Best cad for 3d printer
Best CAD Software for 3D Printing - 2023 CAD Programs
The best CAD software for 3D printing is going to depend on two main factors: the nature of your project, and your experience using CAD programs for 3D prints.
In this guide I’ll walk you through my experience with the most popular 3D printing CAD software, comparing them across functionality, price, and who they would suit best – so you can make a confident decision.
My top recommendation for creative and artistic applications is Blender, while FreeCAD and Fusion 360 are more focused on engineering and technical applications.
Both Blender and FreeCAD are free and open-source, but the $60 pricetag or Fusion360 still represents good value because it’s the most comprehensive and powerful software of the three.
For complete beginners, TinkerCAD does the best job of simplifying the process of creating 3D models. Rookies should start with this free, browser-based software.
We’ll also discuss professional picks like SolidWorks and CREO. They’re expensive – and way beyond the needs (and budget) of most users – but worth considering if you need best-in-clas quality.
Table Of Contents
- Best CAD Software for 3D Printing (for Hobbyists & Professionals) – Full Round-Up
- How Does CAD Software Work With 3D Printing?
- Best CAD Software for 3D Printers
- Blender
- FreeCAD
- Fusion 360
- SolidWorks
- CREO
- TinkerCAD
- SketchUp Free
- Best CAD Software for 3D Printing Buyer’s Guide – Things To Consider
- What You Plan On 3D Printing
- Your 3D Printer’s Quality and Type
- File and Slicer Compatibility
- Best CAD Software for 3D Printing – FAQs
- What is the best CAD software for 3D printing?
- What is the best free CAD software for 3D printing?
- Can CAD software export STL files for 3D printing?
Top Picks
Best CAD Software for 3D Printing (for Hobbyists & Professionals) – Full Round-Up
- Blender
- FreeCAD
- Fusion 360
- SolidWorks
- CREO
- TinkerCAD
- SketchUp Free
How Does CAD Software Work With 3D Printing?
CAD software gives you tools to create a 3D model from scratch that can then be processed, sliced, and sent to a 3D printer for printing.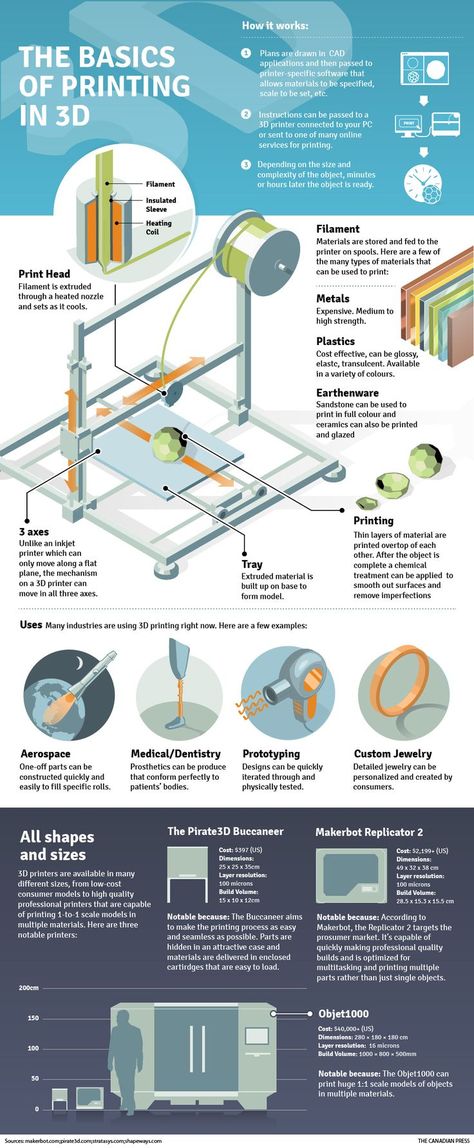
It’s the starting point from which a fully formed 3D model emerges, a digital blank canvas that allows you to transform an idea or concept into a real-world 3D printed object.
On a more granular level, CAD software for 3D printing also allows you to export it to a file format, such as STL or OBJ, compatible with and ready for slicing.
3D slicing software then translates the model into a set of G-code instructions interpretable by a 3D printer.
The printer can then print a physical, real-world replica of the CAD software-created digital model.
Best CAD Software for 3D Printers
Blender
- Price: Free, open-source
- Supported 3D Printing File Formats: STL, OBJ
- Operating System Support: Windows, macOS, Linux
Blender is an open-source CAD program that leans heavily towards the artistic side of computer-aided design. It’s one of the most expansive and feature-rich free modeling software for 3D printing.
The software features a potent trove of features and tools suited to creative applications, including modeling, simulation, animation, digital art, video editing, and much more.
Though not innately geared towards 3D printing, the relatively new 3D Print Toolbox and Mesh Analysis features take strides to make Blender a far more 3D printing-friendly program.
Here, the idea is to simplify and process the often very complex polygonal models made with Blender to achieve better 3D printer results.
These new features include a series of checks and fixes that refine and clean up any model for export with 3D printing in mind. These include checking scale and measurement, wall thickness, edges, overhang geometry, support positioning, and hollow areas.
Although not a new addition, Blender also offers export to a selection of the most popular 3D printing formats, including STL.
Aside from this, Blender features a full-fledged modeling and sculpting toolbox to create high-quality 3D models. If anything, Blender suffers from this versatility and comes sided by a hulking learning curve, which means beginners may be overwhelmed by what’s offered here.
If anything, Blender suffers from this versatility and comes sided by a hulking learning curve, which means beginners may be overwhelmed by what’s offered here.
FreeCAD
- Price: Free, open-source
- Supported File Formats: STL, OBJ
- Operating System Support: Windows, macOS, Linux
FreeCAD is a free CAD software best described as a Swiss Army knife for all kinds of 3D modeling.
It’s a parametric modeler, meaning every aspect of a model is updated when changing a single parameter, part, dimension, or rule. Despite FreeCAD’s drab interface, the program is a powerful design tool that lends itself well to 3D printing.
FreeCAD works based on Workbenches, or toolsets, with different functions.
In the case of 3D printing, the interesting ones are Part and Part Design, which have a range of sketching, constraint, and modeling functions to create 3D models based on a library of geometric shapes.
There’s also a Mesh Workbench, which contains analysis and repair tools to iron out any potential errors that could lead to a failed print.
From there, FreeCAD allows you to export your model to the STL format, among others, and send it to a slicer program to 3D print cad files.
Fusion 360
- Price: Limited free version (non-commercial license) or $60/month
- Supported 3D Printing File Formats: STL, OBJ
- Operating System Support: Windows, macOS
Our top pick for the best CAD software for 3D printing, Fusion 360 is developed by AutoDesk, the company behind AutoCAD, Maya, and other leading CAD, animation, and visual effects programs.
Although intuitive to use and laid out for simplicity, Fusion 360 is a potent CAD tool that houses a dizzying array of professional 3D design, modeling, machining, schematics, and simulation tools.
It’s also a potent tool for creating models for 3D printing and easily one of the best CAD program for 3D printing
Useful features include many you’d usually expect in slicers, such as automatic orientation, infill patterns, support structures, and a print simulation tool to verify the integrity of the build process before sending it to a 3D printer.
In essence, Fusion 360 covers every step from design to model and part preparation.
There’s a free limited non-commercial version available for hobbyists and personal use. Alternatively, you can pay $60/month for the full version, which throws in fully-featured CAM, CAE, and PCB tools along with collaboration features and access to an unlimited number of active projects.
SolidWorks
- Price: Limited free trial, $4,000/year
- Supported 3D Printing File Formats: STL
- Operating System Support: Windows, MacOS
SolidWorks is a professional-grade 3D printing CAD software launched way back in 1995.
Although it houses state-of-the-art modeling tools, SolidWorks is relatively easy to use and is often praised for its clean user interface and intuitive workflow.
SolidWorks allows you to adjust model settings in preparation for 3D printing.
These include resolution fine-tuning, tolerance deviations, and visualization tools to ensure a model won’t result in a failed print. You can export models to STL, ready for slicing.
You can export models to STL, ready for slicing.
SolidWorks costs a pretty penny at $4,000 a year for the most basic licenses, so it isn’t a viable choice for amateurs and hobbyists, who’d be better served with a less feature-rich but far more affordable alternative such as Fusion 360.
CREO
- Price: 30-day free trial, $2,000-$3,000/year
- Supported 3D Printing File Formats: STL
- Operating System Support: Windows, Linux
Creo is CAD software designed for solid 3D modeling for the most demanding applications and industries.
It’s through and through a professional application, making it particularly suited to uses where high-quality, precise 3D prototypes and models are required.
Beyond a comprehensive suite of design and modeling tools, Creo allows users to optimize designs for 3D printing by detecting potential errors, providing optimal print positioning, and offering support simulation.
Creo can also export models in the STL file format.
Creo is notoriously challenging to master because it’s geared towards the most complex CAD needs and requirements. As such, we can’t recommend it for beginners, but only to seasoned professionals and businesses.
The price of entry is also very high – around $2,000 to $3,000 for a year-long license.
TinkerCAD
- Price: Free
- Supported 3D Printing File Formats: STL, OBJ, GLB, SVG
- Operating System Support: Browser-based
If the thought of firing up a complex, professional free modeling software for 3D printing has you worried, then TinkerCAD should be your go-to first and best CAD for 3D printing.
Schools and educators favor TinkerCAD across the globe for its effortless ease of use, intuitive design, and colorful interface.
It’s no exaggeration to say it’s the most accessible CAD software for 3D printing.
The design phase is a walk in the park, using a Lego-inspired shape-based approach that’s easy to pick up.
You modify shapes, tune colors, adjust dimensions, add texts, include holes, and more effortlessly. If you want the quickest path from a simple idea to a 3D model to a real-world printed part, no program makes it as easy and fast as TinkerCAD.
Developer AutoDesk also provides an extensive library of tutorials, learning resources, and projects to help you make that first step to creating a CAD design for 3D printing.
As a browser-based program, TinkerCAD works on virtually any device and offers STL and OBJ exporting for slicing.
SketchUp Free
- Price: Free
- Supported 3D Printing File Formats: STL
- Operating System Support: Browser-based
SketchUp Free is a free browser-based CAD program used to create high-quality 3D models and designs without navigating complex systems.
It’s particularly forgiving to beginners, thanks to being a fun and very predictable way to dabble in 3D design for 3D printing for the first time. Getting to grips with basic navigation and functions takes minutes.
Getting to grips with basic navigation and functions takes minutes.
Every model starts from a basic geometric shape, which can then be modified, scaled, added to, and subtracted from to create solid models for 3D printing.
Furthermore, SketchUp Free features a free library of user-generated and manufacturer-produced 3D models, the 3D Warehouse, which can be used to spark inspiration, find a part to fit a particular build volume, or remix a model that’s already been vetted for 3D printing success.
Because SketchUp Free runs on any browser and has a companion SketchUp Viewer app to visualize models from a mobile device, it’s the perfect CAD program if you’re often on the move.
It also exports to all your favorite 3D printing file formats like STL.
Best CAD Software for 3D Printing Buyer’s Guide – Things To Consider
What You Plan On 3D Printing
Simply put, this is about complexity and choosing a CAD Software for 3D printing capable of bringing your ideas to life.
While valuable tools for beginners, programs like TinkerCAD can only help you create pretty rudimentary models due to their reasonably limited toolset.
On the other hand, when using professional programs like Fusion 360 and SolidWorks stacked with advanced features, you’re only ever hemmed in by your skillset, experience, and the quality of your modeling ideas rather than the software itself.
In other words, if you plan on creating and 3D printing intricate, feature-rich models, be sure to use advanced CAD software.
The more beginner-friendly options will serve you well if you’re simply testing the waters or only have a basic print in mind.
Your 3D Printer’s Quality and Type
Spending hours modeling a pristine 3D model only to find out your 3D printer isn’t up to the task is not an experience we recommend to anyone.
As such, it’s essential to be well aware of your printer’s capabilities and choose a CAD Software that matches your 3D printing needs.
This is especially important if your model includes overhangs, sharp outward angles, precise surface details, or requires support structures. All these add complexity to the printing process, and not all printers are up to the task.
The type of technology underpinning your printer matters, too.
While cheaper and better suited to larger prints, FDM printers often fail when it comes to printing small, high-detailed models. On the other hand, resin printers excel at doing just that, prized for their ability to pump out high-resolution prints with plenty of fine detail and texture.
Look at your printer’s resolution and minimum layer height to get an idea of what level of detail you can expect.
File and Slicer Compatibility
Consider what file types a particular CAD software for 3D printing supports, especially export formats.
These largely determine compatibility with slicing software. Working hours on a model only to find out the program can’t export to a supported format is something you want to avoid.
As a rule of thumb, opt for CAD software for 3D printing that includes STL exporting at the very least.
Best CAD Software for 3D Printing – FAQs
What is the best CAD software for 3D printing?
Shoving the critical question of cost to the side for a moment, Fusion 360 is one of the best CAD software for 3D printing around.
It bundles all the features and tools you’d conceivably ever need to create any 3D model, along with easy exporting for slicing your work ready for 3D printing.
It’s widely used by professionals in numerous fields, rubbing shoulders with the likes of AutoCAD as one of the most respected and accessible fully-featured CAD programs available today.
What is the best free CAD software for 3D printing?
It depends on your aims.
For beginners looking for a fun and easy route into CAD design, little rivals TinkerCAD’s simplicity and user-friendly appeal. A complete novice will be designing within a matter of minutes.
For more advanced users and professionals, free open-source options like Blender and FreeCAD are better because they offer a vastly broader palette of tools and features. The resulting models are far more complex and hit a quality threshold suitable for professional applications.
The resulting models are far more complex and hit a quality threshold suitable for professional applications.
Can CAD software export STL files for 3D printing?
Yes, most CAD software for 3D printing can export models in the STL file format for 3D printing, pending processing through a slicer program.
However, we recommend checking the respective feature list of the program you have your eye on to double-check this is indeed the case before committing to a purchase.
Other articles you may be interested in:
- Cura vs Slic3r
- The best free CAD software
- The best 2D CAD software
- Best 3D rendering software
- Best 3D sculpting software
- The best CAD software for beginners
The Best CAD Software for 3D Printing
Welcome to the Thomas guide to the best 3D printing software 2023. Thomas has been connecting North American industrial buyers and suppliers for more than 120 years. When you purchase products through our independent recommendations, we may earn an affiliate commission.
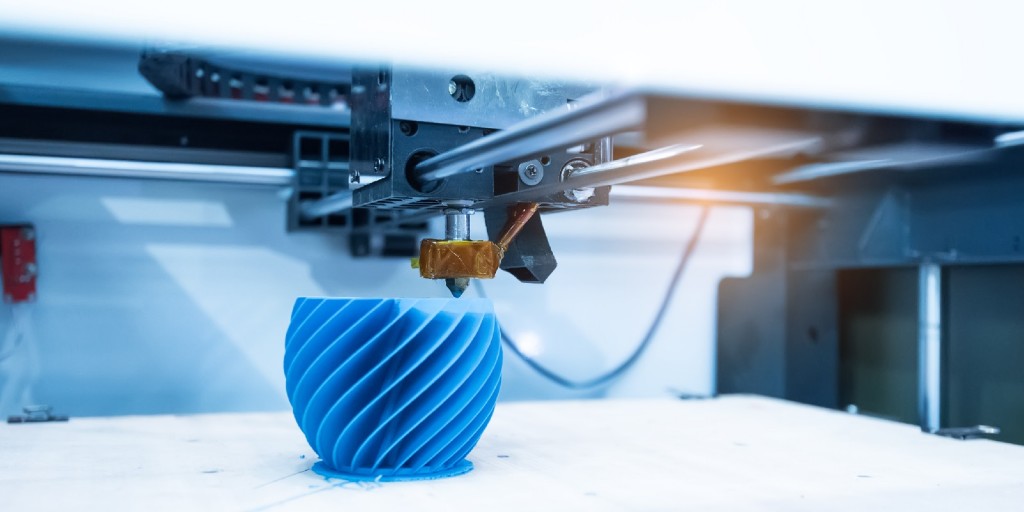
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is one of the most powerful design tools for realizing ideas. CAD software allows users to digitally represent 3-dimensional projects, and this software is incredibly versatile as a design, analysis, and manufacturing tool. With the recent popularity of additive manufacturing (AM) technology, CAD software is now more valuable than ever as a means of planning and printing models using 3D printers. There are numerous types of CAD/CAM software available that pair well with 3D printing technology, so this article will help those interested in CAD software find the best ones for 3D printing applications.
Image credit: Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock.com
What is CAD/CAM Software?
CAD software allows users to plan and digitally build the geometry, size, and framework of a project as well as define its material and functional properties. CAD software was invented to increase design productivity, as previous design techniques required lots of fabrication using physical materials. Thanks to powerful computers with CAD programs installed, users only need electrical power to create models that are more accurate and more detailed — all made in less time than with traditional methods. CAD finds uses in nearly every industry now and is used to perform such tasks as:
Thanks to powerful computers with CAD programs installed, users only need electrical power to create models that are more accurate and more detailed — all made in less time than with traditional methods. CAD finds uses in nearly every industry now and is used to perform such tasks as:
- Creating and preparing designs for AM applications (3D printing)
- Creating renderings for products in development
- Managing assemblies by cataloging a design’s bill of materials (BOM)
- Documenting databases of common/industry-standard part models
- Simulating stress, thermals, aerodynamics, etc. as well as generative-based design for optimization
- Determining clearance issues/motion of an assembly
- Reverse-engineering existing products using imported real-world 3D scans
- Texture mapping, material analysis
and more.
It is difficult to speak on every type of CAD software, as some programs specialize in application-specific directions. For example, freeform modelers allow the user to “sculpt” objects out of a digital base mesh just as a sculptor would use clay, while solid modelers start with a blank workspace, and users add and subtract geometries to create new features. Depending upon the application, either software may be the best fit or may lengthen design times. Luckily, many companies are creating hybrid CAD programs that allow users to implement many different CAD approaches.
For example, freeform modelers allow the user to “sculpt” objects out of a digital base mesh just as a sculptor would use clay, while solid modelers start with a blank workspace, and users add and subtract geometries to create new features. Depending upon the application, either software may be the best fit or may lengthen design times. Luckily, many companies are creating hybrid CAD programs that allow users to implement many different CAD approaches.
3D printing technology has had a huge impact on CAD/CAM software. Every 3D print requires a 3D model blueprint, and as a result, many CAD programs include support for AM applications. Depending upon the specific program, certain features are included such as model slicing, file compatibility/transfers, virtual reality connectivity, scaling for different printers, geometry touch-ups, and more. Most CAD software provides for exports to file types used in 3D printing (.STL files), meaning a model built in one environment can quickly be transferred to other compatible software.
Though versatile tools, CAD programs require practice to wield effectively which splits up the market based on skill. Beginner programs are often free and provide more basic functionality in place of an easier user experience overall. More advanced programs are often very expensive and have an extensive array of capabilities barred behind a higher learning curve. This article will contain CAD software on both ends of the spectrum, but note that more advanced programs are more often used in industry and are therefore more popular.
Here is a list of the best 3D printing software, followed by a buying guide to help you select the best 3D printing software for your needs.
Thomas’ Top Picks for the Best CAD/CAM Software for 3D Printing 2023
Below is the best CAD/CAM software for 3D printing. This list is not in a particular order and includes entry-to-advanced level software, each with its own unique benefits.
Best Overall Software: Autodesk Fusion 360® | Buy Now
Best Single-Part 3D Modeling Software: SOLIDWORKS | Buy Now
Best Freeform Modeling Software: Rhinoceros 3D | Buy Now
Best Professional Mechanical Software: Autodesk® AutoCAD® | Buy Now
Best Entry Level 3D Modeling Software: Sketchup | Buy Now
Most Advanced Modeling System: CATIA 3D Innovator | Buy Now
Best Multi-Functional Modeling Software: Creo® | Buy Now
Most Advanced CAD Software: Siemens NX | Buy Now
Best Collaborative Modeling Software: OnShape | Buy Now
Scroll down to read more about the best CAD/CAM software for 3D printing to choose the right one that will work for you.
*Prices listed in this article were as shown in US$ on the websites of the following companies as of December 2022.
1. Best Overall Software—Autodesk Fusion 360
®Autodesk® Fusion 360® provides full control of designs with cloud-based collaboration in freeform, solid, and mesh modeling. Fusion 360® is entirely free for students and startups and allows for parametric solid modeling in seven different workspaces. Fusion 360® can perform mechanical, vibratory, thermal, and impact analysis in its simulation workbench, as well as provide shape optimization and optional generative design features that are ideal for 3D printing applications.
Fusion 360® is especially useful in 3D printing applications, as well as users without the computational power to handle more resource-intensive programs. It is free for students/startups or is available with a paid subscription for non-students.
2. Best Single-Part 3D Modeling Software—SOLIDWORKS
Dassault Systemes’s SOLIDWORKS is an industry standard for experienced 3D designers and is considered the most widely used professional CAD software. Based on constraints, models are not sculpted but built out of extrusions and tightly interconnected shapes, making it more restrictive than other programs. The benefit is that SOLIDWORKS will dynamically update designs as they are redefined.
SOLIDWORKS also natively saves files as STL files and will help optimize 3D print quality and reduce support structures. Both its price point and difficulty level are not for beginners, but SOLIDWORKS is a versatile professional tool that can model, surface, assemble, simulate, analyze, render, mesh, and optimize designs. It is a subscription-based service and is available on a request basis.
BUY NOW: From US$99 Per Year, SOLIDWORKS3.
 Best Freeform Modeling Software—Rhinoceros 3D
Best Freeform Modeling Software—Rhinoceros 3D Rhino3D is a feature-packed 3D modeling software for architectural, automotive, furniture, footwear, landscaping, computer graphics, and other curve-based modeling applications. By using NURB mathematical modeling, Rhino3D adds dimensions and free-flowing shapes in any viewpoint. Its wide array of features allows users to create complex 3D models — granted that they have the skills to implement them.
Rhino is notoriously difficult, and for that reason, it is an advanced CAD software best suited for professionals already familiar with the 3D modeling process. Rhino models are importable to SOLIDWORKS, IGES, OBJ, SketchUp, AutoCAD, MicroStation, STEP, STL, and other formats. Rhinoceros 3D comes in a variety of packages for paid plans.
BUY NOW: From US$195 Per Year, Rhinoceros4. Best Professional Mechanical Software—Autodesk
® AutoCAD®
AutoCAD® is another Autodesk product and an interesting addition to this list, as it is originally built for 2D projects and non-parametric designs. Used by architects, interior designers, fine artists, engineers, and others, AutoCAD® is a fully professional software with a variety of features and supported file types for maximum compatibility with other programs.
Used by architects, interior designers, fine artists, engineers, and others, AutoCAD® is a fully professional software with a variety of features and supported file types for maximum compatibility with other programs.
AutoCAD®’s Mechanical software package is ideal for AM applications as it includes mechanical design modification, direct-to-print commands, and easy file translations across software or storage locations. AutoCAD® also includes a mobile app and cloud-based storage, and while not for beginners, AutoCAD® combines the versatility of high-end programs with an easier learning curve.
BUY NOW: US$235 Per Month or US$1865 Per Year, Rhinoceros5. Best Entry Level 3D Modeling Software—Sketchup
SketchUp by Trimble, Inc., is an entry-level 3D modeler popular amongst architects, landscapers, and general visualization applications. SketchUp comes in web-based and desktop formats, making it highly flexible for individuals without computing power. It also comes with access to a massive library of existing models in its 3D Warehouse, which includes furniture, appliances, and other common objects.
SketchUp comes in web-based and desktop formats, making it highly flexible for individuals without computing power. It also comes with access to a massive library of existing models in its 3D Warehouse, which includes furniture, appliances, and other common objects.
SketchUp can draw complex curves, chamfers, and fillets, do meshing and product documentation, and export files to STLs for 3D printing applications. Though not nearly as intensive as others on this list, SketchUp is both free and highly accessible to those without significant CAD experience, making it a great choice and one of the best entry-level software applications on the market. SketchUp provides a free version of its software, as well as subscription plans.
BUY NOW: US$119 Per Year, Trimble6. Most Advanced Modeling System—CATIA 3D Innovator
Another Dassault Systemes product, CATIA is considered the most advanced modeling system in the world. CATIA is not just a CAD program — it is a complete digital manufacturing infrastructure that includes sheet metal design, tooling, assembly design, drafting, renderings, 3D printing prototyping/design, virtual reality, all types of engineering analyses, generative design, sculpting, and so much more. A favorite of industrial and creative designers, CATIA is a mainstay in companies such as Boeing, Ford, Honda, and others that require demanding assemblies.
CATIA is not just a CAD program — it is a complete digital manufacturing infrastructure that includes sheet metal design, tooling, assembly design, drafting, renderings, 3D printing prototyping/design, virtual reality, all types of engineering analyses, generative design, sculpting, and so much more. A favorite of industrial and creative designers, CATIA is a mainstay in companies such as Boeing, Ford, Honda, and others that require demanding assemblies.
CATIA is not for the faint of heart — its price point, a library of features, and level of difficulty are best suited for established companies looking to optimize their existing workflow and improve upon their complex products in automotive, aerospace, and product design applications. It is a subscription-based service and is available on a request basis — but expect to pay a flat fee with an annual maintenance fee.
BUY NOW: US$3,024 Per Year or US$906 Per Quater, Dassault Systeme7.
 Best Multi-Functional Modeling Software—Creo®
Best Multi-Functional Modeling Software—Creo® PTC, known previously for its successful Pro/Engineer CAD products, sells its wildly popular Creo® parametric modeling software for product design applications. Creo® allows for assemblies of 1000+ parts and seamlessly combines many different modeling styles into one workstation with simulation and optimization capabilities. Creo® is also an ideal software for AM processes and is truly versatile in product design settings.
Creo® is an advanced-level program built for professional use and is regularly used in the industry by companies such as Harris Corp, Blue Origin, Raytheon, Toyota, and other market leaders. It comes in a variety of tiers with optional add-ons and extensions.
BUY NOW: From US$2,780 Per Year, PTC8. Most Advanced CAD Software—Siemens NX
Siemens NX (previously known as Unigraphics) is an advanced design, assembly, and drafting CAD software. NX is a more versatile package when compared to Siemens’ other product Solid Edge, as NX is easier to use and is an overall better modeler with its hybrid freeform, mesh, solid, and surfacing functionalities. NX stands out from other CAD software for its amazing rendering capabilities, as well as its highly adaptive UI with predictive functionality based on the user’s previous commands.
NX is a more versatile package when compared to Siemens’ other product Solid Edge, as NX is easier to use and is an overall better modeler with its hybrid freeform, mesh, solid, and surfacing functionalities. NX stands out from other CAD software for its amazing rendering capabilities, as well as its highly adaptive UI with predictive functionality based on the user’s previous commands.
NX also includes a direct-to-print mode for AM applications, where it will directly connect to supported printers (such as HP’s Multi Jet Fusion printers) and optimize models for printing. Rivaling top-tier programs like CATIA, NX is being adopted by future-forward companies like Apple, Tesla, Nissan, and others. NX comes in a variety of packages and has a free 30-day trial.
BUY NOW: From US$279 Per Month, Siemens9. Best Collaborative Modeling Software—OnShape
OnShape is another cloud-based modeling software (created by the cofounder of SOLIDWORKS) and combines the intensive toolkit of advanced CAD programs with synchronous collaboration across PCs, tablets, and even smartphones. It is a constraint-based parametric modeler built for the part and product design and includes task automation content libraries, mold designs, analytics, and more.
It is a constraint-based parametric modeler built for the part and product design and includes task automation content libraries, mold designs, analytics, and more.
OnShape is best for professional agile teams that require fast turnaround times and integrated product design features. OnShape is available in both free and premium versions and works on all operating systems. It comes in a variety of packages.
BUY NOW: US$1,500 Per Year, OnShapeThe Best CAD/CAM Software for 3D Printing—Summary
This article summarized the best CAD software for 3D printing on the market today, for a variety of skill levels. Be sure to consider what you need in a CAD program, including tools, simulation capabilities, collaboration support, and end-use-related needs.
Choosing the Best CAD/CAM Software for 3D Printing—Buying Guide
Choosing the right CAD software for 3D printing involves your application, your level of expertise, and the demands of the CAD design. Use the set of general considerations below to determine what to look for in CAD software for 3D printing and what to avoid:
Use the set of general considerations below to determine what to look for in CAD software for 3D printing and what to avoid:
- Simplicity vs. Features: Should the program be user-friendly, or feature-intensive? If looking to model highly complex functional assemblies, consider a program with more capabilities, but if just looking for a basic modeler, then consider something with more intuitive controls.
- Customization: How customizable should the software be? Consider if you need things like sculpting, editing history, direct printer connection, and other options.
- Collaboration: Some software allows for cloud-based collaboration on projects and even real-time cooperative modeling. This feature requires a program built specifically for collaboration.
- File format(s): File format compatibility is a vital part of CAD software. If you experience a mismatch in file types, then pieces of a model can be lost between transfers which can cause lengthy delays.
 Also, if your file type does not match your 3D printer, then you won’t be able to print.
Also, if your file type does not match your 3D printer, then you won’t be able to print. - Application: What will the 3D model need to do? Will it be purely structural, or will simulations, technical drawings, technical analysis, or other aspects be required? If used for 3D printing, will you require additional slicer software and/or additional AM features?
- Cost: Certain programs are free; other premium software packages are offered as enterprise packages and are expensive. Consider your budget and the subscription plan of the software before choosing the right one.
This list is not exhaustive but should help when considering the above programs for your 3D printing project.
And to learn more, visit our Thomas Supplier Discovery Platform where we have over CAD/CAM software suppliers listed.
Sources:
- Choosing the Best 3D CAD Software: A Comprehensive Guide (formlabs.com)
- Top 10 Best CAD Software For All Levels - 3Dnatives
- Solid Edge vs Solidworks: What are the main differences? (sculpteo.
 com)
com) - 12 Best CAD Software 2023 (For Every Skill Level!) - 3DSourced
- 17 Best 3D Printing Software of 2023 (CAD and Modeling Tools) (adamenfroy.com)
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- Autodesk®, AutoCAD®, and Fusion 360® are registered trademarks of Autodesk, Inc., San Rafael, CA.
- Creo® is a registered trademark of PTC Inc., Needham, MA.
Other CAD and Software Articles:
- Top Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Software Companies in the USA and Internationally
- Top Cloud Services Providers and the USA and around the Globe
- Top Predictive Maintenance Companies in the USA and Globally
- Top Simulation Software Companies in the US and Globally
- Top U.S.A and International CAE/CAD/CAM Software Companies
- Top Data Analysis Software Companies in the USA and Internationally
- Top USA and International Desktop Virtualization Software Companies
- Top USA and International Data Acquisition Software Companies
- Top Preventative Maintenance Software Companies in the USA and Globally
- Top Computer Security Software Companies in the USA and Globally
- Top Artificial Intelligence (AI) Software Companies in the USA and Internationally
- A Guide to CAD/CAM Software
- Top CAD/CAM Software Companies in North America
- Top Virtual Reality Companies (Equipment and Software) in the USA and Globally
- 5 Sources of Free Industrial Part CAD Files
- Artificial Intelligence in Smart Procurement
- What is Artificial Intelligence
- Best VPN for Business in 2023
- Best Payroll Software for Small Business
- Best Payroll Software for Trucking Companies
Other Best Product Articles
- The Best Vacuum Pumps
- The Best Industrial Vacuum Cleaners
- The Best Forging Presses (including Hydraulic)
- The Best Diaphragm Pumps
- The Best CNC Router
- The Best Baler Machines
- The Best Industrial 3D Printer
- The Best Condensing Boilers
- Best Explosion Proof Fans
- The Best Gantry Cranes
More from Engineering & Consulting
REC Wiki » Best 3D Printing Software in 2022
3D printing is a multi-step process, because you first need to design a 3D model, check it for errors, convert it to machine code, and only then the 3D printer goes into business . In this article, we will share examples of programs that can help at every stage of preparatory work and directly during 3D printing.
In this article, we will share examples of programs that can help at every stage of preparatory work and directly during 3D printing.
Contents:
1. 3D modeling software:
- Tinkercad
- ZBrushCoreMini
- 3D Builder
- SketchUp Free
- Fusion 360
- FreeCAD
- Blender
2. Editing and repairing STL files:
- Meshmixer
- MeshLab
3. Slicers:
- Cura
- PrusaSlicer
- ideaMaker
- ChiTuBox Basic
- Lychee Slicer
- Kiri:Moto
- IceSL
4. Control programs:
- OctoPrint
- MatterControl 2.0
- AstroPrint
5. G-code Visualizers
- UVTools
- WebPrinter
- Gcode Analyzer
- Design Software
1.
 3D modeling software
3D modeling software If you are ready to create from scratch, you will have to learn special 3D modeling software. Many of them, especially professional computer-aided design systems, can be expensive investments, but on the other hand, there are plenty of quite capable and at the same time free offers on the market.
Tinkercad
Tinkercad is a browser-based application from Autodesk that is great for no-experience users, even kids, because of its simplicity. In this program, 3D models are built on the basis of basic blocks - simple geometric shapes that are joined together and then "filed" to the finished look. You can also convert 2D vector images into 3D models. Of course, you have to pay for simplicity - in the case of Tinkercad, rather primitive functionality that makes it difficult to create truly complex models. But such a task is not worth it: having gained basic skills on Tinkercad, you can always move on to more complex and more capable programs on our list.
Official website
ZBrushCoreMini
ZBrushCoreMini is primarily a 3D sculpting tool, especially popular among those who create human and animal figures, computer game characters, comics, and the like. This software is mainly aimed at beginners and users with moderate experience, but at the same time, it is full of impressive features that make the work easier. For example, dynamic tessellation algorithms constantly analyze the surface of the working model and automatically add polygons so that detail is not violated.
ZbrushCoreMini is offered free of charge and is positioned as an entry-level program for learning and gradually moving to more capable and complex options - ZBrush and ZbrushCore.
Official website
3D Builder
This program was developed by Microsoft and was included with Windows 10 for some time, although now it needs to be downloaded and installed separately. 3D Builder allows you to edit models in STL, OBJ, and 3MF formats, as well as create models from scratch. In this regard, the program is quite primitive, but it is simple and understandable even for novice modelers.
In this regard, the program is quite primitive, but it is simple and understandable even for novice modelers.
One of the interesting features of 3D Builder is the ability to simplify meshes by reducing the number of polygons, file weight and processing time in the slicer - useful in cases where the original designer obviously went too far with polygons. Additionally, you can import models from the library and even use Kinect sensors to 3D scan and import models of physical objects.
Official website
SketchUp
SketchUp is a web application with a great combination of simplicity and functionality. The user-friendly interface is intuitive and greatly facilitates learning, and the set of tools is quite diverse even for advanced users - hence the wide popularity of this program.
The free version was formerly called SketchUp Make, but is now simply called SketchUp Free. It includes everything you need for 3D modeling for 3D printing, just don't forget to download the module for exporting STL files - it's also free. The kit comes with 10 GB of storage for projects in the cloud and access to the 3D Warehouse, a repository with open source user-generated content.
The kit comes with 10 GB of storage for projects in the cloud and access to the 3D Warehouse, a repository with open source user-generated content.
Official site
Fusion 360
Professional CAD developed by Autodesk and famous for its ease of use and advanced functionality. This includes parametric modeling and mesh analysis and load distribution tools, including through generative design with topological optimization. The program is great for those who are engaged in 3D printing of functional products, for example, for industrial applications.
Some versions of Fusion 360, such as hobby and student versions, are even available free of charge. FreeCAD FreeCAD The program relies on a parametric approach: at any point in history, you can scroll back and make changes to the parameters. The program even includes finite element analysis and a robotic system simulator.
Official site
Blender
One of the most popular 3D modeling programs, but quite difficult to master. Not the best choice for a novice designer, but a great tool for those who have already gotten their hands on simpler editors. Fortunately, the popularity of Blender has led to a huge number of guides, tutorials, and visual examples published by experienced users for beginner colleagues.
Not the best choice for a novice designer, but a great tool for those who have already gotten their hands on simpler editors. Fortunately, the popularity of Blender has led to a huge number of guides, tutorials, and visual examples published by experienced users for beginner colleagues.
Developers are trying to make the program more convenient without sacrificing functionality: the interface has recently been updated, rendering has been improved, and 3D design and animation capabilities have been expanded. And yes, it's open source and freeware, so you don't risk anything.
Official site
2. Editing and repairing STL files
If you find an interesting 3D model on the Internet, this does not mean that it can be immediately sent to a 3D printer. Many models are created for completely different needs, such as animations or video games, and in principle are not intended for 3D printing. But there is a solution: before processing such models into G-code, they must first be repaired so that the slicer can do its job well. The following programs on our list will help you cope with the repair.
The following programs on our list will help you cope with the repair.
Meshmixer
Meshmixer is an advanced and free program from Autodesk that allows you to view and check 3D models for errors in polygonal meshes that can ruin 3D printing. If such problems are detected, the program can automatically repair meshes. One example of an application is finishing 3D scans to a state suitable for 3D printing.
Additional functionality includes mesh blending, 3D sculpting, surface writing, cavity creation, support branching, mesh smoothing, and more.
Official website
MeshLab
MeshLab is another open source program for editing polygonal meshes. MeshLab has the necessary tools for editing, checking, cleaning and converting meshes with the ability to combine meshes into one model and patch holes that can lead to incorrect processing of models into G-code.
Official website
3. Slicers
After receiving a 3D model, it must be converted into machine code - a series of commands understandable to CNC machines, including 3D printers. Slicers are responsible for this task - programs that accept digital models (usually in the form of files with STL, OBJ or 3MF extensions), analyze their structure, and then compile lists of actions for 3D printers, called G-code (Gcode). Such lists contain all the information necessary for the equipment: to what temperature to warm up the extruders and tables, whether to use airflow, along what trajectory and at what pace to lay the plastic.
Slicers are responsible for this task - programs that accept digital models (usually in the form of files with STL, OBJ or 3MF extensions), analyze their structure, and then compile lists of actions for 3D printers, called G-code (Gcode). Such lists contain all the information necessary for the equipment: to what temperature to warm up the extruders and tables, whether to use airflow, along what trajectory and at what pace to lay the plastic.
Cura
Cura is a slicer from the Dutch company Ultimaker, designed primarily for proprietary 3D printers, but open source and compatible with most other FDM/FFF systems. The program is easily customizable with various plugins. Since this is a very popular program, the chances are that it already has a profile with optimal settings for your 3D printer. If not, then nothing prevents you from creating a profile manually or using profiles prepared by other users.
The program has several levels of difficulty depending on the level of training - basic, advanced, expert and complete. The higher the level, the more access to customizable options. At a basic level, the program takes the bulk of the work on itself, helping inexperienced users.
The higher the level, the more access to customizable options. At a basic level, the program takes the bulk of the work on itself, helping inexperienced users.
Cura is constantly being developed and improved through regular updates and is also offered free of charge, although a paid version of Cura Enterprise is available to professional users with licensed plug-ins from the Ultimaker Marketplace, technical support and additional security measures.
In addition to converting 3D models to G-code, Cura can also take on the role of a control program, but this will require a constant connection between the 3D printer and the computer throughout the 3D printing. Professionals appreciate another feature of Cura - seamless integration with professional computer-aided design systems such as SolidWorks and Siemens NX.
In general, Сura is suitable even for novice users, especially since a huge number of training videos and step-by-step guides are available for this program, both from developers and enthusiasts.
Official website
PrusaSlicer
3D printer manufacturer Prusa Research, under the leadership of the legendary Czech engineer Josef Prusa, whose designs are copied and refined around the world, has developed its own open source software based on the Slic3r slicer. PrusaSlicer quickly gained popularity as it not only retains the original program's extensive customizations, but also adds a number of useful features not found in Slic3r.
A redesigned interface, support for Original Prusa branded 3D printers, and profiles with settings to work with many common polymers are just some of the improvements. Additionally, algorithms for generating support structures have been improved, support for multimaterial 3D printing and the ability to dynamically adjust the layer thickness have been added.
PrusaSlicer can process models not only for FDM 3D printers, but also for stereolithographic systems printing with photopolymers. As with Cura, the user can select a difficulty level with appropriate access to fine-tuning.
Official website
ideaMaker
Raise3D's slicer is optimized for branded additive hardware in the same way that PrusaSlicer is optimized for Original Prusa 3D printers, and Cura is optimized for Ultimaker 3D printers, but this does not mean that it cannot be use with third party systems. The organization of workflows and the interface is somewhat more complicated than in Cura and PrusaSlicer, but on the other hand, ideaMaker allows you to set up individual layers and apply textures for product customization.
ideaMaker users can connect to the cloud platform and access hundreds of 3D printer profiles and materials created by other operators, or create their own library of settings.
Add the ability to customize support structures, split models for more efficient 3D printing of large parts, integrated mesh repair tools, and OctoPrint compatibility, and you have a flexible, versatile program to suit the needs of most 3D printers.
Official website
ChiTuBox Basic
This is a specialized slicer for those who use stereolithographic 3D printers that print with photopolymer resins.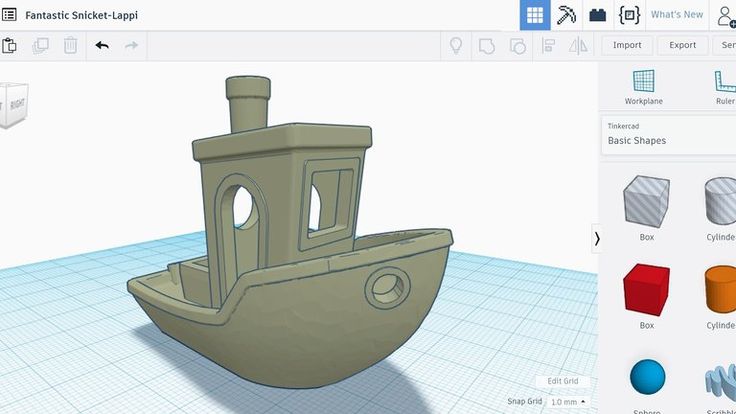 Most budget LCD masked stereolithography (MSLA) 3D printers rely on motherboards and firmware from ChiTu Systems, which also developed this software.
Most budget LCD masked stereolithography (MSLA) 3D printers rely on motherboards and firmware from ChiTu Systems, which also developed this software.
Users gain control over technology-specific parameters such as layer exposure time, as well as access to predefined profiles with settings for many popular 3D printers. The slicer takes into account such moments as the orientation of the model and the automatic construction of support structures with the possibility of manual optimization.
Official website
Lychee Slicer
A program from the independent Franco-Belgian team Mango 3D, not associated with 3D printer manufacturers, but with support for many popular stereolithographic 3D printers, including those from Elegoo, Anycubic, Phrozen and Creality.
One of the features of this program is the high level of automation. If you wish, you can simply click on the "magic" button (it's called Magic), and the slicer will do everything by itself: it will orient the model on the platform, generate supports, and so on. Although, here you are lucky: the results are not always optimal, but usually adequate for relatively simple models. Otherwise, everything can be configured manually.
Although, here you are lucky: the results are not always optimal, but usually adequate for relatively simple models. Otherwise, everything can be configured manually.
The program is offered in free and paid versions. The functionality of the free version is slightly reduced, but it has everything you need.
Official site
Kiri:Moto
Browser solution for those who lack computing power. Kiri:Moto can prepare 3D models for both 3D printing and laser engraving or milling. The settings are somewhat more primitive than in locally installed slicers, but are sufficient for most users.
Official website
IceSL
IceSL is a combination software that combines slicing with 3D modeling. In the left window, you can edit 3D models using scripts in the Lua language, which makes it possible to perform parametric modeling. On the right side, the 3D printing settings are displayed. For beginners, pre-configured settings are available, while experienced users can take advantage of features such as specific adjustment of parameters for individual layers with automatic gradation of intermediate areas. For example, this allows you to gradually reduce or, conversely, increase the filling density of the product as it is built, or gradually change the thickness of the layers.
For example, this allows you to gradually reduce or, conversely, increase the filling density of the product as it is built, or gradually change the thickness of the layers.
Official website
4. Control programs
Control programs are designed for exactly this - managing workflows during 3D printing. Although you can insert a G-code drive into almost any 3D printer and press the start button, this is not always convenient, especially when you have to work with several 3D printers at the same time, and even more so when you do it remotely. This is where control programs come to the rescue. In addition, some of them offer additional functionality, including slicing and even editing 3D models.
OctoPrint
A web-based appliance that requires connection to a 3D printer via a microcomputer such as a Raspberry Pi equipped with a Wi-Fi module. This system allows you to control 3D printers remotely. OctoPrint accepts G-code from almost any slicer and provides the ability to visualize - view files before and during 3D printing. Alternatively, STL files can be loaded and processed directly in OctoPrint.
Alternatively, STL files can be loaded and processed directly in OctoPrint.
OctoPrint not only provides all the necessary tools for remote management, but also allows you to track the work in progress using notifications via various instant messengers.
This is a completely free, open source program with many plug-ins created by enthusiasts and available on the official website.
Official website
MatterControl
MatterHackers offers its own control program, slicer and 3D editor in one package. MatterControl allows you to directly control and observe 3D printing, slice, export G-code to SD cards for offline printing, and even create 3D models from scratch. The 3D printer will need a Wi-Fi or USB connection to run MatterControl.
The interface is well structured: on the left side there is a file browser and a library of simple geometric shapes. Interestingly, these shapes can be dragged into the 3D model and used as support structures.
Basic functionality is available in the free basic version, advanced users can pay to upgrade to MatterControl Pro.
Official website
AstroPrint
AstroPrint is a cloud-based management platform that allows you to remotely monitor and control multiple 3D printers simultaneously, store files, convert 3D models to G-code, and track workflow statistics. The functionality ranges from basic in the free version to advanced with different levels of paid subscriptions.
The 3D printer will require a Wi-Fi module to fully work with AstroPrint. In conjunction with the Raspberry Pi, the system is similar in functionality to OctoPrint: you can process models and send the finished code to a 3D printer via a web interface without the need for additional software. Another plus is integration with popular repositories of 3D models Thingiverse and MyMiniFactory, as well as 3D editors 3D Slash and Leopoly.
Official website
5.
 Programs for visualizing G-code
Programs for visualizing G-code What if you find an old file with a G-code, but you have no idea what it is and why - maybe garbage, or maybe an excellent, but long-forgotten model without a clear marking in the file name? The programs in this section will help you visualize the contents of such files.
UVTools
This program combines file browsing with layer editing and even model repair for stereolithographic 3D printing. The program can also be used as a plug-in for PrusaSlicer, adding support for third-party photopolymer 3D printers - although PrusaSlicer is open source, support for stereolithographic systems is still limited to branded equipment. At the same time, UVTools allows you to print calibration samples to check the exposure time and other parameters, which can be useful, for example, when working with new photopolymers that have not yet been tested.
Official website
WebPrinter
A simple browser tool for quick G-code preview, developed by the same team that created the IceSL slicer and 3D editor. The application works very simply: follow the link, upload the file with the G-code and see how the 3D printer will grow the model according to the commands provided. Unfortunately, the functionality is limited: for example, the application does not provide information about temperature settings. On the other hand, you can quickly figure out what kind of model is hidden in a file with an incomprehensible name.
The application works very simply: follow the link, upload the file with the G-code and see how the 3D printer will grow the model according to the commands provided. Unfortunately, the functionality is limited: for example, the application does not provide information about temperature settings. On the other hand, you can quickly figure out what kind of model is hidden in a file with an incomprehensible name.
Official website
Gcode Analyzer
An old but still very capable and popular G-code analysis web application. The 3D simulation doesn't work very well, but the 2D and G-code previews work great. In 2D mode, you can conveniently view individual layers, moving from layer to layer and following the construction path step by step using two sliders. G-code viewer displays a complete list of commands, allowing you to see what a particular line of code is doing.
Official website
Adapted translation of The Best Free 3D Printing Software of 2022 article.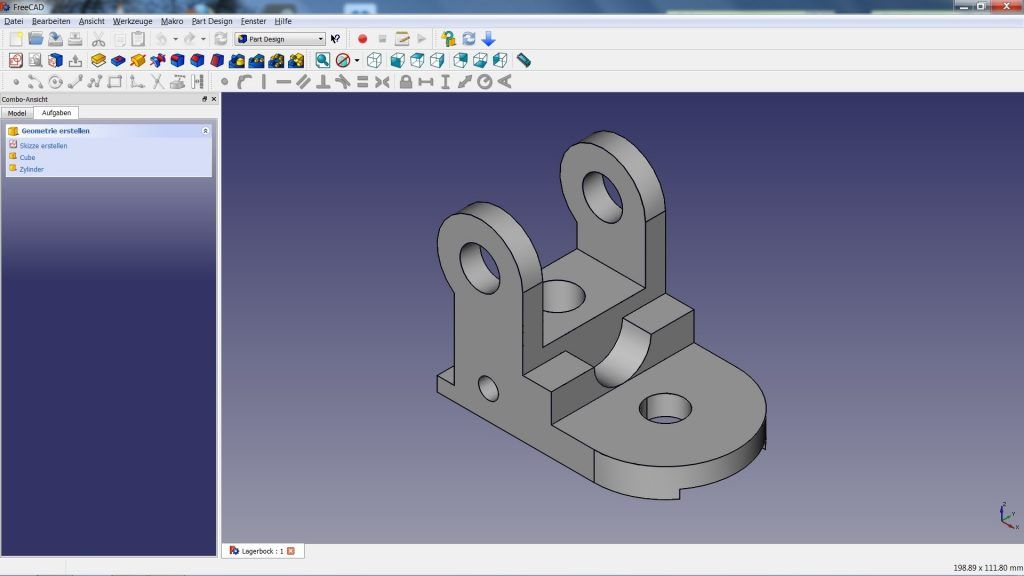
Top 20 Free 3D Printing and 3D Printing Software
Looking for 3D printing software? We've rounded up the top 20 software tools for beginners and professionals alike. Most slicers are free.
What is a slicer? This is a program for preparing a digital model for printing. Models for 3D printing are usually distributed in STL files. To turn an STL file into G-code (a language that a 3D printer understands), a slicer program is required. It is called a slicer because it cuts (to slice - English) a 3D model into many flat two-dimensional layers, from which a 3D printer will add a physical object.
Which slicer should I choose? In this article, we will tell you which slicer is the best choice for 3D printing for each stage of your work. Which one is better for preparing a 3D model for printing? But what if you need to create a 3D model from scratch? And if you are only taking the first steps in 3D?
Don't be afraid: we've answered all of these questions, including the required skill level for each program and where you can download it. The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
The great thing is that most of these programs are completely free and open source.
- Cura
- CraftWare
- 123D Catch
- 3D Slash
- TinkerCAD
- 3DTin
- Sculptris
- ViewSTL
- Netfabb Basic
- Repetier
- FreeCAD
- SketchUp
- 3D Tool
- Meshfix
- Simplify3D
- Slic3r
- Blender
- MeshLab
- Meshmixer
- OctoPrint
#1: Cura
For beginners who need a slicer to prepare STL files for 3D printing
Cura is the default slicer software for all Ultimaker 3D printers, but can be used with most others , including RepRap, Makerbot, Printrbot, Lulzbot and Witbox. The program is completely open source, its capabilities can be extended using plugins.
This program is very easy to use and allows you to manage the most important 3D printing settings through a clear interface. Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings. If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Start in Basic mode to quickly get up to speed and change print quality settings. If finer control is required, switch to Expert mode.
Cura can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: Cura
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#2: CraftWare
3D printers by the Hungarian startup CraftUnique to support their CraftBot crowdfunding machine. However, the program works with other printers.
Like Cura, CraftWare allows you to switch from "Easy" to "Expert" mode, depending on how confident you feel. It's a colorful application featuring a visual G-code visualization where each function is represented by a different color. But the most outstanding feature is the individual support service. As far as we know, only the paid program Simplify3D has this.
Please note, however, that this program is still in beta, so bugs may occur.
Download: CraftWare
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#3: 123D Catch
-systems, smartphones and tablets, which allows you to convert images of objects into a 3D model. Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
Pictures can be taken with a smartphone/tablet or digital camera.
You need many photos of the object from different angles - the more the better - after which they will be compiled into a 3D model.
123D Catch is more of a fun app than a professional 3D printing tool, but after some tambourine dancing, you can get good results, especially when paired with an STL editor like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Android, iOS, Windows Phone
#4: 3D Slash
and surprisingly simple, and refreshingly new. With 3D Slash, you can design 3D models using your dice skills.
You can start with a large block and, like a virtual sculptor, remove small cups from it with tools such as a hammer or drill, or start from empty space and build a model from cubes and other shapes. You can paint with flowers or use template pictures.
Other features worth mentioning are tools for creating logos and 3D text. The Logo Wizard imports an image and creates a 3D model, while the Text Wizard allows you to enter and format text, and then turn it into 3D.
Recommended!
Download: 3dslash.net
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux, Browser
#5: TinkerCAD
- A computer-aided design (CAD) system for 3D printing, which is a good starting point for beginners. Since its capabilities are limited compared to Blender, FreeCAD and SketchUp, many users switch to more powerful tools after some time.
As in 3D Slash, here you can build models from basic shapes. At the same time, unlike 3D Slash, TinkerCAD allows you to create vector shapes in 2D and convert them into three-dimensional models.
Come in: Autodesk TinkerCAD
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#6: 3DTin
For beginners who want to create 3D models for printing
online is another easy and intuitive tool choice for beginners in 3D modeling. All you need is a Chrome or Firefox browser with WebGL enabled.
Choose from a huge library of 3D shapes and add them to your sketch. All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
All sketches are stored in the cloud, access to them is free if you honor the Creative Commons license. Everything can be exported to STL or OBJ formats.
Enter: 3DTin
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#7: Sculptris
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
clay. This is a fantastic 3D modeling program if figurines are your main task. For example, you can make a bust of your favorite video game or comic book character. Sculptris is completely free and bills itself as a stepping stone to the more complex (and expensive) ZBrush tool.
Download: Pixologic Sculptris
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac
#8: ViewSTL
For beginners who want to view STL files
ViewSTL is the easiest way to view STL files . Simply open a web page and drag the STL onto the dotted box.
The STL online viewer allows you to display the model in one of three views: flat shading (for a quick view), smooth shading (for a high-quality image), and wireframe.
Come in: ViewSTL
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#9: Netfabb Basic
some nice features that allow you to analyze, "repair" and edit STL files before moving on to the model cutting stage.
A good choice if you need more than just a slicer and want to be able to quickly fix STL files without having to learn programs like MeshLab or Meshmixer.
Don't let the "Basic" in the name fool you, Netfabb Basic is actually a very powerful 3D printing tool. It's "basic" only in the sense that it doesn't cost €1,500 like Netfabb Professional!
Download: netfabb.de
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
No. 10: Repetier
For advanced to prepare STL files for 3D printing
9002 If you are ready to upgrade to the next level of 3D printer slicer software, but if you want to stay open source, you should look into Repetier. It is the great grandfather of 3D printing software and a favorite of the RepRap community.
Today the program is moving by leaps and bounds from the level for beginners to advanced users. Packaged in an all-in-one configuration, it supports up to 16 extruders, multi-slicing via plug-ins, and virtually every fusing 3D printer on the market. Get ready to tinker!
What's more, Repetier Host works remotely via Repetier Server, so that the 3D printer can be controlled via a browser, tablet or smartphone.
Download: Repetier
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#11: FreeCAD
The program is a great option for developing your design skills. More technically, this parametric 3D modeling program allows you to easily change the project by rolling back through the history of the model and editing the parameters.
Download: freecadweb.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#12: SketchUp
For beginners who want to create 3D printable models
SketchUp functionality, with a user-friendly interface and a relatively flat learning curve (i. e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
e., as experience grows with the time spent), the ideal program for developing three-dimensional models.
The Make SketchUp version is free and will have everything you need for 3D modeling if you also download and install the free STL exporter. There is also a professional edition for architects, interior designers and engineers.
Download: sketchup.com
Price: Free (SketchUp Make), $695 (SketchUp Pro)
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#13: 3D-Tool Free Viewer
view and check STL files
3D-Tool Free Viewer is a sophisticated tool that, among other things, allows you to check the structural integrity and printability of your file. With the Cross-Section function, for example, you can look at the model from the inside and check the wall thickness. Very useful if you want to check your STL file for killer errors before printing.
Download: 3D-Tool
Price: Free
Systems: PC
#14: Meshfix
your model for errors.
Price: Free
Systems: Browser
#15: Simplify3D
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing print. A flexible algorithm checks the model for problems, fixes them, shows a preview of the printing process (ideal for identifying potential problems), and then slices it.
This slicer offers the best infill pattern options in the competition. For models that require supports, Simplify3D will create the appropriate structures on its own and give you full control over their placement. For printers with a dual extruder, when printing with different materials, the Dual Extrusion wizard will help, as a result of which, for example, it will be easier to remove the dissolving filament.
Simplify3D supports 90% of today's commercially available desktop 3D printers and is compatible with Marlin, Sprinter, Repetier, XYZprinting, FlashForge, Sailfish and MakerBot firmware. Simplify3D can also be used to directly control the printer, but then the printer and computer must be connected to each other.
Download: simplify3d.com
Price: $149
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#16: Slic3r
source code, which has a reputation as a carrier of super new functionality, which you will not find anywhere else. The current version of the program is able to show the model from multiple angles, so that the user gets a better preview experience.
There's also an incredible 3D honeycomb infill, the first of its kind that can extend over multiple layers rather than repeating itself like a stamp. This significantly increases the strength of the internal filling of the model and the final printout.
Another option is direct integration with Octoprint. Once the files on the user's desktop are sliced, they can be directly uploaded to Octoprint with one click.
Download: Slic3r
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#17: Blender
For professionals who want to create 3D printable models
Blender is a popular computer-aided design (CAD) system with a steep learning curve. Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
Not at all the best choice for beginners, but what you need if you are quite experienced and need something more complex for modeling and printing.
In short, Blender is one of the most powerful tools in existence. Its community is always ready to help, there are a lot of educational materials. It's also open source, so enthusiasts often write extensions to make it even better and more powerful.
Download: blender.org
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#18: MeshLab
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing
MeshLab - advanced editor. It allows you to remove parts of a 3D model, merge two models into one, patch holes. If you need a program to modify models for 3D printing or some kind of "repair" work, MeshLab is the right choice.
Price: Free
Systems: PC, Mac, Linux
#19: Meshmixer
For professionals to prepare STL files for 3D printing files. It's especially good for identifying potential problems and fixing them automatically.












