Is 3d printing a gun legal
3D Printed Guns: What is The Law?
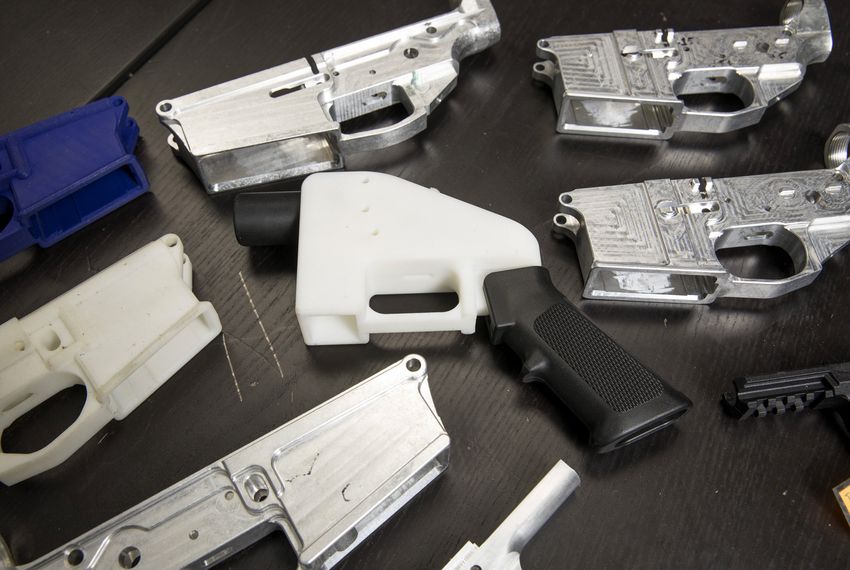
Skip to contentLiberator 3D Printed Gun
3D printed guns are a hot-button issue. The Liberator took center stage in 2013 when blueprints were released for this 3D-printed, fully-operational single-shot pistol. The inventor of the Liberator, Cody Wilson, started a company called Defense Distributed for the purpose of sharing his invention with the world. Thousands downloaded the blueprints, allowing them to print a plastic gun on a compatible 3D printer.
The federal government quickly took down the blueprints, stating that providing blueprints online was illegal trafficking of firearms. Additionally, the federal government argued that the Liberator, being that it is printed entirely from plastic, isn’t detectable by standard metal detectors, making it illegal under federal law.
Cody Wilson responded by filing a lawsuit for the violation of his First Amendment right to free speech. He argued that the source code is a form of speech and he has a right to share it with the world. Government censorship would be unconstitutional; and so, this case was settled prior to reaching the Supreme Court. Without guidance from the highest court, we may see some legal battles on the horizon.
Enjoying this content? Find out how you can get more sent straight to your inbox.
Are 3D Printed Guns Legal to Build?
Yes. Americans have always been able to manufacture their own firearms and 3D-printed guns aren’t any different. Just like machining parts to build your own AR-15, you can use the blueprints of the Liberator to print your own polymer pistol.
3D Printing Gun Law
While federal law freely allows individuals to make firearms, for their personal use, in light of the 3D-printed gun technology, some states that embrace anti-gun laws are beginning to discuss legislation that will prevent people from building their own guns.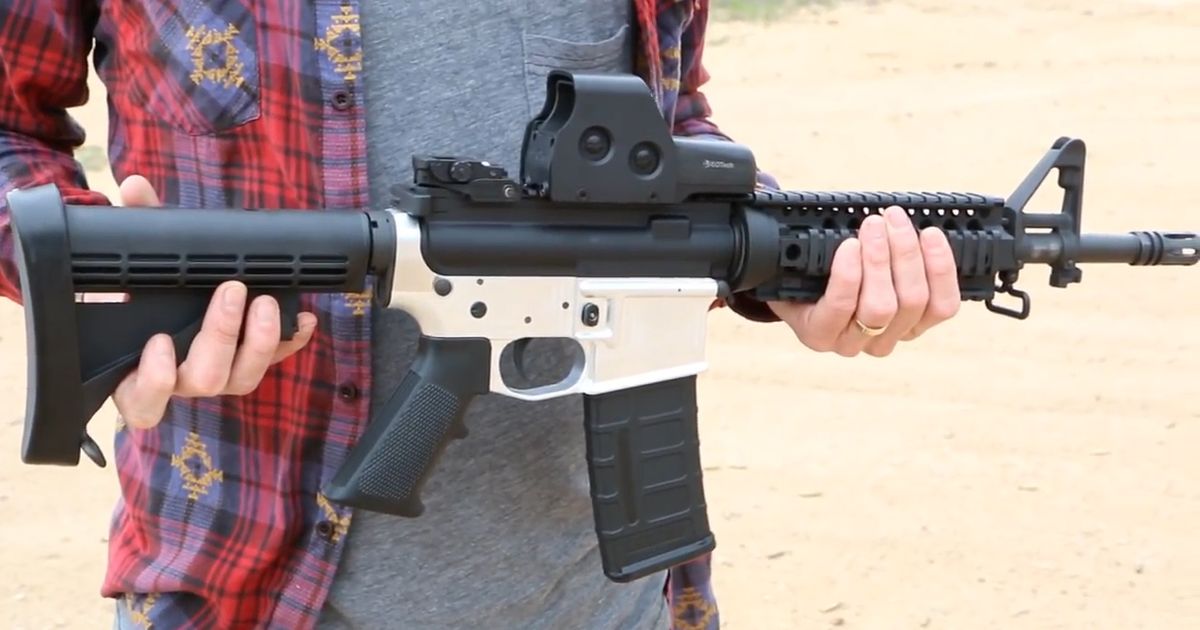
For example, New Jersey has drafted and passed a ban on homemade firearms that is not yet law, and California, while not prohibiting them outright, requires them to be serialized and registered. So be sure to get in touch with your state’s U.S. LawShield Independent Program Attorney for the current status of your state’s law.
It is important to keep in mind that these items are still firearms. Even though you can print one in the comfort of your own home, if you are disqualified from possessing a firearm you cannot possess a 3D-printed gun either.
You cannot sell these firearms as part of a commercial business without first becoming a licensed manufacturer. There is no bright line here. If you decide to manufacture 80 guns for private sale you might start to look like an unlicensed firearm dealer and you’ll find yourself subject to some unwanted legal scrutiny.
There’s a lot of controversy surrounding 3D-printed guns and you will likely see headlines in the near future addressing some of the remaining legal issues. In the meantime, U.S. & Texas LawShield will always keep you informed with the latest in gun laws, safety, and stories from our members across the nation.
In the meantime, U.S. & Texas LawShield will always keep you informed with the latest in gun laws, safety, and stories from our members across the nation.
BECOME A MEMBER
Your Protection Starts Here!
Become a part of the nation’s best Legal Defense for Self Defense® Program and get armed, educated, and prepared today.
BECOME A MEMBER
- All CategoriesBuild your skillsConcealed CarryConstitutional CarryDiscussionFeaturedGear ReviewGuarding the FamilyGun Owners’ RightsGun Safety & EducationHistoryHuntingLawLegislationMember’s VoiceNew Gun OwnersNewsNonvideoPepper SprayPets & AnimalsPoliticsPressSecond AmendmentSelf-DefenseTexas LawShieldTravelU.S. LawShieldVideosWhat To Do In An Emergency
Go to Top
What Are 3D-Printed Guns, and Are They Legal?
For decades, weapons manufacturing has been the domain of arms industry heavyweights: Glock, Sig Sauer, Remington, Sturm, Ruger & Co. Making a gun from scratch at home required thousands of dollars of machining equipment and years of engineering expertise.
Making a gun from scratch at home required thousands of dollars of machining equipment and years of engineering expertise.
But in recent years, that has begun to change. Advancements in 3D-printing technology have yielded increasingly reliable 3D-printed firearms, many of which require no federally regulated components to function. Below, we break down the basics of plastic, 3D-printed firearms, and the controversy generated by the swelling movement to deliver them to the masses.
What is a 3D-printed gun?In the simplest terms, it’s any firearm that includes components manufactured with a 3D printer.
But 3D-printed guns vary a lot. Some models — like the 3D-printed gun company Defense Distributed’s “Liberator” — can be made almost entirely on a 3D printer. Others require many additional parts, which are often metal. For example, many 3D-printed gun blueprints focus on a weapon’s lower receiver, which is basically the chassis of a firearm. Under federal law, it’s the only gun part that requires a federal background check to purchase from a licensed dealer.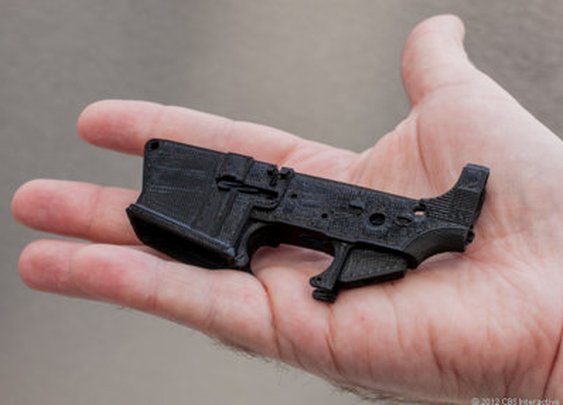 To subvert regulators, some people print lower receivers at home and finish their guns using parts that can be purchased without a background check — metal barrels, for example, or factory buttstocks. Many gun retailers sell kits, which include all the components necessary to assemble a gun at home.
To subvert regulators, some people print lower receivers at home and finish their guns using parts that can be purchased without a background check — metal barrels, for example, or factory buttstocks. Many gun retailers sell kits, which include all the components necessary to assemble a gun at home.
Advances in printing technology have driven the price of 3D printers down — they’re now around $200 on Amazon — and gun groups offer guides for getting started. These developments have lowered the barriers to entry for those in search of untraceable guns, which have turned up at crime scenes with increasing frequency over the past few years.
The process still remains more involved than most methods of obtaining a firearm, though. For instance, 3D printers require meticulous setup — the component that extrudes plastic must be calibrated, software must be downloaded to convert designs into 3D-printable slices, and the printer must undergo a slew of upgrades to reliably print weapons parts, which themselves require precise construction to ensure they can contain the explosion from a gunshot.
Because 3D-printed guns are made outside traditional supply chains, and don’t require background checks, they’re effectively invisible to law enforcement agencies. They are a form of ghost gun: unserialized, and unable to be traced if recovered by law enforcement.
There isn’t good data on the number of 3D-printed firearms that have turned up at crime scenes, though state attorneys general opposed to the technology insist that some have been recovered. On a few occasions, crimes involving the guns have made headlines. In February 2019, police arrested a Texas man after he was found test-firing a 3D-printed gun in the woods. He was prohibited from purchasing firearms and had a hit list of lawmakers on him.
Of particular concern to many law enforcement agencies are guns that can be completely 3D-printed at home without metal components. Politicians and law enforcement professionals fear that such guns would be able to evade metal detectors, and thus slip into places where firearms are prohibited, like airports or government buildings. At present, these fears are largely unfounded — 3D-printed gun designers have yet to develop an alternative to metal bullets, and security officials say that X-ray detection in place alongside most metal detectors can identify the outline of 3D-printed firearms with ease. Indeed, Transportation Security Administration officers have seized 3D-printed firearms at airports on several occasions.
At present, these fears are largely unfounded — 3D-printed gun designers have yet to develop an alternative to metal bullets, and security officials say that X-ray detection in place alongside most metal detectors can identify the outline of 3D-printed firearms with ease. Indeed, Transportation Security Administration officers have seized 3D-printed firearms at airports on several occasions.
Still, the weapons’ lack of traceability has already caught the attention of terror groups, according to Mary McCord, a former U.S. attorney and prosecutor in the Department of Justice’s National Security Division. “We know from a counterterrorism perspective that there’s great interest among terrorist organizations in being able to have workable, usable, efficient, functioning 3D-printed weapons.”
Is it legal to make a gun using a 3D printer?In most cases, yes. Federal law permits the unlicensed manufacture of firearms, including those made using a 3D printer, as long as they include metal components.
In the absence of federal regulation, a handful of states have taken their own steps to clamp down on the creation of homemade guns. In California, anybody manufacturing a firearm is legally required to obtain a serial number for the gun from the state, regardless of how it’s made. In New Jersey, you are supposed to obtain a federal manufacturing license before 3D-printing a gun. The state also criminalizes the manufacture, sale, or possession of undetectable firearms, and made it illegal to purchase parts to make an unserialized gun. Several states — including New Mexico and Virginia — are considering bills that would enact similar restrictions.
What about sharing the blueprints online?The legality of sharing the files required to print guns and gun components is murkier territory. No federal legislation bans the practice. But in 2013, the State Department ruled that releasing blueprints online violated arms export laws. In 2018, after a lengthy court battle with Defense Distributed over the guidance, the State Department settled, and agreed to permit the files’ release. But before the prohibition was lifted, a coalition of states sued to keep it in place — and won. Now, gun groups intent on sharing the files online have exploited a loophole in the State Department’s policy, which allows for the distribution of blueprints exclusively to U.S. residents. Defense Distributed maintains it has established a vetting procedure to ensure only U.S. residents are able to download them.
But before the prohibition was lifted, a coalition of states sued to keep it in place — and won. Now, gun groups intent on sharing the files online have exploited a loophole in the State Department’s policy, which allows for the distribution of blueprints exclusively to U.S. residents. Defense Distributed maintains it has established a vetting procedure to ensure only U.S. residents are able to download them.
In 2019, the Trump administration transferred oversight of gun exports from the State Department to the Commerce Department, which would have rolled back restrictions on releasing 3D-printed gun blueprints. But a second suit filed by the coalition of state attorneys general has kept oversight of the files with the State Department, pending future litigation.
New Jersey Attorney General Gurbir Grewal is a plaintiff in the case. “If a company like Defense Distributed can simply sell printable [gun blueprints] to their customers without running the usual required background checks to make sure someone’s not a criminal, it would blow up the entire regime of firearm laws that we have in this country,” he said.
In 2019, after Grewal sought an injunction to block Defense Distributed from releasing files to New Jersey residents, the company countersued. It alleges that the blueprint files are a form of speech, and that Grewal’s effort to block their release violates the First Amendment. The case has yet to go to trial.
Who is printing guns — and why?The first 3D-printed firearm to make a splash in the popular consciousness was the “Liberator” — a near fully plastic gun designed by a self-described anarchist and ghost-gun advocate named Cody Wilson. (Designs for the Liberator call for a small steel block to be sealed inside the plastic in order to comply with federal law.) Wilson founded Defense Distributed to advance and share the technology, and has initiated many of the group’s highest profile legal battles. In 2019, Wilson was sentenced to probation and ordered to register as a sex offender after soliciting sex from a minor.
Though Wilson’s is the best-known and formally recognized gun printing “company,” the practice is mostly advanced by informal collectives across the internet.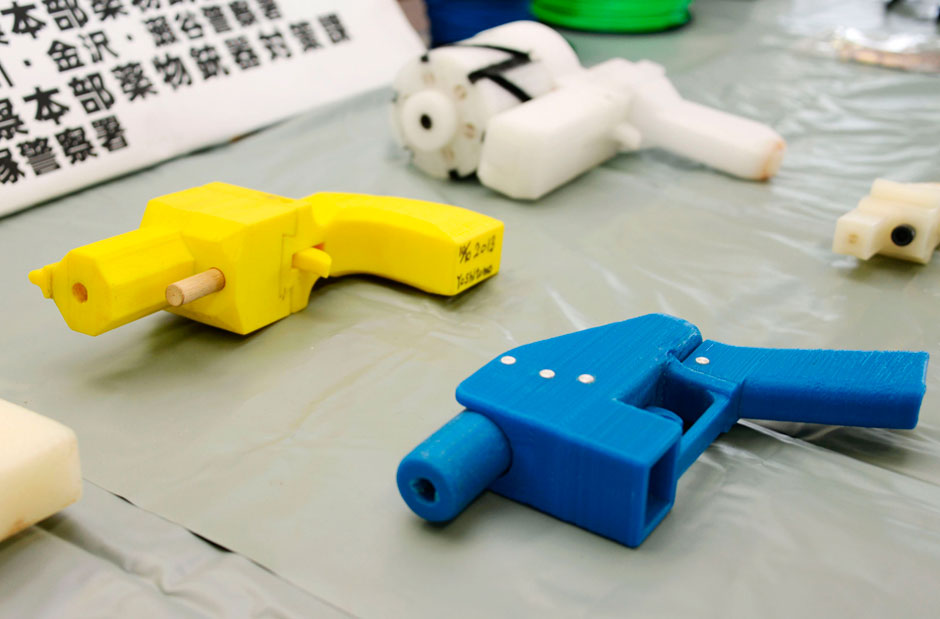 These groups, like Deterrence Dispensed and Fosscad, gather anonymously in chat rooms and on social media platforms to crowdsource the development of new gun designs and spread them across the web. They have thousands of members, but remain mostly decentralized, making it difficult for technology companies or law enforcement agencies to police them.
These groups, like Deterrence Dispensed and Fosscad, gather anonymously in chat rooms and on social media platforms to crowdsource the development of new gun designs and spread them across the web. They have thousands of members, but remain mostly decentralized, making it difficult for technology companies or law enforcement agencies to police them.
Over the past two years, however, the groups have run up against censorship policies at major tech platforms, many of which prohibit weapons content. As a result, they’ve been forced to increasingly obscure corners of the internet. Most recently, the operations hub for most of the 3D-printed gun groups — an encrypted chat and file-sharing platform called Keybase — pledged to remove all weapons-related content, and told the groups they would be banned.
Proponents of the technology fall into several different camps. Some, like Mustafa Kamil, a creator of 3D-printable guns based in Romania, and a member of the Deterrence Dispensed team on Keybase, think that concerns over homemade weapons are overblown. Gun printing, he says, is mostly the domain of hobbyists like himself: technical experts interested in tinkering and engineering. To 3D-print a gun: “you need to have enough money to buy a printer. Then you need enough expertise and experience to know how to use the printer. If your axis is off by 0.15 millimeters the gun isn’t going to work,” he said. “To buy a black market firearm would be much easier.” Kamil said he’s owned 32 printers and completed two apprenticeships with gun manufacturers.
Gun printing, he says, is mostly the domain of hobbyists like himself: technical experts interested in tinkering and engineering. To 3D-print a gun: “you need to have enough money to buy a printer. Then you need enough expertise and experience to know how to use the printer. If your axis is off by 0.15 millimeters the gun isn’t going to work,” he said. “To buy a black market firearm would be much easier.” Kamil said he’s owned 32 printers and completed two apprenticeships with gun manufacturers.
Others see the potential for armed conflict with the government as the driving force behind their creations. Members of Deterrence Dispensed and Defense Distributed have fashioned a brand out of this perceived threat, adopting popular Second Amendment slogans like “Come and Take It,” “Live Free or Die,” and “Free Men Don’t Ask.” Leaders of the groups share a deep conviction that gun ownership is the only way to ensure freedom: In an interview with Popular Front, a conflict journalism outfit, the founder of Deterrence Dispensed — a man who goes by the username jstark — continuously pointed to the threat of government tyranny as a justification for creating 3D-printed guns and distributing their blueprints. “Just look at the Uighurs in China,” he said, referring to the ongoing genocide of the ethnic minority. “Just look what’s happening to them. No one’s helping them. Nobody does shit. You know what would help them? If they were armed. That would be a deterrence.”
“Just look at the Uighurs in China,” he said, referring to the ongoing genocide of the ethnic minority. “Just look what’s happening to them. No one’s helping them. Nobody does shit. You know what would help them? If they were armed. That would be a deterrence.”
To jstark, identical threats exist anywhere where civilians are largely unarmed, including in Europe, where he lives. When asked if he would fight police who tried to confiscate his guns, he was frank: “Basically, yes. Live free, or die. These are not empty words.”
Are these groups aligned with extremists?While politicians and law enforcement agencies have dubbed the advocates of 3D-printed firearms extremists, the movement has no unifying political ideology. Jstark, for his part, said in the Popular Front interview that Deterrence Dispensed has no tolerance for people who wish to harm others: “If they do show through [their actions] that they’re extremists, racists, islamic terrorists — then we would kick them out immediately,” he said. He did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
He did not respond to multiple requests for comment.
The alarmism about about looming government tyranny has attracted groups eager to ignite government conflict, particularly in the U.S. Members of groups connected to the boogaloo, a loose-knit coalition of anti-government extremists that advocates a violent civil war, have seen 3D-printed gun advocates as allies in an overlapping struggle. Last summer, Megan Squire, a professor at Elon University, tracked online boogaloo-connected groups as they navigated crackdowns from social media platforms. Many ended up on Keybase, drawn by the large and growing 3D-printed gun community.
In early April, Deterrence Dispensed released blueprints for a printable auto sear — a component that can be used to turn a semiautomatic rifle into an illegal, fully automatic firearm — called the “Yankee Boogle,” an apparent boogaloo reference. In September, two boogaloo adherents were charged for allegedly attempting to sell auto sears to representatives of Hamas, the Islamist extremist group. In court documents, prosecutors alleged that one of the defendants in that case said he obtained the auto sears from a supplier who 3D-printed them. In a separate case, federal prosecutors charged a man from West Virginia with 3D-printing auto sears and selling more than 600 of them online, including to several boogaloo adherents. One man who bought the 3D-printed auto sears is accused of killing a police officer and a security guard in California. It is unclear if any of the auto sears used in these crimes were designed by Deterrence Dispensed.
In court documents, prosecutors alleged that one of the defendants in that case said he obtained the auto sears from a supplier who 3D-printed them. In a separate case, federal prosecutors charged a man from West Virginia with 3D-printing auto sears and selling more than 600 of them online, including to several boogaloo adherents. One man who bought the 3D-printed auto sears is accused of killing a police officer and a security guard in California. It is unclear if any of the auto sears used in these crimes were designed by Deterrence Dispensed.
Correction: An earlier version of this article highlighted a case in which police in Rhode Island said a suspect used a 3D-printed gun in a murder. While police initially made that claim, an analysis by the state crime lab later ruled the method of manufacture “undetermined.” The story has also been updated to include that Defense Distributed’s “Liberator” gun model includes a small metal component for federal compliance.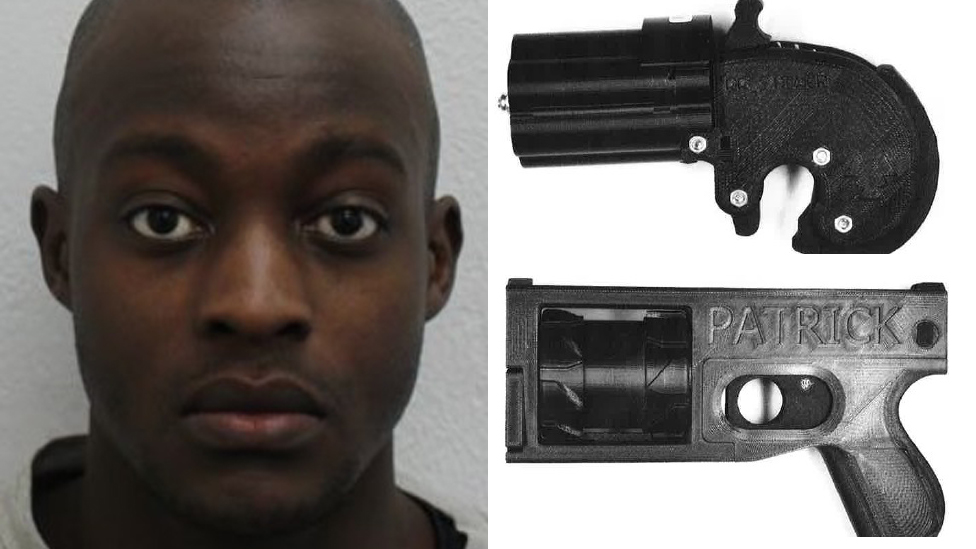
Printing weapons on a 3D printer and article 223 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation / Alexey Nyankin / Pravo.ru
Nowadays, progress has reached such a high level that with the help of 3D printing technologies it has become possible to produce mock-ups of technically complex products, which in their characteristics are not inferior to the originals.
In the summer of 2018, a scandal erupted in the United States caused by a dispute between the arms manufacturer Defense Distributed and the US State Department, which ordered the removal of graphic drawings of parts for the production of the Liberator pistol from the public domain. However, after Defense Distributed challenged the injunction in court, the State Department withdrew the injunction. Currently, a number of US states have filed independent claims against Defense Distributed, involving US President Donald Trump as a co-defendant. nine0003
In Russia, there is no talk of allowing the creation of firearms using 3D printing. The design and manufacture of firearms in our country, as in most other countries, belongs to the state monopoly and is under its complete control.
The design and manufacture of firearms in our country, as in most other countries, belongs to the state monopoly and is under its complete control.
Based on Art. 1 of the Federal Law "On Weapons", a firearm is a weapon designed to mechanically hit a target at a distance with a projectile that receives directed movement due to the energy of a powder or other charge. nine0003 If the purpose of a person who creates a 3D model of a weapon is to manufacture a firearm for later use, or at least for firing one shot, then such activity formally contains signs of a criminally punishable act.
Thus, the method of printing weapons on a 3D printer requires the development of forensic methods (the procedure for investigating certain types of crimes) and the decision to award the status of a criminal offense to the preparation for the creation of weapons and their parts from polymeric materials. nine0003 Article 223 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation criminalizes the illegal manufacture, alteration or repair of firearms.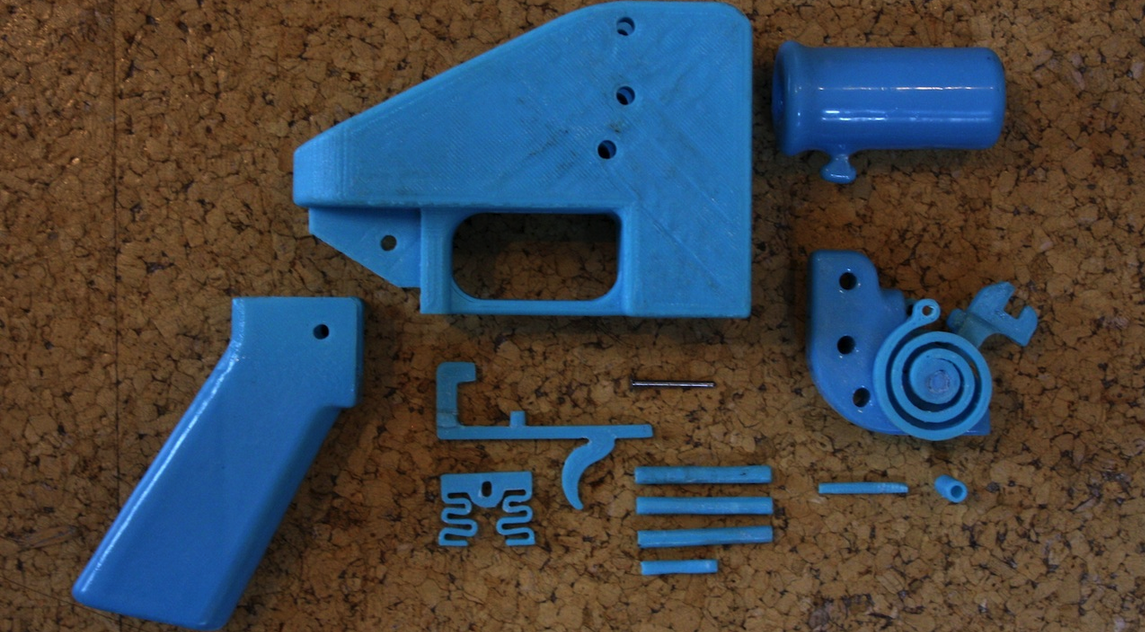 If the specified act is committed without signs of complicity (not by an organized group or a group of persons by prior agreement), then it belongs to the category of crimes of medium gravity.
If the specified act is committed without signs of complicity (not by an organized group or a group of persons by prior agreement), then it belongs to the category of crimes of medium gravity.
The onset of criminal liability is directly related to the success of experiments to develop a 3D model of weapons. Unsuccessful experiments on its creation, most likely, will not entail criminal punishment, because there is no criminal liability for preparing to commit a crime of medium gravity. However, if the successes turned out to be more significant, the weapon was manufactured and, according to its main characteristics, it turned out to be capable of firing a shot, then the actions of Kulibin-loner will be subject to criminal law qualification as a completed crime, or as an attempt on him. nine0003 At the same time, the production of weapons by 3D printing by prior agreement by two or more persons, regardless of the degree of implementation of the plan, entails criminal liability. According to parts 2-3 of Art.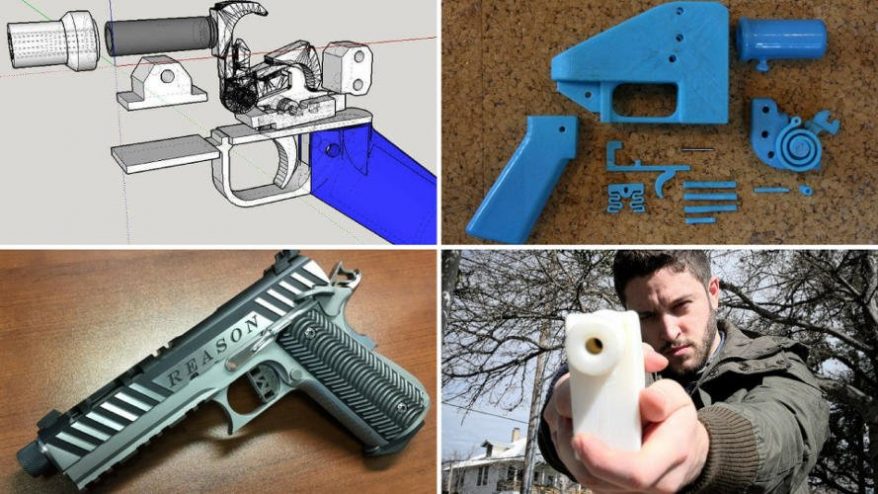 223 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, criminal liability arises even for preparation for a crime in the absence of signs of a voluntary refusal to commit it.
223 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, criminal liability arises even for preparation for a crime in the absence of signs of a voluntary refusal to commit it.
Evaluation of the ability of a manufactured weapon or part of it to fire a shot is the responsibility of an expert with special knowledge in the field of ballistics. nine0003 Consequently, if the intent to manufacture firearms is proved, the investigating authorities have enough reasons to prosecute for an unfinished crime, even in cases where the experiment with the manufacture of weapons on a 3D printer failed.
Legal 3D printing | RBC Trends
The development of 3D technologies raises questions for lawyers: who owns the rights to 3D models, is it legal to post weapon drawings on the Internet, and who still owns the Iron Throne from the Game of Thrones
3D printing is already actively used in some industries, such as medicine, automotive and aircraft manufacturing, light industry. Moreover, a 3D printer can be used not only as a tool for such familiar purposes as the production of small-scale parts. For example, North Carolina-based Precise Bio has developed a bioprinter to create an artificial cornea.
Moreover, a 3D printer can be used not only as a tool for such familiar purposes as the production of small-scale parts. For example, North Carolina-based Precise Bio has developed a bioprinter to create an artificial cornea.
3D printing works like a conventional printer. To make a plastic phone case, you first need to create a 3D model of it using a special application on your computer. This model is then sent for printing, just like a regular document. Modeling involves various forms of creating a three-dimensional object. For example, selective laser sintering (the laser, scanning the model, “sculpts” the future object), layer-by-layer deposition. Instead of ink, a variety of materials are used, such as plastic, laser powder, metal, and even human tissue. nine0015
In connection with the development of three-dimensional printing, the issue of the legal regime of three-dimensional models is of particular relevance. It can be assumed that 3D objects will become more in demand in commercial circulation than their physical counterparts. For example, it will be possible to buy not the thing itself, but its three-dimensional prototype or “assemble” the model to fit your needs. For example, Under Armor, Adidas and Nike are already working to introduce a custom 3D sneaker service. And the domestic manufacturer of trucks KAMAZ uses technology to create digital twins of products. nine0015
For example, it will be possible to buy not the thing itself, but its three-dimensional prototype or “assemble” the model to fit your needs. For example, Under Armor, Adidas and Nike are already working to introduce a custom 3D sneaker service. And the domestic manufacturer of trucks KAMAZ uses technology to create digital twins of products. nine0015
It is important to understand the legal regime of a 3D model and its legal protections. In some cases, this is an object of intellectual property, for example, when it comes to a model with an original design or a model containing patentable solutions.
Traditionally, patent law, unlike copyright law, protects the content of a solution, not its form. Therefore, the use of a patented solution, as a general rule, is considered to be its “reification” in an object of the material world or the subsequent commercial use of such a material object. Such "reification" proves the use of the essence of the solution. At the same time, dissemination of information about a patented object, including drawings, drawings, verbal descriptions, is not considered the use of a patent.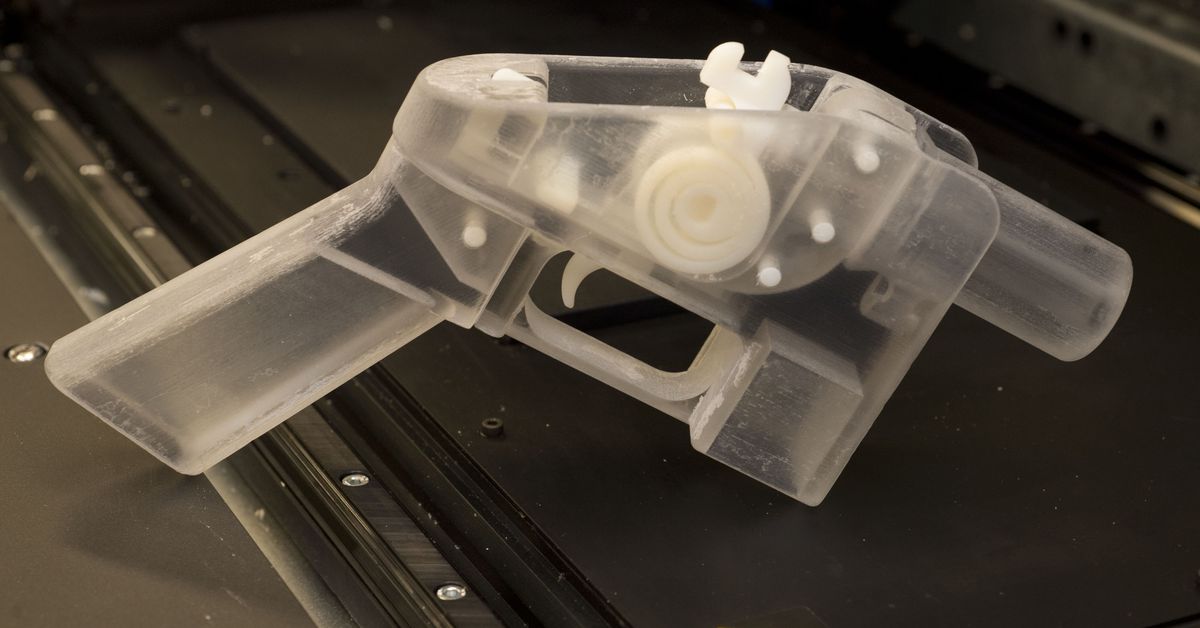 This position is also confirmed in court decisions, and in the Civil Code of Russia, all of the listed methods of using patents are associated with the implementation of a patented solution in a product or product, that is, in an object of the material world (Article 1358 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). nine0015
This position is also confirmed in court decisions, and in the Civil Code of Russia, all of the listed methods of using patents are associated with the implementation of a patented solution in a product or product, that is, in an object of the material world (Article 1358 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). nine0015
Of interest is the role of online platforms and services for the distribution of three-dimensional models, of which there are already a lot (Pinshape, Turbosquid, Thingiverse, Free3d). Such sites contain large databases of 3D products, the legality of which placement and use in some cases is questionable. For example, on such resources, you can download models of key rings with trademarks of famous brands, toys in the form of famous cartoon characters, designer vases, and even spare parts for car engines. nine0015
HBO has filed a claim against designer Fernando Sosa, who created a 3D model of the Iron Throne iPhone stand from Game of Thrones and put it up for sale. According to representatives of HBO, using the image of this throne when creating the model, the designer violated the copyright of the channel. After receiving the claim, Sosa removed the model from the site.
According to representatives of HBO, using the image of this throne when creating the model, the designer violated the copyright of the channel. After receiving the claim, Sosa removed the model from the site.
Another question that is gaining relevance in connection with the development of 3D modeling: who will be responsible for the damage caused by the printed object? nine0015
The technical capabilities of 3D printers have reached such a level that even firearms and human organs can be created. Now the cases of printing such objects are rare, and the distribution of devices on which you can simulate such complex objects is not even a matter of tomorrow.
However, this future will certainly come. The story of Cody Wilson, the owner and founder of the Defense Distributed project, raises questions about the safety of using 3D printing. Wilson created and 3D printed the first working model of a single-shot Liberator pistol. The company posted drawings of the components of these weapons on the website in the public domain in 2013, which caused concern to the authorities, including because such pistols cannot be detected by metal detectors.