Good 3d printer under 500
The Best 3D Printers Under $500 in 2023
Just a few years ago, finding a 3D printer under $500 would have been almost impossible. Now there are dozens to choose from. This brings 3D printing within the reach of modelers, hobbyists, and small businesses. Of course not every cheap 3D printer has the same capabilities. They produce different-sized models with varying levels of detail. Many are filament models, but several resin printers also come within this price bracket. Getting the right balance between cost and performance can be difficult, and the technology can be confusing. This article demystifies the jargon, and finds the best 3D printers under $500 for whatever kind of model making appeals to you.
— Best Overall: Anycubic Photon Mono X 4K Resin 3D Printer
— Best Budget: ELEGOO Neptune 2 FDM 3D Printer
— Best for Beginners: Creality Ender 3 3D Printer
— Best Large Volume: Artillery Sidewinder SW-X2 3D Printer
We imposed a price ceiling of $500 to ensure each of our picks fell within what could be expected as a reasonable price for those buying their first 3D printer. The result is some of the best budget 3D printers currently available. However, price was far from the only consideration.
Build Volume: Many 3D modelers focus on small projects, or create complex assemblies from a number of small components. Others want to go big as soon as possible. Fortunately, buying a low cost 3D printer doesn’t necessarily limit the scale of your ambitions. We sought a range of alternatives to cover all potential users.
Set Up and Ease of Use: The best resin 3D printers within our price bracket come ready to use, but many filament models require some assembly. How easy they are to operate also varies. Our picks illustrate this variety, allowing buyers to choose a model that is appropriate to their experience level.
Value: Price doesn’t always equate to value. Despite the relatively low cost of our top picks, these are not always the cheapest 3D printers on the market. However, one we selected comes from a brand recognized for their expertise and quality. As a result they should offer long-term reliability.
As a result they should offer long-term reliability.
Why It Made The Cut: By any standards, the Anycubic Photon Mono X 4K is a high quality 3D printer. To find it priced below $500 makes it terrific value.
Specs:
— Type: Resin
— Built Volume: 7.55 inches L x 4.72 inches W x 9.84 inches H
— Speed: 1.97 inches per hour
Pros:
— Highly detailed prints
— Durable, stable all-metal chassis
— Easy setup and use
Cons:
— No direct computer connection
— Gimmicky WiFi
Anycubic has long been one of the leading names in 3D printers with a wide range of innovative, high-quality machines. The Anycubic Photon Mono X 4K set new standards for speed and detail when introduced, and while larger, faster models are now available, few can challenge this model in the under $500 bracket.
With resin printers like this, screen resolution has a big impact on the detail provided. This one has an 8.9-inch 4K LCD, resulting in 3,840 x 2,400 pixels per inch. It‘s capable of printing layers at just 50 microns (0.0019 inches) thick, and at almost 2 inches per hour, it is also one of the fastest resin printers in its class.
The general structure of this 3D printer has the solidity necessary for consistent results and its built-in fans keep things at a constant temperature. The setup is somewhat time consuming, though more straightforward than most filament models. A 2.8-inch touch screen accesses many functions, but files have to be input via a USB stick. There is a WiFi app but its functions are limited and setting it up can be frustrating, so many independent testers consider it not worth the effort. The Photon Workshop software also has its critics, though popular alternatives are available from ChiTuBox and Lychee.
When introduced, the Anycubic Photon Mono X 4K was around 30 percent more expensive than it is today. It has dropped into our price range mostly because 6K and 8K versions now exist. At the moment, we think the Anycubic Photon Mono X 4K is the best 3D printer under $500 on the market.
It has dropped into our price range mostly because 6K and 8K versions now exist. At the moment, we think the Anycubic Photon Mono X 4K is the best 3D printer under $500 on the market.
Why It Made The Cut: There are plenty of cheap 3D printers on the market, but none come with the clear instructions and high print quality of the Elegoo Neptune 2.
Specs:
— Type: Filament
— Built Volume: 8.66 inches L x 8.66 inches W x 9.84 inches H
— Speed: 1.97 inches per second
Pros:
— Clear assembly instructions
— Good print quality
— Low cost
Cons:
— Manual leveling
— Poor interface
The entry-level Elegoo Neptune 2 comes in at well under half our $500 price limit, making it the best budget 3D printer in purely monetary terms. That alone would make it attractive to those thinking of trying 3D printing for the first time, however, the Elegoo Neptune 2 has more to offer than just low cost.
The majority of 3D filament printers come as self-assembly kits. Care is necessary because errors can impact performance later on. Fortunately, the Elegoo Neptune 2 comes with clear instructions, and obvious components, so setup is comparatively simple. It’s not quite all plain sailing though, as bed leveling is a key feature for accurate prints, and this needs to be done manually. Getting it right can be time consuming which may be frustrating for complete beginners. Also, while the touch screen display provides a lot of information, much of it can be unclear and confusing. Fortunately, the provided Cura software is very good, and helps enormously.
Mechanically and functionally the Elegoo Neptune 2 is a very good 3D printer for the money, though sadly the interface lets it down. There are plenty of online sources that can help resolve problems, and results will be worth it, but getting the best from the machine will require patience.
Best for Beginners: Creality Ender 3 3D PrinterAn Excellent Learning Resource. Comgrow
ComgrowWhy It Made The Cut: Creality was one of the first to produce high-quality, budget-friendly 3D printers. The Ender 3 has become hugely popular and has outstanding learning resources.
Specs:
— Type: Filament
— Built Volume: 8.66 inches L x 8.66 inches W x 9.84 inches H
— Speed: 7.9 inches per second
Pros:
— Excellent component quality
— High-quality output
— Outstanding customer support
Cons:
— Manual bed leveling
— Assembly instructions could be improved
At first glance the Creality Ender 3 looks a lot like a whole bunch of other low-cost 3D printers. In fact, Creality is renowned for 3D filament printers that combine quality components with competitive pricing, and as a result, there are many copies.
The Creality Ender 3 can produce layers at 100 microns (0.0038 inches) thick, which, while not as high as resin printers, is good for a budget 3D printer and results in smooth models. Unlike many cheap rivals that only use PLA filament, the Creality Ender 3 can use ABS, PETG, and TPU. The machine is very quiet, heats up quickly, and the user interface is clear and informative.
Unlike many cheap rivals that only use PLA filament, the Creality Ender 3 can use ABS, PETG, and TPU. The machine is very quiet, heats up quickly, and the user interface is clear and informative.
It isn’t a particularly easy machine to assemble. Creality says it takes two hours, but we feel that’s optimistic and the instructions could certainly be improved. So if that’s the case, why do we recommend this as one of the best 3d printers for beginners?
The main reason is the incredible support network, and the potential for multiple machine upgrades. Not only is Creality’s own customer support very responsive, but the popularity of the Creality Ender 3 means there are dozens of videos and other resources available online. After mastering the basics of 3D printing, add-ons are available so that those who want to improve their knowledge don’t need to buy a whole new machine. It is an excellent introduction to 3D printing, and for the money, there is no better learning platform.
Best Large Volume: Artillery Sidewinder SW-X2 3D PrinterImpressive Build Volume. Artillery
ArtilleryWhy It Made The Cut: The Artillery Sidewinder offers an impressive build volume for a printer at this price, and doesn’t compromise on quality or user-friendly features.
Specs:
— Type: Filament
— Built Volume: 11.8 inches L x 11.8 inches W x 15.75 inches H
— Speed: 5.9 inches per second
Pros:
— Large build volume
— Arrives 95 percent assembled
— Auto bed-leveling
Cons:
— Filament holder could be improved
— Poor customer support
With its impressive print volume, the Artillery Sidewinder is definitely the best affordable 3D printer for creating large models. It would be no surprise if the company had cut corners elsewhere in order to offer a machine of this capability for the money, but that doesn’t seem to be the case. While there are a couple of areas that could be improved, issues are minor.
The Artillery Sidewinder is not particularly fast, but can create layers of 100 microns (0. 0038 inches) each, so quality is comparable with many smaller devices. It comes almost complete, just needing ribbon cable and the spool holder assembled. The quality of the latter isn’t the best, resulting in occasional feed errors, but the printer will restart from the same point if interrupted. The touch screen controls are also very easy to use.
0038 inches) each, so quality is comparable with many smaller devices. It comes almost complete, just needing ribbon cable and the spool holder assembled. The quality of the latter isn’t the best, resulting in occasional feed errors, but the printer will restart from the same point if interrupted. The touch screen controls are also very easy to use.
Unusually for a cheap 3D printer, the Artillery Sidewinder has auto-leveling, which saves time and frustration. The glass bed heats up in around two minutes, so it’s ready to print quickly, and very quietly. It can take a while to get the Artillery Sidewinder working at its best, but that’s not unusual with budget 3D printers. In general, the machine is very reliable, though owners have been critical of customer support when problems have occurred.
Things To Consider Before Buying A 3D Printer Under $500There are so many good machines available today that choosing a 3D printer under $500 presents few restrictions. However, there are a few key points that need some thought.
However, there are a few key points that need some thought.
The size of the projects a 3D printer can create will have a big impact on most people’s choice, but this is just one aspect. It’s a good idea not to be focused on size alone, as this can result in weaknesses in other areas.
Resin or FilamentResin 3D printers tend to be more expensive than their filament counterparts, but often create more detailed models. On the other hand, filament tends to produce a stronger model. The type of filament can make a big difference and is worth looking into further if you are unaware of how each performs. Bear in mind while the best 3D printers can use a wide variety of materials, sub-$500 models may have more limited choices.
SpeedMost people are understandably impatient to see their 3D object finished, and print speed can vary considerably. Filament printers are usually much faster than resin. However, figures can be confusing because resin 3D printer speeds are given as the height of model created per hour, whereas filament 3D printer speeds are how fast the nozzle travels. Neither give a very accurate indication of how long a particular model will take, but they can be used for comparisons.
Neither give a very accurate indication of how long a particular model will take, but they can be used for comparisons.
Also bear in mind with filament printers the maximum speed may seldom be used. For instance, our best budget 3D printer can run as fast as 7 inches per second, but for common filaments like PLA, the optimum speed is only around 2 inches per second.
FAQsQ: Are 3D printers illegal?3D printers are completely legal. What is illegal is the copying and sale of patented or copyrighted objects. Making popular games figures for your own use, for example, is okay, but. trying to sell them is not, and may bring a lawsuit from the rights owner.
Q: Are cheap 3D printers worth buying?Absolutely. In the last few years prices have dropped considerably, so today’s best 3D printers under $500 are very capable, great fun, and can also be very educational.
Q: What can I create with low cost 3D printers?What you can print with low cost 3D printers largely depends on print volume. Toys, models, figurines, and jewelry are popular. Credit card holders and phone cases are possible, as are plant pots and other containers. There are hundreds of free-to-download files available, or you can create your own.
Toys, models, figurines, and jewelry are popular. Credit card holders and phone cases are possible, as are plant pots and other containers. There are hundreds of free-to-download files available, or you can create your own.
Not all cheap 3D printers use PLA, although many do. Some can also use ABS or TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane). Our pick for best 3D printer under $500 is a resin model, which is liquid plastic rather than PLA, which is a filament.
Q: Can 3D printers under $500 work with any software?A great deal of software works with 3D printers under $500, but there are some restrictions. It’s important to check before purchasing, particularly if you have a particular package in mind.
Q: Do I need a good computer for a cheap 3D printer?Whether you need a good computer depends on the 3D models you intend to produce. Most of the standard SLA files that are available online are quite small, and don’t need a lot of computing power to process. However, if you intend to create your own unique models, the software required can be memory- and processor-intensive. In that case, using a budget computer might prove limiting.
However, if you intend to create your own unique models, the software required can be memory- and processor-intensive. In that case, using a budget computer might prove limiting.
The ANYCUBIC Photon Mono X is an excellent 3D printer, and no other machine currently available under $500 can match the output quality. Unfortunately, resin printers produce toxic fumes so it’s very much a tool for a well-ventilated garage or workshop.
The Elegoo Neptune 2 is great value. It takes a while to set up but instructions are excellent, and many 3D printing enthusiasts feel it’s optimal to know the ins and outs of their machine. Unfortunately, the horrible interface detracts from what is otherwise a good entry-level device. Solutions are readily available, though.
This post was created by a non-news editorial team at Recurrent Media, Futurism’s owner. Futurism may receive a portion of sales on products linked within this post.
Share This Article
The best 3D printers under $500
We may earn revenue from the products available on this page and participate in affiliate programs. Learn more ›
Written By Gabriel Morgan
Updated Feb 17, 2023 11:55 AM
Just a few years ago, 3D printers under $500 were simply toys. They weren’t very capable and they wasted more filament than they used correctly. That has changed in recent years, however, and now you can get a very capable machine for less than half a rack. You can even now buy great 3D printers for kids.
While there are (loosely) three main families of 3d printers out there, there are two which are widely available at the sub $500 price point. These are fused deposition modeling printers (FDM), which use thermoplastics in the form of filament, and stereolithographic printers (SLA), which use thermosetting plastics such as resin. Generally the more common FDM printers are better for larger projects, components, and prototyping, while SLA printers are better for intricate prints, figurines, and art pieces.
Maybe you’re after an FDM printer to prototype that perfect Hellboy mask to sell on your Etsy shop, or instead you might need an affordable SLA printer to craft a perfect rendering of the Drider Ranger Chief that will be causing havoc in your next D&D campaign. Either way the best 3d printers under $500 have the tools you need to get there.
- Best overall: Creality Ender 3 S1
- Best budget: Creality Ender-3
- Best resin: ANYCUBIC Photon M3
- Best for beginners: Voxelab Aries
- Best for home: ELEGOO Mars 3 Pro
To ensure our list of the best 3d printers under $500 was as authoritative as possible, we researched numerous printers from leading manufacturers, diving deep into their specs and feature-sets and comparing them to the competition. We made sure to include a number of 3d printers for specific applications, including both SLA and FDM printers. Along the way we looked for a few specific criterias:
Along the way we looked for a few specific criterias:
Versatility is always important in gadgets — especially those meant for creation. We prioritized printers that can handle more materials, and noted those that do a better job with this. On FDM models the temperature the extruder reaches is critical to this, and resultantly we noted max heat for each FDM. SLA printers also come with specific resin limitations, we also noted these.
Leveling is highly important, as a level print substrate makes for precise prints. We factored the leveling controls in all the printers we looked at. Where they included solid auto-leveling we highlighted it.
Print size defines the edges of your creative space. We noted the max print size of all the printers we featured, both in X and Y parameters as well as in Z.
Precision translates into fewer flaws and mistakes in your print. We looked for printers that are capable of high levels of precision, for smooth forms without lines or ridges.
Assembly can make or break a printer experience — especially for those who are new to the game. We looked at how difficult all of the printers we featured are to assemble, as well as how much maintenance is required to keep them printing.
The best 3D printers under $500: Reviews & RecommendationsBest overall: Creality Ender 3 S1
Why It Made The Cut: Versatile, easy to set up, and upgradeable, this super precise FDM is capable of printing with a decent amount of materials, and offers an all-around solid print cycle.
Specs:
- Print technology: FDM
- Size: 19.2 x 17.8 x 24.5
- Build size: 8.6 x 8.6 x 10.2 inches
- Supported materials: PLA, TPU, PETG, ABS
Pros
- Solid precision
- 16 point automatic leveling
- Supports multiple slicing softwares including Cura
- Easy assembly
- Easily modded for laser engraving with presets
Cons
- Loud prints
- Some of the instructions are confusing
Where FDM printers are concerned, the Creality Ender 3 series has to have some of the best name recognition around, and the Creality Ender 3 S1 exemplifies the qualities that made the brand so famous.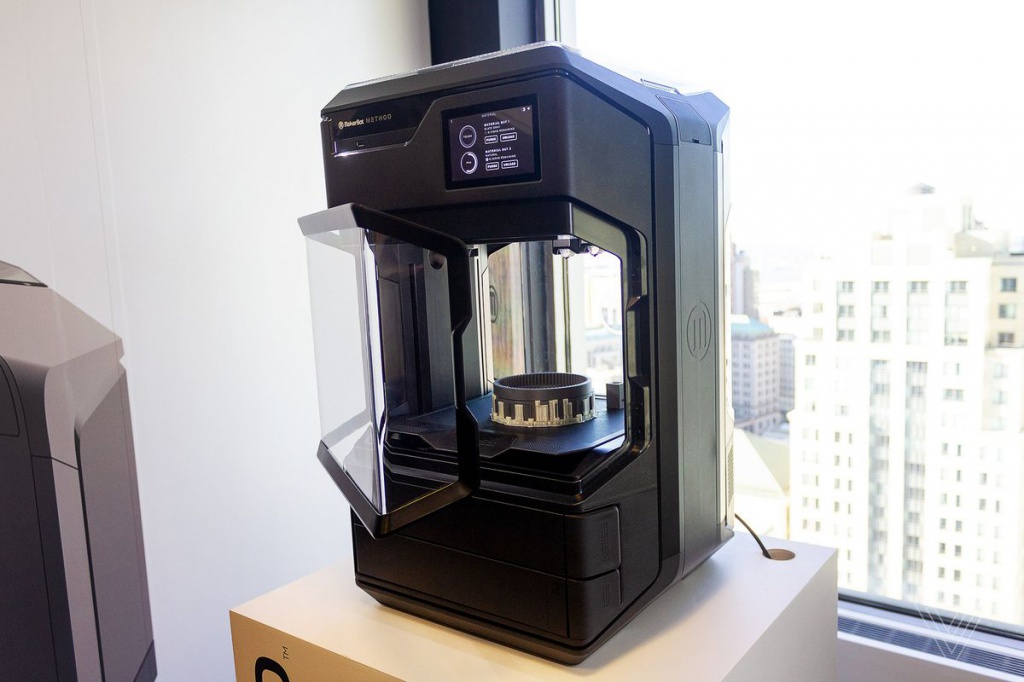 At the sub $500 price point it really doesn’t get much better than this.
At the sub $500 price point it really doesn’t get much better than this.
The S1 harnesses a few flawlessly designed features, and unifies them into a super-precise whole. The powerful extruder hits temps up to 500 degrees fahrenheit, and delivers a significant punch of pressure, even while it lightly moves across axes. It uses a geared Z-axis lift, with two motors. The system also offers an auto leveling bed. Altogether this means that the system is precise and versatile. It supports PLA, TPU, PETG, and ABS.
With a decent sized build space, a versatile list of materials supported, good precision, and an auto-leveling bed, the Ender 3 S1 is about as good as it gets at the sub $500 price point. It’s worth real consideration for anyone looking for a good fused deposition.
Best budget: Creality Ender-3Why It Made The Cut: Probably the most famous starter 3d printer out there, this open sourced classic delivers lots of great basics, with a sensible design that’s easy to mod and expand on.
Specs:
- Print technology: FDM
- Size: 17.3 x 16.1 x 18.3 inches
- Build size: 8.7 x 8.7 x 9.8 inches
- Supported materials: PLA, TPU, ABS
Pros
- Easy to use
- Moddable
- Great community support
- Very affordable
Cons
- Requires manual leveling
- Noisy
- Assembly is involved and best use will require extra work
Released back in 2018, the Creality Ender-3 is to 3d printing what the Squier is to electric guitarists — ubiquitous, cheap, and trustworthy. The younger cousin to our best overall pick, the Ender-3 is a basic 3d printer that has everything most people need to get started, even if it’s missing some of the premium features and perfectly leveled components.
With a manual leveling tray that heats to 230 Fahrenheit, and a basic extruder that heats to 491 Fahrenheit, the Ender-3 might not be capable of dealing with the most advanced thermoplastics, but it’s certainly capable of handling the classics: PLA, TPU, and ABS, and even exceeds temps available in some higher-priced printers. It also sports a resume print function that will get it back online after interruptions, power outages, or filament shortages.
It also sports a resume print function that will get it back online after interruptions, power outages, or filament shortages.
The main downside of this printer is its involved assembly. While it can be assembled in about two hours, the process isn’t easy, and print quality will be improved when extra time and care is spent on correcting for imperfections. That said, the printers vast community support in online forums and potential for moddability is one of its selling points, and the printer’s open-sourced DIY ethos is also one of its strongest assets. At the end of the day if you treat your Ender-3 as a 3d printer building kit, rather than just a 3d printer, it can give you everything you need, including some of the quiet, and comfort you’ll find in premium contemporary machines that are priced far higher.
Best resin: ANYCUBIC Photon M3Why It Made The Cut: This simple to use plug-in SLA printer delivers consistent detailed prints with zero system print-errors, and its deep community support makes for easy adoption and troubleshooting.
Specs:
- Print technology: SLA
- Size: 16.7 x 10.6 x 10.1 inches
- Build size: 7.1 x 6.4 x 4.0 inches
- Supported materials: Resin
Pros
- Extremely precise 4k LCD print
- LCD control screen
- Wide user base for support
- Decent build size for price
Cons
- Requires manual leveling
4k prints — they offer better resolution, smoother texture, and greater detail, and if you’re after a 4k 3d LCD printer for your home or workshop, you can’t do much better than the ANYCUBIC Photon M3. The Photon offers slightly larger print sizes than the ELEGOO Mars 3 Pro. It’s a budget printer from a line of 3d printers that includes some true premium tech.
The Photon M3 features a textured checkerboard build plate for better adhesion, and pairs this feature with a high contrast 4k screen. One of its standout features is a LCD control screen on the front, that allows for greater control of the device. Speaking of control, the printer allows for adjustable UV power that makes it compatible with a (somewhat) wider range of resins, but check the UV rating on your resin choice before you buy anyway to make sure it’s supported. Finally, it also features a UV-blocking cover that filters out harmful light from the LCD exposure process.
One of its standout features is a LCD control screen on the front, that allows for greater control of the device. Speaking of control, the printer allows for adjustable UV power that makes it compatible with a (somewhat) wider range of resins, but check the UV rating on your resin choice before you buy anyway to make sure it’s supported. Finally, it also features a UV-blocking cover that filters out harmful light from the LCD exposure process.
The Phonton M3 is a great choice for its deep user support network, excellent clarity, UV-blocking shield, and its controls with LCD panel. Whether it wins out over the ELEGOO is up to you, but its print quality is indisputably excellent for its moderate price.
Best for beginners: Voxelab AriesWhy It Made The Cut: Built for beginners, the Voxelab is a great place to start (and graduate), with a supremely easy setup, relatively-easy manual-leveling, wifi, and simple controls.
Specs:
- Print technology: FDM
- Size: 16.
 69 x 15.98 x 18.46 inches
69 x 15.98 x 18.46 inches - Build size: 7.9 x 7.9 x 7.9 inches
- Supported materials: PLA, ABS, PETG
Pros
- Easy auto-leveling
- Simple to control with Wifi
- Voxelmaker software allows control of multiple printers simultaneously
- Arrives assembled
Cons
- Leveling requires manual inputs
- Loud and annoying sounds
For those who might be experiencing a little trepidation about getting into the 3d printing game, the Voxelab Aries is an easy front runner to help you get settled and explore. The printer’s namesake Aries might be the Greek god of war, but the Voxelab capitalizes on simple harmony. With an open box appearance, this printer ships pre-assembled, and pre-loaded with PLA filament, offering near plug-and-play performance.
While the Aries doesn’t feature true auto-leveling, it does make it easy on you, with simple knob adjustment and a 3 point leveling system — this is why the company advertises the device as “semi-auto leveling. ” With a max extruder temp of 482 Fahrenheit the printer is capable of printing PLA, ABS, and PETG. Its textured glass bed heats to 212 Fahrenheit for decent adhesion.
” With a max extruder temp of 482 Fahrenheit the printer is capable of printing PLA, ABS, and PETG. Its textured glass bed heats to 212 Fahrenheit for decent adhesion.
The real joy of this device is its simplicity and connectivity. The Aries uses Voxelmaker software that slices, and is capable of controlling multiple Voxelab printers. Setting adjustments are also easily configured via your computer. With its pre-assembled design, Wifi connectivity, and even 8 GB of internal memory, the Voxelab Aries is a great learners rig.
Best for home: ELEGOO Mars 3 ProWhy It Made The Cut: With exceptional resolution and detail, this SLA printer does wonders at detailed art prints.
Specs:
- Print technology: SLA
- Size: 8.93 x 8.93 x 17.28 inches
- Build size: 3.5 x 5.6 x 6.9 inches
- Supported materials: Resin
Pros
- High detail prints
- Consistent print quality
- 4k monochrome light
- Free Chitubox sample subscription
Cons
- Setup instructions aren’t the clearest
Resin prints offer resolution and detail that’s sure to wow anyone, whether it’s your Instagram followers cheering on your custom Warhammer figurines, or your mom when you print her that intricate new corn-cob skewer-set for the potluck. Whatever you’re printing, if it’s details that count, then you can’t do much better than the ELEGOO Mars 3 Pro.
Whatever you’re printing, if it’s details that count, then you can’t do much better than the ELEGOO Mars 3 Pro.
This 4k monochrome printer offers an ultra-high-resolution, taking advantage of super dense chip-on-board integrated LCDs, this translates to greater detail with fewer mistakes. It features heat dissipation software that will improve its longevity, and also boasts an improved release film that elevates it above preceding models. With a one year subscription to Chitubox shipped with the device you’ll have access to powerful SLA print software that delivers all the basics, plus options that will take even experienced 3d printmakers into the weeds. If Chitubox isn’t your thing, the Mars 3 Pro also works with Lychee Slicer.
It’s when your Mars 3 Pro pairs with an ELEGOO Mini Air Purifier that it becomes a truly great kit for home use. Not many resin printer companies do as good of a job with air purifier accessories as ELEGOO, and it’s these types of health add-ons that can make your printer safe for use at home.
Related: Best 3D printers under $1000
3D printers are inherently technical, and there’s a lot that goes into which one is right for you. These devices would have seemed like tech from “the future” in the 1950s or 60s. While 3D printers have gotten much more accessible in recent years, they’re still fairly complicated and involve a learning curve. Modern 3d printers link with your computer to slice 3d CAD models, process them, and then extrude the slices of the model into plastic (or another material), generating the model as a plastic form using one of a number of methods.
Bill Masters filed the first US patent for a 3d printer process, and his inspiration for the tech is actually a pretty useful metaphor for understanding its process. Laying on the banks of the Chattanooga river one night, he imagined a star as a seed point, then that adding more and more stars, you could make whatever shape you’d like. He has also likened 3d printing to shooting “spit wads” through a straw: “When you shoot a lot of wads, they begin to take shape. If you can control the direction of the wads and the motion of the device shooting them, you can produce any desired shape.”
If you can control the direction of the wads and the motion of the device shooting them, you can produce any desired shape.”
There are several popular 3D printing technologies out there, that range in capabilities from light prototype creation with simple thermoplastics like ABS, to high end SLS machines (and beyond) that can print in advanced materials such as nylons, medical grade polymers, metals, and more. Some hyper advanced systems are now even able to bioprint cells.
Constrained by a $500 dollar price point, this article will only focus on simple FDM and SLA printers. Entry level SLS printers generally cost thousands of dollars more. When you’re shopping, consider your print goals when you decide between an FDM and SLA model.
FDM PrintersFDM printers make up the lion’s share of the printers found on the market. They deposit melted filament at precise coordinates on a flat tray. FDM stands for fused deposition modeling, though these systems are also sometimes known by another term, fused filament fabrication (FFF).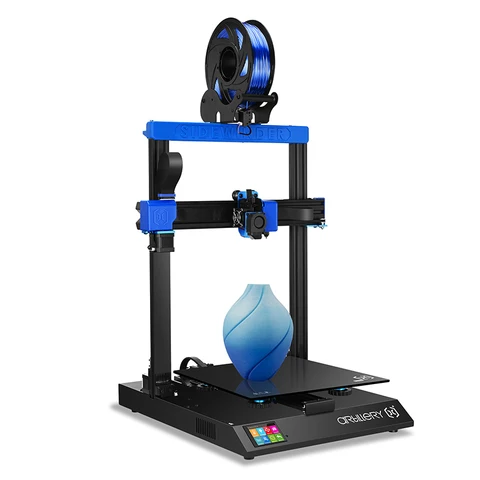 Much like a glue gun, thermoplastic filament is superheated through a nozzle and deposited onto X,Y, and Z coordinates on a leveled bed. Generally FDM printers are visually recognizable as printing “down,” in that a nozzle deposits plastic downward onto a bed. FDM printers do a good job with simple prototyping, proof-of-concepts, and less complicated economical prints.
Much like a glue gun, thermoplastic filament is superheated through a nozzle and deposited onto X,Y, and Z coordinates on a leveled bed. Generally FDM printers are visually recognizable as printing “down,” in that a nozzle deposits plastic downward onto a bed. FDM printers do a good job with simple prototyping, proof-of-concepts, and less complicated economical prints.
SLA, or stereolithography printers are capable of far more intricate detail, and use LED lights or lasers to cure liquid resin and extrude it from a liquid bath. SLA process is known as photopolymerization. Unlike FDM printers SLAs recognizably print “up,” as the model is extruded upwards (visually pulled) from the uncured liquid-state plastic bath. SLA printers do a great job with detail, high-resolution prints, and functional prototypes.
ThermoplasticsFDM printers use thermoplastics. These common plastics are able to melt, take shape, and melt again, much as water can be frozen into a shape, thawed, and frozen again, making them recyclable and reusable. Unlike water, a thermoplastic’s properties will change slightly as they are repeatedly melted. Some of the common thermoplastics used in FDM printers include ABS, PLA, PETG, and Nylon. Though not every printer will be able to service a wide range (especially at the under $500 range). These plastics often have useful properties, PLA is biodegradable, while PETG can be food safe, and nylon is safe for long term skin contact.
Unlike water, a thermoplastic’s properties will change slightly as they are repeatedly melted. Some of the common thermoplastics used in FDM printers include ABS, PLA, PETG, and Nylon. Though not every printer will be able to service a wide range (especially at the under $500 range). These plastics often have useful properties, PLA is biodegradable, while PETG can be food safe, and nylon is safe for long term skin contact.
SLA printers use thermosetting plastics, or thermosets. These plastics cure to a solid form, and cannot be remelted and reused, rather they decompose with heat. These resins offer greater precision than most thermoplastics. Resins come in many forms, including clear resins, high-rigidity resins, and flexible resins.
ProcessYour 3d printer will connect with your computer. To print, use a CAD modeling software to create a design, then slice it with the help of your printer software. Generally the software will then bounce the files out to your printer over your line connection or wireless connection. The printer can then begin work.
The printer can then begin work.
Some materials require post-processing. Often SLA prints will require an isopropyl alcohol wash to remove uncured resin before sanding and finishing. Other post-print processes help to strengthen or otherwise improve the properties of the materials your printer uses. There are specific post-processing machines that work well with specific materials.
FAQsQ: What is a good 3D printer to start off with?If you’re looking for a great 3D printer to start off with, you can’t do much better than the Voxelab Aries. Arriving pre-assembled and preloaded with filament (in select markets), the Voxelab also connects to your computer with Wifi and offers a simple slicing program, it’s a great budget starter for anyone looking to get into 3D printing.
Q: What is the most cost effective 3D printer?The Creality Ender-3 is the most cost effective 3D printer. While many of its components are more basic than the competition, the Ender-3 has all the features you’ll need for solid 3D printing.
While many of its components are more basic than the competition, the Ender-3 has all the features you’ll need for solid 3D printing.
Not all cheap 3D printers use PLA, but the vast majority of filament based 3D printers do. There are two basic types of budget 3D printers, FDM and SLA. FDM printers use filaments, of which PLA is a common type. FDM printers use resin instead of filament, and won’t support PLA.
Q: Can 3D printers under $500 work with any software?3D printers under $500 work with lots of software, but not all printers work with all software. Check the spec sheet on the printer you’re interested in to find out if it’s compatible with your preferred software.
Q: Are 3D printers under $500 good?There are many 3D printers under $500 that are very good. The Creality Ender 3 S1 is the best overall.
Q: Which type of 3D printing is cheapest?If you’re looking for the cheapest type of 3D printing, usually FDM printers are the most cost effective. While SLA resin printers can often be bought for around the same price as FDM filament printers, filament is generally somewhat cheaper over the long term.
While SLA resin printers can often be bought for around the same price as FDM filament printers, filament is generally somewhat cheaper over the long term.
Final thoughts on the best 3D printers under $500
When you invest in a 3d printer under $500, you invest in bringing your vision into physical form. These incredible devices extrude 3d prints from plastics with a few clicks of your mouse. Connect your SLA printer for detailed, high-resolution art prints, and strong prototypes with good rigidity. Plug in your FDM thermoplastic printer for large, affordable proof-of-concepts, or affordable accessories printed for your wardrobe. If you’re new to the game, the Voxelab Aries is the best option for beginners, coming pre-assembled and preloaded with filament, and offering easy Wifi connectivity with good controls. If you’re after exceptional detail for prints of figurines, or rigid prototypes, the ELEGOO Mars 3 Pro is an exceptional resin printer with excellent accuracy. If you want the most bang for your buck under $500, the Creality Ender 3 S1 is an amazing FDM printer that comes with some premium components such as an auto-leveler, and can be upgraded and modded into something that’s even more capable with a little work. Whatever you choose, expect great prints.
Whatever you choose, expect great prints.
Which 3D printer to choose for home and hobby use
A few years ago, 3D printers were bulky industrial machines, but now 3D printing is becoming more accessible for home use. When buying their first printer, many are disappointed. This may be due to the unsatisfactory quality of the resulting models or the complex setup and maintenance of the 3D printer.
In the reviews that are found on the Internet, printers are often shown after a lot of upgrades or a long selection of settings for printing. This is not at all the result that a beginner who first got acquainted with 3D printing will get.
In order not to be disappointed, before buying, you need to understand which model is suitable for your tasks. First of all, it is worth deciding what the printer will be used for. What is the main property that finished products should have? What is more important, the physical properties of the model or the ideal surface and detail? Not only the model depends on this, but also the technology by which the 3D printer will work.
Which technology to choose? FDM or LCD?
If you need to make a small detailed figurine with a perfectly smooth surface, you should pay attention to models that work on LCD technology (LCD works on a principle similar to DLP - Digital Light Processing or “digital light processing”).
LCD prints using a photopolymer resin that cures under UV light. This makes it possible to produce without deformation, even small and thin products that cannot be manufactured using FDM technology.
Resin model
Now on sale there are many photopolymer resins with different properties. A few years ago the choice was not great. Basically, finished products were not strong enough for use in functional models. Now engineering resins have begun to appear on sale. Products from them are not inferior in strength to models made using FDM technology from ABS or even nylon.
If it is necessary to produce large products with different properties, or the tasks will be very diverse, then the choice is with FDM technology. But it is important to understand that finished products will not have a perfectly smooth surface. Of course, you can polish the model, but this is additional time and labor costs.
But it is important to understand that finished products will not have a perfectly smooth surface. Of course, you can polish the model, but this is additional time and labor costs.
FDM technology builds a model using molten plastic filament, which is fed from the print head. The print head (extruder) “grows” the model layer by layer on the printing table.
FDM Models
FDM technology became widespread much earlier than DLP. Thanks to this, a wide variety of 3D printers and consumables for them has appeared. You can find many decorative plastics that mimic various materials, or engineering plastics for making functional models or mock-ups.
Choosing an LCD printer
Photopolymer printers work on one of 3 technologies - DLP, LCD or SLA.
As home printers, devices based on LCD technology are usually used due to their availability and low price.
Printer design
SLA technology appeared the very first among photopolymer printers. With the help of a point-focused beam, the desired areas of the resin are gradually illuminated. This is repeated layer by layer.
With the help of a point-focused beam, the desired areas of the resin are gradually illuminated. This is repeated layer by layer.
How SLA 9 works0018
Since the surface of the model is perfectly smooth, SLA has become used in the jewelry and dental industries.
Pros:
Cons:
DLP technology appeared later than SLA, but it is very similar to it. The main difference is that the light source is not a focused beam, but a projector. This made it possible to illuminate the entire layer at once, which significantly accelerated the production of models. The quality of the surface was slightly inferior to SLA, but modern DLP printers, in terms of the quality of models, are almost as good as SLA technology.
How DLP works
Pros:
-
Faster production of models due to the illumination of the entire layer
-
Consumables are slightly cheaper than SLA
-
High surface quality (although may be inferior to SLA)
Cons:
LCD technology is the youngest of all. The DLP principle is taken as a basis, but an LCD display is used as a matrix or illumination pattern. LEDs are used as a source of UV light in LCD technology. Thanks to inexpensive components, we managed to get a simple, but high-quality and affordable photopolymer printer.
The DLP principle is taken as a basis, but an LCD display is used as a matrix or illumination pattern. LEDs are used as a source of UV light in LCD technology. Thanks to inexpensive components, we managed to get a simple, but high-quality and affordable photopolymer printer.
How the LCD printer works
Pros:
-
small cost
-
Cheap parts
Cons:
-
Low accuracy compared to SLA and DLP (for jewelers and dentists, the quality of LSD prints may not be enough, although more and more accurate models appear with the development of technology)
-
Possible stray light
-
The quality of models may decrease at the edges of the printable area (this can be corrected programmatically)
Resins that are used as a consumable for photopolymer printing can smell strongly and unpleasantly during operation.
Try to use the printer in a well-ventilated area, or choose a printer with a sealed cabinet and filter.
When choosing an LCD printer, pay special attention to the rigidity and positioning accuracy of the platform along the Z axis. If there are poor quality guides along the Z axis or even a slight play, then the surface quality of the finished model may turn out to be sloppy or the model will turn out to be unevenly striped.
Rating of the best LCD 3D printers for home
Anycubic Photon Mono
This is an LCD printer with a matrix that allows you to increase the speed and accuracy of printing. Anycubic Photon Mono will be a good helper for hobbyists and modellers.
Anycubic Photon Mono SE
Anycubic Photon Mono SE has an unusual parallel light source. This minimizes distortion at the edges of the printable area. You can effectively use the entire working area of the machine and produce many small models at a time.
Phrozen Sonic Mini 4K
Model with high resolution LCD display and large print area. The monochrome display transmits UV rays better and allows you to print much faster than similar devices with a conventional display. The manufacturer claims a screen life of more than 2000 hours. Phrozen Sonic mini 4k is suitable for almost any task.
Wanhao GR1
Wanhao GR1 has high precision and large print area (140x78x200mm). The manufacturer tried to reduce distortion at the edges of the display, this allows you to make the most of the entire work area. High precision and large print area make Wanhao GR1 not only for hobby use, but also for production.
Anycubic Photon Zero
Small and very budgetary LCD device. Its resolution and small working area (total 97x54x150 mm) is enough for printing small miniatures, figurines or small engineering models. Anycubic Photon Zero is a good choice for beginners who want to get into photopolymer printing without spending a lot of money.
Choosing an FDM printer
If you plan to produce large and diverse functional models or experiment, a 3D printer that prints using FDM technology is an excellent choice.
First, decide on the size of the printable area and the properties that the finished model should have. After all, some materials require a closed chamber or good airflow to work.
Some printer models can be “upgraded” in the future. For example, if necessary, purchase spare parts for a closed case, put a nozzle of a different diameter, or change the thermal barrier to an all-metal one. But not all manufacturers provide for the possibility of such upgrades.
Printer design
Despite the same principle of operation, there are several different mechanics, which have their pros and cons.
Kinematics “Prusa” (Prusa)
Perhaps the most popular kinematics among home FDM devices. Mainly due to its simplicity and low cost. The main feature is the table that moves along the Y axis, while the extruder moves along the rest of the axes. Because of this, such kinematics was nicknamed “dragstol”.
The main feature is the table that moves along the Y axis, while the extruder moves along the rest of the axes. Because of this, such kinematics was nicknamed “dragstol”.
Prusa kinematics
Pros:
Cons:
-
Slow print speeds. A massive table with a model is forced to constantly move along the Y axis, because of this, print quality will be worse at high speeds.
-
Some models have design flaws (for example, insufficient frame rigidity), they can be fixed, but for this you have to be a little inventor. Or find a ready-made solution on the Internet.
This category also includes 3D printers with console kinematics. The same prusa, only halved. Because of this, the frame is less rigid, but the printer itself is more compact.
Kinematics Ultimaker
The extruder moves along the X-Y axes, and the table only along the Z axis. All motors are trying to be fixed on the body to lighten the weight of the moving mechanisms, thanks to which it is possible to achieve high print quality at high speeds.
All motors are trying to be fixed on the body to lighten the weight of the moving mechanisms, thanks to which it is possible to achieve high print quality at high speeds.
Ultimaker kinematic diagram
Pros:
Cons:
H-BOT or Core-XY
These are 2 similar but more complex kinematics - the table moves only along the Z axis, and the extruder along the X-Y. But to move the extruder, 1 or 2 long belts and 2 stepper motors work in concert.
Example Core-XY kinematics
Pros:
-
High print quality
-
High print speeds without loss of quality.
-
Can be easily closed completely
Cons:
MakerBot Kinematics
Similar to Ultimaker kinematics, but one of the motors is located on the Y or X axis carriage.
Pros:
Cons:
Delta
Deltas do not have the usual XYZ axes. There are 3 columns in the deltas, along which the carriages move, and the position of the extruder in space is calculated using a complex formula. The table is usually statically fixed to the body.
Delta printer example
Pros:
Cons:
Nuances of choosing an FDM 3D printer
In addition to kinematics, when choosing a printer, it is important to take into account some design features.
One or two extruders?
Two extruders can be used for dual color printing, but most commonly the second extruder is used for solvent support printing. If you need to print complex parts with internal cavities, then you should choose a dual extruder printer.
Closed or open printer?
Printing of functional models and parts uses plastic, which usually requires a closed chamber. If you plan to print functional prototypes or various models, you should look at printers with a closed chamber.
If you plan to print functional prototypes or various models, you should look at printers with a closed chamber.
Bowden or direct?
There are 2 types of material supply to the print head of the printer - bowden and direct.
In a bowden, the feed mechanism motor is located on the printer body. This allows you to reduce the weight of the extruder and print at higher speeds without losing quality. But because of the long tube, printing with very soft plastics can be problematic.
Bowden feed pattern
In direct feeding, the motor and feed mechanism are located on the extruder. This increases the weight of the print head, but allows you to print with any kind of plastics.
Direct feeding scheme
Heated table or not?
The heating of the table improves the adhesion of the first layer of the model. And engineering plastics cannot be printed without a heated table.
And engineering plastics cannot be printed without a heated table.
Many manufacturers add useful additional features. They do not affect the quality of the print, but save time and nerves. The most useful additional functions are the filament presence sensor and remembering the print location after a power outage.
Filament sensor.
It will automatically pause printing if the plastic runs out. When there is a little plastic left on the spool, this feature will allow you not to stand over the guard printer until the old spool runs out in order to have time to push in a new bar “on the go”.
Power outage protection.
Remembering where to print when the power goes out can save you a lot of nerves when printing large models. You won't have to worry that after a power outage, you will have to run the model again for many hours or cut and reprint a piece of the model. It is especially disappointing to throw away a complex underprinted model with supports due to a one-minute outage.
There are also many extras. features that make using the printer more comfortable. For example, automatic calibration, touch screen, Wi-Fi and others.
Rating of the best FDM 3D printers for home
Anycubic Mega Zero 2.0
Inexpensive model with Pryusha kinematics. Good for getting started with 3D printing without a big investment. Despite the low cost, Anycubic Mega Zero 2.0 has a heated table and a resume function after a power outage. Thanks to direct feed, printing with soft materials should not be difficult.
Creality3D Ender 3 Pro
A very popular device due to its low price. But despite this, the Ender 3 Pro has a heated table and a decent print area. Can be sold assembled or as a DIY kit.
Flash Forge Finder
Small home appliance intended for children or educational institutions. The Finder doesn't have a heated table, but it does have a calibration assistant, a Wi-Fi module, and other extras that make getting to know it a lot easier. All moving and heated elements are hidden as much as possible in the case so that the child cannot get burned.
All moving and heated elements are hidden as much as possible in the case so that the child cannot get burned.
Wanhao Duplicator 6 Plus
Wanhao Duplicator 6 Plus was based on Ultimaker kinematics, but instead of bowden feed, they made direct. Because of this, it will not be possible to print super fast, without quality loss, but there will be no problems with printing with soft types of plastics. There are 2 trim levels - with a closed case and without.
Flashforge Dreamer
The Dreamer is a closed body dual extruder printer with MakerBot kinematics. Thanks to this, he can cope with printing models of any complexity. Using a second extruder for soluble support, models with complex geometries can be produced. A good choice for engineers and those who like to experiment with different materials.
FlyingBear Ghost 5
Most commonly sold as a kit (assembly kit). Assembly usually does not cause any great difficulties, even for people far from electronics or mechanics. Flying Bear is equipped with a filament sensor, a function to resume printing after a power outage and Wi-Fi connectivity.
Flying Bear is equipped with a filament sensor, a function to resume printing after a power outage and Wi-Fi connectivity.
The Flying Bear makes a great first printer for the novice user who is ready to build their own printer.
Totals
In order for the printer not to become a useless toy, you should clearly understand what it is for.
For a fan of miniatures or detailed figurines, a photopolymer printer is a good choice. A small work area is more than offset by the detail that cannot be obtained using other technologies.
For an engineer or a fan of experiments, an FDM machine with a closed chamber and two extruders is well suited. This will allow you not to limit yourself in the choice of plastics and comfortably experiment with any materials.
For a beginner who has not yet decided whether he needs 3D printing, you can opt for inexpensive machines with slick kinematics. Due to their great popularity, you can find a lot of upgrades and reviews on them. In the future, it will be possible to modify the printer for specific tasks or change it to a more suitable model.
In the future, it will be possible to modify the printer for specific tasks or change it to a more suitable model.
For a child, safety is paramount. As the first children's printer, models without a heated bed are suitable, in which the main emphasis is on printing with safe PLA plastic. Or models in which all moving and heating mechanisms are hidden in the case.
A 3D printer is a handy tool, and whether it brings joy or frustration depends on the user.
All about the 3D printer in dentistry: features, applications, technologies
The first attempts to use 3D printing in dentistry were made by Align Technology in the 1990s. Using a 3D printer, mouth guards were made, which served as a start for the development of this technology in the dental industry. The process of making teeth was looked at from a radically new point of view.
But development did not progress as fast as we would like: it took almost 20 years to achieve satisfactory print quality and optimize performance. The first implant was printed by Layer Wise in 2012. In the same year, for the first time, it was possible to implant a patient with a titanium lower jaw, which was made using a 3D printer. Since then, the technology has evolved and raised the quality bar.
The first implant was printed by Layer Wise in 2012. In the same year, for the first time, it was possible to implant a patient with a titanium lower jaw, which was made using a 3D printer. Since then, the technology has evolved and raised the quality bar.
Benefits of using a 3D printer
Today, a 3D printer for dentists makes it possible to produce durable and high-quality models of crowns, bridges, veneers, etc. This greatly simplifies and speeds up the work of a dental laboratory: a wide range of materials allows you to solve almost any problem in a short time. With a dental 3D printer, a significant number of required instances can be modeled in a single session. All projects are saved in files, so in the future you can re-make the same model if necessary.
It is no longer necessary to send the patient for 2-3 days to wait for the production of plaster models. Now everything happens much faster: the doctor builds a 3D model in a few minutes using an intraoral scanner and instantly transfers the data to the laboratory, where printing also does not take much time. Speed and maximum precision increase the level of treatment and really save resources and time.
Speed and maximum precision increase the level of treatment and really save resources and time.
What you can print
Let's highlight the most common uses of 3D printing in dentistry. Using the printer, you can create:
- demonstration and collapsible models of the jaw, sectoral reproduction of the upper and lower jaws in the occlusion;
- ashless constructions, caps, bases for crowns and bridges, clasp prostheses;
- surgical templates for implantation, individual trays, guides for maxillofacial surgery.
Such a promising area as the printing of permanent and temporary orthopedic structures, bases for removable dentures is actively developing. About the types of printing We will understand the printing technologies and their features.
Stereolithography (SLA or SL). With this technology, a laser beam selectively impacts a container of liquid resin through the printable area. Thus, the resin hardens in layers in specific places and forms a three-dimensional figure.
Thus, the resin hardens in layers in specific places and forms a three-dimensional figure.
Stereolithography gives the best surface finish on parts and is most commonly used in today's 3D printer models. SLA machines provide a large area of restoration construction and work with a wide range of materials designed for a variety of tasks.
To switch from one material to another, it is enough to change the cartridge and the resin bottle. Relatively compact dimensions, ease of workflow and affordable price make SLA printers the best choice for dental laboratories. An example of SLA models - Form 2 and Form 3 from Formlabs, SLASH PLUS from Uniz Technology, Basic Dental from Omaker, Asiga PICO2.
Digital LED projection (DLP). Here the chemical process is similar to SLA, however, a digital projector is used as a light source for curing the resin instead of a laser. DLP printers have a simple interaction process, a fairly modest footprint, and a good selection of material options, but at a higher price compared to SLA.
Due to the nature of the illumination of the LED projector, there is a tendency for voxel lines-layers formed by small rectangular bricks of material. Models made by DLP have inferior surface quality to SLA models. But it is worth noting that DLP printers print much faster than laser ones. Examples of DLP printers include Varseo S by Bego, AccuFab-D1 by Shining 3D, D2-150 by Veltz 3D, Versus by Microlay.
PolyJet technology. The process is similar to that of a regular inkjet printer, but instead of inkjet drops on paper, the 3D printer blows layers of liquid resin onto the printable area. The layers harden when exposed to light.
Once upon a time PolyJet gained popularity in the dental industry, but its development was slowed down by two factors: the high cost of equipment and the impressive dimensions of the devices. Models made using PolyJet technology require long post-processing and are again inferior to SLA in terms of surface quality.
PolyJet systems produce parts very quickly, but are limited in scope due to expensive proprietary consumables. Therefore, in the context of our industry, it is better to buy a dental 3D printer with SLA technology.
SLS and EBM. Allows titanium printing of ready-made elements for replacement of jaw parts. These technologies work on the principle of laser sintering of metal clay, a special metal powder for dentistry. So, the SLS and EBM systems allow you to work with a biocompatible titanium alloy. Since pure metal powder does not require a binder filler, the finished models do not differ in porosity. To achieve the required mechanical strength, the products do not require additional firing. An example of a printer capable of printing with metals is the EP-M150T from Shining 3D.
Filament printing. Technology is not relevant in dentistry and now we will explain why.
Printed with filament, a material similar to fine garden trimmer wire. The wound filament is charged directly into the 3D printer head, which moves on three axes.
The wound filament is charged directly into the 3D printer head, which moves on three axes.
Compared to other materials for 3D printing, this filament is quite inexpensive, but gives low accuracy compared to powders. The most popular types of filament are ABS and PLA plastic.
Comparison of the main 3D printing technologies used in dentistry
To clearly show the main pros and cons of each technology, we compare them in a table format.
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Digital Light Processing (DLP) | PolyJet Technology | SLS and EBM technologies | |
| Precision | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ |
| Surface finish | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Print speed | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Availability of materials | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★☆☆☆ |
| Metal printing | ||||
| Benefits |
|
|
|
|
| Drawbacks | Slow single print speed |
|
|
|
Our Resume
PolyJet technology is becoming a thing of the past due to high cost and imperfect print results.