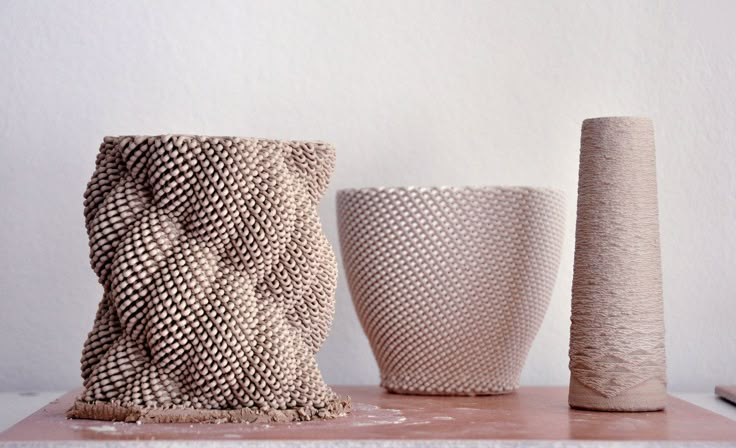
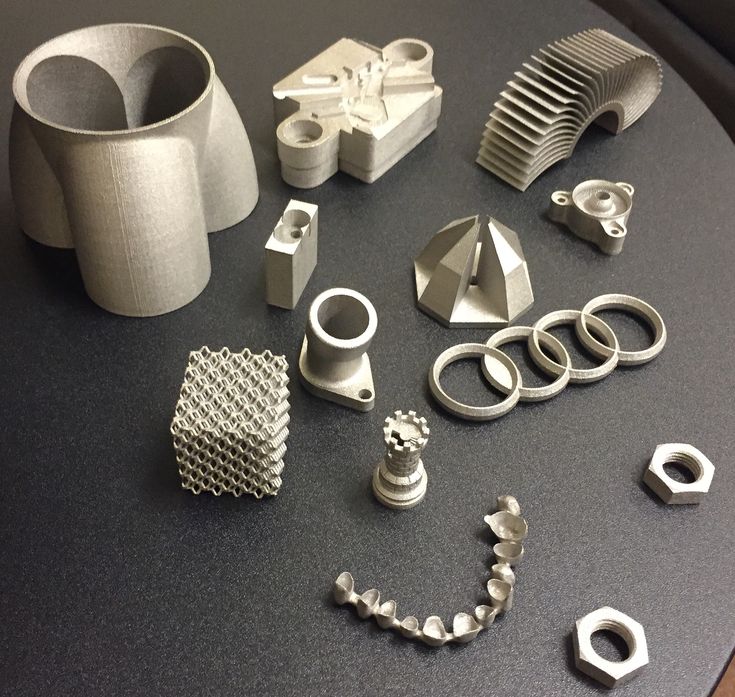
Best material for 3d printing
Ultimate Materials Guide - Tips for 3D Printing with PETG
Overview
PETG is a Glycol Modified version of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), which is commonly used to manufacture water bottles. It is a semi-rigid material with good impact resistance, but it has a slightly softer surface which makes it prone to wear. The material also benefits from great thermal characteristics, allowing the plastic to cool efficiently with almost negligible warpage. There are several variations of this material in the market including PETG, PETE, and PETT. The tips in this article will apply to all of these PET-based filaments.
- Glossy and smooth surface finish
- Adheres well to the bed with negligible warping
- Mostly odorless while printing
- Poor bridging characteristics
- Can produce thin hairs on the surface from stringing
Hardware Requirements
Before 3D printing with PET / PETG make sure your 3D printer meets the hardware requirements listed below to ensure the best print quality.
Bed
Temperature: 75-90 °C
Heated Bed Recommended
Enclosure Not Required
Build Surface
Glue Stick
Painter’s tape
Extruder
Temperature: 230-250 °C
No special hot-end required
Cooling
Part Cooling Fan Required
Best Practices
These tips will help you reduce the chances of common 3D printing issues associated with PET / PETG such as stringing, oozing, and poor bed adhesion.
Invest In a Good Build Surface
Some 3D printers come with a glass bed or blue painter’s tape installed on the bed. Although these surfaces might work fine for PETG, we recommend using a heated build platform for best results. The heated bed can significantly improve the first layer adhesion, making things much easier for future prints. Many of these heated beds come with a glass surface, allowing you to print directly on the bed without needing to apply any additional layers of tape or glue.
Calibrate Retraction Settings to Reduce Stringing
One of the few common issues that we see with PETG is stringing. These strings are thin hairs, similar to a spider web, that run between the different surface of your 3D print. Preventing these strings requires precisely calibrated retraction settings, so make sure to adjust your retraction distance and speed for the best results. Simplify3D also includes several useful features that can further reduce stringing. The first is called Coasting, which works by reducing the pressure in the nozzle right before the end of a segment. This way, when moving to the next segment, there is less pressure in the nozzle, so you are less likely to see stringing and oozing during that move. Another great option can be found on the Advanced tab of your Simplify3D process settings. By enabling the “avoid crossing outline for travel movements” option, the software will automatically adjust the travel movements of your print to stay on top of the interior of your model as much as possible. This means that the strings stay inside of your part where no one can see them, instead of being on the outside of your model.
These strings are thin hairs, similar to a spider web, that run between the different surface of your 3D print. Preventing these strings requires precisely calibrated retraction settings, so make sure to adjust your retraction distance and speed for the best results. Simplify3D also includes several useful features that can further reduce stringing. The first is called Coasting, which works by reducing the pressure in the nozzle right before the end of a segment. This way, when moving to the next segment, there is less pressure in the nozzle, so you are less likely to see stringing and oozing during that move. Another great option can be found on the Advanced tab of your Simplify3D process settings. By enabling the “avoid crossing outline for travel movements” option, the software will automatically adjust the travel movements of your print to stay on top of the interior of your model as much as possible. This means that the strings stay inside of your part where no one can see them, instead of being on the outside of your model. If you are looking for more tips to reduce stringing, we have an entire section dedicated to this issue on our Print Quality Guide: How to Reduce Stringing and Oozing.
If you are looking for more tips to reduce stringing, we have an entire section dedicated to this issue on our Print Quality Guide: How to Reduce Stringing and Oozing.
Optimize Extruder Settings to Prevent Blobs and Zits
When 3D printing at higher temperatures associated with PETG, you may notice small blobs or zits on the surface of your model. These print defects typically occur at the beginning or end of each segment, where the extruder has to suddenly start or stop extruding plastic. There are several ways to eliminate these print defects such as enabling “Extra Restart Distance” or “Coasting” options located in the Extruder tab. Simplify3D also includes an option to perform a dynamic retraction, where the filament is retracted while the extruder is still moving. This completely eliminates blobs that are typically formed from a stationary retraction. To learn more about these features and other tips for reducing blobs on the surface of your print, please refer to our Print Quality Guide.
Pro-Tips
- The glossy surface of PETG is especially useful when using rafts. The part separates easily from the raft and maintains a clean surface finish.
- Try disabling your part cooling fan for the first few layers of the print to prevent warping. This trick especially works well for larger prints.
Get Started with PET / PETG
Now that you are ready to start printing with PET / PETG, here are a few ideas to help you get started – from common applications to popular filament brands.
Common Applications
- Water proof applications
- Snap fit components
- Planter Pot
Sample Projects
- Self-watering Planter
- Water Bottle
- Snap Fit Parts
Popular Brands
- ColorFabb PETG
- eSun PETG
- E3D Spoolworks Edge
- Hatchbox PETG
- HobbyKing PETG
Ultimate Materials Guide - 3D Printing Flexible Filament
Overview
Flexible filaments are made of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) which are a blend of hard plastic and rubber. As the name suggests, this material is elastic in nature allowing the plastic to be stretched and flexed easily. There are several types of TPE, with Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) being the most commonly used among 3D printing filaments. In many cases, these terms are used interchangeably, along with popular brand names such as Ninjaflex. The degree of elasticity in the plastic depends on the type of TPE and the chemical formulation used by the manufacturer. For example, some filaments can be partially flexible like a car tire but others can be elastic and fully flexible like a rubber band. This guide will cover tips to help you with both of these variations of flexible filaments.
As the name suggests, this material is elastic in nature allowing the plastic to be stretched and flexed easily. There are several types of TPE, with Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) being the most commonly used among 3D printing filaments. In many cases, these terms are used interchangeably, along with popular brand names such as Ninjaflex. The degree of elasticity in the plastic depends on the type of TPE and the chemical formulation used by the manufacturer. For example, some filaments can be partially flexible like a car tire but others can be elastic and fully flexible like a rubber band. This guide will cover tips to help you with both of these variations of flexible filaments.
- Flexible and soft
- Excellent vibration dampening
- Long shelf life
- Good impact resistance
- Difficult to print
- Poor bridging characteristics
- Possibility of blobs and stringing
- May not work well on Bowden extruders
Hardware Requirements
Before 3D printing with flexible filaments, make sure your 3D printer meets the hardware requirements listed below to ensure the best print quality.
Bed
Temperature: 45-60 °C
Heated Bed Optional
Enclosure Not Required
Build Surface
PEI
Painter’s Tape
Extruder
Temperature: 225-245 °C
Direct Drive Extruder Recommended
Cooling
Part Cooling Fan Required
Best Practices
Flexible filaments come with many unique challenges that you want to be aware of. These tips will help you reduce the chances of common 3D printing issues such as clogging, kinking, and stringing.
Use Direct Drive Extruders
While some partially flexible filaments work fine with Bowden Extruders, most fully flexible filaments require a Direct Drive extruder for best results. The distance between the drive gear and the melt zone of the hot-end needs to be as short as possible to efficiently feed the filament into the nozzle. Additionally, the pathway through which the filament travels into the melt zone should have tight tolerances to prevent the filament from kinking or coiling inside.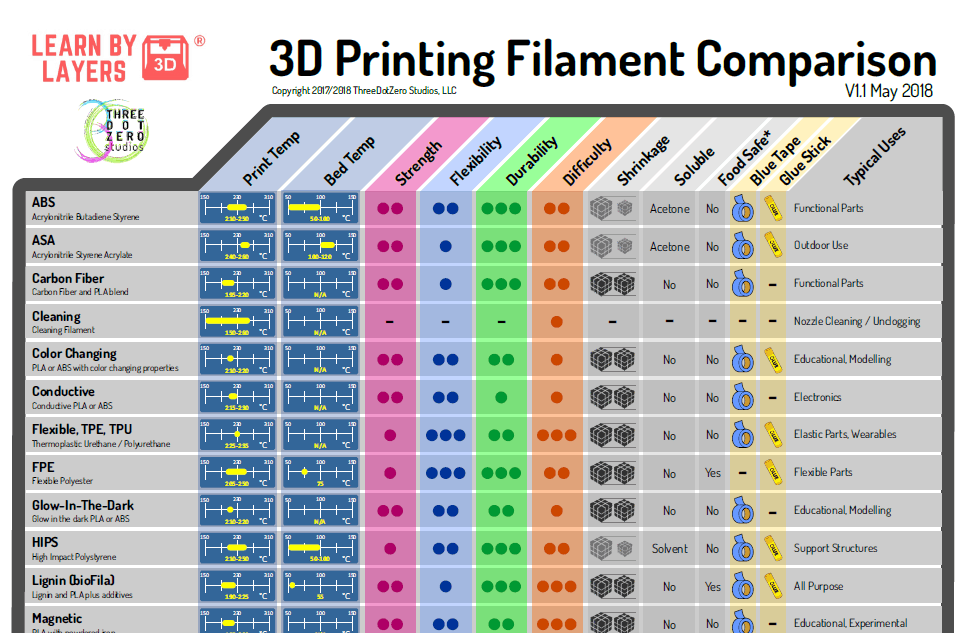 For these reasons, it is typically much easier to print flexible filaments with a Direct Drive extruder versus a Bowden extruder. If you are unsure about your 3D printer’s capabilities, you may want to check with the manufacturer to see if the extruder has been approved for use with flexible filaments.
For these reasons, it is typically much easier to print flexible filaments with a Direct Drive extruder versus a Bowden extruder. If you are unsure about your 3D printer’s capabilities, you may want to check with the manufacturer to see if the extruder has been approved for use with flexible filaments.
Use Slow and Consistent Feed Rates
Flexible filaments typically print best using a slow and consistent feed rate. Because the material is elastic, it can be very difficult to control sudden changes in the print speed. Higher print speeds can cause the filament to compress and will most likely result in a jam. Slow and steady is the best approach. Simplify3D provides all of your feed rate settings on the Speeds tab of your process settings so that you can easily configure these values. Finding the optimal print speed for your material can take several attempts based on trial and error. We have seen that speeds of 1200 mm/min (20 mm/s) can be a good starting point for most materials.
Reduce Resistance from the Filament Spool
A few tweaks to your material spool can also make a big difference with flexible materials. Typically, your extruder will pull the filament into the nozzle, forcing the filament spool mounted on your printer to unwind a bit of plastic in the process. However, because flexible materials are elastic, this will stretch the filament out as it is being pulled in and can actually result in under-extrusion. Try mounting the spool above your printer so that the filament unwinds in a downward direction which can reduce the resistance. It can also be incredibly helpful to mount the spool’s hub on a bearing to allow the spool to spin as freely as possible.
Tune Your Retraction Settings
The elastic nature of flexible filament makes it sensitive to quick movements such as retractions. In order to successfully print the filament, you will need to optimize your retraction settings to reduce these movements. While you are first starting with this material, we would recommend disabling retraction completely. You can make this change in Simplify3D on the Extruders tab of your process settings. With retraction disabled, you can focus on finding the perfect speed and extrusion rates that allow you to reliably print your models. After you are more confident in these settings, you may wish to add a very small amount of retraction with a slower retraction speed to help with any potential oozing from the hot-end. Simplify3D also includes a unique option called Coasting, which will automatically help lower the pressure in the nozzle when you approach the end of a segment, which can significantly reduce blobs and stringing with these materials. If you want more information about other options that can help reduce hairs and stringing on your prints, we have an entire section on our Print Quality Guide dedicated to that issue: How to Reduce Stringing and Oozing.
You can make this change in Simplify3D on the Extruders tab of your process settings. With retraction disabled, you can focus on finding the perfect speed and extrusion rates that allow you to reliably print your models. After you are more confident in these settings, you may wish to add a very small amount of retraction with a slower retraction speed to help with any potential oozing from the hot-end. Simplify3D also includes a unique option called Coasting, which will automatically help lower the pressure in the nozzle when you approach the end of a segment, which can significantly reduce blobs and stringing with these materials. If you want more information about other options that can help reduce hairs and stringing on your prints, we have an entire section on our Print Quality Guide dedicated to that issue: How to Reduce Stringing and Oozing.
Optimize Your Travel Movements
Retractions can be particularly troublesome for flexible materials, so it is typically best to minimize the number of retractions required for your print. Simplify3D has a great feature that was built specifically for this situation. Instead of moving in a straight line from point A to B, the software will actually choose a completely new path when moving between these points, with the goal of staying within the interior of your object so that there won’t be any oozing or stringing. With this unique feature enabled, you can greatly reduce the amount of retractions required for your print and significantly improve your print quality. To use this feature, click on the Advanced tab of your process settings, and enable the “Avoid crossing outline for travel movement” option.
Simplify3D has a great feature that was built specifically for this situation. Instead of moving in a straight line from point A to B, the software will actually choose a completely new path when moving between these points, with the goal of staying within the interior of your object so that there won’t be any oozing or stringing. With this unique feature enabled, you can greatly reduce the amount of retractions required for your print and significantly improve your print quality. To use this feature, click on the Advanced tab of your process settings, and enable the “Avoid crossing outline for travel movement” option.
Pro-Tips
- Optimize the feed rate by printing at lower layer heights in the 0.1mm – 0.2mm range. The lower layer height requires less plastic, so it allows your extruder to use a lower feed-rate, relieving the burden on the filament.
- Try to avoid using rafts with flexible materials, as the base layers of the raft have higher extrusion rates which may create issues.

- If you are designing a flexible part that needs to fit on top of another object, try using a negative tolerance between the parts so that the flexible part will need to stretch to fit over the other object snugly.
Get Started with Flexible Filaments
Now that you’re ready to start printing with flexible materials, we have a few tips to help you get started. View some typical applications below, try out a few of our sample projects, or choose a popular filament brand to purchase for your next project.
Common Applications
- Vibration dampening
- Grip Sleeves
- Phone cases
Sample Projects
- RC Car Tire
- Phone case
- Bike Handle
Popular Brands
- NinjaTek Ninjaflex, Armadillo, Cheetah
- Polymaker PolyFlex
- eSun TPE
- Sainsmart Flexible TPU
Selection of materials for 3D printing. Part 1.
Hello fellow printers!
In touch 3DMindex.
I am a frequent user of the portal 3DToday.ru , and every time I see another article called “another technological plastic” I get a slight shiver. In the period from 2019 to 2020, so many materials were published that it will be very difficult for even an experienced user to figure out why and for what this or that material is needed. nine0003
In my article tetralogy, I decided to make a detailed review of the materials presented by various manufacturers, excluding those that do not deserve special attention. I will make my own rating, according to which I will recommend this or that material from key manufacturers for purchase, and I will tell you about the experience of using them on various 3D printers. The following material manufacturers were chosen by me: Filamentarno, REC, PrintProduct, BestFilament and FD Plast (as the most popular manufacturer among garage craftsmen) nine0006
Equipment I work on : Hercules Strong . In my work, I came across many printers, such printers as Ultimaker S2 , Up Mini , Picaso Designer ( different versions ), Magnum Create , Zenith , Raise N2 , VolgoBot version A4 PRO, and others. nine0003
In my work, I came across many printers, such printers as Ultimaker S2 , Up Mini , Picaso Designer ( different versions ), Magnum Create , Zenith , Raise N2 , VolgoBot version A4 PRO, and others. nine0003
I searched for information bit by bit from different sites, and seasoned them with a little touch of subjective opinion, and also tried to combine everything in my (several) articles.
Let's start:
In this article I will talk about the most famous materials from which everyone begins to get acquainted with the 3D industry. I’ll tell you what to expect and what to fear when working with this or that material, indirectly go through the print parameters, talk about the technical characteristics, application, touch on the economic component when working with a certain material, list some features and sum up my “TOP manufacturers” for production materials and printers( in the high price category ) when working with these materials.
#1 ABS
ABS High impact engineering thermoplastic resin. In 3D printing is the most one of the most popular material.
Print options:
- Extrusion temperature - 210-245°C
- Table temperature - 90-120°C
- Interlayer cohesion - medium nine0078
- Table adhesion - medium
This is one of those materials that must be printed in a closed chamber. Fortunately, all modern manufacturers equip printers with a closed case (with the exception of Magnum 'a). In this regard, the printing becomes less toxic, and also (which is no less important) there is a better sintering of the layers (cohesion). For the better, I can note the company Volgobot , they developed an active thermostatic chamber in the PRO version on their printer. In other words, in addition to a heated table (up to 150°C), they have a heating element with a convection fan, thanks to which a single temperature is maintained throughout the entire print volume. According to the manufacturer, the temperature difference in the chamber varies by ± 2°C at 100°C. With this thermal chamber, new frontiers can be opened for use ABS plastic. For example, you can put a model with 100% infill on the entire print area, and their print area is about 297/210/200mm. How does Picaso behave when printing? So in terms of print quality ABS ’om ( as well as other materials ), they are objectively the first in Russia in this parameter, but the issue of stable operation is acute for them. I know that they are very worried about this, and this is their key merit, but my friends and I who work with this printer have malfunctions, in general, the issue of malfunctions can be attributed to any technique, but once it happened like this that Picaso did not start working out of the box yet ( this happens sometimes in case of careless transportation, and applies to all manufacturers of 3D printers ), but fast ( like-nowhere ) and qualified ( especially ) technical support helped to solve this and not only problems, thanks to them for that.
According to the manufacturer, the temperature difference in the chamber varies by ± 2°C at 100°C. With this thermal chamber, new frontiers can be opened for use ABS plastic. For example, you can put a model with 100% infill on the entire print area, and their print area is about 297/210/200mm. How does Picaso behave when printing? So in terms of print quality ABS ’om ( as well as other materials ), they are objectively the first in Russia in this parameter, but the issue of stable operation is acute for them. I know that they are very worried about this, and this is their key merit, but my friends and I who work with this printer have malfunctions, in general, the issue of malfunctions can be attributed to any technique, but once it happened like this that Picaso did not start working out of the box yet ( this happens sometimes in case of careless transportation, and applies to all manufacturers of 3D printers ), but fast ( like-nowhere ) and qualified ( especially ) technical support helped to solve this and not only problems, thanks to them for that. As for other manufacturers, some print “good”, and some “satisfactory”, the question is more about how much manufacturers sell their goods for, and which goods are worth their money and which are not. nine0003
As for other manufacturers, some print “good”, and some “satisfactory”, the question is more about how much manufacturers sell their goods for, and which goods are worth their money and which are not. nine0003
Specifications:
- Melting point - 175-210°C
- Softening point - 100°C
- Operating temperature -40+80°C
- Hardness (Rockwell) - R105-R110
- Elongation at break - 6%
- Bending strength - 41 MPa
- Tensile strength - 22 MPa
- Tensile modulus - 1.6 GPa nine0078
- Flexural modulus - 2.1 GPa
- Density - 1.1 g/cm³
- Shrinkage in the manufacture of products - up to 0.8%
- Moisture absorption - 0.45%
Application:
This material is found everywhere in our lives. It is widely used in industry, it is used to make large car parts (dashboards, radiator grilles), cases of large household appliances, sports equipment, plumbing products. In 3D printing, it was the first polymer used. Unfortunately, in this area it is not as easy to handle as we would like. Due to the specifics of the technology, it is difficult to make large objects from it due to shrinkage, detachment and delamination of the model occur. A closed print chamber partially solves this problem, in order to almost completely get rid of it, it is necessary to have a thermostatic chamber. nine0003
In 3D printing, it was the first polymer used. Unfortunately, in this area it is not as easy to handle as we would like. Due to the specifics of the technology, it is difficult to make large objects from it due to shrinkage, detachment and delamination of the model occur. A closed print chamber partially solves this problem, in order to almost completely get rid of it, it is necessary to have a thermostatic chamber. nine0003
Pros:
- Good combination of strength and elasticity makes it suitable for mechanical applications.
- A wide range of temperatures used allows the use of products from it for technical purposes.
- Ease of machining, combined with chemical smoothing of the surface with inexpensive solvents such as acetone, allows you to make decorative items or cases with a high surface quality. nine0078
Cons:
- Does not tolerate UV radiation well, turns yellow in sunlight, which limits the use of unpainted surfaces outdoors
- Does not like drafts when printing, which limits the use of cheap printers with an open case.

- Due to relatively high shrinkage it is prone to delamination (delamination), requires a heated bed, without it there are problems with the first layer sticking to the bed. nine0078
- During the printing process, an unpleasant odor may form, it is better to print in a ventilated room, or to equip the printer with a special exhaust ventilation system, with output outside the apartment.
Economic component:
Here is a table with manufacturers, with current prices for January 21. Since manufacturers sell coils in different weights, I decided to find the cost of the material per gram of the product by the ratio of price to weight. The result is presented in column “ ₽/M ”. The column “ Quality ” is absolutely subjective, because I gave points in it absolutely arbitrarily, based on the experience of working with material from one or another representative, but in general, the quality of today's production mastodons is ± on the same level, and the problems I have with printing can be related to the storage conditions of materials. Column “ Recommendation ” - is the ratio of “ Quality ” to “ ₽/M ”, it is needed in order to reduce these values to a common denominator, the higher the score in it, the more I recommend the material from this manufacturer.
Column “ Recommendation ” - is the ratio of “ Quality ” to “ ₽/M ”, it is needed in order to reduce these values to a common denominator, the higher the score in it, the more I recommend the material from this manufacturer.
What is the result?
1st place - FD Plast (Recommended for test printing)
2nd place - Filamentarno (I highly recommend)
3rd place - PrintProduct
4th place - Bestfilament
5th place - REC nine0003
To my surprise, FD Plast has the first place in this championship, and REC is outsiders. What are the reasons? Of course in price. About 5 years ago, REC was the top quality with corresponding prices, but over the past couple of years, other manufacturers have pulled up in this parameter, but the prices are kept lower than REC, hence the connection. Maybe after this article, REC will stop slightly jacking up prices for their material, and will be more accessible to ordinary buyers.
As for FD Plast, in my opinion, their material is suitable for test or home printing, but if you have a serious large-scale project and tight deadlines, then it is better to contact trusted manufacturers. It will turn out more expensive, but spend less time and nerves in case the seal fails. nine0003
It is also worth noting that there are many brands and composites based on ABS, and therefore the prices for the material can vary so much, unfortunately, the manufacturer does not offer a technological map for the material, which is why it is impossible to fully find the answer to Question: Why is it so expensive?
If you order 3D printing from various companies, then on average in the provinces the price for printing with this plastic is from 10 to 30 rubles per gram, if you order from top3Dshop, then the price for ABS is 45 rubles per gram. nine0003
In general, using this plastic is quite a profitable business if you are going to fulfill orders for 3D printing.
Top ABS 3D printers:
1 Place - Picaso
2 Place - Hercules (slightly not up to Picaso in quality, I think the price tag for equipment is too high, I took it myself solely from the recommendations of comrades and a large (high) print area. )
3rd place - Volgobot (the quality is comparable to Hercules strong, but the price tag is lower, I put it in 3rd place due to the fact that the company is not as large as direct competitors, although it has its own development vector, and their thermal chamber works wonders with ABS, however this is not their only worthy development, they have a configurator with a large list of options in which you can assemble a printer for your tasks, however, you should contact the manufacturer for all the details. but the guys try and keep in touch with all their customers.) nine0006
All other printers have approximately the same level of ABS printing, since for 5-8 years of the existence of companies, all ± have learned to work with this material.
Worth mentioning: Ultimaker / Raise Pro 2 I am not satisfied, and the price tag is also not small) nine0003
#2 PLA
PLA-plastic (polylactide, PLA) is a biodegradable thermoplastic aliphatic polyester, the structural unit of which is lactic acid. PLA is made from corn, sugar cane, potato or corn starch, and cellulose. It is one of the most popular materials for 3D printing. Due to its natural raw materials in the composition of the polymer, it can be used for various purposes without a threat to humans.
Print options: nine0006
- Extrusion temperature - 190-230°C
- Table temperature - 20-60°C
- Interlayer cohesion - good
- Table adhesion - good
- It is essential to dry the filament spool before use for more stable printing.
Specifications:
- Melting point - 175-180°C
- Softening point - 50°C nine0078
- Product operating temperature -20+40°C
- Hardness (Rockwell) - R70-R90
- Elongation at break - 3.
 8%
8% - Bending strength - 55.3 MPa
- Tensile strength - 57.8 MPa
- Tensile modulus - 3.3 GPa
- Flexural modulus - 2.3 GPa
- Density - 1.23-1.25 g/cm³
- Manufacturing shrinkage - no
- Moisture absorption - 0.2-0.4%
Application:
PLA plastic shows itself excellently in mock-up workshops and in creating master models that are not designed to bear long-term mechanical loads. With it, models with careful detail are obtained, and are also used when working with children.
Pros:
- Does not shrink during printing, which allows you to get an exact match of the dimensions of the printed product to the simulated one. nine0078
- Does not require a heated bed and is not afraid of drafts when printing, which means it can be used for printing on the cheapest Chinese printer with an open case.
- Non-toxic. During printing, it smells pleasant and slightly, which allows you to print it in the apartment without using a special hood.

- Hard, durable and slippery, wide range of applications.
- Produced from natural ingredients, can be used in food contact. nine0078
- Biodegradable, this plastic does not harm the environment when disposed of.
Cons:
- Exposure to air and ultraviolet light, like any natural material, becomes more brittle over time, so it is not recommended for long-term use at high physical exertion or use without a protective coating in the open air.
- Low softening temperature (50°C) - in the inside of a car left in the sun on a hot day, easily softens and loses its shape. nine0078
- Narrow temperature range (-20 to +40°C).
- The high hardness of the plastic makes it difficult to machine.
- Due to the high content of residual monomers, plastics from some manufacturers are prone to plugging in all-metal hot ends.
Economic component:
PLA prices are slightly higher, and therefore our TOP has shifted slightly: nine0003
1st place - Filamentarno (Recommended)
2 Place - FD Plast (Worth a try for a test print)
3rd place - PrintProduct
4th place - REC
5th place - BestFilament
PLA is a material that absorbs a lot of moisture, due to which its characteristics drop significantly, and the already fragile material becomes almost glassy. FD Plast once again takes its price, bypassing its competitors by 1.5, or even almost 2 times, but I suffered a lot with it, it draws moisture from the air, probably as much as silica gel from shoes. nine0003
FD Plast once again takes its price, bypassing its competitors by 1.5, or even almost 2 times, but I suffered a lot with it, it draws moisture from the air, probably as much as silica gel from shoes. nine0003
If you order 3D printing from various companies, then on average in the provinces the price for printing with this plastic is from 10 to 20 rubles per gram, if you order from top3Dshop, then the price for PLA is 35 rubles per gram.
Based on the issue of profit, the use of this plastic brings less money per 1 gram of material, but due to its features, there are much fewer problems in printing with this plastic than with the same ABS.
Top 3D printers for PLA: nine0006
1st place - Picaso (In the past, they had problems printing this material, the extruder often clogged, but as far as I know this problem has been fixed)
2nd place - All remaining manufacturers. (As of January 21, all manufacturers have learned to produce approximately the same print quality for PLA, in principle, this is one of the easiest materials to work with, and I don’t see much point in crucifying, put more airflow and print on health)
Worthy of mention: Raise PRO 2 (this is perhaps one of the worst printers for PLA printing, I tried to print on it in one CMIT, and from the stuffy room the extruders clogged literally on every print, in general, it also depends on the material manufacturer, but one and the same coil on different printers showed itself in completely different ways, and therefore I highly do not recommend printing with PLA plastic on this printer)
#3 PET-G
PETG (polyethylene tereflatate glycol, PETG) highly impact resistant plastic, due to glycol modification it does not crystallize, making deep drawing thermoforming more possible. At the moment, plastic is actively gaining popularity, all because it combines the positive qualities of many other polymers. nine0003
At the moment, plastic is actively gaining popularity, all because it combines the positive qualities of many other polymers. nine0003
For some manufacturers you will not find such material as PET in the catalog, this is due to the fact that marketers probably decided to rename this material, and therefore Filamentarno has Prototyper as an analogue of PET, and RELAX for REC.
Print options:
- Extrusion temperature - 215-245°C
- Table temperature - 20-80°C
- Interlayer cohesion - very high
- Table Adhesion - Medium nine0078
Specifications:
- Extrusion temperature - 215-245°C
- Table temperature - 20-80°C
- Interlayer cohesion - very high
- Table Adhesion - Medium
- Specifications
- Melting point - 222-225°C
- Softening point - 80°C
- Operating temperature -40+70°C
- Hardness (Rockwell) - R106 nine0078
- Elongation at break - 50%
- Bending strength - 76.
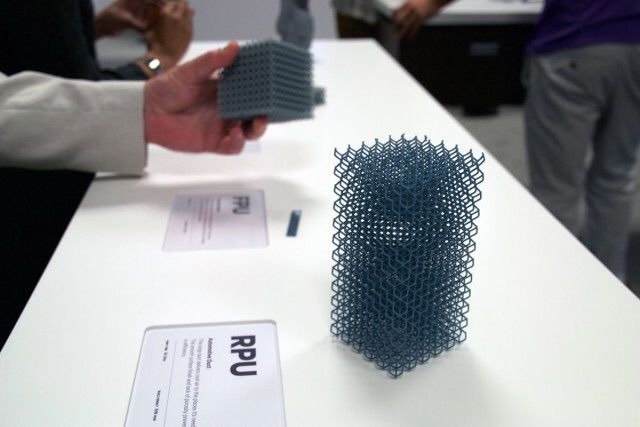 1 MPa
1 MPa - Tensile strength - 36.5 MPa
- Tensile modulus - 2.6 GPa
- Flexural modulus - 1.12 GPa
- Density - 1.3 g/cm³
- Manufacturing shrinkage - no
- Moisture absorption - 0.12%
Application:
In everyday life PET is used to make plastic bottles, due to its chemical neutrality it is used in the food industry. By itself, PET-G is similar to PET material. In 3D printing, it has proven itself as a versatile material that can be used both in technical parts bearing low loads and in prototyping. nine0003
Pros:
- Odorless Printing - Allows you to print at home without the need for an optional exhaust fan.
- No shrinkage for high dimensional accuracy.
- Very strong sintering between layers - can print thin-walled products with high strength.
- UV resistant - printed designs can be used outdoors.
- Wide operating temperature range.
 nine0078
nine0078 - Printing does not require a closed chamber.
- Good slip and impact resistance - can print gears, bushings and other machine parts.
- Non-toxic, can be printed on articles intended for contact with food.
Cons:
- High fluidity requires careful adjustment of the retracts.
- High printing temperature quickly disables the fluoroplastic insert in the hot end and makes you think about switching to all-metal thermal barriers. nine0078
- Strength and softening point lower than ABS.
- A fairly versatile material, good print behavior but not outstanding performance.
Economic component:
1st place - FD Plast
2nd place - Filamentarno
3rd place - BestFilament
4th place - PrintProduct
5th place - REC nine0003
Surprisingly, the PET-G rating is, in my opinion, the most honest. Due to the fact that PET is more stable in terms of storage and printing material, there was a large increase in points in the “Quality” column. REC is again an outsider, once again I repeat that this is due to the high cost of the material, and it hurts me to see this company at the end of the top.
Due to the fact that PET is more stable in terms of storage and printing material, there was a large increase in points in the “Quality” column. REC is again an outsider, once again I repeat that this is due to the high cost of the material, and it hurts me to see this company at the end of the top.
If you order 3D printing from various companies, then on average in the provinces the price for printing with this plastic is from 15 to 35 rubles per gram, if you order from top3Dshop, then the price for PET-G is about 40 rubles per gram (I did not find the exact price ). nine0003
Based on the issue of profit, the use of this plastic brings less money per 1 gram of material, but due to its features, there are much fewer problems in using this plastic than with the same ABS.
Top 3D printers for PET-G:
NOT top by PLA) nine0003
#4 HIPS
HIPS (High Strength Polystyrene) is a fairly soft plastic designed to be used with ABS to support dual extruder 3D printing. This was facilitated by its following properties: the same extrusion temperature as ABS, low sintering with ABS, the presence of a solvent (D-Limonene), which dissolves HIPS and does not dissolve ABS. Some manufacturers do not have this material in their catalog, in fact, I do not see its widespread use at the present time, and therefore it is not a pity. nine0003
This was facilitated by its following properties: the same extrusion temperature as ABS, low sintering with ABS, the presence of a solvent (D-Limonene), which dissolves HIPS and does not dissolve ABS. Some manufacturers do not have this material in their catalog, in fact, I do not see its widespread use at the present time, and therefore it is not a pity. nine0003
Print options:
- Extrusion temperature - 210-245°C
- Table temperature - 90-120°C
- Interlayer cohesion - medium
- Table Adhesion - Medium
Do not start work without drying the coil!
Specifications:
- Extrusion Temperature - 210-245°C
- Table temperature - 90-120°C
- Interlayer cohesion - medium
- Table Adhesion - Medium
- Do not start work without drying the coil!
- Specifications:
- Melting point - 175-210°C
- Softening point - 97°C
- Operating temperature -40+70°C
- Hardness (Rockwell) - L79
- Elongation at break - 64%
- Bending strength - 37.
 6 MPa nine0078
6 MPa nine0078 - Tensile strength - 16.4 MPa
- Tensile modulus - 0.93 GPa
- Flexural modulus - 1.35 GPa
- Density - 1.05 g/cm³
- Manufacturing shrinkage - 0.4%
- Moisture absorption - 1%
Pros:
- Less shrinkage than ABS, making it suitable for precision printing.
- Lighter density than PLA, allowing for prints where lightness is required. nine0078
- Softness of the surface, which guarantees ease of machining.
- A matte finish that gives a smooth effect to garments.
- Almost same softening point as ABS, making it suitable for outdoor use.
Cons:
- Like ABS, it requires a heated platform and is prone to delamination, although to a lesser extent.
- Lower bending strength than ABS and, as a result, more brittle products. nine0078
- Poor UV resistance, which limits the use of products in sunlight.
- All this makes it possible to use this plastic for the production of furniture decor and interior decorations.
Application: once this material appeared it was used to print supports on 2 extruder printers, the supports themselves were dissolved in limonene. To date, this is no longer so relevant, due to the appearance of such material as PVA, the material itself is completely unnecessary today. The material itself is quite stable, although it requires careful drying. nine0003
Economic component:
1st Place - FD Plast
2nd place - Bestfilament
3rd place - REC
As far as buying recommendations, it can be safely replaced with PVA, in general I consider HIPS already out of fashion, so I doubt that anyone spends it in large quantities. nine0003
Top 3D Printers for HIPS:
1 Place - Hercules / Volgobot
2nd place - Picaso (Picaso dropped to second place due to the fact that slippage occurs when printing with HIPS, it is quite possible that they got rid of this problem on new printers, but in 2019 it was like that)
№5 SBS
SBS (styrene butadiene styrene) is another relatively new player in the 3D printing plastics market.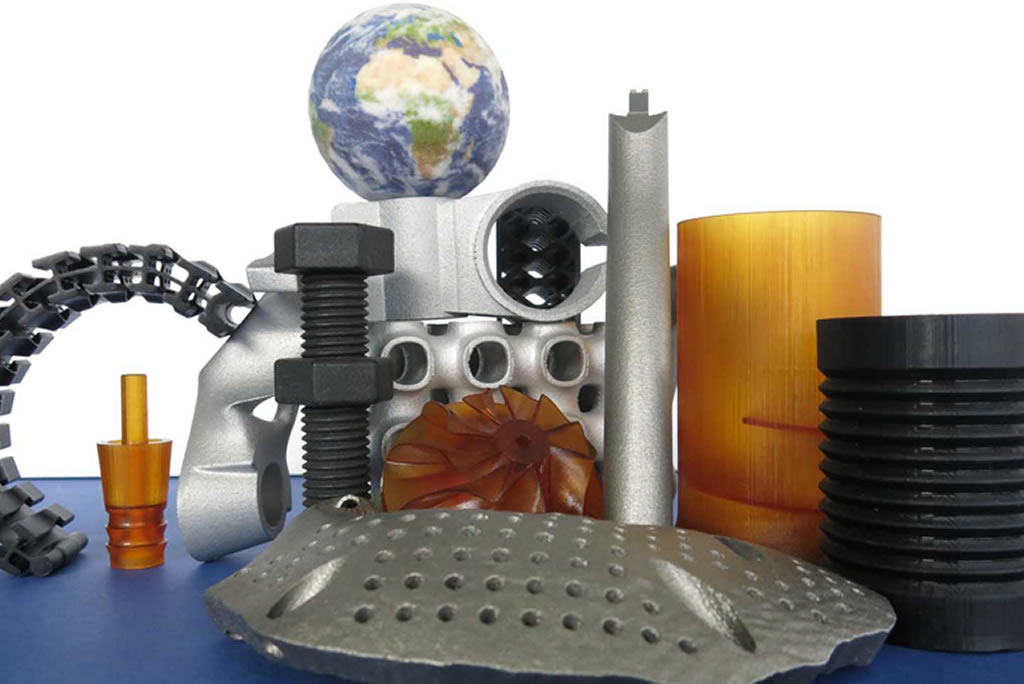 It is characterized by low toxicity and shrinkage, as well as high strength. Its main advantage is its transparency. Products printed with this plastic and processed with a solvent acquire the transparency of colored glass. nine0003
It is characterized by low toxicity and shrinkage, as well as high strength. Its main advantage is its transparency. Products printed with this plastic and processed with a solvent acquire the transparency of colored glass. nine0003
This material has different names for different manufacturers, for example, BestFilament calls it WATSON, and some manufacturers do not have it at all.
Print options:
- Extrusion temperature - 220-240°C
- Table temperature - 70-90°C
- Interlayer cohesion - low
- Table Adhesion - Medium
Specifications: nine0006
- Melting point - 190-210°C
- Softening point - 76°C
- Operating temperature - -80+65°C
- Hardness (Rockwell) - R118
- Elongation at break - 250%
- Bending strength - 36 MPa
- Tensile strength - 34 MPa
- Tensile modulus - 1.35 GPa
- Flexural modulus - 1.
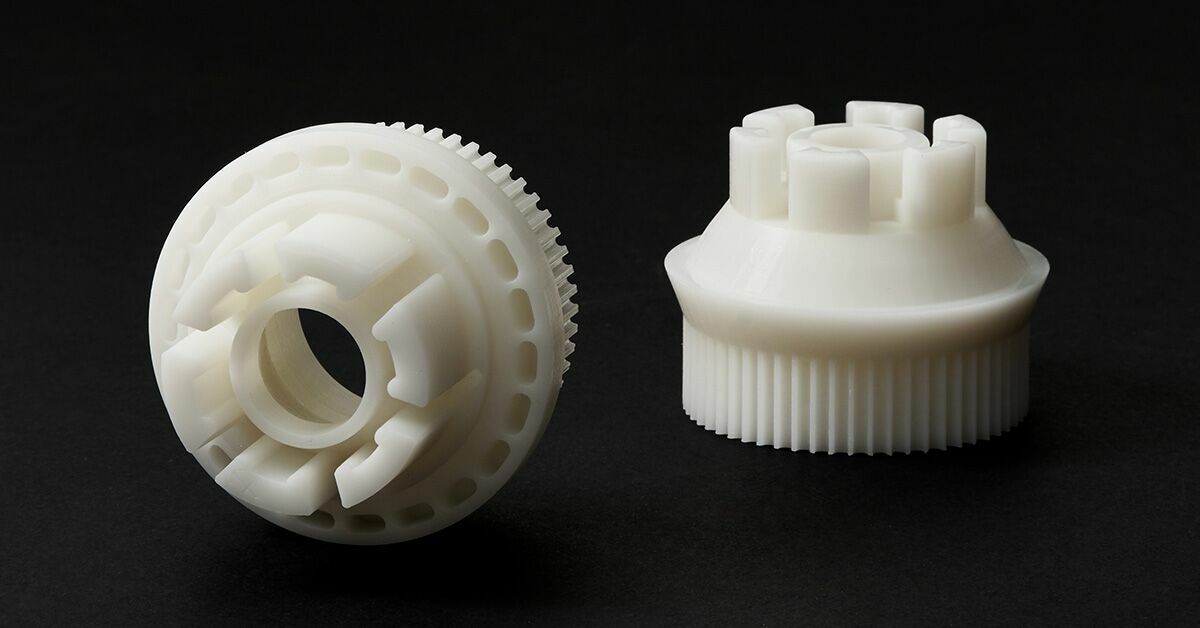 45 GPa nine0078
45 GPa nine0078 - Density - 1.01 g/cm³
- Shrinkage in the manufacture of products - 0.2
- Moisture absorption - 0.07%
Pros:
- Relatively low shrinkage, allowing printing in open case printers.
- High adhesion to the table.
- Potential for food contact.
- Impact resistant.
- Beautiful colors for creating unique decor items. nine0078
- Transparency after processing, can be used in luminaires.
- Wide operating temperature range, frost resistance.
- Easy post-processing by both chemical and mechanical methods.
Cons:
- Poor intercoat cohesion, requires large orifice nozzles or 100% coverage.
- Relatively high print temperature, similar to PETG. nine0078
- Applications: Most often used in decorative elements and creating custom lamps.
Economic component:
1 Place - FD Plast
2nd place - Filamentarno
3rd place - BestFilament
Top 3D printers for SBS:
1st Place - Picaso
2nd place - VolgoBot nine0003
3rd place - Hercules
Conclusion:
As for the article: it turned out to be shorter than I planned, this category of materials did not include such materials as Flex (various modifications), Nylon and other PC At the time of the final editing of the article, I realized that not all printers are capable of printing with these materials, Flex’a needs special extruders capable of printing rubber-like materials, for a PC, the presence of a closed case does not mean success in work, and the material loves temperature very much. Therefore, if the article receives some response, I will talk about “engineering plastics”, composites created on their basis, and also talk about materials that are at the forefront of progress, so my dear reader, adequate criticism is welcome. nine0003
Therefore, if the article receives some response, I will talk about “engineering plastics”, composites created on their basis, and also talk about materials that are at the forefront of progress, so my dear reader, adequate criticism is welcome. nine0003
As for material manufacturers, a few words about each:
FD Plast : wins in public domain although I don't agree with it because I think their policy of dumping the market is wrong, but the company has many followers who prefer goods from the “cheap and cheerful” category.
Filamentarno: for me personally is the best manufacturer with an adequate price, not a small list of products, and with a constant quality that has never let me down. nine0003
Print Product: before switching to Filamentary, he mainly used the products of this company, in the past the company had a colossal list of products, but in the last year they decided to change the vector of development, and relied on materials whose quality can be sufficiently ensured .
REC : in the past, the clear favorite in terms of the quality of the materials provided, now the quality is at the same level, but the price tag bites.
Best filament it seems to me that the quality floats slightly from batch to batch, gaps form on Hercules when printing with ABS plastic.
Types of Plastic for 3D Printer
Content
-
- PLA
- ABS
- HIPS
- Petg
- decorative platery
- SPIRICAL PLASS 9007 SPIRI0078
- Totals
Every year 3D printing becomes more popular and accessible. Previously, a 3D printer was more like a complex CNC machine, but now manufacturers are meeting users. Simplified and automated settings that many beginners drove into a stupor. Despite this, it can be difficult for a novice user to understand the variety of constantly appearing plastics for a 3D printer.
The choice of plastic for a 3D printer is very important, especially when the goal is to print a functional model with certain properties. It will be a shame if the printed gear breaks almost immediately, or the decorative model quickly loses its beauty. nine0003
It will be a shame if the printed gear breaks almost immediately, or the decorative model quickly loses its beauty. nine0003
It is important to understand whether the printer will be able to work with the selected plastic. Some materials (most often engineering) require certain conditions for successful printing.
First, decide which model you want to print. What properties should it have? Does the model need to be durable? Or is it a master model for further replication, in which the quality of the surface is important?
90% of 3D printers use 1.75 diameter filament. 3mm diameter is rare, but it is better to check in advance which size is used in your printer. nine0003
PLA
PLA (Polylactide) is the most popular and affordable 3D printer plastic. PLA is made from sugar cane, corn, or other natural raw materials. Therefore, it is considered a non-toxic, biodegradable material.
Extruder temperature - 190-220 degrees. Table heating is not needed, but if the printer's table has a "heater" for better adhesion, you can heat it up to 50-60 degrees. PLA is very easy to work with. The only requirement is to blow the model. There is practically no shrinkage in this material. When printed, it is practically odorless, and if it smells, it smells like burnt caramel. nine0003
Table heating is not needed, but if the printer's table has a "heater" for better adhesion, you can heat it up to 50-60 degrees. PLA is very easy to work with. The only requirement is to blow the model. There is practically no shrinkage in this material. When printed, it is practically odorless, and if it smells, it smells like burnt caramel. nine0003
Pros:
-
Does not shrink. This makes it easy to build prefabricated or huge models without changing dimensions.
-
There are no specific requirements for a 3D printer. Any working 3D printer will do. PLA doesn't need a heated table or a closed case.
-
Non-toxic. Due to this, during printing it does not smell or has a barely perceptible aroma of burnt caramel. nine0003
-
Diverse color palette.
Cons:
-
PLA is poorly sanded and machined.
-
It begins to deform already with a slight heating (about 50 degrees).

-
Fragility. Compared to other materials, PLA is very brittle and breaks easily. nine0003
-
Decomposes under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Of course, it will not fall apart into dust, but it can become more brittle and fade.
PLA is perfect for making dimensional or composite models. For example, decorative interior items, prototyping, electronics cases, etc.
Recently, PLA+ has appeared on the market. It may differ from conventional PLA in improved performance. For example, more durable, with improved layer adhesion. nine0931
Dummy turbine
Decorative coasters
ABS
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the second most popular plastic for 3D printing due to its properties, availability and low price.
Extruder temperature - 220-240 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees.
For printing, a heated table is required at the printer. It is desirable to have a closed chamber, because ABS "does not like" drafts. Due to a sharp temperature drop, it can “unstick” from the table or crack in layers. ABS can smell bad when printing, so it is recommended to use the printer with a closed chamber and filters, or print in a well-ventilated area. nine0003
Pros:
Good strength characteristics allow the production of functional prototypes from ABS.
Simple mechanical and chemical processing. ABS is easy to sand and drill, and with an acetone bath you can achieve a perfectly smooth surface.
It is currently the most inexpensive type of plastic for 3D printing. nine0003
Large selection of colors and shades.
Cons:
High shrinkage. Because of this, it can be problematic to manufacture overall products.
Printing requires a heated bed and a closed chamber.
nine0078Without this, the ABS may peel off the table or crack in layers.
During the printing process, ABS can smell bad. Therefore, it is recommended that you print in a ventilated area or use the printer with a sealed chamber and filter.
ABS is an engineering plastic. It is suitable for the manufacture of simple functional products.
ABS after chemical treatment in an acetone bath
nine0003
RU model made of ABS
ABS+ differs from regular ABS in improved strength characteristics (elasticity, stiffness, hardness), less shrinkage and sometimes resistance to certain oils and solvents (eg gasoline).
HIPS
HIPS (high impact polystyrene) - originally conceived as a soluble support plastic for materials with high printing temperatures. For example for ABS or Nylon. nine0003
The extruder temperature is 230-260 degrees.
The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. It is desirable to have a closed camera for a 3D printer.
Pros:
Less shrinkage than ABS.
Ease of machining.
The matte surface looks very advantageous on decorative products. nine0003
Food contact allowed (but be sure to check with a specific manufacturer for certificates)
Cons:
For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber.
More flexible and less durable than ABS. Because of this, it will not be possible to produce functional products. nine0003
Small palette of colors.
Most often, HIPS is used for its intended purpose for printing on 2x extruder printers as a support for ABS. It dissolves perfectly (though not very quickly) in limonel.
Sometimes HIPS is used as an independent material.
Products from it are not very durable, but this plastic is loved for easy post-processing. HIPS can be used for models that will subsequently come into contact with food (not hot). nine0003
Using HIPS as a soluble support
Decorative vase made of HIPS
PVA
PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) is a material that was developed as a water-soluble support for PLA.
Extruder temperature - 190-210. Table heating is not required. PVA is a slightly "capricious" material, it is not recommended to overheat it and print at high speeds. nine0003
PVA is very hygroscopic and dissolves in plain water. Therefore, it is only used as a support for PLA or other plastics with print temperatures close to PVA.
Soluble PVA Support
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
Manufacturer Tiger3D nine1153Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Tiger3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer EsunAdd to compare
Product added to compare Go nine0003
Manufacturer EsunPETG
PETG (polyethylene terephthalate) combines the best properties of PLA and ABS.
It is easy to work with, it has a low percentage of shrinkage and excellent sintering of the layers.
Extruder temperature - 220-240 degrees. Table temperature - 80-100 degrees. During the printing process, the model must be well blown.
Pros: nine0003
Excellent sinterability of layers.
PETG is very strong and wear resistant. Good impact resistance.
Virtually no smell when printing.
Non-toxic.
- nine0085
Little shrinkage.
Cons:
PETG is perfect for printing functional models. Due to its low shrinkage, it is often used to make large or composite models. Due to its low toxicity, PETG is often used for products that will come into contact with food.
Cookie cutters and patterned rolling pin
SBS
It is a highly transparent material. At the same time, it is durable and resilient.
SBS is a low toxicity plastic. It can be used to print food contact models. nine0003
Extruder temperature - 230 -260 degrees. Table temperature - 60-100 degrees. You can print without the closed case on the printer.
Pros:
slight shrinkage
- nine0077
Transparency. After treatment with solvent, limonel or dichloromethane, beautiful transparent products with an almost smooth surface can be obtained.
Easily processed mechanically or chemically.
Allowed contact with food.
Cons:
SBS is excellent for translucent vases, children's toys and food containers. Or functional things that require transparency, such as custom turn signals for a motorcycle or car, lamps or bottle prototypes. nine0003
Vases are perfectly printed with a thick nozzle (0.7-0.8) in one pass (printing in 1 wall or spiral printing in a slicer).

Models of bottles after chemical treatment
Nylon
Nylon (polyamide) is considered the most durable material available for home 3D printing. In addition to good abrasion resistance and strength, it has a high slip coefficient. nine0003
Extruder temperature - 240-260 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. Nylon is a very capricious and hygroscopic material - it is recommended to dry the coil with plastic before use. For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber, without this it will be difficult to print something larger than a small gear.
Pros:
High strength and wear resistance.
nine0078High slip factor.
Heat resistance compared to other 3D printing plastics.
High resistance to many solvents.
Good for mechanical processing.
Perfectly polished and drilled.
nine0009 Cons:
Nylon is perfect for making wear-resistant parts - gears, functional models, etc. Sometimes nylon is used to print bushings.
Nylon gear
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Tiger3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Tiger3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer EsunAdd to compare
Product added to compare Go nine0003
Manufacturer Bestfilament Soft plastics
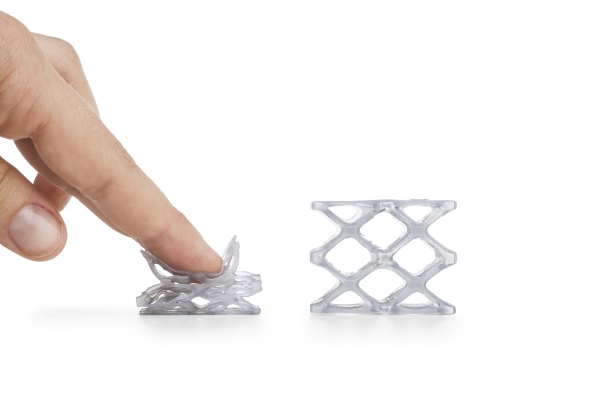
FLEX (TPU, TPE, TPC) is a material similar to silicone or rubber. It is flexible and elastic, but at the same time tear-resistant. For example, TPE is a rubbery plastic, while TPU is more rigid.

FLEX are printed at a temperature of 200-240 (depending on the material). A heated table is not required. On printers with direct material feed (feed mechanism on the print head), there are usually no problems with printing. On a bowden feeder (the feed mechanism is located on the body), printing with very soft plastics can be difficult. Usually it is necessary to additionally adjust the clamping of the bar. The main nuance is the very low print speeds - 20-40mm. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
Depending on the type of FLEXa, the models can be flexible or rubber-like. This material, depending on its softness, can be used to print gaskets, insoles, belts, tracks or other models that require flexibility or softness.
FLEX belt
nine0005 Trainers with flexible soles
Wheel for switchgear model
Decorative plastics
Decorative plastics are PLA plastics with various fillers (wood or metal shavings).
Or with dyes selected to imitate different materials. Since the base of the plastic is PLA, it is very easy to print.
Extruder temperature - 200-220 degrees (depending on the manufacturer). A heated table is not required. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
Some fillers (eg clay) are abrasive. For such plastics, the standard brass nozzle cannot be used. Will have to buy a harder steel nozzle.
Some decorative plastics can clog the small nozzle (0.4 or less). For them, you need to use a “thicker” nozzle. nine0003
Depending on the filler, different material properties are obtained. Plastics that use only dye do not require additional processing. Materials with "fillers" may sometimes require additional post-processing.
Plastics with metal fillers after printing must be processed with a metal brush. Then the Metal content will show through and the model will resemble a metal casting.nine0931
Plastics with metallic powder
These plastics are often used for printing key chains, decorative models and interior details.
If the plastic has a high content of wood dust, then it is recommended to use a larger nozzle diameter (0.5 or more), a smaller nozzle can quickly become clogged during printing.
Wood-filled plastic ground
Plastic key rings with copper dust
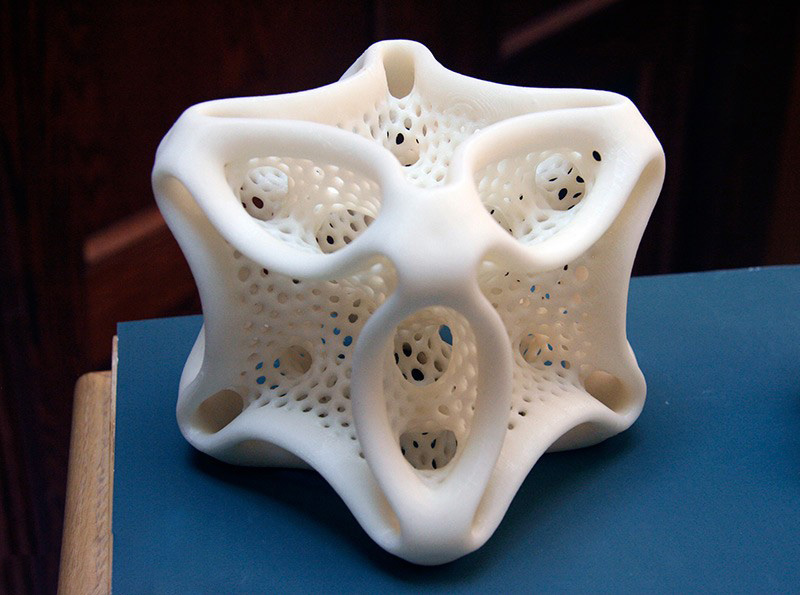
Engineering plastics
These are nylon-based plastics with fillers that improve strength, heat-resistant and other characteristics, help to achieve less shrinkage of the material. For example - carbon fiber, carbon fiber or fiberglass.
Extruder temperature - 240-300 degrees (depending on the manufacturer). Table temperature - 90-110 degrees. Since plastics are based on nylon, the requirements for printing are similar. This is a heated table and a closed printer case.

Pros:
Hardness and strength.
Low flammability or non-combustibility.
- nine0085
High precision due to low shrinkage.
Cons:
3D printers use brass nozzles, some plastics can quickly “waste” it during printing. For such materials it is recommended to use steel nozzles.
These are highly specialized plastics used for a specific task, depending on the filler. For example, functional parts that do not lose their shape when heated, are resistant to many solvents, etc. nine0003
Functional carbon fiber composite prototype
Composite frame
Polycarbonate ashtray
Totals
This is of course not the whole list of materials for 3D printing. There are many highly specialized engineering and decorative plastics for specific tasks.
nine0003
Manufacturers are constantly trying to replenish the range of materials for 3D printing. Already familiar materials are improved for more comfortable printing. There are many interesting decorative plastics imitating different materials - ceramics, clay, wood, metals.
And of course, the assortment of engineering plastics is constantly updated. Now there are many interesting materials for highly specialized tasks - for example, burnable plastic with a low ash content for subsequent casting in metal. nine0003
Burnout plastic
Before buying a coil, read the information on the website of the manufacturer or seller. There you can find some nuances of printing for a particular plastic. The manufacturer indicates the recommended temperature range on the box. Sometimes, for quality printing, it is recommended to print several tests to adjust the temperature settings, retract, etc.
Try to store the started coil in silica gel bags.

Learn more