3D printing vegetables
New Method Developed to Create “Food Inks” for 3D Printing Fresh Vegetables
A ‘foodscape’ assembled with 3D-printed designs made from garden peas, carrots, and corn. Credit: SUTD / NTU / KTPH
Singapore researchers develop new method for ‘printing’ fresh vegetables, leading to tastier, more nutritious food for patients with swallowing difficulties.
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH) have developed a new way to create “food inks” from fresh and frozen vegetables, that preserves their nutrition and flavor better than existing methods.
Food inks are usually made from pureed foods in liquid or semi-solid form, then 3D-printed by extrusion from a nozzle, and assembled layer by layer.
Pureed foods are usually served to patients suffering from swallowing difficulties known as dysphagia. To present the food in a more visually appetizing way, healthcare professionals have used silicone molds to shape pureed foods, which is labor and time intensive, and requires storage.
While 3D food printing means food can be easily produced in a desired shape and texture in a shorter time, the dehydrated food and freeze-dried powders used as food inks usually contain a high percentage of food additives such as hydrocolloids (HCs) to stabilize the ink and enable a smoother printing process. High concentration of HCs usually changes the taste, texture, and aroma of the printed food, making it unappetizing to patients with dysphagia. This may lead to reduced food consumption and malnutrition among patients.
To overcome this challenge, the research team explored various combinations of fresh and frozen vegetables to make the food inks stable.
Not only were they able to better preserve the nutrition of the printed food, they also made it more palatable. This new method of making food inks should lead to increased meal consumption by patients, contributing positively to their physical health and mental state of mind.
Representative images of 3D printed shapes with five formulations of one food ink type, images with boxes drawn around them represent the optimized formulations of the inks. Print scores represented on the top right corner assessed by shape fidelity and shape stability. Credit: SUTD / NTU / KTPH
Print scores represented on the top right corner assessed by shape fidelity and shape stability. Credit: SUTD / NTU / KTPH
Additionally, the team discovered that vegetables could be broadly classified into three categories with each requiring a different hydrocolloid treatment in order to become printable. For instance, garden pea, carrot, and bok choy were chosen as representatives in each category, requiring no HCs, one type of HC and two types of HCs, respectively (refer to images).
Prof Yi Zhang, the principal investigator from the NTU team said, “Our technology helps to provide dysphagic patients with adequate nutrient-rich and safe diets. Their feeding is more dignified, enabling them to socialize and consume meals that look, feel and taste like regular food. Our method of 3D printing fresh vegetables can be used easily in hospitals, nursing homes, daycare centers for the aging population with dysphagia and other swallowing disorders. Our research is also another step forward in digital gastronomy, where we can cater to specific requirements prescribed by dieticians, such as nutrition customization and visual appeal.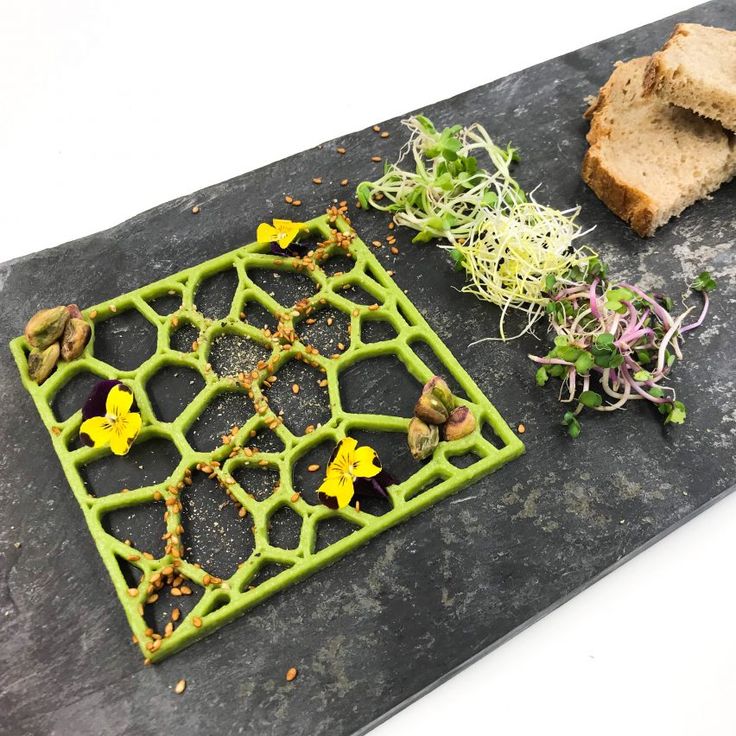 ”
”
Prof Chua Chee Kai, corresponding author and the Head of Pillar, Engineering Product Development at SUTD, added: “The next frontier of additive manufacturing is 3D food printing. As the 3D food printing landscape is increasingly evolving, we are excited to continue pushing the boundaries of this industry to find innovative solutions for global issues such as food security and sustainability.”
Gladys Wong, co-principal investigator and Senior Principal Dietitian from KTPH said: “3D Food Printing is more than a novelty. I believe it will be a viable approach in the near future in providing sustenance and nourishment to our increasing aging population. Our frail, elderly patients as well as those with swallowing difficulties will be able to enjoy a visually presentable and pleasurable dining experience even with a restrictive diet of smooth pureed dishes.”
Reference: “3D food printing of fresh vegetables using food hydrocolloids for dysphagic patients” by Aakanksha Pant, Amelia Yilin Lee, Rahul Karyappa, Cheng Pau Lee, Jia An, Michinao Hashimoto, U-Xuan Tan, Gladys Wong, Chee Kai Chua and Yi Zhang, 17 December 2020, Food Hydrocolloids.
DOI: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106546
Funding: National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Cluster Project, National Research foundation Singapore
3D Printing Nutritional and Appetising Vegetables
3D printing news News Researchers Develop More Nutritional and Appetising Method of 3D Printing Vegetables
Published on February 11, 2021 by Amelia H.
Singaporean researchers have developed a novel method of 3D printing vegetables using food hydrocolloids. Previous three-dimensional food printing (3DFP) methods have largely relied on freeze-dried vegetable powders. This method, however, is centred around the use of fresh and frozen vegetables to create “food inks” for 3D printers. The advantage of using fresh and frozen, rather than dried vegetables, is that it better preserves their nutrition and flavour. Additionally, this novel method of 3D printing food is cheaper than the majority of existing methods.
This discovery was the result of a collaboration between Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH). The research was targeted toward helping people with dysphagia. Dysphagia describes difficulty swallowing. This is a commonly experienced issue for elderly people and people suffering from debilitating illnesses. People suffering from dysphagia are confined to foods that are soft and safe to swallow. Therefore, they either require a restrictive diet, or food that has undergone textural modifications. In order to prevent malnutrition foods should also be visually pleasing to encourage a greater uptake.
The research was targeted toward helping people with dysphagia. Dysphagia describes difficulty swallowing. This is a commonly experienced issue for elderly people and people suffering from debilitating illnesses. People suffering from dysphagia are confined to foods that are soft and safe to swallow. Therefore, they either require a restrictive diet, or food that has undergone textural modifications. In order to prevent malnutrition foods should also be visually pleasing to encourage a greater uptake.
Researchers experimented with different levels of hydrocolloids to optimise the taste, texture and printability of the vegetable food inks.*
A hydrocolloid is a particle, or colloid, which has been mixed in water, or hydrated. Hydrocolloids are responsible for providing several common foods with the right viscosity, texture or structure. Traditionally, the powders used in food inks contain high levels of food additives, particularly hydrocolloids. While these are useful for stabilising the ink and making the printing process easier, a high concentration of hydrocolloids changes several aspects of the food, including the smell, taste and texture. This often causes the food to become considerably less appetising, which in turn can act as a deterrent and result in those suffering from dysphagia to reduce their food consumption, and in some cases even become malnourished. The research team thus wanted to find a way to limit the detrimental effects of hydrocolloids. They experimented with different levels of hydrocolloids in order to find the minimum amount that would still render the inks printable.
This often causes the food to become considerably less appetising, which in turn can act as a deterrent and result in those suffering from dysphagia to reduce their food consumption, and in some cases even become malnourished. The research team thus wanted to find a way to limit the detrimental effects of hydrocolloids. They experimented with different levels of hydrocolloids in order to find the minimum amount that would still render the inks printable.
Thanks to this novel method of 3D printing vegetables, the research team were able to print more appetising, and more nutritional vegetables by limiting the amount of hydrocolloids in the food ink as well as by using fresh and frozen, instead of powdered vegetables. Yi Zhang, the chief investigator of the NTU team commented; “Our technology helps to provide dysphagic patients with adequate nutrient-rich and safe diets. Their feeding is more dignified, enabling them to socialize and consume meals that look, feel and taste like regular food”.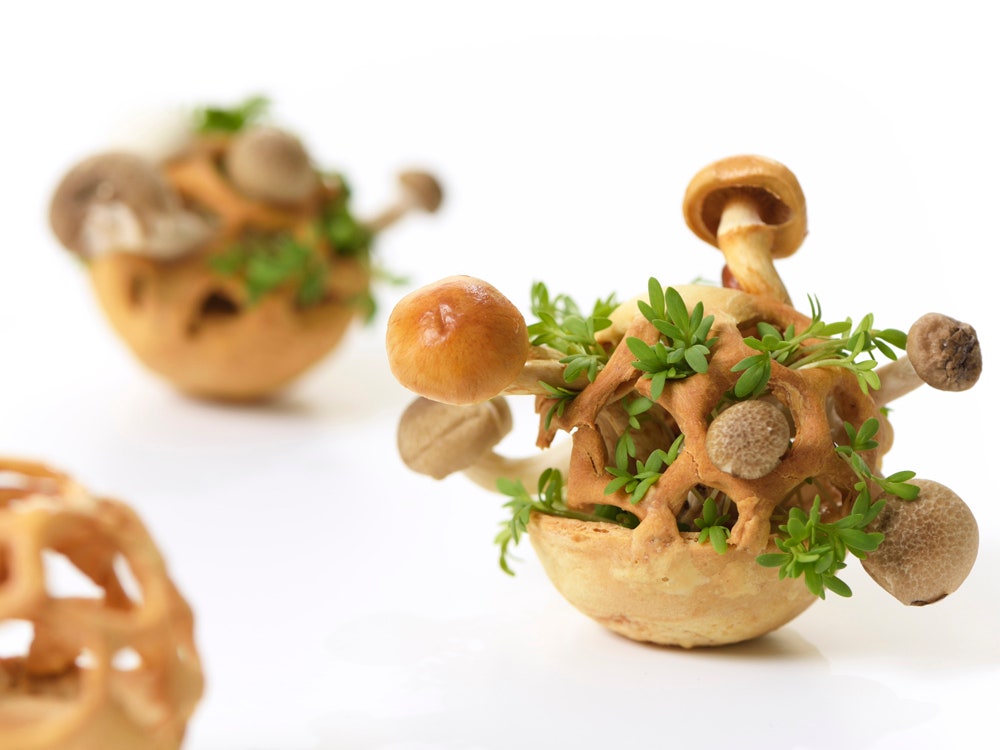
*All pictures credited to Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and Khoo Teck Puat Hospital (KTPH).
If you would like to read the full findings of this research, you can find the full paper HERE. What do you think about this novel method of 3D printing vegetables? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn pages! Sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox!
90,000 characteristics, pros and cons of each model07.04.2021
Content
-
- What is a food 3D printer
- Field of use
- used raw materials
- 9000 9000 9000 9000
- Top 10 Best Food Printers: A List of the Most Current Models
- 1. PancakeBot 2.0
- 2. Wiiboox Sweetin
- 3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
- 4. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus Food 3D Printer with Cooling Chamber
- 5.
 byFlow Focus
byFlow Focus - 6. Chefjet Pro
- 7. Foodini
- 8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer Commercial ArtcakesOT7 .90BOT Printer F5
- 10. ZMorph VX
- What is a food 3D printer
- Selection guide
- Output
A food printer is a high-tech device that is used to create culinary masterpieces. The decorative design of food products has reached a new level thanks to the use of modern technologies: high-quality and large-format printing is carried out on cakes, waffles, pancakes and even coffee. Here are the top best 3D food printers in different price categories for people who are fond of cooking. nine0003
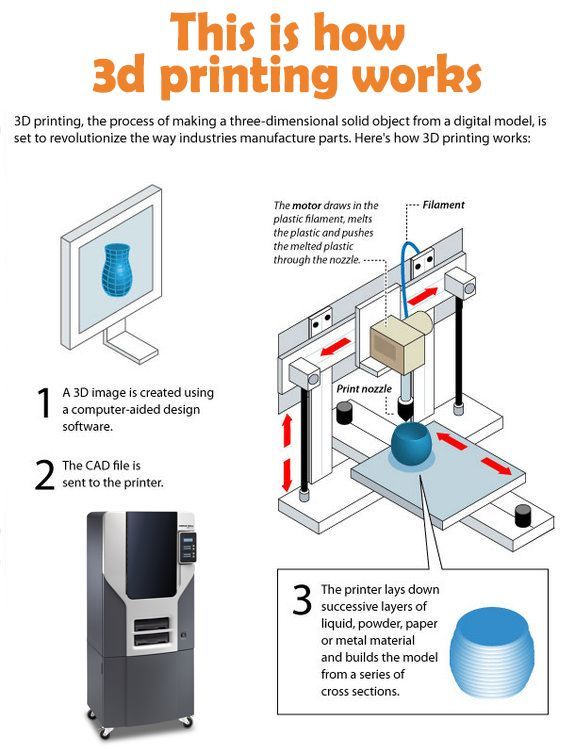
What is a 3D food printer
The main feature of a food 3D printer is the raw materials used: instead of printing ink, the device is filled with edible ingredients. The database stores a large number of different recipes, and in order to print a dish, you just need to select one of them and activate the printing process. The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer. nine0003
The final product is layered on a work surface or on a plate: it can be baked in the oven or sent to the freezer. nine0003
Application
Futuristic 3D Printed Sugar Candy
Cookies printed with icing
Chocolate logos of famous companies
Cream Photo Print
Buying a food 3D printer is worth the owners of coffee houses, author's bakeries and private workshops. The finished product has a unique shape and bright appearance. Food printers are often used to create custom wedding cakes, cartoon character cookies, Christmas gingerbread cookies, and so on. The possibilities of a baker who owns such a device are endless: the main thing is to buy quality products. nine0003
Raw materials used
The following ingredients are used as raw materials:
-
Chocolate without additives and impurities;
-
Mastic;
-
Sugar;
-
Whipped cottage cheese;
-
Vegetable and fruit pastes; nine0003
-
Fish and meat pates;
-
Flour;
-
Cheese, etc.

The confectionery pattern is applied to sugar, wafer or shock transfer paper. The first type has a sweetish aftertaste and aroma of vanilla. Due to the snow-white surface, no additional coating is required: the drawings look bright and clear. The wafer paper is made from rice flour and does not have a special taste, due to the light shade, the final drawings look less clear. Shock transfer paper is completely transparent and is suitable for transferring a design to a product (for example, a cake). For the packaging of finished products, food-grade plastic for a 3D printer is used. nine0003
Interesting! Food printers are involved in waste reduction. Unattractive fruit and confectionery leftovers are used in the preparation of printing mixes. This makes it possible to use the means of production more efficiently.
Types of 3D food printers
Cooking enthusiasts can take advantage of the following food printing devices:
-
Food 3D printers are devices that print dishes whose recipes are listed in a database.
 The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges; nine0003
The final product is layer-by-layer superimposed on the work surface, and the raw material comes from filled cartridges; nine0003 -
Confectionery printers are used to transfer images onto specialty paper or to design small confectionery products such as candies. Such printers print an image on pre-prepared paper: rice, wafer or shock transfer;
-
Food plotters transfer the image not to paper, but directly to the finished product. For example, a plotter is used to transfer an image directly onto a cake. nine0003
There are several types of food 3D printers:
-
Extrusion - paint is applied to the surface before the dish is created. The process is controlled by the computer with the loaded image. The system has an extruder that heats the food mixture, and the distribution of raw materials depends on the print head. The raw material is loaded into a syringe placed in the head. This means that in order to combine different shades, you have to periodically stop printing and change the syringe; nine0003
-
A carousel-type food 3D printer also has an extruder, but its main feature is the method of feeding raw materials: the containers rotate around the working surface, the supply and dosage of the material used depends on the recipe specified in the program.
 The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
The storage can contain countless recipes, and operation does not cause difficulties even for an inexperienced user.
Popular brands
Eminent manufacturers offer the best value for money food 3D printer. Quality devices provide accurate printing, high speed, durability, simplicity and ease of use.
Wiibox
This company manufactures 3D printers with high build quality and high productivity. These are universal mechanisms that fill both chocolate paste and mashed potatoes. Numerous positive reviews confirm the high quality of Wiibox products. nine0003
byFlow
The Dutch company byFlow specializes in food printing technology. The pursuit of excellence helps the company open up new horizons: the technique prints products from spinach, meat emulsion and other materials. High build quality, ease of use and durability - all these characteristics are applicable to the products of this company.
Choc Edge
Choc Edge is committed to revolutionizing the world of chocolate making.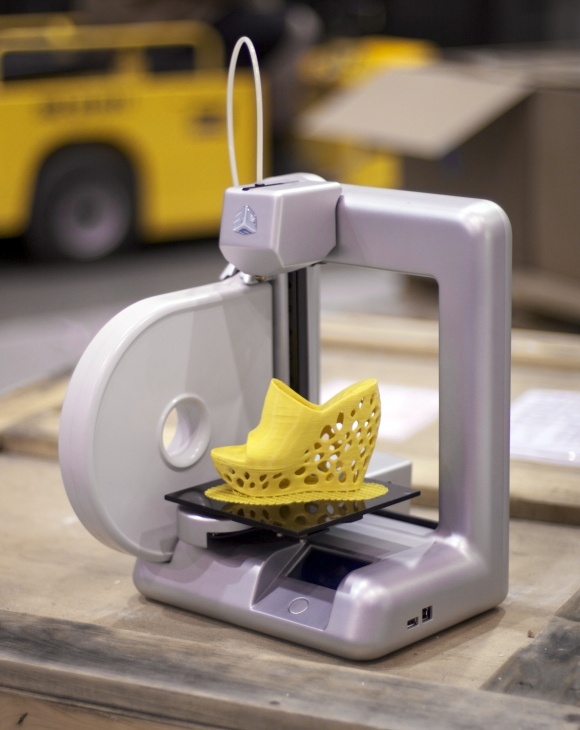 Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Numerous experiments and focus on consumer feedback help to create more powerful devices that provide the optimal temperature for preparing and storing chocolate figures.
Attention! Printing dishes helps save time on cooking: instead of culinary worries, the user can simply activate the printing process and get on with other things.
nine0134Free shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Available on credit. To checkout, add the product to the cart and follow the instructions Go nine0003
Manufacturer Wiiboox Free Shipping
Add to compare
Item added to compare Go
Manufacturer Choc Edge Top 10 Best Food Printers: List of the Most Current Models
Before you buy a food 3D printer, you need to familiarize yourself with the most popular devices on the world market.
The top is based on ratings and customer reviews. nine0003
1. PancakeBot 2.0
PancakeBot 2.0 is easy to use, which means it's suitable for inexperienced users too. Users can choose from suggested designs in the software, or create their own. Used to print pancakes.
Pros:
Ease of operation;
A wide range of proposed projects; nine0003
High speed.
Cons:
2. Wiiboox Sweetin
Buying a food printer from Wiiboox is worth not only for confectionery lovers, but also for ordinary chefs: the device prints cakes, cookies and even mashed potatoes. The main raw materials can be meat, cheese, chocolate, jam, mashed potatoes, dough and much more. A convenient touch panel helps to set the desired mode of operation, and a stylish appearance complements the interior of any establishment. nine0003
Pros:
Versatility: the ability to print not only sweet dishes, but also side dishes;
Attractive appearance;
High build quality;
Convenient control by touch panel.

nine0173 Cons:
High price.
3. Choc Creator V2.0 Plus
When talking about which chocolate 3D printer to buy, it is worth mentioning the numerous advantages of Choc Creator V2.0 Plus. The new model has become more perfect: the developers have worked hard to eliminate the shortcomings of the previous version. The modern model has small dimensions, thanks to which it can be used in any kitchen, and the uniform heating of the syringe ensures high-quality and uninterrupted operation. In practice, the chocolate printer has shown tremendous potential: it prints complex figures from chocolate. nine0003
Pros of :
Attractive appearance;
Uninterrupted work;
Durability;
The ability to create durable and beautiful chocolate figures.
Cons :
4.
Choc Creator V2.0 Plus 3D food printer with cold chamber
The new version of the Choc Creator V2.0 Plus printer is equipped with cooling chambers by popular demand. Users say that maintaining the optimal temperature in the room to preserve the integrity of chocolate figures is too problematic: therefore, the new device cools the raw materials. The price of a food 3D printer with a cooling system is slightly higher than a classic one, but the high performance of the final product justifies any costs. nine0003
Pros of :
Availability of a cooling system for finished products;
High printing precision;
Long service life;
Ease of use: You can turn the fans on and off with the side buttons.
Cons :
High price.
Attention! Confectionery food 3D printers are often used by artists to create edible masterpieces.
This is a unique technology that helps to unleash the creative potential of the chef.
5. byFlow Focus
Food printer from the Dutch company byFlow, which specializes in 3D printing of food. The compact high-tech device is used for the bakery industry, and the cartridges are suitable for the application of any pasty ingredients. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
6. Chefjet Pro
Buying a ChefJet Pro food printer is a must for people who dream of making bright and stylish sweets. The device is created on the principle of inkjet printing: sugar-containing powder materials are used instead of paints. The final product is made by powder layering. The printer is suitable for combining different shades and creating gradients. nine0003
Pros:
The ability to create unique flavors;
Neat and bright printing;
Aesthetic appearance of the device.

Cons:
- nine0015
High price.
7. Foodini
The 3D food printer from Foodini works on the principle of a stationary printer, but instead of printing inks, layer-by-layer imposition of edible raw materials is used: dough, cream, chocolate, cream, etc. The device is versatile: the user himself can choose the material, or use ready-made cartridges with products.
Pros:
Practicality; nine0003
High build quality;
Attractive appearance;
Availability of an online platform with unique recipes.
Cons:
8. Mmuse – Chocolate 3D Printer
The closed MMuse 3D printer is suitable for chocolate printing. Chocolate beans are used as raw materials: they are heated in an extruder and fed to the work surface through the print head.
nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
9. ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5
ZBOT Commercial Art Pancakes Printer F5 3D Printer
A food printer from Chinese manufacturers is used in the process of making pancakes of various shapes. Ease of operation allows the device to be used by children under adult supervision. nine0003
Pros:
Ease of operation;
High build quality;
Affordable cost.
Cons:
10. ZMorph VX
A multifunctional 3D printer capable of printing not only food, but also rubber, ABS plastic, polylactide, PVA, nylon, elastic and metal materials. The product is able to print with chocolate, butter, cookies, icing and other ingredients. In addition, there is a function of engraving and CNC milling. nine0003
Pros:
Cons:
High price.

Selection guide
The modern market offers a wide range of food printers. Before making a purchase, you need to carefully study the characteristics of each model and build on your own preferences. Experts have created several recommendations for choosing: nine0003
In case you want to create realistic images for confectionery 3D printing, pay attention to the diameter of the nozzle: the narrower it is, the more accurate the image will be;
- nine0007
It is better for people living in regions with a warm climate to purchase chocolate 3D printers with a cooling system: such devices ensure that the figurines are kept at the optimum temperature;
The possibility of self-refilling the cartridge is the most practical and economical way to operate the printer;
Print speed is an important consideration for restaurant owners. Large batches of dishes must be produced quickly, and for home use this is not a very strict selection criterion.

Output
In the catalog of our online store, you can choose the best food printers from famous brands to create culinary masterpieces. Explore our range, learn about the characteristics of each printer and make great purchases. nine0003
#Useful
Expert in the field of additive and subtractive technologies, 3D equipment and CNC machines with over 10 years of experience.
Share
all materials
South African designers use 3D printer to turn defective vegetables into delicious jelly
News
Designers from South Africa's Studio H reduce food waste by 3D-printing substandard produce into unusual but delicious food. nine0003
How often do you see ugly vegetables or fruits on the shelves of large stores? Rarely, because all sorts of "mutants" are usually sent to the trash, at best, for livestock feed or processing into fertilizers, so as not to scare away picky buyers.
In fact, there is nothing wrong with deformed fruits, because these are just pranks of nature, but in the same South Africa, about a third does not go on sale purely because of the unsightly appearance. 44% of "substandard" products are fruits and vegetables. The rest is grain, meat, root crops, seeds, and so on. nine0003
Studio H designers are not satisfied with this situation, and therefore the guys launched a demonstration project Salad 2.0 for 3D printing nyamok from not the most beautiful-looking, but quite tasty and healthy vegetables and fruits. To implement the project, the team purchased a 3D food printer manufactured by the Dutch company ByFlow. The device is capable of printing with various viscous materials, at least the same chocolate, but in the South African project, fresh fruit and vegetable purees are mainly used as consumables, and gelatin is added to keep the products in shape. nine0003
“3D printing could be a great way to reduce food waste.

Learn more