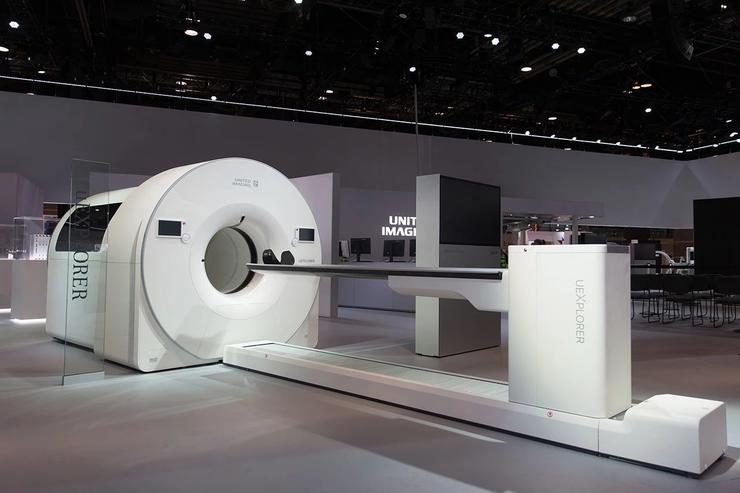
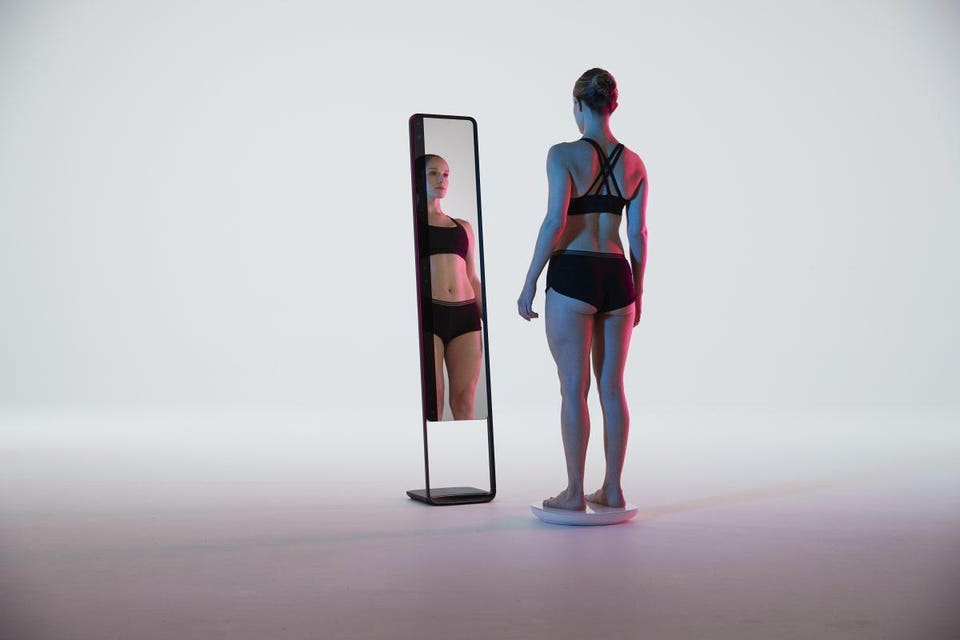
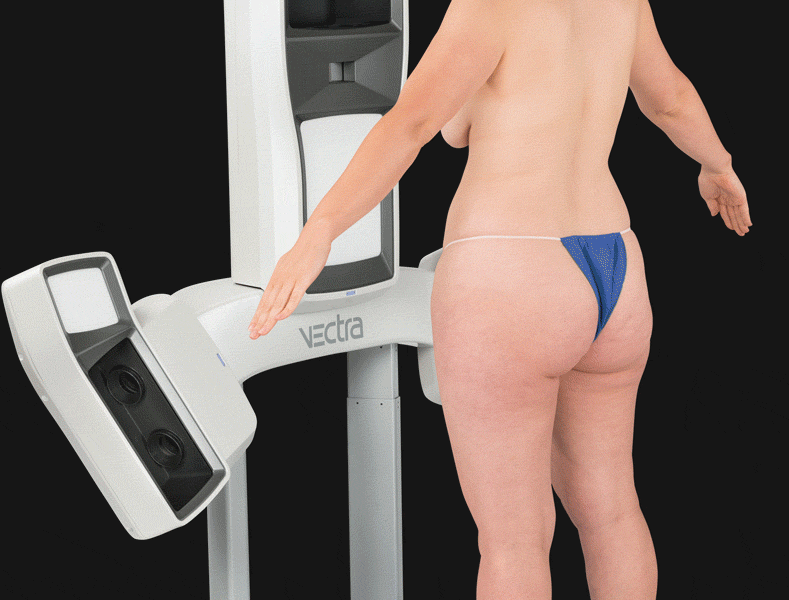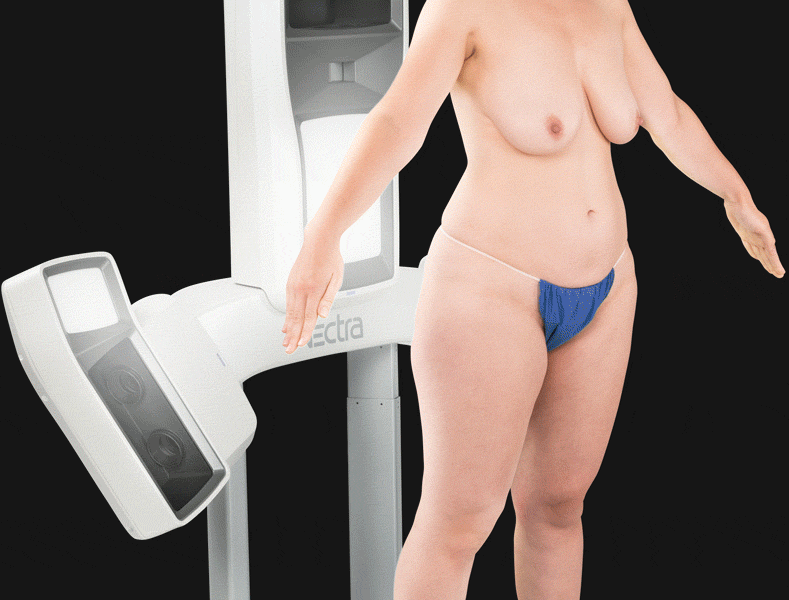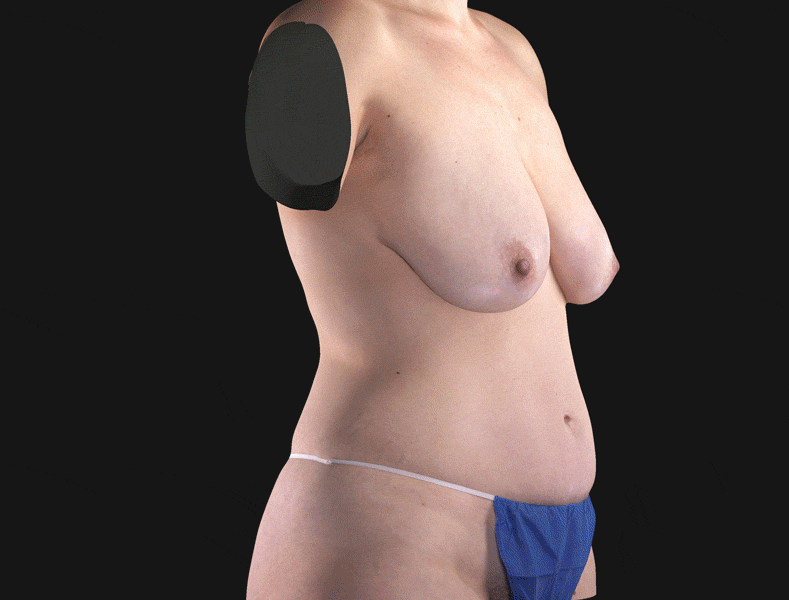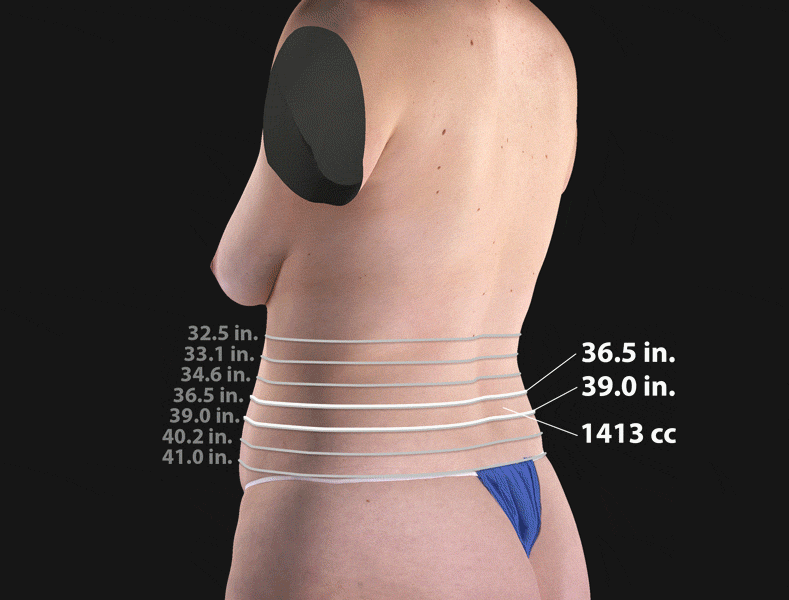
3D total body imaging scanner
This total body scanner shows 3D images of the whole body
[Image from UC Davis]
A University of California Davis-developed medical imaging scanner has produced the first 3D picture of the whole human body at once.
The scanner, known as the Explorer, is a combination of a positron emission tomography (PET) and X-ray computed tomography (CT). It is able to image the entire body using both scanning methods and can produce the image in as little as one second. Over time, Explorer can make videos that can track specially tagged drugs as they move through the body.
UC Davis scientists Simon Cherry and Ramsey Badawi developed the scanner and suggest that the technology could be used in a number of applications that include improving diagnostics, tracking disease progression and researching new drug therapies. Explorer was developed in a partnership with Shanghai-based United Imaging Healthcare and will manufacture the devices for a broader healthcare market.
“While I had imagined what the images would look like for years, nothing prepared me for the incredible detail we could see on that first scan,” Cherry, a professor in the UC Device Department of Biomedical Engineering, said in a press release. “While there is still a lot of careful analysis to do, I think we already know that Explorer is delivering roughly what we had promised.”
Images from the Explorer scanner were collected in a collaboration with United Imaging Healthcare and the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Zhongshan Hospital in Shanghai, China.
“The level of detail was astonishing, especially once we got the reconstruction method a bit more optimized,” Badawi said. “We could see features that you just don’t see on regular PET scans. And the dynamic sequence showing the radio tracer moving around the body in three dimensions over time was, frankly mind-blowing. There is no other device that can obtain data like this in humans, so this is truly novel.”
The UC Davis scientists thought of the total-body scanner 13 years ago.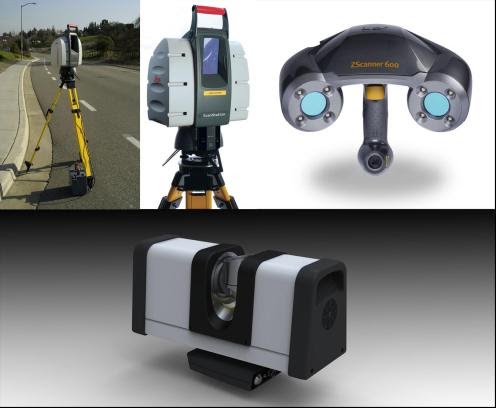 They kickstarted the idea in 2011 with a $1.5 million grant from the National Cancer Institute that allowed them to gather a consortium of researchers and other collaborators. The team received a $15.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health in 2015 that allowed the team to team up with a commercial partner and to build the first Explorer scanner.
They kickstarted the idea in 2011 with a $1.5 million grant from the National Cancer Institute that allowed them to gather a consortium of researchers and other collaborators. The team received a $15.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health in 2015 that allowed the team to team up with a commercial partner and to build the first Explorer scanner.
Cherry and the other researchers suggest that the Explorer scanner will have an impact on clinical research and patient care because of its higher-quality diagnostic PET scans. Explorer is able to scan up to 40 times faster than current PET scans and can produce a diagnostic scan of the whole body in 20 to 30 seconds.
With all of the imaging capabilities, Explorer is still able to scan with a radiation dose up to 40 times less than a current PET scan.
“The tradeoff between image quality, acquisition time and injected radiation dose will vary for different applications, but in all cases, we can scan better, faster or with less radiation dose, or some combination of these,” Cherry said.
The Explorer scanner would be able to evaluate what is going on in all the organs and tissues in the body at the same time, according to the researchers. Blood flow could be quantitatively measured and the scans could show how the body takes up glucose. The researchers suggest that the scanner could be used to study cancer that has spread beyond a single tumor site, inflammation, infection, immunological or metabolic disorders and many other diseases.
“I don’t think it will be long before we see at a number of Explorer systems around the world,” Cherry said. “But that depends on demonstrating the benefits of the system, both clinically and for research. Now, our focus turns to planning the studies that will demonstrate how Explorer will benefit our patients and contribute to our knowledge of the whole human body in health and disease.”
The researchers are currently working with UIH to get the first system delivered and installed in a leased space in Sacramento. The researchers hope to begin a research project and image patients using the Explorer scanner as early as June 2019.
Best 3D body scanners in 2022
3D body scanners are a modern and popular way to precisely acquire body measurements and features. Results can be used for rig animation, for fitness or healthcare follow-ups, and even in the fashion retail industry for virtual fitting rooms. This guide lists the best full-body scanners available this year. We also list a few affordable handheld 3D scanners that are suitable for body scanning.
Last update March 25, 2022
In our last update, we added a section to list a couple of color handheld 3D body scanning solutions from Scantech and Shining 3D.
Table of contents
What is a 3D body scanner?
Best 3D body scanners 2022: our selection
Proscanner
SS20 3D Body Scanner
Scanatic™ 360 Body Scanner
Portal MX
Portal BX
BOTSCAN NEO
iReal 2E
EinScan H
Fitness and personal health
Fashion and apparel: made-to-measure clothing
3D printed figurines and 3D photo
Healthcare
Closed 3D body scanning booth (or body scanning cabin)
Full body scanner with rotating platform or turntable
What is a 3D body scanner?
3D body scanners are designed to capture your full body in 3D.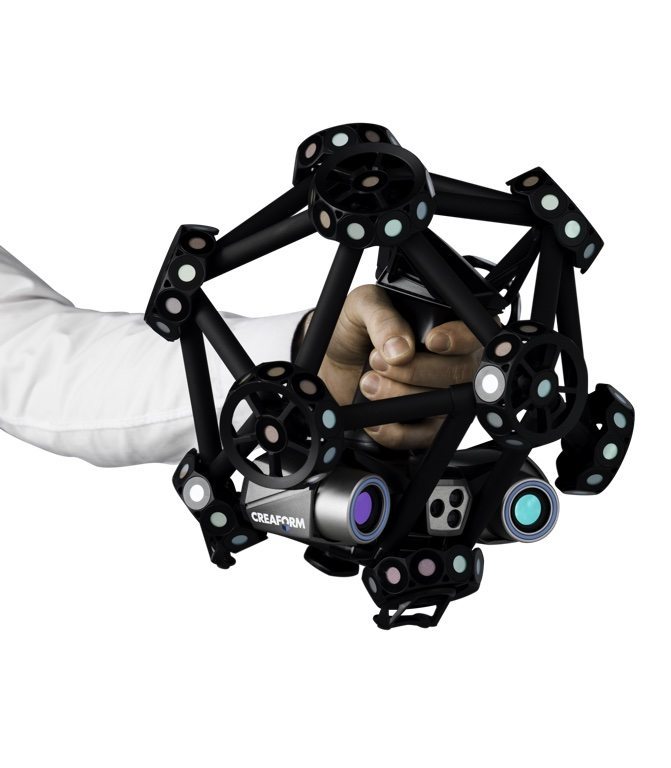 The result is a 3D model (also called 3D avatar) of your exact body shape with accurate data such as body measurements, posture analysis, textures, …
The result is a 3D model (also called 3D avatar) of your exact body shape with accurate data such as body measurements, posture analysis, textures, …
Originally developed for the fashion industry as fast and accurate 3D measurement solutions, 3D body scanners are now used in various other fields such as healthcare, 3D figurines and 3D photos, fitness, and entertainment.
We’ve selected some of the best body 3D scanners available and listed them here in this guide. Our selection focuses on full-body 3D scanning systems that are exclusively designed for 3D body scanning. We list a few handheld 3D scanner options further down the article.
A Texel 3D body scanner being used to attract customers to an event. Source: TexelBest 3D body scanners 2022: our selection
The table below recaps our selection of some of the best full-body 3D scanning options. The goal is to provide a quick, visual overview of the market; there are of course numerous other factors to take into account (software, customer service, …) to get the full picture for each solution and eventually make the right choice.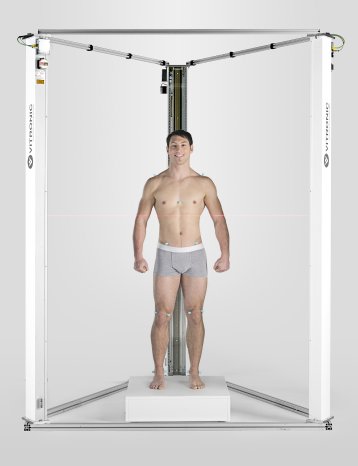
| Brand | Product | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fit3D | Proscanner | United States | $ 10,00010 000 €8,870 £1,490,560 ¥ | Quote |
| Size Stream | SS20 3D Body Scanner | United States | $ 15,00015 000 €13,306 £2,235,840 ¥ | Quote |
| TG3D Studio | Scanatic™ 360 Body Scanner | Taiwan | $ 15,00015 000 €13,306 £2,235,840 ¥ | Quote |
| Texel | Portal MX | United Kingdom | $ 34,90030 000 €30,958 £5,202,054 ¥ | Quote |
| Texel | Portal BX | United Kingdom | $ 45,65040 000 €40,493 £6,804,406 ¥ | Quote |
| botspot | BOTSCAN NEO | Germany | $ 200,000179 000 €177,408 £29,811,200 ¥ | Quote |
Expand to see more specs
The products in the table are ranked by price (low to high).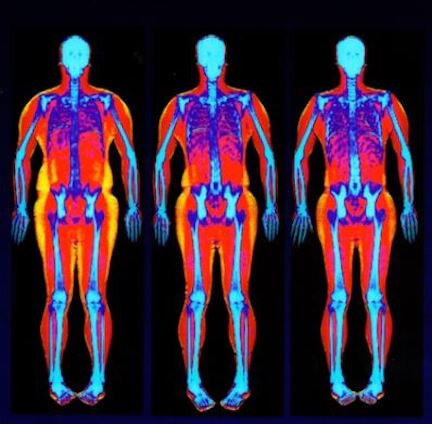
| Brand | Product | Technology | Max resolution | Country | Price Approximate starting prices based on supplier-provided information and public data. Prices may vary by region, over time and do not include additional products or services (taxes, shipping, accessories, training, installation, …). | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fit3D | Proscanner | Structured light | – | United States | $ 10,00010 000 €8,870 £1,490,560 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Size Stream | SS20 3D Body Scanner | Photogrammetry | – | United States | $ 15,00015 000 €13,306 £2,235,840 ¥ | Get a quote |
| TG3D Studio | Scanatic™ 360 Body Scanner | Laser triangulation | – | Taiwan | $ 15,00015 000 €13,306 £2,235,840 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Texel | Portal MX | Structured light | 1 mm0.039 in | United Kingdom | $ 34,90030 000 €30,958 £5,202,054 ¥ | Get a quote |
| Texel | Portal BX | Structured light | 1 mm0. 039 in 039 in | United Kingdom | $ 45,65040 000 €40,493 £6,804,406 ¥ | Get a quote |
| botspot | BOTSCAN NEO | Photogrammetry | 0.1 mm0.003937 in | Germany | $ 200,000179 000 €177,408 £29,811,200 ¥ | Get a quote |
Overview of the best full body 3D scanners
In this section, we give some more context and information about each 3D scanner from our selection.
The Fit3D Proscanner is a 3D body scanner for fitness and healthcare applications. It’s designed to provide a comprehensive wellness assessment based on a detailed 3D body capture.
This body scanning system is mainly used in gyms, health clubs, and fitness studios. The Fit3D Proscanner is able to accurately 3D scan a person in 40 seconds and to provide a posture analysis as well as a body shape wellness score.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Size Stream SS20 3D body scanner is a versatile full body measurement system, designed to capture thousands of data points to create a 3D model of a person’s body.![]() This 3D body scanning booth is primarily designed for 3D measurement to create custom clothing.
This 3D body scanning booth is primarily designed for 3D measurement to create custom clothing.
The Size Stream body scanner can also be used for 3D printing, measurement tracking, size surveys, and healthcare and fitness applications.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Scanatic 360 Body Scanner by TG3D is designed for the fashion industry. It is lightweight and easy to move, and can be fully integrated within a fitting room. Scans take 3 seconds, and measurement points are available in 30 seconds.
TG3D develops software and applications that are tailored for the clothing industry.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The Texel MX can be used for the entertainment and advertising industry, for medical applications, and even as a digital fitting room.
It takes the Texel MX 30 seconds to perform a full 3D body scan, and just 60 seconds to create a digital 3D model with automatic rigging. As with the BX version, results can be directly used for 3D printing or 3D animation.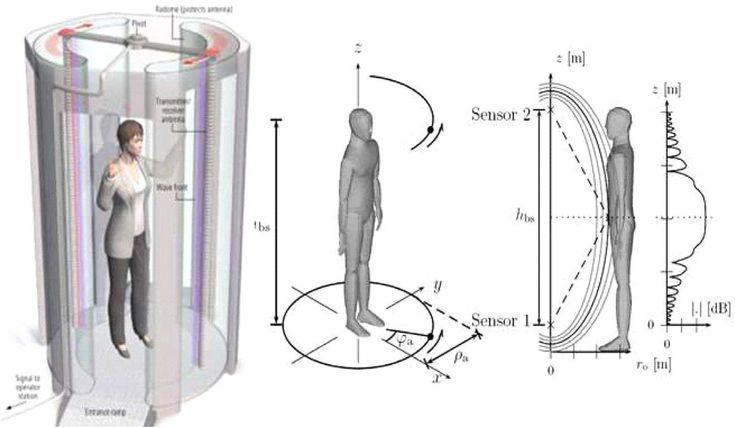
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Texel (or Texel Graphics) is one of the leading manufacturers of 3D body scanners. Their solutions are suitable for a wide range of applications and can be customized for specific events, stores, or environments.
The BX is able to scan up to 40 people per hour and comes with a registration tablet for users to input their names and email address. 3D avatars are directly sent to their inbox and can be shared via social media.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The botscan NEO by German manufacturer botspot features a modular design and is customizable. This system uses a combination of structured light and photogrammetry to provide accurate and colored meshes.
For an easy user experience, the NEO comes with an intuitive mobile app. Its maximum scanning volume capacity is 1000 x 1000 x 2000mm.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
Handheld 3D body scanning options
Some handheld color 3D scanners are suitable for 3D scanning faces, hands, arms, … They can also perform full-body scans, though the process takes a while and requires the customer or patient to stay still during that time. The portable color 3D scanners listed below can therefore be good options to scan specific body parts (e.g. head and chest for 3D avatars, an arm or leg for prosthetics) or for infrequent full-body scans.
The portable color 3D scanners listed below can therefore be good options to scan specific body parts (e.g. head and chest for 3D avatars, an arm or leg for prosthetics) or for infrequent full-body scans.
The iReal 2E is a versatile 3D scanning option in the entry-level price range. It uses VCEL structured light to capture medium- to large-sized objects. Like infrared light, VCEL light is invisible to the human eye and is therefore also particularly adapted to face and body 3D scanning.
Scantech has reported diverse use cases for the iReal 2E 3D scanner, namely in forensic investigations, healthcare, and even culture preservation. In the latter, Scantech’s customer 3D scanned a woman performing different Tai Chi movements– an interesting and uncommon application!
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
The EinScan H was launched alongside the EinScan HX in September 2020. It uses a combination of structured LED light and infrared light, with a built-in color camera for texture acquisition.
This 3D scanner can therefore serve a range of applications involving color capture, with uses in retail, art preservation, healthcare, and more. Furthermore, its infrared light is eye-safe and won’t blind users during a face or body scan.
Shining 3D’s versatile EinScan H is a great entry-level deal for most basic use cases, and its software is getting more intuitive by the update.
Contact manufacturer Get a quote Add to comparison
3D body scanning applications
Fitness and personal health
Fitness body scanners
Body scanners can be used in fitness clubs, gyms, and healthcare facilities. Fitness body scanners allow you to track the evolution of a person’s body through various 3D measurements such as body shape and posture.
Visualizing these evolutions on a 3D avatar is a strong motivational boost that can help increase gym members’ engagement and improve patient recovery processes.
Home body scanners
These 3D body scanners are consumer appliances made to monitor personal health and body shape as well as posture evolution, among other data points. Homebody scanners usually have a 360° rotating platform on which the user stands.
These 3D body scanners typically work with a smartphone app acting as a personal trainer, so users can easily track all their data and reach their fitness goals.
Fashion and apparel: made-to-measure clothing
The fashion and apparel industry was among the first to embrace 3D body scanning for several applications:
- Fast and accurate 3D measurements
- Made-to-measure clothing (custom clothing)
- Highly personalized recommendations
- Measurement surveys and anthropometric characterization
- Virtual fitting rooms
Users can obtain their own 3D avatar on their smartphone and use it to see how clothes fit without physically trying them on.
This is as useful for luxury, tailored clothing as it is for retail and e-commerce.
3D printed figurines and 3D photo
Also known as 3D selfies or 3D portraits, these miniature figurines of people are typically 3D printed from a 3D body scan. If you want to learn more about this application, you can visit our article dedicated to 3D printed figurines.
Here are a few 3D body scanner options that are designed for 3D figurines:
- Artec Shapify Booth
- Doob Dooblicator
- KODAK Full Body 3D Scanner
- Picanova 3D.me
- Pics3D Cobra
- Scanologics ScanLounge v2.5
- Twindom Twinstant Mobile
Healthcare
Healthcare and medical sectors are filled with opportunities for 3D body scanning. From monitoring body shape and posture during pregnancy to making custom 3D printed prosthetics and more, body scanners are increasingly used for use in the medical field.
Body scanning can also be used to accurately monitor skin recovery in the case of burns or to detect skin diseases at an early stage, thanks to specific 3D imaging systems.
How do 3D body scanners work?
To obtain a full body scan, the person holds a pose for a few seconds, which is the time it takes for the 3D scanner to capture images from all angles. The 3D software then reconstructs the final 3D model of the body by “stitching” all of the images together, generating a highly detailed 3D model. Models can have colors and textures depending on the type of body scanner that’s used.
During the 3D capture process, the subject can either stand on a rotating turntable facing a fixed 3D body scanner, or stand still while the sensors located all around the body scanning booth capture images from all angles.
Closed 3D body scanning booth (or body scanning cabin)
A body scanning booth is a closed cabin that is rigged with cameras or 3D scanners. These full-body 3D scanners look a bit like regular fitting rooms.
Full body scanner with rotating platform or turntable
To use these body scanners, the person stands on a rotating table facing a 3D body scanner, typically a vertical unit.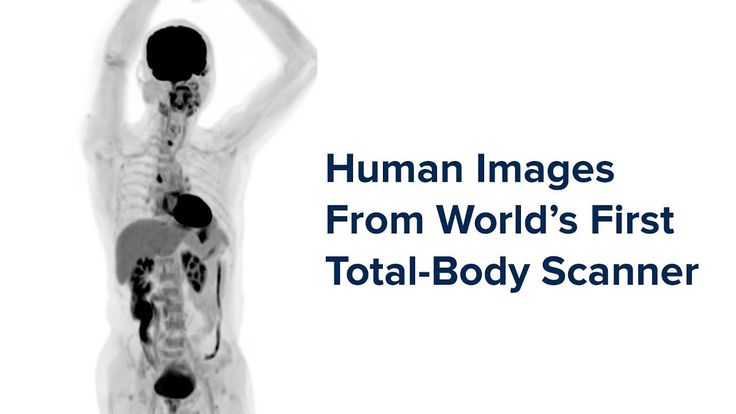 During the scanning process, the turntable rotates 360°, allowing the subject to be captured from all angles. The 3D model is generated once the full rotation is complete.
During the scanning process, the turntable rotates 360°, allowing the subject to be captured from all angles. The 3D model is generated once the full rotation is complete.
3D scanning in medicine. Types of 3D scanners and areas of use in medicine
Content
-
- Using 3D scanning in medicine
- Advantages 3D scanning
- Types of 3D scanning
- Optical
- Laser
- The main directions in medicine
- Dentistry
- Plastic surgery and cosmetology
- Orthopedics
- Prosthetics
- Student education
Medical use of 3D scanning
3D scanning of a person is necessary for plastic surgeons, dentists, orthopedists and even cosmetologists. Before the advent of 3D technology, doctors had to take measurements manually, as well as create realistic models based on the information received: this is a hard and routine job that took a lot of time. 3D scanners have made medical procedures much easier: detailed information about a patient's anatomy can be obtained in minutes.

During the scan, the device recognizes the geometry of the body, and the sensors form a cloud of points. Based on the information received, the device software designs a polygonal body model and transfers it to the computer screen. The three-dimensional model becomes the basis for choosing the optimal method of surgical intervention, creating surgical prostheses, orthopedic shoes, and so on.
Benefits of 3D scanning
The 3D human scanner is used in all areas of medicine. Modern 3D scanners are replacing outdated diagnostic methods due to a number of advantages:
-
Three-dimensional models are more accurate and informative. At the diagnostic stage, some medical equipment makes errors, while 3D scanners show the best result;
-
Orthopedic corsets and insoles, created on the basis of a three-dimensional model of the patient, are much more accurate than plaster ones due to the consideration of aspects of individual anatomy;
-
Due to the high speed of work, new technologies allow you to get the necessary information urgently.
 Delay in medicine can cost a person's health and even life, and three-dimensional scanners help prevent the development of undesirable conditions;
Delay in medicine can cost a person's health and even life, and three-dimensional scanners help prevent the development of undesirable conditions; -
Due to its safety, the technology is relevant for the diagnosis of adults and children.
Interesting! 3D scanning is used for cardiovascular surgery. Due to the high accuracy of the information received, surgeons choose the most relevant method of surgical intervention.
Types of 3D scanners
According to the principle of action in medicine, laser and optical 3D scanning is used. Each of these varieties has its own advantages, which we will discuss below.
Optical
The areas to be examined are illuminated with structured light, while the cameras record the result from different angles. The area is illuminated with a strip of light or a specific pattern (black and white stripes or squares).
 The deformation of the light or pattern conveys to the device information about the shape and depth of the object. The process is recorded by one or two cameras, which transmit information about the structure of the object to the computer software.
The deformation of the light or pattern conveys to the device information about the shape and depth of the object. The process is recorded by one or two cameras, which transmit information about the structure of the object to the computer software. Such devices can be manual and desktop. In the first case, manual control of the device is used, in the second, the scanner is placed on the table. The main advantage of optical devices is the high speed of operation and the ability to transmit color.
Laser
The laser scanner measures the distance to the object under investigation and determines the actual length of the beams. The direction of the laser is controlled by encoders. Based on the analysis of the reflection of rays, a cloud of points is formed, which makes up a three-dimensional image of the object under study. The main advantage of such devices is the ability to digitize objects with a complex shape.
Attention! For the most accurate scan results, the patient must remain static.

Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Shining 3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Shining 3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Range Vision Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Range Vision Main directions in medicine
Three-dimensional scanning is actively used in almost all medical fields. The presence of an accurate anatomical model helps to determine the current treatment regimen or to model a prosthesis. We must not forget the importance of virtual models for medical students: such schemes allow us to study the human anatomy in the most detailed way.
Dentistry
The use of an intraoral 3D scanner for diagnostics
The use of a dental 3D scanner to create a digital model of a plaster jaw prosthesis
Due to oncology, the Australian had to remove 80% of the upper jaw.
 The use of a 3D scanner helped create the perfect jaw prosthesis
The use of a 3D scanner helped create the perfect jaw prosthesis 3D dental scanning helps to create detailed virtual pictures of the patient's teeth. Thanks to this, the most complex restoration and restoration work is carried out, orthodontists design prostheses. The technology significantly reduces the time of manufacturing complex structures, and also saves the cost of producing plaster and other models.
The 3D scanner is actively used in dentistry due to a number of advantages. The device is suitable for working with patients with an increased gag reflex. Just a few years ago, to create an impression of the teeth, an impression mass was placed in the patient's mouth: this procedure brought great discomfort. Nowadays, 3D-scanning of teeth is carried out contactlessly and does not bring discomfort.
Attention! The use of a 3D scanner in dental practice has a great advantage: the data obtained during the diagnostics are instantly transmitted to the laboratory.

Plastic surgery and cosmetology
face scan
Familiarization of the patient with the expected result of rhinoplasty based on a three-dimensional image of her face
3D face scanning is actively used in cosmetology and plastic surgery. The study is assigned to study problem areas before carrying out some cosmetic manipulations, as well as to design the expected result of plastic surgery. Thanks to this technology, the patient can get acquainted with how his face will look after surgery. The scanner is used for performing operations on the face (rhinoplasty, blepharoplasty) and body (mammoplasty, abdominoplasty, etc.).
Orthopedics
3D scanning of the spine
3D scanning of the foot to study the anatomical curves
Orthopedic insole printed on the basis of a 3D image of the foot
3D scanning of the body is relevant in the process of determining the type and stage of curvature of the spine or foot.
 The use of x-rays to diagnose the spine and lower extremities does not provide such accurate information, moreover, this procedure is contraindicated in some patients. 3D scanning helps to obtain detailed information about the pathology and develop actual orthopedic products (insoles and corsets).
The use of x-rays to diagnose the spine and lower extremities does not provide such accurate information, moreover, this procedure is contraindicated in some patients. 3D scanning helps to obtain detailed information about the pathology and develop actual orthopedic products (insoles and corsets). For the manufacture of insoles, previously it was necessary to make an impression of the foot. If the doctor made mistakes, the cast turned out to be inaccurate, which affected the quality of the insoles. New technologies help to obtain the most accurate information, regardless of the doctor's actions.
Surgery
3D model of the heart created from scanned data
Siamese twin chest model. Based on the data obtained as a result of the scan, the surgeons managed to perform the most difficult operation to separate them.
The application of new technology plays an important role in surgery. Scanning is aimed at studying the features of the pathology, its location and blood supply.
 This information helps to carry out more accurate and safer operations, to prevent complications during surgery. In addition, scanning is used in the process of bioprinting tissues and organs for transplantation.
This information helps to carry out more accurate and safer operations, to prevent complications during surgery. In addition, scanning is used in the process of bioprinting tissues and organs for transplantation. 3D scanning is closely related to 3D printing: the surgeon gets the opportunity to study the model of the operated organ or part of the body, develop an actual scheme for surgical intervention and “hone” the movements.
Prosthetics
The use of a 3D laser scanner in transplantation
Prosthesis based on scan data
In the process of creating manual prostheses, it is necessary to accurately determine the location of tissues, muscles and blood vessels. If errors are made during the diagnosis, local necrosis may develop due to tissue rejection. Modern technologies allow collecting the most accurate information about the shape of the stump and the location of tissues to create high-quality and comfortable prostheses.

Student education
A student studies pathological anatomy based on a 3D cadaver model
Scanning helps medical students study anatomy more effectively. The new method is much more efficient than the use of 2D images in classical anatomical atlases. Some programs allow you to observe the surgical intervention: for example, the trajectory of the scalpel during the operation.
Interesting! In France, a 3D scanner is being used to study pathological anatomy. There was no need for an in-person autopsy, and the resulting schemes make it possible to study the human body in layers.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Medit Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer 3Shape Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer ScanPod3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Shining 3D Popular medical 3D scanners
A high-quality three-dimensional scanner provides accurate body diagnostics and successful operations.
 Next, we list a few scanners that have managed to establish themselves in the global market.
Next, we list a few scanners that have managed to establish themselves in the global market.
Shining Autoscan DS-EX
The device has an open, user-friendly platform that facilitates the scanning process. Various modules are easily installed on the platform, thanks to which the models are scanned in the articulator, the dental impression is examined from various angles, etc. A 3D scanner is used in a dental laboratory to create a virtual patient model, create a treatment plan, design crowns and jaw prostheses. The device is compact and highly accurate.
ScanPod 3D UPOD-S
An orthopedic scanner is used to obtain monochrome and color images. Despite its compactness, the device has a large scanning area, and high speed allows you to use the scanner in emergency mode. In addition, ScanPod 3D UPOD-S is capable of performing 40 operations on the resulting image, and also provides the ability to compare the anatomical features of the right and left foot.
 You can learn more about the features of the scanner in our review.
You can learn more about the features of the scanner in our review. Medit i500
The intraoral 3D scanner allows you to scan the entire oral cavity in a matter of minutes. A 3D Full HD color image is displayed on the screen. A small scanning module provides convenience to the doctor during the examination and does not bring discomfort to the patient. Due to its low weight, it is convenient to use even during long-term diagnostics.
3Shape TRIOS 3 Basic Pod
The compact device provides maximum comfort for both doctor and patient during diagnostics. The intraoral scanner works non-contact: no special powders need to be used for the procedure. The resulting color image is sent to the computer screen in high resolution. The CAD/CAM software provides the ultimate in ease of use, and thanks to the USB port, the 3Shape TRIOS 3 Basic Pod can be connected to any computer.
ScanPod3D USOL
ScanPod3D USOL is a compact orthopedic scanner that allows you to quickly and accurately scan the foot of one foot.
 The resulting image can be scaled and rotated for detailed viewing. Diagnostics can be carried out without load, with partial and full load. The device scans the arch of the foot, insoles and lasts, and the RX shape setting is used to create orthopedic shoes.
The resulting image can be scaled and rotated for detailed viewing. Diagnostics can be carried out without load, with partial and full load. The device scans the arch of the foot, insoles and lasts, and the RX shape setting is used to create orthopedic shoes. Caliber
The portable handheld scanner allows you to get a digital image of objects from 20 cm to 10 m. Weight is 900 g, so operation is not difficult. The touch screen displays the result of the scan, so there is no need for constant checking with the computer. The scanner is used to examine the fine details, and the powerful software ensures easy operation. Calibry is used in 3D scanning of the spine, face, joints and other parts of the body.
Shining 3D EinScan H
The handheld scanner is lightweight and compact, making it easy to carry around. The use of the latest developments in data capture helped to achieve stunning scan results: up to 1,200,000 points per second.
 Shining 3D EinScan H has a number of advantages:
Shining 3D EinScan H has a number of advantages:
-
Whole body scanning solution;
-
Reliable color reproduction;
- Fast scanning 1200000 points / sec.;
-
High accuracy of 0.05mm scan data.
The new 3D scanner for human scanning provides the most accurate and detailed information about the structure of tissues and organs.
Forecasts of the development of 3D technologies in medical practice
According to International Data Corporation (IDC) forecasts, by 2023 the industry is expected to grow by 635 million units. This means that due to the high accuracy of diagnostic data and the improvement of software, most modern clinics will prefer the use of three-dimensional scanners instead of outdated diagnostic equipment.
Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Thor3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer Shining 3D Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer 3Shape Add to compare
Product added to compare Go
Manufacturer ScanPod3D Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
3D scanners in medicine and dentistry
Supplier of 3D equipment since 2010
+7 495 646-15-338 800 333-12-82
3D scanners3d-printer-printer-printer service
On the Project-Zakopupkupovservisancyclopedia
an important attribute of medical research centers and practicing medical institutions around the world. With the help of three-dimensional scanners, it is possible to obtain, for example, an accurate 3D model of the structure of the human body or its individual parts. Plastic surgeons can obtain an accurate color 3D model of the breast, face and any other part of the body in minutes and visually demonstrate the results of future work.
- 3D-innovations in medicine
- Opportunities
- Choosing 3D scanner
- 3D (medicine in medicine
- Possibly
- selection 3D scanner
3D-innovations in medicine
Three-dimensional scanners are successfully used by prisons and orthopedists to create high-precision scans of body parts.
 This means that specialists can produce prostheses that are ideally suited to their patients without spending as much money on design as before.
This means that specialists can produce prostheses that are ideally suited to their patients without spending as much money on design as before. Previously, the process of producing prostheses and corsets was labor-intensive and uncomfortable. The patient was covered with plaster and waited. After hardening, the gypsum was cut off and sent to production. The manufacturer received the form and manually took measurements.
Now that medical institutions have the opportunity to use 3D scanners, there is no longer a need for expensive and time-consuming work to create plaster models, there is no need to contact the delivery service and wait for the cargo to arrive. Corsets created according to a 3D model are more accurate than plaster corsets, because they take into account all the nuances of the body structure.
Most recently, the design of dentitions took several weeks. Now, thanks to the advent of ultra-precise 3D scanners, the process is simplified and accelerated to several days.

3D innovations in medicine
3D scanners are successfully used by prosthodontists and orthopedists to create high-precision scans of body parts. This means that specialists can produce prostheses that are ideally suited to their patients without spending as much money on design as before.
Previously, the process of producing prostheses and corsets was labor-intensive and uncomfortable. The patient was covered with plaster and waited. After hardening, the gypsum was cut off and sent to production. The manufacturer received the form and manually took measurements.
Now that medical institutions have the opportunity to use 3D scanners, there is no longer a need for expensive and time-consuming work to create plaster models, there is no need to contact the delivery service and wait for the cargo to arrive. Corsets created according to a 3D model are more accurate than plaster corsets, because they take into account all the nuances of the body structure.

Most recently, the design of dentitions took several weeks. Now, thanks to the advent of ultra-precise 3D scanners, the process is simplified and accelerated to several days.
Capabilities
Placement of prostheses
- Scan any part of the body to create functional prostheses
- 3D archiving - no need to store multiple castings
- Modeling and planning in plastic surgery
- Orthopedics and cosmetology, dentistry
Diagnosis of the development of the skull of children
- Scanning of the head of a child to fit a soft helmet
- Subsequent head scan to track change
Wound care
- Color and texture wound scanning for quick selection of treatment methods.
Capabilities
Placement of prostheses
- Scan any part of the body to create functional prostheses
- 3D archiving - no need to store multiple castings
- Modeling and planning in plastic surgery
- Orthopedics and cosmetology, dentistry
Diagnosis of the development of the skull of children
- Scanning of the head of a child to fit a soft helmet
- Subsequent head scan to track change
Wound care
- Color and texture wound scanning for quick selection of treatment methods.

Learn more
-