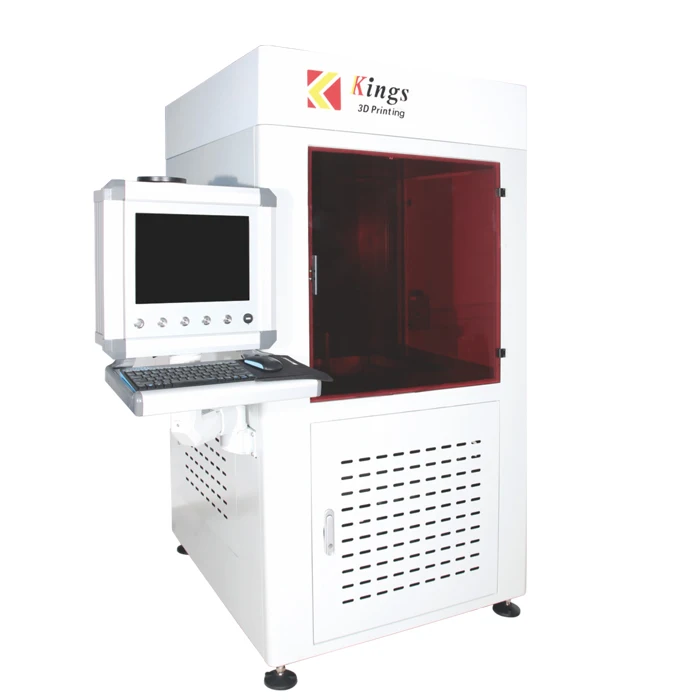
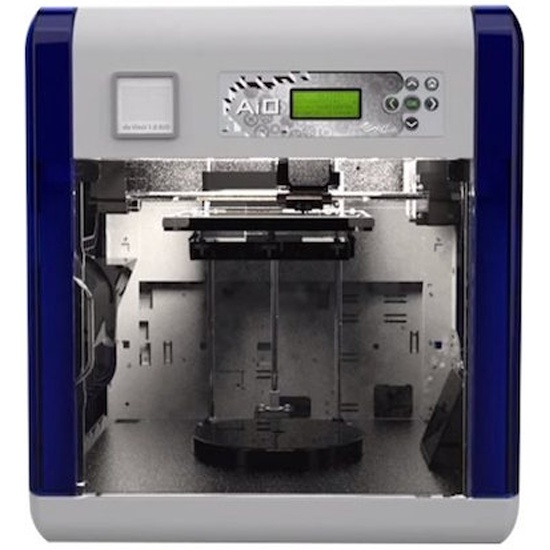
Laser sla 3d printer
Best resin 3D printers in 2022
What is the best resin 3D printer on the market?
Resin 3D printers are able to offer a very high level of detail and smooth surfaces. They are most commonly seen in dental labs and clinics as well as in jewelry workshops but are also increasingly popular with hobbyists and makers.
The way a resin 3D printer works depends on its technology: laser SLA (stereolithography), DLP (Digital Light Processing), or LCD-based (using an LCD screen to mask projected light).
All resin 3D printers involve the same workflows, however, requiring several post-processing steps such as resin removal and post-curing.
In this guide, we take a look at some of the best resin 3D printers available in each category (SLA, DLP, and LCD) and provide you with key concepts linked to resin 3D printing.
The best resin 3D printers (SLA/DLP/LCD)
| Brand | Product | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | Original Prusa SL1 | 120 × 68 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.68 × 5.91 in | Czech Republic | $ 1,6991 727 €1,507 £253,246 ¥ | Buy |
| Peopoly | Phenom | 276 × 155 × 400 mm10.87 × 6.1 × 15.75 in | China | $ 1,9991 899 €1,773 £297,963 ¥ | Contact |
| Formlabs | Form 3 | 146 × 145 × 185 mm5.75 × 5.71 × 7.28 in | United States | $ 3,4993 557 €3,104 £521,547 ¥ | Quote |
| UNIZ | SLASH 2 | 190 × 120 × 200 mm7.48 × 4.72 × 7.87 in | – | $ 3,5003 558 €3,105 £521,696 ¥ | Quote |
| FlashForge | Hunter DLP | 120 × 67 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.64 × 5.91 in | China | $ 3,9994 065 €3,547 £596,075 ¥ | Quote |
| DWS | XFAB | 180 × 180 × 180 mm7. 09 × 7.09 × 7.09 in 09 × 7.09 × 7.09 in | – | $ 6,6006 000 €5,854 £983,770 ¥ | Quote |
| B9Creations | B9 Core 550 | 96 × 54 × 127 mm3.78 × 2.13 × 5 in | – | $ 9,95510 119 €8,830 £1,483,852 ¥ | Quote |
| Asiga | MAX | 119 × 67 × 75 mm4.69 × 2.64 × 2.95 in | – | $ 10,99011 171 €9,749 £1,638,125 ¥ | Quote |
| ETEC | Envision One | 180 × 101 × 175 mm7.09 × 3.98 × 6.89 in | Germany | upon request | Quote |
Expand to see more specs
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).
| Brand | Product | Technology | Build size | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prusa Research | Original Prusa SL1 | LCD | 120 × 68 × 150 mm4. 72 × 2.68 × 5.91 in 72 × 2.68 × 5.91 in | Czech Republic | $ 1,6991 727 €1,507 £253,246 ¥ | Buy on Prusa |
| Peopoly | Phenom | LCD | 276 × 155 × 400 mm10.87 × 6.1 × 15.75 in | China | $ 1,9991 899 €1,773 £297,963 ¥ | Contact manufacturer |
| Formlabs | Form 3 | SLA | 146 × 145 × 185 mm5.75 × 5.71 × 7.28 in | United States | $ 3,4993 557 €3,104 £521,547 ¥ | Get a quote |
| UNIZ | SLASH 2 | LCD | 190 × 120 × 200 mm7.48 × 4.72 × 7.87 in | – | $ 3,5003 558 €3,105 £521,696 ¥ | Get a quote |
| FlashForge | Hunter DLP | DLP | 120 × 67 × 150 mm4.72 × 2.64 × 5.91 in | China | $ 3,9994 065 €3,547 £596,075 ¥ | Get a quote |
| DWS | XFAB | SLA | 180 × 180 × 180 mm7.09 × 7.09 × 7.09 in | – | $ 6,6006 000 €5,854 £983,770 ¥ | Get a quote |
| B9Creations | B9 Core 550 | DLP | 96 × 54 × 127 mm3. 78 × 2.13 × 5 in 78 × 2.13 × 5 in | – | $ 9,95510 119 €8,830 £1,483,852 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Asiga | MAX | DLP | 119 × 67 × 75 mm4.69 × 2.64 × 2.95 in | – | $ 10,99011 171 €9,749 £1,638,125 ¥ | Get a quote |
| ETEC | Envision One | CDLP | 180 × 101 × 175 mm7.09 × 3.98 × 6.89 in | Germany | upon request | Get a quote |
Overview of the best resin 3D printers (SLA/DLP/LCD)
This overview is divided into three sections according to the resin 3D printers’ technology (SLA, DLP, or LCD).
The best SLA 3D printers (laser stereolithography)
Formlabs has been one of the main players on the professional resin 3D printer market for years. The Form 3, evolution of the award-winning Form 1 and Form 2, is their latest model, along with the Form 3L (large volume). This professional liquid resin printer boasts an array of practical features that make it a great choice for many businesses.
In the past, users have praised Formlabs’ hardware quality and precision, while criticizing the company’s decision to limit compatible materials to expensive Formlabs proprietary resins only. Today, the Form 3 features an “Open mode” that allows the use of generic materials.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Phenom is an affordable and large-format LCD (MSLA) 3D printer that is suitable for hobbyists and professionals alike. An advantage of this resin 3D printer is large-format. The Peopoly Phenom 3D printer also exists in larger versions: Phenom L, Phenom Noir, Phenom XXL.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
DWS Systems is specialized in manufacturing professional and industrial-grade resin 3D printers. The XFAB stereolithography 3D printer is their most affordable option, but is capable of delivering high-quality results. One of this SLA 3D printer’s most interesting characteristics is its cartridge resin system.
This makes material handling much easier and cleaner than with non-cartridge systems.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The best DLP 3D printers (Digital Light Processing)
This professional resin 3D printer boasts a number of user-friendly features including a touchscreen, automatic calibration, and Wi-Fi connectivity. FlashForge develops its own resins, but users may also use third-party materials.
With its special jewelry support mode, the Hunter DLP mainly targets jewelers.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
B9Creations’ Core series of 3D printers all provide fine levels of detail for professionals. According to the manufacturer, the B9 Core 550 resin 3D printer offers faster printing speeds (100+ mm/hour) than most DLP 3D printers in the same price range.
This digital light processing 3D printer is available with a smaller build volume (B9 Core 530).
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Envision One is a professional resin 3D printer produced by ETEC.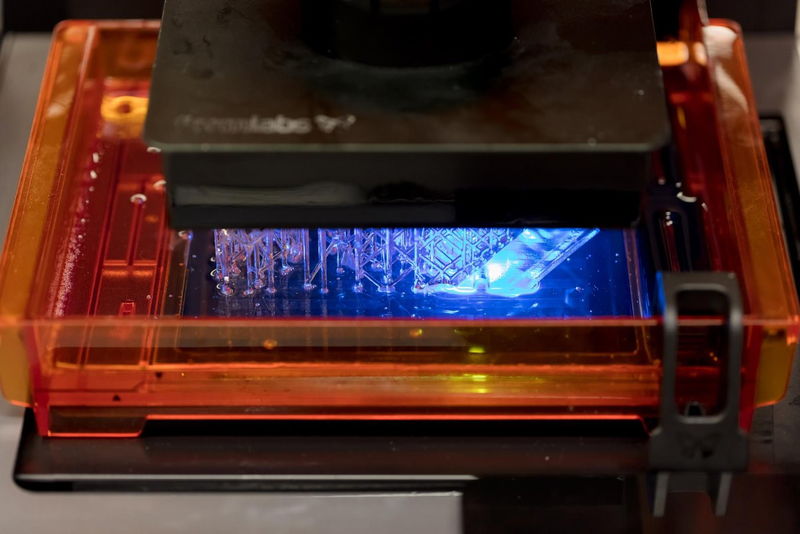 ETEC, a German company known as EnvisionTEC before its acquisition by Desktop Metal in 2021, manufactures professional DLP 3D printers. The ETEC Envision One uses CDLP 3D printing technology. This 3D printer offers a build volume of 180 x 101 x 175 mm.
ETEC, a German company known as EnvisionTEC before its acquisition by Desktop Metal in 2021, manufactures professional DLP 3D printers. The ETEC Envision One uses CDLP 3D printing technology. This 3D printer offers a build volume of 180 x 101 x 175 mm.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Asiga MAX is equipped with a resin level sensor, automatic calibration function and touch screen. Asiga also provides free lifetime technical support.
This 3D printer is particularly suitable for the medical and dental sectors, being compatible with silicone resins.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The best LCD 3D printers (liquid crystal display)
For many years, Prusa Research has been famous for manufacturing reliable 3D printers. The Original Prusa SL1 is Josef Prusa’s first resin 3D printer, but there is no doubt that it has been endowed with as much quality as the award-winning Prusa MK3 FDM 3D printers.
This LCD 3D printer– which is also available as a DIY kit– is packed with features such as a tilted print bed, auto calibration, vapor extraction, and more.
Buy on Prusa Get a quote Add to comparison
The SLASH 2 is a desktop resin 3D printer produced by UNIZ. UNIZ is a 3D printer manufacturer based in China. The UNIZ SLASH 2 uses resin 3D printing technology. This 3D printer offers a build volume of 190 x 120 x 200 mm.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Resin 3D printers under $1,000
As LCD screens are very affordable, they have been the key to bringing resin 3D printing to the masses. Indeed, more and more manufacturers are launching affordable desktop resin 3D printers with LCD 3D printing technology, and the price drop is radical.
These affordable resin 3D printers obviously can’t be expected to provide the same level of detail and accuracy as the professional 3D printers listed above.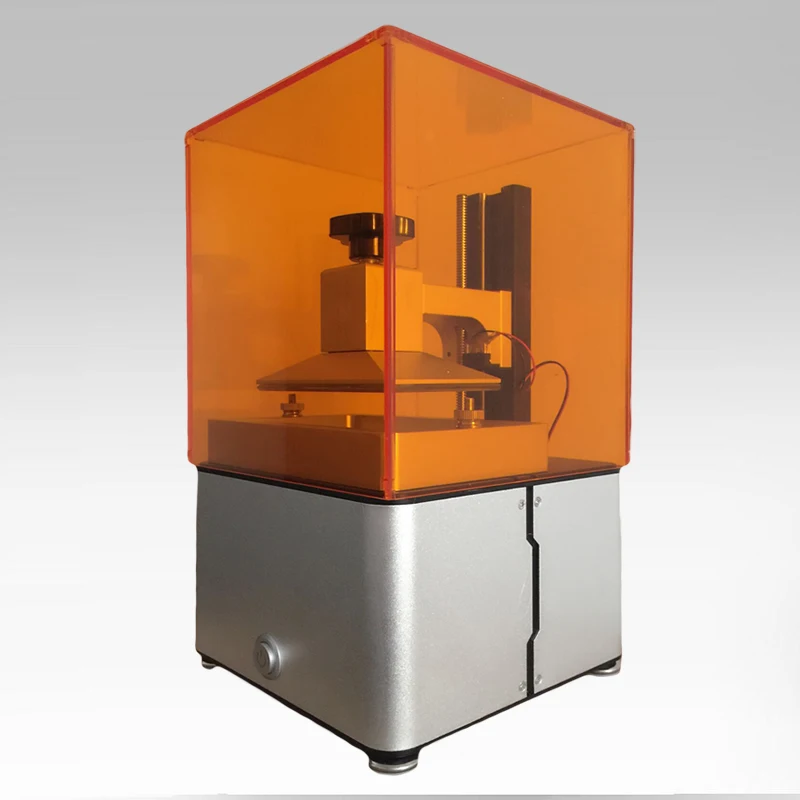 However, they are great as an introduction to resin 3D printing and they do produce good quality prints.
However, they are great as an introduction to resin 3D printing and they do produce good quality prints.
Read our full-length budget resin 3D printer article for a list of affordable machines (starting from $149).
Post-processing for resin 3D prints: necessary steps
Resin removal
Since the objects are printed within a tank of resin, resin drips off of the objects as they are lifted up and out of the tank. There’s always a layer of uncured resin left on the object, and it must be removed with IPA (isopropyl alcohol).
This can be done manually by dipping the part in an IPA bath and gently scrubbing the part with a soft brush, but it is quite time-consuming.
For users that produce resin parts on a regular basis, there are machines called resin washers, or resin cleaners. Ackuretta, for example, markets Cleani, a dual-tank resin cleaner that can wash both the parts and the printer’s platform (yes, that needs to be washed, too. ).
).
Post-curing
When removing a resin 3D printed part from the build plate, it is still soft and slightly malleable. To reach its final physical state the part must go through a post-curing step. This means exposing the object to heat or light. Various SLA post-curing techniques exist:
UV curing chamber / UV cure box
Professional users will definitely want to use a dedicated UV curing chamber for their parts in order to get the most out of the material (strength, for example). Most resin 3D printer manufacturers have UV curing chambers available separately.
UV nail lamp
For small parts, nail UV lamps can do the trick. There are dozens of nail UV lamps available for less than $50.
DIY UV curing chamber
Crafty people also have the possibility to make their own UV curing station!
How do resin 3D printers work and what are the differences between LCD, DLP, and SLA 3D printing?
SLA 3D printers, LCD 3D printers, and DLP 3D printers all use liquid resin as a 3D printing material. The resin, a photopolymer, becomes solid when cured (activated) by a specific light source.
The resin, a photopolymer, becomes solid when cured (activated) by a specific light source.
That light source cures the liquid resin, which is stored in a tank or vat, to form the object layer after layer.
The resin solidification process (photopolymerization) is at the core of three main 3D printing technologies:
- Laser-based Stereolithography (SLA): a UV laser cures the resin in the tank to form the object point by point.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): the resin is cured by a light projector one whole layer at a time. The light shines in a specific shape depending on the layer.
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) or Masked SLA (MSLA): An array of LED lights shine through an LCD screen. The LCD screen acts as a mask or stencil between the LED and the bottom of the resin tank, only letting light through in specific shapes.
All of these resin-based 3D printing technologies form part of the same family: stereolithography. That’s why some manufacturers include “SLA” in the name of their 3D printers, while they actually use DLP or LCD-based technology.
That’s why some manufacturers include “SLA” in the name of their 3D printers, while they actually use DLP or LCD-based technology.
Laser-based SLA 3D printing technology
An SLA 3D printer cures the liquid resin spot by spot with a laser, so it is potentially more precise than DLP 3D printing.
Contrary to DLP 3D printing, the build volume is completely independent of the resolution of the 3D print. A 3D print with a laser stereolithography 3D printer can be of any size and resolution.
DLP 3D printing technology (digital light processing)
DLP 3D printers use a light projector. The layer’s shape is defined by reflecting or deflecting light with mirrors. With DLP, the 3D printer is able to cure a whole layer of resin at once. Therefore, a DLP 3D printer can potentially 3D print faster than an SLA 3D printer, as an entire layer is exposed all at once instead of one spot at a time with a laser.
However, a DLP 3D printer’s resolution depends on its projector and how many pixels/voxels are available (a full HD projector usually offers 1080p). A 3D printer with a large build volume has a fixed number of pixels, making it impossible to 3D print small details when building at full scale.
The projector used by the DLP 3D printer is less expensive and easier to change than the laser used by SLA 3D printers.
LCD-based resin 3D printing technology
Most LCD resin 3D printers use an LCD screen as a photomask– like a stencil– above another light source (LED, UV…). This is where LCD resin 3D printing is different than DLP 3D printing, which makes use of mirrors or other complex systems to direct the light into a certain shape. The technology is also called Masked Stereolithography (MSLA).
Since LCD screens are inexpensive, this technology has made resin 3D printing much more affordable than before and there are now dozens of low-cost, budget resin 3D printers available for a couple of hundred dollars.
In some cases, the light emitted by an LCD screen is used to directly cure the daylight-sensitive resin.
What is best between LCD, DLP, and SLA 3D printers?
The answer depends on the user’s needs in precision, speed, and budget. We can highlight that:
- Laser SLA 3D printers are best for 3D printing highly detailed and intricate 3D prints, big or small.
- LCD and DLP 3D printers are best for 3D printing batches of small parts, or quickly 3D printing large parts without too many details.
- LCD-based 3D printers are generally much more affordable than SLA and DLP 3D printers.
Main resin 3D printing applications
Samples by La Bête à Pois, SprintRay, and Photocentric (top to bottom). Source: AniwaaResin 3D printers mostly target professional users. Indeed, they are suited for specific applications requiring high levels of detail and top-quality finishes. These applications include:
These applications include:
Resin 3D printers for jewelry
Jewelers use high-precision 3D printers to create molds with the lost wax technique and create incredible jewels.
SLA, DLP, and LCD 3D printers in dentistry
Dentists and dental labs are starting to use resin 3D printing to build dental crowns, mouth guards, surgical guides, and much more.
Resin 3D printing in medical and healthcare fields
SLA and DLP 3D printing can be used to create medical appliances such as hearing aids.
Hobbies: resin 3D printer for miniatures
Some tinkerers, DIYers, and cosplayers love 3D printing miniatures and figurines.
Key benefits and limitations of resin 3D printing
Benefits of LCD, DLP, and SLA 3D printing technologies
These are some of the advantages of 3D printing with resin:
- Ability to build small and very detailed parts or objects with fine, complex geometries
- Diversity of 3D printable resin materials (ceramic, metal, biocompatible, flexible, rigid, etc.
 )
) - Smooth finish of the parts produced (no easily visible layers like with FFF 3D printers)
Limits of resin 3D printing
As with any technology, resin 3D printing has its limits:
- Post-processing is mandatory (removing delicate support structures, post-curing, resin removal, etc.) and requires a UV curing chamber for good results
- Requires time-consuming cleaning time (for the vat and for the 3D printed part)
- Very smelly and toxic fumes
- Safety precautions required when handling the material
Resin 3D printer price
Laser SLA resin 3D printer price
SLA 3D printer prices depend on many factors. The price for a basic SLA 3D printer kit like the Peopoly Moai usually starts at about $1,200. Industrial resin 3D printers, on the other hand, can reach several hundred thousand dollars.
DLP resin 3D printer price
The price of a DLP 3D printer generally starts around $2,000 or $3,000. DLP 3D printers with higher precision and more features cost around $10K to $20K. More expensive digital light processing 3D printers also exist.
DLP 3D printers with higher precision and more features cost around $10K to $20K. More expensive digital light processing 3D printers also exist.
LCD resin 3D printer price
LCD-based resin 3D printers are the most affordable resin 3D printer type. There are many LCD resin 3D printers available for under $1,000, and even under $300. Higher-quality LCD 3D printers may cost a few thousand dollars.
UV curing chamber price
Most resin 3D printer brands sell UV curing chambers separately, with prices starting around $300 to $500.
FAQ
What does SLA stand for in 3D printing?
In 3D printing, SLA stands for stereolithography.
What does DLP stand for in 3D printing?
In 3D printing, DLP stands for Digital Light Processing.
What does LCD stand for in 3D printing?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, which is a type of screen used in electronic devices (smartphone, TV, etc.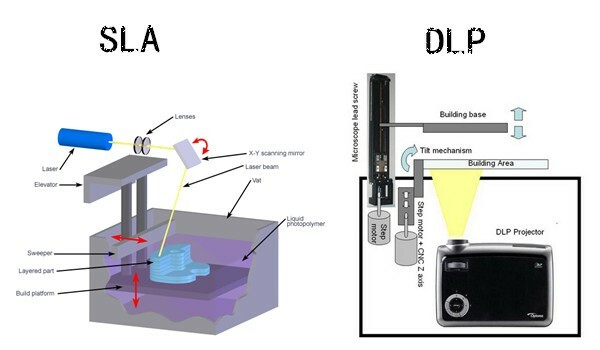 ). A growing number of resin 3D printers use an LCD screen’s light to cure light-sensitive resin and form objects in 3D.
). A growing number of resin 3D printers use an LCD screen’s light to cure light-sensitive resin and form objects in 3D.
What is SLA resin made of?
SLA resin is a photopolymer material, which is mainly composed of monomers, oligomers, and photoinitiators. Depending on the “recipe”, the stereolithography resin can be plastic, ceramic, or even metal-based.
How much does a resin 3D printer cost?
A resin 3D printer can cost anywhere from $500 to over $250,000. However, there are many resin 3D printers available for under $10,000.
What is a resin 3D printer?
A resin 3D printer (stereolithography) is a machine that solidifies liquid resin layer by layer to form an object in 3D.
Where are resin 3D printers for sale?
There are resin 3D printers for sale on major e-commerce sites like Amazon, AliExpress, GearBest, and Banggood. Online retailers specialized in 3D printing also exist, such as MatterHackers.
Online retailers specialized in 3D printing also exist, such as MatterHackers.
Laser SLA 3D Printer Resins
- Home
- Store
- 3D Printer Resins
- Light Source
- Laser SLA Resins
High-quality Laser SLA 3D printer resins and 3D printer photopolymers available for a variety of stereolithography 3d printers, including high-temperature resins, castable resins, and flexible resins. What is SLA Laser 3D Printing? SLA 3D Printing uses a laser that focuses on a vat of resin and photopolymers. The laser follows a 3D design or model and cures the resin point-by-point to create the design. SLA 3D printing is popular for projects/industries that require highly-detailed 3D printed parts.
Laser SLA Resins Collections
All Laser SLA Resins Browse by Light Source
Laser SLA Resins
Peopoly SLA Resins
SLA 3D printer resins formulated for 405µm curing lasers and LCD arrays
PhotoCentric 3D UV Laser Resins
Formulated to work in a large number of third-party SLA printers.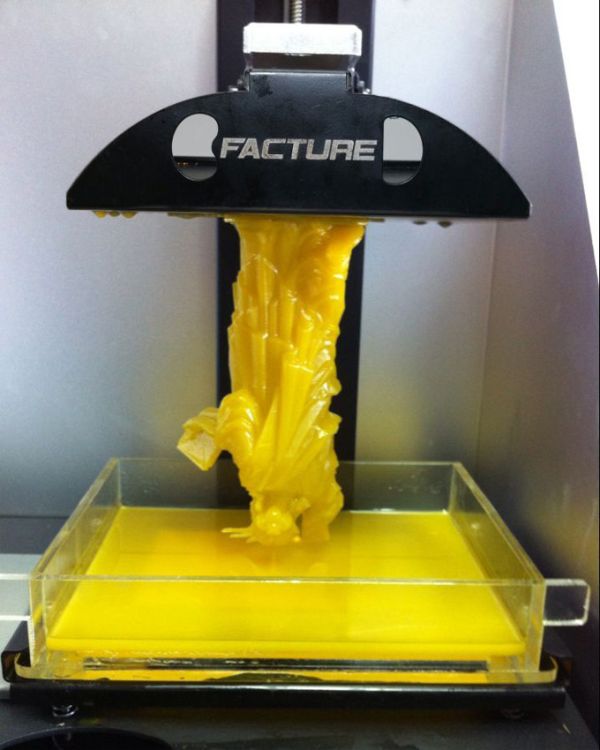
Guides & Articles
How To: Perfectly Level Your Resin 3D Printer's Build Plate
With any 3D print, a perfect first layer is essentially, especially so with resin 3D printing. Let's take a look at how you might be able to increase the adhesion of your resin 3D prints.
How To Succeed with LayerLock SLA Build Surfaces
Successfully achieve strong bed adhesion for Laser, DLP, and SLA resin prints using LayerLock SLA Resin 3D Printing Build Surfaces.
How to Succeed When 3D Printing with MH Build Resin
Make SLA resin 3D printing easier with this helpful detailed article on how to successfully fine-tune photopolymer resin to your 3D printer.
MH Build Resin Profile Settings for SLA 3D Printing
Succeed with MH Build Resin using these helpful printer and support ChiTuBox profile settings for your specific SLA machine.
Tech Breakdown: Peopoly Phenom Noir Resin 3D Printer
For high definition resin 3D printers, Peopoly is hard to beat, and with the Phenom Noir you can print faster than ever.
Getting Started with the Peopoly Moai SLA 3D Printer
MatterHackers' Pros detail the unboxes and set-up steps of the awesome Peopoly Moai SLA 3D printer.
How To: Print, Clean, and Post-Process SLA 3D Prints
Laser and resin 3D Printers have a very different workflow from the more common extruder and plastic 3D printers. Learn what it takes to use these high-resolution machines.
How To: Safely Handle, Use, and Dispose Resins for SLA 3D Printers
3D prints from SLA 3D printers solidify liquid resin to create high-resolution parts. These resins need to be handled with care from opening to disposal.
Tech Breakdown: Peopoly's Moai SLA 3D Printer
MatterHackers' pros take an in-depth look at why this incredibly precise resin 3D printer is quickly becoming a crowd favorite.
3D printing SLA - all about laser stereolithography
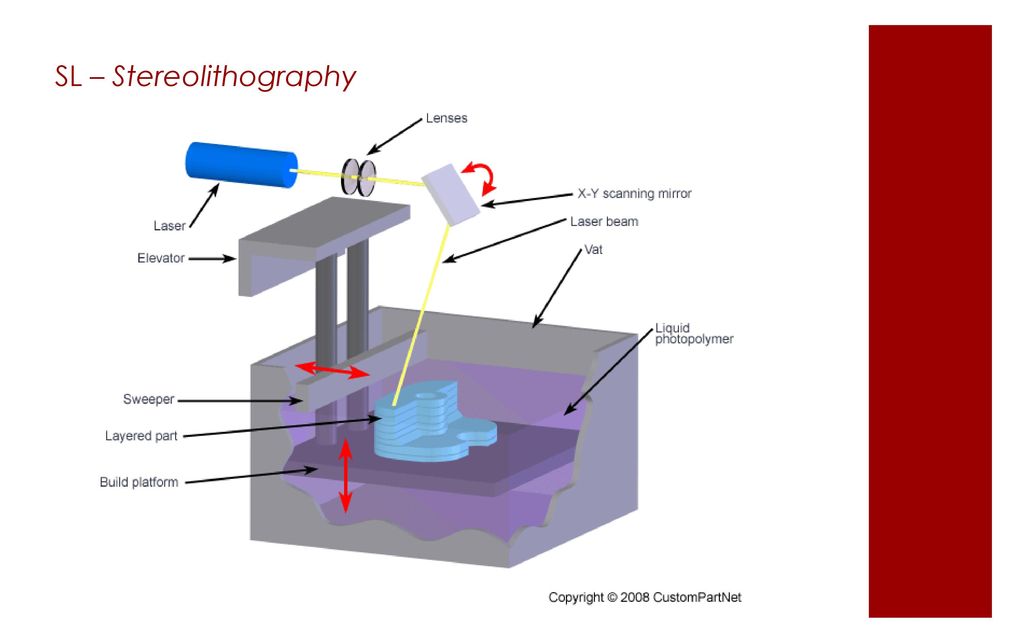
What is 3D printing SLA?
Laser stereolithography, also known as SLA 3D printing, is not only one of the first 3D technologies in the world, but also one of the most accurate additive manufacturing techniques. In some ways, it is unique, because it uses liquid photopolymer resin as a consumable. The essence of the technology lies in the illumination of a photopolymer according to a certain algorithm (set by a slicer program based on a 3D model). Under the influence of laser radiation, the resin solidifies, forming a finished object. nine0005
In some ways, it is unique, because it uses liquid photopolymer resin as a consumable. The essence of the technology lies in the illumination of a photopolymer according to a certain algorithm (set by a slicer program based on a 3D model). Under the influence of laser radiation, the resin solidifies, forming a finished object. nine0005
As in FDM 3D printing, SLA 3D printing in parallel with the construction of the object requires the construction of supporting structures in the presence of overhanging elements in the model. In fact, this technique resembles SLS 3D printing, but instead of a powder, a liquid photopolymer is used. Otherwise, this is the same layer-by-layer reproduction of products according to given 3D models. More details on how SLA 3D printing works will be discussed below.
Features of work
In order to understand how the 3D printing process works, it is necessary to understand how the SLA 3D printer works. The image attached below will help you with this, which shows a diagram of a classic stereolithographic printer. We say classic because that's exactly what the patented SLA printing technology is. This design is also used in industrial devices for 3D printing SLA. As for desktop SLA 3D printers that have already come into use, they use the so-called “upside-down SLA 3D printing”. What does it mean? nine0005
We say classic because that's exactly what the patented SLA printing technology is. This design is also used in industrial devices for 3D printing SLA. As for desktop SLA 3D printers that have already come into use, they use the so-called “upside-down SLA 3D printing”. What does it mean? nine0005
Let's first describe the printing process in the image above. In it, the laser is located on top, and the working platform gradually lowers down. So, a mesh platform is immersed in a container with a photopolymer, to a depth of no more than 0.05-0.13 mm (this is exactly what the layer thickness is). After that, the laser is activated, which affects certain areas of the material (specified by the program). Exposure to laser radiation causes the first layer of photopolymer to harden. Then the platform descends one more layer lower, the laser is activated again, continuing to form the object, and so on until the final construction of the product. nine0005
As for the 3D printing process used in desktop 3D printers, the principle is exactly the same. The only difference is that the laser is located under a container with a photopolymer, and when building a product, the platform does not fall, but gradually rises up. Common to both options is washing the product in special solutions upon completion of 3D printing, as well as irradiating the finished model with ultraviolet light. The first is necessary for the final cleaning of the product from the remnants of the photopolymer, and the second for the complete curing of the product. nine0005
The only difference is that the laser is located under a container with a photopolymer, and when building a product, the platform does not fall, but gradually rises up. Common to both options is washing the product in special solutions upon completion of 3D printing, as well as irradiating the finished model with ultraviolet light. The first is necessary for the final cleaning of the product from the remnants of the photopolymer, and the second for the complete curing of the product. nine0005
Differences from DLP 3D printing
Several other techniques have been developed based on SLA 3D printing, one of which is DLP 3D printing. In view of the acquisition of the latter sufficient popularity, we considered it appropriate to say a few words about it. There is no fundamental difference between these methods, but some differences should be mentioned. So how is SLA 3D printing different from DLP 3D printing? Everything is very simple: instead of a laser, DLP 3D printers use a projector that illuminates the whole layer at the same time, and not gradually, like a laser in stereolithography. nine0005
nine0005
It is believed that due to this, DLP printing allows you to reproduce objects a little faster. However, this difference is not large enough to force stereolithographic printers out of the 3D printing market. In addition, DLP 3D printers use photopolymer resins with a different light wavelength, and the quality of 3D printing on some models is inferior to that of SLA printers. But, again, there are no significant differences between the technologies.
Applicable materials
As we wrote above, 3D printers using laser stereolithography technology use liquid photopolymer resins, also called photopolymers. These are special substances that change their properties when exposed to light. The most common active radiation is ultraviolet. Dentists are familiar with the term "photopolymer", because similar substances are widely used in dental practice. In fact, this is the case when there were several different uses for one thing. nine0005
What photopolymers does SLA 3D print use? The most diverse.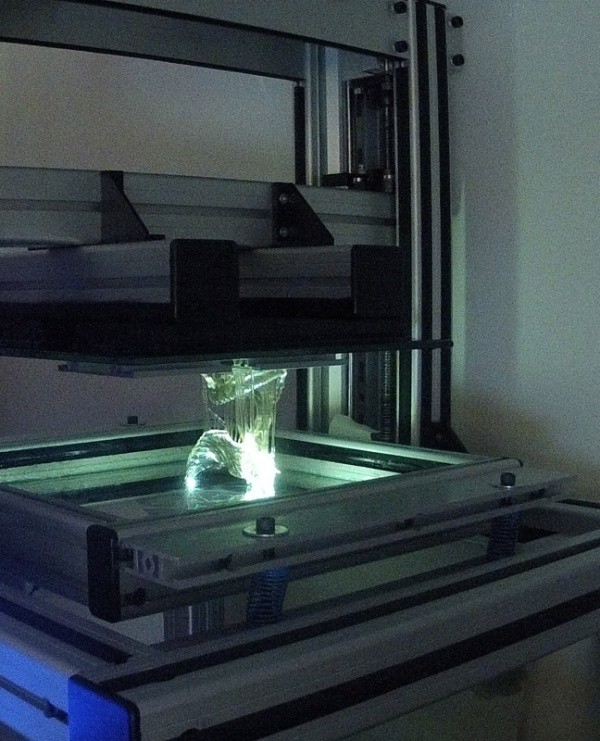 Even in the desktop 3D printer market today you can find flexible and rigid, engineering and decorative, dental and burnout photopolymer resins of all colors and shades. Of course, the range is not yet as wide as, for example, in FDM 3D printing, but it is SLA 3D printing and consumables that are in second place in popularity among users.
Even in the desktop 3D printer market today you can find flexible and rigid, engineering and decorative, dental and burnout photopolymer resins of all colors and shades. Of course, the range is not yet as wide as, for example, in FDM 3D printing, but it is SLA 3D printing and consumables that are in second place in popularity among users.
3D Printing SLA Benefits and Applications
Let's start with the benefits that SLA 3D printing provides to users. We will touch on both industrial and desktop devices for reproducing objects. So, here are the advantages of the technique:
- High precision 3D printing;
- Manufacture of products of any complexity;
- Large selection of different materials;
- Ability to manufacture ready-to-use products;
- Low material consumption for supporting structures.
Now let's describe the areas of application of the methodology:
- Jewelery;
- Dentistry;
- Design;
- Modeling;
- Prototyping;
- Model making for injection molding.

And in general, everything that requires the reproduction of 3D models in high quality, because it is SLA 3D printing that allows you to get extremely detailed products, even tiny sizes. And thanks to the availability of burnable photopolymers on the market, the possibility of casting on printed models is greatly simplified. nine0005
Hardware
To get a better idea of the 3D printers used in this printing technology, check out our SLA 3D Printers section for a variety of offers in this category. In particular, we have the following devices:
- Form 2 from Formlabs;
- KLD 3D printers in stock;
- Wanhao SLA 3D printers;
- LiquidCrystal 3D printers;
- B9Creator and many others.
For more information about this and other equipment, please call or e-mail listed in the "Our Contacts" section. We look forward to collaborating!
Return to the main
“Budget” laser 3D printer for printing metal powders
News
Subscribe to
Subscribe
I do not want
5
German company One Click Metal. a laser additive system for 3D printing with metal powder compositions costing only half a Gelendvagen (we used to measure in Rolls-Royces). nine0005
a laser additive system for 3D printing with metal powder compositions costing only half a Gelendvagen (we used to measure in Rolls-Royces). nine0005
One Click Metal is, in fact, a subsidiary of the well-known German engineering company Trumpf, which is also engaged in the production of industrial additive installations. The startup entered the market in 2019, showcasing the first iteration of its own PBF 3D printer called MPRINT at Formnext. The company is trying to find a specific niche, namely the production of low-cost additive systems for 3D printing with metal powders. Budget is a relative concept, but shortly before the premiere, One Click Metal CEO Bjorn Ullman estimated the cost at fifty thousand euros. In fact, the original 3D printers cost about that much, while the upgraded systems are offered for one and a half times more, but still much cheaper than most competitive offers ranging from a quarter to half a million dollars. nine0005
The updated MPRINT+ model differs from the original in a number of improvements aimed primarily at improving performance and resolution.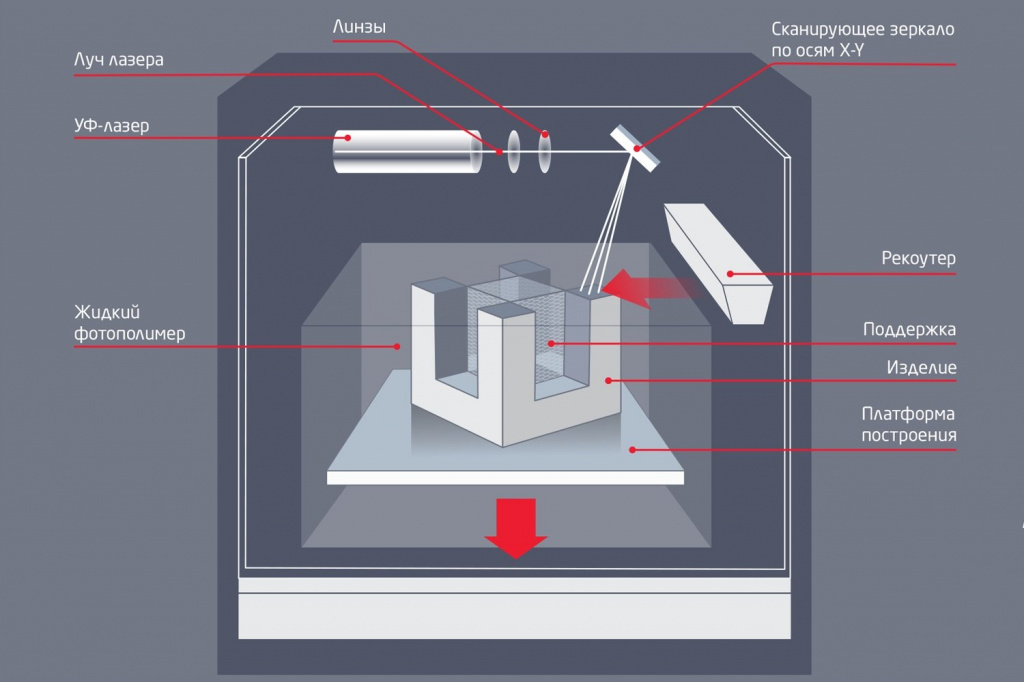 The 3D printer is equipped with a more powerful 200-watt fiber laser compared to the 100-watt in the original version. With the positioning system, not everything is clear yet. The fact is that the original used a moving head with a diode laser from Trumpf - imagine your FDM 3D printer, but with an engraving laser nozzle on steroids. We have already seen something similar on the XM200 and XM300 3D printers of the American company Xact Metal. nine0005
The 3D printer is equipped with a more powerful 200-watt fiber laser compared to the 100-watt in the original version. With the positioning system, not everything is clear yet. The fact is that the original used a moving head with a diode laser from Trumpf - imagine your FDM 3D printer, but with an engraving laser nozzle on steroids. We have already seen something similar on the XM200 and XM300 3D printers of the American company Xact Metal. nine0005
The new system allegedly uses a galvanometric scanning system that provides hatching speeds up to 3 m/s. Ullman at one time argued that a radical reduction in the cost of equipment became possible precisely due to the development of his own, relatively inexpensive scanner, so that a noticeable price jump can be fully explained by the transition to a more complex and expensive, but at the same time faster and more accurate galvanoscanner, if such the transition actually took place. Xact Metal, by the way, did just that, a year after the premiere, remaking the XM200 into the XM200S. nine0005
nine0005
The spot diameter is 45 microns versus 100 microns for the original MPRINT, the layer thickness is set within 20-80 microns, the size of the construction area is 150x150x150 mm, and the density of finished products reaches 99.5%. Printing is carried out in a sealed chamber with a protective nitrogen atmosphere, which allows you to work with active metals and alloys. The company's range of consumables currently includes powders based on aluminium, stainless steel and tool steel. nine0005
The system accepts four consumable cartridges with a 250% overload to reduce downtime. Cartridges are equipped with NFC tags to help you track media type and stock. An optional MPURE station with ultrasonic screening is available for cleaning finished products and preparing residual materials for reuse. The MPREP software is responsible for preparing digital 3D models and managing workflows.
And the moment you've all been waiting for is the cost. The MPRINT+ 3D printer is offered at a selling price of €76,900, and an additional €21,500 will have to be paid for the MPURE station.












