Heat resistant 3d printing filament
Finding The Best Heat Resistant 3D Printing Filament
Jun 5, 2020
A wide range of innovative and sophisticated heat resistant materials are available for 3D printing. They open the door to new possibilities of manufacturing and design. Here, we help you find which heat resistant 3D printing filament is best for you.
There are several heat resistant 3D printer materials that manufacturers can use for objects that are required to withstand high levels of heat. In this article, we’ve rounded up the best heat resistant 3D printing materials for FFF printing.
1. PET-GA great heat resistant filament is PET-G (polyethylene terephthalate glycol-modified). This 3D printing material is great for beginners because it’s just as easy to print as PLA, but more technically resistant to different stressors such as heat, water, and corrosive chemicals.
For instance, it can withstand operating temperatures of up to 70ºC. It’s commonly used is for end-use parts that need good mechanical and thermal strength. Furthermore, PET-G is employed for its strong water and moisture resistance, making it an ideal material for water-tight materials and waterproof functions.
2. ABSABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is a commonly used thermoplastic filament that is popular among professional printers due to its stiffness and heat resistance. This 3D printing filament is frequently used for prints that will undergo high-stress applications, like heat or impact.
ABS is a great option for a heat resistant 3D filament, as it can withstand temperatures of up to 100ºC. Besides being heat resistant, it is also water and impact-resistant, even at temperatures as low as -10ºC.
3. PPPP (polypropylene) is well known for its extraordinary chemical resistance, especially against alkali, acids, and organic solvents. But, along with being chemically resistant, it is a heat resistant 3D filament as well.
But, along with being chemically resistant, it is a heat resistant 3D filament as well.
PP can withstand temperatures of up to 100ºC. Thanks to its smooth, lightweight, and clear appearance, it is often used for food containers, liquid bottles, and other printed parts that come into contact with water or harsh chemicals.
4. PP GF30PP GF30 (polypropylene 30% glass fiber) is similar to its non-glass fiber counterpart, but with an even higher heat resistance of 120ºC plus the added benefit of UV resistance. These two qualities make PPGF30 a great filament option for parts that need to be able to resist a variety of weather conditions.
This 3D printing material is also commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industry thanks to its strong heat and chemical resistance and strength. However, it is still a lightweight 3D printing material. Therefore, it can be used to create prints that are equally strong, rigid, and weather-ready.
PA (polyamide) is another thermoplastic that is suitable for heat resistant 3D printing. Featuring a thermal resistance of up to 120ºC, PA can withstand this high heat for an extended period of time, making it a great option if your print will be subjected to heat.
PA is also semi-flexible due to its semicrystalline structure, meaning this material’s strength goes beyond heat resistance. PA is frequently used to print parts that must be exposed to a variety of environments thanks to its high heat, abrasion, oil, and impact resistance. It used to print a variety of manufacturing materials, like jigs, washers, bearings, handles, and snap-fit joints.
6. The most heat resistant 3D printing filament of all: PAHT CF15PAHT CF15 (high-temperature polyamide carbon fiber reinforced) is a very strong and technically advanced material. Thanks to its 15% carbon fiber, it is both heat and chemical resistant, landing itself as the most heat resistant 3D printing material on this list.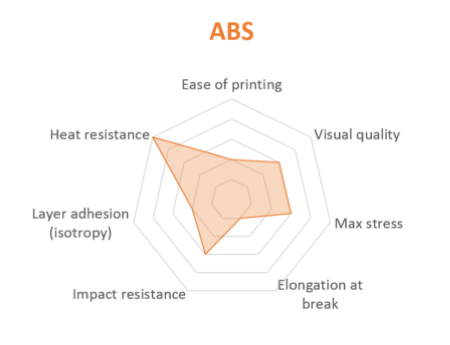
It can withstand continuous temperatures of 150ºC, making it the ideal filament to use if your print will be subjected to high heat for long periods of time. Alongside being heat resistant, PAHT CF15 is also characterized by high stiffness, strength, and printability. This filament is best suited for the most technical printing applications, like moving parts or even metal replacement.
In conclusion, when it comes to finding a 3D printing material that is heat resistant, the options are plentiful. Each heat resistant 3D printing filament comes in many different cost points, skill levels, and strengths. Beyond just being heat resistant, many have additional features that can help narrow down choosing the perfect filament for your print. Should you be interested in learning more, be sure to download our dedicated white paper below, or for a quick fix have a go at our material selector!
Top 5 Most Heat-Resistant 3D Printing Filament – 3D Printerly
When it comes to 3D printing materials, one common characteristic that people look for filament that is heat-resistant, so I decided to put together a list of some of the best ones out there.
Some of the best heat-resistant filaments are fairly pricey, but there are budget options you can go with and still get great results.
1. ABSABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a popular thermoplastic polymer in the 3D printing industry. It is a strong, ductile material with high heat and damage resistance.
It has a printing temperature of up to 240°C, a bed temperature of 90-100°C, and a glass transition temperature of about 105°C.
The glass transition temperature is the temperature at which a polymer or a material changes from a rigid, strong material, to a soft but not fully melted material. It is generally measured by stiffness of the material.
That means you can use ABS filament for applications that reach near to the 100°C and still have a fairly intact model. You want to avoid having an ABS print at these higher temperatures if it serves some functional purpose which is load-bearing.
I’d recommend going for the HATCHBOX ABS Filament 1Kg Spool from Amazon. It has many thousand positive ratings from plenty of happy customers. They say once you have the right temperatures set, printing becomes a lot simpler.
It has many thousand positive ratings from plenty of happy customers. They say once you have the right temperatures set, printing becomes a lot simpler.
For example, if you had some kind of bracket or mount that holds something up, but gets near to the glass transition temperature, the part is likely to fail very quickly and not hold up.
ABS is a great material for products which need to be durable, but also for applications where high heats are present. A 3D print for a vehicle is a good example where you get very hot weather.
When the sun is out, temperatures can get really hot, especially when the sun is beaming directly on the part. PLA wouldn’t last very long in those conditions because it has a glass transition around 60-65°C.
Do keep in mind, ABS is hygroscopic, so it is prone to absorbing moisture from the immediate environment. Storing your filament in a dry, cool place is the recommended measures to take.
ABS can be fairly hard to 3D print with since it goes through a phenomenon called warping, which is when the plastic rapidly cools and shrinks to the point where it causes a curved surface on the corners of your prints.
It can be controlled with the right measures, such as using an enclosure and applying a good 3D print bed adhesive to have the part stick in place.
ABS is actually susceptible to direct sunlight and UV rays, so you can also decide to go for the more protected version, called ASA. It has more protection against UV rays and is a better choice for outdoor use.
Check out some SUNLU ASA Filament from Amazon for a clog-free and bubble-free 3D printing experience.
2. Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon is a polyamide (a group of plastics) that is a strong, impact resistant thermoplastic. With an incredible amount of strength, high chemical resistance, and durability, it is a versatile 3D printing material to work with.
What makes Nylon an interesting 3D printing filament is that it is strong yet flexible, which makes it tough and shatter-resistant. It comes with a high inter-layer adhesion.
If you’re looking to produce objects with intense layer adhesion and toughness, Nylon filament is a good purchase.
However, Nylon is also extremely susceptible to moisture, so you should take drying measures before printing and during storage as well.
This type of filament typically requires an extruder temperature of up to 250°C. It has a glass transition temperature of 52°C and a bed temperature of 70-90°C.
Nylon filament is bright white with a translucent finish. It also possesses a hygroscopic property, meaning it can absorb liquids and moisture from the air. This will allow you to add color to your printed parts with dyes.
It is important to note that absorbing moisture will affect your printing process and quality of the prints.
Nylon filament has a short lifespan and can be difficult to store. It can shrink during cooling, so you may have to compromise on the intricacy of prints. Nylon is also prone to warping, making bed adhesion of concern. One needs to care of these nitpicks while printing.
All these properties exhibited by Nylon make it a befitting choice to make strong functional parts, living hinges, medical equipment, prosthetics, etc.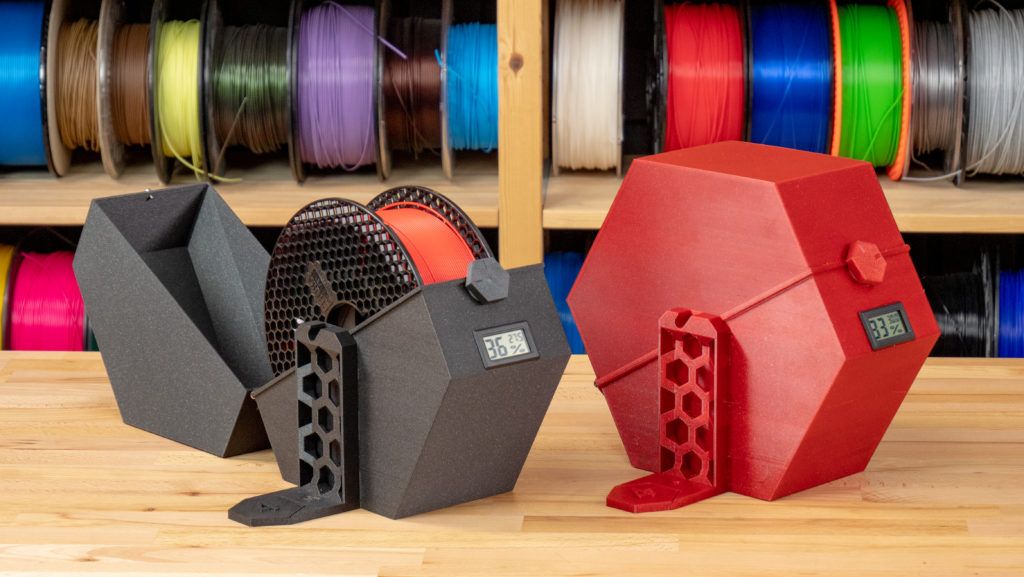 Nylon filament is in the price range of $18-$130/kg, and comes in a variety of sizes.
Nylon filament is in the price range of $18-$130/kg, and comes in a variety of sizes.
Get yourself some eSUN ePA Nylon 3D Printer Filament from Amazon. It has a really low shrinkage rate, great for producing really durable models, and you even get guaranteed customer satisfaction.
3. PolypropylenePolypropylene is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic, widely used in the industrial sector. It has high chemical and impact resistance, excellent electrical insulation, is lightweight, and resistant to fatigue.
It has a unique blend of characteristics making it an exemplary choice for different sectors ranging from industrial applications to sportswear to home appliances.
Polypropylene is commonly used to make utensils, kitchen tools, medical equipment and functional parts. It’s a filament which is dishwasher-safe, microwave-safe due to the high heat resistance, and works well for food contact.
Polypropylene requires an extruder temperature of 230-260°C, a bed temperature of 80-100°C, and has a glass transition temperature of about 260°C.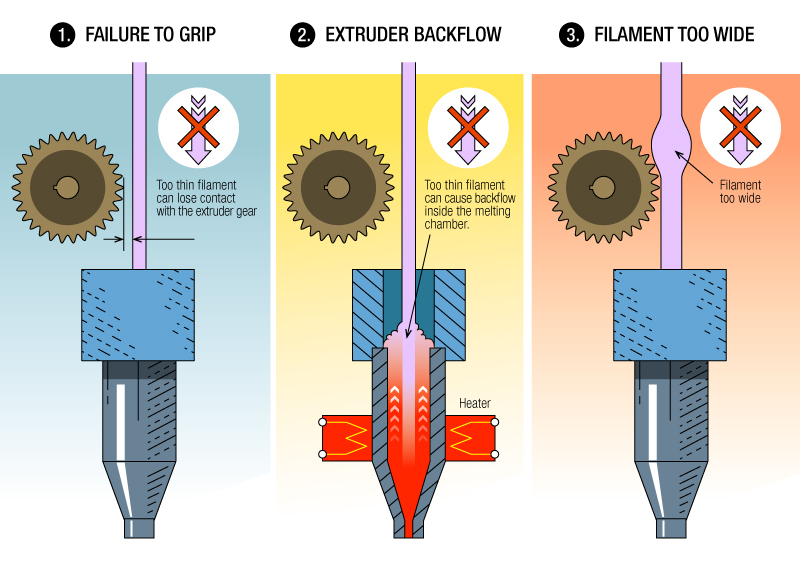
Durability and resistance makes Polypropylene a good fit for 3D printing, although it can be tricky at times. The semi-crystalline structure of this material causes the prints to warp upon cooling.
It can be taken care of by using a heated enclosure, but it’s still a difficult 3D printing filament to get the hang of.
There is also the issue of poor bed adhesion, which needs to be taken into account while printing.
Although it has some good resistance, overall its a fairly low strength filament that works best for prints that give fatigue over time such as hinges, leashes, or straps.
One thing many people love about this filament when they dial in their settings is the smooth surface finish they can get.
It is available in the price range of $60-$120/kg.
Get a spool of FormFutura Centaur Polypropylene Filament from Amazon.
4. PolycarbonatePolycarbonate is a popular thermoplastic widely known for its strength and durability. It has high heat and impact resistance, optical clarity, is lightweight and strong, and makes a great choice for a wide variety of applications.
It has high heat and impact resistance, optical clarity, is lightweight and strong, and makes a great choice for a wide variety of applications.
Polycarbonate requires an extruder temperature of 260-310°C, a glass transition temperature of 150°C, and a bed temperature of 80-120°C.
Polycarbonate has a hygroscopic property, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. This will have an adverse impact on the printing process, quality of the prints and strength. It is very important to store the material in air-tight, moisture-free containers.
Owing to its high heat resistance, 3D printing with this filament requires high temperatures. Therefore, it is optimal to use a machine that has a closed chamber and can operate efficiently with high bed and extruder temperatures.
To ensure proper layer adhesion, cooling fans should be turned off.
It should be kept in mind that Polycarbonate filament is prone to warping and oozing while printing. To help prevent this, you should try increasing the retraction distance and speed.
Customizing first layer settings is also likely to aid in the prevention of warping.
Common applications of Polycarbonate include high-strength parts, heat-resistant prints, and electronics cases. It comes in a price range of $40-$75/kg.
A great Polycarbonate filament you can get is the Polymaker PC-Max from Amazon which is harder and stronger than regular Polycarbonate.
5. PEEK
PEEK stands for Polyether Ether Ketone, a semi-crystalline thermoplastic with exceptional properties. It is regarded as one of the highest performing polymers in the 3D printing market at this time.
With outstanding mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties, PEEK is an optimal choice of material for projects.
For you to print with PEEK filament, you require a 3D printer that can heat up to 360 to 400°C. It has a glass transition temperature of 143°C and bed temperature of 120-145°C.
Owing to its high-temperature resistance, excellent mechanical strength and chemical resistance, PEEK is rigid, strong, and durable. Working with this material is complicated, often requiring experience, knowledge, and the appropriate system.
Working with this material is complicated, often requiring experience, knowledge, and the appropriate system.
PEEK is an ideal choice to produce engineering parts such as pumps, bearings, compressor valves, etc. It is also used widely in the medical and healthcare sector, and in the automotive and aerospace industry.
There are many specialized 3D printers that are designed to handle PEEK, and they usually have an enclosed heated chamber in a fairly expensive price range.
It belongs to the category high-performance filaments, exhibiting extraordinary tensile strength, heat and water resistance, and biocompatibility. However, this also means it is premium and high-end, ranging from $400-$700/kg.
Get yourself a spool of the finest Carbon Fiber PEEK Filament from Amazon.
3D Printable Nylon
- 1 Description
- 2 Specifications
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages of nylon
- 3.1 Features
- 3.
 2 Disadvantages
2 Disadvantages - 4 3D printing use
- 5 Use of available materials
Description
Nylon is attractive as a material for 3D printing due to its high wear resistance, affordability and excellent slip coefficient, which allows the use of nylon in bearings and other similar mechanisms, often without the use of lubricants.
An example of a model created using Stratasys Nylon 12
Despite the widespread use of nylon in the industry, the use of this material in 3D printing is quite limited due to certain technological difficulties. However, in recent years, specialized nylon consumables have appeared, focused on use with SLS and FDM printers.
Taulman and Stratasys nylon threads are the most popular examples.
Specifications
| Taulman 618 | Taulman 645 | Stratasys Nylon 12 | |
| Density | 1. 134 g/cm³ 134 g/cm³ | – | – |
| Hygroscopicity | 3.09% | 3.09% | – |
| Tensile strength | 65.99 MPa | 85.68 MPa | 48.26-53 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | Over 300% | Over 300% | 9.5-30% |
| Melting point | 218°C | 214°C | 178°C |
| Glass transition temperature | 49.4°C | 68.2°C | – |
| Extrusion temperature | 235-260°C | 235-260°C | – |
| Pyrolysis temperature | 350-360°C | 350-360°C | – |
Stratasys Nylon 12 is designed for use with Fortus brand 360mc, 400mc and 9 professional rigs00mc, while Taulman's nylon filaments are designed to work with any home and office 3D printer optimized for the popular ABS plastic. In addition, Taulman is testing a range of laser sintered nylon materials, including a powder version of Taulman 618.
In addition, Taulman is testing a range of laser sintered nylon materials, including a powder version of Taulman 618.
Advantages and disadvantages of nylon
Advantages of
- High wear resistance
- High elasticity
- Resistant to most organic solvents
- High temperature resistance
- Easy to machine
Disadvantages
- High hygroscopicity
- Release of toxic fumes during pyrolysis
- Taulman brand nylon threads available in 1.75mm and 3mm diameters
3D printing use
Taulman brand nylon filaments are available in 1.75mm and 3mm diameters
Nylon printing technology is similar to ABS printing, but with some differences. Like ABS, nylon is prone to twisting and warping when cooled unevenly, requiring the use of a heated bed.
The nylon layers have excellent adhesion, which minimizes the chance of delamination of models. Users of Taulman plastics note the durability of models at the level of analogues made by traditional injection molding.
Users of Taulman plastics note the durability of models at the level of analogues made by traditional injection molding.
Nylon is almost impossible to bond, which makes it difficult to manufacture large-sized parts from components. Alternatively, it is possible to connect nylon parts by melting the surfaces to be joined.
Nylon can be dyed with acid-based dyes.
Nylon does not adhere to glass or other smooth surfaces, so it is recommended to apply painter's tape to the desktop or use a wood backing when printing.
Due to the high hygroscopicity of nylon (the ability to absorb moisture), it is recommended to dry the nylon filament immediately before printing. Otherwise, water vapor may be released from the nozzle, which is not catastrophic for the extruder, but may affect print quality.
Use of scrap materials
Some hobbyists prefer to use inexpensive nylon line for printing, which is fraught with some unpleasant consequences. As a general rule, trimmer line is preferred, available in 3mm diameter, which is the same diameter as commercially available ABS filaments for FDM printing. However, these "nylon threads" are not pure nylon, which is evident due to their excessive stiffness, which is not characteristic of nylon. The reason for this is additives - usually in the form of fiberglass. Additives are designed to both increase stiffness and reduce the cost of the material. It should be borne in mind that the melting point of fiberglass is much higher than the melting point of nylon and, in fact, exceeds the pyrolysis temperature of nylon. Thus, it is impossible to achieve complete melting of such composite materials. As a result, tough glass fiber particles will contribute to increased wear and clogging of the extruder nozzle.
As a general rule, trimmer line is preferred, available in 3mm diameter, which is the same diameter as commercially available ABS filaments for FDM printing. However, these "nylon threads" are not pure nylon, which is evident due to their excessive stiffness, which is not characteristic of nylon. The reason for this is additives - usually in the form of fiberglass. Additives are designed to both increase stiffness and reduce the cost of the material. It should be borne in mind that the melting point of fiberglass is much higher than the melting point of nylon and, in fact, exceeds the pyrolysis temperature of nylon. Thus, it is impossible to achieve complete melting of such composite materials. As a result, tough glass fiber particles will contribute to increased wear and clogging of the extruder nozzle.
Go to the main page of the Encyclopedia of 3D Printing
BCN3D PAHT CF15 2.85mm 750g: 3D printer supplies BCN3D
from BCN3D
Starting price 12 100 ₽ - starting price 12 100 ₽
Starting price
12 100 ₽
12 100 ₽ - 12 100 ₽
Current price 12 100 ₽
| /
Savings 0 ₽ Savings -12. 100 ₽
100 ₽
1 in stock. Ship today
The PAHT CF15 filament from BCN3D impresses with its high temperature and chemical resistance.
PAHT CF15 (High Temperature Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polyamide) from BCN3D impresses with its high temperature and chemical resistance with extreme mechanical properties.
Polymer Properties | |
| Material type | FDM |
| Plastic diameter | 2.85 mm |
| Material | PA |
| Application | Engineering |
PAHT CF15 from BCN3D
PAHT CF15 allows, compared to standard PA, to operate at a continuous operating temperature of 150°C and a maximum of 180°C. The 15% carbon fiber reinforcement makes it more rigid, opening up new possibilities for printing complex applications. The thread also has high wear and abrasion resistance, resistance to solvents, aggressive chemicals and low moisture absorption.
The 15% carbon fiber reinforcement makes it more rigid, opening up new possibilities for printing complex applications. The thread also has high wear and abrasion resistance, resistance to solvents, aggressive chemicals and low moisture absorption.
Applications PAHT CF15
The heat resistance of the thread makes it suitable for use as structural and functional parts exposed to high temperatures and aggressive environments. It is also used as a metal substitute in the automotive industry, as PAHT CF15 is renowned for its extreme rigidity and impact resistance.
Recommended products
- Saving 1 000 ₽ Savings 0 ₽
Plastic PETG monofilament for 3D printing with LPD deposition filament printing, made of ethylene polymers (ethylene terephthal polymer.
 ..
.. Ultimaker
Starting price 5 500 ₽
Starting price 5 500 ₽ - starting price 5 500 ₽
Starting price 5 500 ₽
Current price 4 500 ₽
4 500 ₽ - 4 500 ₽
Current price 4 500 ₽
- Saving 1 600 ₽ Savings 0 ₽
Plastic PVA monofilament for fusing 3D printing, from hydrolysis products (vinyl acetate polymer), filament diameter 2.