Metal 3d printing canada
3D Printing Services for Canada
Back
-
Materials
Materials by Service
Injection MoldingCNC Machining3D PrintingSheet Metal
Materials by Type
PlasticsMetalsElastomers
Related Links
Customer Supplied ResinsColors
Injection Molding Material Alternatives Guide
Struggling with thermoplastic material shortages? We created a detailed guide to resin substitutes for ABS, PC, PP, and other commonly molded thermoplastics.
Download
-
Resources
Design Tips Guides and Trend Reports Success Stories Design Aids Webinars and Trade Shows
Blog Videos FAQs Educators and Students Glossary
Industries Medical Aerospace Automotive Consumer Electronics Industrial Equipment
-
About Us
Who We Are Why Protolabs? Research and Development Cool Idea Award Partnerships Sustainability and Social Impact
Careers Investors Locations Press Procurement
Contact Us
Proto Labs, Inc.
5540 Pioneer Creek Dr.
Maple Plain, MN 55359
United StatesP: 877.479.3680
F: 763.479.2679
E: [email protected]Best-in-Class Online Quoting
After uploading your part design, you'll receive an online quote that includes manufacturing analysis to help improve part manufacturability. Within your quote, you can also adjust quantity and material and see price changes in real-time.
Learn More
Get a QuoteSign In
Parts ship to Canada as fast as 1 day. Upload a 3D CAD model to get an instant quote.
GET INSTANT QUOTE View Materials
CERTIFICATIONS
ISO 9001:2015 | AS9100D | ITAR Registered
Our 3D Printing Processes
From rapid prototyping to end-use production and plastics to metals, our 3D printing service offers a broad range of capabilities that will meet your project requirements.
Metal 3D Printing
LEARN MORE
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
LEARN MORE
Stereolithography (SLA)
LEARN MORE
PolyJet
LEARN MORE
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
LEARN MORE
Carbon DLS
LEARN MORE
Compare 3D Printing Technologies
Examine 3D Printing Materials by Technology
Metal 3D Printing (DMLS)
- Aluminum (AlSi10Mg)
- Cobalt Chrome
- Copper (CuNi2SiCr)
- Inconel 718
- Stainless Steel (17-4PH and 316L)
- Titanium (Ti 6-4)
Stereolithography (SLA)
ABS-Like
- ABS-Like Gray (Accura Xtreme Gray)
- MicroFine™ (Gray and Green)
- ABS-Like Translucent/Clear (WaterShed XC 11122)
- ABS-Like Black (RenShape SL7820)
- ABS-Like White (Accura Xtreme White 200)
PC-Like
- PC-Like Translucent/Clear (Accura 60)
- PC-Like Advanced High Temp (Accura 5530)
- Ceramic-Like Advanced HighTemp (PerFORM)
PP-Like
- PP-Like Translucent White (Somos 9120)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- PA 12 White (PA 650)
- PA 11 Black (PA 850)
- PA 12 40% Glass-filled (PA 614-GS)
- PA 12 Mineral-filled (Duraform HST)
Multi Jet Fusion
- PA 12 Nylon Black
- PA 12 40% Glass-Filled Black
PolyJet
- Digital Clear/Translucent
- Digital Black
- Digital White
Carbon DLS
- Carbon RPU 70
- Carbon FPU 50
If you have any issues getting your guide, click here to download.
3D Printing Surface Finish Guide
Get this quick reference guide to explore your surface finish options across our six 3D printing technologies.
United States of AmericaAfghanistanÅland IslandsAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntarcticaAntigua and BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelarusBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBolivia, Plurinational State ofBonaire, Sint Eustatius and SabaBosnia and HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCape VerdeCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos (Keeling) IslandsColombiaComorosCongoCongo, the Democratic Republic of theCook IslandsCosta RicaCôte d'IvoireCroatiaCubaCuraçaoCyprusCzech RepublicDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEthiopiaFalkland Islands (Malvinas)Faroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard Island and McDonald IslandsHoly See (Vatican City State)HondurasHong KongHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIran, Islamic Republic ofIraqIrelandIsle of ManIsraelItalyJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea, Democratic People's Republic ofKorea, Republic ofKuwaitKyrgyzstanLao People's Democratic RepublicLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacaoMacedonia, the Former Yugoslav Republic ofMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesia, Federated States ofMoldova, Republic ofMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmarNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorthern Mariana IslandsNorwayOmanPakistanPalauPalestine, State ofPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairnPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarRéunionRomaniaRussian FederationRwandaSaint BarthélemySaint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da CunhaSaint Kitts and NevisSaint LuciaSaint Martin (French part)Saint Pierre and MiquelonSaint Vincent and the GrenadinesSamoaSan MarinoSao Tome and PrincipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSint Maarten (Dutch part)SlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSomaliaSouth AfricaSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSouth SudanSpainSri LankaSudanSuriNameSvalbard and Jan MayenSwazilandSwedenSwitzerlandSyrian Arab RepublicTaiwan, Province of ChinaTajikistanTanzania, United Republic ofThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad and TobagoTunisiaTurkeyTurkmenistanTurks and Caicos IslandsTuvaluUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited States Minor Outlying IslandsUruguayUzbekistanVanuatuVenezuela, Bolivarian Republic ofViet NamVirgin Islands, BritishVirgin Islands, U. S.Wallis and FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabwe
S.Wallis and FutunaWestern SaharaYemenZambiaZimbabwe
I agree to receive email messages containing service updates and Design Tips from Protolabs and its affiliates
Why Choose Protolabs for 3D Printing in Canada?
Get design feedback from our experienced engineering team that has helped thousands of customers bring their products to market with quality 3D-printed parts. We will also work with you to determine optimal part orientation based on your application's requirements.
Across our six 3D printing technologies, we use a range of commercial-grade thermoset resins, and thermoplastic and metal powders to 3D print parts that are suitable for various part applications and industries.
If required for your parts, we offer a variety of post-process options such as heat treating, secondary machining, plating, painting, and dyeing to further enhance mechanical properties and cosmetics.
LEARN MORE
Our industry-leading tolerances and surface finish quality stems from a dedicated process engineering and quality team for each 3D printing technology. We also offer a proprietary material called Microfine™, which can build features as small as 0.0025 in.
We also offer a proprietary material called Microfine™, which can build features as small as 0.0025 in.
SEE MICROFINE DETAILS
Our facility is home to more than 120 3D printing machines that produce metal and plastic parts. This means we'll always have capacity when you need parts fast.
Consultative Quoting
Wide Material Selection
Precision and Repeatability
Unmatched Scale
Custom Finishing for 3D-Printed Parts
Looking to boost the strength, clarity, or appearance of your 3D-printed parts? Choose from microfluidic and micro-resolution materials, metal plating, secondary machining, and custom finishes like painting, clear coating, and decaling.
VIEW FINISHING OPTIONS
What's in Your Instant 3D Printing Quote?
Once you upload a 3D CAD file you'll get an instant quote on your 3D printing design. See real-time cost implications based on your choice of 3D printing material and resolution level.
GET INSTANT QUOTE VIEW SAMPLE QUOTE
3D Printing Resources
Design Tip
Designing for Direct Metal Laser Sintering
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) produces complex, durable, lightweight metal parts. Depending on the design, DMLS can be a reliable way to manufacture metal parts.
Read Design Tip
Blog
3D Printing Micro Features with Stereolithography’s MicroFine Material
MicroFine is an ABS-like stereolithography (SLA) material specifically designed to 3D print parts with features as fine as 0.0025 in.
Read Blog
Guide
3D Printing Materials: Select the Right Plastic or Metal for Your 3D-Printed Part
Explore material properties available for plastic and metal 3D printing processes
Read Guide
Design Tip
Selecting a Material for Stereolithography (SLA) 3D Printing
Compare materials for stereolithography with one another and with injection-molded plastics.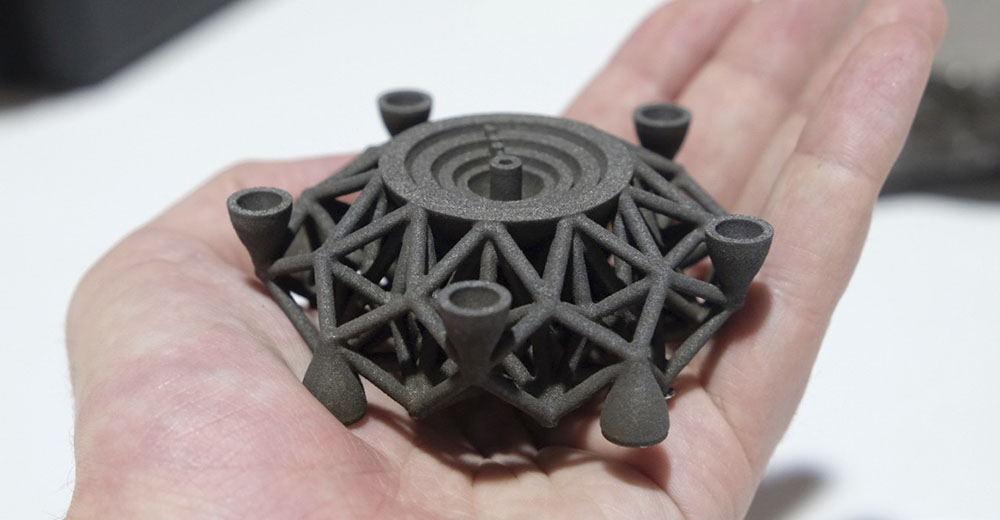
Read Design Tip
3D Printing Service Canada | Instant Quotes Online
Our 3D printing capabilities
We have over 90 3D printing shops in our network and are well known for manufacturing high-quality parts at competitive prices, from rapid prototyping with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) to functional end parts made with Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) or Multi Jet Fusion (MJF).
Gallery of 3D printed parts manufactured by Hubs
With over 65,000 customers from every industry, including aerospace, defense, robotics, medical, machinery, automotive and electronics, we have extensive experience meeting a diverse range of 3D printing requirements, from prototyping to production: Visual aids, concept models, injection-molding prototypes, form-fit & function prototypes, tooling and casting patterns, jigs, grips and fixtures, and durable end parts.
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22.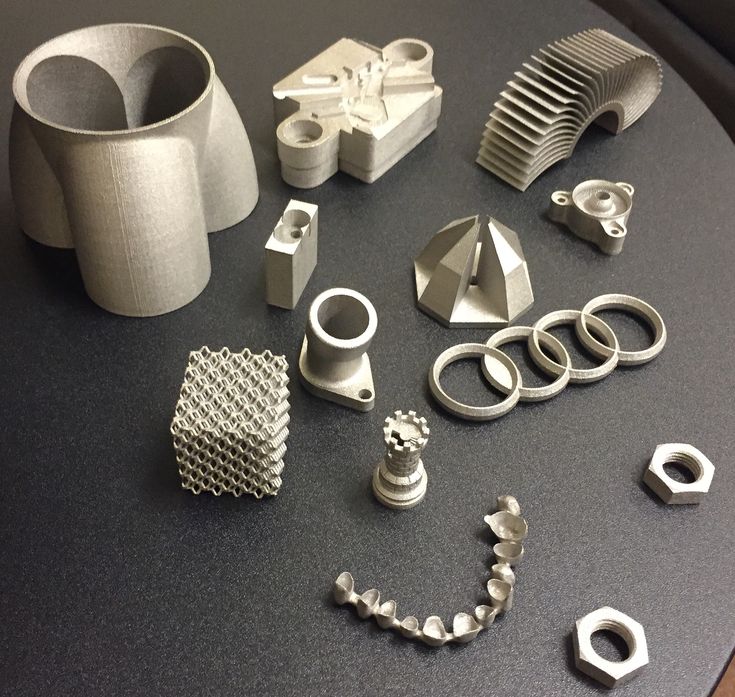 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22.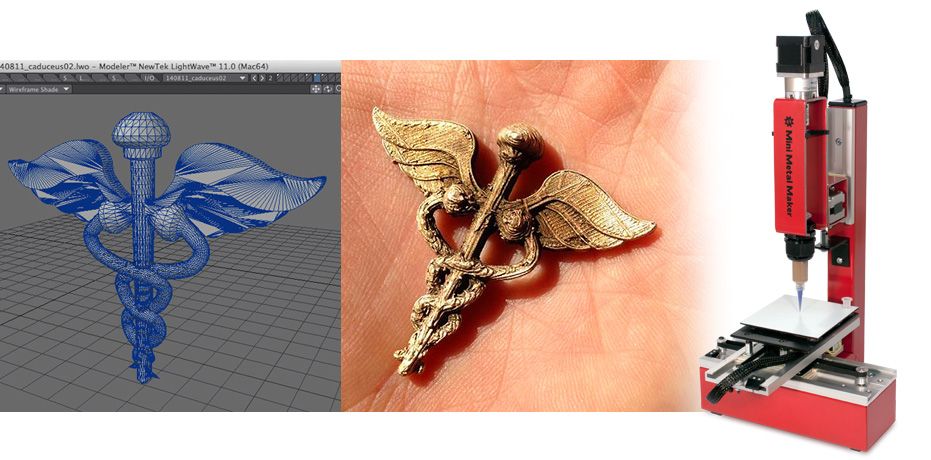 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22. 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29. 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
HP PA 12 - Dyed Black
| Customer | True North Design |
| Purpose | Structural and vacuum EOAT components |
| Process | SLS / MJF |
| Unit price | $69.23 / $34.33 |
| Industry | Automotive |
Prototyping PLA
| Customer | Allision Conner |
| Purpose | End caps and cable strain relief for sheet metal enclosure |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $7.92 / $4.72 / $2.80 |
| Industry | Industrial Automation |
HP PA 12
| Customer | US Hammer |
| Description | A part for gasoline engine powered jackhammers |
| Process | MJF |
| Unit price | $22.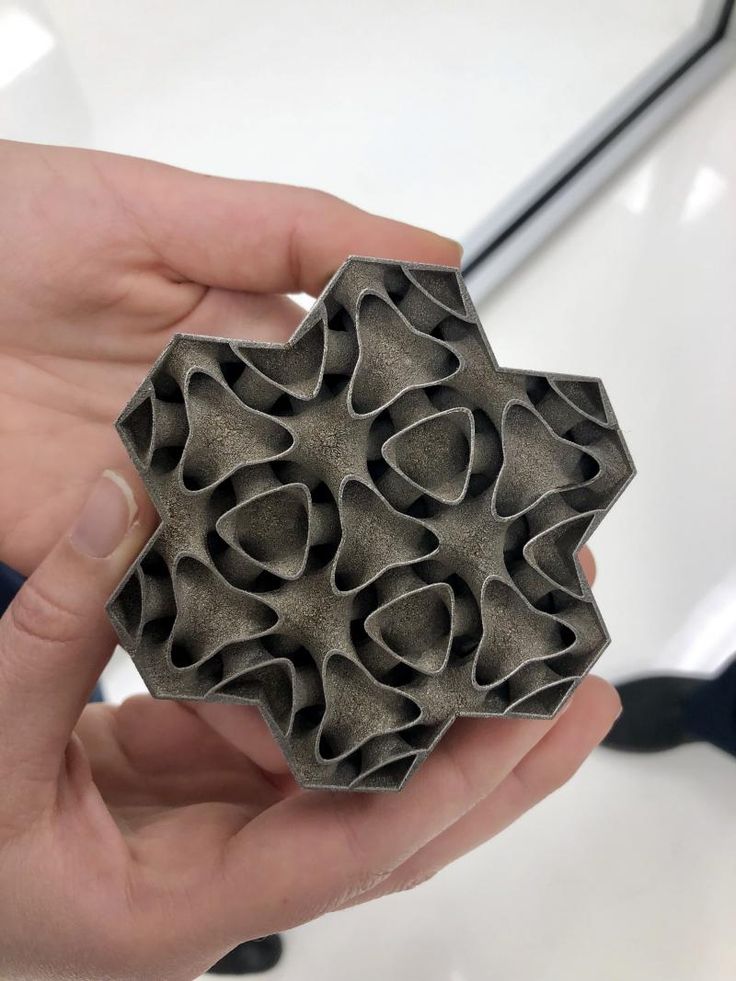 18 18 |
| Industry | Construction |
Markforged Onyx - Black
| Customer | Autocom Manufacturing |
| Purpose | A production part for 3D printed lathe gantry gripper fingers |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $48.86 |
| Industry | Automotive |
PC Stratasys - white
| Customer | Terumo medical corporation |
| Purpose | Prototyping parts used for a disposable electrical device |
| Process | FDM |
| Unit price | $55.38 / $32.96 |
| Industry | Medical |
Formlabs Clear Resin
| Customer | Aversan Inc |
| Purpose | A prototyping part of an injection molded component for an automated door mechanism |
| Process | SLA |
| Unit price | $29.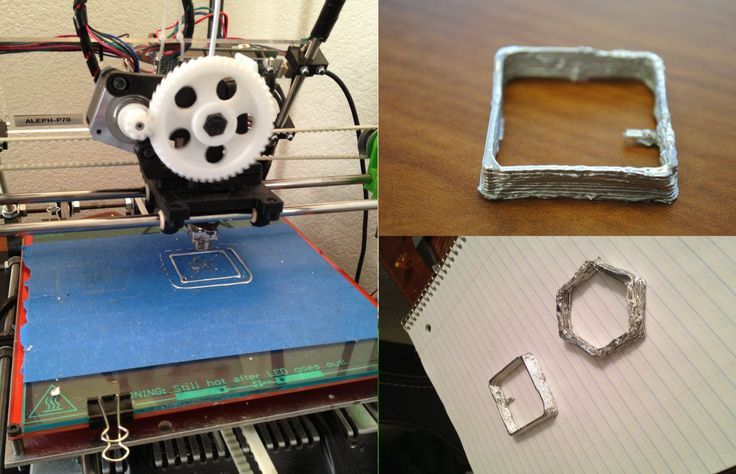 83 83 |
| Industry | Aerospace |
Instant, online 3D printing quotes
-
Upload a CAD to start (STEP, STP, IGES, IGS, SLDPRT, 3DM, SAT, STL, OBJ or X_T)
-
Price updates in real-time as you change materials, lead time, etc..
-
No hidden costs. Our instant quotes are not just indications, but the actual price, and include shipping and customs up front.
Learn about how our quoting algorithm works
Our ordering process
Receive instant quote
Upload your CAD to our online quoting platform
Confirm specs
Configure your part specifications and select a lead time that suits your schedule
Production
We select the best manufacturer for your order, and production begins immediately
Quality control
We take full responsibility for making sure your parts are manufactured according to our standards
Delivery
Our 3D printing service has been rated 4.
 9/5
9/5 Over 139 customers are satisfied with our 3D printing service.
“Always a perfect part, and prompt service.”
“Very speedy with printing job and very courteous when figuring out scheduling for pick up. Also very friendly.”
“You're the best in my city to date, hands down.”
“Came exactly as I wanted looks great and fast service”
“For our application the parts were well printed, Travis eas really great too providing regular updates and details of the project.”
“Prints were just as expected. Good and Timely”
“Sorry for delayed response, very busy with vacation weeks in the middle.”
“Communication with vendor was great, pick up was easy, thanks!”
“Very nice print, super fast turnaround, great service. Thank you!”
“Fast and efficient.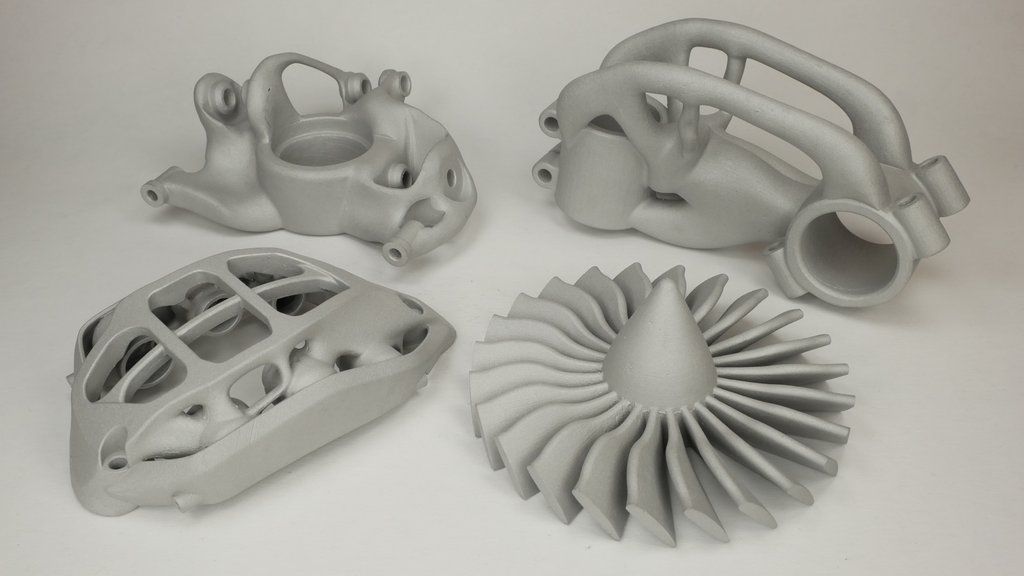 Great communication. ”
Great communication. ”
“Got back to me quickly and got my parts to me even quicker.”
“Amazing quality and processing. Couldn't ask for better service!”
“Awesome! Thanks for the quick print over a gallon weekend”
“Speedy communication and a faster turn around than expected. The parts were high quality and a perfect fit. I would definitely send more work to in the future. Thanks!”
“Great service! Superb communication, quick production and shipping, good quality parts. ”
“Quick turn around, great communication. Thanks!”
“Got my part printed and shipped very quickly! Great communication -- I was kept up to date every step of the way, and was even sent pictures of the part before it shipped. The quality of the part is exactly what I was hoping for, and the price was quite reasonable.”
“Good communication and fast response/updates”
“Excellent service! The provider spent much time in messages with me back and forth on the improvement on my amateurish design.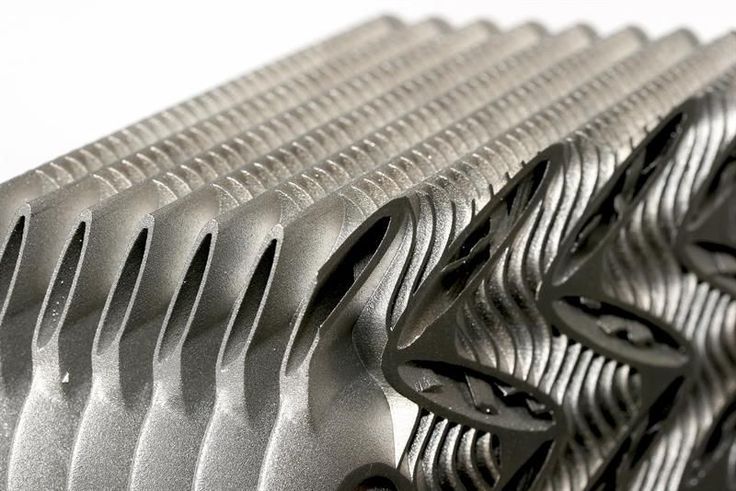 The final product is professional enough to be used in laboratory research. ”
The final product is professional enough to be used in laboratory research. ”
“The order is finished on time in good quality. ”
“Very helpful, parts arrived faster than expected as well!”
“Fast and exactly what I wanted. Really amazing what is possible in today's world. Thanks again.”
“Amazing quality! Very happy with parts- re-quoting new parts now!”
“100% fill is the trick nice and strong! worked well thanks”
“Good source for large (~10 inch) parts. Fast turn.”
Show more reviews
Show less reviews
Teams build better parts
Create your Hubs team and start collaborating
Read more
The Hubs Standard - consistent quality, every time
Hubs takes the stress out of manufacturing by guaranteeing the quality and consistency of every part.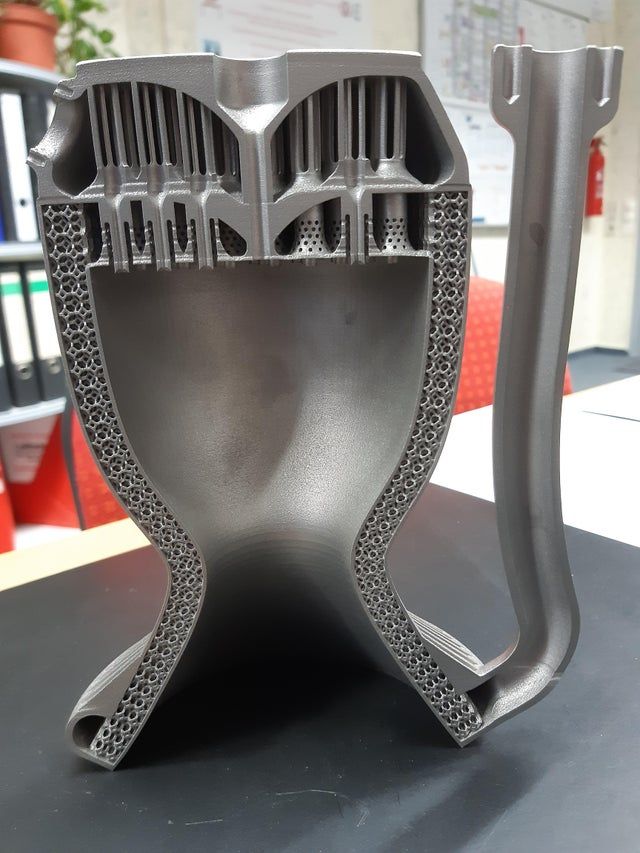 Each order is dimensionally and visually inspected to make sure it meets the Hubs Standard.
Each order is dimensionally and visually inspected to make sure it meets the Hubs Standard.
3D printing materials
We can generate instant 3D printing quotes for 25+ plastics. For metal 3D-printed parts, you can request a quote from our parent company, Protolabs.
Available materials
SLS
PA 12 Glass filled PA 12
Desktop FDM
Prototyping PETG Prototyping ASA Prototyping TPU Prototyping ABS Prototyping PLA
Desktop SLA
Formlabs Standard Resin Formlabs Clear Resin Formlabs Tough Resin 2000 Formlabs Rigid Resin 4000 Formlabs Grey Pro Resin Formlabs Flexible Resin 80A Formlabs High Temp Resin Formlabs Durable Resin
MJF
HP PA 12 Glass filled HP PA 12
Industrial FDM
Markforged Onyx ABSplus Stratasys ULTEM 9085 Stratasys Stratasys ASA ABS M30 Stratasys ULTEM 1010 Stratasys
Industrial SLA
Accura 25 (PP-like) Accura ClearVue Accura Xtreme White 200 (ABS-like)
3D printing locations near Canada
Thunder Bay Winnipeg Duluth, MN
Grand Forks, ND St. Cloud, MN Fargo, ND
Cloud, MN Fargo, ND
Blaine, MN Coon Rapids, MN Brooklyn Park, MN
Maple Grove, MN
The 3D Printing Handbook
No one understands 3D printing like us - our founders literally wrote the book. Click here to download the sample chapters.
Buy the book from Amazon
FAQ's
How much does your 3D printing service cost?
The cost of your 3D printed parts depends on factors such as part volume, part complexity, choice of material, which 3D printing technology is used, and if any post processing is required. For more details on these cost factors, see our article on the cost of 3d printing. To check the cost of your 3D printed part, simply upload a CAD (. STL) file and select your material and 3D printing technology to receive a quote within seconds.
STL) file and select your material and 3D printing technology to receive a quote within seconds.
How do you guarantee the quality of my prints?
Your parts are made by experienced 3D printing shops within our network. All facilities are regularly audited to ensure they consistently meet the Hubs quality standard. We include a standardized inspection report with every order and offer a First Article Inspection service on orders of 100+ units.
We have partners in our network with the following certifications, available on request: ISO9001, ISO13485 and AS9100.
Follow this link to read more about our quality assurance measures.
How do I select the right 3D printing process for my prints?
You can select the right 3D printing process by examining which materials suit your need and what your use case is.
By material: if you already know which material you would like to use, selecting a 3D printing process is relatively easy, as many materials are technology specific.
By use case: once you know whether you need a functional or visual part, choosing a process is easy.
For more help, read our guide to selecting the right 3D printing process. Find out more about Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) and Stereolithography (SLA).
How can I reduce the cost of my 3D prints?
In order to reduce the cost of your 3D prints you need to understand the impact certain factors have on cost. The main cost influencing factors are the material type, individual part volume, printing technology and post-processing requirements.
Once these have been decided, an easy way to further cut costs is to reduce the amount of material used. This can be done by decreasing the size of your model, hollowing it out, and eliminating the need for support structures.
To learn more, read our full guide on how to reduce the cost of 3D printing.
Where can I learn more about 3D printing?
Our knowledge base is full of in-depth design guidelines, explanations on process and surface finishes, and information on how to create and use CAD files. Our 3D printing content has been written by an expert team of engineers and technicians over the years.
Our 3D printing content has been written by an expert team of engineers and technicians over the years.
See our complete engineering guide to 3D printing for a full breakdown of the different 3D printing technologies and materials. If you want even more 3D printing, then check out our acclaimed 3D printing handbook here.
We have an extensive range of online resources developed to help engineers improve their capabilities.
Introductory guides
Design guides
Material guides
Applications
CAD & file preparation
Post processing & finishing
Our other manufacturing capabilities
CNC machining
CNC machining
Milling (3-, 4- & full 5-axis), turning and post-processing
-
50+ metals and plastics & 10 surface finishes
-
Tolerances down to ±.
 0008” (0.020 mm)
0008” (0.020 mm) -
Lead times from 5 business days
See our CNC machining services
Put your 3D printed parts into production today
Get an instant 3D printing quote
The impact of 3D printing and FrameCAD technologies on home construction in Canada
In 2014, a breakthrough began in the field of building construction. Buildings are built from concrete using a 3D printer. Many people already know what a 3D printer is - it is a numerically controlled machine that uses the layer-by-layer method of creating a part.
Vancouver's high home prices make buying a home an impossible dream for most residents. Therefore, fortunately for many who want to buy a house for themselves, an affordable alternative will appear on the market - houses built by 3D printers.
New construction solution based on laser 3D printing of custom modular and steel beams and panels. The technology allows you to quickly create completely new tasks for printing. These steel parts are created with the design of the building under construction in mind, and then sent to the construction site and assembled in a short time.
The technology allows you to quickly create completely new tasks for printing. These steel parts are created with the design of the building under construction in mind, and then sent to the construction site and assembled in a short time.
Construction company LifeTec Construction Group uses a 3D printer to print metal structures to speed up the building process. The company is based in Vancouver.
Traditionally, large wooden trusses are used in the construction of small residential buildings. Their production noticeably slows down the construction process.
The new technology involves the replacement of wooden trusses with metal ones. At the same time, there is an important feature - they are printed on a special 3D printer using Framecad technology. It was developed in New Zealand and has since been tested around the world. Builders say building is faster and more efficient when trusses can simply be printed.
In addition to speed, builders note the increased durability of such structures. Printing also allows for less construction labor, which is especially true in Vancouver.
Printing also allows for less construction labor, which is especially true in Vancouver.
It is impossible to distinguish a 3D printed house from a traditional house. A 3D printer is laying the foundation of a house by pouring cement in layers. Then roofing, electricity and plumbing are added. For a small fee, customers can customize the settings for their future homes and thus design their own home the way they want. A four-bedroom house will only cost $20,000. The foundation of the house with an area of 2500 sq.m. can be built in 24 hours.
Benefits of 3D printed houses
- Uses lightweight metal parts that are stronger and more durable than regular construction wood.
- Easy and quick to assemble.
- Low labor intensity, it will help to make up for the lack of construction labor.
Of course, 3D printing will be increasingly used in construction. Thus, the main US military department has already declared its interest in new technologies and has allocated a substantial amount for research. There are similar projects involving public and private investors in other countries. This is not surprising - humanity is growing at a rapid pace, and everyone needs housing, and 3D printing is proving to be a quick and cheap construction option. Therefore, in 5-10 years, the expression "print a house" is unlikely to surprise anyone.
There are similar projects involving public and private investors in other countries. This is not surprising - humanity is growing at a rapid pace, and everyone needs housing, and 3D printing is proving to be a quick and cheap construction option. Therefore, in 5-10 years, the expression "print a house" is unlikely to surprise anyone.
Steel 3D printing - a quick guide
Any metal 3D printing technology can print with steel. This is the most popular material. But which steel grades and which technology is best for your application? Will printed steel parts really be as strong and durable as traditionally made parts?
Let's see how a 3D printed steel part is revolutionizing manufacturing and opening doors to new applications in aerospace, medical equipment, automotive, tool making, heavy industry, architecture and more. In addition, more affordable desktop printers are expanding the scope and scope of real steel 3D printed parts.
Strength of steel printed parts.
 Cast steel part (left), 3D printed version (center). On the right, a fully 3D printed hinge requires no assembly. (Source: Desktop Metal)
Cast steel part (left), 3D printed version (center). On the right, a fully 3D printed hinge requires no assembly. (Source: Desktop Metal) The most common question when it comes to a 3D printed metal model is "Will it be as strong as a forged or cast part?" ?". The short answer is yes... and no.
3D printed steel parts can be just as strong, and sometimes even stronger, than those made in the traditional way. It depends on many factors such as: end use, type of steel, choice of 3D printing method, post-processing and shape of the part. Also, the comparison depends on which of the strength characteristics you focus on: tensile strength, static load strength, fatigue strength, etc.
Parts printed from steel are used in the aerospace industry, for the military, and also, for example, for the manufacture of a footbridge, shown below. Therefore, the strength of printed products is beyond doubt, but let's take a closer look.
Queen Maxima of the Netherlands officially opens a 3D printed metal bridge.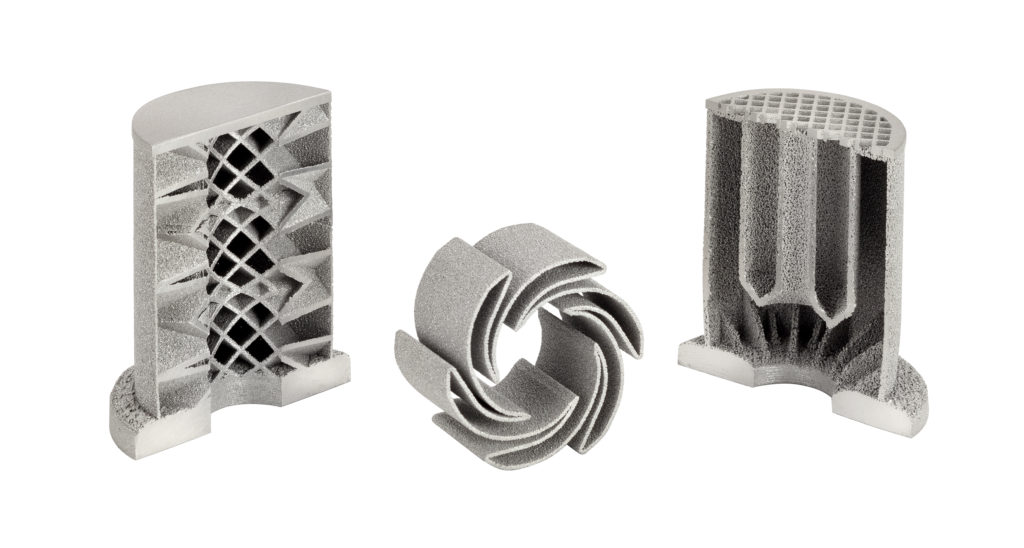 Photo by Adriaande Groot (Source: MX3D)
Photo by Adriaande Groot (Source: MX3D) A 3D printed or laser powder sintered (LPBF) steel part has a finer grain structure than cast metal products. This provides better tensile strength characteristics, but in other respects the cast parts are currently still stronger. Most often, LPBF 3D printing is used to replace cast components, but in some cases, 3D printed components can replace forged parts.
One study showed that, under certain conditions, stainless steel parts made using LPBF 3D printers were three times stronger than parts made from the same steel using the traditional method.
In experiments comparing 3D printed steel parts to traditionally made steel parts, researchers create identical parts using two methods and compare their performance. However, head-to-head comparison of details is only part of the big picture.
The main advantage of printing with steel is not only its strength, but also the unique ability to create internal channels and lattice fillings in parts, which is impossible using traditional manufacturing methods. Metal 3D printing makes it possible to produce parts faster than traditional production, since this method does not require the use of special equipment and tools, it allows you to create assemblies as a whole, eliminating the need for subsequent assembly and welding. Designing a printed part usually means that less metal is needed to make it, and therefore less weight, for the same strength.
Metal 3D printing makes it possible to produce parts faster than traditional production, since this method does not require the use of special equipment and tools, it allows you to create assemblies as a whole, eliminating the need for subsequent assembly and welding. Designing a printed part usually means that less metal is needed to make it, and therefore less weight, for the same strength.
Steel 3D printing is also more stable and cost effective as it reduces waste. When using subtractive manufacturing methods, such as CNC machining, you make a part by cutting it out of a large one, with a lot of waste. With additive manufacturing, you only use the material you need to make the finished product.
Steel 3D printing is not intended to replace traditional methods in all areas, but it may be a better choice for a wide range of applications. Particularly when the required parts are unique and designed for specific applications, such as rocket engines, racing cars or the oil and gas industry. 3D printing is the fastest and most flexible technology for mass production and prototype production. For military and industrial applications, steel 3D printing is a faster and more efficient way to create individual parts for vehicles and machines. Stainless steel 3D printing is rapidly finding applications in medicine to create unique surgical instruments and implants.
3D printing is the fastest and most flexible technology for mass production and prototype production. For military and industrial applications, steel 3D printing is a faster and more efficient way to create individual parts for vehicles and machines. Stainless steel 3D printing is rapidly finding applications in medicine to create unique surgical instruments and implants.
If you know what characteristics your final product should have (tensile strength, compressive strength, hardness, density, etc.), then all these parameters can be incorporated into the product at the production stage.
Types of steel for 3D printing
Metal powder is the most used metal material for 3D printing (Source: GKN Additive)There are thousands of different grades of steels and alloys with different mechanical properties, used in traditional manufacturing but in 3D printing there are only a few dozen of them, and some of them are unique, created specifically for this technology. Among the steel options, the following can be distinguished:
-
Stainless steel (316L, 304L , 17-4PH, 15-5PH, 420, 254, Ph2, GP1, 630, 410).

-
Tool steel (D2, M2, h23, h21, MS1, 1.2709).
-
Low alloy steel (4140).
-
Structural alloyed (20MnCr5).
Recently, unique alloys have been developed specifically for 3D printing to solve the problems that come with traditional manufacturing methods.
For example, 3D printer manufacturer Desktop Metal released a patented stainless steel in 2022 that the company says combines the tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance of 13-8 PH stainless steel, combined with the hardness low alloy steel like 4140. The company says customers can go to market with this material and skip the galvanizing step to protect products from corrosion.
ExOne offers two special blends of steel and bronze that the company says allows 3D printed steel parts to achieve increased corrosion resistance while being easy to machine and polish.
While most of the metal powders used in 3D printing are similar to those used for other manufacturing methods, their numbers are on the rise as more companies adopt the technology.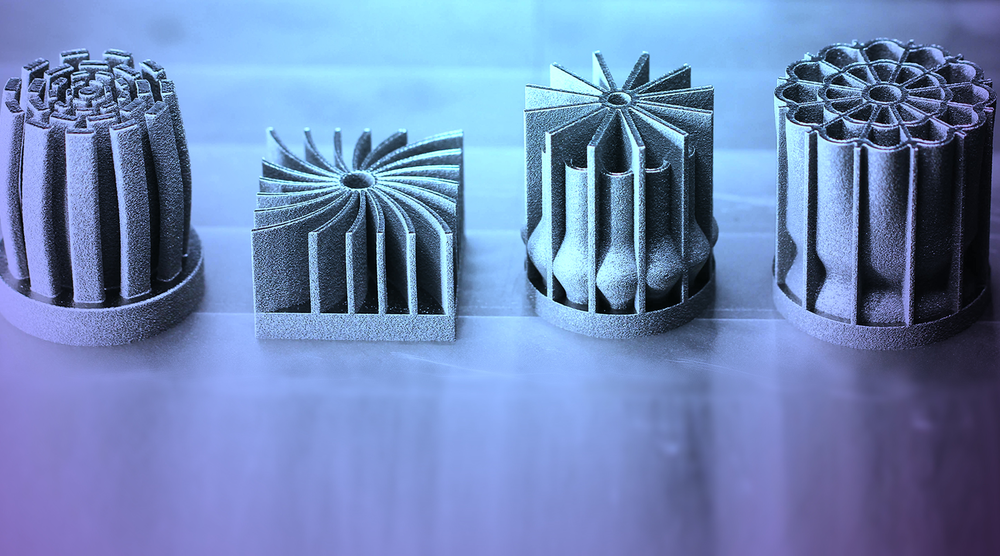 Some metal powder manufacturers, such as GKN, also make custom powders for specific 3D printing applications.
Some metal powder manufacturers, such as GKN, also make custom powders for specific 3D printing applications.
How to print with steel
The strength, properties, and applications of 3D printed steel products largely depend on which 3D printing technology you use. Some methods produce stronger parts, other methods provide better hardness or abrasion resistance, and some technologies are simply very fast.
Below are the main metal 3D printing methods, their properties and some of the most common application examples.
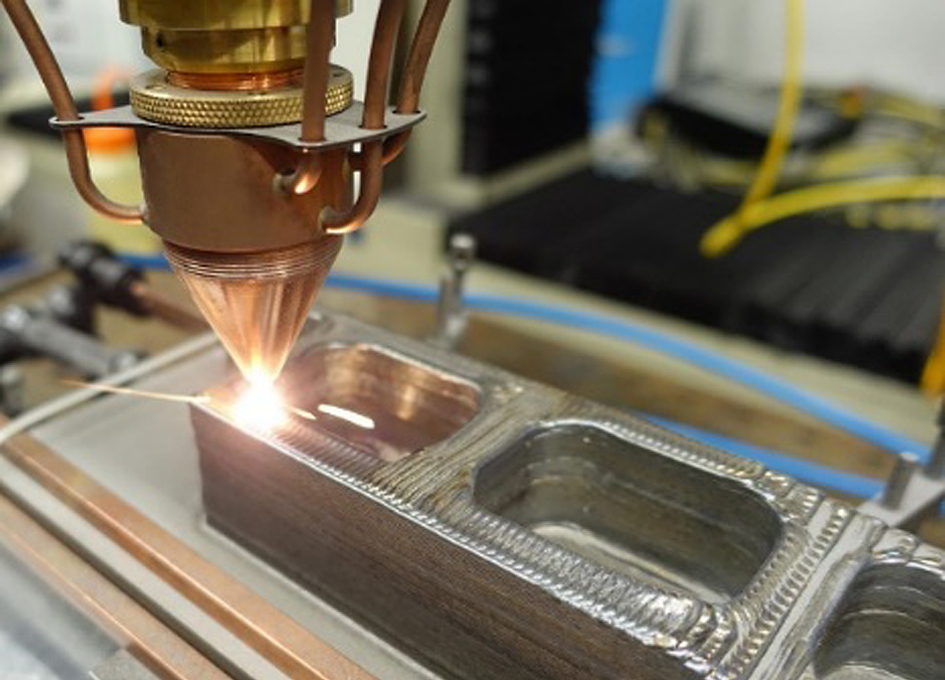
Fused Deposition Printing (FDM)
BCN3D's Epsilon printer extrudes metal filament from stainless steel (Source: BCN3D) as more printer manufacturers certify metallic filaments for use on their printers, such as Ultimaker, BCN3D, Makerbot, Raise3D. Raise3D has recently released a complete metal printing suite - Metalfuse (3D printer, debinding oven and sintering oven). This method is still much more popular for printing plastics, but with new plastic filaments filled with stainless steel powder, strong metal parts can be produced.
FDM media was once limited to thermoplastics. Companies like BASF Forward AM and The Virtual Foundry now offer metal filaments that can be used on almost any FDM printer as long as it has a hardened steel nozzle for abrasive media.
These materials are approximately 80% metal and 20% plastic. After printing, the post-processing process removes the plastic, resulting in 100% metal parts.
Due to the removal of the bonding plastic, FDM metal parts shrink during post-processing. The amount of shrinkage is constant and can be taken into account in CAD systems, which allows to obtain relatively accurate finished parts.
Forward AM's 316L Stainless Steel Ultrafuse filament produces finished parts with material properties that the company claims are comparable to injection molded metal parts.
(Source: BCN3D) While 3D printing with metallic materials may not be suitable for demanding applications such as aerospace, the economics of producing simple metal components without critical loads on an affordable FDM printer can outweigh the impossibility of applying them in some areas.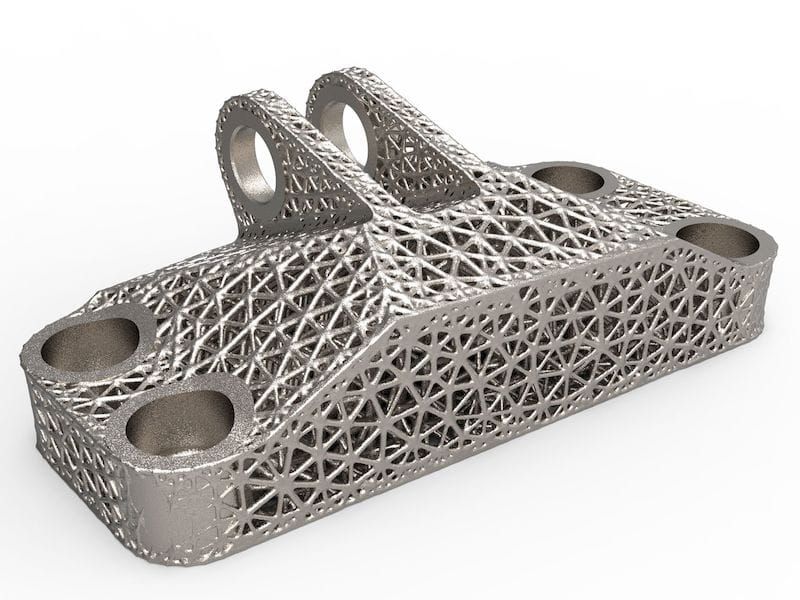
Metal prototype parts and finished parts that will not be subjected to extreme stress are ideal uses for this technology.
Bound Metal Deposition (BMD)
Desktop Metal's Studio System 3D printer used bonded metal bars that were extruded layer by layer to form a metal part (Source: Desktop Metal)Similar to FDM, Metal mesh deposition method (BMD) or bonded powder extrusion (BPE) is a 3D printing process based on extrusion. This method uses bonded metal rods or bonded powdered metal filaments, which consist of a much higher percentage of metal powder than the filaments used in FDM. As with FDM, post-treatment to remove the binder and heat treatment in a final sintering oven are required.
There are only a few 3D printers using this method such as Desktop Metal, Markforged and more recently 3DGence, but more companies are entering this market, so stay tuned. These printers are valued as a convenient solution for office 3D metal printing, they are more expensive than most FDM printers, but cheaper than the powder-based metal 3D printing technologies described below.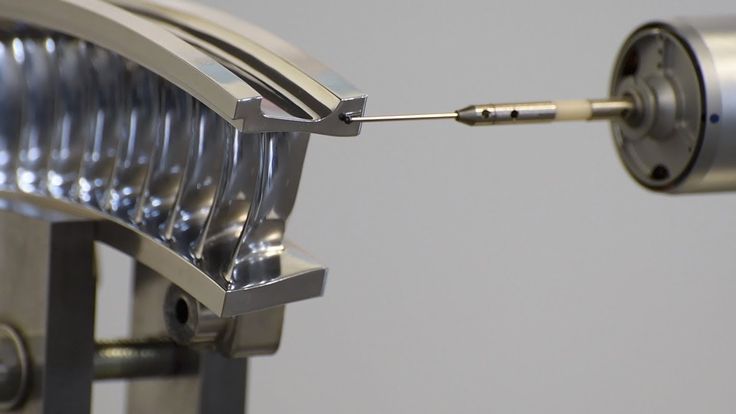
These printers use their own proprietary filament. Desktop Metal and Markforged offer four types of steel.
Ideal niches for this technology are metal prototype parts, where it is necessary to test the functionality of a part before mass production using traditional methods. Popular applications are molds, punching dies, nozzles, impellers, fasteners and heat exchangers.
For example, Shukla Medical uses Markforged's Metal X printer to print steel prototypes of its orthopedic implant removal tools.
Laser powder sintering.
Laser powder sintering technology uses one or more lasers to melt powdered metal into a desired shape layer by layer (Source: GE Additive) metal printing. This technology is used by 80% of all metal 3D printers on the market.This method uses powerful lasers to selectively sinter metal powder layer by layer.
LPBF 3D printers are available in a wide range of sizes, prices and laser powers. These and other characteristics affect the properties of the finished part, print speed and other parameters of the finished products.
Steel and steel alloys are the most popular material for LPBF equipment and, unlike FDM and BMD, metal powders are commercially available as they are most commonly used in traditional production methods.
LPBF is a technology that maximizes the quality of a 3D printed part. Applications include aerospace components such as monolithic thrust chambers, rocket engine components and heat exchangers, molds, tools and other applications, as well as high wear parts and surgical instruments.
Binder Jetting
Binder Jetting 3D printing technology uses powdered metal and a binder to form metal parts (Sorrce: ExOne) binder, and not with a laser. During post-processing, the binder is removed.Binder application stands out for its high printing speed compared to other 3D printing methods or traditional manufacturing, and metal parts made with this technology have material properties equivalent to those made by metal injection molding.
The number of manufacturers producing metal-bonded inkjet 3D printers is much smaller than that of LPBF machines. Leading manufacturers include ExOne, Desktop Metal, Digital Metal, GE Additive and HP.
Leading manufacturers include ExOne, Desktop Metal, Digital Metal, GE Additive and HP.
Binder blasting is ideal for medium to high volume production of metal tools and spare parts.
In fact, HP claims that its Metal Jet 3D printer was designed specifically for mass production of 316L stainless steel products. HP has partnered with Parmatech to produce metal parts for the medical industry. Pennsylvania-based ExOne uses this technology to manufacture hard metal cutting tools and tool steels.
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
(Source: GE Additive)Electron Beam Melting (EBM) is another powder cladding technology. It works in a similar way to selective laser melting (SLM), but instead of using a laser as the energy source, it uses a much more powerful beam of charged particles.
The recoater moves the powder onto the printing plate and an electron beam selectively melts each layer of powder. After each layer is printed, the plate is lowered and another one is applied on top of the previous layer.
EBM can be much faster than SLM, but SLM produces smoother and more accurate pieces. The electron beam is wider than the laser beam, so EBM cannot produce the same precise parts as SLM. Another difference is that the manufacturing process takes place in a vacuum chamber, which reduces the amount of impurities in the material that can lead to defects. That is why EBM is often chosen for printing components for the aerospace, automotive, defense, petrochemical and medical implant industries.
Titanium is the most popular metal for most EBM applications, however steel can be used.
Cold Spray
(Source: Impact Innovations)Cold spray 3D printing is done by injecting metal powders through a jet nozzle into a supersonic stream of pressurized gases such as air, nitrogen or helium. The process is called "cold" because the metal particles do not melt, but hit the metal substrate and adhere to its surface during the so-called plastic deformation.
Cold spray printed products are not prone to porosity, thermal cracking and other defects associated with melt-based technologies. This method has several advantages over other production methods. The technology is used in the military and aerospace industries around the world. For example, the US Army uses cold spray to repair the mounts of a worn Bradley 25mm steel turret gun.
This method has several advantages over other production methods. The technology is used in the military and aerospace industries around the world. For example, the US Army uses cold spray to repair the mounts of a worn Bradley 25mm steel turret gun.
In the automotive industry, cold spray steel is used for crash repairs because the high strength steel substrates in cars can be susceptible to thermal repair methods such as welding.
Direct Energy Deposition (DED) and Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
MX3D WAAM Steel Parts (Source: MX3D) Direct Energy Deposition (DED) uses welding powder or wire that enters through a nozzle and is fed into the power source to melt the metal. A melt region is created and applied to the substrate. DED is a new process, reminiscent of an old building technology known as "cladding", in which a coating is applied to a substrate, often for thermal insulation or weather resistance. DED is useful for fabricating large objects as a whole, as well as complex geometries that require extensive machining.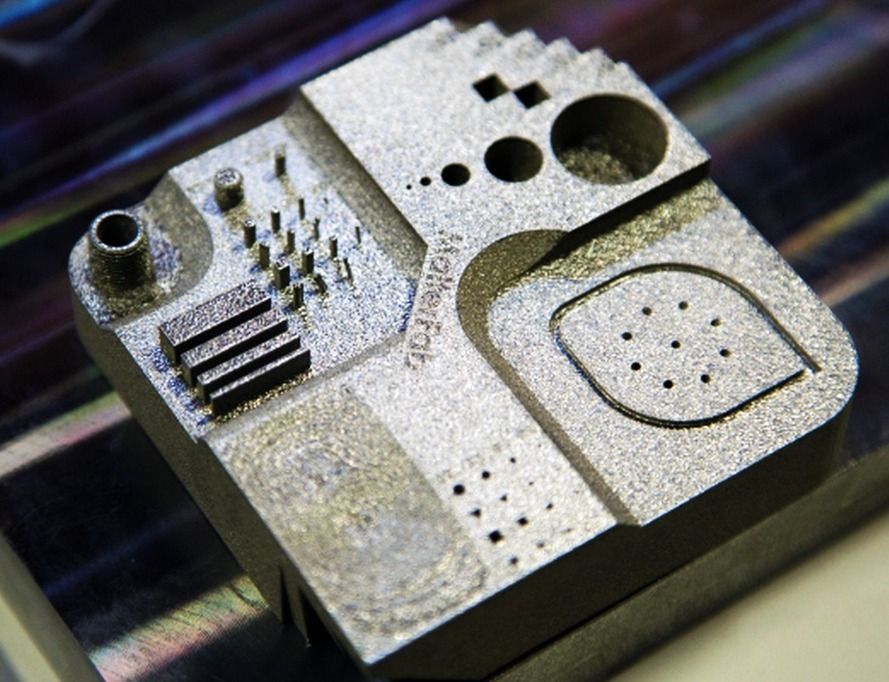 DED can get such parts much closer to finished than traditional CNC machining.
DED can get such parts much closer to finished than traditional CNC machining.
Because DED uses a coating process, it can be used to add complex geometries to existing steel parts, thus combining complexity with cost reduction. For example, the French company AddUp advertises a rocket nozzle that uses a preformed large 304 stainless steel hopper cone printed with an isogrid structure, usually made from a larger piece by traditional methods.
A technology related to DED is wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Instead of powder, WAAM uses a metal wire that is melted by an electric arc. The process is controlled by robotic arms. WAAM is also capable of producing large-sized metal parts, as demonstrated by the Dutch company MX3D and its nine thousand-pound 41-foot stainless steel bridge in Amsterdam, as well as an oil and gas equipment repair part, proving that parts can be made in the field.
Micro 3D printing
Micro parts printed from steel (Source: 3D MicroPrint) Micro scale additive manufacturing, or micro 3D printing, can produce products with a resolution of a few microns (or less).











