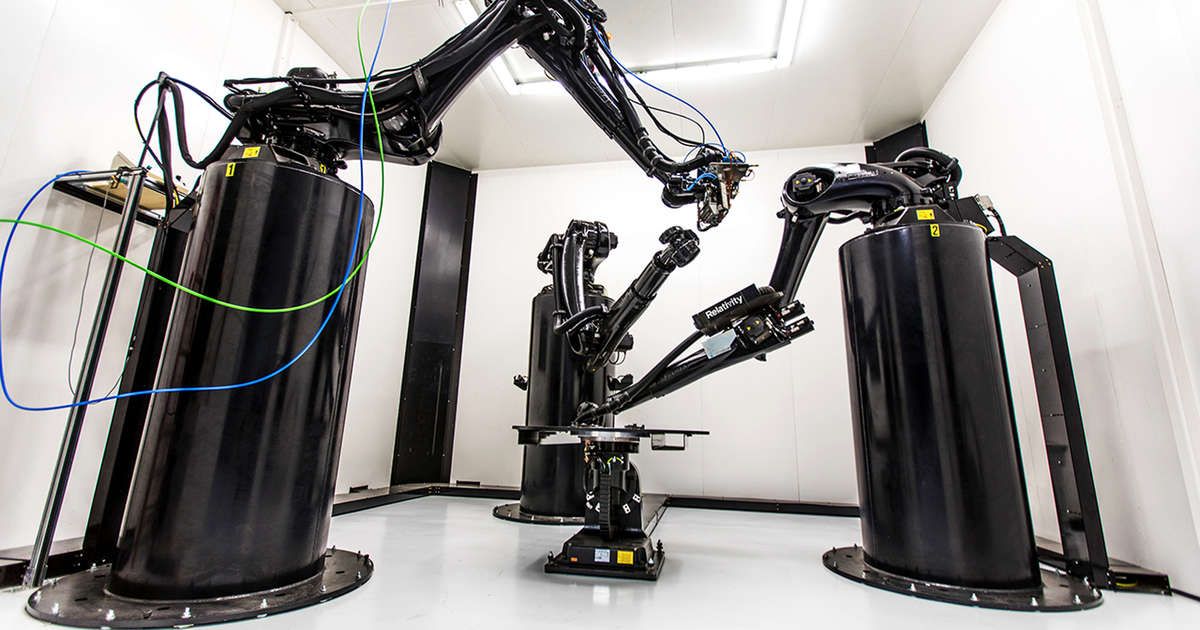
Companies that manufacture 3d printers
5 Biggest 3D Printing Companies
DDD, PRLB, and FARO lead the 5 biggest 3D printing companies list
By
Nathan Reiff
Full Bio
Nathan Reiff has been writing expert articles and news about financial topics such as investing and trading, cryptocurrency, ETFs, and alternative investments on Investopedia since 2016.
Learn about our editorial policies
Updated August 01, 2022
Reviewed by
Thomas Brock
Reviewed by Thomas Brock
Full Bio
Thomas J. Brock is a CFA and CPA with more than 20 years of experience in various areas including investing, insurance portfolio management, finance and accounting, personal investment and financial planning advice, and development of educational materials about life insurance and annuities.
Learn about our Financial Review Board
The manufacturing process known as 3D printing is one of the most promising and rapidly developing technologies with applications across a multitude of industries. 3D printing involves the additive layering of thin sheets of material that are fused together to create a physical product from a digital design. While the industry is currently hampered by relatively slow production times, advocates believe that 3D printing ultimately will have the capability to mass produce everything from medical equipment to automotive parts to airline components. Below, we look at the 5 biggest 3D printing companies by 12-month trailing (TTM) revenue. This list is limited to companies that are publicly traded in the U.S. or Canada, either directly or through ADRs. Some foreign companies may report semiannually, and so may have longer lag times. All data are from YCharts as of September 8, 2020.
- Revenue (TTM): $566.6 million
- Net Income (TTM): -$78.4 million
- Market Cap: $632.3 million
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: -24.6%
- Exchange: New York Stock Exchange
3D Systems invented 3D printing in 1989 with the development and patenting of its stereolithography technology, which uses ultraviolet lasers to help create highly precise parts. DDD built on that by developing new technologies, including selective laser sintering, multi-jet printing, film-transfer imaging, color jet printing, direct metal printing, and plastic jet printing. 3D Systems has three business units: products, materials, and services. The products category offers 3D printers and software and includes small desktop and commercial printers that print in plastics and other materials.
DDD built on that by developing new technologies, including selective laser sintering, multi-jet printing, film-transfer imaging, color jet printing, direct metal printing, and plastic jet printing. 3D Systems has three business units: products, materials, and services. The products category offers 3D printers and software and includes small desktop and commercial printers that print in plastics and other materials.
- Revenue (TTM): $451.0 million
- Net Income (TTM): $58.6 million
- Market Cap: $3.9 billion
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: 58.2%
- Exchange: New York Stock Exchange
Proto Labs was founded in 1999 with a focus on building automated solutions to develop plastic and metal parts used in the manufacturing process. The company expanded to launch an industrial-grade 3D printing service that allowed developers and engineers to move prototypes into the production process. The company's primary business services include injection molding, sheet metal fabrication and 3D printing.
- Revenue (TTM): $334.7 million
- Net Income (TTM): -$79.7 million
- Market Cap: $1.0 billion
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: 20.6%
- Exchange: NASDAQ
FARO specializes in 3D measurement and other services for the fields of architecture, engineering, and construction. With a 40-year history, FARO' began before the advent of 3D printing. The company's products include coordinate measuring machines, laser trackers and projectors, mappers, scanners, and software. FARO also serves the aerospace, automotive, and power generation industries.
- Revenue (TTM): $205.3 million
- Net Income (TTM): -$2.7 million
- Market Cap: $1.9 billion
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: 94.8%
- Exchange: NASDAQ
Belgian company Materialise has a 30-year history providing 3D printing solutions and related software. It provides platforms to facilitate the development of 3D printing applications in industries such as healthcare, automotive, aerospace, and art and design. Some of the company's first 3D printing activities included anatomical models in both dental and hearing aid products. Materialise also produces eyewear and automobile products.
Some of the company's first 3D printing activities included anatomical models in both dental and hearing aid products. Materialise also produces eyewear and automobile products.
- Revenue (TTM): $52.9 million
- Net Income (TTM): -$14.5 million
- Market Cap: $238.2 million
- 1-Year Trailing Total Return: 48.3%
- Exchange: NASDAQ
ExOne specializes in manufacturing 3D printing machines for customers across various industries. It also produces 3D printed products to specification for industrial customers. ExOne 3D printers utilize binder jetting technology, fusing powder particles of materials like metal or sand into molds, cores, and other products.
Article Sources
Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate.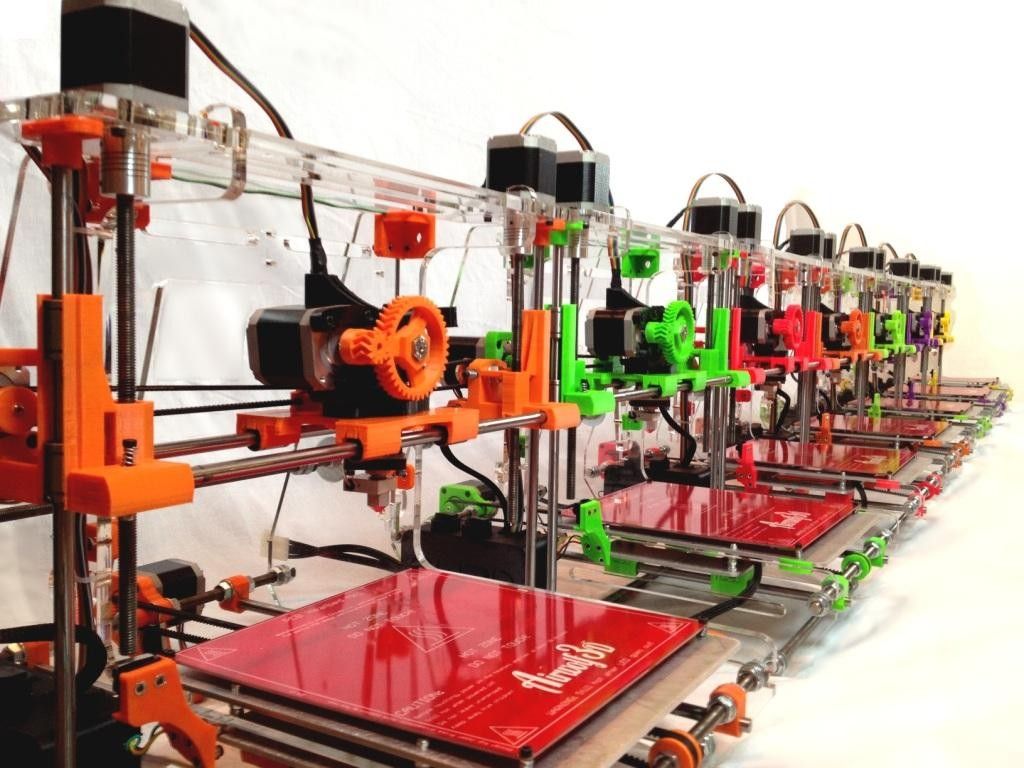 You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy.
You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in our editorial policy.
YCharts. "YCharts."
3D Systems. "Our Story."
Materialise. "Timeline."
25 Top 3D Printing Companies You Should Know 2022
Think of 3D printing as erosion in reverse. Bodies of water wear substances down layer by near-imperceptible layer; 3D printers build substances up in a similar way. Like all technology, of course, 3D printing isn’t nearly as old as the tides.
The concept dates back to the early ‘80s, when Dr. Hideo Kodama almost patented it in Japan. Due to a bureaucratic issue, though, Kodama’s patent never went through. Consequently, credit for 3D printing typically goes to Charles Hull, an American engineer who founded 3D Systems, the original 3D printing company, back in 1986. It made the first machines that could translate digital designs into 3D cured-resin artifacts.
Nowadays, 3D printing is a thriving industry. Modern printers range from desktop models to industrial giants to “bioprinters,” which can create human tissue. That’s not to mention the 3D-printing software, where objects get designed and optimized, and on-demand printing shops.
Modern printers range from desktop models to industrial giants to “bioprinters,” which can create human tissue. That’s not to mention the 3D-printing software, where objects get designed and optimized, and on-demand printing shops.
Here are 25 companies that are thriving in the 3D printing space.
Top 3D Printing Companies to Know
- GE
- HP
- Carbon, Inc.
- Glowforge
- Fast Radius
- 3D Fortify
- Markforged
- SprintRay
- Desktop Metal
- Divergent
25 3D Printing Companies to Know
Location: Boston, Massachusetts
The GE Additive team specializes in hardware, software and consulting services for 3D-printed metal parts. Utilizing direct metal laser melting and electron beam melting processes, the company’s additive machine hardware melt and layer metal powders to build custom part solutions. GE Additive products have created parts for use in orthopedic implants, aircrafts, automobiles and industrial manufacturing tools.
Location: Palo Alto, California
Known for its PC and related hardware, HP also offers personal 3D printers as well as 3D-printing software, services and varied materials. HP’s Jet Fusion printer series are multi-material compatible and scalable to manufacturing needs, with its Jet Fusion 5210 model able to print approximately 550 parts per week. The company’s 3D printing services have come in handy for industries ranging from aerospace to consumer goods and electronics.
Location: Boston, Massachusetts
3D Fortify relies on a magnetic system that arranges reinforcement fibers with a digital light processor. By arranging the fibers in the object, 3D Fortify can create high-strength tools for engineers. So far, the company’s products include FLUX printers, materials, software and applications.
Get Alerted for Jobs from 3D Fortify
Location: Somerville, Massachusetts
Formlabs makes various 3D printers, which range from desktop to industrial formats.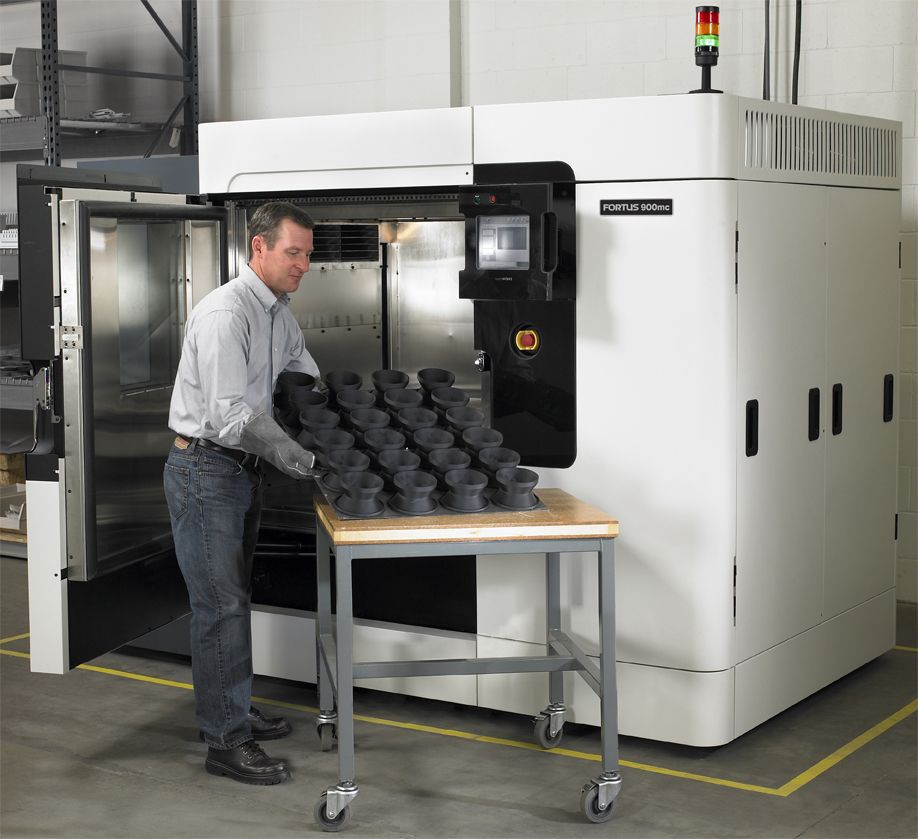 The Form 3 and Form 3L, two of the smaller styles, rely on laser light and a flexible tank of resin to print quickly and precisely. Both can create features as narrow as one thousandth of an inch, which comes in handy for printing New Balance’s new midsoles. Made from a substance called Rebound Resin, these bouncy creations look less like traditional foam and more like sprays of Spiderman’s webbing.
The Form 3 and Form 3L, two of the smaller styles, rely on laser light and a flexible tank of resin to print quickly and precisely. Both can create features as narrow as one thousandth of an inch, which comes in handy for printing New Balance’s new midsoles. Made from a substance called Rebound Resin, these bouncy creations look less like traditional foam and more like sprays of Spiderman’s webbing.
Location: Watertown, Massachusetts
Many 3D printers use plastic filament, but not those made by Markforged. Its industrial printers can print hardier substances, including nylon, carbon fiber and even metal — hence the “forge” in Markforged. (Continuing the metal theme, it also makes AI manufacturing software called Blacksmith.) Integrated into factories worldwide, this company’s printers reportedly have helped transform supply chains by accelerating prototype and replacement part manufacturing.
Location: Gaithersburg, Maryland
Xometry began as a way to simplify prototyping. Its software eliminated the need for companies to slowly and laboriously gather quotes from manufacturers. Instead, they could access six different types of 3D printers on demand and at instantly-quoted rates. That model has attracted high-profile clients like car manufacturer BMW, which relies on Xometry for custom trim, logos and other unique and tooling-heavy touches that are printed from carbon fiber tubing.
Its software eliminated the need for companies to slowly and laboriously gather quotes from manufacturers. Instead, they could access six different types of 3D printers on demand and at instantly-quoted rates. That model has attracted high-profile clients like car manufacturer BMW, which relies on Xometry for custom trim, logos and other unique and tooling-heavy touches that are printed from carbon fiber tubing.
Location: New York, New York
Focused less on 3D printing hardware than software, nTopology’s NTop Platform can be integrated into 3D printing engineering workflows. A standout feature: It can autonomously tweak and streamline existing designs, removing clunkiness and excess weight so designers can focus on more important problems and avoid busywork — whether they’re printing medical devices or rocket nozzles.
Location: New York, New York
Shapeways 3D prints designs on demand in a choice of more than 50 materials, including plastic, sandstone and platinum. Customers simply log in to the site, upload a design and place an order, which prints in one of the two Shapeways factories and arrives via mail. It’s online shopping, really, but instead of browsing the wares, shoppers design them. Shapeways also has a team of designers on hand to help users bring their visions to fruition.
Customers simply log in to the site, upload a design and place an order, which prints in one of the two Shapeways factories and arrives via mail. It’s online shopping, really, but instead of browsing the wares, shoppers design them. Shapeways also has a team of designers on hand to help users bring their visions to fruition.
Get Alerted for Jobs from 3D Systems Corporation
More on 3D PrintingPros and Cons of 3D Printing
Location: Rock Hill, South Carolina
The original 3D printing company remains on the cutting edge of the field. 3D Systems Corporation makes a broad spectrum of 3D printers, which work via stereolithography, a liquid-to-solid process, and a powder to solid process called selective laser sintering. Printers make everything from metal artifacts to plastic filaments to custom dental implants. 3D Systems also offers a constellation of related products, like 3D scanners and design software.
Get Alerted for Jobs from 3D Systems Corporation
Location: Seattle, Washington
This company’s namesake 3D printer, Glowforge, can print with almost any material. Kid-friendly and intended for home use, it creates custom designs from plastic, wood and even chocolate. Though it allows for creativity, that’s not required; the hardware comes pre-loaded with a catalog of cool designs for everything from monogrammed macarons to a wooden Settlers of Catan game board.
Kid-friendly and intended for home use, it creates custom designs from plastic, wood and even chocolate. Though it allows for creativity, that’s not required; the hardware comes pre-loaded with a catalog of cool designs for everything from monogrammed macarons to a wooden Settlers of Catan game board.
Location: Chicago, Illinois
Fast Radius has replaced old-school, centralized factories with a network of smaller “manufacturing lighthouses” — a move for which the company was named one of the globe’s leading factories by the World Economic Forum. At each of its fabrication plants, the company 3D-prints and injection-molds parts for industrial use and quickly ships them off. Its partnership with UPS, paired with the company’s distributed structure, means it can often offer next-day delivery, even on custom builds.
Location: Redwood City, California
This startup has a minimal web presence — it’s still in stealth mode — but it focuses on 3D printed buildings. Specifically, Mighty Building makes tiny-house-esque “backyard studios” with a massive printer that barely fits in a warehouse. The company offers three studio models so far, which max out at less than 600 square feet. That’s smaller than many studios, but the pint-sized standalone structures are surprisingly stylish and functional, outfitted with floor-to-ceiling windows and working bathrooms.
Location: Redwood City, California
Every 3D printing process involves fusing layers into a whole, but Carbon has reinvented the fusing process. Called Digital Light Synthesis, the technique smooths away the “seams” that 3D printing often produces. This creates a seamless finish, and a stronger product — traditionally 3D-printed objects’ strength can vary, depending on whether the nozzle moved clockwise or counterclockwise in production.
Location: Los Angeles, California
Divergent 3D aims to streamline and decentralize car manufacturing. That means moving production out of multi-million-dollar factories and into a networked cluster of 3D printing shops. In these smaller, warehouse-like spaces, the Divergent 3D team relies on end-to-end design software and industrial printers to create light, safe, fast cars. As of 2017, the company had prototyped two vehicle models: a motorcycle called the Dagger, and a sleek low-riding sports car called the Blade. (Cutting-edge, indeed!)
Location: Los Angeles, California
SprintRay is a 3D printing company specializing in dental products. The company’s RayWare software is specifically designed with dental professionals in mind as it pairs CAD automation and allows for connection to SprintRay’s printers, making modeling dental products more streamlined. The software also allows users to save edited models and export to other CAD services. In addition, SprintRay offers a host of 3D dental printers as well as cloud solutions that reduce the need for hardware and allow for more mobile printing.
Location: Burlington, Massachusetts
Desktop Metal condensed a steel mill into a box smaller than a refrigerator that easily fits through an office door. No special ventilation is required, and there’s no open flame, laser light or loose powder involved. It just needs power and an internet connection to 3D-print with steel. More specifically, this company’s printer extrudes rods of a powdered steel alloy, wax and polymer binder. (The company is developing copper and nickel filaments, too.) The printer first cooks away the binding. It then welds steel layers together in its furnace. Though it’s a very contained process, it’s also transparent — users can watch it unfold via livestream.
More on 3D PrintingFive 3D Printing Applications in Construction
Location: Waltham, Massachusetts
Nano Dimension’s combines 3D printing products with AI to create streamlined 3D-printed circuits and devices. Imbued with its DeepCube neural network, the company’s printers are able to detect and correct manufacturing errors in real-time, improving part quality and reducing material costs. In addition, Nano Dimension hosts surface-mount technology hardware and software for automated assembly needs.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Nano Dimension
Location: Solana Beach, California
With 3D-printed tissue, this company takes lab testing to the next level. Organovo’s bioprinting technology builds fabricated multicellular tissues, giving a wider three-dimensional view of cellular function and structure in comparison to views in a two-dimensional petri dish. Specialists can utilize these tissue creations to assess pharmacology and structural factors of a disease, and have already been able to simulate liver, kidney, bone and other cellular environments.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Organovo Holdings
Location: Miami, Florida
Rokk3r has helped more than 30 companies streamline their business plans with “exponential technologies.” (That means tech that helps them outperform competition by a factor of at least ten. ) Those technologies include blockchain, Internet of Things connectivity, and, you guessed it, 3D printing. The latter can exponentially reduce the number of parts required in complex manufacturing, which accelerates and simplifies the whole process.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Rokk3r Labs
Location: New York, New York
Though MakerBot printers have many industrial applications, the company also makes a newbie-friendly desktop printer, the Replicator+, that’s found in more than 7,000 classrooms. Makerbot complements that popular hardware with free lesson plans that incorporate 3D printers and are available via download or book form. In one suggested earth science lesson plan, for instance, students print models of different cloud types to literally grasp the distinction between cumulus and cirrus. And that’s just one of the new options Replicator+ opens up for students who learn best through touch and action.
Get Alerted for Jobs from MakerBot
Location: San Mateo, California
This company specializes in 3D printing for gamers. Whether clients want custom board game pieces or 3D-printed replicas of their ship in the Star Trek video game, Mixed Dimension’s printer can make it happen. Capable of more than 10 million colors, it’s high-resolution enough for photo-caliber projects. Users can upload screenshots or CAD designs of their desired spaceship, or work with staff artists to turn imagined gaming tableaus into 3D realities.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Mixed Dimensions
Location: Eden Prairie, Minnesota
Stratasys has been in the 3D printing industry since 1988 — almost as long as 3D printing has existed. During that time, it has racked up more than 250 granted or pending patents worldwide. Today, the company helps clients like Audi and Lockheed Martin perfect their manufacturing process with 3D printing. It also manufactures printing hardware for Hewlett-Packard as well as its own brands. Ever the industry leader, Stratasys remains on the cutting edge, especially when it comes to recycling. Clients can send used cartridges, print engines and other parts back to the company for green disposal.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Stratasys
Location: Cambridge, Massachusetts
CELLINK focuses on “bioprinting,” the 3D printing of bone, cartilage, and, maybe someday, functioning human organs. Any and all of that is possible with the company’s patent-pending universal bioink — a soup of stem cells and alginate derived from brown seaweed. More than 700 labs worldwide currently use the substance. The company also makes complementary technology: 3D printers, software and specialty inks designed for specific types of tissue.
Get Alerted for Jobs from CELLINK
Location: Maple Plain, Minnesota
Protolabs speeds up the manufacturing process. As its name suggests, the business began as a quick-turnaround prototyping company. In 2014, however, it added a 3D printing shop to speed the transition between the prototyping phase and small batch testing. That shop now has more than 100 printers that can print metal, plastic and other materials.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Protolabs
Location: Leuven, Vlaams-Brabant, Belgium
Materialise focuses on 3D printing software, which makes complex printing hardware accessible to engineers, healthcare professionals and even fashion designers. Designer Anoul Wipprecht, for example, used Materialise software to print a surreal, bubble-wrap-like dress that also tracks the wearer’s mood. The company’s comprehensive digital suite includes tools for drafting and optimizing designs, controlling printers mid-job and managing 3D printing workflows.
Get Alerted for Jobs from Materialise
Largest listed companies in the 3D printing sector
3D printing dates back to the late 1980s. At the end of 2018, the size of the 3D printing market, according to various estimates, reached from $9 trillion to $10 trillion. Calculations were made based on the cost of producing printers, components and 3D printing.
In the coming years, expert agencies (IMARC, Inkwood Reasearch, Marketwatch, etc.) predict a steady growth of at least 20% per year. In this scenario, by the end of 2025, the scale of the entire 3D printing segment will reach at least $ 32 trillion - 3.5 times higher than the current values.
The outlook for the sector makes it attractive to investors. Consider the largest and most stable companies in this segment, whose shares can be considered for purchase and take their rightful place in your portfolio.
1. HP Inc Capitalization: $29.3 billion
HP manufactures computers, printers, tablets and a number of other devices. The release of 3D printers is not the main specialization of the company, but in the 3D printing segment, HP occupies one of the leading positions. In 2014, the company developed Multi Jet Fusion technology, which increased productivity and reduced the cost of professional (industrial) 3D printers. The technology has been successfully applied in mass production of printers since 2016.
In 2017, HP opens the world's first 3D lab, equipped with printers in various build states and essential tools for device experimentation. The company has opened up the first opportunities to test new materials in 3D printers to increase efficiency.
In 2018, HP will open a manufacturing center with China's Guangdong in Guangdong, China, which is the largest such 3D printing project in Asia Pacific and Japan. The facility is equipped with ten next-generation high-tech HP Metal Jet printers to produce parts and prototypes for industrial customers.
2. Proto L abs (NYSE: PRLB). Capitalization: $2.56 billion
The company was founded in 1999 and has more than 10 production sites in seven countries. The head office is located in Minnesota. The company specializes in the production of parts for other manufacturing companies. The corporation positions itself as the fastest in the world in the production of custom prototypes and finished parts for industrial customers. In 2014, Proto Labs launched 3D printed parts.
In addition to 3D printing, the company produces CNC (Computer Numerical Control) parts, injection molding and sheet metal parts. In 2015, Proto Labs bought Alphaform (specializing in innovative 3D printing) with divisions in Germany, Finland and the UK. This allowed the company to expand its 3D printing business in Europe. To diversify its business and introduce sheet metal manufacturing, the company acquired Rapid Manufacturing in 2017 for $120 million. 9 Systems ( NYSE: DDD). Capitalization: $1.01 billion
3D Systems was founded by inventor Chuck Hull in 1986 as the world's first 3D printing company. It produces 3D printers and components, including software, and also designs them. The company provides services at various stages of design, development and production of products for many large industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, entertainment and other areas. It should be noted that the corporation also works with retail consumers. Business diversification within the 3D segment makes the company financially stable.
3D Systems is headquartered in Rock Hill, South Carolina, USA. The number of employees of the company exceeds 2600 (as of the end of 2018), which is twice as high as five years ago.
4. Stratasys ( NASDAQ: SSYS). Capitalization: $0.98 billion
The company was founded in 1989 by Scott Crump. The technology was based on the idea of creating the shape of a figure by layering after Scott decided in 1988 to make a toy toy for his daughter using a gun filled with glue. At 1992 Stratasys released its first 3D Modeler product.
Today, Stratasys manufactures industrial and desktop 3D printers and related accessories. The range of services includes installation, maintenance and training in working with printers. The company serves various industries by developing technologies for the production of prototypes and parts. The first public offering of Stratasys shares took place in 1994 at $5 per share and a total volume of $5.7 million. The head office is located in Minnesota.
5. Materialize Capitalization: $0.88 billion
Incorporated in 1990 in Leuven, Belgium, Materialise specializes in 3D printing services and 3D printer software. Like other leaders in this sector, Materialize works with various major manufacturers around the world (Adidas, HP), but a significant share of the business is in cooperation with medical centers and institutions. The company's portfolio includes more than 150 medical patents. Materialize offices are located in 18 countries, including one office located in the CIS in Ukraine.
Issuer Comparison
The most valuable company among the leaders is HP, which is due to the scale and diversification of the company's business in the entire technology segment. 3D Systems, Stratasys and Materialize specialize exclusively in the 3D printing segment, while their capitalization is on the same level. Proto Labs has three businesses besides 3D printing and is in the middle of our list in terms of capitalization.
The most undervalued company in terms of EV/EBITDA is HP, but it is not correct to compare it with other issuers by this multiplier due to the differentiation of the company's products and services. 3D Systems has the highest EV/EBITDA, and from this point of view, the paper is not so attractive to buy. Moreover, over the past four years, 3D Systems shares have been in a stable sideways trend without technical prerequisites for growth.
The remaining three companies, in our opinion, may be of interest. At the same time, if your long-term goal is to get the maximum increase from the growth of the 3D printing sector, then investing in HP shares is less preferable compared to other securities. After all, the reaction of the shares of companies with a direct specialization is more sensitive to changes in the sector. Below are the consensus forecasts of investment houses according to Reuters, according to which Stratasys (14. 9%) and Materialize (13.6%) shares have the greatest potential now.
HP Inc (NYSE: HPQ): $20.5 (+3.4%)
Proto Labs (NYSE: PRLB): $98.7 (+3.0%)
3D Systems (NYSE: DDD): $8 .6 (+0.6%)
Stratasys (NASDAQ: SSYS): $20.8 (+14.9%)
Materialize (NASDAQ: MLTS): $19.2 (+13.6%)
OPEN ACCOUNT
BCS Broker
Top 10 companies in the field of 3D printing listed on the stock exchange
So, we present to your attention the rating of companies in the field of 3D printing in terms of annual turnover.
Stratasys: $750 million
Industry leader Stratasys grew 54% over the past year with sales exceeding $750 million. This is partly driven by demand for the new Object500 Connex3 model, as well as the traditionally popular PolyJet and industrial FDM 3D printers. Another growth driver was the acquisition of other companies such as Solid Concepts and Harvest Technologies (now part of Stratasys Direct Manufacturing). At the same time, the American-Israeli company (which includes, among other things, MakerBot Industries and SolidScape) recorded a net loss of $119 in its financial statements.million. This figure is more than four times higher than last year, which is also due to active acquisitions and investments. The forecast for 2015 is positive, it is expected that the revenue will be $940 million. If Stratasys manages to beat expectations by 6%, it could become the first pure 3D printing company to reach $1 billion in revenue.
3D Systems: $650 million
Although 3D Systems' revenue rose 27% to a record high, the company still lost the top spot to Stratasys last year. The head of the company, Avi Reichental, said he was not entirely satisfied with how the company realized the potential of its technology portfolio. 3D Systems has some of the most advanced 3D printing technology in the industry, but hasn't shown enough willingness to go mainstream. However, according to 3D Systems financial statements, the company turned out to be in positive territory with a net profit of $1. 6 million at the end of the year. Although the forecast for 2015 is generally positive, it is likely that 3D Systems will again be behind Stratasys, with revenues of $850-900 million.
Materialize: $81 million
Materialize is one of Europe's leading 3D printing service providers and a developer of innovative 3D printing software. In 2014, the company's revenue amounted to $81 million, which is 18.4% more than last year. The company's net profit reached $1.8 million, half of what it was in 2013, but still significant. Materialize's core business is the development and sale of 3D printing software (22% of sales) and medical 3D printing services (37%). The industrial segment, including the i.materialise 3D printing service, generated 40% of the company's total revenue. Materialize is expected to grow by 20% next year and reach €100 million in annual turnover.
ExOne: $43.9 million
Last year, ExOne grew by 10% with revenues of approximately $43. 9 million. The main contribution to this result was made by the fourth quarter, during which sales increased by 50%. This state of affairs resulted in a gross profit of $10 million, but ExOne's operating costs were $21 million. This was mainly due to investments in the expansion of the company (new production facilities in Russia and Italy), as well as research and development (more than $8 million). In addition, ExOne announced the creation of a new large-scale 3D printer, Exerial.
Arcam: $39 million
Arcam, a Swedish manufacturer of electron beam melting (EBM) systems, recorded revenues of approximately $39 million. Thus, sales grew by 70% in a year, and profits exceeded $6 million. However, it is likely that in the financial markets such results were considered too good to be true. Compared to a record high at the end of 2013, Arcam's shares are down more than 70% and are now trading for around $17.
SLM Solutions: $36 million
Germany's SLM Solutions posted similar results to Arcam, with record earnings of approximately $36 million and 56% growth in 2014. At the same time, the company's shares fell from a record high of €21 to €18. However, SLM Solutions boasts a more stable stock price than most other members of the 3D printing industry. At the moment, for the past period of 2015, SLM Solutions reports an increase in the number of orders twice year-on-year.
Alphaform: $30 million
German company Alphaform offers rapid prototyping services. Alphaform made its first steps in the consumer market as part of the Artshapes project to apply 3D printing to the arts. The company reported record revenue of $30 million in 2014, up 11.6%. While Alphaform lost more than $3 million in the same period, this is a significant improvement from $6.5 million in 2013.
voxeljet: $17-18 million
Analysts have criticized the German company voxeljet for not selling enough devices while offering special deals to customers to increase orders. However, it should be taken into account that voxeljet manufactures large industrial equipment, the print volume of which reaches 8 cubic meters - in other words, the company occupies a very specific niche. Estimated revenue for 2014 (updated data will be available at the end of March) is $17-18 million. In addition, according to voxeljet forecasts, the company expects to grow by almost 50% this year.
Organovo: $0
Organovo is the only listed biomaterials 3D printing company. However, most of Organovo's activities are still research and the first commercial product, exVive3D human liver tissue, was released just recently. The company has created its own bioprinter and uses it to 3D print organic tissues, which it then sells to major pharmaceutical companies for research purposes. The company's annual operating costs are approximately $20 million. At the same time, Organovo is confident that its products can bring more than $100 million in profit in the foreseeable future.
Renishaw: data not available
Rounding out the top ten was British company Renishaw, which recorded revenue of $520 million and a slightly lower profit of $100 million.