Diy robotic arm 3d printer
The 10 Coolest DIY 3D Printable Robotic Arm Projects
Exploring 3D printing robotics is easier and cheaper than ever before, so there is no excuse not to give it a go. Having said that, it takes a lot of time and practice to become an expert. While you might not be ready to build a Terminator in your bedroom, 3D printing robotic arms is an excellent starting point for enthusiasts.
Easily programmable, with fewer moving parts and simple functions, robotic arms are an accessible entry-level sector in 3D printing robotics.
That being said, the current state of print-at-home robotics is nothing close to I-Robot. Robotic arms are little more than controllable or programmable pick-and-place tools right now.
But, there is plenty of cutting-edge technology here to whet anyone’s appetite. And many are open source, so anyone can download the files and have a go at printing themselves. They are a fantastic tool for anyone interested in robotics to teach themselves about robotics, and impress your friends.
1. LittleArm- The Entry Level
As the name suggests, LittleArm is the smallest, most simplistic, and easiest to print of all the robotic arms on this list. But that does not make it totally useless. Crucially, it is that simplicity that makes it so useful.
How to Draw Unicron G1 Transformer ...
Please enable JavaScript
How to Draw Unicron G1 Transformer - Decepticon
Everybody has to start somewhere, especially in 3D printing, and LittleArm is the ideal entry level project to get you hooked on 3D printed robotics. With only 3 degrees of freedom, meaning 3 points of movement on the arm, it is very easy to understand, both when 3D printing and programming.
With little more than a 2C motor and a roll of PLA filament, you can construct the 31 parts needed to build this rugged and flexible arm that can be assembled in less than an hour. Just like David against Goliath, don’t write off the little guy just yet.
2.
 EEZYbotARM MK3: The Second Base
EEZYbotARM MK3: The Second BaseThe EEZYbotARM is an ever-evolving 3D printing project that is currently on its third form. Developed by Carlo Franciscone, an engineer from the Novara, Italy, the EEZYbotARM is a slight step up in complexity from LittleArm.
The main enhancement is its 4 directions of freedom, with a rotating base, 2-finger gripper, and a pivot in the arm that allows it to bend. While it doesn’t have the strength to handle a significant payload, it’s definitely a project worth using as an experiment.
The MK3’s design is very similar to its original. The MK2 was created to be a little larger and stronger than its predecessor, but the MK3 returns to the smaller design, with a focus on cheaper motors and construction costs. It was made using ABS, but PLA is also very possible.
If you are looking to try something a little more physically impressive, the MK2 is the clear choice. But when focusing on the accessibility of 3D printable robotic arms, the EEZYbotARM MK3 is your best bet.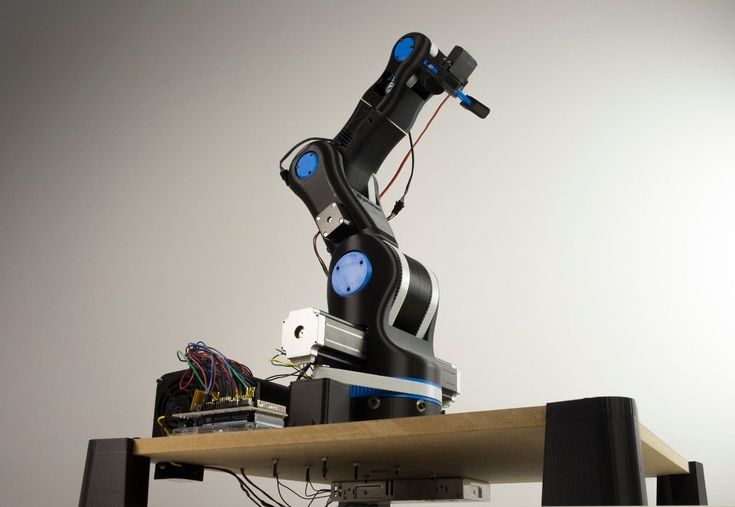 Image credit: Eezybotarm
Image credit: Eezybotarm
3. MeArm: The Everyman 3D Printed Robotic Arm
Hailing from United Kingdom, MeArm is the 3D printed robotic arm project that can cater to anyone. The kits are available to buy on Amazon if you didn’t feel like printing it yourself, but you can also access all the open-source files you need. You can even use a laser cutter if you don’t have a 3D printer to hand.
The MeArm is intended to be easy and fun, with an array of different color schemes. The parts are deliberately simple and easy to fit together. And on top of all that, it comes with a healthy choice of control options for whatever tools you have available.
Want to control the arm using joysticks? MeArm has kits for Arduino and Raspberry Pi, as well as many more. Want to pre-program the arm? There’s a BBC micro:bit kit compatible with Microsoft Make Code. Do you have your own controller you prefer using? You can just get a MeArm without any add-ons. Whatever you need, they have you covered.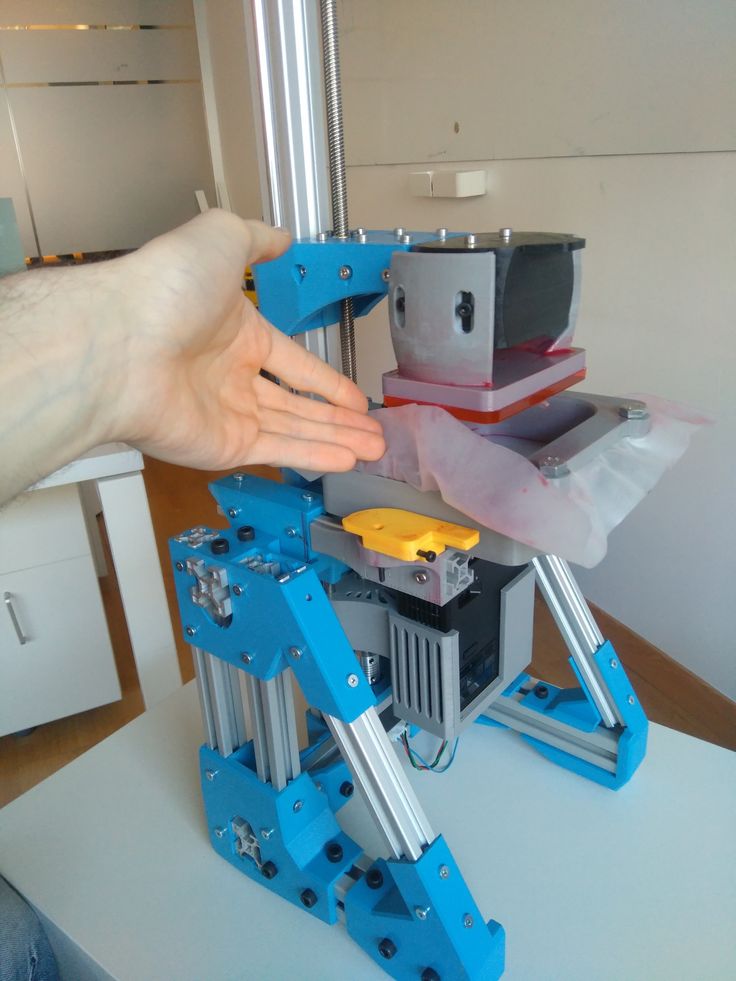
4. Instructables 3D Printed Robot Arm
This is where the scale and intricacy start to rise. The Instructables Workshop has featured lots of amazing 3D printing projects over the years, with a library big enough to have something for everyone. And their 3D printed robot arm is as grand as it is cool.
With circuitry that can be purchased from any good electronics store or wholesaler, the 3D printed arm is a great example of progression for hobbyists or professionals looking to hone their skills. A full list of materials and components, as well as a useful step-by-step guide, can be found on their website.
Its compact control base makes operation incredibly easy, and all the parts snap together for handy assembly that is surprising fast for an arm of this size. Once you get the basics right, this is the best next step.
5. Kauda Robotic Arm
While a lot of the more advanced 3D printing robotics projects are designed for educational purposes, the Kauda robotic arm is the most widely accessible. Its smaller size means that it is a handy teaching tool for computing students of all ages and abilities.
Its smaller size means that it is a handy teaching tool for computing students of all ages and abilities.
While Giovanni Lerda’s bulky and more classic design isn’t to everyone’s aesthetic taste, it makes visually understanding the mechanism much easier, vital for younger students. And its small, desktop scale make it an ideal and affordable tool for classrooms across the world.
Computing is fast becoming one of the most important subjects at schools as technology evolves at breakneck pace. Children will increasingly become reliant on education into programming. Few robotics projects on the market today can rival Kauda for ease of access, and it is all made possible by 3D printing.
6. How To Mechatronics’ Robotic Arm
A big way to enhance these 3D printed robotic arm projects is to integrate technology that everyone has access to. With that in mind, online engineering site How To Mechatronics have created a controllable 3D printed robotic arm that is operated by a self-designed smartphone app.
The custom android app can be connected via Bluetooth to a node built into the arm, and the user can control the robot using a series of sliders. While the app is not available to download from any store, they do break down how it works and encourage others to recreate its functions and features.
With 3 pivot points, the arm itself is extremely flexible and responsive, making the arm more dexterous and precise. This gives the arm a wider range of industrial applications when the technology becomes more ubiquitous.
And the guide on how to make it is very detailed, walking you through every step carefully. Combining the advanced technology of 3D printed robots with the everyday technology we all have at our disposal is a significant step forward for the industry.
7. Zortrax 3D Printed Robotic Arm
Polish manufacturer Zortrax has developed a 3D printed robotic design with perhaps one of the sleekest and most attractive designs around. It is one to drop anyone’s jaw. The concept art produced looks beautiful, and the files to recreate the design are available to all.
The concept art produced looks beautiful, and the files to recreate the design are available to all.
But the Zoftrax 3D printed robotic arm isn’t just a pretty face. It also has a range of useful applications. The design’s 5 degrees of freedom make it as flexible as the best on the market, and the hand at the end is designed to be replaceable with tools like screwdrivers, drills, wrenches, or electromagnets. This makes it a valuable tool for mechanics and construction companies.
The boundless possibilities of this arm through its range of attachable tools make it a very exciting project, and one to keep an eye on as the developers no doubt work on its evolution.
8. Roboteurs RBX1
Technology companies are always looking to go that one step further with their projects. One more turbocharger, one more processor, one more centimeter. It’s no surprise then to see the Roboteurs RBX1, the first 3D printed 6-axis robotic arm.
At this point, there are few practical applications of an arm this complex, other than impressing yourself and anyone else who is interested.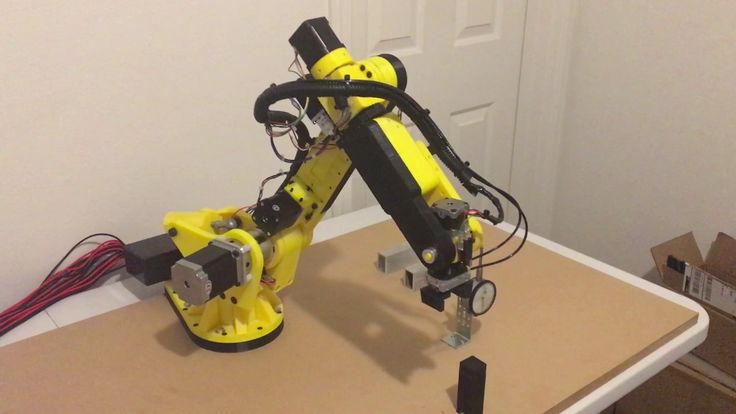 But while it may be on the sillier end of the spectrum in that regard, there is a lot here to be excited about.
But while it may be on the sillier end of the spectrum in that regard, there is a lot here to be excited about.
Roboteurs sell their construction kits online for a modest price considering the level of technology involved. It is one of the only 3D printable robotic arms that require no external machined components, with everything needed provided in the kit.
It is also extremely easy to operate. It is compatible with the most common operating software, and photos provided on their website even feature an Xbox controller! If a 12-year-old Fortnite player could handle this machine, so can you.
9. Haddington Dynamics Robotic Arm
Based in Las Vegas, Nevada, Haddington Dynamics have developed the Mark Henry of 3D printable robot arms. Previous attempts to create a robot arm, affectionately named ‘Dexter,’ using PLA were too weak for HD’s liking. However, after one customer’s advice, and in collaboration with NASA, they began using a Markforged printer.
This allowed them to redesign the robot and begin using carbon fiber, reducing the number of parts from 800 to just 70. The result was a much larger and more robust design with fewer joining points between components that drastically increased its payload weight. The current iteration has a reach of 770mm, and can lift objects as heavy as 3 kilograms.
The result was a much larger and more robust design with fewer joining points between components that drastically increased its payload weight. The current iteration has a reach of 770mm, and can lift objects as heavy as 3 kilograms.
That might not sound like a lot in the grand scheme of things, but in the world of 3D printed robotic arms, that much weight would put Atlas to shame.Image credit: Markforged.
10. BCN3D MOVEO- The King
The BCN3D MOVEO is one of the best and most well-rounded 3D printed robotic arms projects around. The biggest reason is that it incorporates all of the features we’ve mentioned here into one machine.
Developed at the Departament d’Ensenyament from the Generalitat de Catalunya in Spain, it was originally designed with education in mind, currently used in 15 different institutes around Catalonia as an educational tool. It has a flexible 5-axis construction with an attractive design, and while it is not capable of extreme weightlifting, it is comparable in function with any of its similar peers.
This pick-and-place device is among the most advanced all-round machines in the industry, with the express purpose of being accessible to anyone. It’ll take a lot of expertise to make your own, but there are few more promising devices around for robotics enthusiasts.
Other fun 3D printing project articles:
- Coolest 3D printer projects
- Beginner 3D printer projects
- 3D printer projects for engineers
- Robotic arm 3D printer projects
The Top Robotic Arm 3D Printing Solutions
3D printing news News What Are the Robotic Arm 3D Printing Solutions on the Market?
Published on October 14, 2022 by Claire S.
One of the trends we have increasingly seen as additive manufacturing industrializes is an increased focus on large-format additive manufacturing. Though this can of course be achieved with large machines, notably those using FDM, robotic arms offer a number of advantages for users. Robotic arms allow not just for large-scale printing thanks to the long reach of the arms, but also more freedom thanks their multiple axes as well as the fact that the resulting parts often do not require support structures.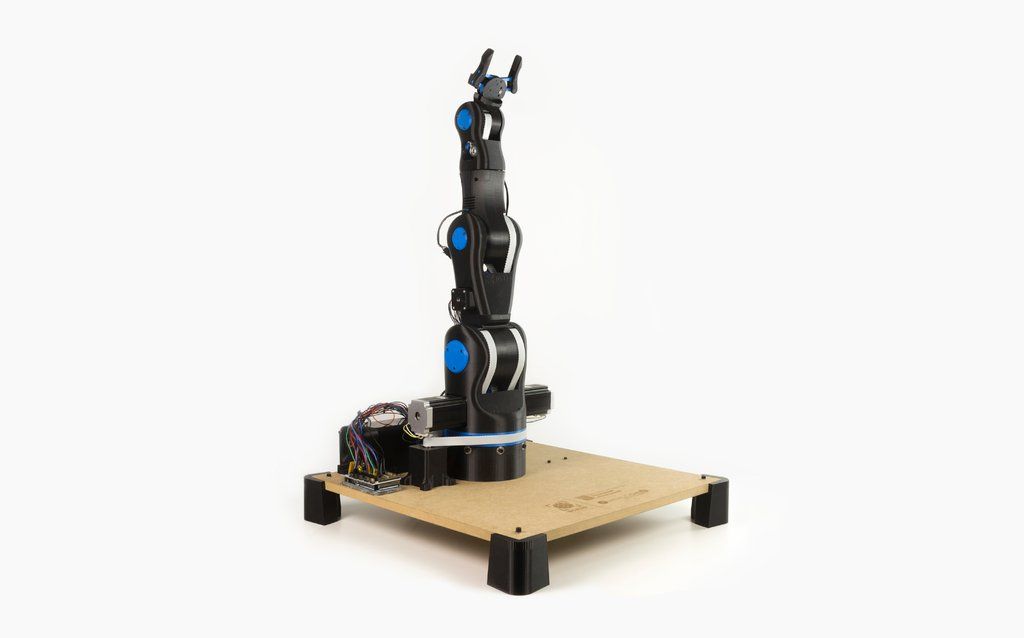 Though there are only a handful of manufacturers who create the robotic arms, they have been adapted by 3D printing manufacturers for both polymer and metal AM solutions. In the following list, in no particular order, we take a closer look at what is currently on the market, both for original arms and adapted solutions.
Though there are only a handful of manufacturers who create the robotic arms, they have been adapted by 3D printing manufacturers for both polymer and metal AM solutions. In the following list, in no particular order, we take a closer look at what is currently on the market, both for original arms and adapted solutions.
Original Robotic Arms Manufacturers
KUKA
The German company KUKA is undoubtedly one of the leaders in the automation market, offering robots that enable the electronics, automotive and healthcare industries to simplify their manufacturing processes. KUKA develops solutions that can be adapted for additive manufacturing. It is therefore not surprising to find the KUKA brand on many robotic 3D printers, whether for designing metal, plastic or even concrete parts. One example is the KR QUANTEC line of robotic arms, which offers machines with a reach of 2,671 to 3,904 mm and a load capacity of 120 to 300 kilos.
The KR QUANTEC arm was equipped with a nozzle to extrude concrete for the Besix3D company (photo credits: KUKA)
ABB
ABB group is a multinational company which produces robotic arms, including those used for 3D printing. Their robotics portfolio is diverse with different types of industrial robots to fulfil consumer needs.Their RobotStudio® programme is the world’s most popular offline programming and simulation tool for robotic applications. According to the company, with its solution, users can unlock flexibility and upgrade their business productivity to the next level. They are even able to design robots to suit their own unique needs, notably in additive manufacturing. As you will see further down the list, ABB six axis industrial robot is used by Massive Dimension, a company which works on sustainable development in the 3D printing industry.
Their robotics portfolio is diverse with different types of industrial robots to fulfil consumer needs.Their RobotStudio® programme is the world’s most popular offline programming and simulation tool for robotic applications. According to the company, with its solution, users can unlock flexibility and upgrade their business productivity to the next level. They are even able to design robots to suit their own unique needs, notably in additive manufacturing. As you will see further down the list, ABB six axis industrial robot is used by Massive Dimension, a company which works on sustainable development in the 3D printing industry.
Massive Dimension and ABB Additive Manufacturing Demonstration at IMTS 2022. (Photo credit: Massive Dimension)
Comau
Comau is an Italian industrial automation and robotics company. The company develops systems, products and services compatible with Industry 4.0. In particular, its portfolio includes a complete family of robots, including robotic arm solutions. Since 1978, Comau has been manufacturing these machines with the aim of integrating and improving innovative applications in all industrial sectors. There are several robotic arms, and they differ in their payload capacities. Still, they leverage IoT and AI technology to operate autonomously.
Since 1978, Comau has been manufacturing these machines with the aim of integrating and improving innovative applications in all industrial sectors. There are several robotic arms, and they differ in their payload capacities. Still, they leverage IoT and AI technology to operate autonomously.
Third Party 3D Printing Companies Using These Solutions
CEAD
CEAD is a Dutch company based in Delf that develops large-scale 3D printers. This company stands out as it offers robot-based solutions that combine printing and CNC milling processes in one process. Another solution is the AM Flexbot, a robot-based solution for large-scale 3D printing. Siemens Sinumerik controllers are responsible for controlling the Comau robot arm, thus not requiring any robot controller. This controller can control 31 axes at the same time as it moves along its path. Your AM Flexbot can be expanded with additional functions such as a rotary table, additional robots, or other production processes such as CNC milling. It is the perfect choice for a customized solution with a specific application.
It is the perfect choice for a customized solution with a specific application.
DXR Series from Weber Additive
German company Weber Additive, dedicated to the development of different manufacturing technologies, also has robotic arm solutions for 3D printing. Weber’s DXR robotic system features a high-quality extruder capable of 3D printing. The extruder is powered by a 6-axis industrial robot that allows it to move precisely. Its robotic arm based on the manufacturer Kuka and its AE series extruders are adapted to the needs of its customers to provide the most optimal results. These systems offer great advantages, such as 3D printing with 6-axis kinematics, a variable angle of the manufacturing head or overprinting on existing parts, among others. You can take a look at the solution in the video below:
The robotic arm from Hyperion Robotics
Founded in 2019 in Helsinki, Hyperion Robotics is a company specializing in the construction industry. It uses additive manufacturing to design more affordable structures, wanting to make the market more sustainable and most importantly, more automated. To do this, it relies on KUKA robots on which it mounts an extruder capable of depositing Hyperion Robotics’ material. This is a special concrete mix that uses a reduced amount of cement thanks to recycled waste components. It also designed its own software that allows it to work with any robot. In terms of applications, the Finnish company has already built decorative elements, structures imitating coral reefs and energy infrastructures.
Photo credits: Hyperion Robotics
Massive Dimension
Massive Dimension, as their name undoubtedly suggests, is a manufacturer of large format 3D extruders and full solutions, including turnkey robotic printing cells. Specifically, the company was founded with the goal of contributing to sustainable solutions in order to reduce waste on the planet. Currently, Massive Dimension’s solutions are centered around polymer pellet 3D printing. For their robotic cells, they include six-axis industrial robotic arms from ABB. When combined with the ABB 3D Printing Powerpac software, users have access to a comprehensible workflow for pellet 3D printing. The company notes that their robotic arms have been custom-tailored for robotic printing, including large format printing thanks to a build volume of 3ft x 5ft x 5ft. Moreover, these cells can also be further customized to fit each user’s individual needs.
Specifically, the company was founded with the goal of contributing to sustainable solutions in order to reduce waste on the planet. Currently, Massive Dimension’s solutions are centered around polymer pellet 3D printing. For their robotic cells, they include six-axis industrial robotic arms from ABB. When combined with the ABB 3D Printing Powerpac software, users have access to a comprehensible workflow for pellet 3D printing. The company notes that their robotic arms have been custom-tailored for robotic printing, including large format printing thanks to a build volume of 3ft x 5ft x 5ft. Moreover, these cells can also be further customized to fit each user’s individual needs.
Massive Dimension
Orbital CompositesOrbital Composites aims to disrupt the 3D printing industry. They believe that robotics is the answer to the limitations faced by the industry, such as scale, speed, strength and design. Their Orbital S, the first robotic 3D printer built for industrial scale, was released to tackle these problems. The impressive robot has a maximum speed of 2m/s, has a maximum payload of 10kg and a maximum reach of 1.1m. The build platform is 1m x 1m x 1m, giving the ability to create relatively large end use parts. Furthermore, the user has a choice of materials. It uses the Kuka KR10 R1100 robot arm; Kuka is an official partner of the company.
The impressive robot has a maximum speed of 2m/s, has a maximum payload of 10kg and a maximum reach of 1.1m. The build platform is 1m x 1m x 1m, giving the ability to create relatively large end use parts. Furthermore, the user has a choice of materials. It uses the Kuka KR10 R1100 robot arm; Kuka is an official partner of the company.
Orbital Composites’ Orbital S robotic 3D printer. Photo Credit: Orbital Composites
Dyze Design et Pulsar
Pulsar is a state-of-the-art, large-scale, high-speed plastic pellet extruder. It was designed with one goal in mind: to 3D print large parts as quickly and inexpensively as possible. Pulsar is compatible with robotic arms for 3D printing and is capable of producing up to 500 mm3/s (2.5 kg/h) of material. It can also be used with large nozzles from 1.00 mm to 5.00 mm. Finally, Pulsar is ready for all environmental conditions. The water cooling loop ensures that the entire system is at a constant temperature. With an additional heat shield, Pulsar can withstand a 200°C environment. This makes the machine compatible with plastic materials such as PEEK, Ultem and PSU.
This makes the machine compatible with plastic materials such as PEEK, Ultem and PSU.
Branch Technology
This company combines additive manufacturing, prefabrication and digital technology on a large scale. Thanks to their patented technology, it allows the team of designers and architects to imagine, compose and finally build those structures that were previously impossible with traditional construction methods. One example of a project they have carried out is in the construction of a 3D printed pavilion in which they have used KUKA robotic technology. The combination of robots with 3D printing has enabled the architects and designers from Gould Turnes Group with whom they have collaborated to not only tackle the construction of the final structure but the design process from start to finish. The 3D printing process applied to the KUKA robots is a great combination as it allows the production of precise, lightweight and cost-effective components from a variety of materials.
At this point, if you are interested in WAAM technology, you have almost certainly heard of MX3D. The Dutch company made waves for its creation of an entirely 3D printed, metal bridge which is currently located in the center of Amsterdam. This among other large-scale metal 3D printing feats has made them a popular choice in many sectors. And the company uses robotic arms for its solutions. More specifically, MX3D uses an 8-axis ABB industrial robotics system in its M1 metal AM system, allowing for the creation of medium to large-scale metal parts. To ease the process, the company also offers MetalXL, a software that controls their WAAM-based systems, ensuring that the part is manufactured as intended, controlling everything from design through monitoring during the actual printing.
mx3D printer
Continuous CompositesContinuous Composites was recently selected by NASA to produce low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) open isogrid composite structures for space applications, using its patented Continuous Fiber 3D Printing (CF3D) technology. This printer combines high performing composite materials with rapid curing thermoset resins. They say that this will demonstrate the printer’s capability to produce high quality and consistent printing, with excellent accuracy and precision. The printer is configurable and scalable and therefore can be applied to projects of various dimensions. They turned to Comau for their robotic arm needs.
This printer combines high performing composite materials with rapid curing thermoset resins. They say that this will demonstrate the printer’s capability to produce high quality and consistent printing, with excellent accuracy and precision. The printer is configurable and scalable and therefore can be applied to projects of various dimensions. They turned to Comau for their robotic arm needs.
A robotic 3D printer with Comau arm capable of producing thermoset objects with continuous carbon fiber (Photo credit: Continuous Composites)
What do you think of this listing? Have we missed any? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
Top 10 DIY 3D Printing Manipulators
3DPrintStory Reviews 10 Best DIY 3D Printing Manipulators
There are many different configurations of robotic arms, but most of them work on the same general principles of movement. Unlike mechanisms that work in the Cartesian coordinate system, such as, for example, 3D printers, manipulators mostly use the polar coordinate system for movement and have an arc-shaped work area. Robotic arms are unique in that they are not limited by footprint and take up very little space compared to other machines with similar functions.
Unlike mechanisms that work in the Cartesian coordinate system, such as, for example, 3D printers, manipulators mostly use the polar coordinate system for movement and have an arc-shaped work area. Robotic arms are unique in that they are not limited by footprint and take up very little space compared to other machines with similar functions.
In robotics there is such a definition as degrees of freedom (DOF). The term is used to refer to the number of rotating joints or axles on a particular arm, for example a 4DOF arm can be rotated by four separate joints.
Robotic arms are used in a variety of ways, but most are capable of picking up and moving, while some are designed to work in tandem with CNC machines, laser engraving, and even 3D printing.
Because there are hundreds of great designs and designs to consider when choosing a good arm to buy or 3D print, we've narrowed it down to 10 of the best and most popular arms that you can find and reproduce designs using your 3D printer as well. .
.
UFactory uArm
UArm is probably one of the most versatile of all the robot arms on this list. At the moment, this design already has the third release version - uArm Swift and more functional Swift Pro.
This open source robot arm is fully compatible with Arduino, Raspberry Pi and Seeed Studio Grove kits. It's unique in that the Swift Pro can do laser engraving and 3D printing - provided it's equipped with the right heads - and can "learn" the movements without the need for a computer.
This is a 4DOF manipulator with an accuracy of 0.2 millimeters.
You can find more information and where to buy it on the UFactory product page.
Thor
This arm, developed by Hackaday AngelLM, is completely open source and can be used for 3D printing. This is a 6DOF paddle with a maximum payload of 750 grams and a unique design for great flexibility.
You can find all the 3D printing files for this robot on the Thor project page.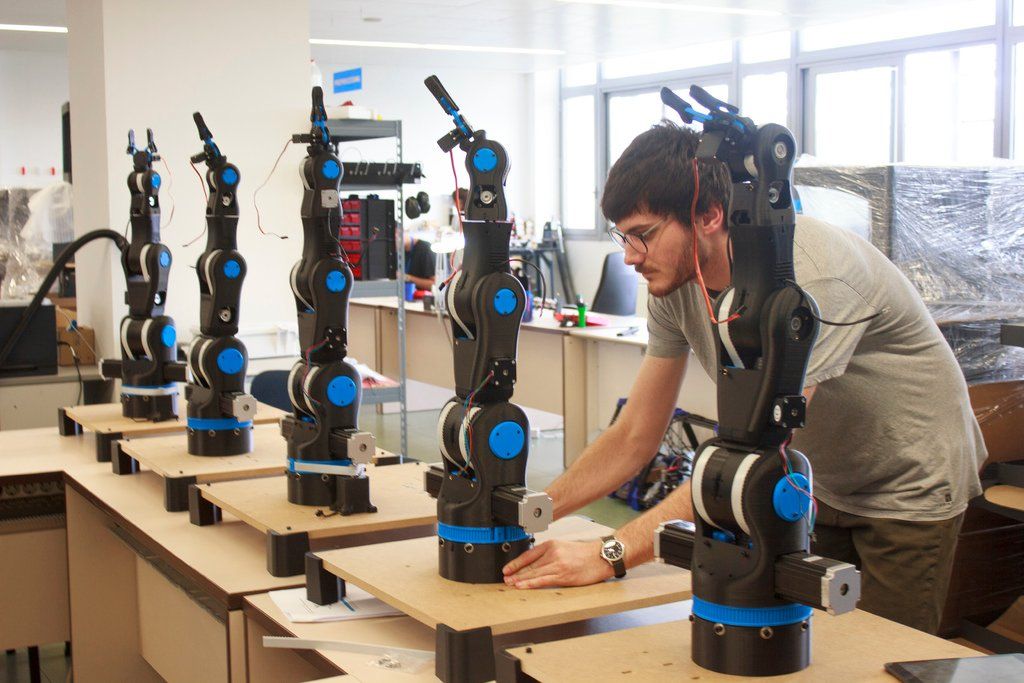
EEZYbotARM MK2
The EEZYbotARM MK2 is a 4DOF reference arm that is fully 3D printed with excellent building instructions. This robotic arm has won several competitions and is probably one of the easiest robotic arms to make. An MK3 version is also being developed.
You can find complete assembly instructions on the EEZYbotARM webpage.
Roboteurs RBX1
This is another great fully 3D printed robot arm that has amazing flexibility and aesthetics. In addition to purchasing the components yourself, Roboteurs offers a complete parts kit with a proprietary stepper motor driver to run the RBX1. All you need is a Raspberry Pi and a 3D printer. This manipulator is a 6DOF type design and has a beautiful appearance.
You can find the complete specification and parts kit on the Roboteurs product page.
LittleArm
LittleArm, designed by Slant Concepts on Hackaday.io, is the simplest robotic arm on this list.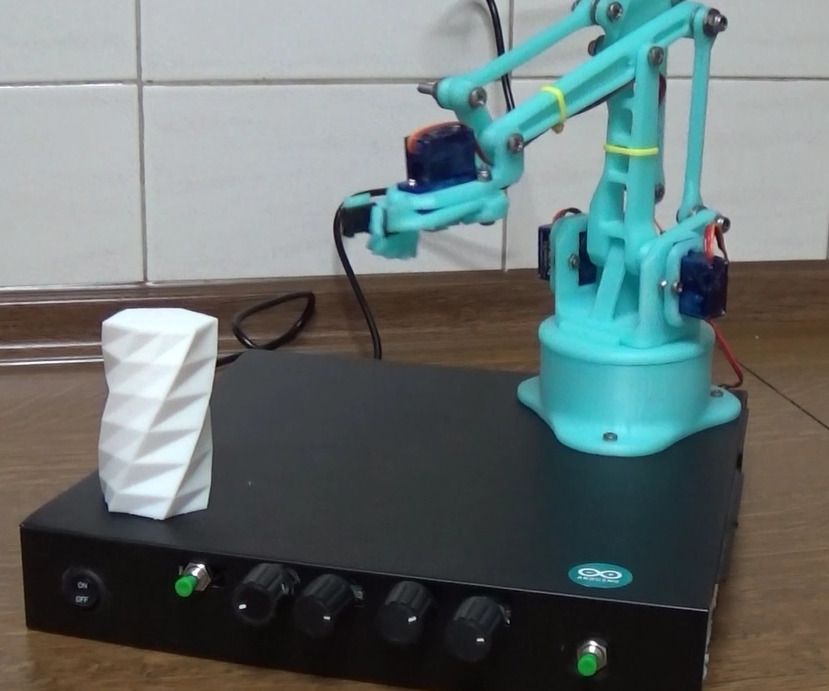 With only 3DOF, this arm can be a great introduction to Arduino programming for students and opens exciting doors of new technologies for newcomers to the world of 3D printing and robotics.
With only 3DOF, this arm can be a great introduction to Arduino programming for students and opens exciting doors of new technologies for newcomers to the world of 3D printing and robotics.
This fully 3D printed arm is very easy to assemble. The creators even developed an application with a simple interface for computers that can be used with this robot.
You can find full documentation on the LittleArm project page.
3D Printable Robot Arm
Created by Andreas Helldorfer on Hackaday.io. It's a large arm, fully 3D printed, with many uses. The creator developed it for 4 iterations before making a really worthy industrial design that is available to everyone. With a 6DOF design and a maximum payload of up to 2kg, this arm can really be used in many applications.
To find the 3D print files for this arm and the full specification, visit the project page.
MeArm
MeArm is one of the most popular manipulators and for good reason.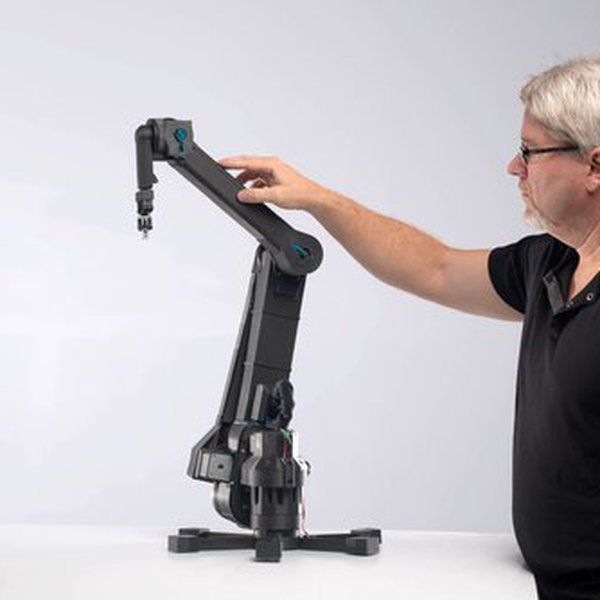 It consists of simple parts that can be laser cut or 3D printed and features a simple yet robust 4DOF construction.
It consists of simple parts that can be laser cut or 3D printed and features a simple yet robust 4DOF construction.
This design is so popular that two others on this list copy it. This is a manipulator equipped with four servos and either an Arduino or a Raspberry Pi. It is available in several different colors as a kit, or you can make all the parts yourself.
For pre-assembled kits, check out the MeArm product page.
For 3D printing files, take a look at MeArm on Thingiverse.
Zortrax Robotic Arm
The 5DOF Zortrax Robotic Arm is not the strongest for its size, with a maximum payload of only 100 grams, but it has a very impressive design. And it's a fully 3D printed arm, making it worthy of a mention on the current list. Its uniqueness lies in the fact that only three axles are driven, while the rest are set manually.
This manipulator is primarily used for supplying a set of interchangeable tool heads.
For a complete list of part files, including those for 3D printing, visit the project page.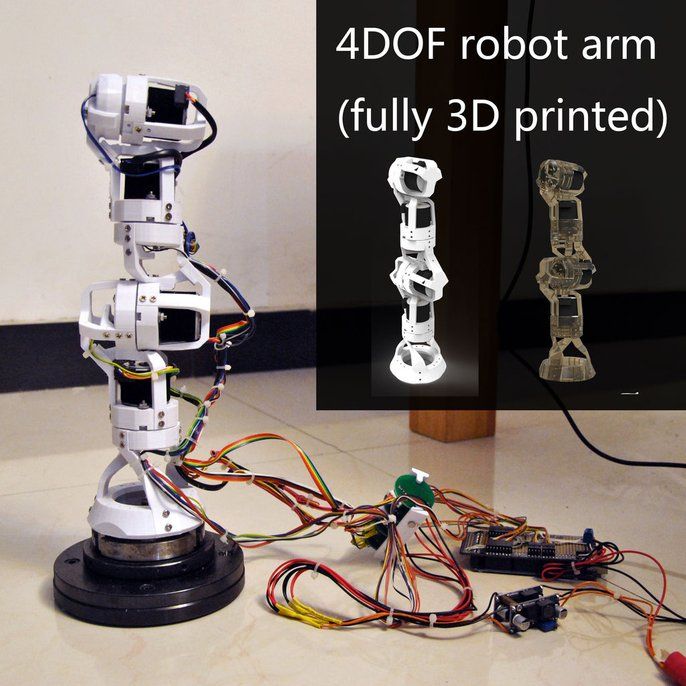
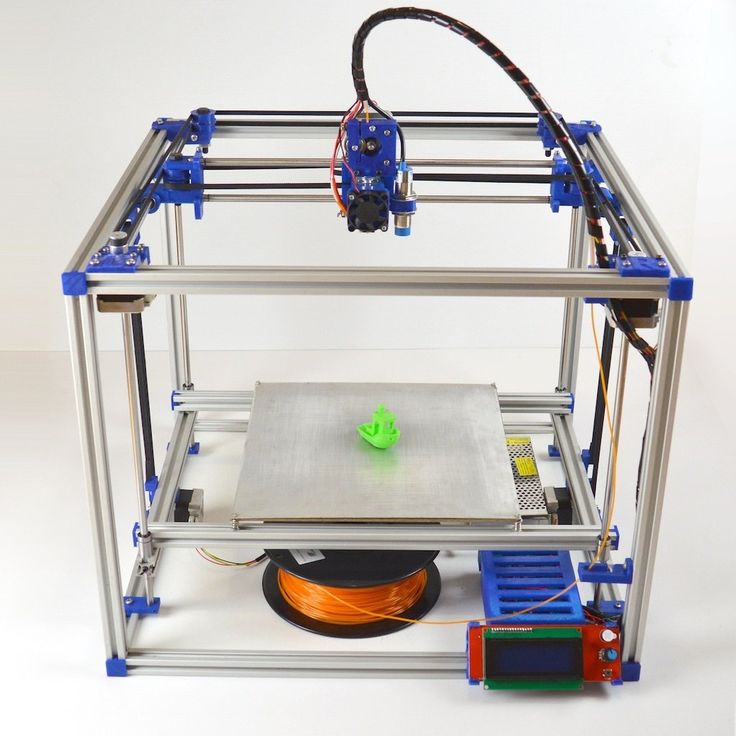
BCN3D Moveo
BCN3D Moveo is an impressive Arduino controlled 4DOF robot arm. It is fully 3D printed, open source, and has been well tested as a mockup for educational purposes and is already in active use in educational institutions.
Being open source, this manipulator is not limited to its intended use and, as such, can be modified to perform all kinds of tasks and can be used as a dedicated household apprentice or used on an industrial scale.
For more information, visit the BCN3D Moveo web page.
OWI Robotic Arm Edge
Another 4DOF design, the OWI Robotic Arm Edge is a simple manipulator designed for educational purposes. It is only available as a kit.
When powered by DC motors without encoders, accuracy is limited, making this manipulator more suitable for use as a toy. We included it on this list because it's a fantastic kit for students interested in robotics and technology, and it can be a great "desk toy" during boring lunch breaks. It can also be extensively modified to serve as a base platform for Arduino projects and other DIY developments.
It can also be extensively modified to serve as a base platform for Arduino projects and other DIY developments.
You can buy it on the OWI website, well, or Amazon, Aliexpress is also at your service.
Manipulator 3d model
DOWNLOAD
-
Rating:
-
Difficulty:
Medium -
Weight:
9.72 MB -
Parts:
22 pcs.
Everyone knows the robotic arm that is used in factories and other enterprises. Perhaps the robotic arm is the most popular model for assembly and control experiments among robotics fans. In addition, she teaches children very well at RobotON robotics circles in Nizhny Novgorod, the guys study her with great pleasure, programming and forcing them to perform various manipulations. Of course, this robot has a lot of details, and printing them with high quality on a 3D printer is not an easy task for a beginner. But for this, we have prepared articles on 3D printing that will definitely help you cope with this task.
But for this, we have prepared articles on 3D printing that will definitely help you cope with this task.
The instructions for assembling the robotic arm look very simple. It is worth collecting in 3 stages. First you need to assemble the base - the base on which the robot rotates around its axis in azimuth. Then you need to assemble the claw, and then the multi-lever mechanism of the crane itself. When assembling it, you need to make sure that each assembly rotates very easily. Otherwise, the servomotors will not have enough power to move the entire structure.
What causes poor mobility? Well, first of all, it can be caused by 3D printing defects. When you print a 3D model with a certain size of screw holes, you need to take into account the flow of plastic around the edges. That is, for example, if you have a round hole, then most often when printing, its diameter will decrease by 0.5 mm or even 1 mm. Because of this, the screw will hardly fit into this hole and cut the thread there. Therefore, there are 3 ways out here: pre-clear the hole with a screwdriver (or something else), develop a movement along the thread by assembling the knot, or simply put this error in the 3D model. This problem occurs depending on the printer, so it is quite individual.
Therefore, there are 3 ways out here: pre-clear the hole with a screwdriver (or something else), develop a movement along the thread by assembling the knot, or simply put this error in the 3D model. This problem occurs depending on the printer, so it is quite individual.
Another reason why a structure can be too stiff is overtightening the bolts or using the wrong sizes of connecting elements.
Features:
An important detail of the assembly is the pre-setting of the servos before attaching them to the crane or claw. The fact is that these places, due to the design and capabilities of servo motors, have dead zones. Therefore, before installing the servos on the crane, you need to program them at an angle of 90 degrees to be able to move the crane both to the right and to the left. We set the claw servomotor to 0, close its blades and fix it with a gear.