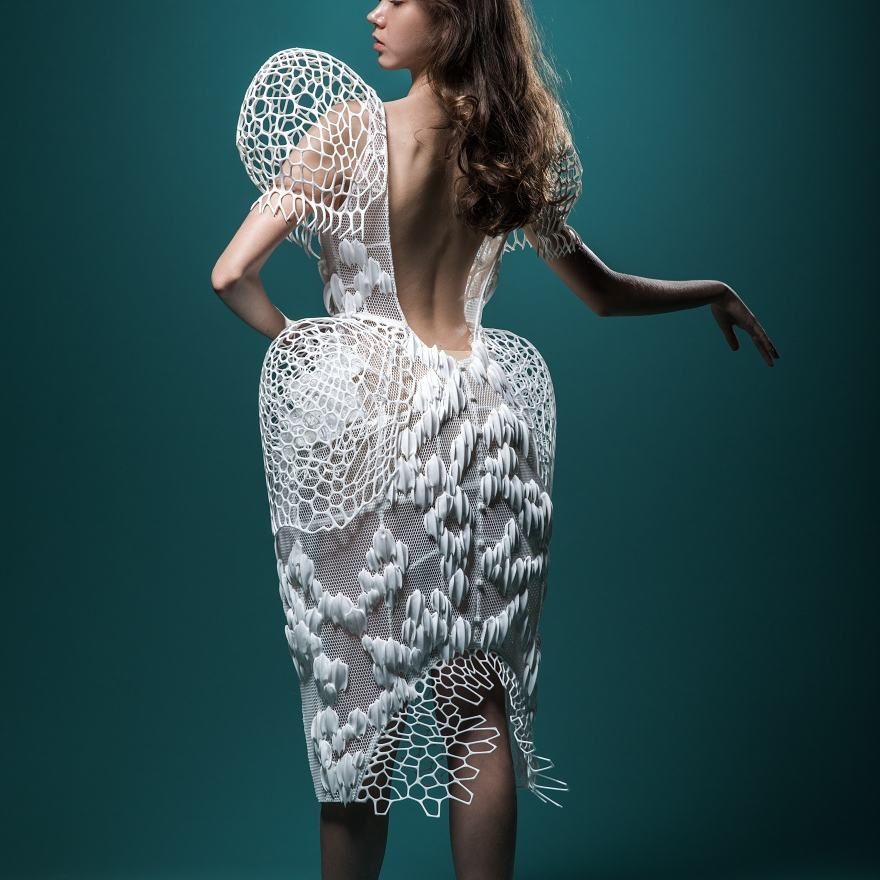
3D printing clothes
What are the best projects?
3D Learning Hub
See all categories
Contents:
- Introduction
- Fashion and 3D printing: 3D printed fashion is the new revolution
- What are the best 3D printed clothes projects?
- 3D printing footwear
- 3D printed jewelry
- 3D printed bags
- Evolution of 3D printed clothes: What is the future of fashion?
Introduction
Fashion and 3D printing: 3D printed fashion is the new revolution
3D printing for the design aspect
Additive manufacturing is interesting for fashion as it allows to work more easily on fashion designs and to create amazing things for the fashion industry such as garments, ornaments, and meshes.
This technology is really giving a lot of freedom to the designers in terms of geometry. It is, for example, possible to create intricate designs for various projects inside the fashion industry. From shoes and accessories to 3D printed dresses, the fashion industry starts to embrace the full potential of 3D printing and to develop interesting objects.
Some of the garments developed thanks to 3D printing technology would have been too complex and expensive to create with another manufacturing method.
New considerations for the fashion industry
Sustainable manufacturing and eco-friendly products
There is obviously an evolution in the way that we are thinking about fashion and clothes manufacturing. New aspects are now taken into account and now, the reasons why designers are choosing 3D printing are changing: it is becoming important to use 3D printing for sustainable and eco-friendly purposes.
For instance, textiles are part of the waste problem around the world, that is why a lot of elements of the manufacturing process need to be rethought in order to be more eco-friendly.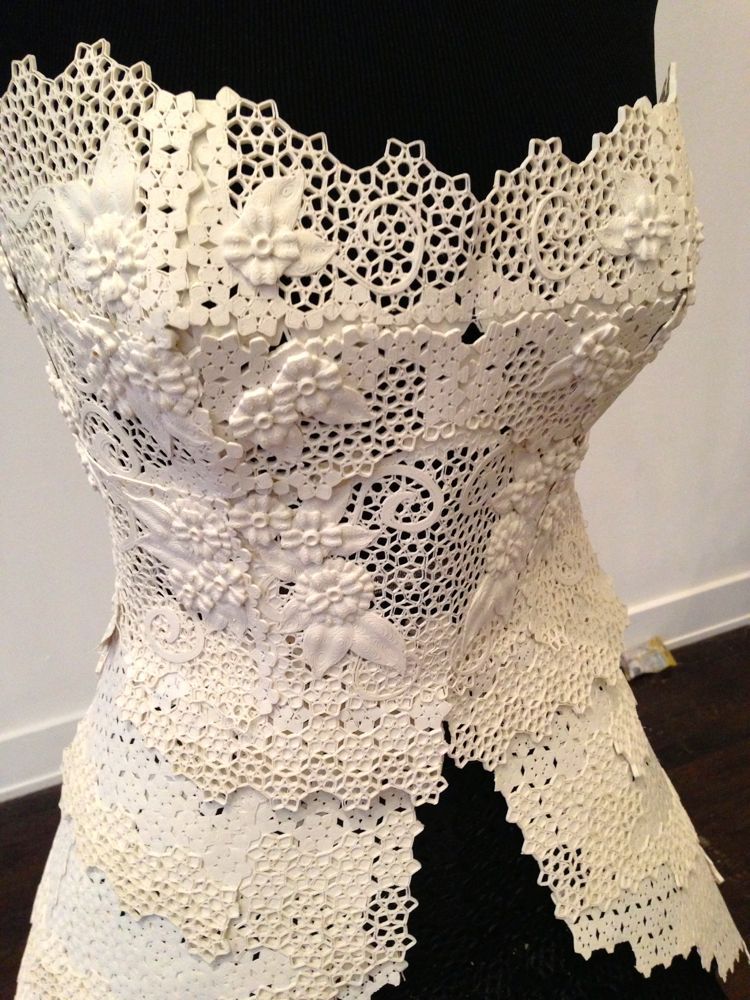 Using 3D printing allows to reduce waste, you only need to use the amount of material that is needed to create your project.
Using 3D printing allows to reduce waste, you only need to use the amount of material that is needed to create your project.
It is also a way to use some recycled materials for the manufacturing process. Adidas created a 3D printed midsole for one of its sneakers, made with recycled plastic found in the ocean. Creating new materials and using plastic in a more responsible way are new reasons to use 3D printing for fashion companies, and even for big brands such as Adidas.
3D printing comfortable clothes
The use of 3D printing to create clothes is evolving. It first has been used to create extremely complex and impressive pieces. The use of 3D printing in this sector was a way to push the boundaries of the fashion world to create outstanding projects, that were visually impressive.
Now some designers are more interested in using 3D printing to develop collections of regular clothes, using additive manufacturing as a traditional manufacturing method. They are not only using 3D printing for the design benefits but as an advantageous manufacturing method to create customizable and comfortable clothes.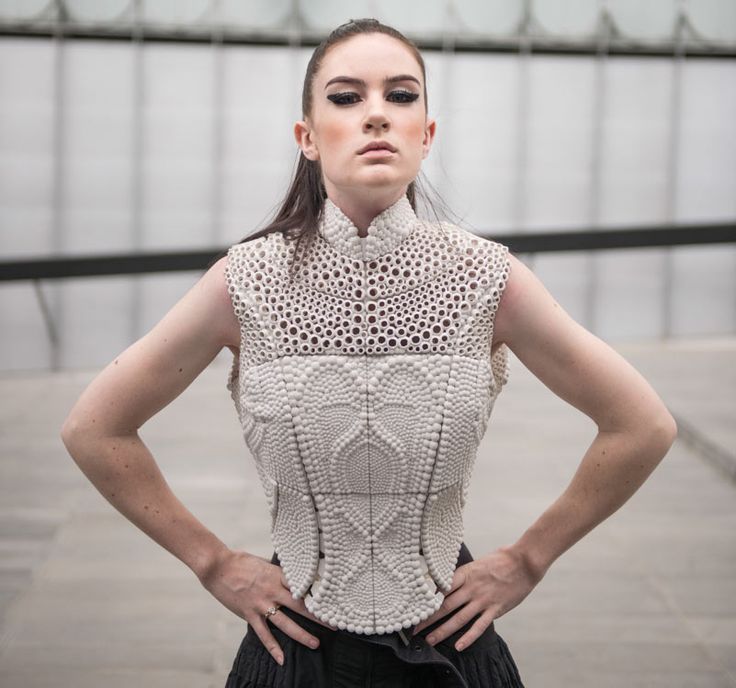 Additive manufacturing is a great way for all industries to improve their manufacturing process. It is allowing them to work on their prototypes with faster and cheaper methods, but also to produce customizable products in the end. These two elements are quite important in the fashion industry.
Additive manufacturing is a great way for all industries to improve their manufacturing process. It is allowing them to work on their prototypes with faster and cheaper methods, but also to produce customizable products in the end. These two elements are quite important in the fashion industry.
While using 3D printing, we can notice more freedom on the customization side. Indeed, additive manufacturing is the perfect technique for mass customization. We know that customization can be an expensive process in the fashion industry. Producing garments and accessories made to measure are made possible thanks to 3D printing.
3D printing could also totally help to create clothes adapted to the movement of all bodies! 3D printing is not only a manufacturing method for haute couture creations anymore.
What are the best 3D printed clothes projects?
The Spider Dress
The Spider Dress of Anouk Wipprecht has mechanical arms that extend and retract as a response to external stimuli when people approach. The wearer’s own breath will help to signal the defense posture of the robotic arms. The dress is fully 3D printed with the Selective Laser Sintering technology.
The wearer’s own breath will help to signal the defense posture of the robotic arms. The dress is fully 3D printed with the Selective Laser Sintering technology.
The Spider Dress
3D printing regular clothes
The idea of Julia Daviy is to use 3D printing to create biodegradable fashion, believing that we can change the way we produce clothes!
Her collection included 3D printed dresses and tops. Most of the time, the 3D printed clothes made by designers are not easy to wear. But it is not the case with the clothes 3D printed by Julia Daviy. She is really thinking about 3D printing as a new method to create garments without wasting a lot of textiles, and avoid the mass-production aspect.
credit: https://www.3dprint.com/212640/julia-daviy-3d-printing/
Multicolor 3D printing for garments
This dress is a piece made by the American designer Travis Fitch, with 30 different sections. It has been printed with a colorful multi-material. The material is flexible in order to respond to the movements of the body. The 3D printing process is a good way to give life to objects with really complex designs and to make them wearable as traditional garments.
The 3D printing process is a good way to give life to objects with really complex designs and to make them wearable as traditional garments.
The use of color on this project is quite unique, 3D printing projects in the fashion world are often monochrome, and are not as colorful. This technique offers new possibilities as multicolor 3D printing is not often used in these kinds of projects.
credit: https://3dprintingindustry.com/news/3d-printed-dress-debuts-new-york-fashion-week-95736/
3D print knits
Ministry of supply developed a 3D printed knit blazer, a sustainable way to create garments that will last longer! The 3D printing process and the work on the 3D designs that they are creating are allowing to make pieces more adapted to the body and to its movements.
Their goal is to develop an agile supply-chain and create on-demand products that are more comfortable and durable. Their 3D printing technology is an eco-friendly method to create knits, and they are noticing a reduction of 35% regarding material waste.
New generation of 3D printed clothes collections
Danit Peleg is a designer who decided to create a fashion collection that she entirely 3D printed by herself. By doing that, she shows that 3D printers are great tools, allowing to rethink the manufacturing process of the fashion industry. The collection took her 2 000 hours to print completely.
https://www.3ders.org/articles/20150724-danit-peleg-3d-prints-entire-ready-to-wear-fashion-collection-at-home.html
Her goal? To create comfortable clothes that she could wear herself. Once again, we see the will of designers to create wearable 3D printed clothes.
3D printing, still useful to give life to outstanding designs
Alexis Walsh is a talented designer who created an impressive dress 3D printed using Selective Laser Sintering. The dress has 400 tiles assembled by hand. Here, 3D printing has been used to develop the design of the dress. It took at least six months to the designer to develop this impressive garment using 3D printing.
The 3D printed comfortable dress
We were talking previously about more comfortable clothes. Dresses made by designers are not what we can call comfortable, as it is not their primary goal. But do you know about the Kinematic dress? By 3D scanning her model, Jessica Rosenkrantz created a dress perfectly fitting her body.
By using this innovative manufacturing technique, the designer wanted to show a new approach of manufacturing for her fashion collection. Moreover, 3D printing is perfect to make several iterations for these kinds of dress, to be sure that they respond correctly to the movements of the model.
http://www.youfab.info/2015/youfab-award-ceremony-1.html
3D printing costume
It is now possible to use additive manufacturing to create costumes for the film industry, but also for video games. You might have heard about Sculpteo’s collaboration with Ubisoft for their Just Dance 2020 video game! The goal here was to create a lightweight costume, with an ambitious design but that shouldn’t hinder the dancer’s performance.
Get more info about this great project in the following video:
3D printed fashion for men
We can see that most of these creations are dresses or tops, intended for women. But what about men?
There is actually the 3D printed tie developed by Viptie 3D. This company is more focused on the mass customization aspect of 3D printing technology. They want to join luxury and high tech to create ties and bowties, as unique products for their customers.
3D printing footwear
More than garments, additive manufacturing is revolutionizing the footwear industry. Some important brands such as Adidas are making the most of additive manufacturing to develop impressive projects.
Adidas and the Futurecraft 4D
Adidas actually launched its Futurecraft 4D project: they create shoes with a midsole created in partnership with Carbon 3D, using a new process called Digital Light Synthesis (formerly known as CLIP). Thanks to digital light synthesis, oxygen-permeable optics, and liquid resin, this process can produce durable and resistant polymeric goods.
Thanks to digital light synthesis, oxygen-permeable optics, and liquid resin, this process can produce durable and resistant polymeric goods.
Using additive manufacturing in the footwear industry allows working on new designs to improve a previous product, for example. That is precisely what happened with this project, Adidas created an impressive midsole using a lattice structure!
This project is also showing an interesting aspect of the use of additive manufacturing. Indeed, these shoes are not only produced using 3D technology, but they are mass-produced using 3D printing! We can say that Carbon and Adidas are taking additive manufacturing a step further with this project.
Olivier Van Herpt developing the fully 3D printed shoe
For the moment, 3D printing is mainly used in the footwear industry to 3D print midsoles, which offers, once again, to get custom made products, adapted to any morphology. But is it even possible to 3D print an entire shoe? Designer Olivier Van Herpt is using 3D scans and 3D printing to create new shoe structures, making them unique, lightweight and really resistant. These 3D printed shoes guarantee you the perfect fit.
These 3D printed shoes guarantee you the perfect fit.
3D printed jewelry
3D printed jewelry is now becoming more and more common. 3D printing is a perfect method to launch a jewelry business, for both prototyping and production, additive manufacturing can be used to improve your product and process on many different levels! At Sculpteo, we offer great 3D printing technologies, suitable for the creation of your jewelry parts.
It’s possible to use metal 3D printing, with technologies such as Lost Wax Casting, and different materials such as Brass, Sterling Silver, or Bronze. These precious metals can be beneficial for your projects. Resin and plastic 3D printing can also be used for jewelry projects, Selective Laser Sintering or Polyjet technologies can be useful to create accurate parts.
If you don’t want to produce your jewelry using additive manufacturing, keep in mind that this technology can be used to create your jewelry molds. An interesting use of additive manufacturing is the creation of master 3D printed molds for your parts!
The Nervous System collection
This collection of rings, bracelet and necklaces called Nervous System is made with nature-inspired designs, structures that it would have been impossible to create without 3D printing.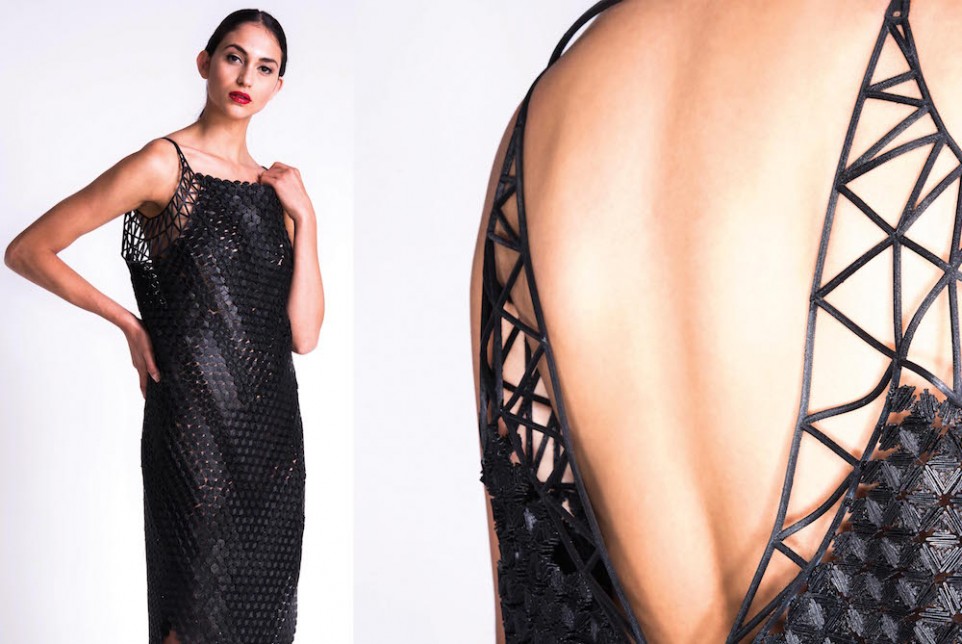 These jewelry parts are created using the Lost-Wax Casting process!
These jewelry parts are created using the Lost-Wax Casting process!
ABL’s 3D printed watch
Is it possible to 3D print a watch? ABL “Atelier le Brézéguet” is a french brand from Toulouse. This company is specialized in watches and used our 3D printing service to produce the black rings, on the top and the bottom of the watch. These parts are 3D printed using polyamide material.
3D printed bags
Accessories such as bags can also be produced using 3D technology. For example, the Italian brand XYZ Bag created a 3D printed handbag collection called “DADA”. These bags are customizable, thanks to the use of 3D printing.
Regarding the designs, 3D printing is offering great advantages for the development of bag projects: it is actually offering the possibility to play with geometries and try new things. Working on different structures, like implementing lattices, can be an effective solution to get lightweight but resistants bags!
Evolution of 3D printed clothes: What is the future of fashion?
Some companies are developing new techniques and new 3D printing materials such as Ministry of Supply who used a new method to create knit garments. We can notice that some extraordinary 3D printed designs made for fashion shows are still present as the 3D printing technology is still really convenient to manufacture these unique pieces. But 3D printing tends to be more and more used to create clothes that anybody could wear. Indeed, now that we saw that the 3D printing technology is able to create intricate geometries for garments, comfort is becoming the key to new 3D printed fashion projects.
We can notice that some extraordinary 3D printed designs made for fashion shows are still present as the 3D printing technology is still really convenient to manufacture these unique pieces. But 3D printing tends to be more and more used to create clothes that anybody could wear. Indeed, now that we saw that the 3D printing technology is able to create intricate geometries for garments, comfort is becoming the key to new 3D printed fashion projects.
There is also a growth regarding the use of different 3D printing materials and techniques. In the future, metal 3D printing could be implemented to create some ornaments, but also laser cutting techniques! There are a lot of benefits and possibilities for designers who want to approach the laser cutting and 3D printing industry.
We can also see that the eco-friendly aspects offered by 3D printing are becoming quite important, as, for instance, recycled plastic and biodegradable materials can be used to 3D print some fashion parts.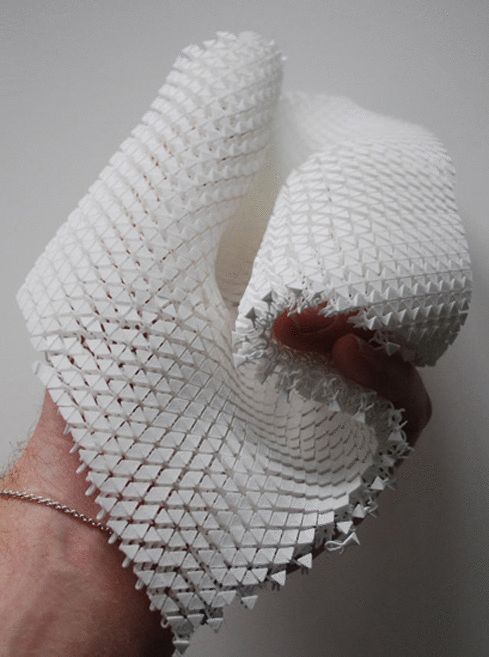 Soon, it could even be possible to use natural materials. Last but not least, we notice that the fashion industry is trying to push the boundaries of 3D printing, but is also implementing other great technologies such as electronics. It is now possible to 3D print smart fabrics, and more of these outstanding projects might be unveiled in the upcoming years!
Soon, it could even be possible to use natural materials. Last but not least, we notice that the fashion industry is trying to push the boundaries of 3D printing, but is also implementing other great technologies such as electronics. It is now possible to 3D print smart fabrics, and more of these outstanding projects might be unveiled in the upcoming years!
If you have a 3D printing idea and want to bring it to life right now, we can help you to choose the perfect CAD software for your fashion project, thanks to this blog post. Then, you will be able to upload your 3D models on our online 3D printing service.
Related Topics
- Return to Top
Get the latest 3D printing news delivered right to your inbox
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to hear about the latest 3D printing technologies, applications, materials, and software.
3D Knitwear: How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing Fashion
Published on December 6, 2022 by Mikahila L.
In recent years, 3D printing has become growingly everpresent. From medicine, aerospace, to design, and construction — every day there’s news about breakthroughs, innovations, and developments in the additive manufacturing industry. However, in one particular industry, it’s still pretty quiet regarding developments around 3D printing. We’re talking about the fashion industry. It cannot be denied that the first experiments and advances in 3D printed clothing have only been recorded relatively recently. Yet, if you have followed these developments in fashion a little more closely, you may have noticed that these are high-end fashion, i.e. clothing created for the runways and red carpet and not for everyday wear. The reason why the combination of 3D printing and clothing seems so difficult is quite simple: The materials used in 3D printing, mostly plastic, and metal, are not flexible enough. To counteract this problem, some fashion and 3D enthusiasts have been looking into suitable options and ultimately honed in on one solution: 3D knitwear.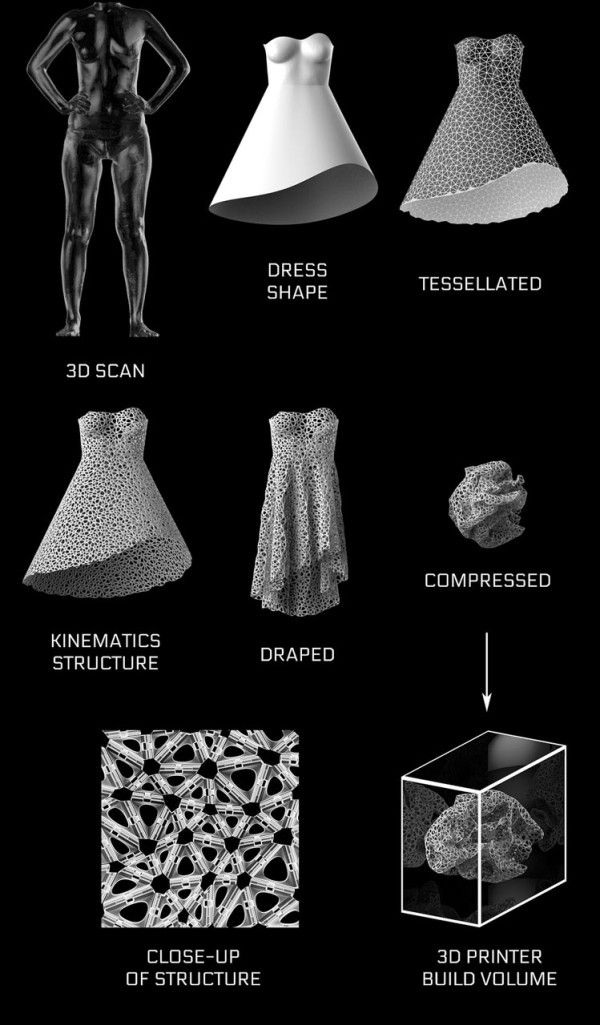 But, what exactly is 3D knitwear? How does its production method differ from additive manufacturing and conventional textile production? Will 3D knitwear be available as ready-to-wear for ordinary consumers in the near future? We got to the bottom of this topic in more detail and we clarify all of these questions with the help of various expert opinions from the industry.
But, what exactly is 3D knitwear? How does its production method differ from additive manufacturing and conventional textile production? Will 3D knitwear be available as ready-to-wear for ordinary consumers in the near future? We got to the bottom of this topic in more detail and we clarify all of these questions with the help of various expert opinions from the industry.
In order to understand the principle of 3D knitwear and its differences and similarities to 3D printing, it is first necessary to take a look at the definitions. Gihan Amarasiriwardena, co-founder and CEO of the Ministry of Supply, defines 3D printing as follows: “In 3D printing, molded products (such as plastics) are produced by adding a layer of material (often plastic or synthetic) according to a given digital Design is ‘printed’.” Rosanne van der Meer, designer and founder of New Industrial Order, offers a broader definition: “3D printing is the production of a three-dimensional shape on the basis of a filament that is formed by a machine. “ In fact, 3D printing is all about computer-controlled machines creating three-dimensional objects and building them up layer by layer. The question now remains whether 3D knitwear is made according to the same principle.
“ In fact, 3D printing is all about computer-controlled machines creating three-dimensional objects and building them up layer by layer. The question now remains whether 3D knitwear is made according to the same principle.
In 3D printing, the object is additively manufactured layer by layer.
Production of 3D Knitwear
The manufacturing process of 3D knitted fabrics is quite similar to other 3D objects. Both begin on a computer: CAD software is used to create the design and ultimately to obtain a programming language. The digital codes are then forwarded to the machine, which then begins the manufacturing process. However, the machine used is where knitwear and traditional 3D printing diverge. The primary difference from additive manufacturing is that the machine is not a 3D printer that processes filament or powder through extruders, rather, a knitting machine that can produce a three-dimensional garment in a single pass by uniting it thread by thread. Consequently, it should be noted that the principle is essentially the same both are based on software and are additively manufactured, but the material creates a big difference between the two methods.
Therefore, it is hardly surprising that industry experts agree in saying that 3D knitted goods are not manufactured using 3D printing, but rather, 3D knitting is a technology in its own right. Gerard Rubio, co-founder, and CEO of Kniterate, a company that sells 3D digital knitting machines, adds the following about his company’s machines and the use of the word 3D in connection with the production method: “These machines are capable of 3D knitting. But these machines are not necessarily 3D knitting machines.” This is because flat, single-layer garments like scarves can also be printed with a Kniterate machine, which eliminates the additive manufacturing aspect. Rosanne van der Meer adds that she deliberately uses the term ‘3D printed knitwear‘ for her products in order to make a clear distinction between 3D knitwear and conventionally produced knitwear.
Compared to Conventional Textile Production
Now that the differences and similarities between 3D knitwear and 3D printing have been outlined, the question remains whether and, if so, why 3D knitwear should be preferred to traditionally manufactured clothing.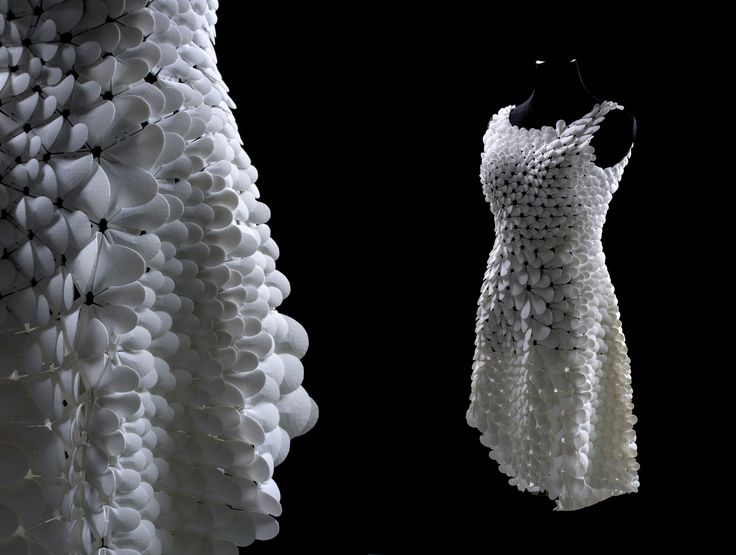 In order to provide a reasonable answer to this, conventional textile production must first be examined more closely.
In order to provide a reasonable answer to this, conventional textile production must first be examined more closely.
This is still a touchy subject, with so few companies keeping their value chains and production methods transparent. Obvious and ongoing issues such as child labor, low wages, and inadequate protective measures in low-cost manufacturing countries are joined by the astronomically negative impact the industry has on the environment. From the cultivation of cotton, whereby both the use of pesticides and an enormous waste of water are recorded, to transit once the material has been broken down, and shipped to be processed into yarn and ultimately fabric in another country — this phase alone requires much examination for improvement.
Then, we have the woven fabric being sent back to be bleached or dyed at another factory. The harmful substances used in this process mostly end up in the wastewater, which in turn leads to the pollution of rivers and oceans. Lastly, the garment is sewn, knitted, and finished again in a different facility, with a large amount of material being wasted in the manufacturing process. The finished products are sent to the various branches around the world. The unbelievably long transport routes, which significantly increase Co2 emissions, rounds out the disadvantages of conventionally produced clothing. Although there are of course also smaller manufacturers who pay attention to sustainable, fair, and regional production, large-scale fashion producers that use traditional production channels still dominate the clothing market.
The finished products are sent to the various branches around the world. The unbelievably long transport routes, which significantly increase Co2 emissions, rounds out the disadvantages of conventionally produced clothing. Although there are of course also smaller manufacturers who pay attention to sustainable, fair, and regional production, large-scale fashion producers that use traditional production channels still dominate the clothing market.
There are many problems with the conventional textile methods of large-scale fashion producers. These include the exploitation of workers in low-wage countries and the negative impact on the environment.
These social and environmental problems are primary focuses for CEOs Gerard Rubio, Gihan Amarasiriwardena, and Rosanne van der Meer, which is why they all pay attention to sustainability in the development of their companies and in the manufacture of their products. Awareness begins with the procurement of materials: While more than half of all clothing is produced using man-made fibers, mainly polyester, but also nylon, elastane, and acrylic, which are obtained from fossil fuels and therefore have a negative environmental impact; new industrial methods use merino wool which is obtained sustainably and as a natural fiber which generally has a smaller footprint compared to synthetic fibers.
Rosanne van der Meer also adds that she relies on high-quality yarn in order to achieve the best possible results and in order to not run the risk of the thread breaking in the middle of the knitting process and thus having to restart production. A special feature here: even if the thread were to break, the half-finished knitted part could be recycled since the knitwear is designed in such a way that it can be separated again. This means that the material used can be recovered — another sustainability factor. As far as the material is concerned, large savings can be made using 3D knitwear, as the machines produce additively In just one pass and therefore only requires the threads that will be used, thereby eliminating numerous production steps and saving a lot of time and costs. Gihan Amarasiriwardena confirms this statement: “With 3D-printed knitwear, only the required fabric is used. This results in approximately 30% less material waste”. Sustainability also plays a role at Kniterate. Gerard Rubio relies on plant-based yarns, which can be recycled, so items of clothing that are no longer wanted can be disposed of properly and not end up in a landfill.
Gerard Rubio relies on plant-based yarns, which can be recycled, so items of clothing that are no longer wanted can be disposed of properly and not end up in a landfill.
The material plays a huge role in the manufacture of 3D knitted fabrics. (Photo Credit: Kniterate)
Since 3D knitwear is on-demand production, problems such as overproduction and inventory waste can also be avoided. Large-scale fashion producers are not able to react flexibly and quickly to changes in the market mainly due to long supply chains, which results in overproduction and overstocking. This is a fatal flaw in today’s fast fashion industry, where new collections and goods hit stores nearly every week. And where should the “old” items of clothing go that have not been bought? These resource and energy-intensive manufactured textiles mostly end up in the garbage or are partially incinerated. On-demand production that takes place on-site/in-house could be a solution here. Not only are transport costs and emissions saved as a result, but practically significantly less waste is produced.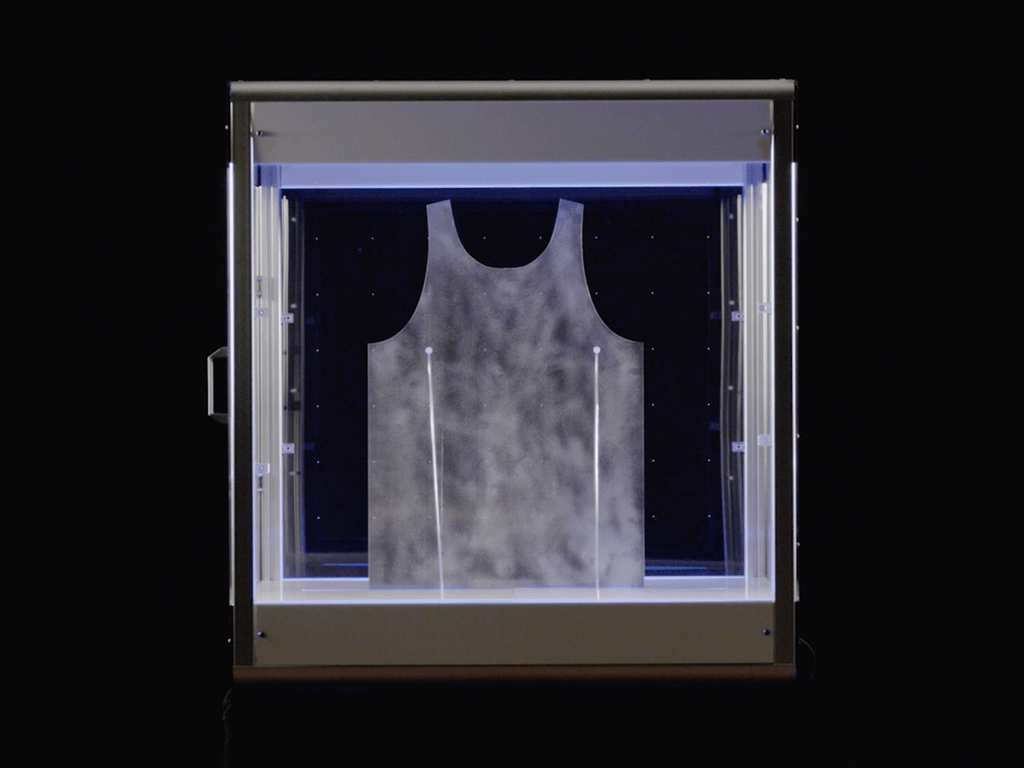
This goes hand in hand with Rosanne van der Meer’s motto: “The starting point for a better climate balance in the fashion industry is less consumption. If you have timeless clothing that fits you really well, you will also consume less.” Thanks to 3D technologies, it is also possible to personalize 3D knitwear. Since the designs are created digitally and every needle stitch is equivalent to a pixel, patterns can easily be modified and adapted to customer requirements, which allows a lot of freedom. A special program from the start-up Shavatar also helped New Industrial Order to improve the accuracy of fit of their 3D knitwear without a 3D scanner – an essential aspect when it comes to buying clothes. With the help of the open-source system and the knitting machine from Kniterate, users are obviously also open to all creations and personalizations. Last but not least, the typical problems such as the exploitation of workers through in-house, regional productions are also eliminated.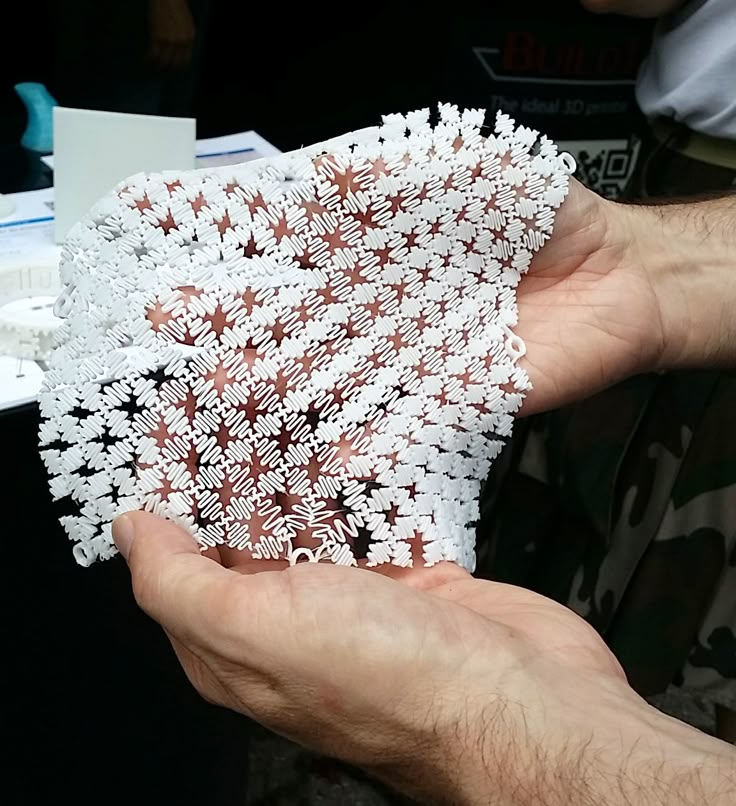
Challenges of 3D Printed Clothing and Predictions for The Future
After explaining the numerous advantages offered by 3D knitwear, the question now remains as to why it is not yet increasingly available in stores. What are the current challenges and what improvements may still need to be made? Will 3D printed clothing and especially 3D knitwear be the future of the fashion industry?
Indeed, additive manufacturing of apparel faces a number of challenges. As mentioned earlier, the material is probably the biggest obstacle – which is why 3D knitwear is being resorted to. When a closer look is taken at previous projects involving 3D-printed clothing, such as products by fashion designer Danit Peleg, it quickly becomes apparent that the options are limited: The materials compatible with a 3D printer are mostly plastics such as ABS, PLA or the currently very popular and very flexible TPU.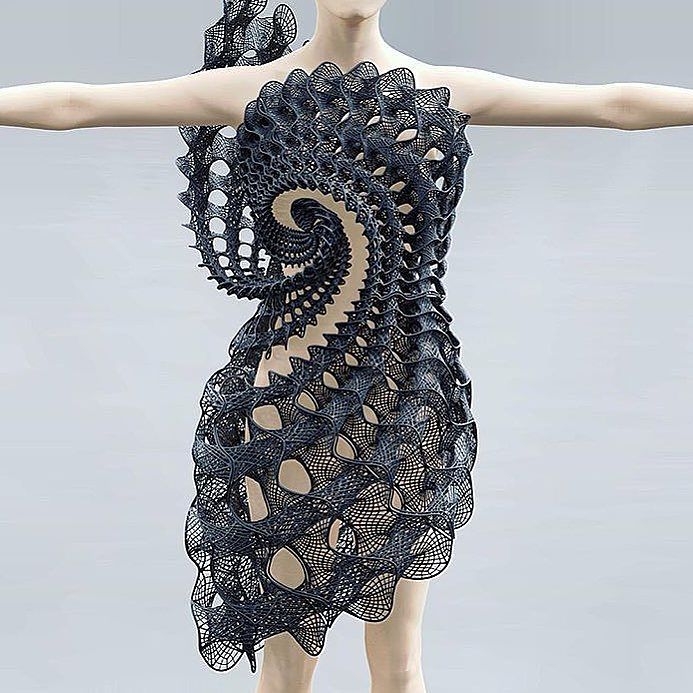 Although the latter can be used to create stretchy, movable 3D objects, it doesn’t begin to compare to the soft, comfortable texture of fabric. Although it could now be argued that the majority of conventionally produced clothing is also made of synthetic polymers, i.e. plastic, the problem lies with the texture. It makes a big difference what form the material is in: Fibers and threads have a filigree, elastic and flowing state, whereas filament has a comparatively thick, hard and rigid state.
Although the latter can be used to create stretchy, movable 3D objects, it doesn’t begin to compare to the soft, comfortable texture of fabric. Although it could now be argued that the majority of conventionally produced clothing is also made of synthetic polymers, i.e. plastic, the problem lies with the texture. It makes a big difference what form the material is in: Fibers and threads have a filigree, elastic and flowing state, whereas filament has a comparatively thick, hard and rigid state.
3D-printed clothing differs in texture from conventionally produced goods. (Photo credit: Danit Peleg)
Furthermore, most 3D printers cannot produce fine enough details. Unlike 3D knitting, where the moving threads are processed by many small needles, the extruders of a 3D printer cannot produce anything comparable. The structure and texture of 3D-printed clothing is heavy and pitted, and the surface texture is likely to be quite cold and unpleasant. Gerard Rubio agrees, saying, “At this point, the materials are not developed enough. However, I strongly believe that 3D-printed clothing will be the future.”
However, I strongly believe that 3D-printed clothing will be the future.”
With regard to 3D knitwear, other problems are encountered. Rosanne van der Meer particularly emphasized here the difficulty of creating the digital codes for the knitting machine. That is why she relies on extensive databases, suitable non-fiction books and an open-source system. The latter should support New Industrial Order’s goal of creating a workflow that makes the codes for 3D knitwear accessible to all those who show interest. Gerard Rubio echoes this sentiment. He, too, describes developing the right parameters as a major challenge. The road from the prototype to the final, commercializable Kniterate machine, which is very complex, was long and difficult, according to him. Referring to the future, however, Rosanne van der Meer sees no problem in this regard: “The technology is already established and ready to function, but the current system works completely differently.”
The biggest difference between 3D printed objects and 3D knitwear is the material. It is easy to see that much finer structures can be created with threads.
It is easy to see that much finer structures can be created with threads.
This is because on-demand production, which is the principle of most current 3D knitwear manufacturers, completely contradicts the market flow. The current fashion market is based on mass production and mass consumption. Changing long-established systems and breaking habits is extremely difficult, which is why more sustainable companies specializing in on-demand production and customization face a major hurdle in entering the market. Also, in terms of production costs, 3D knitwear cannot compete with conventional clothing due to low market compatibility. Therefore, the current products from New Industrial Order and Ministry of Supply are still rather in the luxury segment in terms of price, within the framework of which customers are willing and able to spend a lot for personalization, sustainability and quality.
However, the experts are confident that 3D printing will play a greater role in the fashion sector in the future and firmly believe that novel technologies will revolutionize it. Rosanne van der Meer summarizes: “Changes in the textile industry are slow. Yes: in the future we will find more additively manufactured clothing, but how far this progress is in the future cannot be said.”
Rosanne van der Meer summarizes: “Changes in the textile industry are slow. Yes: in the future we will find more additively manufactured clothing, but how far this progress is in the future cannot be said.”
Ministry of Supply offers, among other things, 3D-printed blazers and masks. (Photo Credit: Ministry of Supply)
What do you think of 3D printed knitwear? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages. Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!
Photo Credit: New Industrial Order
3D-printed clothes: why haven't manufacturers made them mass-produced yet?
ThreeASFOUR showcased their 3D printed clothing collection for the first time at a fashion show at the Jewish Museum in New York. The dresses on the models were patterned and looked ephemeral, like the robes of robotic angels. One was woven from white, angular bubbles, which gave the impression that the girl had just taken a bubble bath.
But the girl who showed this dress to the world could not sit down, otherwise the dress would have broken. “The model wearing the dress was very unhappy,” said Bradley Rothenberg, a 3D architect who collaborates with threeASFOUR founders Gabi Asfor, Angela Donhauser and Adi Gil.
ThreeASFOUR dress at the fashion show at the Jewish Museum.
It happened in 2013, when threeASFOUR began to realize that in order to achieve the goal, they would have to take a step back. They did not even think that they would create such an impractical piece of clothing. On the contrary, they wanted to create an outfit worthy of a superhero. They dreamed that the fabric they printed would become invulnerable to bullets and fire, retain heat and protect the wearer from stress. They dreamed that people would start buying their clothes as soon as they hit stores.
But time has passed. With the Silicon Valley elite building personal bunkers, refugees pouring across the border into Canada, and Margaret Atwood back in vogue, threeASFOUR's vision is as close to reality as an apocalyptic dystopia.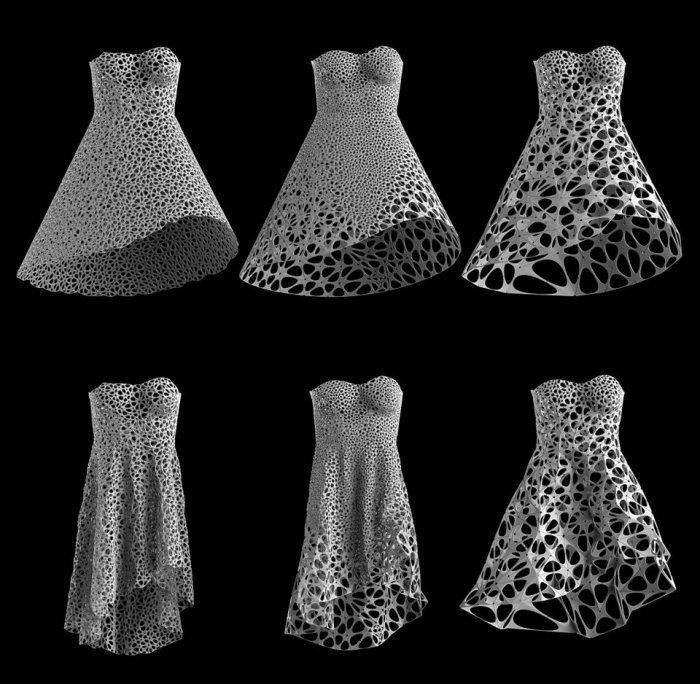 But if everyone has access to the stocks left on Doomsday, becoming a superhero is still unrealistic.
But if everyone has access to the stocks left on Doomsday, becoming a superhero is still unrealistic.
And the reason is quite simple. Thanks to thousands of years of experience, tailored clothes are more practical and comfortable than those printed by a 3D printer. But that doesn't seem to be stopping threeASFOUR and other designers.
“In the fashion world, you can control the patterns and structure of a dress to get the look you want,” Rothenberg says. “The problem is that right now it’s just a possibility. So I think Gaby Asfor is the most interesting person in the industry. We need people who will push the boundaries, striving to show the new.”
The vision of Gabi Asfor is evident in his work. He became interested in 3D printing in 2009 and has been experimenting with the internal structure of fabrics ever since.
Traditional fabric has two dimensions: the threads are arranged horizontally, vertically and diagonally in a certain way to create a weave.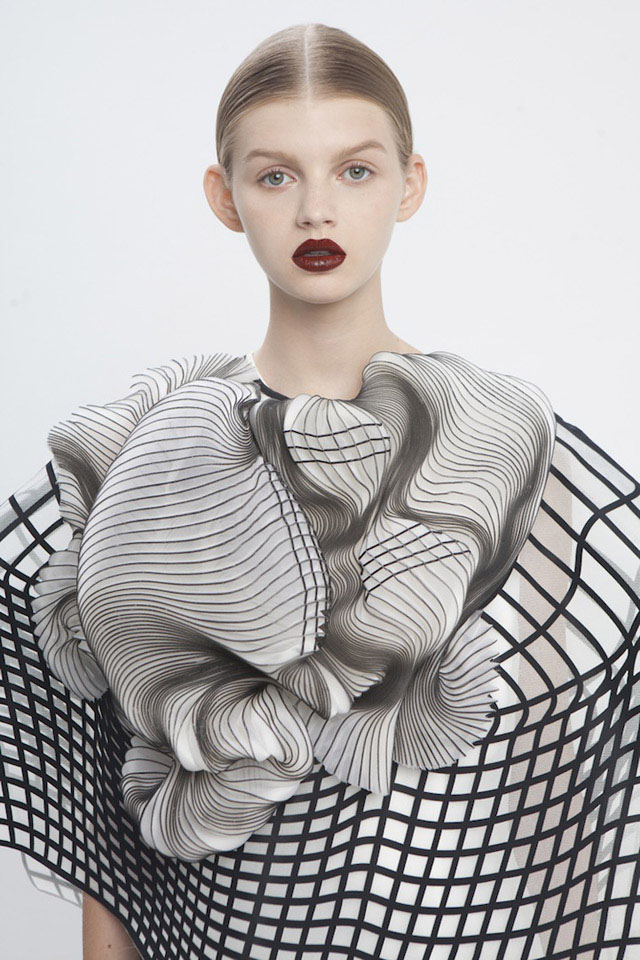 Asfor, who has a degree in mechanical engineering and architecture from the University of Maryland, worked with Donhauser and Gil to come up with a three-dimensional weave that was planned to be laser-cut. The desire to give fabric a third dimension led them to 3D printing.
Asfor, who has a degree in mechanical engineering and architecture from the University of Maryland, worked with Donhauser and Gil to come up with a three-dimensional weave that was planned to be laser-cut. The desire to give fabric a third dimension led them to 3D printing.
“The most innovative recent invention in the industry is the four-way stretch fabric,” says Asfor. “But ordinary fabric can only stretch in the X and Y planes. 3D printing will allow the material to stretch in the Z plane as well.” He believes that such a fabric will be better breathable, less restrict movement, and will not have folds.
ThreeASFOUR was interested in 3D printing, which led them to collaborate with Materialise, a 3D printed model company, and Rothenberg, who came up with 3D printed wings for the 2013 Victoria's Secret fashion show.
“When we first started, Gabi kept asking, “Can you print fabric? What material will be needed for this?” Rotenberg says. It turned out that this would not be easy.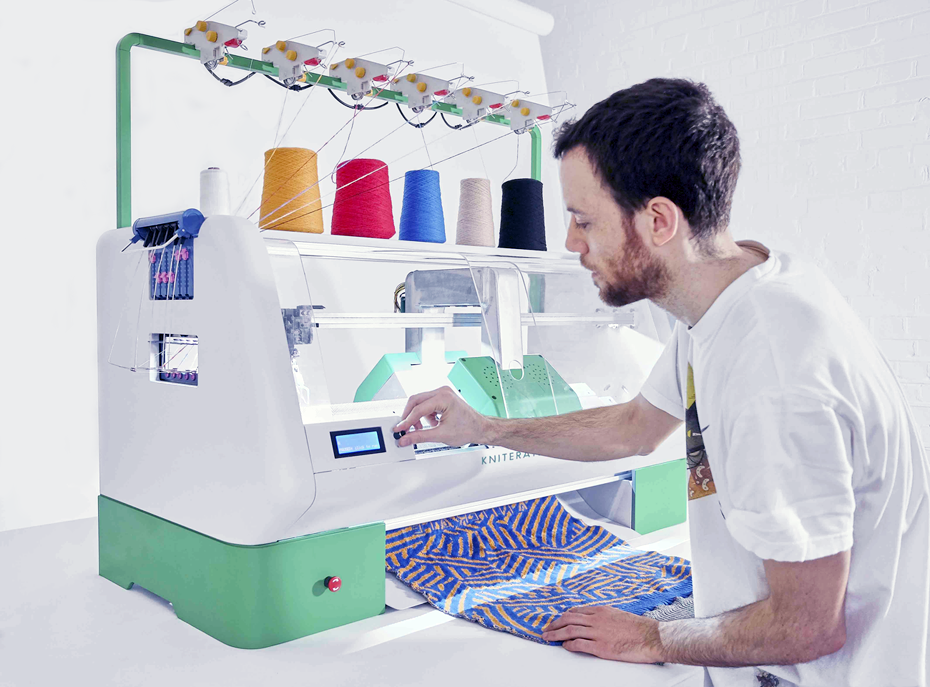
Pangolin dress from the Biomimicry collection. Source: Backchannel
The main problem is that the materials used for 3D printing are stiffer than regular fabric. ThreeASFOUR experimented with the structures of various materials, trying to add elasticity to them, but any printed model came out very fragile.
But new materials have arrived, and ThreeASFOUR has teamed up with Stratasys and Travis Fitch to design dresses like Pangolin for their new fall 2016 collection, which they call Biomimicry. It took 500 hours to print (not including assembly) Pangolin! The dress, named after a scaly mammal, was reminiscent of dark armor (Björk appeared in it during a tour in Australia last year). To create the "scales", the designers used an algorithm that simulates cell division, thus obtaining an intertwining pattern.
On the ground floor of the ThreeASFOUR studio, there are employees who work with the most ordinary sewing machines. The dress itself is located on the next floor. Up close, the Pangolin bib, detached from the other parts of the dress, is somewhat reminiscent of a bicycle tire that has been cut to look like fish scales (it even wiggles like a fish tail). Such a deflection was not possible a few years earlier.
Up close, the Pangolin bib, detached from the other parts of the dress, is somewhat reminiscent of a bicycle tire that has been cut to look like fish scales (it even wiggles like a fish tail). Such a deflection was not possible a few years earlier.
Asphor hands me a piece of another dress, a Harmonograph modeled after a sound wave. It was made from a rubber mesh that can expand and contract like a pillow-top mattress. The bottom of the dress shrinks when a person sits down and returns to shape when they stand up.
Harmonograph dress by ThreeASFOUR. Source: Instagram
With this flexibility, 3D wearers can now sit comfortably, although comfort is far from ideal. “Matter resembles artificial skin. It is not very pleasant to the touch and, in addition, sticks to the skin, ”says Rotenberg.
The idea of making printed clothes gained popularity at the beginning of the 21st century, but developed rather slowly.
Few people know this better than Aaron Rowley, founder of Electroloom, a 3D printed clothing startup. At first, many well-known brands were interested in his work, but gradually, one by one, they left. “There was an idea that people could print tools at home,” says Rowley, referring to the days when there was a lot of hype around 3D printing. It was believed that clothes could also be printed, since wardrobe items are used every day and need to be updated regularly.
At first, many well-known brands were interested in his work, but gradually, one by one, they left. “There was an idea that people could print tools at home,” says Rowley, referring to the days when there was a lot of hype around 3D printing. It was believed that clothes could also be printed, since wardrobe items are used every day and need to be updated regularly.
But progress has not gone far. “The process of creating fabric is fundamentally different [from 3D printing],” says Rowley.
“Textiles are an advanced technology,” says Scott Hudson, a researcher at Carnegie Mellon University who has worked with Disney on soft print materials. Calling the textile industry a technology, he was not exaggerating: some experts believe that the loom is an early version of the computer. In the middle of the 18th century, Joseph Marie Jacquard figured out how to save a fabric pattern on a punched card, which made it possible to set the machine to work and automate the process.
3D printing technology is not that polished yet. “You have to find a compromise between stiffness and strength,” says Hudson. 3D printers create an object by layering, and this process is very different from how fibers are turned into fabric.
“You have to find a compromise between stiffness and strength,” says Hudson. 3D printers create an object by layering, and this process is very different from how fibers are turned into fabric.
Rowley took fabric raw materials and created blends that resemble existing fabrics. However, the 3D printer has created something that looks like a "chaotic web". It took a long time before they got a soft, stretchy, foldable and lightweight material that at first glance resembled fabric. But even the final version was not suitable: the material was torn as soon as it was pulled harder.
“Fibers that are physically connected, as in the case of 3D printing, remain stationary, while woven fibers move smoothly relative to each other,” Rowley explained. Electroloom shut down last October.
Until the material issue is resolved, the printed garment will look more like a work of art than a piece of clothing. A year ago, threeASFOUR dresses were featured at the Met Gala-sponsored Costume Institute show.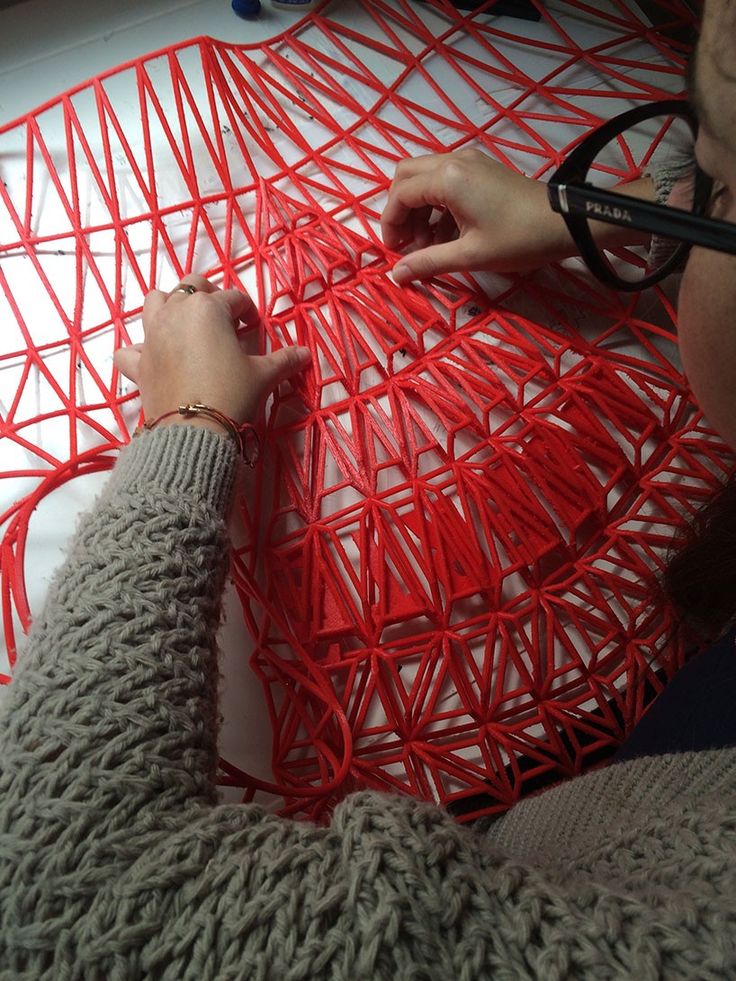 The Manus x Machina show in 2016 also emphasized the role of technology in the fashion world: stars and celebrities dressed in silver at the show, and Zayn Malik appeared in a suit with robot arms.
The Manus x Machina show in 2016 also emphasized the role of technology in the fashion world: stars and celebrities dressed in silver at the show, and Zayn Malik appeared in a suit with robot arms.
Oscillation Dress by ThreeASFOUR. Source: Instagram
This year, threeASFOUR has introduced another novelty: a white and blue lattice dress, pictured above, it hugs a mannequin in their studio. The dress consists of 30 pieces, which are first printed and then carefully assembled.
“We are looking for new technologies,” says Asfor. “I believe that in the near future we will have a unique opportunity to move in this direction.”
At the same time, the quality of other garments (such as jewelry or sportswear) printed on a 3D printer is much higher. Nike and Adidas are using 3D printing to create shoe padding and soles, which are usually made from foam. NASA is developing a project similar to Pangolin - a printed "chain mail" designed to protect astronauts from the impacts in space.
Read also: Adidas launches mass 3D printing of sneakers
Maybe not only astronauts. Although T-shirts and pants are still made in the traditional way, protective armor will soon be printed. It will come in handy in case there is a revolution, aliens attack or you need to flee abroad.
Source.
Related materials:
“Print me food!” – what printing technologies of the 21st century are capable of
Smart home in Russian: how 3D printing helped create a cool gadget
A service for creating models for 3D printing inside virtual reality is launched
Ford is testing 3D printing of car parts
Where to go to learn and work with 3D printing?
3D printed mesh fabric
Prologue
Hello everyone! I am developing "smart sequins" - electromechanical color-reproducing devices for designer clothes. Our team is passionate about the idea of creating clothes and accessories that can change their color at the request of the owner or depending on environmental conditions.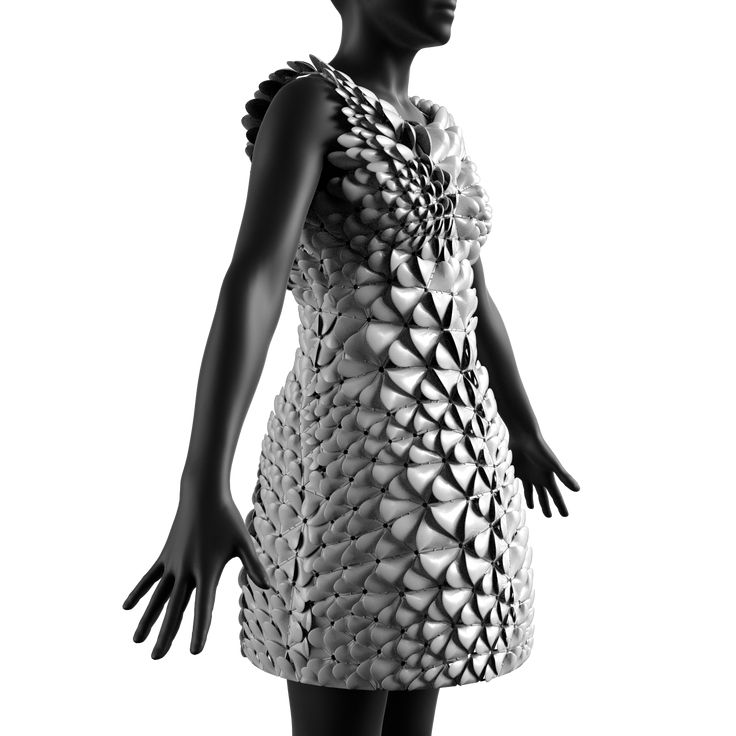
In this article I want to talk about how we used 3D printing in our project, share our experience and tools.
3D printed fabric
One of the tasks that I had to solve was to figure out how to make an elastic fabric out of plastic sequins, which in its properties will resemble textile materials. At the same time, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of easily creating electrical connections between the sequins.
There are quite a few articles and materials about making clothes on a 3D printer. Many different ways have already been invented, from creating hinges right during the printing process to printing with elastic plastics.
While looking for a solution, I came across this video. From it, I first learned about the method of printing on mesh fabric using a conventional FDM 3D printer.
The author himself claims that he spied the idea here: Shorey Designs.
The essence of the method is very simple. We create a 3D model of a fragment of the future canvas, then arrange a lot of fragments so that we get a whole canvas.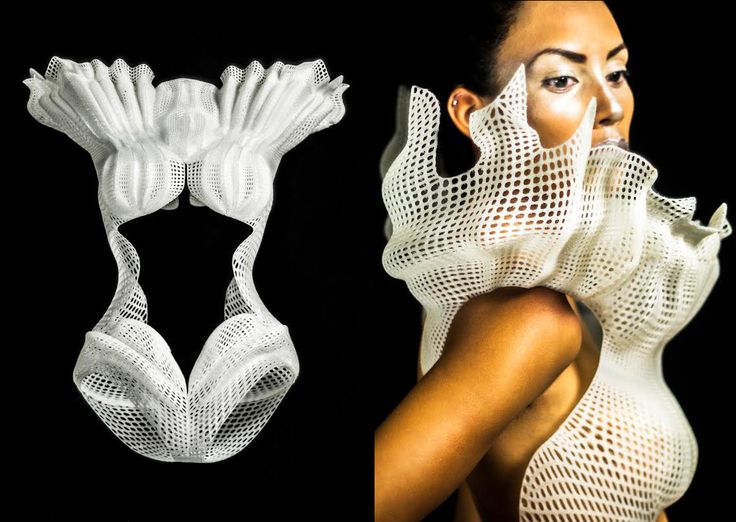 We start the slicer and prepare the G-code. Before sending it to the printer, you need to insert a pause and raise the extruder before printing a certain layer. The printer will stop during operation. At this point, we cover the printed layers with a mesh cloth. We continue to print. Due to the presence of large holes in the fabric, the layers of plastic will interlock with each other, as in conventional printing, and the mesh fabric will be firmly integrated into the parts.
We start the slicer and prepare the G-code. Before sending it to the printer, you need to insert a pause and raise the extruder before printing a certain layer. The printer will stop during operation. At this point, we cover the printed layers with a mesh cloth. We continue to print. Due to the presence of large holes in the fabric, the layers of plastic will interlock with each other, as in conventional printing, and the mesh fabric will be firmly integrated into the parts.
Modify G-code
I use Cura version 3.2.1 as a slicer. 3D printer - homemade H-bot controlled by a board based on ATmega2560 (RAMPS 1.4) with Marlin firmware.
To pause the printer, there is an M25 command. Command for lifting in Z by 20mm: G0 Z20. It is noteworthy that the M25 must go before the ascent, otherwise the next command is processed first. Why this happens is a mystery to me, apparently somehow connected with the processing of commands by the printer.
Add commands to G-code:
Operation automation
Manually searching for the required line in the G-code file and inserting commands is not the most modern solution, I thought and wrote a simple program that allows you to open and view toolpaths.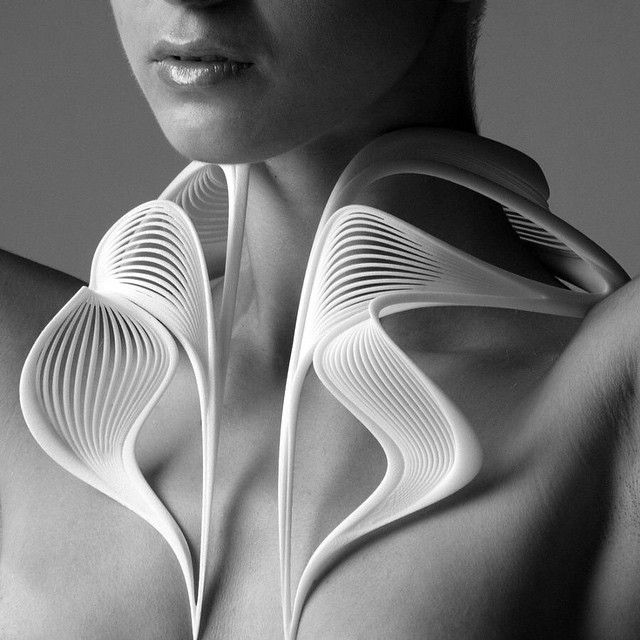
For the convenience of viewing the layers, the "explode" command is provided, which allows you to visually increase the distance between the layers of the model. After pressing the "insert pause" button, the distance between the marked layer (red) and the previous one increases. This means that the print will be interrupted precisely between these layers.
To understand where one layer ends and the next begins, I used the comments that Cura kindly provides in its output files. The keyword ";LAYER:X" allows you to accurately find the boundaries of layers in a text file.
Pressing the "write file" button allows you to save the modified G-code in the specified location.
Save the file to the SD card and bring it to the printer.
It's funny that only while preparing this article, I came across a video in which they tell how you can do the same using standard Cura tools ... But the process is already running, it's too late to slow down! Here, starting at 7:30, it is described in detail how to do it.
Well ... hurry up - learn how to parse G-code!
Trying to print
Formation of the first layers. We print on glass. Heated table. Table temperature 60⁰С, printing temperature 220⁰С. The print material is PLA plastic. Layer height 0.2mm.
During the pause, lay down the fabric and fix with magnets. Since the table is aluminum (paramagnetic), we put the magnets on the top and bottom sides of the table. Fixation is made in 4 places, in the corners of the part. This is quite enough. The main thing is not to place them too close to the print area, otherwise the magnets will stick to the print head.
After 40 minutes, this is the structure. The thickness of each 6 carbon element is 1mm. The gap between the elements is 2mm.
In this experiment, tulle was used as the backing fabric. It is a lightweight mesh fabric of medium stiffness, woven from polyester threads.
Experiments have also been made with mosquito net printing. In the hardware store, there were two types of them: fabric and fiberglass. Fabric mesh is softer than tulle, but has greater mechanical tensile strength, as well as less elasticity. The fiberglass mesh is harder than tulle, its mechanical strength is the highest of all participants in the experiment.
In the hardware store, there were two types of them: fabric and fiberglass. Fabric mesh is softer than tulle, but has greater mechanical tensile strength, as well as less elasticity. The fiberglass mesh is harder than tulle, its mechanical strength is the highest of all participants in the experiment.
Hexagonal sequin printing on fiberglass mosquito net. The gap between the elements is 1mm. The matrix is very hard. Clearance is clearly not enough.
Round sequin printing on fiberglass mosquito net. The gap between the circles is 2mm. It has a lot of flexibility, but there is too much unfilled space between the sequins.
After several test prints, the choice was made in favor of the fabric mesh. She formed the basis of the matrix of smart sequins. The resulting matrix can bend in all directions.
The video demonstrates the operation of the program, the printing process and the final result.
Conclusion
The method of printing on mesh fabric has proved to be very good. This is an ideal solution for our task, because the fabric substrate allows us to weave conductive threads into it, which are used to provide electrical connection between the individual sequins of the matrix. Moreover, the formation of a “pattern” of conductors can be carried out at the preparatory stage. And the 3D printing itself is later.
The strength of the resulting structure depends mainly on the strength of the substrate material. But the flexibility will also depend on the distance between the sequins, as well as their shape.
The developed program still needs to be improved. For example, you can finish the retract before lifting, allow the user to adjust the height of the extruder.
Link to the source code for the processing environment.
And also a link to the release with the .exe file of the program.