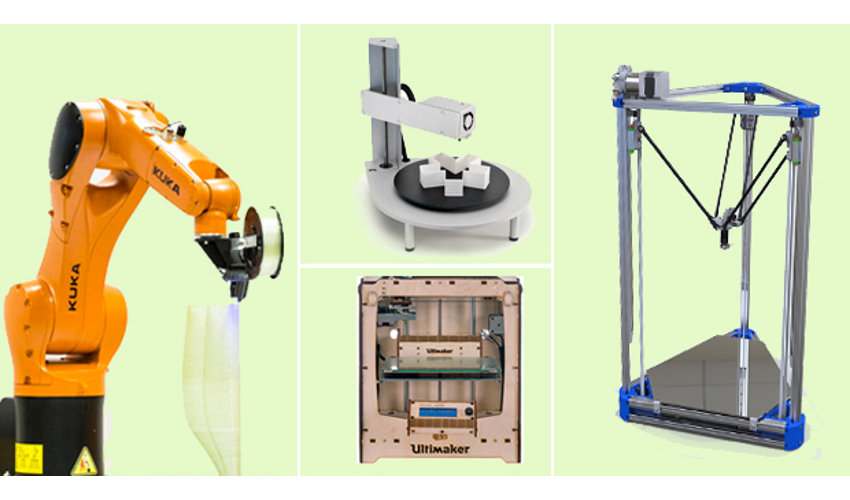
3D printer workshops
Workshops — Illinois MakerLab
Join us at the Makerlab to turn ideas into objects. Besides our open hours, you can sign up for a variety of workshops below. If these workshops or the times don’t work for you, you can even request a private event. Don't forget to sign up for our Newsletter to stay up to date! in person series
Learn the basics of 3D printing in a 90-minute workshop! In this workshop, our Gurus will provide a brief overview of the MakerLab and 3D printing. Different printing methodologies, as well as their benefits and limitations, will also be covered during this session.
This workshop is tailored towards Beginners in 3D Printing.
This workshop will be held in person, University students with SaferIllinois Access required.
Price: $20
Date: 11/03
Time: 5:30 PM - 7:00 PM
Register Here!
______________________
Learn the basics of designing with Tinkercad in a 90-minute workshop! In this workshop, our Gurus will provide an introduction to using Tinkercad. Attendees will be able to learn how to design printable objects.
This workshop is tailored towards Beginners in 3D Design.
This workshop will be held in person, University students with SaferIllinois Access required.
Price: $20
Date: 11/17
Time: 5:30 PM - 7:00 PM
Register Here!
______________________
Learn the basics of designing in Fusion 360 with our gurus! This workshop will demonstrate how to operate the sophisticated 3D Design Software, Fusion 360. The skills learned in this workshop can be easily applied to create functional designs.
This workshop is tailored towards beginners in 3D Design.
This workshop will be held in person, University students with SaferIllinois Access required.
Price: $20
Date: 11/10
Time: 5:30 PM - 7:00 PM
Register Here!
______________________
Digital Maker Certificate:
Attend all 3 of our workshops to complete our Digital Maker Certificate! The Digital Maker Certificate is a visible symbol that you possess the knowledge and skills to design, scan, and print 3D objects. In addition, it certifies to others that you are well versed with cutting-edge 3D tools such as 3d printers/scanners, platforms such as Thingiverse.com , and software such as Tinkercad, and Autodesk Fusion 360. A growing number of firms are recognizing the revolutionary potential of 3D printers. Thus, those with 3D printing skills are in high demand! At a more personal level, you will have the satisfaction of knowing that you have the ability to turn your ideas into objects and your objects into ideas!
In addition, it certifies to others that you are well versed with cutting-edge 3D tools such as 3d printers/scanners, platforms such as Thingiverse.com , and software such as Tinkercad, and Autodesk Fusion 360. A growing number of firms are recognizing the revolutionary potential of 3D printers. Thus, those with 3D printing skills are in high demand! At a more personal level, you will have the satisfaction of knowing that you have the ability to turn your ideas into objects and your objects into ideas!
This certificate is given after completion of Basic 3D Printing, 3D Design with Tinkercad, 3D Design with Fusion 360, and 3D Scanning workshops
3D Printing Trainings & Workshops
Our passion is to enable people and organizations worldwide to use the potential of industrial 3D printing for responsible manufacturing.
In cooperation with renowned partners, Additive Minds Academy has developed a comprehensive online training program to optimize onboarding processes and accelerate your knowledge buildup at the forefront of additive manufacturing innovation.
Our digital trainings target a wide range of users, from machine operators and application specialists to product managers, providing content that is always relevant to you.
The learning paths are designed so that the competence required for a new role in Additive Manufacturing can be built up within only four to six weeks
- The courses combine online and self-study with practical learning based on case studies
- All our trainers have multiple years of experience with industrial 3D printing and are familiar with the obstacles you face when getting started or working on complex tasks
- Participants are supervised throughout the course, receive one-on-one feedback, and can get in touch with tutors and other learners
- At the end of the program, you can take a test to then be certified by the Additive Minds Academy
The knowledge we offer ranges from basic understanding of the Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Melting (DMLS®) technologies to selecting components for AM production, as well as design and AM-appropriate engineering, to scaling and validating production.
Our digital courses make AM knowledge available anytime, anywhere. Thus, they help reduce training time and costs, and by conserving resources contribute to eco-friendly learning.
Do you think learning should be fun and engaging? This is why we design our products with state-of-the art training methods. We are committed to smart learning and promote innovative tools to provide you the best learning experience, while setting the course for future learning with augmented and virtual reality formats.
We offer customer-specific 3D manufacturing solutions for the entire value chain – from conception, design and engineering to production and post-processing, right up to the finished part. Benefit from more than 30 years of experience in additive manufacturing and take advantage of our full portfolio of systems, consulting and services for industrial 3D printing.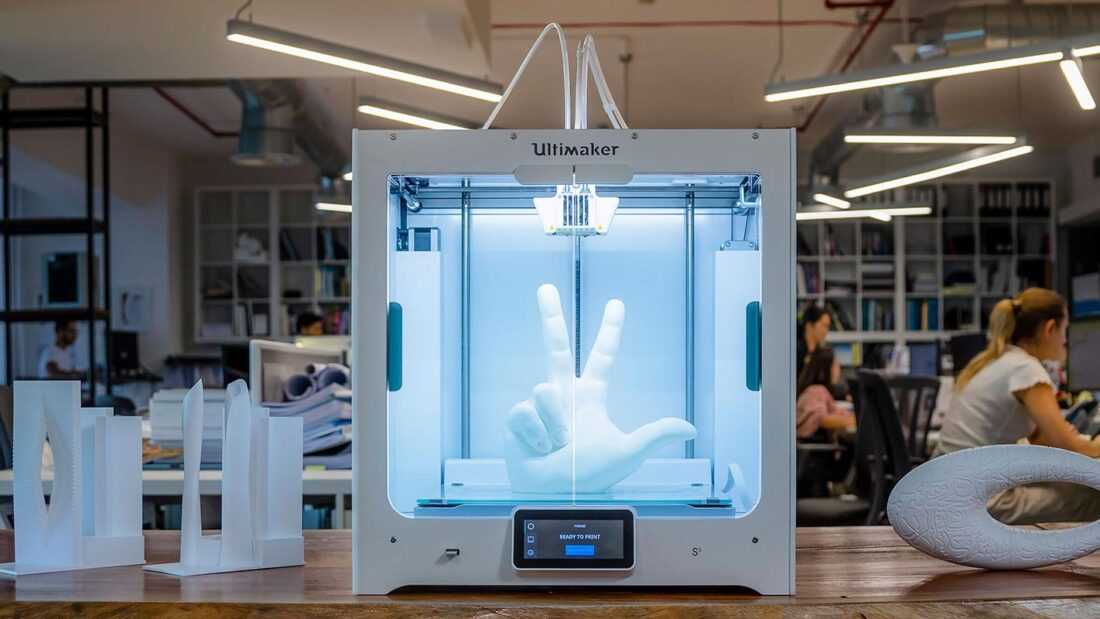 Together with you and our highly effective network of partners, we can develop the solutions that you need for your own production to achieve a comprehensive portfolio of solutions.
Together with you and our highly effective network of partners, we can develop the solutions that you need for your own production to achieve a comprehensive portfolio of solutions.
Fundamentals of 3D modeling. Printing 3D models on a 3D printer.
Training workshop
for teachers
Topic: Basics 3D modeling. Printing 3D models on a 3D printer.
Purpose: formation and development intellectual and practical competencies in the field of creating spatial models.
Tasks:
- to form a positive attitude towards 3D modeling algorithms;
-form ability to navigate in three-dimensional space; nine0003
- give an idea of three-dimensional modeling, appointment, development prospects;
- modify, change objects or their individual elements;
- create simple three-dimensional models;
Form conducting:
students with teachers;
- lecture with presentation elements, practical work.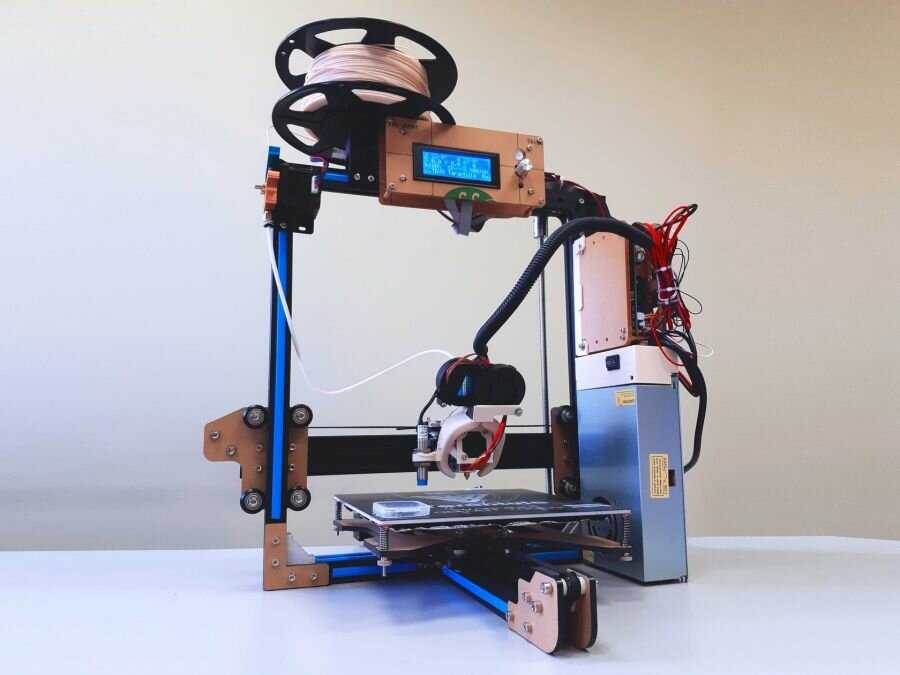
Design:
- presentation on the theme of the master class.
Materials and tools for work: computer, projector, 3D printer, plastic ABC
Structure master class:
1. Introductory part. Announcement of the theme and purpose of the MK. The content of MK in as a whole and individual components.
2. Theoretical and demonstration part. The main stages of the project.
3. Practical part. Basic implementation techniques.
4. Reflection of MK participants. Summarizing.
Master class progress
1. Organizing time. nine0003
Hello, Dear guys and colleagues! Glad to see you all at our master class.
The theme of our master class: Fundamentals of 3D modeling. Printing 3D models on a 3D printer
Purpose of the master class: formation and development of intellectual and practical competencies in the field creation of spatial models.
In the course of our creative activity, you will consolidate and master the basics of modeling using online Tinkercad program and make a "Keychain" model. nine0003
nine0003
2. Theoretical demo part
To continue our wizard class guys will introduce you what is 3d modeling and 3d printing in general terms and we will smoothly move on to our practical parts
3D printing technology.
3D or 3D printing is a layer-by-layer creation of a physical object based on virtual 3D model. Printing comes from several hundred and even thousands of layers on a special device - a 3D printer. 3D printer is called three-dimensional data output device, it is from a conventional printer that outputs two-dimensional information on a sheet, in that it allows you to display three-dimensional information (immediately in three dimensions) according to the principle of layer-by-layer growth The physical model is usually bottom-up. In turn, 3D printing is called the process of creating physical objects from 3D digital models created by 3D modeling in any CAD or CAD program. nine0003
3D technology printing originated in the middle of the twentieth century, at the same time the first 3D printers that looked more like manufacturing machines than printing devices.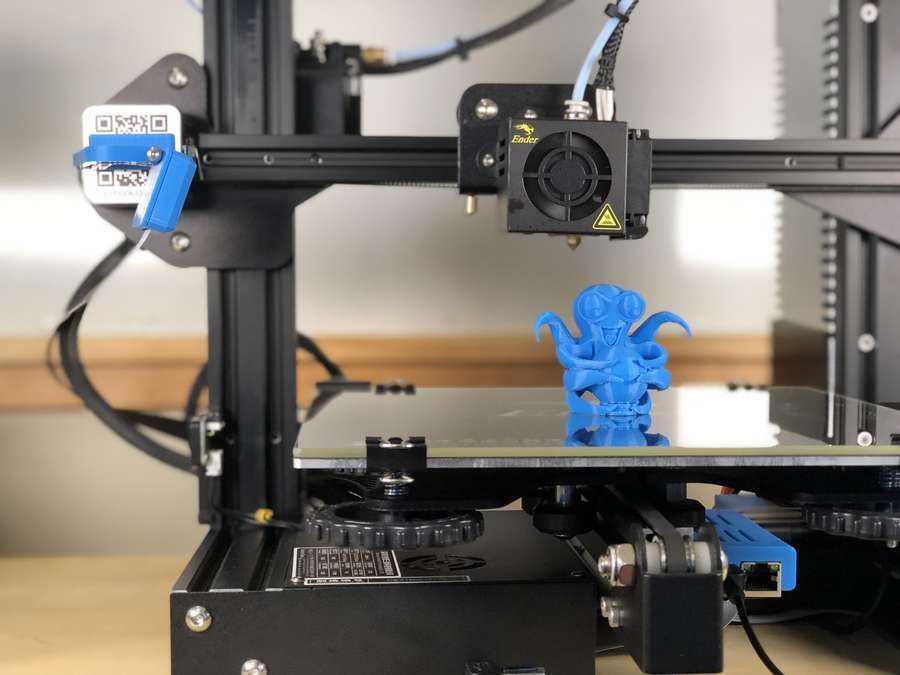 The price of such devices ranged from several tens to several hundred thousand dollars. With the development of 3D printing technology printers became smaller and cheaper. The first devices appeared available not only for industrial enterprises and large commercial organizations, but also for small businesses and households. materials for 3D printing can be very different from the so-called ABC plastic to chocolate. nine0003
The price of such devices ranged from several tens to several hundred thousand dollars. With the development of 3D printing technology printers became smaller and cheaper. The first devices appeared available not only for industrial enterprises and large commercial organizations, but also for small businesses and households. materials for 3D printing can be very different from the so-called ABC plastic to chocolate. nine0003
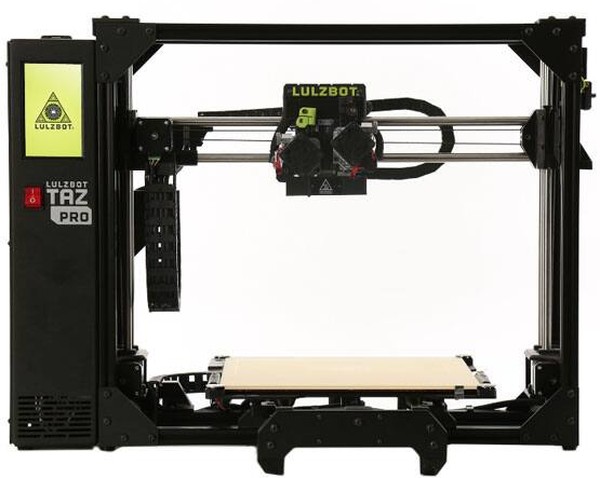
Fig. 1.1. - Modern compact 3D printer
Modern 3D printing devices have learned to create not only household items and clothing, but also own parts, food, human tissues and organs.
3D printing has its own history since 1948, when the American Charles Hull developed the technology layer-by-layer growth of physical three-dimensional objects from photopolymerizable compositions (FPK).
Patent for own the author received the invention only at 1986, the same year he founded the company 3D System and started developing the first industrial device for 3D press, which was presented to the public a year later, in 1987. So since the term "3D printer" has not yet been introduced into circulation, the apparatus of Charles Hull received the name "installation for stereolithography".
So since the term "3D printer" has not yet been introduced into circulation, the apparatus of Charles Hull received the name "installation for stereolithography".
3D features print. Methods for obtaining three-dimensional models.
3D printing capabilities are limitless. With the help of a 3D printer, you can create a variety of things: from shoes to jewelry, from plastic phone cases to implants spine, which are made of medical grade titanium. nine0003
2008 - Objet Geometries announced the creation of a revolutionary rapid prototyping system Connex500™. It was the first system in the world to allow the production of 3D parts. using different materials at the same time.
November 2010 - Urbee the first prototype of a printed car was presented. This is the first a car whose body was printed by a giant 3D printer. All external components - including glass panel prototypes - were created using Dimension 3D Printers and 3D Systems Fortus. nine0003
In 2011, the company Lockheed demonstrated at the British air show in Farnborough a large an unmanned aircraft, most of which was made using the 3D print.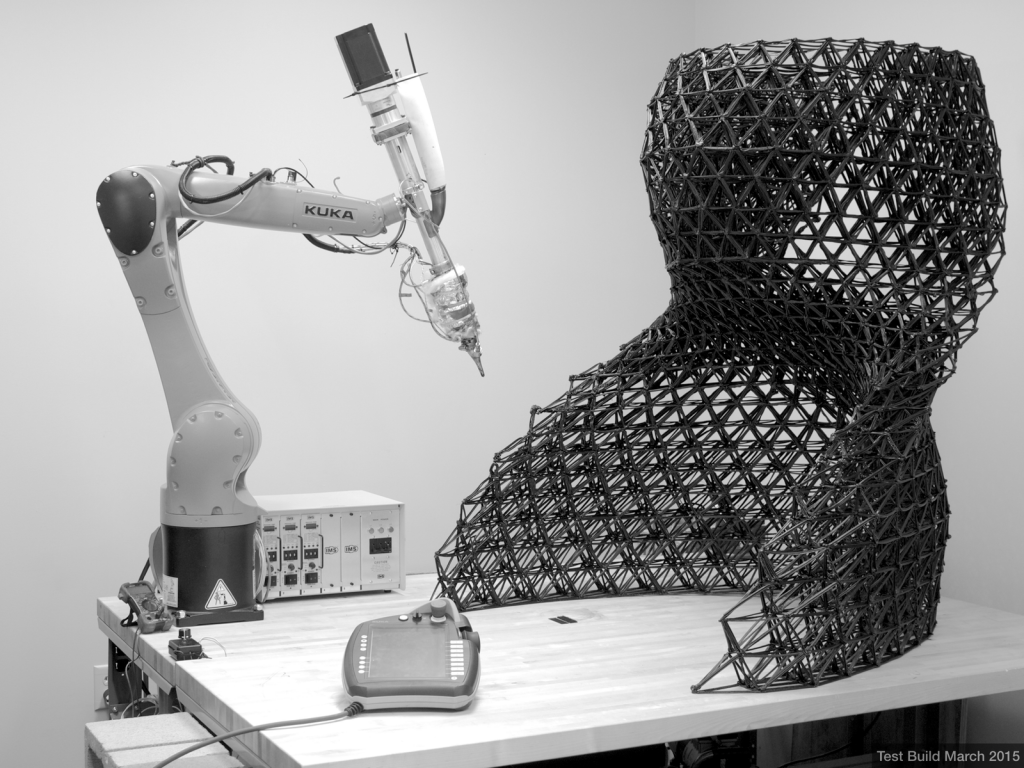 The Polecat aircraft is a flying prototype designed to show performance of new 3D printing technology. To the merits of such parts manufacturing is not only speed, but also relatively low the cost of such parts, and this is the main goal.
The Polecat aircraft is a flying prototype designed to show performance of new 3D printing technology. To the merits of such parts manufacturing is not only speed, but also relatively low the cost of such parts, and this is the main goal.
Production methods 3D models. 3D scanner.
As mentioned Previously, three-dimensional (3D) printing consisted of printing three-dimensional three-dimensional models hundreds or even thousands of layers.
Three-dimensional model, which will need to be printed can be obtained in three ways:
download the finished model, for example, from the Internet;
draw from scratch full 3D model;
scan existing object. nine0003
3D models from ABS plastics are durable, but do not tolerate direct sunlight. Via only opaque models can be obtained from such plastic.
Acrylic. Acrylic used in 3D printing to create transparent models. Using acrylic, the following features must be taken into account: for this material you need higher melting point than ABS and cools very quickly and hardens. In heated acrylic, a lot of small air bubbles appear. bubbles that can cause visual distortion of the finished product. nine0003
Concrete. B At present, trial samples of 3D printers for printing with concrete have been made. These are huge printing devices that painstakingly, layer by layer, “print” concrete construction details and structures. This 3D printer can in just 20 hours to "print" a residential two-story house with a total area of 230 m2.
For 3D printing an improved grade of concrete is used, the formula of which is 95% the same with the formula of ordinary concrete.
Hydrogel . Scientists from the University of Illinois (USA) printed using a 3D printer and hydrogel biorobots 5-10 mm long. Cells were placed on the surface of biorobots heart tissue that spread through the hydrogel and began to contract, driving the robot. Such hydrogel robots are able to move with speed of 236 micrometers per second. In the future, they will be launched into the body human to detect and neutralize tumors and toxins, as well as to transportation of medicines to the destination. nine0003
In the future, they will be launched into the body human to detect and neutralize tumors and toxins, as well as to transportation of medicines to the destination. nine0003
Paper. B Some 3D printers use plain paper as the print material. A4 paper. Since paper is an affordable and inexpensive material, paper models are inexpensive and accessible to users. Such models are printed in layers, with each subsequent layer of paper cut out printer and pasted on the previous one. Paper models print quickly, but cannot boast of strength or aesthetics. They are ideal for rapid prototyping of a computer project. nine0003
Plaster. B gypsum materials are widely used in modern 3D printing. models, made of gypsum, short-lived, but have a very low cost. Such models are ideal for the manufacture of objects intended for presentations. They can be shown as a sample to customers and customers, they perfectly convey the shape, structure and size of the original product. Because plaster models are characterized by high heat resistance, they are used as casting samples. nine0003
Wood fibre. Inventor Kai Parthi has developed a special wood fiber for 3D printing. Fiber consists of wood and polymer and is similar in properties to polyactide (PLA). The combined material allows to obtain durable and solid models, which outwardly look like wooden products and have the smell of freshly sawn tree.
Ice. B 2006 two Canadian professors received a grant for the development of 3D technology ice figure prints. In three years, they learned how to create using 3D printers small ice objects. Printing proceeds at a temperature of -22 ° C, as consumables are water and methyl ether, heated to temperature 20oC. nine0003
Metal powder. No plastic can replace metal with its pleasant soft gloss and high durability. Therefore, in 3D printing it is very often powder from light and precious metals is used: copper, aluminum, their alloys, as well as gold and silver. However, metal models do not have sufficient chemical resistance and have high thermal conductivity, therefore, in metal printing powder add fiberglass and ceramic additives. nine0003
However, metal models do not have sufficient chemical resistance and have high thermal conductivity, therefore, in metal printing powder add fiberglass and ceramic additives. nine0003
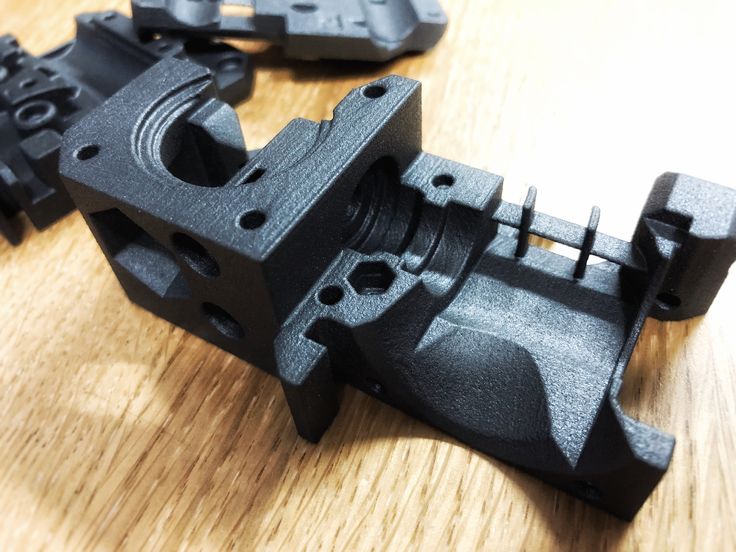
Jewelry from metal powder printed by a 3D printer.
Nylon . Nylon printing has a lot in common with ABS printing. Exceptions are higher printing temperature (about 320oC), high ability absorb water, longer curing time, need to pump out air from the extruder due to the toxicity of the nylon components. Nylon is enough slippery material, for its application it is necessary to equip the extruder with spikes. Despite these shortcomings, nylon is successfully used in 3D printing, since parts from this material are not as rigid as from ABS plastic, and sliding hinges can be used for them. nine0003
Polylactide (PLA). Polylactide is the most biocompatible and environmentally friendly material for 3D printers. It is made from biomass residues, sugar beet silage or corn. Having a lot of positive properties, polylactide has two essential disadvantage. Firstly, the models made from it are short-lived and gradually decompose under the influence of heat and light. Secondly, the cost of production polylactide is very high, which means that the cost of models will be much higher similar models made of other materials. Used in 3D printing technologies: SLS and FDM. nine0003
It is made from biomass residues, sugar beet silage or corn. Having a lot of positive properties, polylactide has two essential disadvantage. Firstly, the models made from it are short-lived and gradually decompose under the influence of heat and light. Secondly, the cost of production polylactide is very high, which means that the cost of models will be much higher similar models made of other materials. Used in 3D printing technologies: SLS and FDM. nine0003
Chocolate. British scientists presented to the public the first chocolate 3D printer that prints any chocolate figurines ordered by the operator. The printer inflicts each next a layer of chocolate on top of the previous one. Thanks to the ability of chocolate to quickly harden and harden when cooled, the printing process proceeds quite quickly. In the near future, such printers will be in demand in confectionery and restaurants.
Nobody knows what what I expected was that houses would not just be built, but printed on 3D printer. The Chinese were able to think of this, and as it turned out, it turned out to be very reasonable. nine0003
The Chinese were able to think of this, and as it turned out, it turned out to be very reasonable. nine0003
The fact is that 3D the printer builds a house from industrial waste, fiberglass and cement, which is, in fact, slag concrete, which is both environmentally friendly and cheap. In addition, absolute automation eliminates costly manual builder's work. As a result, the cost of the finished house is $ 4800, which is negligible.
Teacher : Demonstration by the teacher of the operation of the 3D printer "Anet8". Printing 3D models. -------------------------------------------------- --------------- nine0003
Teacher's story about the benefits of 3D printing:
B why is it needed for educational purposes?
3D printers in education are a great opportunity to develop spatial thinking and creative skills. Practical modeling radically changes the way children think about various objects and makes the process of teaching such sciences as more accessible and understandable programming, design, physics, mathematics, natural science.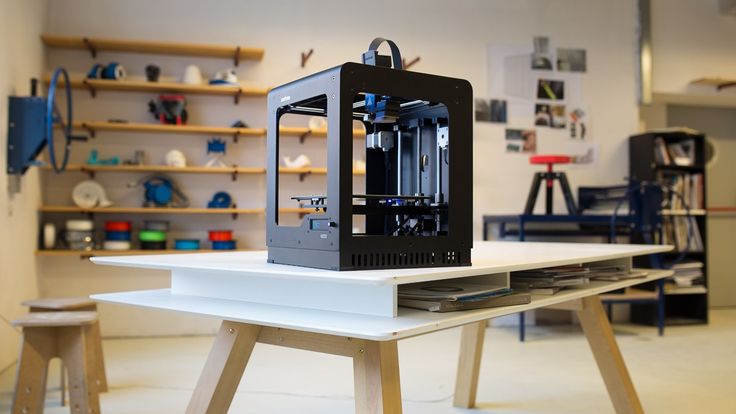 Besides, creating something with your own hands will help to cross the threshold of the usual of our society of passive consumption of typical goods to the realization of their ideas into reality. nine0003
Besides, creating something with your own hands will help to cross the threshold of the usual of our society of passive consumption of typical goods to the realization of their ideas into reality. nine0003
On 3D printer can print:
§ visualization of complex structures, objects and even formulas;
§ layout of a chain reaction or physical process;
§ imitation of a fragment of a human body or organ;
§ reconstruction of historical, archaeological or geographical significance of objects.
Beyond creative development students gain practical experience in prototyping, educational the program is supplemented with new subjects - the basics of design, engineering, design and modeling. nine0003
3. Practical part.
We have fixed and familiarized ourselves with basics of 3d modeling, 3d printing and 3d printers. Now let's move on to our practical part. We will break into groups as follows 1 student + teacher. The guys will be tutors today, will guide you, help you master the Tinkercad online 3d modeling program and At the end, we will print the design keychain you received on our 3d printer
The keychain will consist of from the details that you choose yourself because it is designer, which means flight your imagination is unlimited and then 3D printed.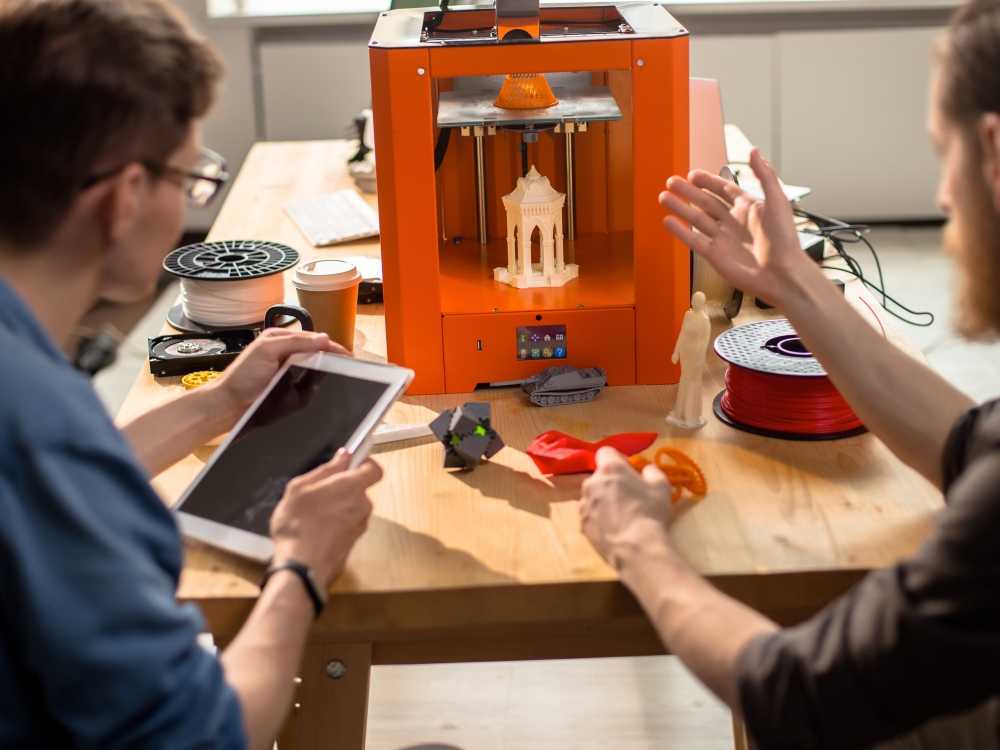 go online editor like this it looks like on the right all forms what you can use on the left field on which we edit our model. Let's get started. nine0003
go online editor like this it looks like on the right all forms what you can use on the left field on which we edit our model. Let's get started. nine0003
4. Printing
Connect the printer to network, select the type of plastic and temperature. We insert a thread of plastic into the hole, located near the power input. I draw your attention to the fact that The end of the thread must be cut evenly. Then click on the download button plastic (left arrow). It is important that the plastic thread is not tangled, do not press on the nozzle and do not touch it with your hands, to stop the flow of plastic, press and hold down the plastic feed button (left arrow). nine0003
5. Reflection.
Our master class has come to an end. I hope you liked it and the knowledge acquired today and skills you can apply in your future work. I AM I thank you for your patience, activity and wish you health, success and professional optimism! Please complete the feedback sheet. And share your thoughts and wishes.
Classes are held on weekdays and weekends.
The complex includes obtaining basic knowledge and practical mastery of 3D scanning, 3D modeling, 3D printing, and work on a laser engraving machine. It is also associated with a new area of science and technology that is actively developing all over the world - innovative materials science. The complex allows you to apply the acquired knowledge of 3D technologies for the manufacture of products from various materials. nine0003
1 session . "3D printing based on ready-made models". Duration: 2 ac. hour *
The first lesson is a story about what you need to know and be able to create simple products on a 3D printer - a modern device for layer-by-layer creation of three-dimensional objects based on a three-dimensional model. The master class will tell you what printers are, how they differ and what different printers are for. The guys will learn where on the INTERNET you can get ready-made models and how to print the product. After that, they will be able to print the product themselves according to the finished model they have chosen (figurines or decorations) under the guidance of a teacher. nine0003
The guys will learn where on the INTERNET you can get ready-made models and how to print the product. After that, they will be able to print the product themselves according to the finished model they have chosen (figurines or decorations) under the guidance of a teacher. nine0003
Location: Sevastopolsky pr. 11A, room 125, CMIT "Territory of Creativity"
Moderator: Anna Smirnova, CMIT equipment specialist.
Phone for time coordination +7 (910) 4401417
2 session . "3D Modeling, Scanning, Printing". Duration: 2 ac. hour *
This lesson is designed for children who are learning the technologies of 3D modeling, scanning and working on a 3D printer for the first time. If the student’s idea is displayed in the form of a drawing or picture, the lesson will teach how to create a 3D model from a drawing, picture or photograph step by step. Students will try to create their own 3D model and print their own model on a 3D printer. It will also be interesting to learn about 3D scanners and to master the technique of 3D scanning in practice. The teacher will tell you why 3D scans are used in practice. Some of the daredevils will receive their 3D photos. nine0003
The teacher will tell you why 3D scans are used in practice. Some of the daredevils will receive their 3D photos. nine0003
Location: Sevastopolsky pr. 11A, room 125, CMIT "Territory of Creativity"
Moderator: Anna Smirnova, CMIT equipment specialist.
Phones for time coordination +7 (910) 4401417
Lesson 3 “We cut and engrave on a laser machine”. Duration: 2 ac. hour *
A laser engraving machine is a more serious device in terms of independent work than a 3D printer. Nevertheless, schoolchildren in grades 5-7 will understand what can be done on a laser engraving machine. What models to use for this, what you need to know and be able to cut with engraving product own design from different materials - plastic, plywood, fabric, cardboard (for example, a photo frame, a gift for mom, favorite teacher or friend). After the 3rd lesson, those guys who have successfully mastered the technique of 3D modeling and printing, understood the essence of laser cutting and engraving and have the idea of their own project will be able to use the CMIT equipment.
Location: Sevastopolsky pr. 11A, room 125, CMIT "Territory of Creativity"
Moderator: Anna Smirnova, CMIT equipment specialist. nine0003
Phones for time coordination +7 (910) 4401417
4 lesson "Forge 3D". Duration: 3 ac. hour *
This is an activity that introduces children to the world of knowledge from physics and chemistry. The children will get an idea of the solid liquid and gaseous state of substances, learn about the properties of some chemicals and materials. They are waiting for a master class on making soap and candles of various shapes with their own hands, made using a 3D printer. Schoolchildren who have an idea for projects on the topic of the master class will be able to use the CMIT equipment in coordination with the master class presenters. ninePh.D. Moscow State University
Phones for time coordination +7 (985) 3086782
Lesson 5 "Composites - the world around us. " Duration: 2 ac. hour *
" Duration: 2 ac. hour *
The lesson includes a fascinating story about when and why they began to use composite materials and how they differ from metal, wood, plastic, they will show samples of materials from which composites are obtained, and products based on composite materials, as well as how to make composite in different ways, and what materials are needed for this. A quiz will be held, which will allow you to choose the materials for the manufacture of the composite, justify their choice and go through a number of stages in the manufacture of a sample of the composite product. nine0003
Place: Sevastopolsky pr. 11A, office 125, Center for Creative Arts Center
Moderator: Yablokova Marina Yuryevna, Associate Professor, Ph.D. chem. Sciences.
Phones for time coordination +7 (916) 9542111. +7 (910) 4401417
Lesson 6 "The Amazing World of Carbon". Duration: 2 ac. hour *
Master class begins with a story about the most beautiful of the chemical elements - carbon.