Metal composite 3d printer filament
Metal Composite Filament | MatterHackers
Metal composite filaments are plastic materials like PLA that are infused with metal powders like bronze, copper, and magnetic iron designed to give your parts a rustic metal look. Metal filament like these infusions have a lot of cool properties - they actually patina and you can polish them to bring out more metal-like features.
If your looking for 100% real metal filament options, click here.
Metallic 3D Printing Filament
Metal 3D Printing Filament
Print with real metal on your desktop 3D printer.
The Virtual Foundry
If you can print plastic, you can print pure metal parts.
Metal Composite Filament
Plastic materials like PLA that are infused with metal powders
Guides & Articles
How to Succeed with Quantum Dichromatic PLA Filament
Follow this guide for tips and tricks on how to get the best results when 3D printing with Quantum Dichromatic PLA filament.
How To Succeed with LayerLock SLA Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for Laser, DLP, and SLA resin prints using LayerLock SLA Resin 3D Printing Build Surfaces.
How To Build A Successful Makerspace
Find out the necessary components to create an effective space for your maker community.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing with Polypropylene
Successfully produce 3D printed parts out of polypropylene filament with these tips on achieving stronger bed adhesion and minimizing shrinkage.
Tech Breakdown and How to Succeed: Ionic Hybrid Support Material
Supporting engineering-grade filament has been difficult without a support material dedicated to higher temperature 3D printing. Ionic aims to solve that.
How To Succeed with OBC 3D Printing Filament
From Dow Chemical, OBC combines flexible and rigid into one unique material with properties of both.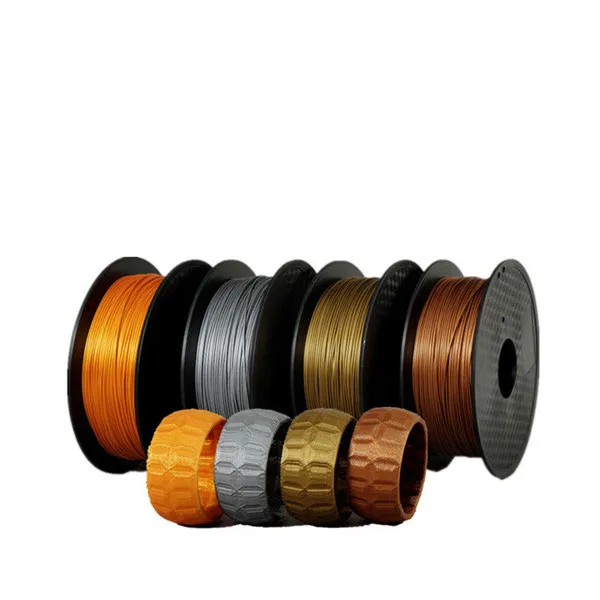
How To Succeed with LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for NylonX, NylonG, and standard filaments using LayerLock Garolite Build Surfaces.
How to Succeed with LayerLock Powder Coated PEI Build Plates
Powder coated PEI steel sheets are a great alternative build surface for strong bed adhesion. Here's how you can succeed using this durable build plate.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With Nylon
Learn how to 3D print Nylon like a pro. Nylon is a stronger and more durable alternative to PLA or ABS and easy to 3D print with using these Tips and Tricks.
How To Succeed When 3D Printing With ASA Filament
Follow this step-by-step guide to learn how to print with ASA, the perfect material for any outdoor projects.
How to Succeed when 3D Printing with Polycarbonate Filament
Follow these helpful steps to start successfully printing with this extremely tough, professional grade material.
How to Succeed with NylonX
NylonX has quickly become one of our favorite filaments for strong, durable, and ready-to-use parts. Here's an in-depth look at Nylon X, and some printing tips to get the most out of this great new material.
Metallic 3D Printing Filament | MatterHackers
- Home
- Store
- 3D Printer Filament
- Metallic 3D Printing Filament
Which metallic filament is right for me?
Real Metal Filament - real stainless steel filament printed on your desktop 3D printer. This metal 3D printing filament can be debinded and sintered, leaving your 3D printed part solid 316L or 17-4 PH stainless steel metal. If you are looking for an affordable way to create one-off, custom metal parts, small-batch manufactured parts, or just want to finally print with real metal on your desktop printer, this is your best option.
Metal Composite Filament - plastic filament infused with metal powders.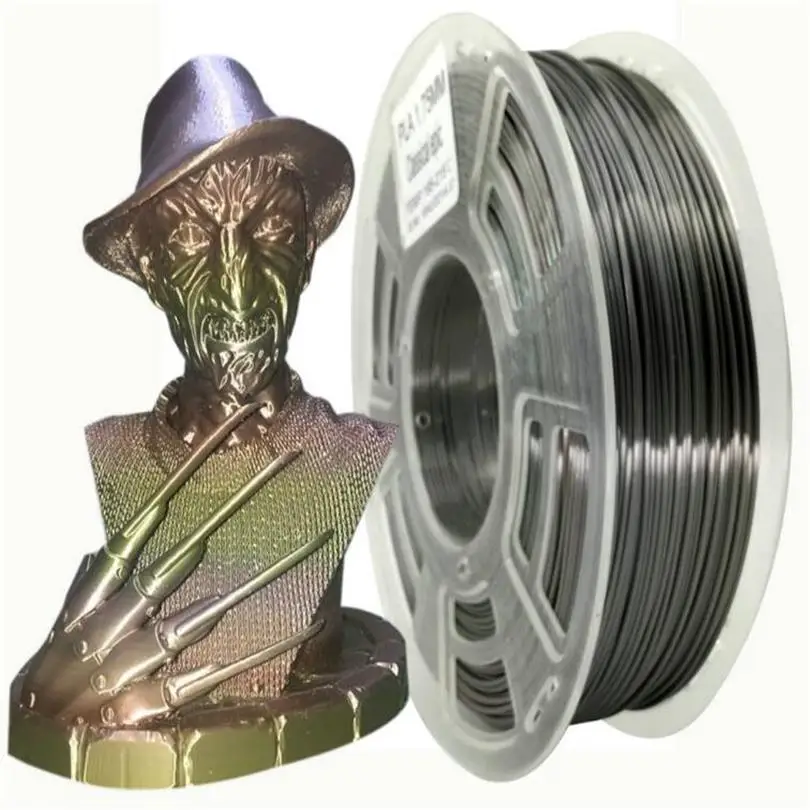 These materials are still mostly PLA plastic and will have typical PLA filament characteristics. The metal powder (bronze, copper, or magnetic iron) provides aesthetic characteristics as opposed to their real metal properties. For example, printed parts in metal composite filament can rust/patina and even be sanded and polished to shine. So, if you are just searching for a metallic look, using a metal composite material is your best option.
These materials are still mostly PLA plastic and will have typical PLA filament characteristics. The metal powder (bronze, copper, or magnetic iron) provides aesthetic characteristics as opposed to their real metal properties. For example, printed parts in metal composite filament can rust/patina and even be sanded and polished to shine. So, if you are just searching for a metallic look, using a metal composite material is your best option.
Metallic 3D Printing Filament Collections
All Metallic 3D Printing Filament 3D Printer Filament
Metallic 3D Printing Filament
Metal 3D Printing Filament
Print with real metal on your desktop 3D printer.
The Virtual Foundry
If you can print plastic, you can print pure metal parts.
Metal Composite Filament
Plastic materials like PLA that are infused with metal powders
Guides & Articles
How to Succeed with 3D Printing Metal on a Desktop 3D Printer
The time is here to explore easy and affordable metal 3D printing. 3D printing with real metal on a desktop 3D printer is now possible using Ultrafuse Metal 3D printing filament from BASF Forward AM.
3D printing with real metal on a desktop 3D printer is now possible using Ultrafuse Metal 3D printing filament from BASF Forward AM.
BASF Forward AM: A Look at One of Additive Manufacturing's Top Chemical Producers
BASF Forward AM is the production branch of BASF that creates a wide range of additive manufacturing materials for businesses and personal 3D printing.
3D Printer Filament Comparison Guide
There are many different kinds of 3D printer filament, and each one has it's own strengths for different projects. Knowing these differences is key to a successful 3D printing experience and so we have created a Filament Comparison Guide with everything you need to know about every type of filament available.
Stainless Steel Metal 3D Printing on Benchtop 3D Printers
A MatterHackers presentation on advanced materials and their rising presence in 3D printing and BASF Ultrafuse 316L, a composite filament that yields pure metal components
Casting Metal Parts From 3D Prints
Follow Sylatech as they transform legacy casting processes with 3D printing.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing With Metal PLA
Learn the best tips and tricks for 3D printing with metal-infused PLA 3D printing filament.
How To: Post Process Metal Filled Filaments
While 3D printing in true metal is still cost prohibitive to most people, 3D printing composite materials to achieve the look and feel of metal is easy, and all it takes is time.
Tech Breakdown: A Detailed Account of ColorFabb SteelFill Filament
An in-depth review of SteelFill 3D filament, the next great metallic PLA from ColorFabb that delights users with its metal characteristics and relatively easy printing.
Ultrafuse 316L Metallic Filament for FDM (FFF) 3D Printing - SMARTPRINT
Composite Metallic Filament with Stainless Steel for FDM (FFF) 3D Printers
Ultrafuse® 316L is an innovative filament for the production of 316L stainless steel parts.
[button target="_blank" hover_type="default" text="Buy Ultrafuse® 316L 1. 75mm" margin="15px 0px 0px 0px" link="https://3dsmart.com.ua/shop/materials/basf- ultrafuse-316l-175″][button target="_blank" hover_type="default" text="Buy Ultrafuse® 316L 2.85mm" margin="15px 0px 0px 0px" link="https://3dsmart.com.ua /shop/materials/basf-ultrafuse-316l-285″]
75mm" margin="15px 0px 0px 0px" link="https://3dsmart.com.ua/shop/materials/basf- ultrafuse-316l-175″][button target="_blank" hover_type="default" text="Buy Ultrafuse® 316L 2.85mm" margin="15px 0px 0px 0px" link="https://3dsmart.com.ua /shop/materials/basf-ultrafuse-316l-285″]
Material Details
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation= » icon_animation_delay=» link=» target='_self'] Product Brochure
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color =" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Data Sheet
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link= » target='_self'] User Manual
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin= » icon_animation=» icon_animation_delay=» link=» target='_self'] Debinding Simulation Guide
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-download' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Processing Guide
Description
It is designed for maximum ease of use on conventional 3D printers with FFF (Fused Filament Fabrication) technology. The BASF Ultrafuse® 316L combines greater design freedom with a lower total cost of ownership—printing metal parts is easier, faster and more affordable. Parts printed with Ultrafuse® 316L develop their final properties, including hardness and strength, through a catalytic debinding and sintering process. The catalytic debinding technology was developed and implemented by BASF and has become the industry standard. nine0005
The BASF Ultrafuse® 316L combines greater design freedom with a lower total cost of ownership—printing metal parts is easier, faster and more affordable. Parts printed with Ultrafuse® 316L develop their final properties, including hardness and strength, through a catalytic debinding and sintering process. The catalytic debinding technology was developed and implemented by BASF and has become the industry standard. nine0005
Benefits at a Glance
=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Easy and Affordable Metal 3D Printing
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Fast material change and easy handling
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] For all open source FFF printers
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color =" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Produces 316L stainless steel parts.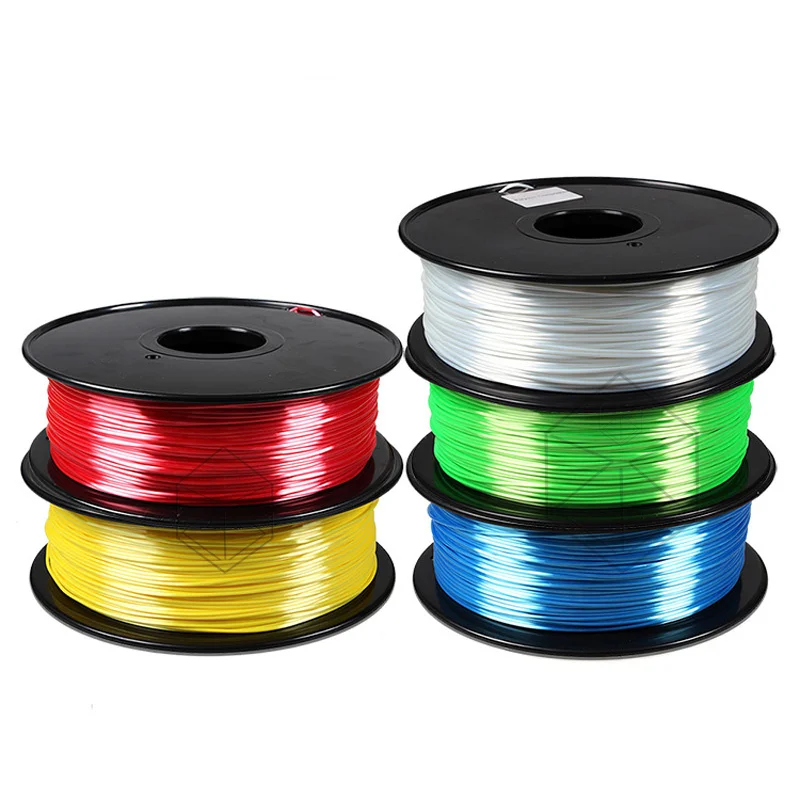 nine0035 [icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Uniform particle distribution improves mechanical properties
nine0035 [icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Uniform particle distribution improves mechanical properties
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] The high flexibility of the filament allows it to print successfully on any FFF printer. nine0035 [icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Compatible with both Bowden and direct drive extruders
Use Cases
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Snap
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link= » target='_self'] Fixtures & Fixtures
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color=" icon_color=" background_color=" margin =" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Function Prototypes
[icons size=" custom_size=" icon='fa-check' type='normal' position=" border='yes' border_color =" icon_color=" background_color=" margin=" icon_animation=" icon_animation_delay=" link=" target='_self'] Limited edition
Process Brief
Easy and cost-effective 3D printing of metal parts with Ultrafuse® 316L
We developed Ultrafuse® 316L to produce high quality metal parts and high productivity.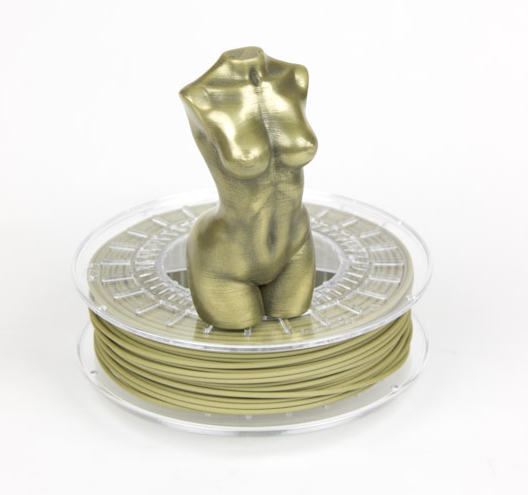 This state of the art metallic filament is suitable for use with any conventional Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printer. Once printed, the final properties of the part are achieved through an industry standard debinding and sintering process developed by BASF. nine0035 Ultrafuse® 316L is economical, easy to process and meets MIM industry standards for catalytic debinding and sintering. This innovative industrial metal-polymer composite supports a wide range of applications, including tools, fixtures and fixtures, small-scale production, functional parts, prototypes, and even jewelry.
This state of the art metallic filament is suitable for use with any conventional Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printer. Once printed, the final properties of the part are achieved through an industry standard debinding and sintering process developed by BASF. nine0035 Ultrafuse® 316L is economical, easy to process and meets MIM industry standards for catalytic debinding and sintering. This innovative industrial metal-polymer composite supports a wide range of applications, including tools, fixtures and fixtures, small-scale production, functional parts, prototypes, and even jewelry.
Ultrafuse® 316L contains thermoplastic binders with 90 weight percent fine metal particles. Our filament has a non-slip surface that allows it to be used in most Bowden or direct drive extruders. Due to its high flexibility, it can be fed through sophisticated idlers and multiple filament transport systems in printers – no additional drying required. Metal-polymer composite as a filament does not have any of the production hazards and safety risks associated with handling fine metal powders, making 3D printing of stainless steel parts affordable, simple and safe. nine0005
nine0005
Which 3D printers should I use with the Ultrafuse® 316L?
Ultrafuse® 316L, designed for safe and easy use with conventional FFF printers, has a wide processing window. To help you succeed in metal 3D printing, we provide printer processing instructions, including Ultrafuse® 316L presets. In addition, on-site consultation and support is available to ensure that the material will work on your printer. nine0005
Would you like a 3D printing and/or post-processing service for your Ultrafuse® 316L part?
Your name (required)
Your e-mail (required)
Your phone number (required)
Your message
Attach a file (up to 10 mb)
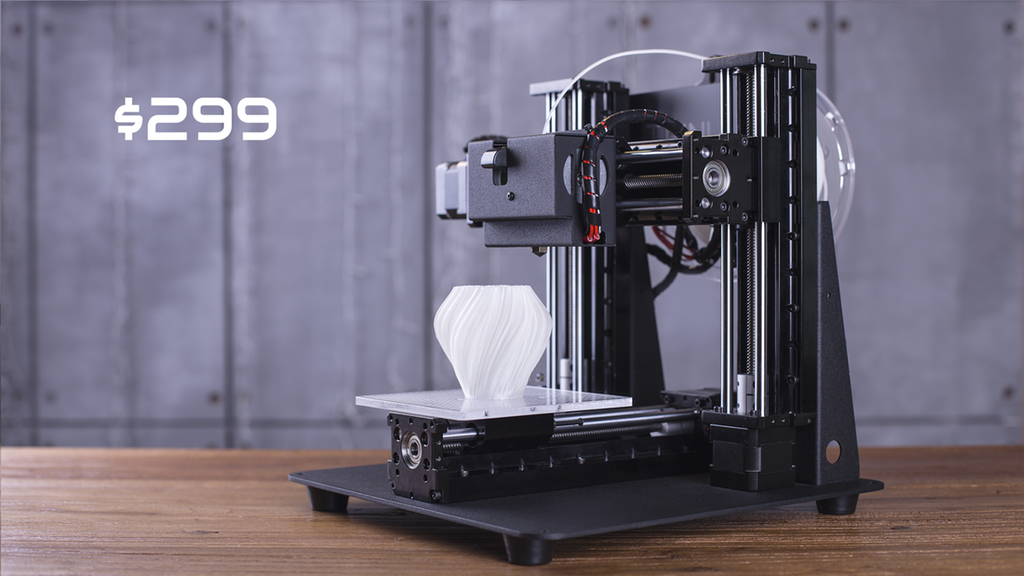
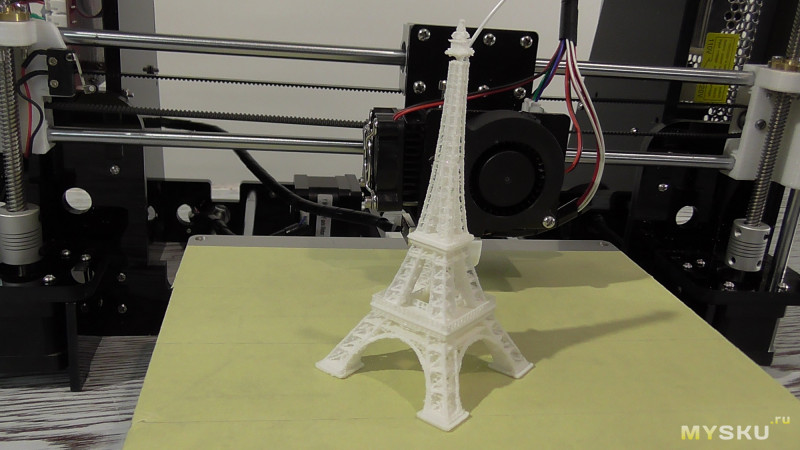
3D printing with metal composite filaments
Added on June 17, 2019 at 02:38 AM
Find out how adding metal composites to plastic filaments makes 3D printed parts look like metal. nine0097
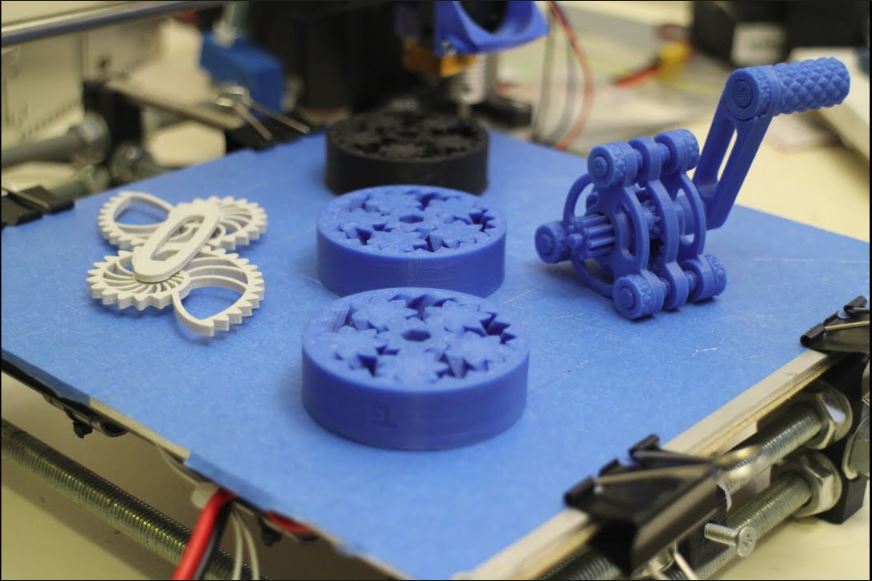
With the exception of professional industrial machines, all 3D printers build objects out of plastic. 3D printers can use quite a few different types of plastic such as ABS, PLA, and nylon; and they can use several different technologies to turn plastic raw materials into parts. But the fact remains, plastics are the materials available for any desktop 3D printer. However, hobbyists using plastic filaments with other additives can 3D print parts that look and feel like metal. nine0005 3D printed objects that look like metal
3D printers can use quite a few different types of plastic such as ABS, PLA, and nylon; and they can use several different technologies to turn plastic raw materials into parts. But the fact remains, plastics are the materials available for any desktop 3D printer. However, hobbyists using plastic filaments with other additives can 3D print parts that look and feel like metal. nine0005 3D printed objects that look like metal
Metal composite filaments, sometimes referred to as metal-filled filaments, contain approximately 40-60% fine metal powder mixed with PLA. They should not be confused with filaments, which are just a metallic color. Metal composite filaments are much heavier than regular PLA filaments. Although they look like metal, oxidize and weather like metal, and are cold to the touch, they can be printed on conventional 3D printers. nine0005
These specialized filaments are available in several different materials: copper, bronze, stainless steel and iron are the most common.
Metal Composite Filament Evaluation Chart In terms of performance and cost, metal composite 3D printing filaments do not quite match conventional plastic filaments. Their main value is their appearance.
In addition to looking like they are made of metal, parts printed with metal composite filaments are much heavier than plastic parts. This is especially true for high density printed parts. Their weight makes the parts even more convincing for use as semi-substitutes for cast metal objects. nine0005 On the left is a detail printed in black PLA with 20% infill. On the right is the same model printed with ColoFabb Copperfill filament at 20% infill.
Cost
It's no surprise that specialized filaments for 3D printers filled with metal powders cost significantly more than regular plastic filaments. Also, metal-composite filaments are produced by a limited number of manufacturers.
ColorFabb and ProtoPasta are the two largest and most respected distributors of these specialized raw materials. The price of a coil of metal-composite filament depends on the type of metal and the quality of the thread. nine.98
The price of a coil of metal-composite filament depends on the type of metal and the quality of the thread. nine.98
Durability
There is a reason why metal-filled plastics are not used in manufacturing. Composite material does not have the strength, durability and malleability of pure metal. Also, the addition of metal powders to PLA filament makes it more brittle than pure PLA.
Objects printed with metal composite filaments are very fragile. nine0024 Post-processingWhen using other types of 3D printing stock, post-processing is an optional step to improve the appearance of your parts. For metal composite filaments, post-processing of parts is required.
Metal-filled parts will not look like metal right out of the printer. They have a matte finish and a color close to the color of the metal they contain.
This part was printed with copperFill filament (with copper), but before post-processing it doesn't really look like copper.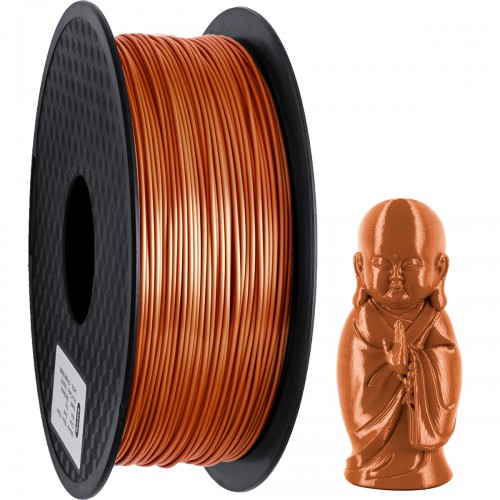 nine0004 Fortunately, post-processing of metal-composite parts is simple, but requires some equipment. Because metal-filled filaments are used as the base material of PLA, sanding parts can be difficult. This material heats up and softens quickly, creating a strange white mark. There are also no readily available chemicals that can be used to polish parts the way ABS is chemically polished.
nine0004 Fortunately, post-processing of metal-composite parts is simple, but requires some equipment. Because metal-filled filaments are used as the base material of PLA, sanding parts can be difficult. This material heats up and softens quickly, creating a strange white mark. There are also no readily available chemicals that can be used to polish parts the way ABS is chemically polished. The best post-processing method for metal composite parts is tumbling. For this, a simple device is used, consisting of a rotating drum filled with polishing agent (in English, this device is called " rock tumbler "). The part after 3D printing is simply placed inside this drum, and as the drum rotates, the polishing agent processes the surface of the part.
Metal-composite filament parts before and after finishing Suppliers offer many polishing materials for 3D printing enthusiasts. One of the more popular means is to use small mounting screws that look like metal-composite plastic. Another option is small pieces of stainless steel the size of rice grains. nine0005 Stainless steel polish for rotating cups After a long time spinning in the cup, the metal composite parts will look much more like real metal rather than metal color plastic
Another option is small pieces of stainless steel the size of rice grains. nine0005 Stainless steel polish for rotating cups After a long time spinning in the cup, the metal composite parts will look much more like real metal rather than metal color plastic
Easy to use
Since metal composite filaments use PLA as the main material, they can be the same settings as when printing with PLA. This is great because PLA is the easiest type of material to 3D print, which is why it's so popular. The metal composite filament is printed at a low temperature, around 200°C. It can also be printed without bed heating. In fact, metal-filled filaments are even less prone to warping than regular PLA. nine0005 Two print samples, PLA on the left, copperFill on the right, were printed with the same print settings. In fact, both models used the same g-code for printing.
However, there are a few caveats when using metal-filled filaments, which makes them more difficult to use than regular PLA filaments.
First, the metal powder in the filament makes this type of specialized raw material more abrasive than pure plastic. Most 3D printers come with a brass nozzle. However, brass is a relatively soft metal and can be worn away by abrasive metal composite filaments, slowly reducing the print quality of your printer. nine0005 On the left is a standard brass nozzle after many hours of printing, including about 3 kg of metal-filled filament. On the right is a brand new hardened nozzle. You can see that the nozzle on the left has begun to be destroyed by the abrasive metal-composite filament.
Second, metal-filled filaments do not bridge as well as pure plastics, nor do they perform canopies as well as other materials. As mentioned above, metal-composite filaments are much heavier than conventional plastics, which makes this material more difficult to hold attachments in the air while the plastic hardens. nine0005
The metal content of metal-composite filament also allows the material to retain heat longer than conventional plastic..jpg) In fact, this is a good feature for preventing warping, as it means that the parts cool more slowly and more evenly. However, this also makes it difficult to bridge and shed.
In fact, this is a good feature for preventing warping, as it means that the parts cool more slowly and more evenly. However, this also makes it difficult to bridge and shed.
For best results, parts should be designed with a minimum number of bridges and canopies - otherwise you will need additional support material. If your part has canopies, don't forget to enable support generation at a fairly high angle. nine0005 Using supports for overhanging elements of the printed object
Printer settings
Printer settings when printing with metal-composite filamentsMost suitable projects for printing with metal-filled filament
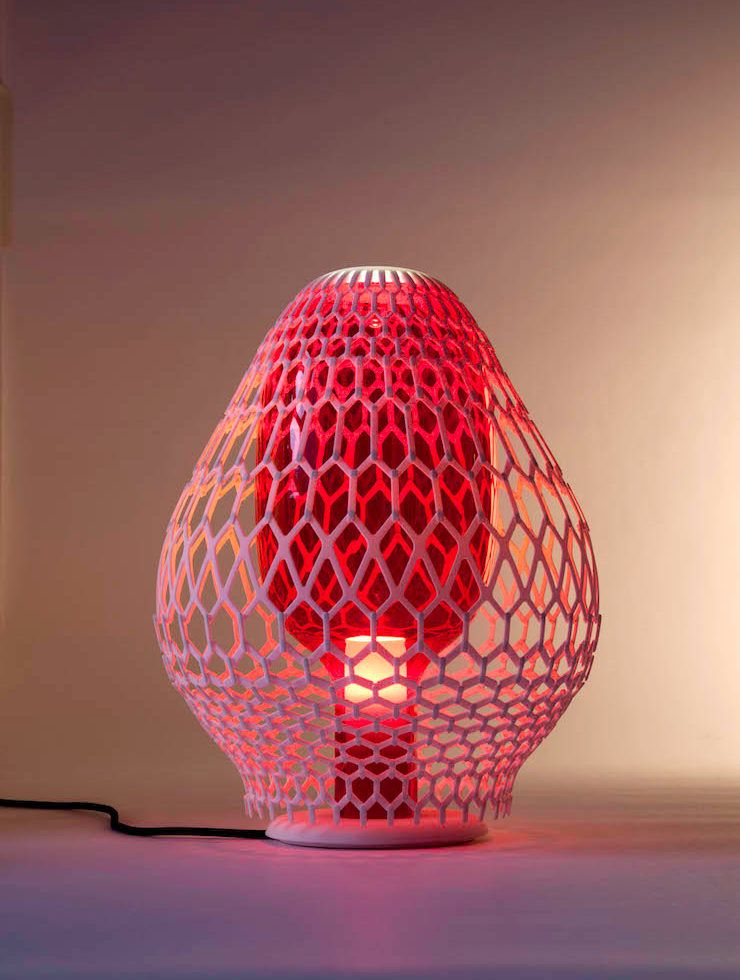
Decorative objects
Considering that metal-composite filaments are mainly useful for their aesthetic properties, they are very suitable for decorative print objects: desktop figurines, figurines, paperweights, wall art are some examples of common decorative items made from composite plastic. nine0005
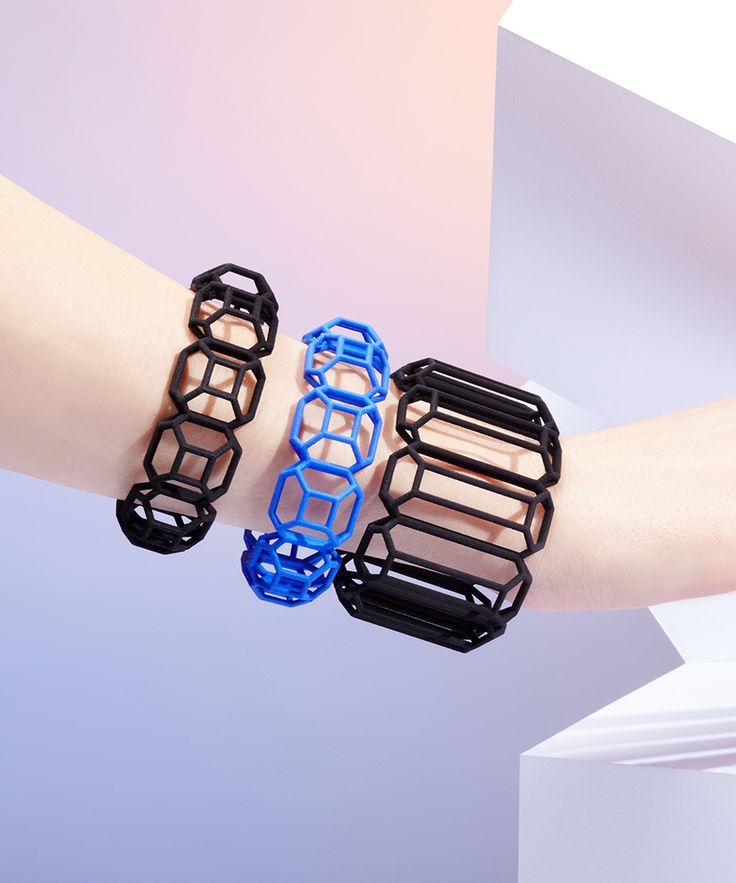
Jewelry
Metal-filled filament can be printed into jewelry, allowing designers to prototype designs or even print sample products without the need for metal casting.