Plastic 3d print
ABS 3D printing service | Hubs
3D printing materials
Commodity plastic, improved mechanical and thermal properties compared to PLA. ABS is a common thermoplastic with good mechanical properties and excellent impact strength, superior to PLA but with less defined details.
Order 3D printed ABS parts
Industrial FDM
ABSplus Stratasys
ABS M30 Stratasys
Description
Applications
Industrial FDM
Strengths
Larger build size compared to Desktop FDM,Industrial-grade materials,Tighter tolerance compared to Desktop FDM
Weaknesses
Expensive printing
Characteristics
Price
$ $ $ $ $
Lead Time
< 2 days
Wall Thickness
0.8 mm
Tolerances
±0. 25% with a lower limit: ± 0.25 mm (±0.01")
Max part size
Layer height
200 - 100
Available materials
ABSplus Stratasys
ABSplus is a production-grade thermoplastic that offers material stability and hands-free soluble support. Available in a range of colors.
Plastic
Learn more Get instant quote
ABS M30 Stratasys
ABS-M30 is ideal for concept models and moderate requirement parts including functional prototypes, jigs, fixtures, manufacturing tools and production parts.
Plastic
Learn more Get instant quote
Get your parts into production today
Get an instant quote FDM is the most widely available 3D printing process, mainly used for low-cost prototyping and design verification with very fast turn around times.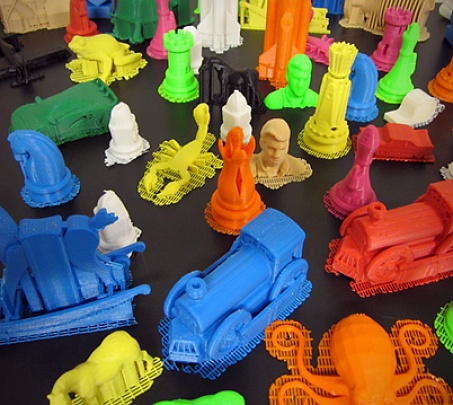
Prototyping ABS
Description
Applications
FDM is the most widely available 3D printing process, mainly used for low-cost prototyping and design verification with very fast turn around times.
Strengths
Low-cost,Fast turnaround times
Weaknesses
Limited dimensional accuracy,Print layers are likely to be visible
Characteristics
Price
$ $ $ $ $
Lead Time
< 2 days
Wall Thickness
0.8 mm
Tolerances
±0.5% with a lower limit of ±0.5 mm (±0.020″)
Max part size
50 x 50 x 50 cm
Layer height
200 - 100
Available materials
Prototyping ABS
ABS (FDM) has good mechanical properties, with excellent impact strength, superior to PLA, but less defined details. Commonly used for enclosure prototypes.
Commonly used for enclosure prototypes.
Plastic Impact resistant
Learn more Get instant quote
Get your parts into production today
Get an instant quote3D Printing Materials Guide: Plastics
Published on June 8, 2020 by Alexandrea P.
A plastic is a material made of synthetic or semi-synthetic compounds that has the property of being malleable (capable of changing its shape). Most plastics on the market are completely synthetic (most commonly derived from petrochemicals). However, given the growing environmental concern, plastics derived from renewable materials such as Polylactic Acid (PLA) are also popular on the market. Due to their low cost, ease of manufacture, versatility and water resistance, plastics are used in a multitude of products and sectors. In the AM sector, 3D printing plastics are also very popular.
In the AM sector, 3D printing plastics are also very popular.
In the following guide, we will take a look at the most common 3D printing plastics. As you may know, the most popular and affordable 3D printing process, FDM, produces parts through the extrusion of plastic filaments. However, the precision on FDM machines is not the same as other AM processes such as SLS or SLA. Plastics are often used with this technology to create prototypes. Therefore, for industrial and end-use parts, manufacturers might decide to opt for SLS (using plastic powders) or SLA (using plastic resins) technologies that offer more accuracy and part quality. Two other technologies that can print with plastics are Material Jetting and Multi Jet Fusion.
What plastics can be used in additive manufacturing? In filament or powder form, the plastic should melt to form the object you are printing layer by layer. In resin form, it should solidify to form the object. Each plastic will require different 3D printing parameters during the building process, and will give parts varying properties.
ABS
ABS filament is the most commonly used 3D printing plastics. It is used in the bodywork of cars, appliances, and mobile phone cases. It is a thermoplastic which contains a base of elastomers based on polybutadiene, making it more flexible, and resistant to shocks. ABS can also be found in powder form for powder bed processes such as SLS, and liquid form for SLA and PolyJet technologies.
ABS is used in 3D printing when heated between 230ºC and 260ºC. It is a tough material, able to easily withstand temperatures of -20ºC to 80ºC. In addition to its high strength, it is a reusable material and can be welded with chemical processes. However, ABS is not biodegradable and shrinks in contact with air, so the printing platform must be heated to prevent warping. Moreover, it is recommended to use a closed chamber 3D printer to limit particle emissions when printing with ABS. Learn more about ABS in our dedicated guide.
PLA
Known as polylactic acid, or PLA, this material has the benefit of being biodegradable, unlike ABS. PLA is manufactured using renewable raw materials such as corn starch. PLA is one of the easiest materials to print, though it does have a tendency to shrink slightly after 3D printing. You don’t require a heated platform when printing in PLA, unlike with ABS. PLA also prints at a lower temperature than ABS, between 190ºC to 230ºC.
PLA is manufactured using renewable raw materials such as corn starch. PLA is one of the easiest materials to print, though it does have a tendency to shrink slightly after 3D printing. You don’t require a heated platform when printing in PLA, unlike with ABS. PLA also prints at a lower temperature than ABS, between 190ºC to 230ºC.
PLA is a more difficult material to manipulate due to its high cooling and solidification speed. It is also important to mention that models can deteriorate when in contact with water. However, the material is consistent, simple to use, and comes in a wide variety of colors, making it suitable for FDM 3D printing. Learn more about PLA in our dedicated guide.
PLA 3D printing filament spools
ASA
ASA is a material that has similar properties to ABS, but has a greater resistance to UV rays. As with ABS, it is advised to print the material with a heated bed platform to prevent warping. When printing with ASA, similar print settings are used to ABS, but extra care must be taken to print with a closed chamber due to styrene emissions.
PET
Polyethylene terephthalate, or PET, is commonly seen in disposable plastic bottles. PET is the ideal filament for any pieces intended for contact with food. Moreover, the material is fairly rigid and has good chemical resistance. To obtain the best results when printing with PET, print between 75 – 90ºC. PET is commonly marketed as a translucent filament, with variants such as PETG, PETE, and PETT also sold. Advantages of PET include that the material doesn’t release any odours when printing, and is 100% recyclable.
PETG
PETG, or glycolized polyester, is a thermoplastic widely used in the additive manufacturing market, combining both the simplicity of PLA 3D printing and the strength of ABS. It is an amorphous plastic, which can be 100% recycled. It has the same chemical composition as polyethylene terephthalate, better known by its acronym PET. Glycol has been added to reduce its brittleness and therefore its fragility. Learn more about PETG in our dedicated guide.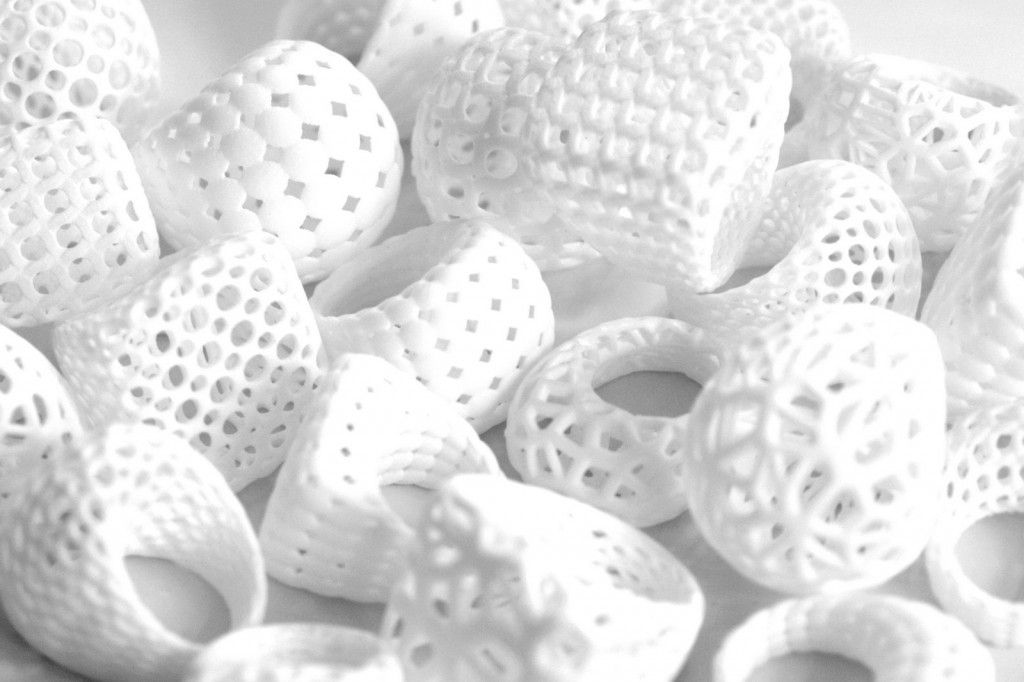
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is a high strength material designed for engineering applications. The material has good temperature resistance, able to resist any physical deformation up to around 150ºC. However, PC is prone to absorbing moisture from the air, which can affect performance and printing resistance. Therefore, PC has to be stored in airtight containers. PC is highly valued by the AM industry for its strength and transparency. It has a much lower density than glass, making it particularly interesting for designing optical parts, protective screens or decorative objects. Learn more about PC in our dedicated guide.
A 3D printed part made from PC
High Performance Polymers (PEEK, PEKK, ULTEM)
The evolution of 3D printing technologies has led to extensive research work on printing materials, enabling the development of a whole range of high-performance filaments with mechanical characteristics similar to those of metals. There are several types of high-performance 3D printing plastics such as PEEK, PEKK or ULTEM – they are distinguished by family such as polyaryletherketones (PAEK) or polyetherimides (PEI). These filaments have a very high mechanical and thermal resistance, are very strong and at the same time much lighter than some metals. These properties make them very attractive in the aerospace, automotive and medical sectors.
These filaments have a very high mechanical and thermal resistance, are very strong and at the same time much lighter than some metals. These properties make them very attractive in the aerospace, automotive and medical sectors.
Due to their characteristics, high performance polymers cannot be printed on all FDM machines on the market. Indeed, the 3D printer must have a heating plate capable of reaching at least 230°C, an extrusion at 350°C and a closed chamber. Today, about 65% of these materials are printed with FDM technology, but they are also found in powder form, compatible with SLS technology. Learn more in our dedicated guides on PEEK and PEKK.
Image via VisionMiner
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is another thermoplastic widely used in the automotive sector, professional textiles sector, and in the manufacturing of hundreds of everyday objects. PP is known for its resistance to abrasion and its ability to absorb shocks, as well as relative rigidity and flexibility. However, drawbacks of the material include its low temperature resistance, and sensitivity to UV rays which can cause it to expand. Due to this, several manufacturers have developed alternative types of PP, simili-propilenos, that are stronger both physically and mechanically.
However, drawbacks of the material include its low temperature resistance, and sensitivity to UV rays which can cause it to expand. Due to this, several manufacturers have developed alternative types of PP, simili-propilenos, that are stronger both physically and mechanically.
Nylon
Objects made from polyamides (nylon) are usually created from a fine, white, granular powder with SLS technology. There are however some variants of the material such as nylon that are also available in filaments used in fused deposition modeling (FDM). Due to its biocompatibility, polyamides can be used to create parts that come into contact with food (except foods that contain alcohol).
Constituted of semi crystalline structures, polyamides have a good balance of chemical and mechanical characteristics that offer good stability, rigidity, flexibility, and shock resistance. These advantages mean that the material has many applications across sectors and offers a high level of detail. Due to its high quality, polyamides are used in the manufacture of gears, parts for the aerospace market, automotive market, robotics, medical prostheses, and injection molds. You can learn more in our dedicated guide on Nylon.
Due to its high quality, polyamides are used in the manufacture of gears, parts for the aerospace market, automotive market, robotics, medical prostheses, and injection molds. You can learn more in our dedicated guide on Nylon.
Image via Sculpteo
Composites
Composites are extremely beneficial when making lightweight yet strong parts. The fibers add strength to a part without adding weight, which is why we also refer to composites as fiber reinforced materials. There are two types of reinforcements, short fiber or continuous fiber. In the first case, chopped fibers, which consist of segments less than a millimeter in length, are mixed into traditional 3D printing plastics to increase the stiffness and to a lesser extent the strength of components. Chopped fibers can be mixed with thermoplastics such as nylon, ABS or PLA.
Alternatively, the fibers can be added to the thermoplastics continuously to arrive at a stronger part. The main fiber used in the 3D printing sector is carbon fiber, but there are also other fibers such as glass fiber or Kevlar. You can find more information in our dedicated guide.
You can find more information in our dedicated guide.
Carbon fiber reinforced filament spool
Hybrid Materials
There are a variety of hybrid materials that mix base plastics with powders to give them a new color, finish or additional material properties. Often based on PLA, these materials are usually made of 70% PLA and 30% hybrid material. For example, wood-based filaments ranging from bamboo, cork, wood dust, and more are available. These wood-based materials mixed with PLA give the hybrid filament a more organic texture. Additionally, some hybrid materials incorporate metal powders to work with FDM-based technologies, to give parts a metal finish. They can be based on copper, bronze, silver, and more.
3D filaments based on wood.
Alumide
Alumide plastic objects are manufactured from a combination of polyamides and aluminium powder using the SLS process. The material has a large, slightly porous surface and a gritty, grainy appearance offering great strength and good temperature resistance (up to 172°C). However, some post-processing treatments are necessary, such as grinding, sanding, coating, or milling.
However, some post-processing treatments are necessary, such as grinding, sanding, coating, or milling.
Alumide is used for complex models, design pieces, or for small series production of functional models that need high rigidity and an appearance similar to aluminium. This technique involves few geometric limits.
Soluble Materials
Soluble materials are materials printed with the intention of being dissolved in a future stage of the manufacturing process. The two most common soluble filament materials are HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) and PVA (Polyvinyl Acetate). HIPS is associated with ABS, and can be dissolved with limonene, whereas PVA is associated with PLA and can be dissolved using just water.
There are also BVOH filaments which are becoming increasingly popular, especially in dual extruder printers. This is because the material is soluble in water, and according to experts has a higher solubility than PVA.
Flexible Materials
A newer type of filament, and one of the most successful, are flexible filaments. They are similar to PLA, but usually made out of TPE or TPU. The advantage of using these filaments for 3D printing is they allow for the creation of deformable objects, widely used in the fashion industry. Generally, these flexible filaments have the same printing characteristics as PLA, though they come in a variety of ranges based on their stiffness. It is worth finding out which type of extruder is best suited to the material to avoid jams when 3D printing.
They are similar to PLA, but usually made out of TPE or TPU. The advantage of using these filaments for 3D printing is they allow for the creation of deformable objects, widely used in the fashion industry. Generally, these flexible filaments have the same printing characteristics as PLA, though they come in a variety of ranges based on their stiffness. It is worth finding out which type of extruder is best suited to the material to avoid jams when 3D printing.
Flexible materials are widely used in fashion and design
Resins (for photopolymerization-based 3D printing)
3D printing technologies based on photopolymerization use UV-sensitive resins to create objects layer by layer. In other words, they use a light source such as a laser or LCD screen to solidify a liquid photopolymer. Technologies include SLA, DLP, and even Material Jetting (PolyJet). Creating parts using resins results in high detail and smooth surface objects, nevertheless, the color range is still quite limited using this process. What differentiates resins from FDM filaments is that it is impossible to mix resins to obtain different results quite easily.
What differentiates resins from FDM filaments is that it is impossible to mix resins to obtain different results quite easily.
Standard resin has properties similar to ABS: the surface finish of the part will be good given the photopolymerization process, however mechanical properties will be moderate. More advanced resins do exist for technical applications such as in dentistry (also need to be biocompatible), or engineering. Additionally, flexible resins that offer greater flexibility and deformation can be used to make jewelry. Over the years, manufacturers have expanded their range of liquid photopolymers to answer manufacturing needs from various sectors. Therefore, you should be able to find resins that have high-temperature resistance, can withstand large impacts, or that have high elongation properties.
The 3D printing resin is poured in a tank
What do you think of our explanation of these 3D printing plastics? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!
90,000 types of plastic for 3D printerContent
-
- Pla
- ABS
- HIPS
- PVA
- Petg
- SBS 9000
Every year 3D printing becomes more popular and accessible. Previously, a 3D printer was more like a complex CNC machine, but now manufacturers are meeting users. Simplified and automated settings that many beginners drove into a stupor. Despite this, it can be difficult for a novice user to understand the variety of constantly appearing plastics for a 3D printer.
Previously, a 3D printer was more like a complex CNC machine, but now manufacturers are meeting users. Simplified and automated settings that many beginners drove into a stupor. Despite this, it can be difficult for a novice user to understand the variety of constantly appearing plastics for a 3D printer.
The choice of plastic for a 3D printer is very important, especially when the goal is to print a functional model with certain properties. It will be a shame if the printed gear breaks almost immediately, or the decorative model quickly loses its beauty.
It is important to understand whether the printer will be able to work with the selected plastic. Some materials (most often engineering) require certain conditions for successful printing.
First, decide which model you want to print. What properties should it have? Does the model need to be durable? Or is it a master model for further replication, in which the quality of the surface is important?
90% of 3D printers use 1.
75 diameter filament. 3mm diameter is rare, but it is better to check in advance which size is used in your printer.
PLA
PLA (Polylactide) is the most popular and affordable 3D printer plastic. PLA is made from sugar cane, corn, or other natural raw materials. Therefore, it is considered a non-toxic, biodegradable material.
Extruder temperature - 190-220 degrees. Table heating is not needed, but if the printer's table has a "heater" for better adhesion, you can heat it up to 50-60 degrees. PLA is very easy to work with. The only requirement is to blow the model. There is practically no shrinkage in this material. When printed, it is practically odorless, and if it smells, it smells like burnt caramel.
Pros:
-
Does not shrink. This makes it easy to build prefabricated or huge models without changing dimensions.
-
There are no specific requirements for a 3D printer. Any working 3D printer will do.
 PLA doesn't need a heated table or a closed case.
PLA doesn't need a heated table or a closed case. -
Non-toxic. Due to this, during printing it does not smell or has a barely perceptible aroma of burnt caramel.
-
Diverse color palette.
Cons:
-
PLA is poorly sanded and machined.
-
It begins to deform already with a slight heating (about 50 degrees).
-
Fragility. Compared to other materials, PLA is very brittle and breaks easily.
-
Decomposes under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. Of course, it will not fall apart into dust, but it can become more brittle and fade.
PLA is perfect for making dimensional or composite models. For example, decorative interior items, prototyping, electronics cases, etc.
Recently, PLA+ has appeared on the market. It may differ from conventional PLA in improved performance.For example, more durable, with improved layer adhesion.
Dummy turbine
Decorative coasters
ABS
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is the second most popular plastic for 3D printing due to its properties, availability and low price.
Extruder temperature - 220-240 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. For printing, a heated table is required at the printer. It is desirable to have a closed chamber, because ABS "does not like" drafts. Due to a sharp temperature drop, it can “unstick” from the table or crack in layers. ABS can smell bad when printing, so it is recommended to use the printer with a closed chamber and filters, or print in a well-ventilated area.
Pros:
-
Good strength characteristics allow the production of functional prototypes from ABS.
-
Simple mechanical and chemical processing.
 ABS is easy to sand and drill, and with an acetone bath you can achieve a perfectly smooth surface.
ABS is easy to sand and drill, and with an acetone bath you can achieve a perfectly smooth surface. -
It is currently the most inexpensive type of plastic for 3D printing.
-
Large selection of colors and shades.
Cons:
-
High shrinkage. Because of this, it can be problematic to manufacture overall products.
-
Printing requires a heated bed and a closed chamber. Without this, the ABS may peel off the table or crack in layers.
-
During the printing process, ABS can smell bad. Therefore, it is recommended that you print in a ventilated area or use the printer with a sealed chamber and filter.
ABS is an engineering plastic. It is suitable for the manufacture of simple functional products.
ABS after chemical treatment in an acetone bath
RU model made of ABS
ABS+ differs from conventional ABS in improved strength characteristics (elasticity, rigidity, hardness), less shrinkage and sometimes resistance to certain oils and solvents (eg gasoline).

HIPS
HIPS (high impact polystyrene) - originally conceived as a soluble support plastic for materials with high printing temperatures. For example for ABS or Nylon.
The extruder temperature is 230-260 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. It is desirable to have a closed camera for a 3D printer.
Pros:
-
Less shrinkage than ABS.
-
Ease of machining.
-
The matte surface looks very advantageous on decorative products.
-
Food contact allowed (but be sure to check with a specific manufacturer for certificates)
Cons:
-
For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber.
-
More flexible and less durable than ABS. Because of this, it will not be possible to produce functional products.
-
Small palette of colors.

Most often, HIPS is used for its intended purpose for printing on 2x extruder printers as a support for ABS. It dissolves perfectly (though not very quickly) in limonel.
Sometimes HIPS is used as an independent material. Products from it are not very durable, but this plastic is loved for easy post-processing. HIPS can be used for models that will subsequently come into contact with food (not hot).
Using HIPS as a Soluble Support
Decorative vase made of HIPS
PVA
PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) is a material that was developed as a water-soluble support for PLA.
Extruder temperature - 190-210. Table heating is not required. PVA is a slightly "capricious" material, it is not recommended to overheat it and print at high speeds.
PVA is very hygroscopic and dissolves in plain water. Therefore, it is only used as a support for PLA or other plastics with print temperatures close to PVA.
Soluble PVA Support
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
PETG
PETG (polyethylene terephthalate) combines the best properties of PLA and ABS. It is easy to work with, it has a low percentage of shrinkage and excellent sintering of the layers.
Extruder temperature - 220-240 degrees. Table temperature - 80-100 degrees. During the printing process, the model must be well blown.
Pros:
-
Excellent sinterability of layers.

-
PETG is very strong and wear resistant. Good impact resistance.
-
Virtually no smell when printing.
-
Non-toxic.
-
Little shrinkage.
Cons:
PETG is perfect for printing functional models. Due to its low shrinkage, it is often used to make large or composite models. Due to its low toxicity, PETG is often used for products that will come into contact with food.
Cookie cutters and patterned rolling pin
SBS
It is a highly transparent material. At the same time, it is durable and resilient. SBS is a low toxicity plastic. It can be used to print food contact models.
Extruder temperature - 230 -260 degrees. Table temperature - 60-100 degrees. You can print without the closed case on the printer.
Pros:
-
slight shrinkage
-
Transparency.
 After treatment with solvent, limonel or dichloromethane, beautiful transparent products with an almost smooth surface can be obtained.
After treatment with solvent, limonel or dichloromethane, beautiful transparent products with an almost smooth surface can be obtained. -
Easily processed mechanically or chemically.
-
Allowed contact with food.
Cons:
SBS is excellent for translucent vases, children's toys and food containers. Or functional things that require transparency, such as custom turn signals for a motorcycle or car, lamps or bottle prototypes.
Vases are perfectly printed with a thick nozzle (0.7-0.8) in one pass (printing in 1 wall or spiral printing in a slicer).
Models of bottles after chemical treatment
Nylon
Nylon (polyamide) is considered the most durable material available for home 3D printing. In addition to good abrasion resistance and strength, it has a high slip coefficient.
Extruder temperature - 240-260 degrees. The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. Nylon is a very capricious and hygroscopic material - it is recommended to dry the coil with plastic before use. For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber, without this it will be difficult to print something larger than a small gear.
The temperature of the table is 80-100 degrees. Nylon is a very capricious and hygroscopic material - it is recommended to dry the coil with plastic before use. For printing, you need a printer with a heated table and a closed chamber, without this it will be difficult to print something larger than a small gear.
Pros:
-
High strength and wear resistance.
-
High slip factor.
-
Heat resistance compared to other 3D printing plastics.
-
High resistance to many solvents.
-
Good for mechanical processing. Perfectly polished and drilled.
Cons:
Nylon is perfect for making wear-resistant parts - gears, functional models, etc. Sometimes nylon is used to print bushings.
Nylon gear
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Bestfilament |
Soft plastics
FLEX (TPU, TPE, TPC) is a material similar to silicone or rubber. It is flexible and elastic, but at the same time tear-resistant. For example, TPE is a rubbery plastic, while TPU is more rigid.
It is flexible and elastic, but at the same time tear-resistant. For example, TPE is a rubbery plastic, while TPU is more rigid.
FLEX are printed at a temperature of 200-240 (depending on the material). A heated table is not required. On printers with direct material feed (feed mechanism on the print head), there are usually no problems with printing. On a bowden feeder (the feed mechanism is located on the body), printing with very soft plastics can be difficult. Usually it is necessary to additionally adjust the clamping of the bar. The main nuance is the very low print speeds - 20-40mm.
Pros:
Cons:
Depending on the type of FLEXa, the models can be flexible or rubber-like. This material, depending on its softness, can be used to print gaskets, insoles, belts, tracks or other models that require flexibility or softness.
FLEX belt
Trainers with flexible soles
Wheel for switchgear model
Decorative plastics
Decorative plastics are PLA plastics with various fillers (wood or metal shavings). Or with dyes selected to imitate different materials. Since the base of the plastic is PLA, it is very easy to print.
Or with dyes selected to imitate different materials. Since the base of the plastic is PLA, it is very easy to print.
Extruder temperature - 200-220 degrees (depending on the manufacturer). A heated table is not required.
Pros:
Cons:
-
Some fillers (eg clay) are abrasive. For such plastics, the standard brass nozzle cannot be used. Will have to buy a harder steel nozzle.
-
Some decorative plastics can clog the small nozzle (0.4 or less). For them, you need to use a “thicker” nozzle.
Depending on the filler, different material properties are obtained. Plastics that use only dye do not require additional processing. Materials with "fillers" may sometimes require additional post-processing.
Plastics with metal fillers after printing must be processed with a metal brush. Then the Metal content will show through and the model will resemble a metal casting.
Plastics with metallic powder
These plastics are often used for printing key chains, decorative models and interior details.
If the plastic has a high content of wood dust, then it is recommended to use a larger nozzle diameter (0.5 or more), a smaller nozzle can quickly become clogged during printing.
Wood-filled plastic ground
Plastic key rings with copper dust
Engineering plastics
These are nylon-based plastics with fillers that improve strength, heat-resistant and other characteristics, help to achieve less shrinkage of the material. For example - carbon fiber, carbon fiber or fiberglass.
Extruder temperature - 240-300 degrees (depending on the manufacturer). Table temperature - 90-110 degrees. Since plastics are based on nylon, the requirements for printing are similar. This is a heated table and a closed printer case.
Pros:
-
Hardness and strength.
-
Low flammability or non-combustibility.
-
High precision due to low shrinkage.
Cons:
3D printers use brass nozzles, some plastics can quickly “waste” it during printing. For such materials it is recommended to use steel nozzles.
These are highly specialized plastics used for a specific task, depending on the filler. For example, functional parts that do not lose their shape when heated, are resistant to many solvents, etc.
Functional Carbon Fiber Composite Prototype
Composite frame
Polycarbonate ashtray
Totals
This is of course not the whole list of materials for 3D printing. There are many highly specialized engineering and decorative plastics for specific tasks.
Manufacturers are constantly trying to replenish the range of materials for 3D printing. Already familiar materials are improved for more comfortable printing. There are many interesting decorative plastics imitating different materials - ceramics, clay, wood, metals.
And of course, the assortment of engineering plastics is constantly updated. Now there are many interesting materials for highly specialized tasks - for example, burnable plastic with a low ash content for subsequent casting in metal.
Burnout plastic
Before buying a coil, read the information on the website of the manufacturer or seller. There you can find some nuances of printing for a particular plastic. The manufacturer indicates the recommended temperature range on the box. Sometimes, for quality printing, it is recommended to print several tests to adjust the temperature settings, retract, etc.
Try to store the started coil in silica gel bags. It is recommended to additionally dry high-temperature plastics before printing to remove excess moisture.
It is recommended to additionally dry high-temperature plastics before printing to remove excess moisture.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Tiger3D |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | Esun |
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
| Manufacturer | FlashForge |
Order 3D plastic printing, professional printing on a 3D printer in Moscow
Order 3D plastic printing, professional printing on a 3D printer in MoscowHigh-strength models and prototypes of complex shapes in a wide range of colors
Plastic is one of the most popular materials for 3D printing using FDM technology. Plastic printing is used in many areas of life, it allows you to work with many different materials. Due to the wide variety of plastics and their different properties, 3D printing can create very different objects, from simple dishes to functional models of complex parts and devices.
Plastic printing is used in many areas of life, it allows you to work with many different materials. Due to the wide variety of plastics and their different properties, 3D printing can create very different objects, from simple dishes to functional models of complex parts and devices.
If you do not have your own equipment, please contact us: we offer 3D printing with thermoplastics, we take on projects of any complexity.
Order service
Types of plastics:
- ABS
- PLA
- PETG / PET / PETT plastic
- PC plastic (polycarbonate)
It has many positive characteristics, including increased impact resistance with high elasticity and softness of the material, as well as simple machining. High solubility in acetone makes it easy to bond parts and smooth the outer surfaces of products. Usually ABS is opaque, but can be easily dyed to any color if required. Finished products without coloring are sensitive to ultraviolet radiation and are endowed with low electrical insulating properties.
The key constituents of PLA are sugar cane and corn, and the material is based on lactic acid. By adjusting its level during production, it is possible to obtain various properties of the polymer, thereby expanding the areas of its use.
By adjusting its level during production, it is possible to obtain various properties of the polymer, thereby expanding the areas of its use.
3D printing with this material is in demand, as PLA products have a smooth and sliding surface.
The material is non-toxic, thanks to which it is widely used for the production of various toys and souvenirs. It has only one drawback - the fragility of operation. The finished product from it can last up to several years with minimal use and temperatures up to +50 degrees.
PET, or polyethylene terephthalate, is the most common type of thermoplastic. For 3D printing, "pure" PET is rarely used, mainly using its variety - PETG. PETG is more durable and has a much lower processing temperature. Another version of PET is PETT, a tougher and more popular material due to its transparency.
It has high strength and wear resistance, as well as increased resistance to physical impact and heat resistance. Withstands temperatures up to 110°C. The material is transparent, flexible, easily bends and does not deform. Excellent for automotive, medical and instrumentation applications.
Withstands temperatures up to 110°C. The material is transparent, flexible, easily bends and does not deform. Excellent for automotive, medical and instrumentation applications.
-
Fused Deposition Material Method (FDM)
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a layer-by-layer deposition method using a plastic filament.
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is one of the most widely used additive technologies.
- Equipment
- Tasks
- Advantages
- Industries
-
ProtoFab PF-S300 3D printer
Affordable SLS Printer
Price on request
Available
Buy More
-
ProtoFab PF-S350 3D printer
SLS Fast Printer
Price on request
Available
Buy More
-
Imprinta Hercules G6/G6 DUO 3D printer
Russian FDM printer for manufacturing large parts from engineering polymers
Price on request
Available
Buy More
-
Wiiboox W400 3D printer
Handy 3D printer for printing small parts 400 x 400 x 500 mm
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Wiiboox W500 3D printer
500mm x 500mm x 600mm fast FDM printer
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Wiiboox W600 Pro 9 3D Printer0045
Convenient and affordable 3D printer for printing 600mm x 600mm x 1000mm parts
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
3D printer F2 Innovations F2 Lite
Professional FDM printer for low volume production up to 600 mm
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Wiiboox W1000, W1200 3D printer
Unique 1000mm x 1000mm x 1200mm large object builder
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Super Discovery 3D Printer Hybrid
Simultaneous printing of parts up to 1.
 1 m with granules and filaments
1 m with granules and filaments Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Super Discovery 3D Printer Workstation
2 in 1 large format printer + milling system
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Discovery 3D Printer 2021
Compact 3D printing solution up to 1100 x 750 x 500 mm
Work with even the most complex objects!
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Sharebot Qwarm 9 3D printer0045
High Temperature Professional 3D Printer
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Sharebot Q DUAL 3D printer
The most accurate printing of plastic parts with two extruders
Price on request
Available
Buy More
-
Sharebot Q 3D printer
High-precision printing of plastic products up to 400 x 300 x 300 mm
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Sharebot Q XXL 3D Printer
Creating large objects with complex geometry using FDM technology
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Sharebot 43 3D printer
2x faster 3D printing with two extruders
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Sharebot XXL Plus 3D printer
Professional solution with working chamber 705 x 250 x 200 mm
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Sharebot SnowWhite 2 3D Printer
3D printing of small items up to 100 x 100 x 100 mm in polyamide
Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Super Discovery 3D Printer
Industrial printing of items up to 2.
 5 m at speeds up to 6 kg/h
5 m at speeds up to 6 kg/h Price on request
On request
Buy More
-
Super Discovery 3D Printer Compact
Create parts up to 1100 x 800 x 500 mm from any thermoplastic
Price on request
On request
Buy More
- production of functional models, prototypes
- serial production
- creation of conceptual and architectural models
- manufacture of spare parts and mechanical parts, medical instruments
- making toys, packaging, signage
- wide range of applications
- variety of colors and textures of material
- ease of machining
- ease of use
- flexible material structure
- making products with smooth and even surfaces
- relatively low cost
-
Aerospace
-
Automotive
-
Construction and architecture
-
Packaging
-
Shipbuilding
-
Medicine
3D plastic printing
Three-dimensional plastic printing, or FDM printing, is one of the most promising areas in the production of various products today. With the help of a 3D printer, this technology allows you to easily and quickly produce objects of various levels of complexity with high detail and excellent surface quality.
With the help of a 3D printer, this technology allows you to easily and quickly produce objects of various levels of complexity with high detail and excellent surface quality.
Compared to traditional methods, plastic 3D printing is affordable and much faster in creating products, which is in demand in a huge number of industries of various types, in particular in industry, prototyping, design and the production of household goods.
One of the key advantages of FDM technology is a wide range of composites and thermoplastics with a wide variety of characteristics. This allows you to easily select the necessary material for any task, as well as choose the optimal color for the final product. Some of the most popular 3D printing materials include affordable high-impact ABS, amazingly flexible polyamide for intricate designs, durable and environmentally friendly PLA, and PETG, a resilient and flexible resin for large-scale 3D printing.
There are several reasons why you should consider 3D printing with plastic:
- High precision workpieces
- Relatively low cost of plastics
- Short terms and efficiency of obtaining the final part
- An extremely wide range of 3D printing materials
- Ability to manufacture geometrically complex products, both small and large sizes
Cost of creating thermoplastic products on a 3D printer
The price of 3D plastic printing is calculated based on several factors:
- Product volume and weight
- Consumable type
- Material layer thickness
iQB Technologies is a Russian distributor of 3D printers from leading manufacturers: the Spanish company Discovery 3D Printer, the Italian developer Sharebot, and the Chinese company Wiiboox.