shortcomings have been eliminated in the improved Lulz Liberator model. This plastic pistol is capable of firing up to 8 shots. Now the drawings are removed from the public domain. And the distribution and printing of Liberator is prohibited by law, although you can find a photo of it without problems. nine0003
The disadvantages of this weapon were that it gave a lot of misfires, and was only capable of one shot. The shortcomings have been eliminated in the improved Lulz Liberator model. This plastic pistol is capable of firing up to 8 shots. Now the drawings are removed from the public domain. And the distribution and printing of Liberator is prohibited by law, although you can find a photo of it without problems. nine0003
There is a video on the Internet that shows the tests and characteristics of the combat Shut-MP1. This is a half-printed firearm, meaning it consists of an AR15 receiver and a printed plastic module.
Non-combat printed weapons
This is not about cosplay, but about other options, such as, for example, airsoft guns and air guns. The printing of such weapons can be carried out on conventional FDM printers. At the same time, there are samples of air rifles printed on 3D printers. This weapon may well be used even in competitions, and it is even capable of outperforming many analogues produced using classical technologies.