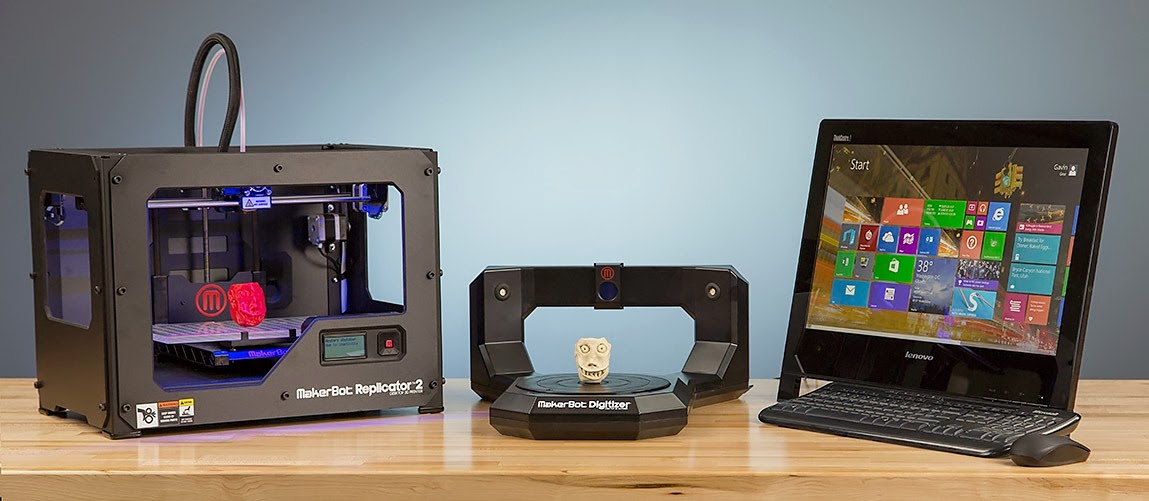
Is it expensive to 3d print
How much does 3D printing cost?
As a 3d printing company, we always get asked: "how much does it cost to 3d print?".
Our answer has always been "it depends" as there are factors that contribute to the cost of 3d printing. You're looking at anywhere between $3 to $1000(or even more) for the cost to 3d print based on these factors.
So today, we're breaking down each factor for you. If you're 3D printing at home, then those factors are your material, electricity and 3D printer cost. But if you're looking for a 3d printing service or looking into starting a 3D printing business, this guide should help you understand how pricing works when it comes to 3d printing.
Factors that affect the price of 3D printing
Cost of buying and running a 3D printer
If you're starting a 3D printing business or looking to make money with 3D printing, you might want to consider the price of a 3D printer in calculating the cost to 3D print something. 3D printers can cost anywhere between $200 to $150,000 depending on the technology being used.
Let's say you purchased a $1500 3D Printer that you plan to use 8 hrs / day for 2 years. We're going to ignore repair cost, electricity, etc. for the sake of simplicity.
8 x 365 x 2 = 5840 total hours
$1500 / 5840 hrs = ~ $0.21/hr
So if your 3D model would take about 4 hours to 3D print, then you need to charge $0.84 on top of your price to account for your machine upkeep.
In a way, the time it takes to 3D print also adds to the cost of 3D printing.
3D Model
3D model of a dinosaur trophy"Send us the 3D model" is the second thing we tell our clients after telling them "it depends". Without the 3D model, it's tough to come up with an accurate quote for a 3D print even for seasoned veterans.
The 3D model gives us essential information that can help us quote a 3d print.
Model volume
With the 3d model on hand, we can calculate the total volume of the model, including the generated supports. The total volume lets us know how much material is needed to 3d print your file.
The total volume lets us know how much material is needed to 3d print your file.
In short, the larger the volume, the higher the cost. There are ways to reduce the cost of 3D printing, and one of them is to hollow your model.
A 3ft model can have less volume than a 1ft model if the 1ft model is solid on the inside, while the 3ft model is hollow.
That is why coming up with an estimate price of 3d printing without the 3d model is not easy.
Complexity
Not all 3d models are created equal. Some are 3d print-ready, while some are just plain crazy. 3d printing takes preparation and planning. For some 3d printing services, everything is automated, which can make transactions faster. For simple products, this can be the right solution.
But what about complex parts and architectural models? We found that even with the most sophisticated algorithm, you still need some human guidance when it comes to 3d printing these type of projects.
A quick story, a client sent us a 3d model of an actual stadium. They wanted a 3d printed version of this. As we inspected the file, we saw that the model had multiple problems. There were loose joints, the walls were too thin, and there were 3d models inside the stadium itself.
They wanted a 3d printed version of this. As we inspected the file, we saw that the model had multiple problems. There were loose joints, the walls were too thin, and there were 3d models inside the stadium itself.
If we just 3d printed it right away, it would have cost us thousands of dollars on wasted material!
Take this into consideration. Are you willing to risk having your 3d model printed as is? Or do you want to make sure that the final print exceeds your expectations?
Type of material
The materials that you choose matters when it comes to the cost of 3d printing. There are tons to choose from so we are going to focus on the popular ones, thermoplastics and resin.
Thermoplastics: Filaments and Powder
Cost: $
Even if you are new to 3d printing, you have probably heard of "ABS" or "PLA". That's because these two are the most widely used 3d printing material out there. Hobbyists love these thermoplastics as they are cheap. These filaments can cost between $20 to $70 per kg.[1]
These filaments can cost between $20 to $70 per kg.[1]
Although they are cheap, getting a high-quality 3d print out of them is not easy. It will take hours of post-processing time to get smooth finishing from these prints. (More on that later.) In addition to that, 3d printing complex 3d models are nearly impossible using this type of material.
Thermosets: Resin
Cost: $$$
Resin is, in our opinion, the best 3d printing material out there. It's versatile for almost any complex project, and it would give you the best quality 3d print. But at the same time, resin material can get quite costly. Standard resin, on average, cost $50 per litre, and some resin materials can go up to $300 per litre. Luckily, 3d printing companies usually have access to discounted prices for this type of material.
Want to find out how much your 3D model will cost?
Use our instant quoting system to calculate how much it will cost to 3D print something.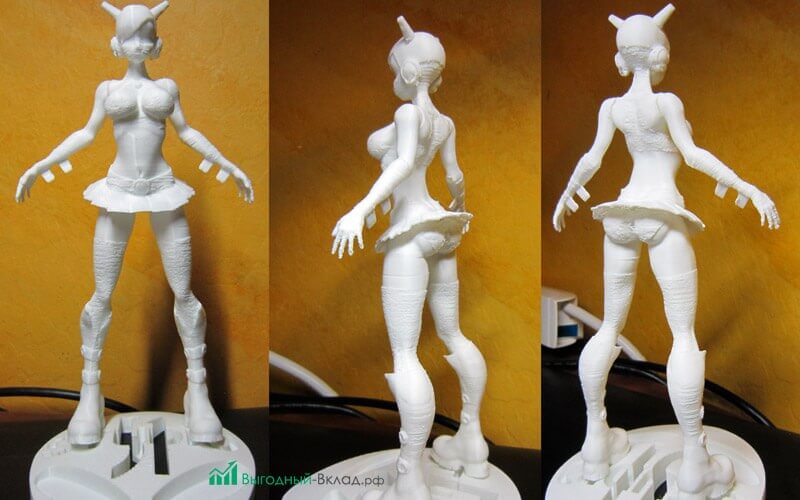
GET 3D PRINTING COST
No signup required.
Post-processing
Most don't realize that 3d printing is not an instant process. Drop your file, print, and it's ready. (We hope it was).
After 3d printing, the resulting print needs to be cured, cleaned and polished before you can consider them useable. That is if the 3d printing service company cares about the quality of their product.
Polishing
Imagine polishing the one on the left to make it smooth? Photo courtesy of Formlabs.For filaments, don't even waste your time. As someone who spent hours removing supports, we don't want to you put you through that hell. If you value your time, the amount of time you will spend sanding these prints would cost a lot. And even then, the quality wouldn't be on par compared to resin.
For resin, it's simpler. Once the pieces are UV cured, we can polish it by hand or using a sandblaster.
Again, the 3d model matters as it could affect post-processing. Some models are so complex that the generated supports are very hard to clean. It would take some expertise and a lot of patience for someone to clean these prints.
Some models are so complex that the generated supports are very hard to clean. It would take some expertise and a lot of patience for someone to clean these prints.
Finishing
At PrintAWorld, the projects that we work on usually require more than just 3d printing. Our clients would ask for their 3d print to have a gold finishing, chrome or even an exact Pantone color. With current 3d printing technology, this is impossible to accomplish. So we offer metal plating and painting on top of our 3d printing services.
Profit margin
For 3D printing companies to stay in business, they need to add a profit margins on top of the 3D printing cost. Profit margins for a 3D printing business can be somewhere between 50% - 90% of material cost. We're using material cost as a basis for the sake of simplicity. But profit margins are actually much lower once you start including labor and overhead costs.
There is also a base price (or a minimum fee) that gets added if if the cost of 3D printing is less than a certain amount. It wouldn't make sense for a company to 3D print something for you for a print that costs $3. Even in a highly automated 3D printing service, there's still some labor involved. Either you add more quantity or pay the base price which is around $30-$90.
It wouldn't make sense for a company to 3D print something for you for a print that costs $3. Even in a highly automated 3D printing service, there's still some labor involved. Either you add more quantity or pay the base price which is around $30-$90.
3D printing service price comparison
Now that we know what factors affect the price of 3D printing, let's see how much it would cost to 3D print this popular WallStreeBets mascot by ChaosCoreTech.
For this test we will be using SLA 3D printing.
We modified the file so we can stress test the on-demand 3D printing services that offer SLA printing.
Scaled it up to 152mm or ~6" high
We hollowed the 3D model. Meaning, the insides are empty.
This makes it use less material, making it cheaper.
Speed up the 3D printing time for SLA, which should lower the cost.

3DHubs
Price: $537
3DHubs won't even allow you to print this in resin as it's bigger than what their manufacturers can print.
i.materialise
Price: $211.17
Cheaper than 3DHubs but they won't clean the supports for you at this price. If you need it cleaned, you need to pay extra.
Shapeways
Price: $2061.56
We're not sure why it's this expensive. They might have miscalculated the model volume which made it seem that this piece would require half a liter of resin to print. But, either way, Shapeways is the most expensive one out of this group.
Most Affordable
PrintAWorld
Price: $136.32
Disclaimer. This is our 3D printing company. For SLA 3D printing, we are definitely the cheapest compared to the others in this group. Removing the supports and polishing is even included in the service.
Try it out
Why are 3D printing services expensive?
3D printing services are expensive because we have to account for factors mentioned beforehand such as labor, post processing and overhead costs. We also have to account the industrial 3D printers that they use, which cost at least $100,000 and upwards. Plus, they have to add profit margin on top of that cost.
We also have to account the industrial 3D printers that they use, which cost at least $100,000 and upwards. Plus, they have to add profit margin on top of that cost.
This begs the question, is it better to buy a 3D printer instead?
Should you buy a 3D printer or hire a 3D printing service?
3D printing services can sometimes cost more than an entry level 3D printer. So you might be wondering if it's better to buy a 3D printer instead.
Here's our thoughts on that:
If cost is a problem for you and you're only 3D printing for fun, then buying a 3D printer might be the better investment in the long run.
If your time is more valuable for you, then hiring a 3D printing service would be the better option. You'll have access to large scale 3D printers and capabilities that is impossible to achieve with DIY 3D printing.
Best Budget 3D Printer
Anycubic Photon Mono
The Photon Mono is the best LCD 3D printer that we've gotten our hands on. We own 8 of these machines and use it as part of our manufacturing process. It's cheap but the print quality is almost the same as the ones that we get from our Formlabs 3. If you're looking to buy your first 3D printer, we recommend going for a resin 3D printer like this one instead of buying an FDM printer.
We own 8 of these machines and use it as part of our manufacturing process. It's cheap but the print quality is almost the same as the ones that we get from our Formlabs 3. If you're looking to buy your first 3D printer, we recommend going for a resin 3D printer like this one instead of buying an FDM printer.
$229.00 from Anycubic
Commisions earned
In Summary
Multiple factors affect the price of a 3d printing service. If you add in all these variables, you're looking at anywhere between $30 to $15,000 for the cost of 3d printing. The price can even be lower or higher, depending on the scale of your project.
Is 3D Printing Expensive or Affordable? A Budget Guide – 3D Printerly
3D printing has gained a lot of popularity in recent times, but people wonder just how expensive or affordable 3D printing is.
3D printing is not expensive and very affordable as you can get a decent 3D printer for around $150-$200 like the Ender 3. The materials you need to 3D print are also relatively cheap, being only around $20 for 1KG of plastic filament. 3D printing items can be several times cheaper than buying them.
The materials you need to 3D print are also relatively cheap, being only around $20 for 1KG of plastic filament. 3D printing items can be several times cheaper than buying them.
There are other consumables involved such as nozzles, belts, and PTFE tubing, but they are pretty cheap.
I’ll get into more details to help answer this question properly so keep on reading for some key information.
Is 3D Printing Really Expensive?
3D printing is no longer an expensive or niche hobby. Due to new advances in additive manufacturing technology, the cost of 3D printing has dropped sharply in the last decade.
The Creality Ender 3 is the most popular 3D printer out there which you can get from Amazon. It has the basic features that you’d want in a 3D printer to create some amazing models. This was actually my first 3D printer and it is still going strong today after a few years.
Once you have your 3D printer, the main factors influencing the price of 3D printing are how often you use it and the sizes of the models you are creating. If you are always printing large models, your expenses on filament will be bigger than if you create smaller models and less often.
If you are always printing large models, your expenses on filament will be bigger than if you create smaller models and less often.
Although for larger 3D prints, a large 3D printer is ideal, you can actually separate models, arrange them on the build plate, then glue them together afterwards.
This is a pretty common practice among 3D printer hobbyists, especially for character models and figurines.
Cheap printing technologies like the FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) and resin SLA (Stereolithography) printers occupy the budget end of the spectrum. These printers are popular with beginners due to their relative cheapness and simplicity.
You can produce some amazingly high quality models at a budget price.
Organizations like NASA have even taken to using these printers for astronauts to create functional models in spaceships. There is however a ceiling to the quality that can be provided.
To get better quality, you can either upgrade your printer or make sure to calibrate your machine so that it runs smoothly.
For industrial and more functional applications, better materials and high precision are desired. At this level, high-level printers like the SLS printers are used. These printers print with higher quality materials producing prints with great accuracy and precision.
Their price range is usually out of the reach of the average consumer.
FDM printing definitely has its uses in the right industrial applications, even going up to laying down concrete to build houses from the ground up.
Finally, adding to the cost of 3D models are the consumables. These represent recurrent costs like printing materials, small upgrades, replacements, electricity, and finishing costs such as coating sprays or sandpaper.
Like the printers, the consumables for high-level printing technologies cost more than those for their budget equivalents.
For hobbyist printing models at home, a budget desktop 3D printer will probably be enough to satisfy all your needs.
These models come at very low costs, their printing materials are cheap, they only require minimal consumables like electricity, and they are easy to use.
The best thing you can do to keep the prices low, is ironically to get a high quality 3D printer which can cost a little extra compared to those very budget options.
Saying that, there is one staple 3D printer that is very loved, and the most popular 3D printer, the Ender 3 V2.
You can pick one of these up from Amazon or BangGood for under $300, and it’s sure to provide great quality prints and easy operation for several years to come.
How Much Does 3D Printing Cost?
We have mentioned some of the factors that affect the cost of 3D printing in the section above. Now, we want to see how those prices stack up and contribute to the cost of the final 3D model.
Here is a breakdown of how all these factors contribute to the cost of the 3D printing process:
How Much Does a 3D Printer Cost?
This is the major cost of 3D printing. It represents the upfront cost or investment in acquiring the 3D printer.
It represents the upfront cost or investment in acquiring the 3D printer.
Like we mentioned earlier in this article, the quality of the 3D model gotten depends on the type of printing technology used. Higher quality models often require additional upfront costs.
Let’s run through the costs of some of the popular printing technology at the various price points.
FDM 3D Printers
FDM printers are some of the most popular on the market due to their low cost. Budget offerings like the Ender 3 V2 start at $270. This relatively low price point makes it popular with amateurs, students, and even professionals to 3D printing.
Budget FDM printers produce good print quality for the price, but for more professional prints, you’ll be looking to upgrade to a more expensive desktop printer. The Prusa MK3S is one of these.
Priced at $1,000, it straddles the range between cost and performance offering a higher print volume and great, professional print quality at a decent price.
Large volume industrial grade FDM printers like the BigRep ONE V3 from Studio G2 are available, but the $63,000 price tag is sure to put it out of the range of most consumers.
It has a build volume of 1005 x 1005 x 1005mm, weighing about 460kg. This isn’t the usual 3D printer of course, compared to the standard build volume of 220 x 220 x 250mm.
SLA & DLP 3D Printers
Resin-based printers like the SLA and DLP are used by people who want slightly better print quality and speed than what the FDM printers offer.
Cheap SLA printers like the Anycubic Photon Zero or the Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K are available in the $150-$200 range. These printers are simple machines geared at beginners.
For professionals, bench top units like the Peopoly Phenom are available for the whopping price of $2,000.
Another respectable SLA 3D printer is the Anycubic Photon Mono X, with a build volume of 192 x 112 x 245mm, at a price tag well under $1,000.
Printers like this are used for creating fine detailed large-sized prints that budget models cannot handle.
SLS 3D Printers
SLS printers are the most expensive on this list. They cost more than your average 3D printer with entry-level units like the Formlabs fuse going for $5,000. These expensive units might not even be able to keep up with the rigors of industrial printing.
Large scale models like the Sintratec S2 are ideal for this with a price range of about $30,000.
How Much Do 3D Printing Materials Cost?This is a major recurring cost in 3D printing. The quality of the printing material to a large extent determines how well the 3D model will turn out. Let’s run through some of the popular printing materials and their costs.
Cost of FDM Printing Materials
FDM printers use thermoplastic filaments. The type of filaments used in printing depends on the strength, flexibility, and conditions required by the model. These filaments come in reels with the quality of the filament determining the price.
These filaments come in reels with the quality of the filament determining the price.
PLA, ABS, and PETG filaments are some of the most popular options. They are used by most FDM hobbyists due to their cheap price (around $20-$25 per spool). They come in several different color options.
These filaments are relatively easy to print with, PLA being the easiest, but they can have the drawback of being too brittle or weak for some applications.
There are fixes for strengthening parts through settings like infill density, number of perimeter walls, or even increasing the printing temperature. If this doesn’t provide enough strength, we can move onto stronger materials.
Special purpose filaments like wood, glow in the dark, Amphora, flexible filaments (TPU, TCU), etc. are also available. These are exotic filaments used for special projects that require these types of special materials, so their prices are above the average price range.
Finally, we have high-quality filaments like the metal-infused, fiber, and PEEK filaments. These are expensive filaments used in situations where material quality and strength is of great importance. They are available in the $30 – $400/kg range.
These are expensive filaments used in situations where material quality and strength is of great importance. They are available in the $30 – $400/kg range.
Cost of SLA Printing Materials
SLA printers use photopolymer resin as the printing material. Resin is a liquid polymer that reacts to UV light and hardens as a result.
There are many types of resins ranging from the standard entry-level resins to high-performance resins or even dentistry resins used by professionals.
Standard resins like the Anycubic Eco Resin and the Elegoo Water Washable Resin are some of the most popular on the market. These resins allow for quick curing of the material which speeds up printing.
They also come in a variety of colors for the buyer. They cost in the range of $30-$50 per liter.
Resins for special applications like dental 3D printing and ceramics are also available. These resins are used to print anything from dental crowns to metal-infused 3D parts. These types of resins can cost anywhere from $100 to $400 per liter.
These types of resins can cost anywhere from $100 to $400 per liter.
Cost of SLS Printing Materials
SLS printers use a powdered medium as their material. The standard printing powder for an SLS printer which is PA 12 nylon costs anywhere from $100 to $200 per kg.
For metal SLS printers, the cost of the powder can be as high as $700 per kg depending on the type of metal.
How Much Do 3D Printing Consumables Cost?
These factors like electricity, maintenance cost, etc. also contribute to the price of the final 3D model. These costs are dependent on the size, printing frequency, and the average time of operation of the 3D printer.
Let’s take a look at some of the consumables for these printers.
Cost of FDM Consumable Parts
FDM printers contain a lot of moving parts so, a lot of parts need to be changed and serviced regularly for the proper running of the machines. One of these parts is the print bed.
The print bed is where the model is assembled. To ensure the model sticks well to the print bed during printing, the bed is covered with an adhesive. This adhesive can be printer’s tape or a special type of tape known as Kapton tape.
To ensure the model sticks well to the print bed during printing, the bed is covered with an adhesive. This adhesive can be printer’s tape or a special type of tape known as Kapton tape.
The average cost for the printer’s tape is $10. Many people use glue sticks for good bed adhesion.
Instead, you can choose a Flexible Magnetic Surface which has great adhesion without requiring any extra substances. When I first got mine, I was surprised how effective it was compared to the stock bed.
Another part that needs periodic maintenance is the nozzle. Due to the extreme heat it undergoes, the nozzle has to be changed every 3 to 6 months to avoid bad print quality and misprints.
A good replacement is the LUTER 24-Piece Brass Nozzle Set which costs $10. Depending on the materials you print with, some of which are abrasive, your nozzle can last a few prints, or many months of prints.
You can opt in to get a Hardened Steel Nozzle, which has amazing durability for any types of filament.
Another part is the timing belt. This is an important part that drives the print head, so it is necessary to upgrade and change it to avoid loss of accuracy. The average price of a new belt is $10, though it doesn’t require change often.
Cost of SLA Consumable Parts
For SLA printers, maintenance often involves cleaning the light sources with an alcohol solution to avoid dirt buildups that can reduce the light quality. But still, some of the parts need to be checked or changed periodically.
FEP film is one of them. The FEP film is a non-stick film that provides a way for the UV light to cure the liquid resin without it sticking to the tank. The FEP film needs to be replaced when it is bent or deformed. The price for a pack of FEP films is $20.
The LCD screen of the printer also needs to be replaced because the intense level of heat and UV rays it faces damages it after some time. The advisable time for changing the screen is every 200 working hours.
The price of the LCD varies from $30 to $200 for the pricier 3D printers like the Photon Mono X, which I did an in-depth review of.
With new releases and developments of 3D printers, there is the new monochrome LCD which can actually last for around 2,000 hours without needing replacement. That’s why it’s a good idea to go above budget 3D printers in some cases.
Cost of SLS Consumable Parts
SLS printers are very complex, expensive machines with high power parts like lasers. Maintenance of these machines is best handled by qualified professionals which can be very costly.
Above all, to keep all printers in tip-top shape, periodic preventive maintenance like cleaning, lubrication, and recalibration has to be carried out regularly. All these can add to labor costs in terms of time used.
Even troubleshooting can be very time-consuming if something goes wrong, or you upgrade something without closely following a tutorial, something I’ve experienced myself.
How Much Does Finishing a 3D Print Cost?
After the model is printed, sometimes there are still some treatments that need to be performed on it before it is ready to be used. These finishing methods vary between printing technologies. Let’s have a look at some of them:
After printing with an FDM printer, the print supports are removed, and the surface of the model is machined to give it a smooth finish. These activities add to the labor costs required.
Resin-based 3D printers often require the models to be washed in a chemical solution and then cured post-printing. The price of these activities varies with each model, but they are relatively cheap.
Some people opt-in for an all-in-one solution like the Anycubic Wash & Cure which can increase your costs, but budget options are always available.
I currently just use a plastic container with isopropyl alcohol and a separate UV lamp with a solar turntable, it works really well.
Treatment of SLS printed parts can be as simple as wiping off the excess powder on the printed parts. For some metal parts, also undergo sandblasting and oven heat treatments. This can also add to labor costs.
For some metal parts, also undergo sandblasting and oven heat treatments. This can also add to labor costs.
Is 3D Printing Cheaper Than Buying 3D Models?
Seeing all the costs and numbers up there by now, you might be wondering if getting a 3D printer might be worth the hassle.
I mean, you could easily send your models to an online printing service and have them do all the work for you right? Let’s examine the cost-effectiveness of that idea.
Looking at some of the offerings from popular 3D printing services on the CraftCloud website, I checked out the price for printing out a simple spice rack from Thingiverse.
You simply download or create your STL file and drag/upload the file on this page.
Next up we come to select the material, with varied pricing depending on which one you choose.
You can choose whether you want your model sanded or left as normal, though it was a very significant increase listed.
Now you get to choose your desired color. They really have a large selection, especially if you’re choosing PLA. Some exclusive colors have large increases in price so you probably want to stick to the basic colors.
They really have a large selection, especially if you’re choosing PLA. Some exclusive colors have large increases in price so you probably want to stick to the basic colors.
At this stage you have your model and it’s specifications all done, so now we move onto the delivery and price offers. The cool thing is that you have many companies who can take your order, some cheaper than others.
The price ran into $27 including shipping for printing with the cheapest filament (PLA), and a lead time of 10-13 days.
This costs even more than a whole 1kg spool of PLA, plus the shipping time was well over a week.
After inputting the model into Cura, and having to scale the model to fit the Ender 3 build plate dimensions, it gave a printing time of 10 hours, and a material usage of 62 grams of filament.
I did have to scale the model to 84% to fit it in my 3D printer, so to convert it back, adding around 20% would be 12 hours and 75 grams of filament.
Compared to the $27 3D printing service price, 75 grams of filament with a $20 1kg roll of PLA translates to just $1. 50, and a much quicker lead time.
50, and a much quicker lead time.
3D printing services are great for large, specialized models that might not be able to be handled in house.
Due to their superior economy of scale, these services can provide multiple specialized printing equipment and expertise that might not be accessible to the average consumer.
To my knowledge, small businesses tend to use these services for one-off prototypes, or for large-scale orders at a discount.
As we’ve shown above, using a 3D printing service for simple small-scale designs that can be handled in-house can be extremely expensive.
Not to mention the long delivery times that take away the advantages touted by rapid prototyping over traditional manufacturing.
If you frequently print a lot of models, it’s best to pay the initial costs and invest in a desktop printer. Although it might take a lot of learning hours and several failed 3D models, at the end of the day, printing your models is worth it.
The future returns when you have fine-tuned your printing process are far greater than constantly hiring 3D printing services.
Is 3D Printing Cost-Effective for Making Things?
Yes, 3D printing is cost-effective for making objects. With a 3D printer, common models or objects can be easily manufactured and customized with ease. This helps reduce the cost of these objects and also helps streamline the supply chain. They are especially cost-effective if you combine CAD skills to create your own models.
But it has to be said, 3D printing does not scale well. Due to the current limitations of technology, 3D printing is only cost-effective over traditional methods when manufacturing small objects in small batches.
As the size and quantity of the models begin to increase, 3D printing loses its cost-effectiveness.
A very interesting fact about 3D printing and it’s effect in industries is how it took over the hearing aids market.
3D printing is perfect for specialized, unique objects that can be personalized for each individual. After 3D printing was adopted into the hearing aid industry, over 90% of hearing aids manufactured today are from 3D printers.
Another industry that has made huge strides is the prosthetics industry, especially for children and animals.
In the right industry, 3D printing can be very cost-effective and rapid in the manufacturing of many objects. The main drawback is actually creating the designs, but that it becoming a lot easier with technological advancements in 3D scanning and software.
Myths about 3D printing and 3D printers: common misconceptions
Myths about 3D printing
As you know, what people are not very good at, eventually acquires a lot of myths and erroneous judgments. 3D printing technology is no exception. Unfortunately, in Ukraine there is an extremely low percentage of awareness about 3D technologies, which does not favor the opinion about innovative methods. Myths about 3D printing are very different, and are built on the basis of what a person has already heard about the technology. Printing on a 3D printer is a very unusual process. But most do not bother to gain deeper knowledge and are content with meager explanations about how the technology works.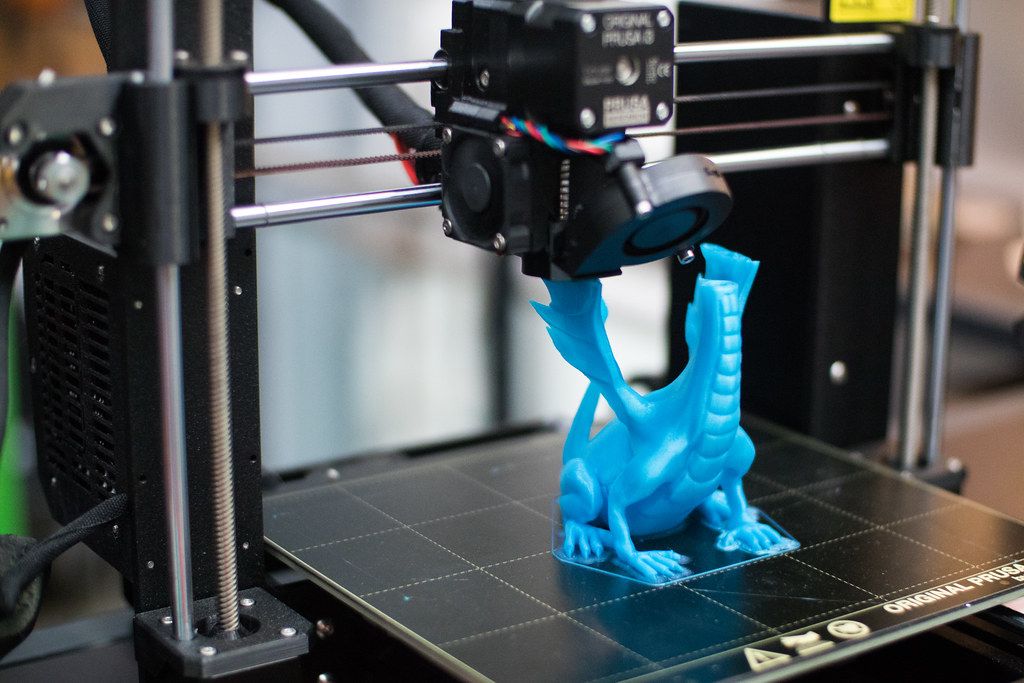 This is how 3D printing myths are born.
This is how 3D printing myths are born.
In this article, we will try to bring the most common myths about 3D printing and dispel them with reasoned facts. We hope this section will help you learn more about 3D technologies and better understand the process of printing with a 3D printer.
The most common myths about 3D printing
Let's start this section with some of the most common myths and misconceptions about 3D printing. So, what do people often think about printing on a 3D printer:
1. It's expensive
Myths about 3D printing are proudly led by the opinion about its cost, and this is not accidental. People are convinced that 3D printing is very expensive and out of reach for the average user. This myth is only half true. Prices for industrial installations for 3D printing are really very high. But that's why it is professional equipment used in production. The cost of desktop 3D printers is much lower and continues to decline as technology advances. The prices of consumables are also falling. Already, this makes 3D printing very accessible, and in the future, a 3D printer will become part of almost every home.
The prices of consumables are also falling. Already, this makes 3D printing very accessible, and in the future, a 3D printer will become part of almost every home.
2. It's professional
Many people think that 3D printing is only suitable for a narrow range of specialized tasks or industrial applications. We can assure you that this is not the case. Of course, the prospects for 3D printing in the industry are extremely promising, but for home use, a 3D printer can be no less useful.
3. Can only be printed with plastic
Now this is a completely absurd opinion. 3D printing technology is steadily moving towards the fact that anything can be used as a material. Already today there are food 3D printers, 3D bioprinters that print with living cells, devices that print with metal, wood, silicone, rubber, clay and even glass. The method of contour construction is also actively developing, that is, 3D printing of houses. As you can see, you can print anything, almost anything.
4. 3D printing is only good for making trinkets
Contrary to the opinion about the professional use of 3D printers, there are thoughts that 3D printing is not suitable for creating serious things. A variety of functional models and final parts made on 3D printers will help to convince skeptics. Many large aerospace and automotive companies use 3D printing in their practice. For example, Airbus launched a plant that uses only additive techniques. And the creation of cars using a 3D printer has become a very common practice.
Don't miss it, you'll love:
Myths about 3D printers
After listing the common myths about 3D printing, let's move on to the myths about 3D printers. Some exaggerate the capabilities of these devices, some downplay. But there are myths about 3D printers, and it's up to us to dispel or confirm them. So, what do ordinary people think about 3D printers?
1. This is a complex device
On the one hand, you can't argue with that. The device is really difficult, but the developers care about the maximum ease of managing 3D printers. Desktop devices are aimed at comfortable and simple work. For example, on Kickstarter, the project of the simplest 3D printer was considered. Moreover, you can assemble some printer models yourself. And if you do everything right, they will work well. Therefore, everything is not as difficult as it seems.
The device is really difficult, but the developers care about the maximum ease of managing 3D printers. Desktop devices are aimed at comfortable and simple work. For example, on Kickstarter, the project of the simplest 3D printer was considered. Moreover, you can assemble some printer models yourself. And if you do everything right, they will work well. Therefore, everything is not as difficult as it seems.
2. Products do not require post-processing
This is perhaps the biggest misconception. No matter how much you want, but just take it and print it will not work. Objects should definitely go through a minimal post-processing process, especially if they were printed with supports.
3. Print in any color
Unfortunately, modern desktop 3D printers are not yet able to print full color samples. There are models with multiple extruders, but the maximum possible is two or three colors. On industrial printers, it is quite possible to print products in full color. However, developers are actively working to eliminate this limitation and are making significant progress. Relatively compact full color printers already exist. It remains to wait for their mass entry into the market and lower prices.
However, developers are actively working to eliminate this limitation and are making significant progress. Relatively compact full color printers already exist. It remains to wait for their mass entry into the market and lower prices.
This concludes the myths about 3D printing. We hope the article was informative. And if you know even more myths and misconceptions about 3D printers and 3D printing that we have not touched on, write to us by e-mail and we, if necessary, will add them! Best regards, 3DDevice team.
Also visit our online store and choose 3D scanners, 3D printers, 3D pens, 3D plastic and accessories. In addition, we provide 3D printing, 3D modeling and 3D scanning services. If necessary, call or email. We are always glad to see you!
Back to main page
How to calculate the cost of printing on a 3D printer
For some ideas, 3D printing is the fastest and easiest solution. In some situations, purchasing your own 3D printer can be a good solution, but sometimes it is much more profitable and faster to order the necessary product from a company specializing in 3D printing. Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
Yes, and many owners of a 3D printer are thinking about how to “monetize” their hobby, but how to correctly calculate their costs?
Despite the fact that it is customary to indicate the price per gram of working material, simply multiplying the weight of the model by the cost of 1 gram will be wrong. In addition to the cost of consumables, many more, at first glance, non-obvious costs are added to the price of the product.
Each 3D printing technology uses its own consumables. Let's analyze the most popular and affordable of them.
Available technologies and key differences
Currently, a huge number of 3D devices have appeared, from small desktop ones that fit on the desktop to huge industrial machines. Among the most affordable, 2 technologies can be distinguished - FDM and photopolymer printers (LCD / DLP / SLA).
FDM 3D printing
Today, the most affordable 3D printing technology is FDM. A variety of materials and 3D printers allow FDM to be applied to a wide range of applications.
Schematic operation of FDM printer
A large selection makes it easy to choose a 3D printer for a specific task or find a universal device.
The material for printing is a plastic thread - filament. On the market you can find filament for various tasks, for every “taste” and budget. These can be very inexpensive ABS and PLA plastics or specific ones - conductive, burnable, etc.
Pros:
Cons:
Despite the fact that FDM allows you to print a wide range of plastics with different properties, the technology has some limitations. For example, it is impossible to obtain a perfectly smooth surface, to produce miniature and very thin elements, or to produce parts with very complex internal geometry with high accuracy.
Photopolymer printing
Photopolymer printers can work on one of 3 technologies - SLA, DLP or LCD. These devices will come to the rescue if you need to make a small but very detailed model with many small details.
How photopolymer printers work
As a consumable material, a photopolymer resin hardened by UV radiation is used. Now there is a wide variety of photopolymer resins for every taste. From particularly strong and precise engineering or jewelry resins to soft flexes.
Pros:
-
High print precision
-
Good surface quality
-
A wide variety of printers and consumables
Minuses:
Photopolymer printers have shown themselves well in a variety of industries that require a perfectly smooth surface and high accuracy. They are used in dentistry, the jewelry industry, for making miniature master models for casting, and much more.
Industrial printers
These are already industrial machines, which require a separate room and sometimes certain requirements for ventilation, etc. In this article, we will not analyze these devices in detail, but briefly consider the most popular technologies.
FDM
In addition to desktop devices using FDM technology, industrial printers that work on the same principle are common.
This category includes devices with a large print area (from 30x30x30 cm and more). For example, Raise Pro2 with a print area of 30x30x30 cm.
Raise Pro2
Or machines designed for printing with refractory materials (eg PEEK). Such 3D printers usually have an active thermal chamber, and the extruder can be heated above 400 degrees.
CreatBot F160-PEEK for use with refractory plastics
Photopolymer printers
Industrial photopolymer devices usually have a much larger working area, compared to their "home" brothers. In addition, many processes have been optimized and automated for faster operation. On such printers, you can quickly and accurately produce a small batch of models, a large prototype or a master model.
Prismlab Large Area Industrial Resin Printer Family
3DP
3DP - Three-Dimensional Printing (translated as three-dimensional printing) is a logical continuation of conventional two-dimensional printers. Printing is done using nozzles that selectively apply a binder to the material (usually gypsum). A dye can be added to the binder and the model will be colored.
Colored plaster model
Since the plaster model is fragile, a similar principle is used for printing with metals. Only the finished product needs to be treated in an oven to remove the binder and improve strength. But despite the processing, such metal prints will still be inferior in strength to cast products.
MJM
This is a proprietary technology of 3D Systems. MJM is a mix of FDM, 3DP and sometimes SLA (depending on material chosen). Printing is done using a variety of small nozzles (from 96 to 488) located on the head of the machine. The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
The accuracy and quality of the surface of models made in this way is in no way inferior to photopolymer printers.
Models made with MJM technology
Such devices can work with photopolymer resins, wax or thermoplastics. You can combine several materials at once - for example, for complex models, you can use wax as a support.
SLM
SLM is the layer-by-layer sintering of metal powder using a powerful laser. There are several similar technologies - SHS/SLS. The principle of operation is the same, only a thermal print head is used instead of a laser beam.
SLM Turbine
As a material for printing, you can use powders of various metals - gold, stainless steel, aluminum, various alloys, etc.
During printing, the working chamber is filled with an inert gas to prevent oxidation of metals. This allows printing even with titanium powder.
Models made by this method are in no way inferior, and sometimes even superior, to cast products. SLM allows you to produce models with complex internal geometry that cannot be produced by another method (casting or milling).
Cost of 3D printing
The cost of a model usually consists of several factors.
-
Equipment depreciation. The printer, like any machine, requires maintenance and periodic replacement of some parts. During operation, belts gradually stretch, bushings or linear bearings wear out. For example, when bushings or linear bearings are worn; shafts may wear out and need to be replaced.
Cost of materials
The main cost item for a 3D printer is, of course, the printed material.;
FDM (plastic filament)
Since FDM technology is by far the most common, the choice of filaments is very diverse.
-
Engineering plastics are usually nylon with various fillers added to improve the physical characteristics of the finished model.
 Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.).
Special cost. plastics starts from 2000r per coil and above. It all depends on the manufacturer and filler (carbon fiber, fiberglass, etc.).
-
Decorative plastics are used to imitate various materials. Plastic can simply be unusually colored (luminous, transparent plastics) or a special filler is added to it (plastics with metal powder). The cost of decorative plastics starts from 1500 rubles per coil and more, depending on the filler.
A big advantage of FDM is the diverse choice of materials to work with. This allows, having one printer, to produce almost any product - from a child's toy to a complex engineering prototype.
Photopolymers (resin)
Photopolymer resin printing technology is becoming more and more accessible. There are many different resins.
-
The cost of ordinary colored resin starts from 2500 rubles per 0.5 kg (volume +/- 0.5 l). You can find a smaller volume of resin (250 gr) on sale.
 You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model.
You can buy several different resins in small containers and find out in practice which one is best for a particular model.
-
Engineering resins are resins with increased strength. They can be used not only for printing decorative items, but also for making functional prototypes and models. The cost for 0.5 kg starts from 5900r and above.
-
Special resins - burnable, dental, soft flexes, etc. Depending on the resin, the price for 0.5 kg can start from 4800 rubles and more. It all depends on the characteristics of the resin.
Photopolymer resins have not yet reached such a variety as FDM filaments, but they are surely catching up. Although due to the fact that a liter of resin costs significantly more than a spool of filament, the cost of the product is much higher.
Print examples
FDM
Mag Pull (quick release loop) for G3 magazines.
The model was downloaded for free from an open source (the file can be downloaded here). Printing with engineering carbon-filled plastic (price per spool from 4700 rubles). The weight of the model with support is about 25 grams. Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished model is 250 rubles.
Plastic fastener
The file was downloaded from an open source (can be downloaded here). Plastic - carbon-filled nylon (price per coil from 4700r). The weight of the finished product is about 20 grams. Print without post-processing. The total cost is 200 rubles.
Model watch
The model is modeled to order (the cost of modeling is from 1000 rubles). The product is printed on an industrial printer using soluble support. Print without post-processing. The cost of the finished product - from 700 rubles per piece (depends on the number of required products).
Traction prosthesis
The model is taken from an open source (you can download the modified version of the prosthesis here). The weight of the used material is about 600 gr, printed with ABS plastic (the cost of the coil is from 800 r). After printing, post-processing and assembly took place. The total cost of the product - from 3000 r (depends on the print material, support material, filling, etc.).
Pedal layout
Production of a 3D model according to the drawing (from 1000 r). The weight of the finished model is about 200 gr. The product was printed with engineering carbon-filled plastic (the cost of the coil is from 4700 r). Post-processing was not needed. The cost of the finished product is about 3000 rubles.
Photopolymer printers
Model jaws for crowns
Files for printing were obtained using a 3D scanner and finalized in a 3D editor (the cost of scanning is from 3000 r, the cost of manual revision is from 1000 r). Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Printing on an industrial photopolymer printer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is from 80 r per gram.
Burnout resin rings
The model is made to order. Printing on a desktop SLA printer with a burnable polymer. Post-processing is not needed. The cost of the finished product is 200 rubles per product.
Miniatures
The models were bought on the myminifactory website (the cost of the model is from $2). Made with a desktop DLP printer. Post-processing was not required. The cost of the finished figurine is from 70 r per gram.
Custom 3D printing
Many owners of 3D printers are thinking about monetizing their hobby. But you should understand that the price of 3D printing “for yourself” and the price of commercial printing are very different.
When starting to print to order, it is better to have several printers working on different technologies.
.jpg)
Cost of commercial 3D printing
In addition to the cost of the model, to the commercial production of products, you can add:
-
Modeling. Often the client needs not only to make a part, but to pre-model it. It can be a simple cogwheel that doesn't take long to model, or it can be a complex sculpture that takes more time to model than it does to make.
-
Model post-processing. This can be simply the removal of supports, with cleaning of the place of their contact with the product, or a complete processing cycle (puttying, surface grinding, painting, etc.).
It should be borne in mind that it is not always possible to print the model the first time. Sometimes it may take several attempts. And these are additional costs.
What is unprofitable to print
Despite the wide possibilities of 3D printing, there are models that are unprofitable to make on a 3D printer. For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
For such models, it is better to use other manufacturing methods.
Commercial print examples
Jewelry for further casting
Manufacture of promotional items and souvenirs
Piece miniatures or master model for further casting
3D printed model
Profitable to print on a 3D printer:
-
If the item is only sold as an assembly. For example, a small gear broke in the mechanism, but the mechanism is sold only “assembly”. It is much cheaper to make the desired gear on a 3D printer than to buy the entire mechanism.
-
A small batch of parts. Small batches, especially models with complex geometry, are more profitable to produce on a 3D printer than by casting or other methods.
Totals
If you need several models or a small project, sometimes it will be more expedient to outsource manufacturing.