3D printing records
The Guinness Book of World Records for 3D Printing!
Subscribe Here!
Email Address
Technology and creations go hand-in-hand. The former is fundamental in building anything that can impact development, lifestyle, and economy. Take for instance, the 3D printing technology and how it rewrites the Guiness Book of World Records.
Though it was introduced three decades ago, it is recently that its impact is felt in industrial and manufacturing sectors. It has paved ways for testing and trying many things that has changed the traditional manufacturing methods.
All that invention and creativity that went into it, have enabled in developing many “worlds first.”
But those 3D-printed objects couldn’t impress the record books. It’s only lately that 3D printing creations have found official entry into the Guinness Book of World Records.
The Smallest Rubrik’s Cube
No doubt there were many miniature creations before the arrival of 3D printing. But when something as popular as the 3D puzzle cube is built that is so small that it can easily fit on the tip of your finger, then why shouldn’t the Guinness Book notice it.
Tony Fisher created the world’s smallest Rubik’s cube in June 2016 using 3D printing technology. Though being tiny, the cube is functional. It’s so small that to rotate its sides, you will need tweezers.
Smallest 3D Printed Sculpture of a Human Form
Was it even possible to imagine a human sculpture so small that can sit within the eye of a needle, or fit on the head of an ant? Jonty Hurwitz not only conceived, but achieved it as well. He first captured an image a real-life woman with the help of 200 cameras and imported them into a software to create a 3D image.
He printed the image using the Nanoscribe 3D printer that functions on Two Photon Polymerization technology. This technology directs a laser light onto photosensitive materials and prints the image one 3D pixel at a time.
Tallest 3D Printed Sculpture of a Human
When 3D printing can create the smallest sculpture, it can as well create the tallest one. Perhaps, this thought might have excited James, the creator and owner of YouTube channel xrobots to try building the tallest sculpture of himself.
Perhaps, this thought might have excited James, the creator and owner of YouTube channel xrobots to try building the tallest sculpture of himself.
He scanned himself with an iPad and then gave the image perfect shape and dimensions. When he got the proportion correct, he used two 3D printers that worked 24/7 to print the sculpture and completed it in 500 hours.
Largest 3D Printed Object
The aerospace industry is at a good space with the advent of 3D printing since it facilitates them to print special tools that were difficult to find, require months to make, and used to be expensive.
At Oak Ridge National Lab, researchers have built a “trim-and-drill” tool using 3D printing technology that weights 1,650 lbs, is of an SUV size, and measures 17.5 feet in length, 5.5 feet in width, and 1.5 feet in height. This world’s largest 3D printed object was built in 30 hours with carbon fiber, and different plastic materials.
Lightest 3D Printed Structure
After smallest, tallest, and largest, it’s time for the lightest. This structure is a 3D printed graphene aerogel. It is so light that even flower petals, and a cotton ball can easily bear its weight. It weighs 0.5 milligrams per cubic centimeter.
This structure is a 3D printed graphene aerogel. It is so light that even flower petals, and a cotton ball can easily bear its weight. It weighs 0.5 milligrams per cubic centimeter.
The world’s lightest structure was built by Dong Lin from Kansas State University. Developed in 2016, it was officially recognized by Guinness World Records as the “least dense 3D printed structure.”
3D Spectra Technologies is proud to be a part of the revolutionary 3D printing technology and spearheading it in India. Based in Pune, Nashik, and Australia, we offer a gamut of engineering solutions to myriads of industries. We would love to hear your ideas and build unique things for you. Let’s add to the Guinness Book of World Records in 3D Printing.
Guinness Book of World Records article and permission to publish here provided by Rohan Kadam at 3D Spectra. Originally published on Supply Chain Game Changer on September 5, 2018.Like this:
Like Loading...
Author [email protected]Posted on Categories Digital Supply Chain, Guest Blog Post, TechnologyTags Automation, Digital, IoT, SCM, supplychain, TechnologyVinyl records are far from dead, now you can 3D-print your own
Pocket-lint is supported by its readers. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Learn more
- Home
- Gadgets
- Gadget news
Elyse Betters, US News Editor
· ·
News Based on facts, either observed and verified firsthand by the reporter, or reported and verified from knowledgeable sources.
Why you can trust Pocket-lint
(Pocket-lint) - You can use 3D printers and custom software to make everything from houses to pizzas, but did you know you could also 3D-print vinyl records?
Developer Amanda Ghassaei from Instructables is known for her alogorithm that converts audio data into 3D geometry data. She has subsequently used that alogorithm to manufacture 3D vinyl records for singles from artists like Nirvana, Pixies, Daft Punk, and Radiohead. More recently, the track Down Boy, performed by Bobbie Gordon and produced by Kele Okereke, was put onto a 3D-printed vinyl record using her alogorithm.
She has subsequently used that alogorithm to manufacture 3D vinyl records for singles from artists like Nirvana, Pixies, Daft Punk, and Radiohead. More recently, the track Down Boy, performed by Bobbie Gordon and produced by Kele Okereke, was put onto a 3D-printed vinyl record using her alogorithm.
An Objet500 Connex 3D printer generated the disc for Down Boy, at fine settings like 600 dpi, with 16 micron steps. Gordon recently performed the tune at a launch party for the world's first 3D-printing record store, where the limited-edition, 3D-printed version of her track went up for sale. Down Boy was a sponsored and documented project by Bacardi Beginnings, and it marked the first time that an original song had been released and sold as a 3D-printed album.
Ghassaei's algorithim uses an 11 Khz sampling rate however, so the resolution of Down Boy is quite low. In fact, the final output is around 25 per cent of what you could get from an MP3. With such a poor rate, the Objet500 Connex actually cuts off high-range tones in most songs. It's been said that 3D-printed records have a sound that is audible and distinguishable but still distant and hollow. Watch the video below for an example.
It's been said that 3D-printed records have a sound that is audible and distinguishable but still distant and hollow. Watch the video below for an example.
READ: Ten houses 3D printed in 24 hours
Ghassaei also said the resin residue of 3D-printed albums will eventually wear down a turntable’s needle, but she insisted it is still "really cool to kind of push the technology." Furthermore, it takes more than a gigabyte of data to 3D print an entire song, meaning a standard 12-inch LP can only hold one single. Her DIY website on Instructables explains in detail how to convert audio files into 33 RPM resin records. It also demonstrates how 3D printers create albums, layer by layer.
Although 3D-printed albums are thicker and stiffer and sound horrible when compared to vinyl records, you must think of all this as a stepping stone of sorts. The technology to produce 3D objects is still new and will likely be honed over time. Maybe one day it'll be responsible for the full comeback of vinyl records. After all, music has been experiencing a vinyl revival over the last decade as audiophiles seek a warm and authentic music sound.
Maybe one day it'll be responsible for the full comeback of vinyl records. After all, music has been experiencing a vinyl revival over the last decade as audiophiles seek a warm and authentic music sound.
You can view Bacardi Beginnings' video documentary for both Down Boy and the first 3D-printing record store (called The Vinyl Factory in central London), below.
Writing by Elyse Betters.
Sections Headphones Speakers
Simple 3D printing timelapse. Webcam, computer and printer only. (Not a manual, more like a sketch)
Why do I need to buy a RASPBERRY to shoot 3D prints?
We have a computer, a printer and a webcam - isn't that enough?
Enough, and now I'll tell you how to organize shooting for printers with MARLIN firmware with only a computer and a webcam.
Strictly speaking, time-lapse can also be shot on a mobile phone, such a mode has long existed in many modern smartphones, but for the needs of 3D printing, this is not a very successful idea, since the picture will turn out to be too jerky, especially when shooting with prush.
So a regular camera will not suit us, unless it can work in webcam mode when connected to a computer, like many modern cameras. A modern camera capable of working in webcam mode is the best webcam.
Raspbery and OCTOPRINT - although they are of higher quality, they are complicated, expensive and redundant for a simple time-lapse, so I'm not even going to consider them. I note that a two-megapixel camera, and in modern models with a higher resolution, is a good plus for Raspbery's karma.
Everything should be easier.
We will need:
- Printer with MARLIN installed
- Any available computer with WINDOWS
- USB webcam
- USB cable to connect the computer to the printer manual editing of the g-code
- A program that receives commands from the printer and forms a picture. (download link)
On the last point, I didn’t find such a program on the Internet, I had to sketch it myself, brazenly stealing from free access the first code I came across to work with the DIRECTSHOW library.
The original webcam program was written in C#, using WPF, which I'm not good at, so I apologize for the somewhat clumsy interface.
However, if you have the desire and ability, then the original project is in the same place, by reference, you can rewrite it for yourself. And if I have time and desire, I will probably finish my WPF education and rewrite it in a more convenient version.
All
Next, we need to cut the printed model in the slicer, adding the command M118 SMILE to the code before each layer change - this command sends the specified message via the serial port to the computer, and the program reads it and takes a picture from the camera.
In order not to edit the code manually, you can use the capabilities of the slicer, for example, for Simplify3D, you need to add the line M118 SMILE to the script Layer changed .
Copy the cut code to the card, connect the printer and webcam to the computer. Download the program and unpack the archive.
Download the program and unpack the archive.
Program settings:
Go to the folder Resources and in the file SerialPortSettings.txt write down your printer connection parameters, com port number, transfer speed, Databits value, according to the instructions for your printer.
Save the file and run the program WebCam.exe .
Here the antivirus may swear at you, because I am an unknown publisher, and the program requires access to the webcam, but I can assure you that there is nothing malicious in the program, it just reads data from the COM port, webcam and writes images to folder Photo inside the program directory.
An exception can be set for Anti-Virus.
The source code is at the link, you can check, rewrite, modify, in general, you can do anything with the code. =)
If you wrote down the port settings correctly, the program will start without warning about the unavailability of the printer.
Otherwise, if the printer is not connected or the port settings are incorrect, the program will be able to record timelapse only by timer. We set the switch to record at the command of the printer, press the "start recording" button, and start printing from the flash drive.
Each print layer will be photographed, numbered and placed in the Photo folder in the program directory.
Well, then, in any available editor, be it Photoshop or OpenShoot Video Editor, open the resulting files as a sequence, set the number of frames and export the video.
Time lapse is ready.
That's all for me, I wish everyone a clean print, to be continued.
Traditional video:
p.s.
The purpose of this article was to give a fresh idea for the implementation of timelapse, without complex and expensive equipment.
What attracts me to the solution is that it is possible to connect any webcam, including a video camera or a camera capable of working in webcam mode, and receive frames on any computer.
Of course, anyone can adapt the process of taking a picture from the camera on command to any available language, system, etc.
Do whatever you want - the printer transmits the command, the computer reads, the camera shoots.
3D printing in Moscow at the 3D Printing Laboratory
Application of 3d printing
Gaining popularity and being in great demand, 3d printing on order in our time is becoming an integral and indispensable part of life.
The manufacture of cases and volumetric products is a very profitable solution when small-scale production is spreading.
Layer-by-layer material growth technologies (or fabber technologies) for creating physical objects came to Russia not so long ago, but their popularity is growing rapidly. Performing 3D printing - in Moscow or in any other city - is not a problem today. Products for various purposes - from prostheses to parts for cars and aircraft - can be made on the basis of the fabber method.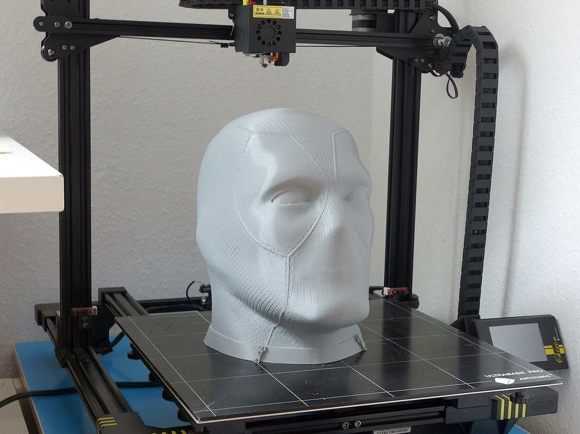
The term “additive manufacturing” is accepted in industry guides, however, this technology has become commonly referred to as “3d printing” and it is in this version that it is used in the startup environment, between entrepreneurs and journalists.
Layer-by-layer build-up is applicable both for creating prototypes, prototypes of a future product, and for direct manufacturing of parts and solid objects.
Where is the 3d printer used
In what case may 3D printing be required? At the stage of product development, when it is required to visualize it and determine the likelihood of defects or unsatisfactory quality during production. It is also in demand for creating prototypes of architectural objects, as well as for prototyping.
Prototyping of parts, production of tooling - for example, molds for casting; assembly tools - this is not a complete list of cases when they decide to use 3D printing on order. Moscow in this regard is in a much more advantageous position compared to other Russian regions, since ideas and technologies, for the most part, are concentrated here.
We use additive technologies and high-quality materials to make your models, which will then be presented in many industries after printing: medicine, science and education, architecture and construction, energy and oil and gas industry, automotive and mechanical engineering, aerospace industry, jewelry manufacturing .
3D printing, ordering the release of a single item or a series is possible only on the basis of three-dimensional modeling based on special software products - this is where work on a separate project begins. If you want to create a copy or form of an existing object, you will need to apply three-dimensional scanning.
The principle of operation of the 3d printer
Ordering 3d printing means placing an order for the reproduction of a digital three-dimensional model of an object in physical form by horizontal layering of a substance. Layering is carried out using additive installations or three-dimensional printers, the variety of which is quite large today.
For each of the layering methods, including lamination, fusion, sintering, extrusion, jet spraying, UV curing, there is a separate category of devices. To create an accurate three-dimensional geometric product (3d model) that can perform any function, "3D printer" is used - this is the general name for a whole family of equipment capable of performing 3d printing on order (Moscow). At its core, each device is a numerically controlled machine that performs layering operations.
To reproduce the desired objects, it is necessary to use different 3D printing technologies that differ from each other.
Here are the main 3D printing technologies:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM). ABS and PLA printing with this technology is the most popular of all 3D printing technologies. It is used in most desktop 3D printers and represents an ideal price / quality ratio, which allows printing by layer-by-layer supply of a filament of molten plastic;
- Laser stereolithography (SLA).
 Photopolymer printing using SLA technology allows you to form an object by layer-by-layer laser illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage;
Photopolymer printing using SLA technology allows you to form an object by layer-by-layer laser illumination of a liquid photopolymer resin, which hardens under the influence of radiation. One of the variations of this technology is DLP 3D printing. It uses a special projector instead of a laser. Both 3D printing methods are used to create objects with a high degree of detail. In the case of DLP printing, speed is also an added advantage; - Selective laser sintering (SLS). Reproduction is performed by layer-by-layer melting of a special powder under the action of laser radiation. This 3D printing method is widely used in the industry for the manufacture of durable metal elements.
To order printing on a 3d printer using any of the above methods, you must select the material in which the product will be made. What will be the composition of the product, such will be the cost of the work.
Printing on a 3D printer is possible using powder forms of gypsum, polystyrene, polyamides, metal alloys; liquid photopolymers, wax and other materials. The specific task and requirements for the final product depend on which consumables are selected. It is important that with this production method, whatever you choose, there is almost no mechanical post-processing required.
The specific task and requirements for the final product depend on which consumables are selected. It is important that with this production method, whatever you choose, there is almost no mechanical post-processing required.
In order to understand the principle of 3D printing, it is necessary to reproduce the step-by-step process of creating models.
Let's describe some stages of 3D printing:
- 3D modeling of the required object according to the specified parameters;
- loading a file with a digital model into a slicer program that generates a control code for a 3D printer;
- setting the required 3D printing parameters;
- writing a code to a removable memory that connects to a 3D printer;
- 3D model reproduction.
Objects are reproduced progressively in the desired shape, the selected material is applied layer by layer, forming the finished product.
The possibilities of 3D printing are almost limitless, that is, you can make anything you want and this is a huge advantage of this type of printing.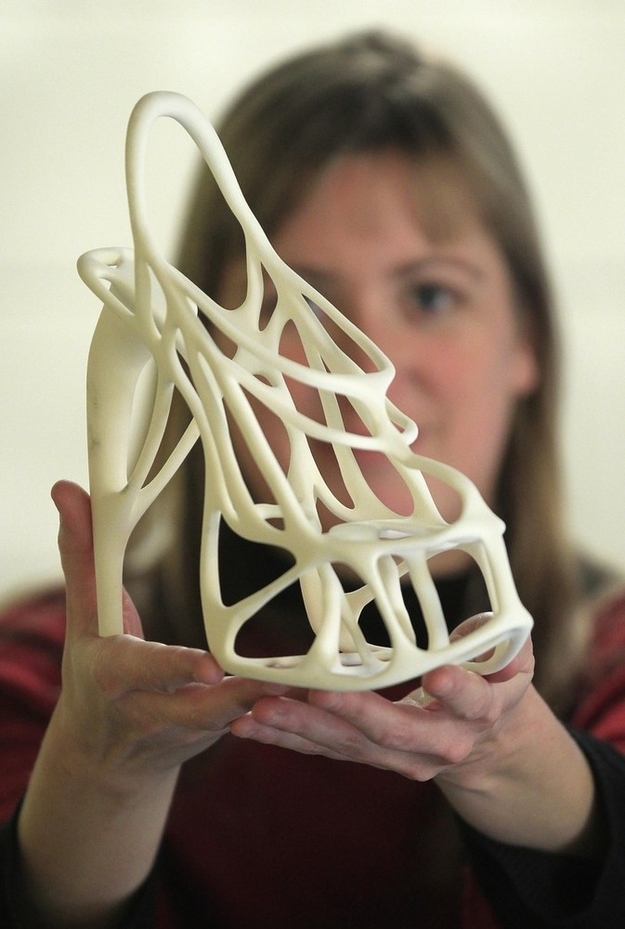 In some technologies, for very thin overhanging elements, supports are provided, thanks to which, sagging can be avoided.
In some technologies, for very thin overhanging elements, supports are provided, thanks to which, sagging can be avoided.
Such a brief description of the stages, where there is no ready and detailed analysis of the complete picture of the 3D printing process, gives only an idea of the essence of the technique.
What equipment does LAB3DPrint 9 have0118
Due to the fact that 3D printers are quite expensive equipment, and not everyone can use 3D technologies, but there is a need, our company provides printing services quickly, efficiently and in accordance with your wishes, will complete your task.
The high speed and accuracy of printing, as well as the maximum reliability of our 3D printers, reduce the cost of all types of 3D printing.
We can order a full range of preparatory work and the actual printing on a 3D printer (Moscow) using various methods and materials. We have all the necessary equipment and software.
Our company works with professional equipment, so the quality of the finished product is guaranteed and the result exceeds all expectations.