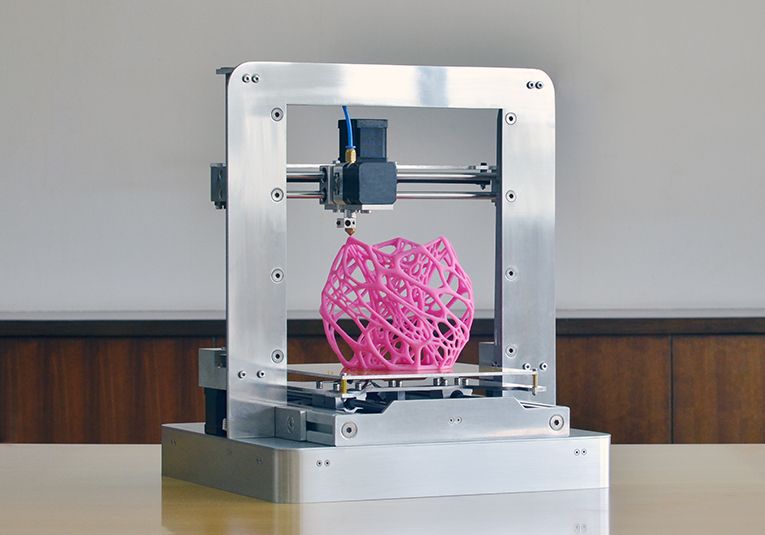
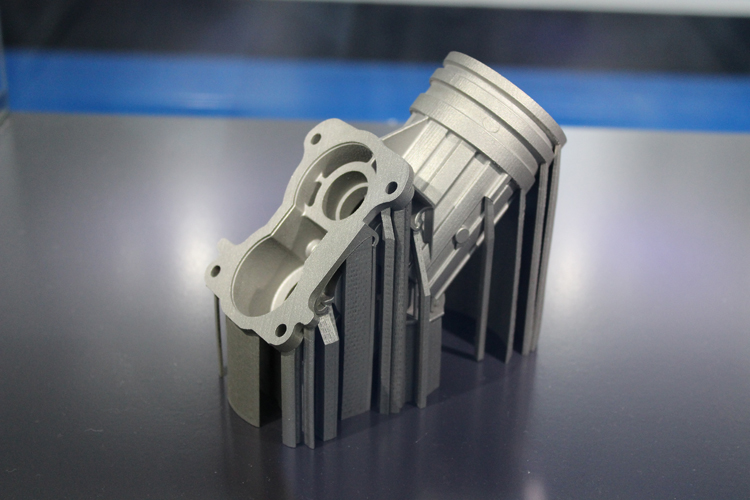
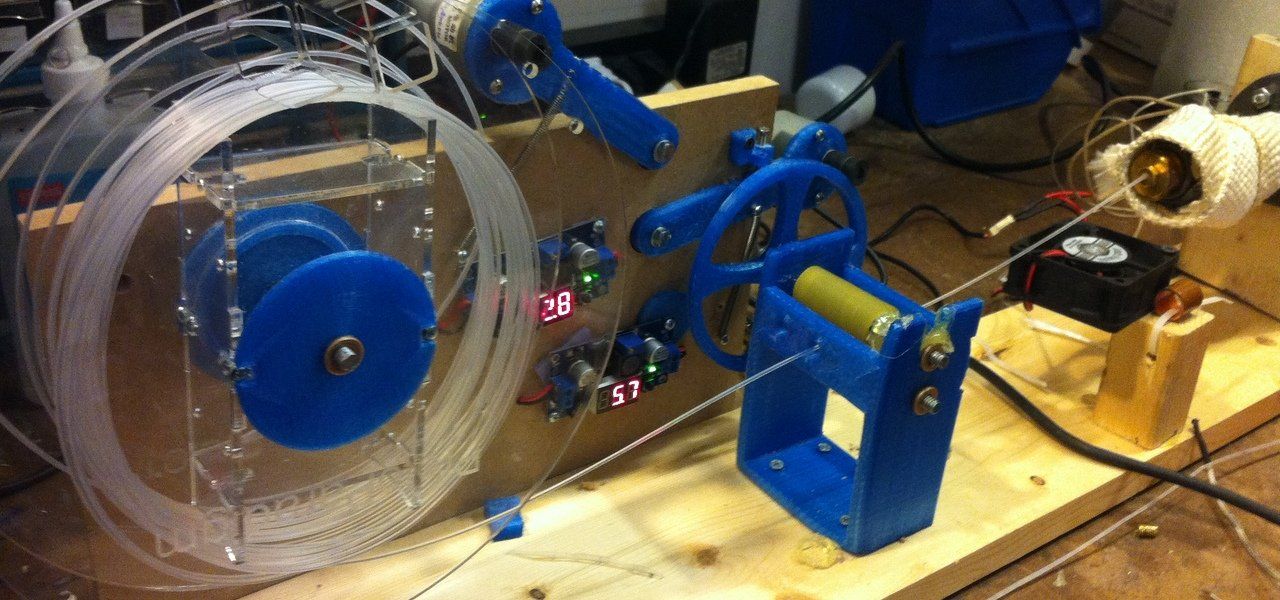
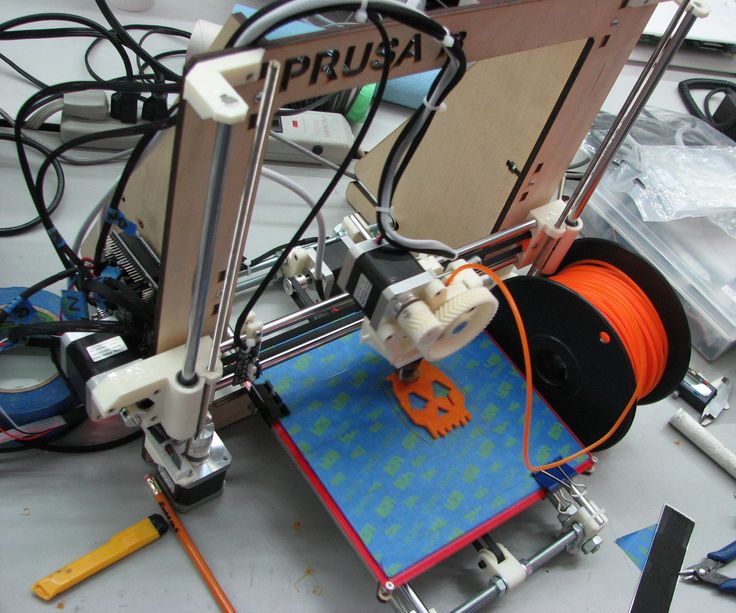
Dremel 3d printer demo
Your First 3D Printer – Envirolaser3D
Congratulations! If you have arrived at this page you are probably considering the purchase of your first 3D printer. This page has been formulated with the first time consumer in mind. If you are looking for a 3D printer for commercial or Industrial application please (click here).
3D printing has been around longer than you might think. The first 3D printer debuted in 1985 where the laser printer was introduced in 1986. 3D printing technology has come a long way since then. Before we get started here is a blog post with common 3D printing terminology.
Terminology post (coming soon)
How does 3D printing work?
3D printing works much like a hot glue gun. A hot glue gun heats the nozzle so that it melts the glue. When you squeeze the trigger hot glue is pushed out the nozzle. If you squeeze it harder more glue comes out. Instead of glue 3D printers use (filaments) and stepper motors push the molten filament through the nozzle. The next time the nozzle passes over the same spot it builds on top of the last layer until your model is complete. This process is known as Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), the general concept as Additive Manufacturing.
There are actually many types of 3D printers used industrially to print everything from prosthetics to parts 3D printed aboard the ISS. It's much cheaper to design a tool or part for the ISS and essentially email it to the space station where it can be 3D printed out of a variety of materials.
Here's a look at a 3D printer in action.
Why buy a 3D printer?
Did you know that over the past decade the demand for employees with 3D printing or design experience is up 11,500%.
Everyday we see new postings for companies looking for people with 3D printing or design experience. Having a 3D printer in your home well help prepare you and your family for lucrative jobs in the future.
Having a 3D printer in your home well help prepare you and your family for lucrative jobs in the future.
Today many classrooms and schools have 3D printers and encourage students to learn and understand the technology. Having a 3D printer at home gives any child an advantage.
If you are budding artist, 3D printing is a fantastic tool that allows you to express your ideas in all dimensions. There is a $50 accessory that is essentially virtual reality goggles that allow the user to start with a giant digital block then chisel away much like a Sculptor. When your Masterpiece is complete, you will have the satisfaction of being able to print your model immediately.
Whether you are interested in designing parts or just 3D printing some of the 500,000 free 3D printable designs on Thingiverse.com or similar sites, you owe it to yourself and family to invest in a 3D printer today.
Designing 3D printable things blog post (coming soon)
Using Thingiverse post (coming soon)
Buying Your First 3D Printer
If you live in Ottawa, you have one of two choices when shopping for a 3D printer. You can go online to sites such as Amazon, they offer a large selection of 3D printers. The problem with online shopping is the lack of customer support. Many online e-commerce sites add items to their stores then simply have them drop-shipped from AliExpress. Often the seller has no 3D printing experience or for that matter, has never seen a 3D printer in operation. All they can do is direct you to the manufacturer's technical support. This means you are dealing with a company in China. It often takes days and sometimes weeks to sort your issues out.
You can go online to sites such as Amazon, they offer a large selection of 3D printers. The problem with online shopping is the lack of customer support. Many online e-commerce sites add items to their stores then simply have them drop-shipped from AliExpress. Often the seller has no 3D printing experience or for that matter, has never seen a 3D printer in operation. All they can do is direct you to the manufacturer's technical support. This means you are dealing with a company in China. It often takes days and sometimes weeks to sort your issues out.
Alternatively you could shop locally at Envirolaser 3D. We are a brick and mortar store located at 199 Colonnade Road in Ottawa that specializes in 3D printing and related equipment. When you visit us, we would be happy to demonstrate a 3D printer in operation. If you find the right printer, you can take it home with you the same day. Envirolaser 3D is the only company in Ottawa that stocks and sells 3D printers (scanners & laser cutters), filaments and all the accessories necessary to get you up and printing as soon as you get home. If you have any questions about set-up or operation of your new printer, simply call us at (613) 225-4726. Our technical team will have you up and running in no time.
If you have any questions about set-up or operation of your new printer, simply call us at (613) 225-4726. Our technical team will have you up and running in no time.
The cost of 3D printers have decreased dramatically in recent years. A printer you might have paid $2,000 or $3,000 a few years ago can now be purchased for less than $500. If you have the technical expertise you can purchase a 3D printer kit that you assemble from scratch for about $300. We don't recommend 3D printer kits for the first time user. There are just too many things that can go wrong if you don't understand the technology.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer
There are several factors you should consider when choosing your first 3D printer. Most consumer level 3D printers can be categorized as open build area verses enclosed build area.
A 3D printer with an enclosed build area will generally produce a higher quality print and are easier and safer for children to use.
3D printers with open build areas generally offer a considerably larger build volume and are less expensive.
When buying your first 3D printer we usually recommend one of three models. The ADIMLab gantry 3D printer the Dremel Digilab 3D20 and the Dremel Digilab 3D40. These three printers provide excellent value and affordability. They are easy to set up and will allow you to start 3D printing right away.
The ADIMLab Gantry 3D Printer
View Product Page
The ADIMLab gantry printer offers a huge build area, 12" X 12" X 16". With this printer you can print useful household items without the need to glue pieces together. They are a little more complicated to use but provide better flexibility when it comes to printing options. And certainly the large build area makes them more practical.
The ADIMLab Gantry Blog Post (coming soon)
The Dremel Digilab 3D20
Most students will be familiar with the Dremel line of printers as they are used in the classroom. If you have children who will use the printer we usually recommend an enclosed printer such as the Dremel Digilab 3D 20. It is pretty much Plug and Play. The Dremel Digilab 3D 20, offers a print volume of 6" X 6" X 9". All of the mechanics are enclosed and it is simpler to operate then many of The Open Build Plate models. Enclosed 3D printers usually start at $900.
If you have children who will use the printer we usually recommend an enclosed printer such as the Dremel Digilab 3D 20. It is pretty much Plug and Play. The Dremel Digilab 3D 20, offers a print volume of 6" X 6" X 9". All of the mechanics are enclosed and it is simpler to operate then many of The Open Build Plate models. Enclosed 3D printers usually start at $900.
View Product Page
The Dremel Digilab 3D 20. Blog Post (coming soon)
The Dremel Digilab 3D40
The 3D40 comes fully assembled from the factory and includes everything you need to go from unboxing to printing in ten minutes. The reliable assisted leveling process takes all the guesswork out of leveling the bed on your printer. The hassle free intuitive touchscreen allows you to easily control the printer. This fast and high quality printer gives you peace of mind when running it for hours. Its fully enclosed space and 3rd party safety certification leaves you without a worry.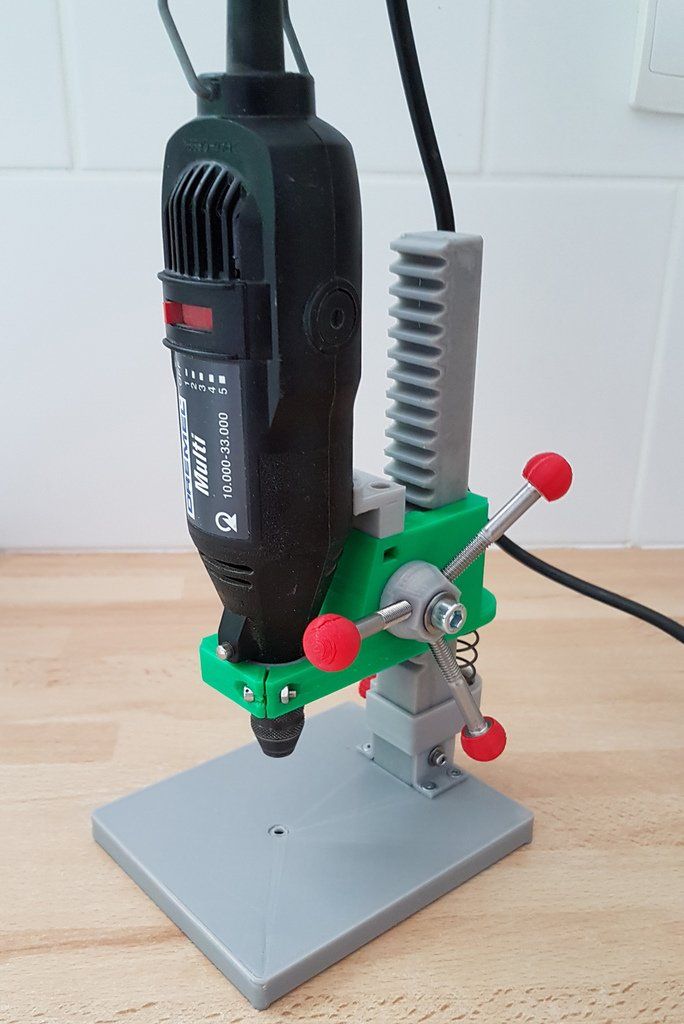
View Product Page
Side-by-Side Comparison
|
Printer |
ADIMLabs |
DigiLab 3D20 |
DigiLab 3D40 |
|
Price |
$499.95 |
$895.95 |
$1,699.00 |
|
Print Volume |
310*310*410 mm |
230*150*140 mm |
255*155*170 mm |
|
Enclosed Build Envelope |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Heated Bed |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Auto Bed Leveling |
No |
Assisted |
Yes |
|
Available Filaments |
PLA, ABS, Wood, HIPS, PC, TPE, Flexible PLA |
PLA |
PLA, ABS, HIPS, PC, TPE, Flexible PLA, & more |
|
Filament Out Sensor |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
Illuminated Build Plate |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Accuracy |
Z 0. |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Print Quality |
100 Microns |
excellent bridging, overhangs and supports in up to 100 micron resolution |
100–300 microns |
|
Setup |
2 sub assemblies |
Full Assembled |
Full Assembled |
|
Ease of Operation |
Moderate |
Easy |
Easy |
|
Best Suited for Children |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Connection |
SD card or USB |
SD card |
Connect to your Wi-Fi or Ethernet |
The 3D Printing Workflow
Once you have chosen the right printer for your application and have set it up, now what. Well it's time to start 3D printing. Printing a 3D model is a little different than printing a document. To start with you will need to decide if you want to download objects or design your own models. If you choose to download objects to print, you can go to websites that offer free or paid 3D models. Most people use Thingiverse.com to find objects to 3D print. There are many other sites available to download things. It is discussed further in this blog post.
Well it's time to start 3D printing. Printing a 3D model is a little different than printing a document. To start with you will need to decide if you want to download objects or design your own models. If you choose to download objects to print, you can go to websites that offer free or paid 3D models. Most people use Thingiverse.com to find objects to 3D print. There are many other sites available to download things. It is discussed further in this blog post.
Using Thingiverse y Blog Post (coming soon)
If you choose to design your own objects for printing, there is an array of design software available to you. Many of which are free or at least have free trial periods. One of the easiest to learn is a website called Tinkercad.com. It is very easy to use and will help you understanding how the 3D printing process works. Some of the free 3D design programs include Tinkercad, Meshmaker or Blender. Are discussed in the following blog post.
Designing 3D Printable Things Blog Post (coming soon)
Once you have downloaded or designed your 3D model you will need to prepare the model for 3D printing.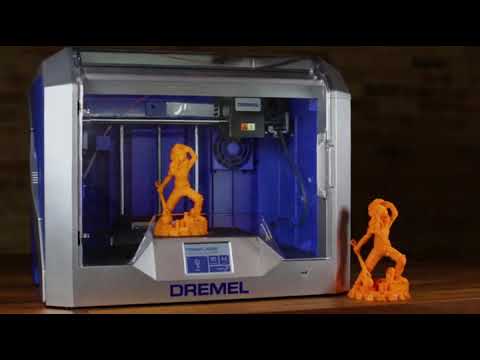 This step is referred to as slicing. There are several options for slicing software. Your 3D printer will always include a slicer with presets for that specific printer. The two most common slicers are Cura and Simplify3d. Cura is free and simply 3D sells for $150.00 USD
This step is referred to as slicing. There are several options for slicing software. Your 3D printer will always include a slicer with presets for that specific printer. The two most common slicers are Cura and Simplify3d. Cura is free and simply 3D sells for $150.00 USD
Slicing software simply takes your model and slices it so your printer is able to print layer after layer. You're slicing software is where you decide how much infill you want, wall thickness, supports and dozens of other settings.
Slicing Software Blog Post (coming soon)
Your First 3D Print Job
Once your model is properly sliced, you will need to preheat your printer and level the bed before starting to print. The slicing software will generate a G-Code file that is sent to the printer and includes all the parameters you have chosen for your model.
You are now ready to start 3D printing. The first or initial layer is of greatest importance. You should keep an eye on the printer until it has printed a couple of layers. If the initial layer is not properly adhered to the build plate your model will fail at one point or another. If the first layer isn't perfect, you are best to restart your print.
If the initial layer is not properly adhered to the build plate your model will fail at one point or another. If the first layer isn't perfect, you are best to restart your print.
Once your model has been printed, wait for your build plate to cool before removing your model from the build plate. Once it has cooled, remove your model and examine it. If you are using supports, you will need to remove this material. Keep in mind that 3D prints take hours and sometimes days to print. You should periodically examine your print as it is progressing to ensure everything is printing properly.
If you have purchased your 3D printer from Envirolaser our staff are always be happy to guide you through the 3D printing process and answer any questions you may have about the setting-up your new 3D printer.
Recommended Blog Posts:
Terminology Blog Post (coming soon)
Designing 3D Prints Blog Post (coming soon)
Using Thingiverse Blog Post (coming soon)
The ADIMLab Gantry Blog Post (coming soon)
The Dremel Digilab 3D 20. Blog Post (coming soon)
Blog Post (coming soon)
Using Thingiverse Blog Post (coming soon)
Slicing software Blog Post (coming soon)
Post Printing Blog Post (coming soon)
STL Downloads | Hero Forge®
Tell me about the downloadable 3D model files and home printing.
At the urging of many makers, tinkerers, inventors, and printers, we have begun offering digital print file distribution. This means, in addition to ordering 3D prints, users now have the option to buy the model file for their custom Hero Forge characters. These files can then be loaded into your 3D printing software for printing at home. Models are tessellated meshes with a polycount of up to 100,000 triangles. They are not rigged for animation.
Models are distributed via your Digital Downloads page in .stl file format. They are typically posted within 15-30 minutes of your purchase, but please allow for up to one business day. Digital models are only guaranteed to be available on your Digital Downloads page for six months from purchase.
Digital models are only guaranteed to be available on your Digital Downloads page for six months from purchase.
Note that Hero Forge miniatures are finely detailed scale models. As a result, some home 3D printers do not have the ability to faithfully replicate the level of detail present in the source model or have issues printing thin, free-standing “wire” parts or the thin supports necessary to support a model during the build process. As a result, Hero Forge does not give any warranty about the models, and does not guarantee that the model will be fit for any particular purposes or be compatible with any specific make or model of printer.
We strongly recommend printing one of our free sample digital models before making a purchase. Sample models are available on your Digital Downloads page.
3D printers come in many shapes, sizes, and employ a wide range of technologies. Different technologies have different benefits and drawbacks. You are invited to submit photos of your prints, along with your printer’s make and model, materials used, and any pertinent settings used to create your print. The most common technologies are as follows:
You are invited to submit photos of your prints, along with your printer’s make and model, materials used, and any pertinent settings used to create your print. The most common technologies are as follows:
SLA and DLP Printers
Some of the highest detail 3D printers are based on SLA (Stereolithography) and DLP (Digital Light Processing) technology. These printers use a pool of liquid resin which, by being exposed to a light source such as a projector or a laser, solidifies the liquid material into a solid layer by layer.
These printers most commonly function by submerging a “build platform” into a pool of liquid resin, allowing a light or laser on the underside to trace the layer’s shape, hardening it onto the build platform, which then serves as the foundation for the next layer. The platform then lifts from the resin, and is resubmerged again to print each successive layer.
SLA and DLP printers are known for producing some of the finest detail on the market, ideal for 30mm scale models for tabletop play. They also tend to be more expensive than other print technologies, both in terms of material costs and hardware.
They also tend to be more expensive than other print technologies, both in terms of material costs and hardware.
Form2 by Formlabs
Material: “Gray Resin v3”
Settings: Printed at the maximum .025mm layer height. The models were oriented on their backs in order to allow high detail areas like the face and chest to remain free of support structures.
FDM Printers
The most common home 3D printers use FDM (fused deposition modeling) print technology. These machines start with a spool of ‘filament,’ typically a long wire of PLA or ABS plastic. The printer uses a heated nozzle to melt the filament, extruding onto a build tray similar to how a hot glue gun works. The material is extruded along a path predetermined by the controlling software. The melted material cools and solidifies, building the print layer by layer, with each new layer using the last as its foundation. This is one of the cheapest 3D printing technologies, and, while it does not match the detail levels of some other printing methods, is great for producing low-cost and large-scale models.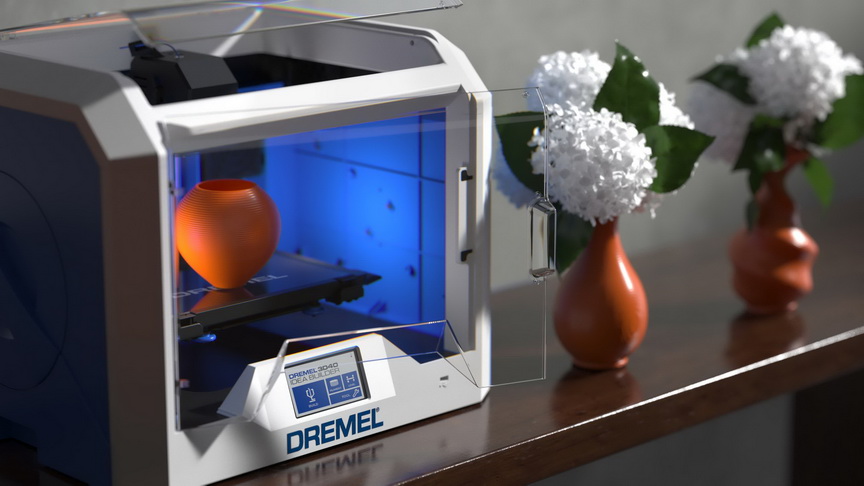
There are many, many companies producing a wide range of printers with a multitude of features, options, and settings. Common brands include Makerbot, LulzBot, XYZprinting, and many more. While we cannot test or provide recommended settings for every printer on the market, what follows are user-submitted images of their prints, along with any settings or material information they’ve provided. We encourage users to print and submit images of our sample models so we can add them to our directory!
Da Vinci Jr. 1.0
Material: “PLA”
Settings: Vertical orientation, 200 micron resolution, raft with supports, slow print speed.
Dremel 3D Idea Builder 3D20
Material: PLA
Settings: Layer Height: 0.12mm, Speed: 2000mm/min, Had to rotate the models X:-90º to stand upright. Support structures were needed.
L3 MK2
Maker Select Plus
Material: PLA
Mono Price Select Mini
Material: Hatchbox Gold PLA, 1. 75mm
75mm
Settings: For Model 1 (Paladin) - 0.04375mm layer height, on back rotated 45 degrees back, grid support. For Model 2 (Elf) - 0.04375mm layer height, laying flat on back, grid support.
MonoPrice IIIP
Material: PLA
Settings: Layer height: .1. Shell thickness: 1.2. Bottom/top thickness: 1.2. Fill density 10%. Print speed: 40. Printing temp: 210c. Bed temp: 65c.
Robo3D R1+
Material: PLA
Settings: Printed at .1mm layer height.
Trinus
Material: PLA filament 1.75mm
Settings: Printed 45deg orientation, 1mm thickness, normal print speed, heated bed, base down, 0.1 layers.
Ultimaker 2+
Material: PLA
Up! Plus2
Material: PLA
Settings: Printed at 0.15mm layer resolution with a 0.4mm nozzle.
Do you have a question not covered by this guide? Please Contact Us!
3D printers: Types, categories and manufacturers
Page content
- -printers
3D printers are being developed at an increasing pace.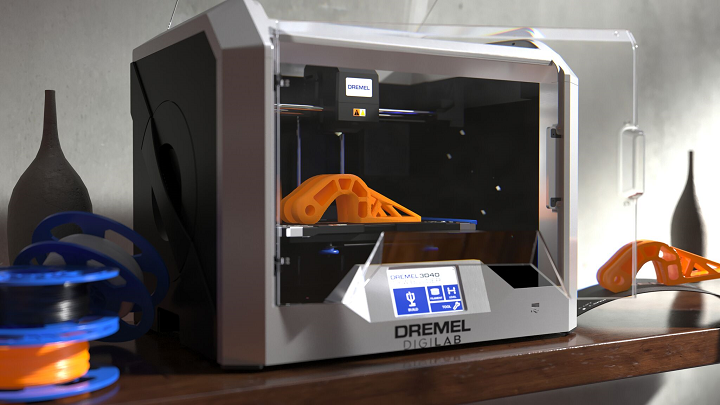 Since 2010, the cost of 3D printers has been declining significantly. For example, one-class printers that cost $20,000 in 2010 are now down nearly 20 times in price, and RepRap kits are already under $500.
Since 2010, the cost of 3D printers has been declining significantly. For example, one-class printers that cost $20,000 in 2010 are now down nearly 20 times in price, and RepRap kits are already under $500.
Reducing the price of 3D printers stimulates the development of domestic production, which leads to a reduction in environmental harm from industrial production by saving consumables and reducing logistics costs.
The customization of 3D printers has produced semi-professional printers for small businesses with printing precision between industrial and consumer printers.
1. Categories of 3D printers
3D food printers. Among the huge variety of 3D food printers, two different groups stand out:
- ordinary printers, in which a variety of products are obtained due to the use of different ingredients and cooking modes;
- high-tech, chemical printers that allow you to carry out the process of synthesis of the desired substances.

Printers of the second group are more complex and versatile, but their developers and testers continue to discuss the issue of their harm to humans. After all, where food is obtained in the process of synthesis of substances, there is always a doubt about its usefulness. However, supporters of such artificial food point out that in the process of synthesis it is possible to control the quantitative composition of protein, fat and carbohydrates, as well as immediately fortify food or add microelements to it.
The widespread use of 3D food printers is currently hindered mainly by two factors:
- the availability of the required components and semi-finished products;
- there is a shortage of programmers to create specialized software that would greatly facilitate production and make it accessible to beginners.
Military 3D printers. It turned out that modern, advanced 3D printers are cost-effective to use in almost the entire production of rocket engines. Such projects are already being carried out at NASA in the manufacture of engine components for the time being.
Such projects are already being carried out at NASA in the manufacture of engine components for the time being.
Steps are being taken to produce fully functional weapons. For example, to demonstrate the promise of 3D printing, a group of developers replicated a popular weapon in the US (M-4). Today, in the United States, virtually free access to fully prepared spatial models of various weapons is organized, which opens up the possibility of printing them on simple three-dimensional printers.
Construction 3D printers. Construction 3D printers, like other categories of printers, are also based on the technology of layer-by-layer extrusion of consumables.
Additive technologies in construction make it possible to create structures with creative forms, and, most importantly, to create houses in all situations where it is necessary to build a lot of housing for people in a short time. In the near future, mass 3D printing in architecture and construction will become a reality from the production of small houses to the construction of skyscrapers.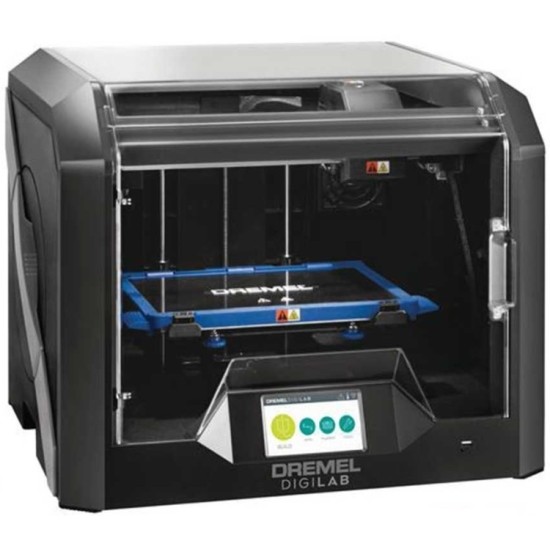
As a practical example, here are some well-known companies that are already implementing projects using additive technology in construction.
WinSun, China. A Shanghai-based company demonstrated a WinSun 3D construction printer. The dimensions of the printer are impressive - length 150 m, width 10 m and height more than 6 m. The economic indicators as a result of using WinSun are significant: 50% cheaper compared to classical construction, up to 60% savings in materials, up to 80% savings in labor costs.
Apis Cor, USA. Apis Cor 3D printer was tested in 2016 together with a number of Russian companies in Stupino, Moscow region. Test object - a residential building with an area of 38 m 2 was AM printed layer by layer in 24 hours. At the same time, the Russian side carried out the decoration of the house, and the American side - its construction. In the construction practice of Russia, this was the first house printed as a whole, and not assembled from printed panels.
ProTo R 3Dp, Netherlands. The ProTo R 3Dp 3D printer was created by CyBe Additive Industries for the construction of free-form structures from special concrete. At the same time, the company announces a reduction in construction time of up to 80%, as design, development and production are combined into a single system. The company has its own recipe for fast-hardening concrete, the composition of which is kept secret, which greatly speeds up construction.
Batiprint3D, France. Project Yhnova is printing a 5-room house of 95 m2 2 using Batiprint3D (3D printing "from the inside"). At the same time, polyurethane is sprayed layer by layer as a formwork for pouring concrete. The developers of the Batiprint3D method point to a reduction in construction time and operating costs, as well as an improvement in thermal insulation properties.
Medical 3D printers. The use of 3D printing technology in medicine dates back to the early 2000s, when it was first successfully tested in dentistry for the manufacture of dentures. Since then, there has been a significant increase in reports of the use of tissue and organ bioprinting to manufacture numerous parts of the body, such as blood vessels, skeletal parts, ears, airways, stem cells, as well as the "printing" of drugs and other applications.
Since then, there has been a significant increase in reports of the use of tissue and organ bioprinting to manufacture numerous parts of the body, such as blood vessels, skeletal parts, ears, airways, stem cells, as well as the "printing" of drugs and other applications.
Bioprinting is carried out on special 3D bioprinters as well as on conventional 3D printers, layer by layer based on a digital 3D model. However, consumables in a bioprinter are conglomerates of cells, which are deposited layer by layer on a special substrate. As a result, a voluminous living organ is formed. Based on bioprinting, it is possible to obtain high-precision 3D models of human organs and some implants.
Since each new successful application of bioprinting left behind corresponding digital models of organs, databases of such models began to accumulate. In this regard, the exchange of work in the medical community has been greatly simplified, and the exchange created in 2014 by national health institutions has facilitated the access of researchers from various countries to ready-made 3D models.
Modern use of 3D printing in medicine is mainly related to the following areas:
- preparation for operations and student education;
- bioprinting of tissues and organs;
- printing of surgical instruments;
- "printing" drugs;
- prosthetics and dentistry.
2. Russian manufacturers of 3D printers
PICASO 3D. Students of the Moscow Institute of Electronic Engineering came up with the idea to create their own 3D printer in 2010. In 2011, their first Gen-X model appeared, and already in 2012, the PICASO 3D Builder model was created, which was the first to go into mass production . PICASO 3D Designer and Designer PRO 250 followed.
The company has repeatedly received awards: "Best Domestic Manufacturer", "Best Innovative Company" and "Brand of the City". In the fall of 2018, at the Top 3D Expo, the company presented the large-format Designer XL model.
Imprint. The company was founded in 2013. The idea of developing their own 3D printer came from the company as a result of dissatisfaction with the performance and cost of existing models.
The company was founded in 2013. The idea of developing their own 3D printer came from the company as a result of dissatisfaction with the performance and cost of existing models.
The first 3D printer appeared in the company six months later, and in 2015 the Hercules Strong model made the company famous. The following year, Hercules Strong participated in an exhibition in Amsterdam. The company celebrated 2018 with the release of the Hercules Strong Duo 3D printer.
Maestro. Show Design Company (legal name) was founded in 2016. It became the successor of an enterprise that was founded in the early 2000s. The first Maestro printer was created in 2017. The company's printers are used in fashion design, education, and architecture.
HARZ Labs. A young Russian company developing high-quality consumables for 3D printing. The company regularly cooperates with educational institutions, scientific and research centers. In addition, the company has its own research and development center equipped with modern equipment.
The manufacturer's line includes materials for DLP, LCD, SLA printing technologies, as well as for industrial applications using SLA, CJP technologies.
Total Z. The company has been operating since 2017. The director of Total Z explains its creation in the following way: “... then, by and large, apart from the words “3D printers” and “3D printing”, we didn’t know anything at all. We bought some ready-made samples, understood what equipment would be needed, hired engineers, and started to delve into the topic from scratch.”
The company's first 3D printer appeared 3 years later. The company develops both universal 3D printers (Anyform 250/250-g3) and industrial 3D printers (Anyform 450-Pro v.3 or Anyform 1200-Pro).
Special Air. The company was registered in 2009 and produced CNC equipment. Since 2012, she has been creating her own 3D printer, which was launched in a series in 2015. It is the undisputed leader in the production of construction printers. Spetsavia is the first company in Europe to print a residential building in 2015. At the moment, the company has developed a range of construction and large-format printers that are used in landscape design and architecture.
Spetsavia is the first company in Europe to print a residential building in 2015. At the moment, the company has developed a range of construction and large-format printers that are used in landscape design and architecture.
Tsar-3D. The company has been working in the field of additive technologies since 2012. Until 2014, the company specialized in the production of only desktop 3D printers. In the future, the company engaged in the production of large-format printers.
Anisoprint. Anisoprint LLC has been operating since 2014. It has gained wide popularity due to the creation of a unique technology for 3D printing of complex objects from composite materials by adding carbon fiber to plastic during the printing process. The use of this technology significantly increases the strength of finished products, in contrast to the use of technology with refractory plastics.
LAR-Technologies. The company specializes in the design and modernization of production complexes with CNC equipment. In 2017, the company created a LAR P metal 3D printer with software for it and became the first Russian company to make such a 3D printer available to a wide range of users.
In 2017, the company created a LAR P metal 3D printer with software for it and became the first Russian company to make such a 3D printer available to a wide range of users.
Laser systems. More than 20 years of experience in the field of laser technologies, not only in the Russian market, but also abroad. The company created and launched into mass production the M250 industrial SLM 3D printer, which became the first domestic industrial 3D printer with a ST-1 certificate of origin.
Lasers and apparatus. Research and Production Center "Lasers and Equipment" was established in 1997. The main direction of work is the creation of laser systems for the defense complex. By 2010, the center actually became a complex of enterprises for the production of special technological equipment, including SLM 3D printers.
Additive solutions. At first, the main activity of the company was the supply of various industrial equipment.![]() Subsequently, she took up the production of 3D printers for the military-industrial complex and other industries. Today, the company's lineup is represented by 3D printers: D130, D250, D500, D130 medical and S800.
Subsequently, she took up the production of 3D printers for the military-industrial complex and other industries. Today, the company's lineup is represented by 3D printers: D130, D250, D500, D130 medical and S800.
Institute of Laser and Welding Technologies (ILIST). has been successfully researching and developing metal 3D laser printing technologies for over 15 years. Implemented more than 50 projects in engineering industries.
3. Overseas 3D printer manufacturers
Wanhao. WanHao Precision Casting Co., Ltd was established in early 2011. In the same year, the first model of a 3D printer was assembled and named Duplicator. This model, made in China, combines the advantages of 3D devices from RepRap and MakerBot. In 2012, the company introduced LCD 3D printers to the market, realizing the ability to 3D print “directly” using an SD memory card installed in the printer. In the same year, WANHAO enters the global market by offering competitive 3D printer models. To date, the fourth generation of WANHAO printers, the Duplicator 4X, is on the market.
To date, the fourth generation of WANHAO printers, the Duplicator 4X, is on the market.
Flash Forge. Zhejiang Flashforge 3DTechnology Co., Ltd. was established in 2011 and is one of the largest in China. The production capacity of the company allows to produce up to 5,000 printers monthly. The company's products have been repeatedly awarded with numerous prizes, and Creator and Dreamer series printers have a high rating. In 2015, they took 2nd and 3rd place in the category of budget models and models for enthusiasts.
Esun. Established in 2002, ESUN is a high-tech enterprise in the field of degradable polymer materials such as PLA and other plastics. Since 2007, the company has been developing materials for 3D printing, and began to produce a plastic high-strength filament with an absolute round shape, a stable melting point, and a variety of colors. Because of this, the plastic filament produced by ESUN is so popular among 3D printer manufacturers, distributors and consumers all over the world.
Raise3D. Raise3D started 3 years ago and created the Duplicator 5 printer series and IdeaMaker software for Wanhao. In 2015, the company announced the creation of a line of printers under its own Raise3D brand. 3D printers produced by Raise3D have won the most prestigious awards in the world of additive technologies, such as the 3D Printing Industry Awards-2017, the first place in the annual ranking of Make magazine, the first place in the 3D HUBS guide in the "Pro" category, etc. At the moment Raise3D manufactures Pro2 series 3D printers designed specifically for industrial use.
Dremel DigiLab. The company was founded in the USA in 1932. Rotary tools were one of the first products of the company. Over its nearly century-long history, the company has invented many innovative products and set its own standards for what reliability and safety means in the industry. Today Dremel DigiLab creates new technologies and modern solutions. Dremel's powerful and reliable 3D printers are tested and safety certified and have already won the trust of users around the world.
Phrozen. Taiwanese company Phrozen was formed in 2014 with the goal of making professional 3D printing equipment more accessible to a wide range of consumers.
The company focuses on the development and production of printers with high precision and printing speed, working on LCD technology, as well as consumables for them. An important point is the “omnivorousness” of printers, as they work great with different quality resins. Now the company is successfully growing and developing, is an active participant in professional exhibitions.
Formlabs. The company was founded by students of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 2011. They joined forces to create a desktop stereolithographic 3D printer. To date, Formlabs' best-known products are the Form 1, Form 1+, Form 2 and PreForm printers (a software package designed to prepare models for 3D printing). Models differ in functionality and size of the construction area.
3D Systems. The company is an innovative leader in the field of 3D printing, in particular the development and production of 3D printers and scanners, consumables and software. In 2014, the company introduced a number of revolutionary products in the line of food 3D printers. The innovative focus of the company is characterized by its inventions:
The company is an innovative leader in the field of 3D printing, in particular the development and production of 3D printers and scanners, consumables and software. In 2014, the company introduced a number of revolutionary products in the line of food 3D printers. The innovative focus of the company is characterized by its inventions:
- 3D printing and the first stereolithographic printer;
- selective laser printing method;
- inkjet 3D printer and multi inkjet printer.
The company's 3D printers are now the industry standard.
Anycubic. The company was founded in 2015 and has grown from a small group of enthusiasts to one of the largest manufacturers of high-tech equipment for additive manufacturing. As of 2021, the company's products are represented in more than 200 countries. The hallmark of the company is high-quality components, a well-designed design and a low price tag.
Last four years. the number of sold 3D printers increased by 100% per year. At the same time, the company remains customer-oriented - each new model of a 3D printer is created taking into account user feedback and wishes.
the number of sold 3D printers increased by 100% per year. At the same time, the company remains customer-oriented - each new model of a 3D printer is created taking into account user feedback and wishes.
Uniz. UNIZ TECHNOLOGY LLC was founded in 2014 in the USA. The company is developing its own 3D equipment and photopolymer resins for both general and narrow purposes (engineering, dental and jewelry). In addition, the company has developed and successfully introduced to the market a new photopolymer printing technology - LCD stereolithography, which is characterized by maximum construction accuracy at high printing speed. At the same time, the company maintains a balance between an affordable price and the introduction of innovative technologies.
CreatBot. CreatBot is a brand created by the Chinese company Henan Suwei Electronic Technology Co., Ltd in 2011. The company specializes in the development and production of professional 3D printers in desktop and industrial versions, which operate on the basis of FDM, SLA and DLP core technologies.
In 2018, the company launches the F160-PEEK industrial-grade printer for high-temperature engineering PEEK printing. In the same year, the company is already releasing the 4th generation of its CreatBot D600 printers, which are distinguished by stability and ease of use.
At the moment the company sells equipment in more than 60 countries and has international certification of its products.
Felix. Company established in Holland. The company has created an innovative Felix 3D printer unlike any other on the market. This Felix
3D printer was originally only available as a DIY kit, but is now a 100% ready-to-use 3D printer with class-leading 50 micron print accuracy. Make Magazine named Felix 3.0 Surprise Hit 2014.
UP! A well-known brand of desktop 3D printers manufactured by PP3DP, which is a subsidiary of China's Tiertime Corporation. UP3D produces 3D printers that are compact, reliable and concise in design for use at home, small businesses or educational institutions. One of the newest branded devices is the Mini 2 3D printer, which is positioned as a printer for schoolchildren, students and beginners in 3D printing.
One of the newest branded devices is the Mini 2 3D printer, which is positioned as a printer for schoolchildren, students and beginners in 3D printing.
Zortrax. European manufacturer and supplier of integrated 3D printing solutions. Zortrax 3D printers are well known in the 3D technology industry for their durability and high level of control over the printing process. Most often, models are used in the fields of architecture, engineering, medicine, education and design. The Zortrax research team is constantly working to expand the product line by developing new innovative features for the Z-Suite software and devices. At the moment, the Zortax line includes models of 3D printers M200, M300 and Inventure.
XYZprinting. Founded in 2013, the company specializes in affordable and advanced 3D printing and 3D scanning products. The company is backed by the world's largest electronics conglomerate, the Kinpo Group. In the 2014 Editor's Choice Award, XYZprinting's first 3D printer won the Consumer Electronics category and was voted the most affordable 3D printer on the market. To date, the company's offices are represented throughout Europe, in the USA, Japan, Thailand, China, South Korea and Taiwan.
To date, the company's offices are represented throughout Europe, in the USA, Japan, Thailand, China, South Korea and Taiwan.
Ultimaker. Company from the Netherlands. Creates high-performance and affordable 3D printers that are popular with both large companies and retail customers. Ultimaker models are most often used for 3D prototyping in FDM technology.
BQ. Spanish brand, part of the Mundo Reader holding. Known as a manufacturer of consumer electronics, as well as desktop options for 3D printers. The most popular 3D printer models are Hephestos with an open build chamber and WitBox with a closed build chamber. For its devices, BQ uses the technology of layer-by-layer deposition of a plastic thread, which is often considered one of the most versatile.
BigRep. German vendor BigRep builds 3D printers that enable fast and accurate large-scale 3D printing.
BigRep's main goal is to make large format 3D printing accessible to a wide audience and integrate it into manufacturing, prototyping and design processes.
Choc Edge. Choc Edge started as a research project at the University of Exeter in the UK. The company's goal is to create a printer that allows you to print objects from materials that have not been used in 3D printing before. Chocolate was chosen as everyone's favorite product, ideal for attracting 3D printing enthusiasts and attracting a new audience not previously interested in 3D printing.
This work resulted in the creation of the Choc Creator V1 3D printer in 2012, which was the first commercially available chocolate 3D printer. This printer generated a lot of public interest and was followed by the Choc Creator V2 and V2 Plus.
Choc Edge aims to revolutionize the world of 3D printed chocolate, enabling the creation of unique products and the overall consumer experience.
HP. Hewlett-Packard is a digital technology giant founded in 1939 in the United States. In 1966, the company created and was the first to market the minicomputer. Today the company pays special attention to the development of promising additive technologies: 3D printers, scanners and software for them.
Today the company pays special attention to the development of promising additive technologies: 3D printers, scanners and software for them.
In 2019, the company opened the 3D Technology Center in Barcelona, bringing together world experts in additive manufacturing. Together with other industry leaders, the company has brought together suppliers of 3D printed parts and polymers to deliver product to market more efficiently.
4. Brief review of modern models of 3D printers
1 provides an overview of modern models of 3D printers.
Table 1. Overview of modern models of 3D printers Printing technology used - FDM; FFF Formed layer thickness from 10 µm Price 449000 ₽ Print technology used - FFF Formable layer thickness from 20 µm Price 299 000 ₽ Used printing technology - FDM Formed layer thickness from 15 µm Price 125 000 ₽ Print technology used - LCD Formed layer thickness from 10 µm Price 79 000 ₽ Print technology used - FFF Formed layer thickness from 10 µm Price 85 000 ₽ Used printing technology - FDM Formed layer thickness from 10 µm Price 549 000 ₽ Printing technology used - LCD LCD mask stereolithography Formed layer thickness from 10 µm Price 38 500 ₽ Working chamber size 192x120x200 mm Print technology used - LCD Formed layer thickness from 10 µm Price 245 000 ₽ Print technology used - SLS Formed layer thickness from 75 µm Price 1 924 748 ₽ Working chamber size 240x240x400 mm Used printing technology - FDM Formed layer thickness from 50 µm Price 264 000 ₽ Used printing technology - FDM Formed layer thickness from 50 µm Price 131 100 ₽ Used printing technology - FDM Formed layer thickness from 50 µm Price 56 900 ₽ Print technology used - LFS Formable layer thickness from 25 µm Price 420 000 ₽ Views: 6 One of the advantages of food products created on a 3D printer is the solution to the problem of the so-called "hidden hunger". Russian scientists have developed a 3D printer for creating meat and other food products. The new technology will make it possible to produce not only meat products, but also chocolate, cakes and dough. Scientists of the Moscow State University of Food Production (MGUPP) told "Izvestia" nuances of printed food production. To make a meat product on a 3D printer, a biopsy is taken from an animal – tissue is plucked off, the cells of which are later multiplied in special bioreactors. However, the process of growing cells takes several months. The second stage is the preparation of raw materials. "A special plant-based substrate is printed on which live cells are applied. Layers of animal and plant materials alternate", – Alexey Kuchumov, Vice-Rector for Research and Development, spoke at MGUPP. One of the advantages of 3D printed food products is the solution to the problem of so-called "hidden hunger". "We are currently working on a database of smart recipes that will be like instructions for the printer, like a costing card for a chef", - said Alexey Kuchumov. In the near future, scientists plan to improve the already developed device so that it can print more complex products - sausage, cutlets and even steak. Now the printer is able to create food from relatively simple ingredients: chocolate, dough, puree masses. One of the problems with making and distributing printed food is its cost. The price of such products is many times higher. For example, 3D printed beef is a thousand times more expensive. How to reduce the price, scientists at SCiFi Foods (California, USA) came up with the help of gene editing of a cell line using CRISPR technology. Picaso Designer XL Pro Working chamber size 360x360x610 Hercules Strong DUO Working chamber size 300x300x400 mm Zenit DUO Switch Working chamber size 160x195x230 mm Phrozen Shuffle XL Lite Working chamber size 190x120x200 mm Picaso Designer Classic Working chamber size 200x200x210 Raise3D Pro2 Plus Working chamber size 305×305×605 mm Anycubic Photon Mono SE Working chamber size 130x78x160 mm Uniz SLASH PLUS Sinterit Lisa Pro Working chamber size 150 x 200 x 260 mm Maestro Duet Total Z Anyform 250-G3 Working chamber size 250x250x250 BiZone Prusa i3 Steel v2 Working chamber size 300 x 300 x 330 mm Formlabs Form 3B Working chamber size 145x145x185 mm Russian scientists have developed a 3D printer to create meat — 07/28/2022 — In Russia on REN TV
 As Kuchumov explained, a person often receives less vitamins, microelements and antioxidants from ordinary foods. It will be possible to add exactly those micronutrients that the human body lacks in printed products.
As Kuchumov explained, a person often receives less vitamins, microelements and antioxidants from ordinary foods. It will be possible to add exactly those micronutrients that the human body lacks in printed products. 
Learn more


 04mm, XY 0.01mm
04mm, XY 0.01mm