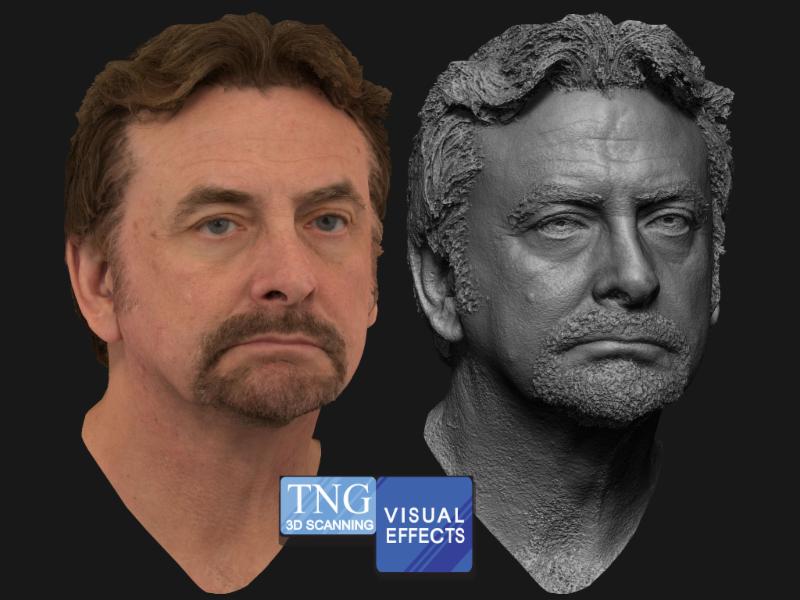
3D scanner resolution comparison
What you need to know
Introduction
Generally, accuracy means how close a measurement is to its true value. In 3D scanning, accuracy generally refers to single scan accuracy, but then there’s also volumetric accuracy.
When it comes to resolution, whose general definition is how sharply an image can be displayed, there can also be two values in 3D scanning. 3D scanner OEMs generally refer to mesh resolution– i.e., the distance between points within a point cloud (3D mesh)– when specifying resolution. But, some also specify measurement resolution.
All of these terms can be a bit confusing, and 3D scanning is already a complex enough technology. Let’s go over the basics!
3D scanning accuracy
What is accuracy?
The general definition of accuracy is how close the measurement is to its true or tolerable value. It is often confused with precision, which is how close different measurements (of the same target) are to each other. The simple graphic below illustrates the difference between accuracy and precision:
In 3D scanning, accuracy is how close the scanner’s measurements are to the object’s true size. If you measure a cube with an industrial caliper and obtain a width of 200mm, but your scanner captures the cube as 205mm-wide, then it is quite off.
Two types of accuracy specifications exist in 3D capture: single scan accuracy and volumetric accuracy.
Single scan accuracy vs volumetric accuracy
In spec sheets, accuracy often means single scan accuracy. It is the accuracy of one image capture.
Example: 0.05mm accuracy.
Most 3D scanner OEMs also specify volumetric accuracy. It is the accuracy of several captures, and this global accuracy diminishes the bigger the scanned part is.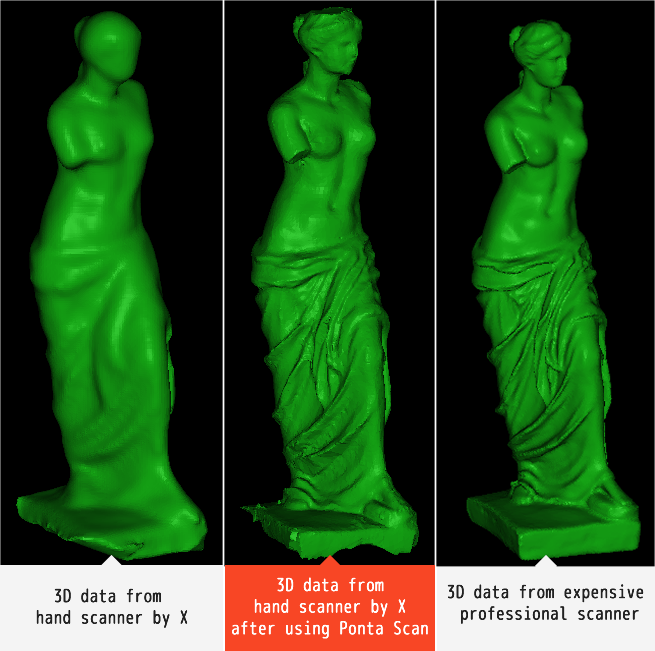
Example: 0.05mm + 0.15mm/m.
Following our example, if your part measures 2 meters long, the accuracy of your scanner will be 0.05 + (0.15*2) = 0.035mm. That’s quite a difference from the original, single scan accuracy! Volumetric accuracy is thus more important to consider than single scan accuracy, especially if you are going to 3D scan large objects (e.g., cars).
That said, some 3D scanners with integrated photogrammetry modules can build up a sort of 3D skeleton of the object (with adhesive markers) before filling it in with the rest. Markers are precise reference points for 3D scanners, like a connect-the-dots drawing. By using a photogrammetry-sourced “skeleton”, your data is bound to be more accurate.
Note: Photogrammetry is a 3D scanning technology that involves taking multiple photographs of an object from different angles in order to calculate its shape and size.
A part fitted with markers. Source: Aniwaa (SIMSCAN review)
Source: Aniwaa (SIMSCAN review)How accurate are these specifications?
Manufacturers indicate specifications which are maximums that were obtained in ideal conditions. If the manufacturer recorded an accuracy of 0.05mm in its lab, it doesn’t mean you will be able to achieve the same accuracy in-house.
A scanner’s accuracy can depend on a number of factors:
- Temperature (a 3D scanner will perform differently at 40°C than it will at 20°C)
- Calibration (how well did you calibrate your 3D scanner? Do you calibrate it regularly?)
- The person performing the scan (though there is less room for error with today’s and tomorrow’s sensors, and more intuitive software)
On another, important note, 3D scanner manufacturers don’t all follow the same standards to measure their scanners’ accuracy. If high accuracy is of utmost importance for your applications, look for brands that have VDI/VDE and/or ISO certifications, for example.
3D scanner resolution
What is resolution?
Resolution can mean many different things depending on what you are talking about (photography, filmography, printing, …), but it has the same fundamental meaning. It is a technical computer science term that characterizes “how well the reality was captured”.
With screens, for example, the resolution is linked to the number of pixels available to recreate an image. The more pixels, the better the resolution and the image quality (the cleaner and crisper your image will seem). We can see this clearly with the circle example below:
Pixel density affects the visual quality of an image. Source: Research Gate (Ivan Terol-Villalobos)In 3D scanning, there is one main type of resolution: the resolution of your 3D mesh, a.k.a. “mesh resolution”. But some manufacturers also specify “measurement resolution”.
Mesh resolution
Most often, “resolution” or “3D resolution” in spec sheets refers to the resolution of the resulting 3D mesh. It is mainly measured in point-to-point distance– ie., the distance between two 3D points in a dot cloud– as it is the easiest to comprehend. The closer your mesh’s points are together, the better it will look. Point-to-point distance is sometimes called “spacial distance between points” or “point distance”.
It is mainly measured in point-to-point distance– ie., the distance between two 3D points in a dot cloud– as it is the easiest to comprehend. The closer your mesh’s points are together, the better it will look. Point-to-point distance is sometimes called “spacial distance between points” or “point distance”.
Resolution can also be measured in PPS (points per scan). The more points your mesh includes, the smoother, more detailed it will look. This can be compared to 2D print quality, where the more PPI (points per inch) your file contains, the sharper your print.
Keep in mind that a higher mesh resolution means longer loading times and heavier files. If you don’t really need an extremely high definition, then there’s no use in putting strain on your RAM/GPU and weighing down your hard drive.
Note: In any case, you will likely need to invest in a high-end, gaming-quality PC in order to run 3D scanning software and load the enormous amount of captured data. Some of the computers we’ve worked with for high-end scanners cost over $5,000.
Some of the computers we’ve worked with for high-end scanners cost over $5,000.
Measurement resolution
The measurement resolution translates to how many points the sensor is capable of capturing in a given area. The more points per unit of surface, the better.
But, in the end, what really matters is the mesh resolution that can be obtained and used in the software after computation. In some cases, the software calculates an average of several measurement points to generate a single mesh point (a vertex).
Note that the requirements for mesh resolution are relative and not absolute: on a sharp edge, you need a good resolution; on a flat surface, only a few points are necessary. Some 3D scanning software suites optimize meshes accordingly to avoid stocking heavy, unusable data (and choking your PC) for nothing.
Note: As a metaphor, let’s take the human body and its sensory receptors.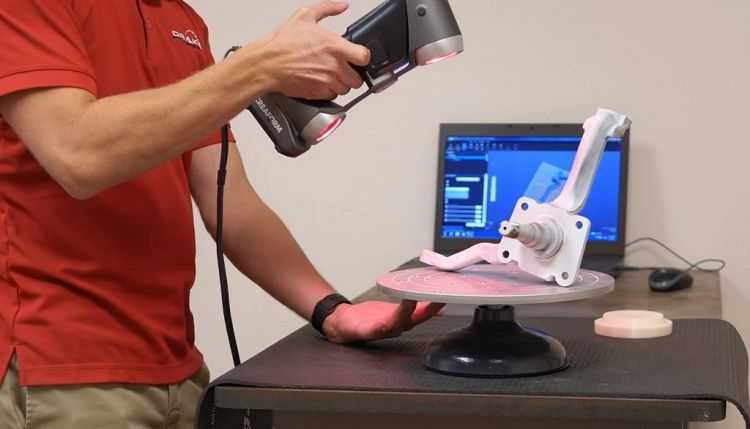 We have thousands of receptors at the tip of our fingers, which we use to touch and interact with almost everything. Our backs, however, have very few sensory receptors, as we don’t really use our backs to feel things.
We have thousands of receptors at the tip of our fingers, which we use to touch and interact with almost everything. Our backs, however, have very few sensory receptors, as we don’t really use our backs to feel things.
Conclusion
Many different terms are thrown around manufacturer websites and spec sheets. What really matters is volumetric accuracy and mesh resolution, and how well they answer your specific needs.
Furthermore, while accuracy and resolution specs are useful to easily and quickly compare one 3D scanner to another, they shouldn’t be deciding factors on their own. You should also consider a brand’s certifications, history, software, customer service, and more.
Feel free to reach out if you’re having trouble deciding on a 3D scanner or unsure of what you’ll actually need for your use case (and budget!).
Things to know before buying a 3D scanner: accuracy, speed, resolution
To make sure that you have all the necessary information prior to committing to a purchase, we have created the following short guide to help you make the right decision. It will address those all-important questions which you need to ask yourself, such as:
- What will I be 3D scanning?
- What technical specifications do I need to take into consideration?
- What is the difference between a handheld and a stationary 3D scanner?
- What is the price range for a professional 3D scanner?
1. Accuracy. How accurate is 3D scanning?
The accuracy of a portable 3D scanner normally ranges between 0.01 mm and 0.1 mm. But hey, what does it actually mean? Let’s say you’ve made a 3D model of your hand. Zoom in on your finger pads and you’ll clearly see the ridges. Fingers aside, how important is accurate 3D scanning for professional applications?
Accuracy, in fact, refers to how close to the actual object we have come in creating its virtual copy. How close are the dimensions of the 3D model to those of the object?
How close are the dimensions of the 3D model to those of the object?
Left: Actual size of the impeller cylinder measured with a micrometer — 29.80 mm.
Right: 3D model — size 29.85 mm
Accuracy is extremely important when key decisions need to be made based on the 3D scan data. This is especially true for industrial applications when precision is of the utmost significance.
To get the best accuracy, the scanner needs to be calibrated. All 3D scanners are initially factory calibrated, where the manufacturer ensures the best possible accuracy of the device. For some 3D scanners, onsite calibration is also possible. This is where the accuracy settings of the 3D scanner can be manually adjusted by the customer to meet the manufacturers’ optimal standards any time after the purchase to better suit his or her needs.
Highly-accurate handheld 3D scanners are great for industrial applications
Key point
Only professional 3D scanners are able to provide high accuracy and though they are pricier than scanners with lower specs, they are almost always worth the investment.
Manufacturers of 3D scanners will always state the accuracy in the specs of their device. The accuracy you require depends on the task at hand, but ultimately the choice is yours.
2. Resolution
Though accuracy is one of the key aspects to consider when choosing a 3D scanner, it is important to explore other factors, such as the resolution of the scanning device.
While accuracy is the measurement of the device’s degree of absolute correctness, resolution is the least possible distance between any two given points within a 3D model and is usually expressed by millimeters, or microns. This means, if you are looking to have an extremely detailed 3D model, you would use a high-resolution 3D scanner to capture the object. This is especially important for applications in quality control, reverse-engineering, animation and VR, heritage preservation, forensics, jewelry and many others.
The higher the resolution, the more detailed your 3D model will look.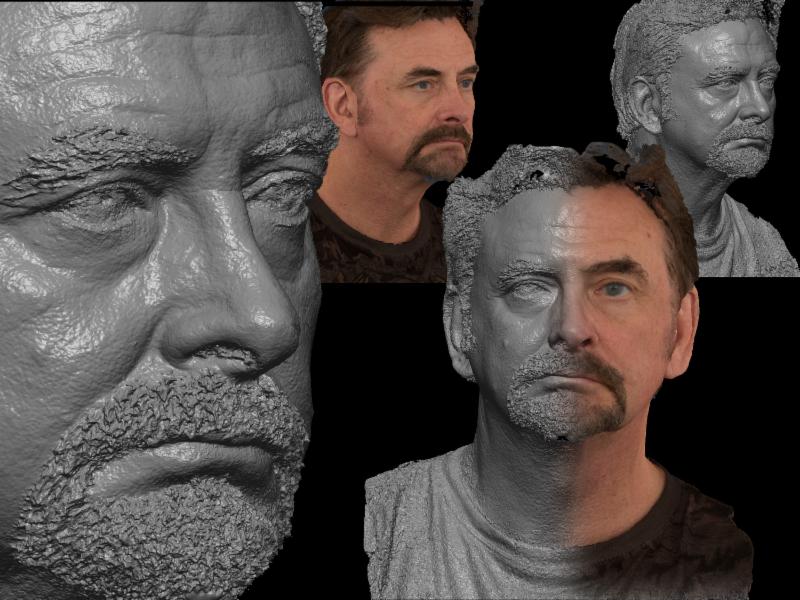
Left: resolution 0.15 mm, Right: resolution 0.3 mm
Sometimes, however, the user will opt for a lower resolution data. The higher the resolution, the heavier the model and the more time it will take to process. This might be a setback for users with less powerful computers, as well as those planning to 3D print the final model. A 3D printer will take much longer to produce a higher resolution model with all of its intricate details. So if processing time and printing speed matters, this is definitely something to keep in mind. Additionally, some 3D printers may not be able to reproduce high-resolution levels.
Depending on the application, users will choose the resolution settings accordingly. If you need your 3D model to be as detailed as possible, go for a 3D scanner that is able to safely and easily capture even the smallest of features.
Opt for a portable, lightweight 3D scanner. Handheld 3D scanners are easy to operate and rotate around the object being scanned. Select advanced models are able to 3D scan objects with a resolution of up to 0.1mm.
Select advanced models are able to 3D scan objects with a resolution of up to 0.1mm.
3. Speed
Time is money and that’s why it is also very important to consider the speed of a 3D scanner.
When we are talking about speed, we refer to how fast a 3D scanner can capture any given object. The way the speed is measured differs depending on the type of technology the device is using. For example, the speed of a structured light 3D scanner is calculated by the number of frames and the number of points captured per second. Some advanced white light 3D scanners only need one second to make 16 frames and capture 2 million points of the object.
A top-of-the-range handheld scanner with VCSEL technology is capable of going as fast as 80 frames per second and capture up to 4 million points in a flash.
A high-end VCSEL 3D scanner with an inbuilt touch screen, battery and WiFI data transfer
The speed of a LIDAR solution is calculated by the millions of points it is able to capture in a single second. A good quality stationary laser scanner would be able to scan at a speed of about 200,000 points per second. These are reference numbers and may vary depending on the scanner, object and scanning distance.
A good quality stationary laser scanner would be able to scan at a speed of about 200,000 points per second. These are reference numbers and may vary depending on the scanner, object and scanning distance.
A faster 3D scanner allows users to capture any object quickly, eliminating unnecessary costs and boosting productivity. This is especially important for large and costly projects on a tight schedule.
4. Ease of use
Ease of use is another important factor to consider when choosing a 3D scanner. To get the best possible results and maximize the output, it is vital to know how to utilize the device’s full potential.
One of the key questions to consider here: «How often will you be using your 3D scanner?»
If you will be doing a lot of 3D scanning or capturing large amounts of data, remember that a professional device with quick data capture abilities will save you time and money in the long run, as well boost your productivity.
Mid and upper-range 3D scanners are usually quite easy and intuitive to use. Although you might be tempted to go with cheaper versions, consider the additional time, training and frustration those might incur.
Although you might be tempted to go with cheaper versions, consider the additional time, training and frustration those might incur.
Key point
Although you might be tempted to go with cheaper versions, consider the additional time, training and frustration those might incur.
The fast frame rate and advanced tracking algorithms in professional solutions make scanning a lot swifter and easier. When considering the post-processing stage, don’t forget that the software plays an important part too. The software that goes with professional scanners is likely to be much more powerful and generally contains many automated features, without compromising on accuracy. As a result, the software is more user-friendly, fast and easy to learn.
5. Part size
Before selecting a 3D scanner, it is important to consider what exactly you will be capturing:
- What is the size of the object or objects you will be capturing?
- Will you be scanning variously sized objects? Or perhaps you are planning to automate your workflow and capture large amounts of identical objects?
- What material are your objects made out of and how detailed are they?
- Are you planning to 3D scan animate or inanimate objects?
Key point
The best 3D scanner for your application will depend on the size of the object, the material of its surface and the amount of intricate detailing you want to be able to capture.
If your workflow includes mostly capturing large to very large objects, such as trucks, trains or even planes, opt for a long-range stationary laser scanner, precise enough to capture those large objects in high detail.
Highly-accurate 3D model of a Klemm L25d VIIR LX-MA airplane with a 13 m wingspan.
For smaller objects, such as furniture, motorcycles or midscale statues, go with a handheld 3D scanner with fast capture and the ability to effortlessly maneuver around the object and capture those hard-to-reach places.
If you are planning to scan a complex industrial part for quality control or measurements, choose a handheld 3D scanner with high accuracy.
For complex objects that are large in size and have small details that need to be precisely captured, it is a great idea to combine two or more 3D scanners for the best results. A stationary scanner captures the large areas fast, while a handheld scanner can fill in the detail.
Size reference. Understanding the size of your object
Understanding the size of your object
6. Portability
Portability is another factor to consider when making a decision.
- Where are you planning to capture 3D data?
- Do you usually work in a controlled environment or out in the field?
Once again, your choice will depend based on your application. Stationary scanning solutions are great for capturing large objects, where a handheld solution would require more time.
Portable 3D scanners offer other advantages. They give a much higher degree of control to the operator, making it a more flexible solution. Able to capture those hard to reach places, portable solutions are easier to manipulate and can be effortlessly maneuvered around tricky angles.
You will also greatly benefit from choosing a 3D scanner that is able to work from an internal or external battery, and so does not require a power source nearby.
A handheld 3D scanner with a portable battery pack for uninterrupted 3D data capture
7.
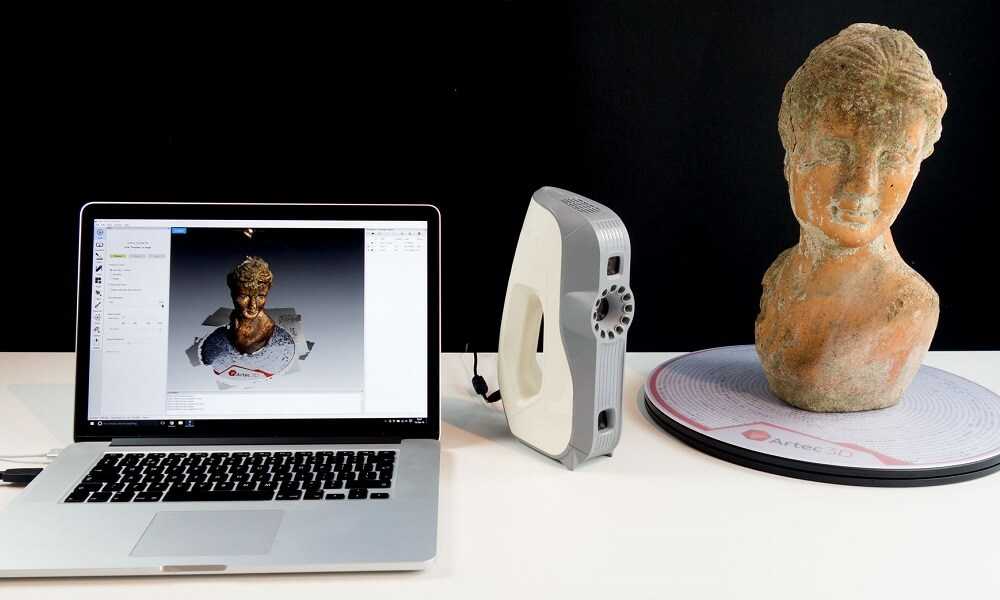 Software features
Software featuresRemember that it is the software that really powers the 3D scanner. Manufacturers of professional 3D solutions strive to develop the optimal 3D scanning software to push the boundaries of their 3D scanners.
An advanced 3D scanner that is able to capture objects of various sizes requires powerful 3D software. It needs to be able to handle and process all of the incoming data quickly and error-free so as to deliver the best possible results with each use.
Some advanced 3D scanning and post-processing software are much more versatile and user friendly than others.
Advanced 3D software for accurate data capture, processing, analysis and more
Give both the 3D scanner and software a try before you commit to the purchase. Explore the useful features that are offered and what tools are at your disposal. Are they enough for you, or do you require a more advanced solution for your projects?
Another thing to pay attention to is whether the manufacturer is continually developing the software and releasing new, updated versions. A new software version can often transform a 3D scanner into a whole new product, drastically increasing speed and usability. Expert companies are constantly developing and improving both their hardware and software to ensure the very best workflow.
A new software version can often transform a 3D scanner into a whole new product, drastically increasing speed and usability. Expert companies are constantly developing and improving both their hardware and software to ensure the very best workflow.
8. Maintenance
Don’t forget about the maintenance your 3D device will require. Just like with any other piece of advanced equipment, you might occasionally need to have your device «checked-up». This guarantees that your device will function properly and deliver accurate results for a long time to come.
Each manufacturer has their own set of maintenance procedures, such as calibration, optics cleaning and so on. Though this is something that might cost you extra, some companies offer up to two years free warranty on their products.
9. Environment
The scanning environment is yet another factor to consider when making your choice.
- What will be the standard conditions you scan in?
- Will you be scanning outdoors in direct sunlight? Or perhaps it will be in a dark and humid place?
Factors such as temperature, humidity and light can greatly affect both the overall performance of the scanner and the quality of the scans themselves.
Combine various 3D scanning technologies for best results
Manufacturers will usually indicate the optimal temperature range, as well as the accepted levels of humidity for their 3D scanning solutions, but there are a few universal rules to ensuring your 3D scanner works properly and delivers accurate results.
- Scanners might overheat when exposed to extremely high temperatures. Similarly, avoid using your device in low temperatures, as a very cold environment also affects the scanner’s accuracy and may cause it to malfunction.
- As with any other electronic equipment, 3D scanners should not be exposed to high humidity or have any contact with liquids
- Keep your device away from dirt, dust and other small particles that may cause damage
- Ensure you have enough light to capture your object
- Only very few 3D scanners can capture in direct sunlight. Most will need you to create shade where possible for better results.
10.
 Price
PricePrice is an important factor to take into consideration when making the decision to buy. The cost of the 3D scanner will correspond to the features provided by the device, as well as the quality and speed of data capture.
Key point
Though less expensive 3D scanners might seem more appealing in the short term, remember that it is an investment and look at the bigger picture.
3D scanners start at around $3,000, with the most advanced models costing over a $100,000. Though less expensive 3D scanners might seem more appealing in the short term, remember that it is an investment and look at the bigger picture. Quality devices are guaranteed to last longer, are less likely to malfunction and will deliver outstanding results for years to come.
However, keep in mind that in some cases, additional expenses may occur when purchasing a 3D scanner. Some companies may charge you extra for the following products and services:
- shipping charges
- installation
- technical support
- sales tax
- training
- standard and extended warranty
Be sure that you enquire about any additional charges prior to making a purchase.
Now that you are familiar with the main criteria for choosing the optimal 3D scanner for your projects, you can now move to the demo stage. Always test the scanners and the software beforehand to avoid any unpleasant surprises. Companies offering quality solutions are always happy to offer a one-on-one demonstration, as well as training, workshops, etc. Talk to the experts today to find out more about 3D scanning technologies and how they can have a long-lasting impact on your business.
comparison and selection based on tasks
3D scanners
Reverse engineering
Geometry control
Author: Ilya Krupennikov
Author: Ilya Krupennikov
What are the advantages of the new SILVER | Go!SCAN SPARK | HandySCAN SILVER | HandySCAN BLACK | Comparison of 3D scanners | What is the best solution for you?
Creaform has updated its HandySCAN 3D line of handheld 3D scanners with the launch of the SILVER series, featuring some of the best features of patented technology at an affordable price. This proven and reliable 3D scanner has been optimized for engineers and other professionals who need an efficient and affordable way to improve their product development process, speed time to market and reduce costs.
This proven and reliable 3D scanner has been optimized for engineers and other professionals who need an efficient and affordable way to improve their product development process, speed time to market and reduce costs.
The SILVER line includes two solutions: HandySCAN 307 and HandySCAN 700.
What are the advantages of the new SILVER
series-
Quality optics: Provides reliable and extremely high measurement quality with an accuracy of 0.030mm.
-
7 Laser Arrays: Capture the surface of large objects quickly with a 275 x 250mm scanning area.
-
Versatility: One device to digitize a variety of parts, no matter their size, complexity, material or color.
-
Ease of Operation: A user-friendly user interface and real-time visualization provide ease of use and a quick learning curve for both experienced and novice users.

-
Portability: Lightweight (850g) and easy to install, the scanner can be set up and ready to go in less than 2 minutes, in any environment, indoor or outdoor.
New 3D scanners are already available for order in our catalog.
Do you want to know the prices of 3D scanners, ask questions or order a free test scan? Fill out online application and our experts will contact you.
We would like to introduce you to the differences between HandySCAN BLACK, SILVER and Go!SCAN SPARK scanners. This review will help you understand which 3D scanner is right for you.
Go!SCAN SPARK: speed, simplicity, efficiency
This model has been developed to provide the fastest and easiest way to make 3D measurements for product development, design and reverse engineering professionals. Go!SCAN SPARK opened up three new possibilities for engineers and designers:
-
develop innovative products of complex shape and design;
-
attract new customers by raising production to a higher level;
-
Gain a competitive edge and accelerate time-to-market for innovative products.

Speed
Thanks 9With 9 lines of white illumination capable of up to 1.5 million measurements per second, Go!SCAN SPARK can scan objects in minutes and quickly transfer data to reverse engineering, CAD or 3D printing software.
Simplicity
Go!SCAN SPARK is not only capable of scanning with fewer marks, but in terms of geometry and texture tracking capabilities, the scanner is second to none. With it, engineers and designers, who are usually not experts in 3D scanning, simply select the most appropriate positioning mode - by geometry, texture or marks. Easier nowhere.
Efficiency
With instant meshing and tight integration with Go!SCAN 3D modeling software, SPARK is considered the most efficient handheld 3D scanner on the market, and the entire measurement workflow from setup to real-time scanning to finished files takes record time.
Thus, Go!SCAN SPARK allows you to quickly and effortlessly measure complex surfaces, scan any object with fewer marks and no preliminary preparation of details, and capture texture and color with an impressive level of detail.
HandySCAN SILVER Series: Precision, Proven Technology, Versatility
SILVER 3D scanners are the best value for money for professionals and entrepreneurs who want to develop products according to the needs and requests of customers, as well as sign more contracts, grow their business and achieve new goals.
Precision
The HandySCAN 307 and 700 provide accurate and reliable 3D measurements regardless of setup quality or user experience. With dynamic referencing, the scanner and workpiece can be freely moved during measurement without sacrificing scan accuracy or quality.
Proven and reliable
technology The SILVER series scanner will be a profitable purchase due to its reasonable price and high performance. The well-proven technology, designed and manufactured in North America and already with over 5,000 users, demonstrates that Creaform prioritizes attentive service, reliability and a commitment to making its solutions available to as many professionals as possible.
The well-proven technology, designed and manufactured in North America and already with over 5,000 users, demonstrates that Creaform prioritizes attentive service, reliability and a commitment to making its solutions available to as many professionals as possible.
Versatility
Thanks to the user-friendly interface and ergonomic design, the SILVER series 3D scanner is very easy to learn and use, regardless of the experience or competence of the user. The versatility of the device allows you to scan objects of any size, complexity, material or color.
The devices are part of the HandySCAN 3D family, the industry standard for metrology-grade portable 3D scanners. Providing the best value for money, this proven and reliable patented technology enables any user to make accurate and repeatable 3D measurements of any complexity in any environment.
HandySCAN BLACK Series: Speed, Metrology Grade Measurements, Versatility
The BLACK series is the flagship of the HandySCAN 3D line, the industry standard for metrology-grade portable 3D scanning. These scanners have been designed for three specific user groups. It:
These scanners have been designed for three specific user groups. It:
-
product development engineers who need to innovate and develop complex shapes to offer better and more competitive solutions;
-
quality control teams and production departments whose tasks include optimizing the production process, identifying and eliminating emerging problems and avoiding downtime;
-
quality control specialists who must verify that customer requirements have been met and confirm that the parts are suitable for their intended use for end users.
Speed
Thanks to 11 blue laser units, combined with high-resolution cameras and original optical components, the scanner can perform up to 1.3 million measurements per second. Comparable to Go!SCAN SPARK, the speed of the entire measurement process, from setup to meshing, saves valuable data acquisition and analysis time.
3D scanning metrology grade
Belonging to the metrological class indicates the high quality of scanning, accuracy and reliability of measurements. The HandySCAN BLACK scanner is ISO 17025 certified and complies with VDI/VDE 2634 part 3 (Germany), and the accuracy of the device is 0.025 mm (with a volumetric accuracy of 0.02 mm ± 0.04 mm/m). With four times the resolution of the SILVER series, the BLACK series is ideal for scanning objects with a high level of detail such as small plastic or sheet metal parts.
High flexibility
In short, HandySCAN BLACK are truly versatile 3D scanners. With an adaptable area and unlimited scan volume, the device can measure any part, regardless of size, shape, surface quality or complexity. In addition, the scanners have several blue lasers, which is the best suited for measuring complex surfaces.
Comparison of 3D scanners
What would be the best solution for you?
If you value speed and convenience more than accuracy and versatility, Go!SCAN SPARK is the one for you. The ISO 17025 accredited HandySCAN BLACK is the best option for achieving the highest accuracy and detail, as well as complete measurement uniformity. HandySCAN 3D SILVER series is a proven and reliable technology, which is characterized by an affordable price and high performance.
Go!SCAN SPARK is a solution for product development and reverse engineering departments who want to bring new products to market faster, while HandySCAN SILVER is a device for professionals and entrepreneurs who need to develop better products to grow their business and achieve new goals. And finally, HandySCAN BLACK are versatile 3D scanners that can be used at all stages of the product lifecycle management process, from development to production, assurance and quality control. All three models have their own characteristics, but what they have in common is the portability, reliability and quality service that Creaform is known for.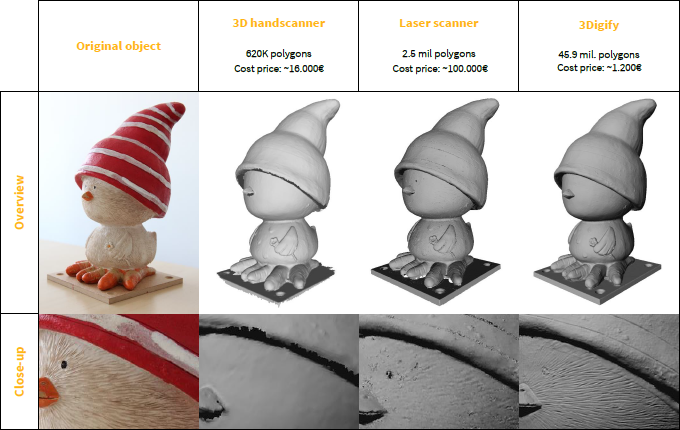
Material provided by Creaform
Article published on 03/17/2021, updated on 03/04/2022
90,000 select 3D scanner: types, advantages, solved tasks3D scanners
Fundamentals 3D
reverse engineering
Geometry Control
The best on the topics
Automation of quality control
Author: Seeds PopaDYADYUK
Author: Semyon Popadiuk
Benefits of 3D Scanners | What tasks does 3D scanning solve | Criteria for choosing a 3D scanner | Professional 3D scanning for fast and efficient production solutions
Modern 3D scanners have a wide range of features and a variety of functionality. They are used everywhere - in manufacturing, construction, education, the entertainment industry and are used even in everyday life. In order to choose the scanner that suits your needs, there are a number of aspects to consider, which we will discuss in this article.
Order a free test 3D scan using equipment from the world's leading manufacturers:
Leave a request
Advantages of 3D Scanners
What is a 3D scanner? This is a device designed to quickly analyze a physical object and create its accurate 3D computer model. The principle of its operation is based on calculating the distance to the object using two cameras. In addition to the cameras, a backlight is used - LED or laser.
The principle of its operation is based on calculating the distance to the object using two cameras. In addition to the cameras, a backlight is used - LED or laser.
3D scanners are classified both according to their form of execution (stationary and portable) and according to the areas of use, mainly divided into professional and household.
Watch the video review series of the ZG AtlaScan handheld 3D laser scanner
3D scanners make it possible to significantly reduce the time and costs at the development stage, improve the quality of products and, ultimately, speed up the release of the product to the market. They can be used at any stage of product lifecycle management and will help to optimize the production process of enterprises in various industries, including:
- automotive industry,
- mechanical engineering,
- aerospace industry,
- oil and gas industry,
- shipbuilding,
- building and architecture,
- arts and culture,
- medicine,
- jewelry,
- science and education.
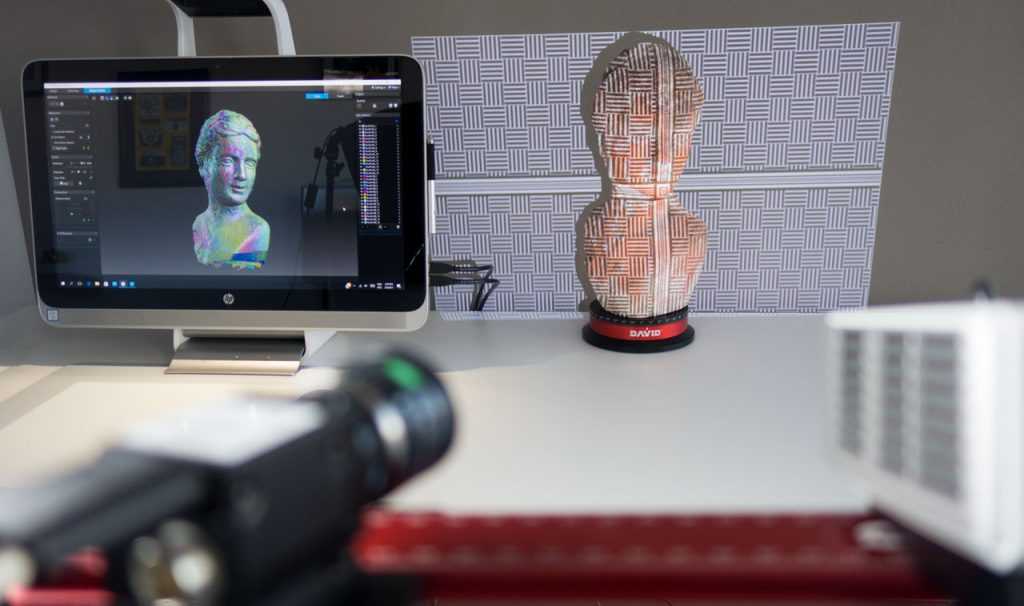

3D scanning devices remove many of the limitations of traditional measuring equipment. Such tools familiar to the metrologist as templates, micrometers, calipers are inexpensive, but they are characterized by subjective readings and are not suitable for complex measurements. Coordinate measuring machines are more accurate than 3D scanners, but they are more expensive, larger, and require specialized operator training.
Optical inspection systems, which include 3D scanners, are the best solution in terms of price and quality, as they provide:
- measurement speed,
- high precision digitizing objects of complex geometry,
- can work autonomously,
- are easy to operate.
Thanks to a 3D scanner, the work of a designer, technologist, and constructor is greatly facilitated: the performance of time-consuming complex measurements and the creation of a design from scratch are a thing of the past.
What tasks does 3D scanning solve
- Quality control: the ability to check any geometric parameters, including input and output control, metrological control of parts and production equipment.
- Reverse engineering of products for prompt receipt of project documentation and product upgrades.
- Design and simulation for the purpose of prototyping and evaluation of the appearance of products, modernization of production facilities and equipment.
- Digital archiving of any required assortment (eg discontinued parts). Models stored in digital libraries are available remotely from anywhere in the world.
3D scanner selection criteria
The main criterion is scanning accuracy . High-precision devices (10-30 microns) will help to get a phenomenal result: they are able to transfer the most complex surface geometry into 3D with minimal errors. Such 3D scanners are used in reverse engineering, quality control, medicine, and are used to digitize molds, device parts, etc. 3D scanners with an accuracy of 30–100 engineering.
3D scanners with an accuracy of 30–100 engineering.
ZG AtlaScan is the world's first 3D scanner with hole capture
When choosing a 3D scanner, you should also consider resolution (detail) , i.e. the degree of discreteness that is available when digitizing an object. The highest level of detail allows you to display the smallest elements in the 3D model.
Р the size of the scanned objects and, accordingly, the mobility of the 3D scanner directly depend on the type of device that you select. When digitizing parts and objects of small and medium parameters, hand-held scanners are usually used. Stationary scanners are suitable for capturing complex small and medium-sized products with small details. Scanning of large objects (buildings, structures, communications) is performed using ground-based laser devices (range finders).
When studying the functionality of 3D scanners, pay attention to such points as the conditions of use, scanning speed, the surface of the scanned object, and color.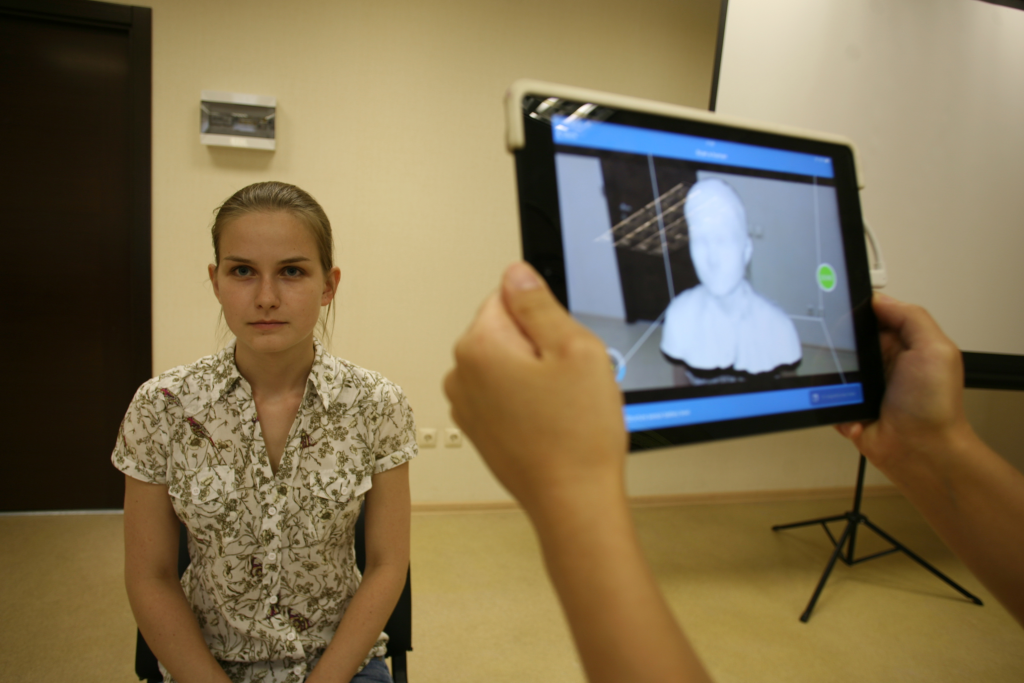
Please note that the next step after scanning is to obtain and further work with the CAD model, and for this you will need specialized software.
Processing 3D Scan Data for Reverse Engineering in Geomagic Design X Software
Professional 3D scanning for fast and efficient production solutions
iQB offers cutting-edge solutions that successfully operate in leading enterprises around the world:
- Portable devices for metrological 3D measurements from ZG Technology (China). The line includes a wide range of instruments, from an affordable handheld 3D scanner to a powerful optical tracking measurement system, as well as photogrammetry and portable CMM. ZG's unique strengths include the world's first handheld MarvelScan solution with three cameras for markless laser scanning and tracker, and proprietary instant hole capture technology. ZG Technology 3D scanners provide measurement speed up to 1 million 350 thousand points per second and accuracy up to 0.
 01 mm.
01 mm. - Stationary Russian-made RangeVision PRO 3D optical scanner is an industrial solution for metrology, available to companies of any level. The device is designed to digitize objects from 1 mm to 5 m and offers the highest level of accuracy (up to 0.018 mm) and 3D resolution (up to 0.04 mm). This is the first domestic 3D scanner approved by the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology as a type of measuring instrument.
- Creaform handheld 3D scanners for digitizing products ranging in size from a few centimeters to 6 meters. The Go!SCAN series devices (including the latest Go!SCAN SPARK) are based on structured illumination technology; HandySCAN 3D and MetraSCAN 3D are laser devices that are certified industrial grade metrology tools. The new generation MetraSCAN BLACK|Elite model is the fastest handheld 3D laser scanner on the market (1.
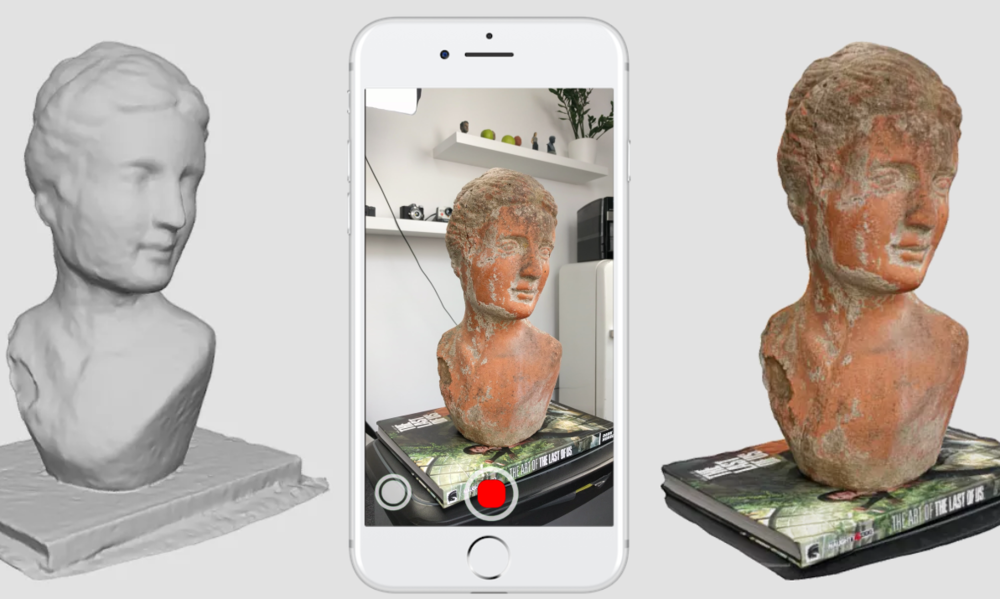 8 million measurements per second). The volumetric accuracy that Creaform technology can provide is up to 80 microns per 16 cc. m.
8 million measurements per second). The volumetric accuracy that Creaform technology can provide is up to 80 microns per 16 cc. m. - Creaform also produces 3D scanners and software under the peel 3d brand, combining affordability, ease of use and high quality. The line is designed to solve the problems of reverse engineering and digitalization of objects in such areas as art, preservation of cultural values, consumer goods, science and education, human body scanning. Peel 3d devices are capable of measuring objects from 0.3 to 3 m with an accuracy of 0.1 mm.
RangeVision PRO Fixed Scanner Creates Yamaha R3 Sport Fairings with Improved Aerodynamics, High Strength and Lighter Weight
- Solutionix fixed optical 3D scanners for small objects (10-500 mm) with many small parts. Allow to receive an error less than 8 microns.
- FARO Focus 3D geodetic laser scanners perform fast and accurate scanning of large objects, complex structures, premises and landscapes. They operate in the range from 0.6 to 350 m, they are distinguished by increased accuracy, ease of operation and the ability to operate in the most difficult environmental conditions.

- EPiC budget 3D terrestrial laser scanners are based on the principles of simplicity, convenience and affordability. Their main advantages are super light weight, high shooting speed (from 30 to 90 seconds), 360-degree panoramic camera and the ability to control from a mobile device.
Many of the above scanners are included in the register of measuring instruments of the Russian Federation and have the appropriate certificates.
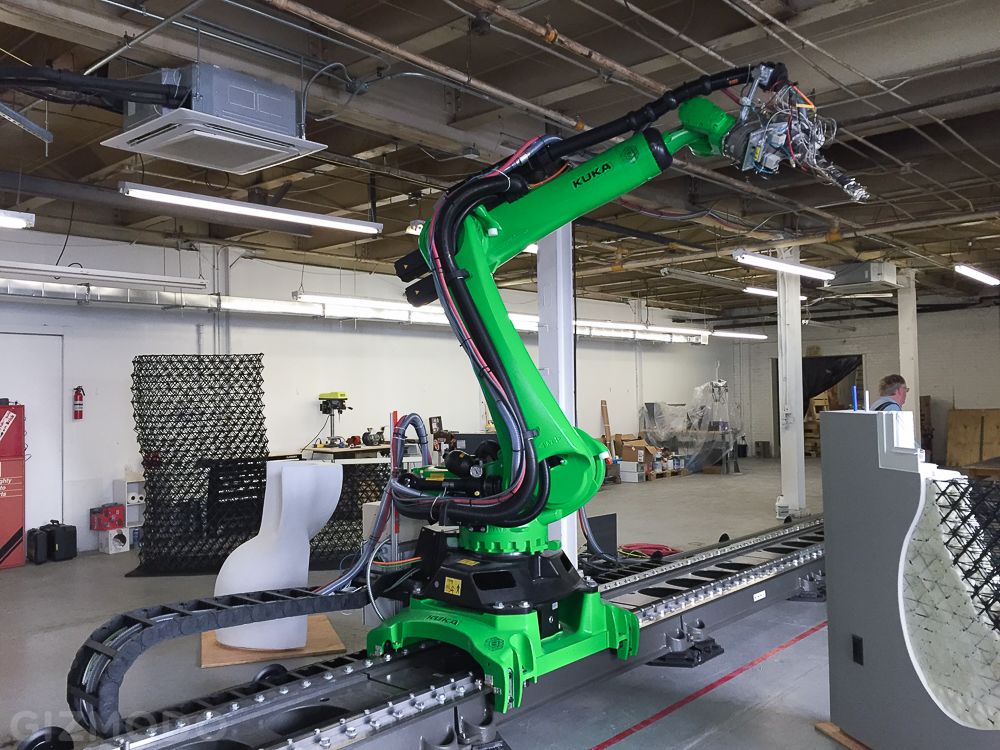
Robotic 3D scanning systems, such as Creaform MetraSCAN 3D-R, allow you to increase the speed and efficiency of quality control directly on the conveyor
A variety of 3D scanning devices on the market will allow you to choose exactly the model that is needed for solving specific problems. The price range is also wide: from simple devices costing up to $500 to high-precision professional 3D scanners costing tens and even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Contact iQB Technologies experts! We will select the optimal solution that will optimize product development and production in your enterprise, design office or research center.